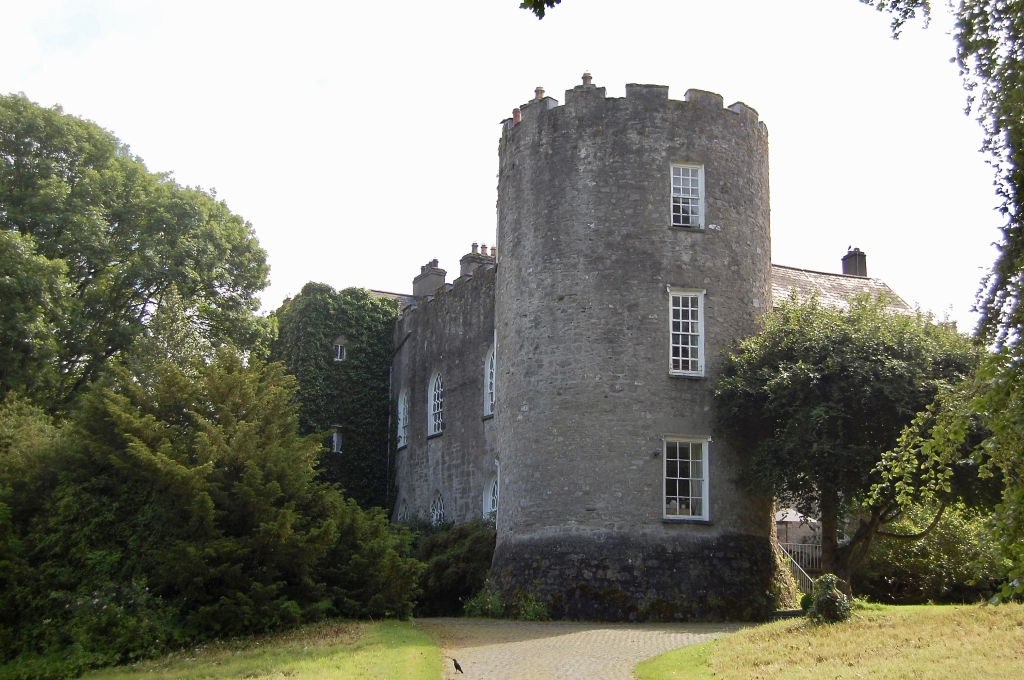
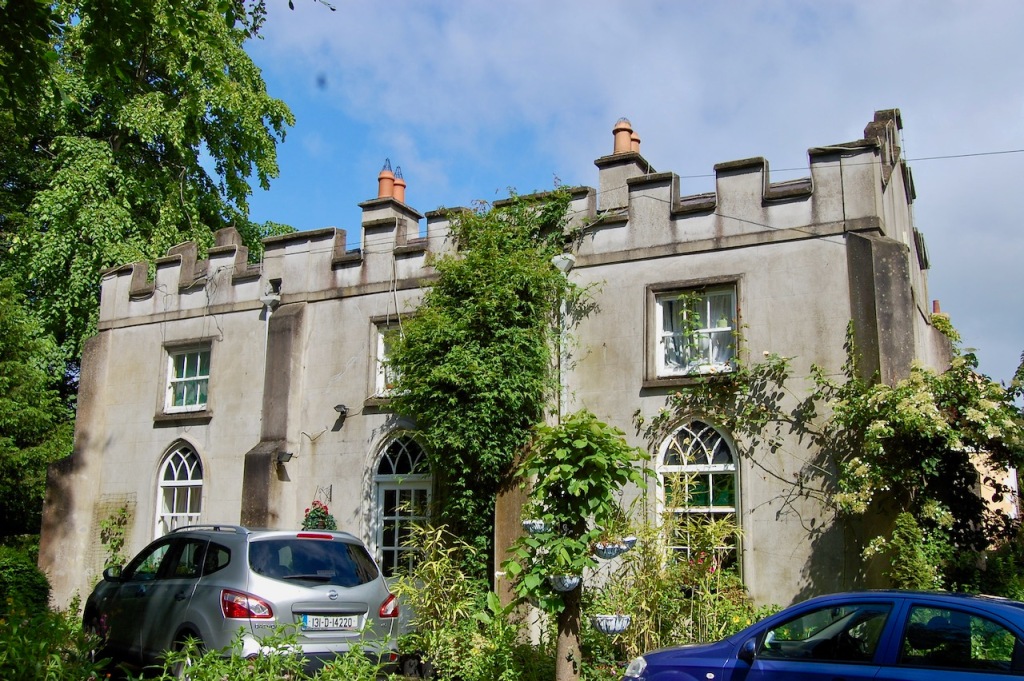
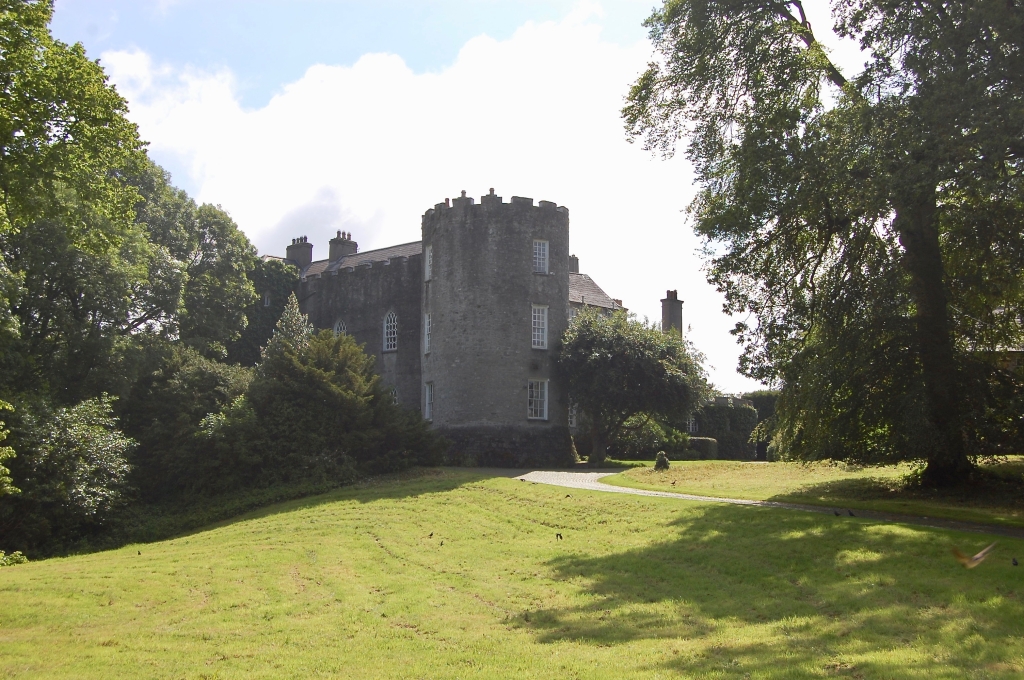
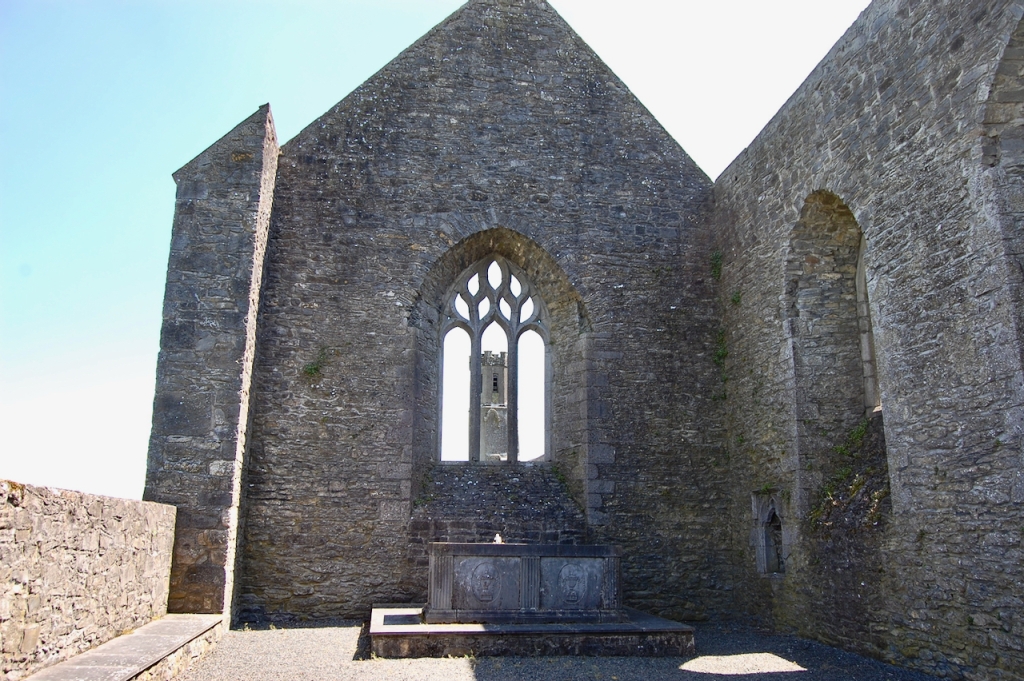
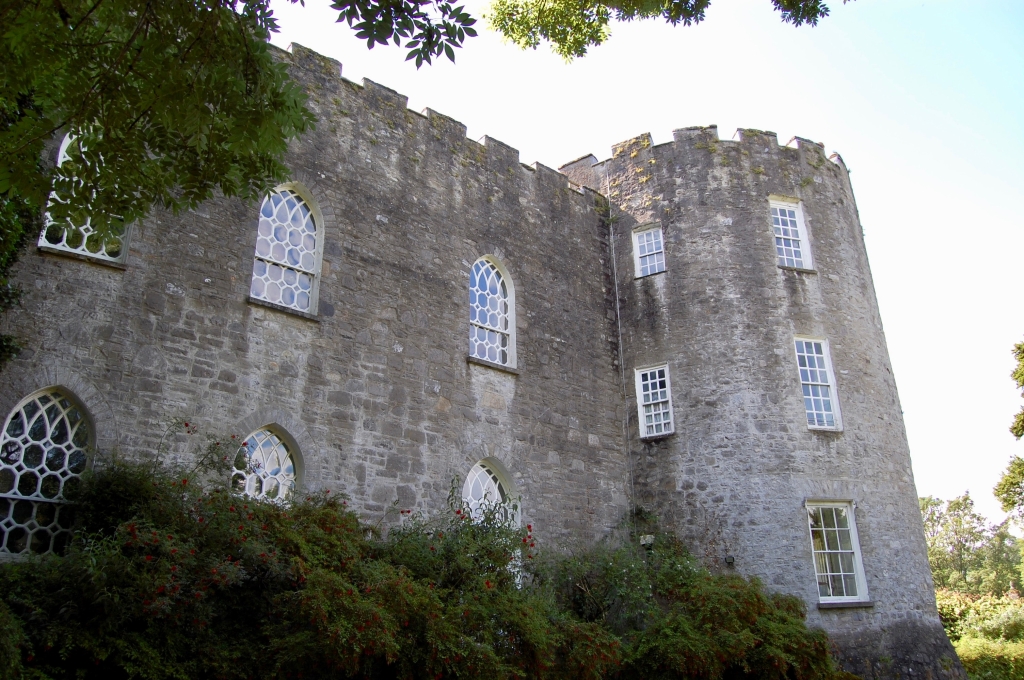
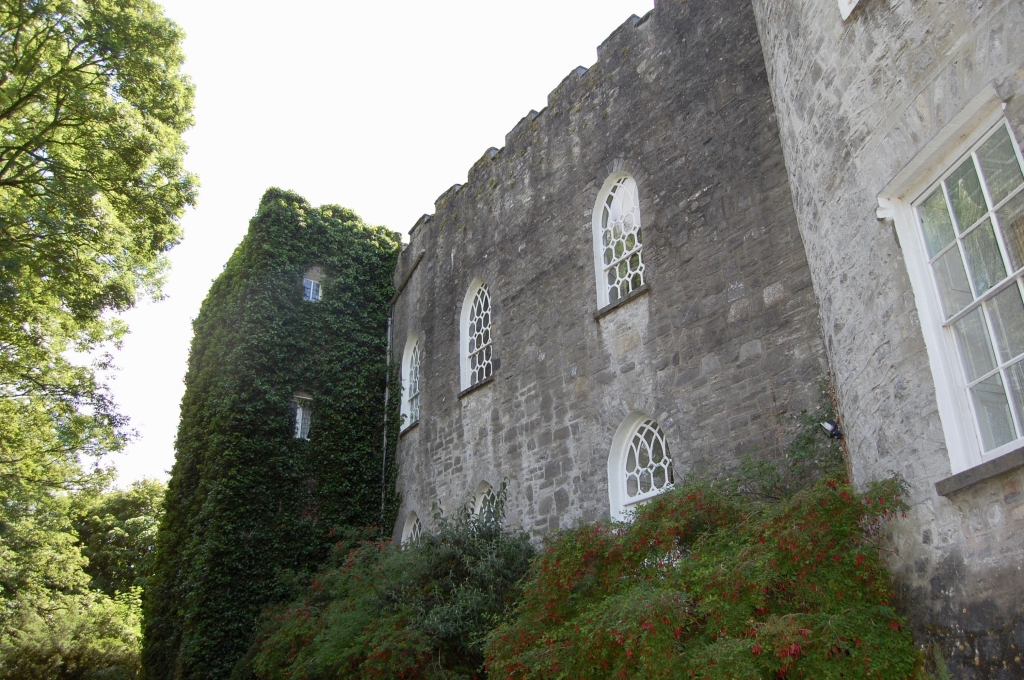
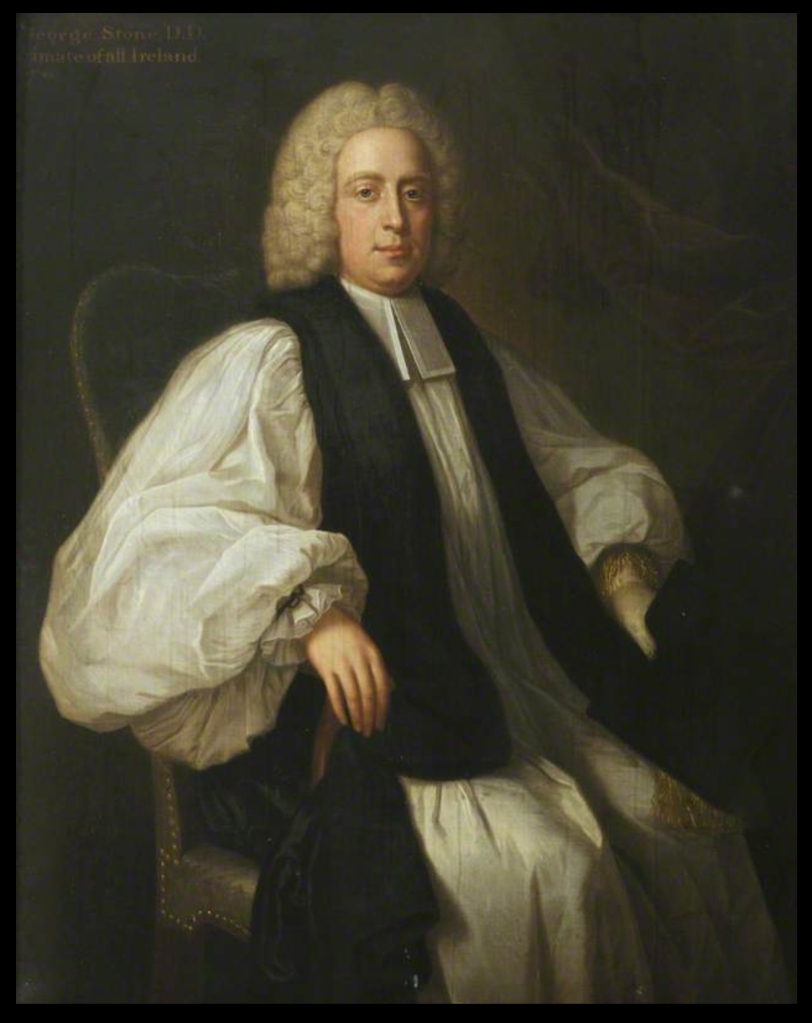
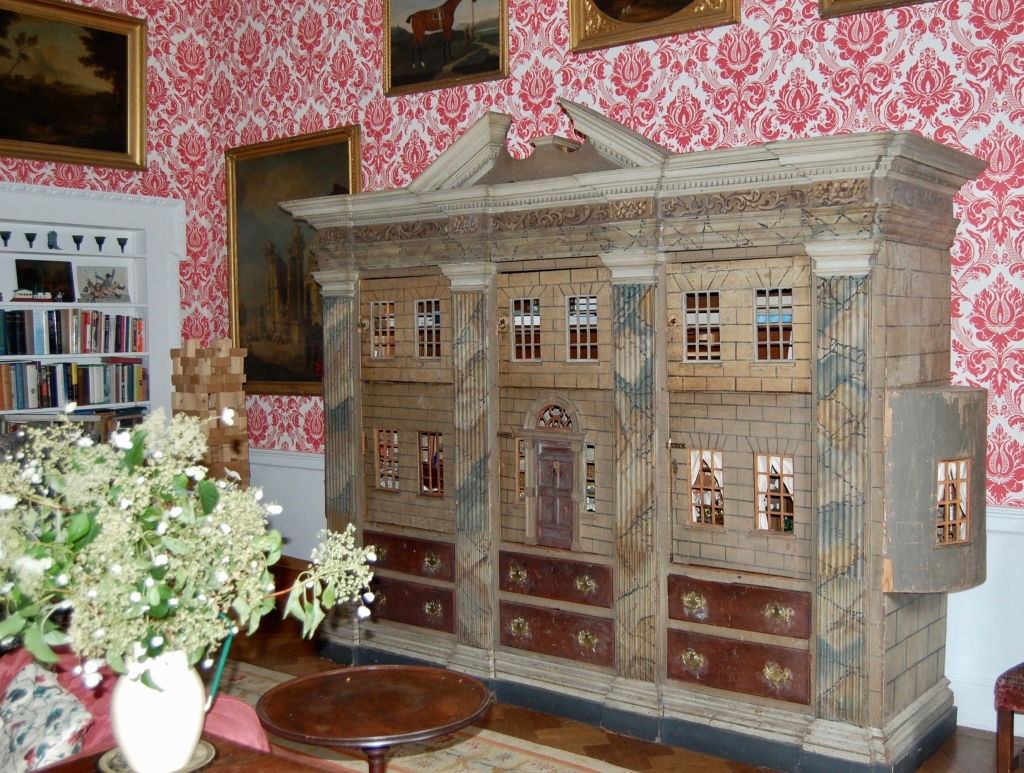
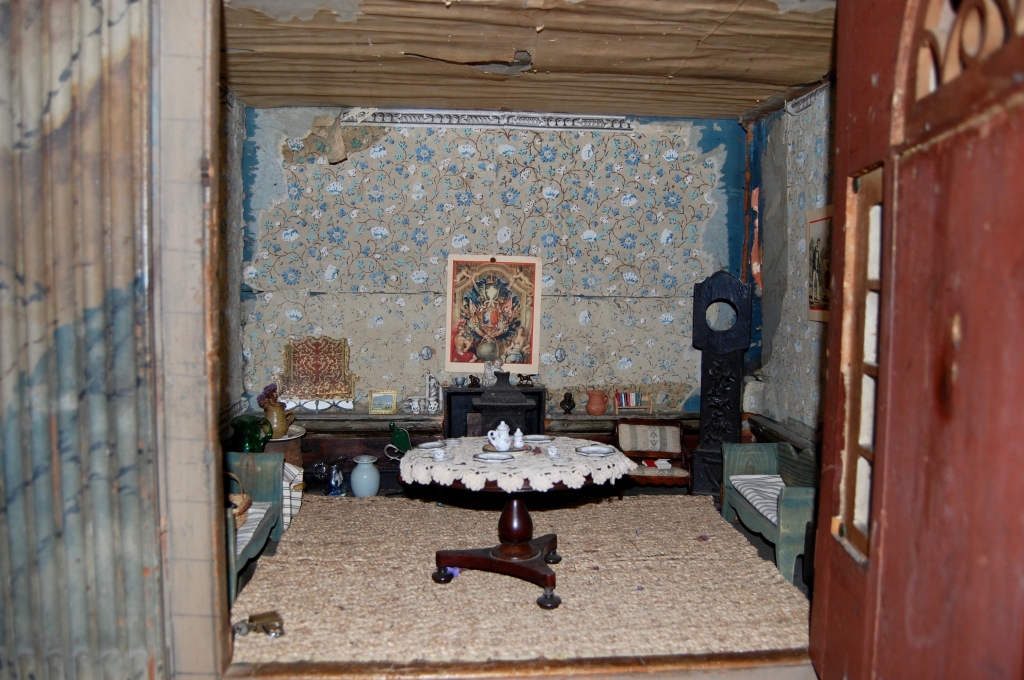
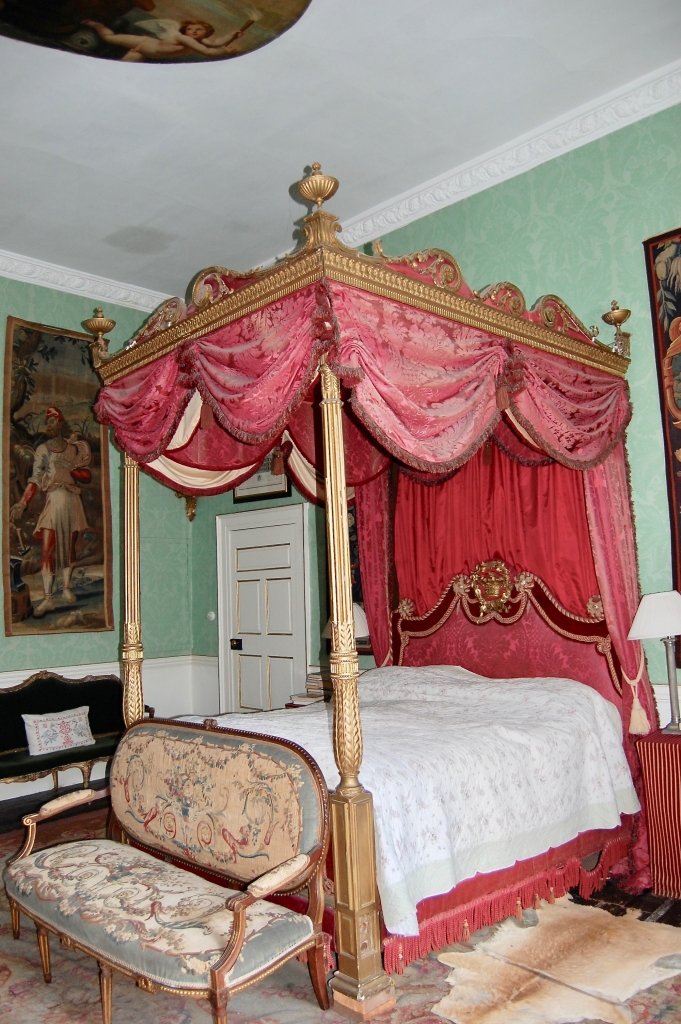
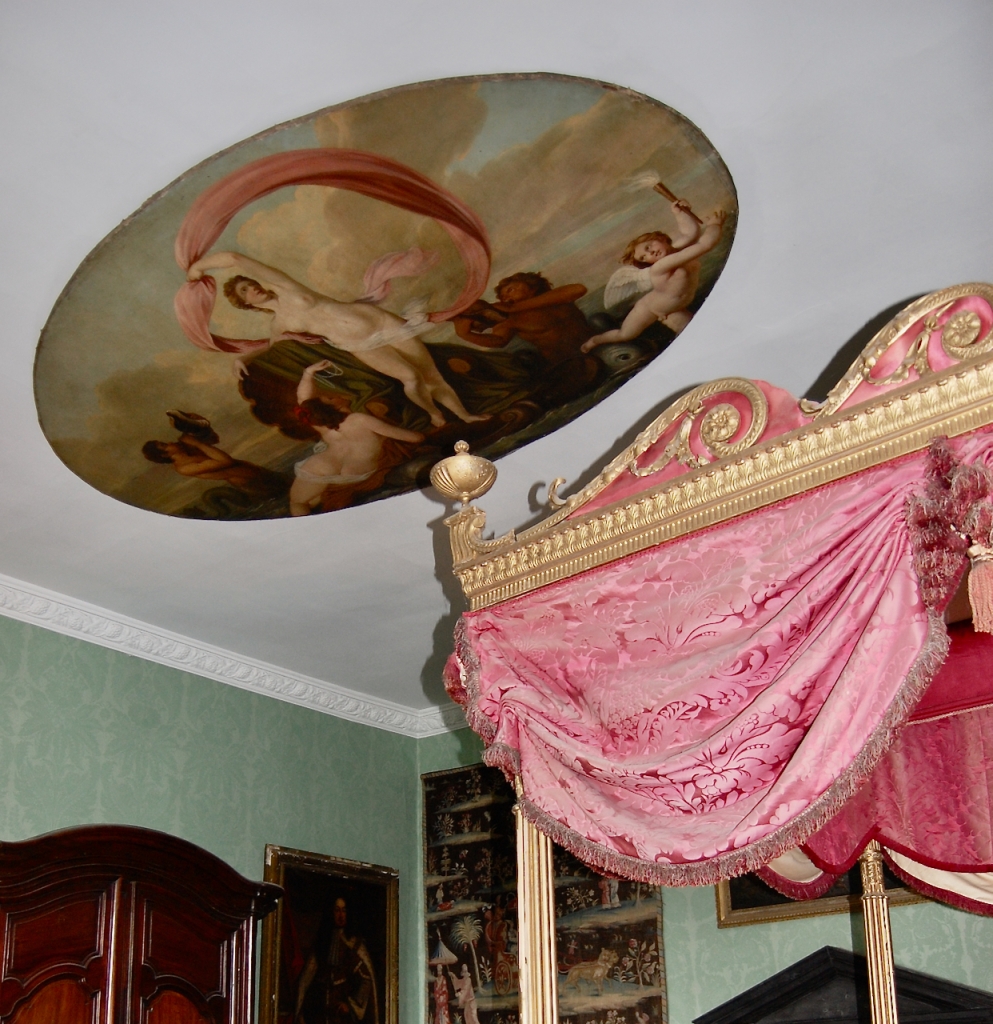
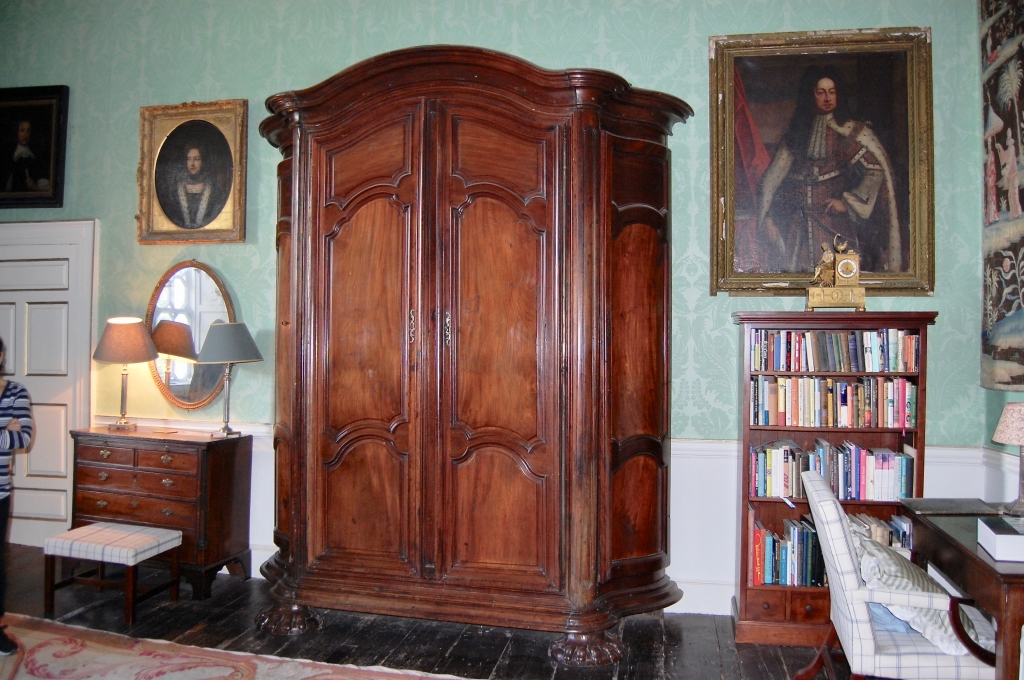
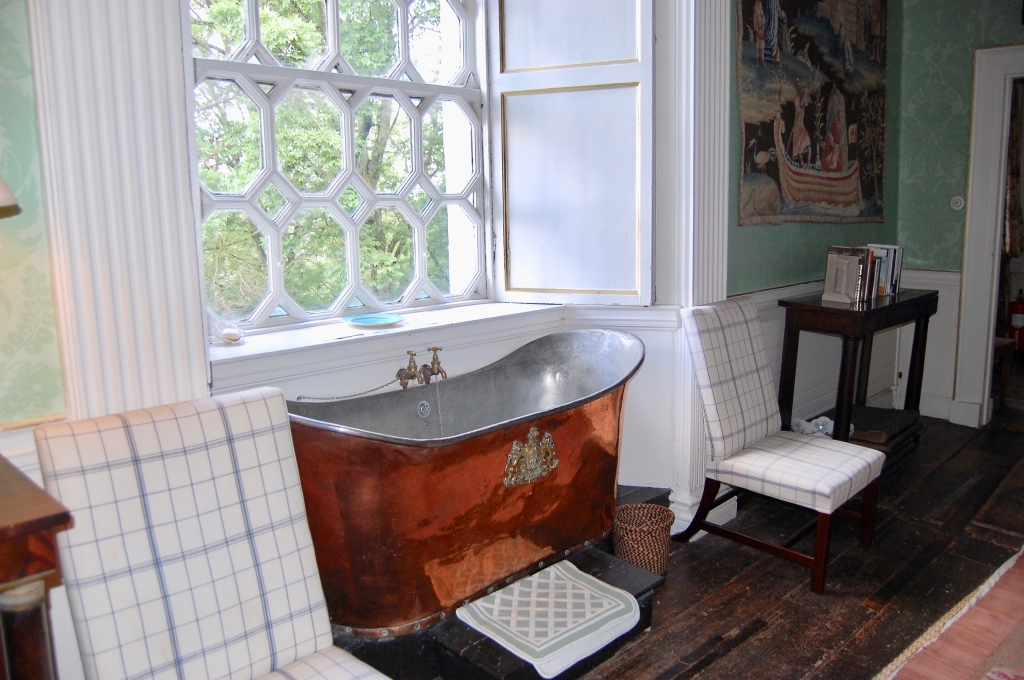
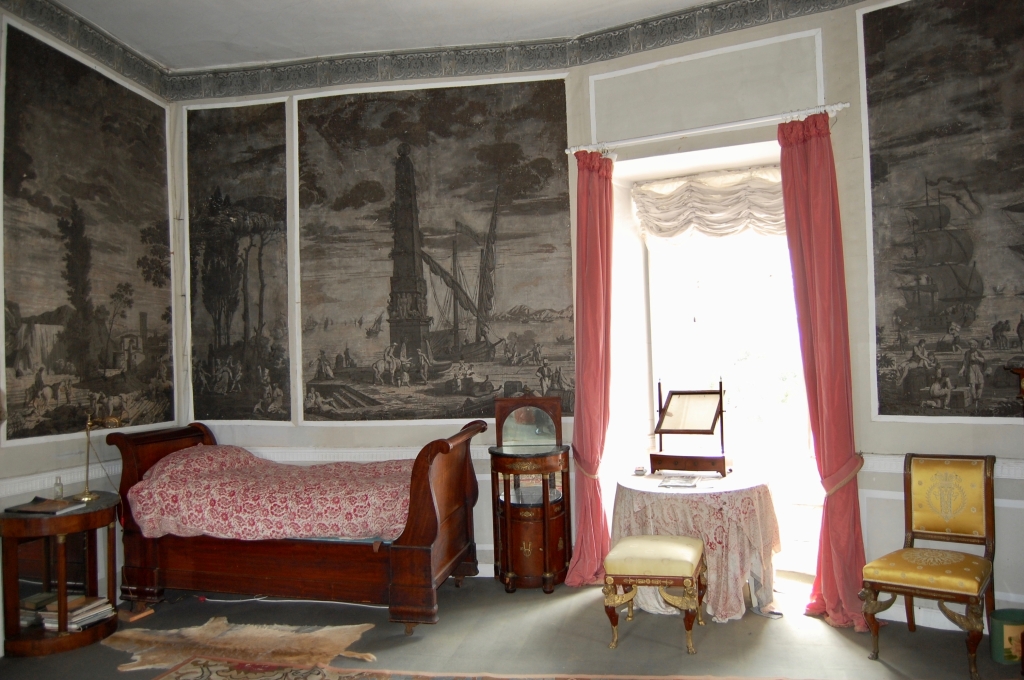
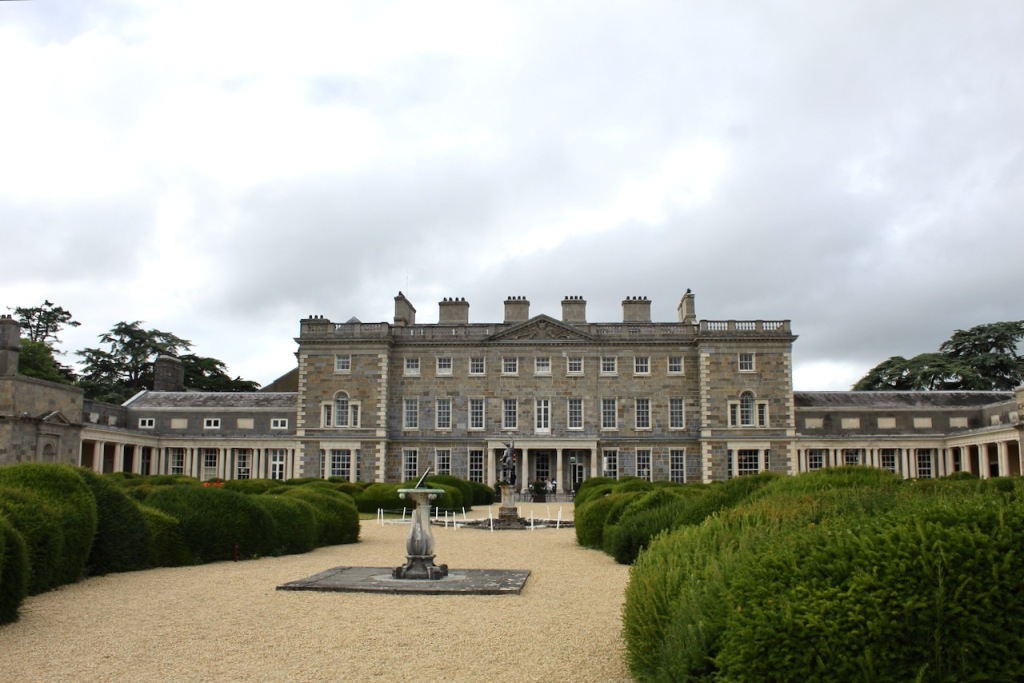
2024 Diary of Irish Historic Houses (section 482 properties)
To purchase an A5 size 2024 Diary of Historic Houses (opening times and days are not listed so the calendar is for use for recording appointments and not as a reference for opening times) send your postal address to jennifer.baggot@gmail.com along with €20 via this payment button. The calendar of 84 pages includes space for writing your appointments as well as photographs of the historic houses. The price includes postage within Ireland. Postage to U.S. is a further €10 for the A5 size calendar, so I would appreciate a donation toward the postage – you can click on the donation link.
€20.00
I have been working to save all my photographs on USB sticks so do not have a new property to post, although I have lots to write up. I am therefore reposting this entry.
On the map above:
blue: places to visit that are not section 482
purple: section 482 properties
red: accommodation
yellow: less expensive accommodation for two
orange: “whole house rental” i.e. those properties that are only for large group accommodations or weddings, e.g. 10 or more people.
green: gardens to visit
grey: ruins
Carlow, Dublin, Kildare, Kilkenny, Laois, Longford, Louth, Meath, Offaly, Westmeath, Wexford and Wicklow are the counties that make up the Leinster region.
As well as places to visit, I have listed separately places to stay, because some of them are worth visiting – you may be able to visit for afternoon tea or a meal.
For places to stay, I have made a rough estimate of prices at time of publication:
€ = up to approximately €150 per night for two people sharing (in yellow on map);
€€ – up to approx €250 per night for two;
€€€ – over €250 per night for two.
For a full listing of accommodation in big houses in Ireland, see my accommodation page: https://irishhistorichouses.com/accommodation/
Kildare:
1. Blackhall Castle, Calverstown, Kilcullen, Co. Kildare – section 482
2. Burtown House and Garden, Athy, Co. Kildare – section 482
3. Castletown House, County Kildare – OPW
4. Coolcarrigan House & Gardens, Coolcarrigan, Coill Dubh, Naas, Co. Kildare – section 482
5. Donadea Forest Park and ruins of Donadea Castle, County Kildare
6. Farmersvale House, Badgerhill, Kill, Co. Kildare – section 482
7. Griesemount House, Ballitore, Co Kildare – section 482
8. Harristown House, Brannockstown, Co. Kildare – section 482
9. Kildrought House, Celbridge Village, Co. Kildare – section 482
10. Larchill, Kilcock, Co. Kildare – section 482
11. Leixlip Castle, Leixlip, Co. Kildare – section 482
12. Maynooth Castle, County Kildare – OPW
13. Millbrook House, County Kildare: House and limited garden access for groups only
14. Moone Abbey House & Tower, Moone Abbey, Moone, Co. Kildare – section 482
15. Moyglare Glebe, Moyglare, Maynooth, Co. Kildare – section 482
16. Steam Museum Lodge Park Heritage Centre, Lodge Park, Straffan, Co. Kildare – section 482
17. Templemills House, Newtown Road, Celbridge, Co. Kildare, W23 YK26 – section 482
Places to stay, County Kildare:
1. Balyna, Moyvalley, Co Kildare – Moyvalley Hotel
2. Barberstown Castle, Kildare – hotel
3. Batty Langley Lodge, Celbridge, County Kildare €€
4. Burtown House holiday cottages
5. Carton House, Kildare – open to public, hotel
6. Castletown Gate Lodge, Celbridge, County Kildare: Irish Landmark € for 3
7. Castletown Round House, Celbridge, County Kildare: Irish Landmark € for 3-6
8. The Cliff at Lyons, County Kildare
9. The K Club, Straffan House, County Kildare
10. Kilkea Castle, Castledermot, Kildare – hotel
11. Leixlip Manor hotel (formerly St. Catherine’s Park) Leixlip, Co Kildare
12. Martinstown House, Kilcullen, Co Kildare – accommodation
13. Moone Abbey, County Kildare holiday cottages
Whole house accommodation in County Kildare:
1. de Burgh (or Bert) Manor, Kilberry, County Kildare – whole house accommodation
2. Firmount, Clane, County Kildare – whole house or weddings.
3. Griesemount House, County Kildare

donation
Help me to pay the entrance fee to one of the houses on this website. This site is created purely out of love for the subject and I receive no payment so any donation is appreciated!
€10.00
Kildare
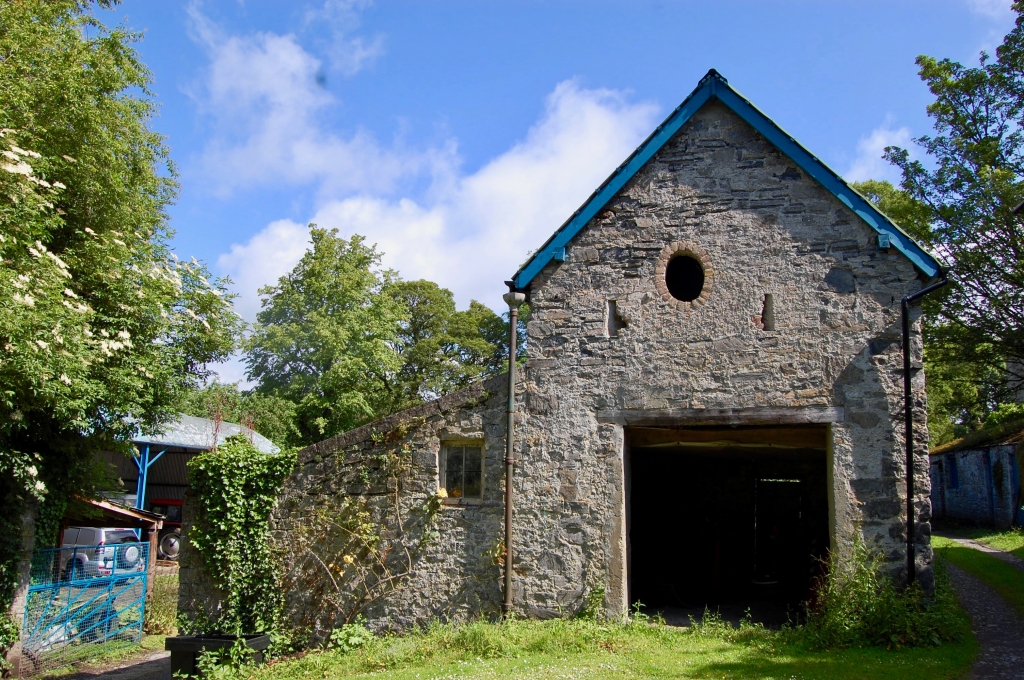
1. Blackhall Castle, Calverstown, Kilcullen, Co. Kildare R56 CR68 – section 482

See my entry:
https://irishhistorichouses.com/2020/05/14/blackhall-castle-calverstown-kilcullen-county-kildare/
Open dates in 2024: May 1-31, Aug 17-25, Sept 1-15, Dec 1-20, 2pm-6pm Fee: Free
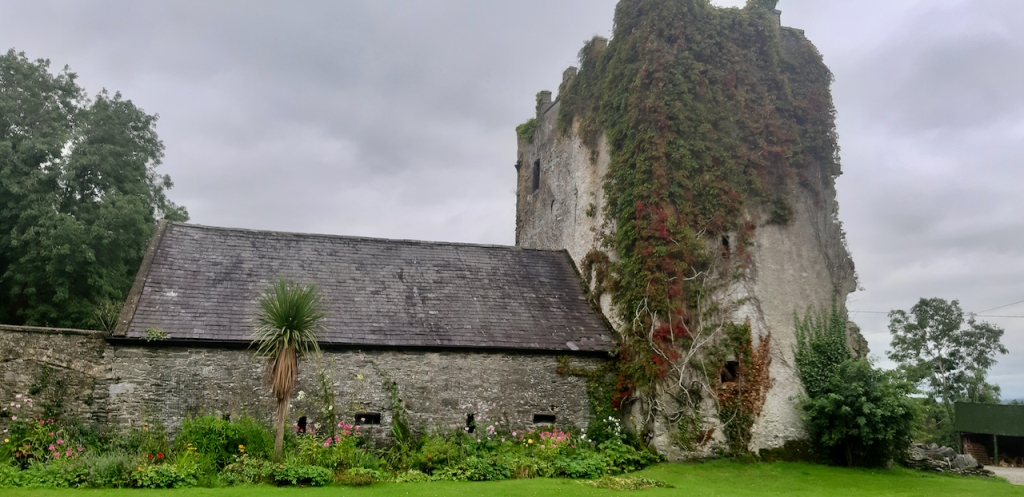
2. Burtown House and Garden, Athy, Co. Kildare R14 AE67 – section 482

www.burtownhouse.ie
Open dates in 2024: May 1-4, 8-11, 15-18, 22-25, 29-31, June 5-8, 12-15, 19-22, 26-29, August 17-25, Sept 4-7, 11-14, 18-21, 25-28, 9am-1pm
Fee: adult €8, OAP/student/child €5

The Historic Houses of Ireland website tells us:
“Ballytore, in County Kildare, was a stronghold of the Irish Quakers and the centre of a sizeable Quaker community. One of their members, Robert Power, built Burtown House as the hub of a two thousand acre farming enterprise in the 1720s. His Georgian villa, shown on early maps as “Power’s Grove,” was only one room deep so wings were added later in the century. These were subsequently removed, though their faint outlines can still be identified and Burtown was further extended in the early nineteenth century when a full height bow was added on the garden front.
“The new extension provided a bow ended room on the garden front, a large bedroom above and a grand staircase, lit by a tall round-headed window. Pretty plasterwork in the manner of James Wyatt was also introduced at the time, most notably in an arched alcove in the bow-ended room, which is likely to have been the original dining room. The alcove is filled with a shallow fan, and delightfully cursive sprays of vine leaves, and is flanked by a pair of classical vases on pilasters of foliage with naive Corinthian capitals.
“Burtown has never been sold in all its three hundred years. The house passed from the Power family to the Houghtons and thence to the Wakefields, who gave it a new roof with widely projecting eaves in the early nineteenth century. They also lengthened the sash windows, installed a new front door with a fanlight in a deep recess, and carried out a number of other alterations.
“When Mr. Wakefield was killed playing cricket Burtown passed to his sister, who had married a fellow Quaker from County Tipperary, William Fennell. Their son, William James was a keen horseman but “was asked to leave the Quaker congregation because of his fondness for driving a carriage with two uniformed flunkeys on the back”.
“Today Burtown is in the midst of two hundred acres of parkland, including ten acres of lush flower, vegetable and woodland gardens with many fine walks. The house has now been home to five generations of the Fennell family, and to the acclaimed botanical artist and illustrator, Wendy Walsh. Coincidentally, the leading Irish botanical artist of the early twentieth century, Lydia Shackleton, also came from the same small Quaker community.” [1]
3. Castletown House, County Kildare – OPW
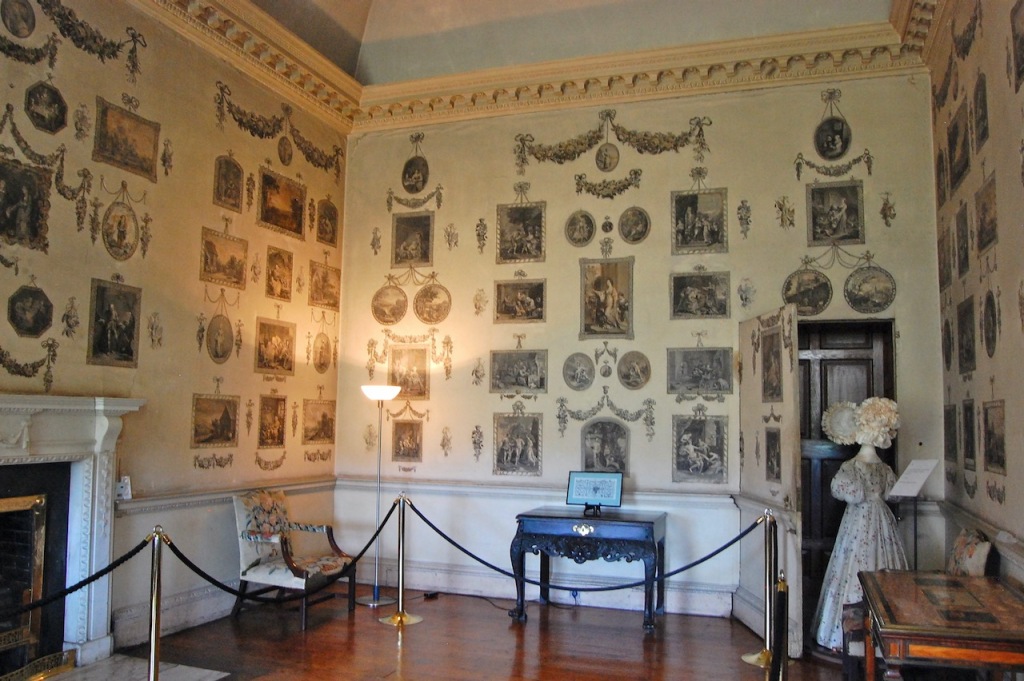

4. Coolcarrigan House & Gardens, Coolcarrigan, Coill Dubh, Naas, Co. Kildare – section 482

See my write-up:
https://irishhistorichouses.com/2020/05/31/coolcarrigan-house-and-gardens-coill-dubh-naas-county-kildare/
www.coolcarrigan.ie
Open dates in 2024: Feb 12-16, 19-23, Aug 1-2, 6-31, Sept 1-8, 23-27, 30, Oct 1-4, 7-9, 9am-1pm
Fee: adult €8, OAP/student €5, child free
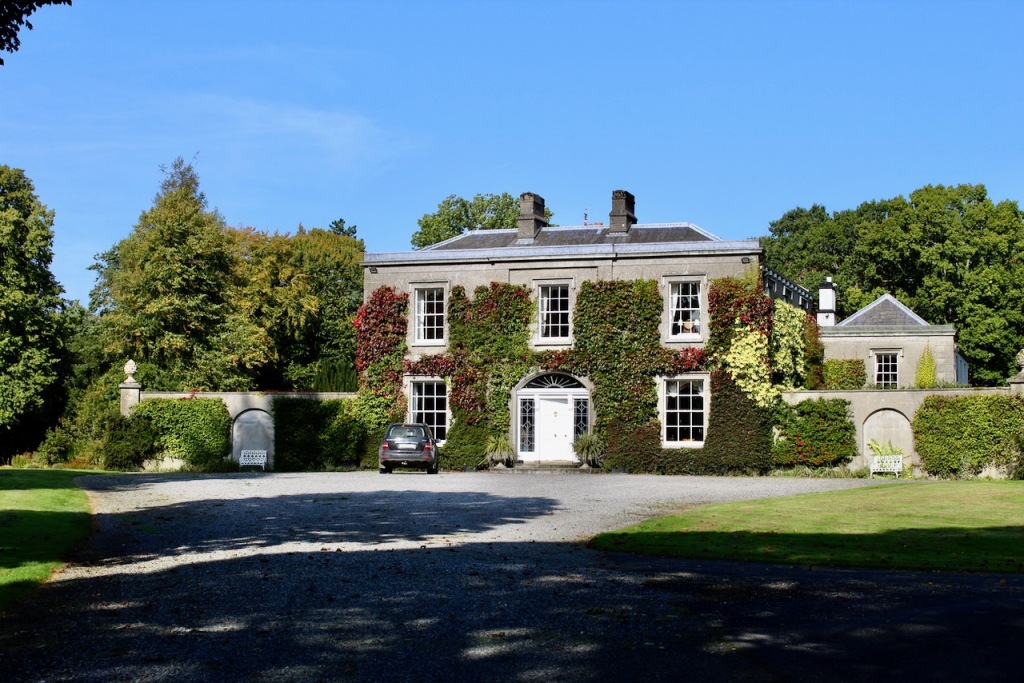
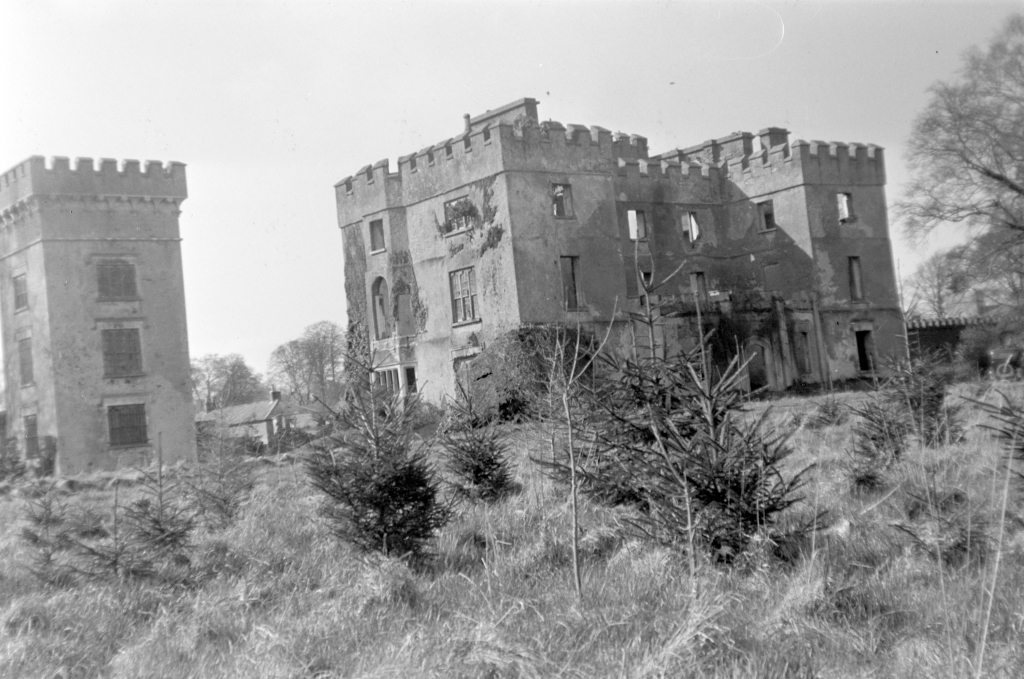
5. Donadea Forest Park and ruins of Donadea Castle, County Kildare
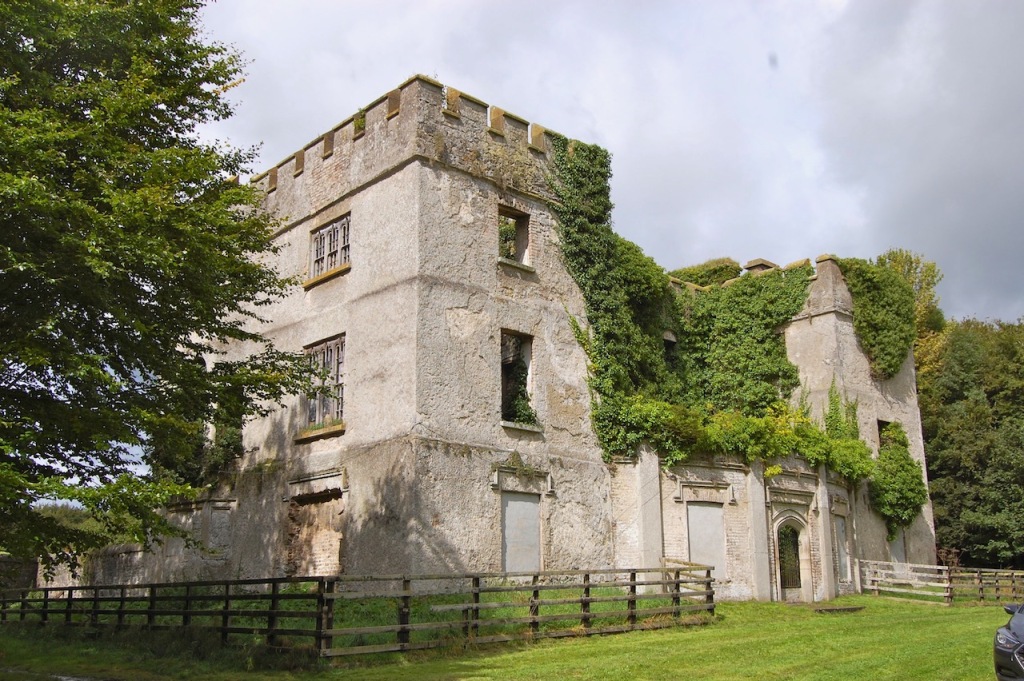

https://www.coillte.ie/site/donadea-forest-park/
The website tells us:
“Donadea Forest Park includes Donadea Castle and estate, the former home of the Aylmer family up until 1935. There are many historical features including the remains of the castle and walled gardens, St. Peter’s church, an ice house and boat house. The Lime tree avenue planted in the 19th century formed the original entrance to the estate. Another feature of the park is the 9/11 Memorial, a scaled replica of the twin towers carved in limestone. The small lake is brimming with ducks, waterhens and has a beautiful display of water lilies in the summer. There is a café open throughout the year.“


In 1581 Gerald Aylmer, (1548-1634), Knight, of Donadea, son of George Aylmer, of Cloncurry, and grandson of Richard Aylmer, of Lyons, built a new tower in Donadea, not fully completed until 1624 and it is now the oldest part of the Castle. [2]
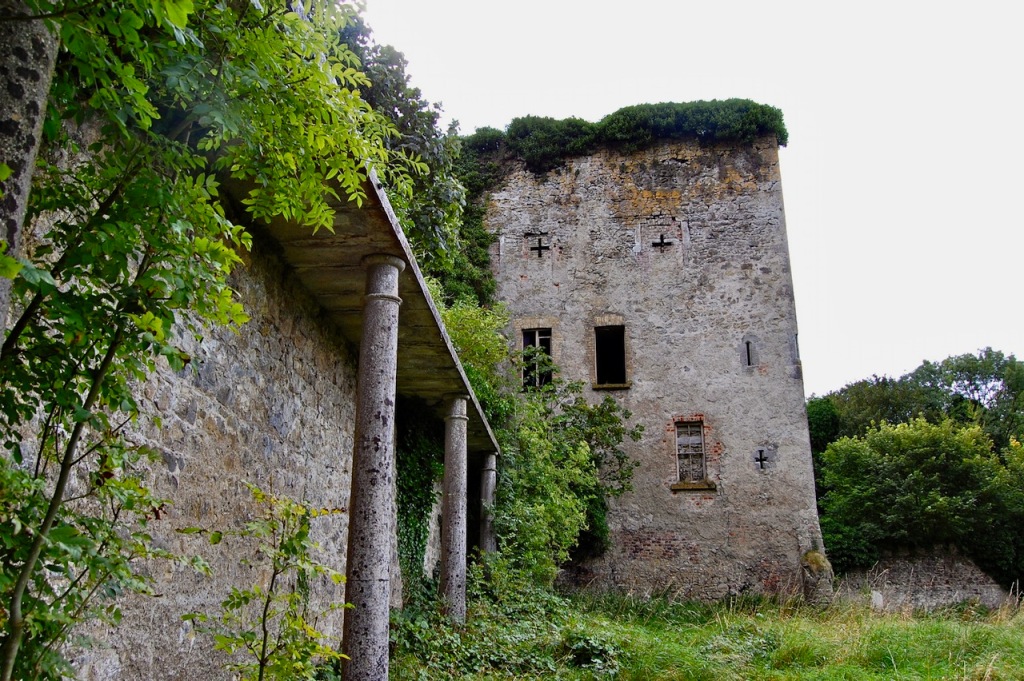

In 1626, he repaired the medieval Church in Donadea and built a new extension in which he established his family burial plot. In the extension he also constructed an Altar Tomb monument as a burial memorial for his family. Gerald was titled by the Crown and became the first Baronet of Donadea.
The Aylmers were connected with the various conflicts and rebellions over the next two centuries. During the wars of the 1640s, Sir Andrew, 2nd Baronet (c. 1610-c. 1671), supported the rebels and was imprisoned at the beginning of the war.
Although he was a brother-in-law of the Lord Lieutenant of Ireland, James Butler, 1st Duke of Ormond, there were no favours granted to him. The Aylmers rebuilt the castle after it was burned by James Butler’s troops.


In 1689, after the battle of the Boyne, Lady Helen Aylmer, widow of the 3rd Baronet, (born Plunkett, daughter of Luke Plunkett 3rd Earl of Fingall) was in charge of the Castle. She was outlawed due to her support for James II, but she managed to hold on to the Castle and lands under the terms of the Treaty of Limerick.
In 1736, Sir Gerald, 5th Baronet, died leaving an only son FitzGerald who became the 6th Baronet.
He was only one year old when his father died and was subsequently raised by his mother (Ellice or Ellen, daughter of Gerald Aylmer, 2nd Baronet of Balrath, County Meath) and her relatives who were members of the established church. FitzGerald subsequently conformed to the established religion. In 1773, he built a new house in front of the Castle and incorporated the Tower in his new residence.


Gerald, 8th Baronet, held the lands of Donadea between 1816 and 1878 and he is accredited with most of the construction work that is visible in Donadea demesne today. He began his building program in the 1820s by re-routing the roads away from the Castle and the construction of a high wall enclosing the demesne. Gate lodges were then built at all the entrances.
He also built a new grand entrance known as the Lime Avenue.
In 1827 he completely remodelled the front of the Castle which gave it an attractive bow shaped appearance. It has been suggested that he employed the renowned architect Richard Morrison to design this new structure.
The older cabin-type dwellings close to the castle were demolished and new estate houses built at the Range. To the west of the Castle he built an eight acre area of gardens and paddocks, surrounded and sub-divided by walls. In the Castle yard he built dwellings for staff and elaborative farm buildings. He also constructed the artificial lake and the Ice House. Large areas of the demesne were planted and, by the time of his death, Donadea demesne was listed as one of the finest parkland settings in the county.

Outside the demesne he was involved in numerous construction projects including the famous ‘Aylmer Folly’, viz. the Tower on the summit of the hill of Allen. (see [2]) Sir Gerald’s grandson Justin, 10th Baronet, died unmarried in 1885. His sister Caroline inherited the castle and much of the demesne, while the baronetcy passed to a cousin. Caroline Maria Aylmer, who was the daughter of Sir Gerald George Aylmer, 9th Baronet, was the last Aylmer to live at Donadea. She died in 1935, leaving the estate to the Church of Ireland who, in turn, passed it bequeathed to the Irish state.
The castle remained unoccupied and its roof was removed in the late 1950s.
For more on the Aylmer family, see The Landed Gentry & Aristocracy of County Kildare by Turtle Bunbury & Art Kavanagh (published by Irish Family Names, 2004).
6. Farmersvale House, Badgerhill, Kill, Co. Kildare W91 PP99 – section 482

Open dates in 2024: Jan 12-31, July 17-31, Aug 1-25, 9.30am-1.30pm
Fee: adult €5, student/child/OAP €3, (Irish Georgian Society members free)
7. Griesemount House, Ballitore, Co Kildare R14 WF64 – section 482
www.griesemounthouse.ie
Open dates in 2024: Feb 12-25, 26, May 13-24, June 17-28, July 8-19, Aug 17-25, 2pm-6pm
Fee: adult €6, OAP €5, child/student €3
The Historic Houses of Ireland website tells us:
“In 1685, the village of Ballitore on the river Griese in the southern corner of County Kildare became the first planned Quaker village in England and Ireland. The Shackleton family from Yorkshire settled here some decades later and besides establishing wool and corn mills, founded the famous village school in 1726. Thanks to an entry by Mary (née Shackleton) Leadbetter in her ‘Annals of Ballitore’, we know that the first stone of Griesemount House (also known as Ballitore Hill House) was laid on Midsummer Day in 1817. While the three-bay side elevation is symmetrical, the two-bay front façade with the front door under the left window is quite modest, as was often the case with Quaker houses. It was built by George Shackleton, who had grown up in Griesebank House beside the now-ruinous Ballitore Mills on the river just below. He married Hannah Fisher and they raised 13 children in the new house, including the noted botanical artist Lydia Shackleton, the first artist-in-residence at the Botanic Gardens in Dublin. One of her first recorded sketches is of the house. The family lived here until the early 20th century; the house then changed hands several times. It was briefly owned and restored by the mother of mezzosoprano Frederica von Stade, and has recently come into new ownership.” [3]
8. Harristown House, Brannockstown, Co. Kildare, W91 E710 – section 482
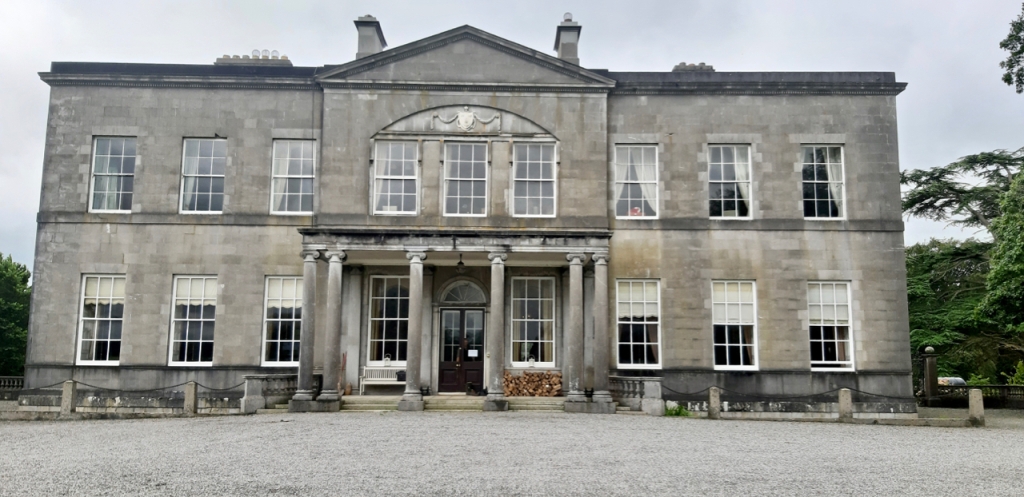

See my write-up:
https://irishhistorichouses.com/2020/09/27/harristown-brannockstown-county-kildare/
https://www.harristownhouse.ie/
Open dates in 2024: Feb 19-27, Mar 11-22, May 6-17, July 8-26, Aug 13-25, 9am-1pm
Fee: adult/OAP/student/child €10
9. Kildrought House, Celbridge Village, Co. Kildare W23 N9P2 – section 482
Open dates in 2024: Jan 9-25, May 18-31, June 1-3, July 1-8, Aug 17-31, 10am-2pm
Fee: adult €10, OAP/student €5, child €5, (under 7 years free)
See my entry, https://irishhistorichouses.com/2023/06/22/kildrought-house-celbridge-village-co-kildare-w23-n9p2/

10. Larchill, Kilcock, Co. Kildare W23 Y44P – section 482
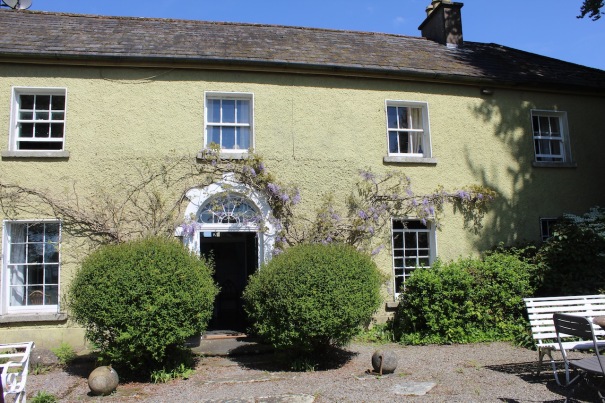

www.larchill.ie
Open dates in 2024: May 1-17, 20-24, 27-31, June 1-7, 11-14, 18-21, 25-28, Aug 17-25, 10am-2pm
Fee: adult/OAP/student €8, child €4 under 4 years free
See my entry: https://irishhistorichouses.com/2022/09/02/larchill-kilcock-co-kildare/
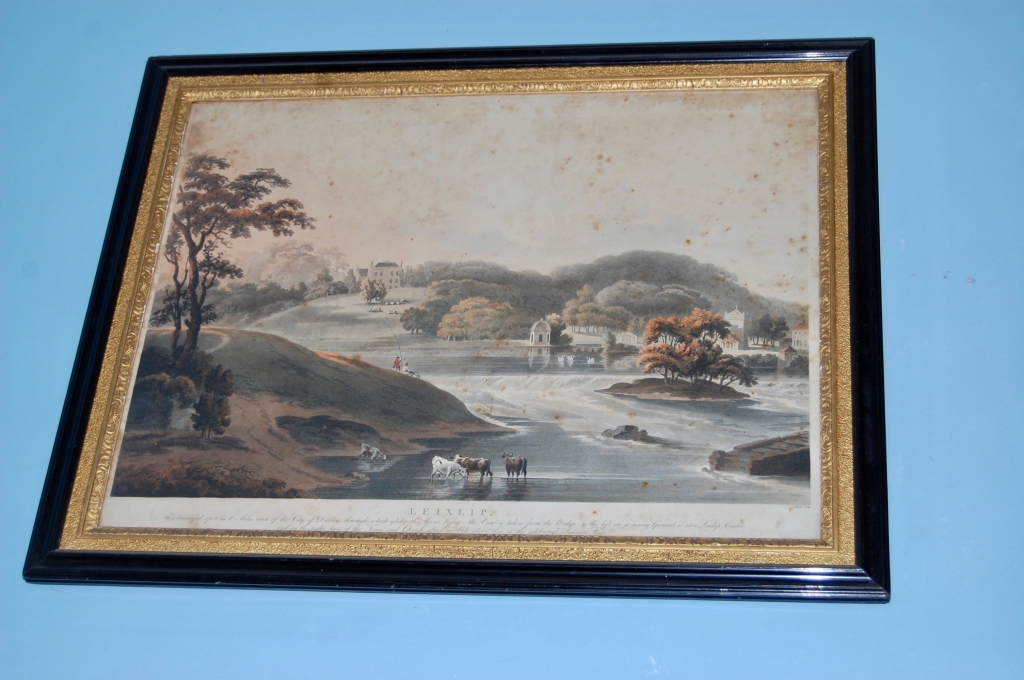
11. Leixlip Castle, Leixlip, Co. Kildare W23 N8X6 – section 482
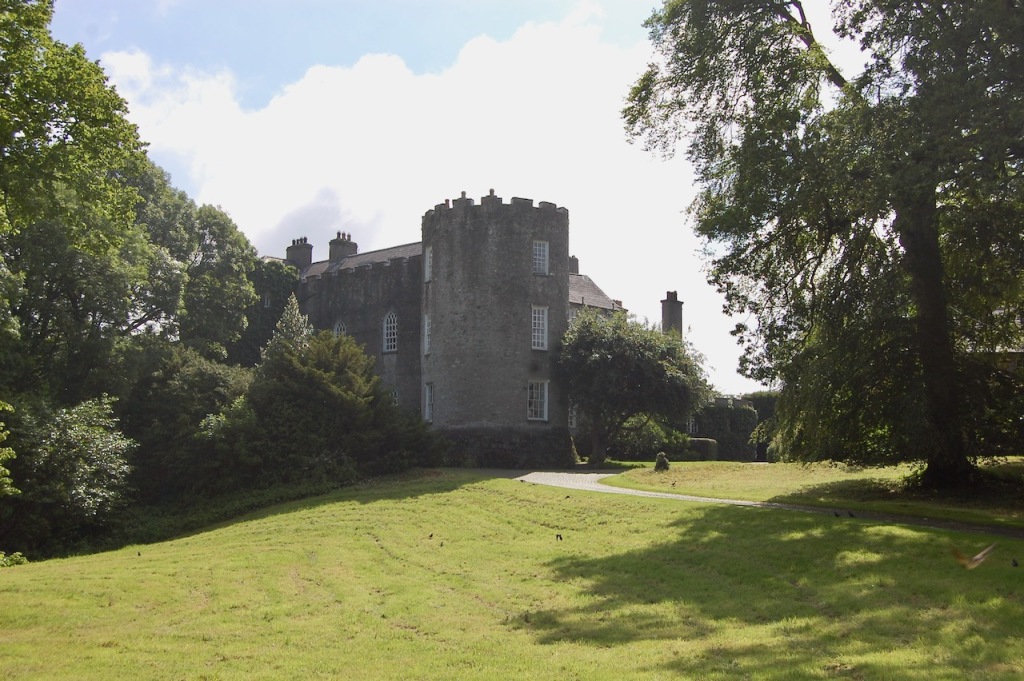

See my entry:
https://irishhistorichouses.com/2020/09/04/leixlip-castle-county-kildare-desmond-guinnesss-jewelbox-of-treasures/
Open dates in 2024: Feb 19-23, 26-29, Mar 1, 4-8, 11-15, May 13-24, June 10-21, Aug 17-25, Sept 2-8, 9am-1pm
Fee: adult €8, OAP/student/child €4, no charge for school groups
12. Maynooth Castle, County Kildare – OPW
13. Millbrook House, Kilkea, Castledermot, County Kildare R14 Y319 – section 482
Open dates in 2024: May 17-31, Aug 12-31, Sept 7-16, Dec 17-31, 9am-1pm
Fee: adult €8, student/OAP/groups €5
The Historic Houses of Ireland website tells us:
“The forebears of the Greenes of Millbrook House in the far south of County Kildare lived at Kilmanaghan Castle and Moorestown Castle [now a ruin] in County Tipperary. A great grandson of the family patriarch Captain Godfrey Greene moved up to settle near Carlow. William Nassau Greene (1714-1781) was a businessman and magistrate, and built a residence known as Kilkea Lodge (c. 1740) adjacent to the ancient Fitzgerald seat at Kilkea Castle, where his descendants are still resident. A younger son, John (1751-1819), who became High Sheriff of Kildare and Captain of the Castledermot Yeomanry, built a neighbouring house at Millbrook with the help of his father. It was completed in 1776 with its attendant mill and millrace off the River Griese, which had replaced an earlier mill in the nearby Kilkea Castle demesne. The house passed through generations of the family until finally the mill ceased operating under Thomas Greene (1843-1900), a poet and author who was made High Sheriff of Kildare in 1895. The house was left by inheritance to one of the cousins from Kilkea Lodge, father of the present owner. Throughout WWII, he had served as a frontline doctor in the 4th Indian Division in North Africa, Italy and Greece, and returned with his wife in 1950 to an utterly neglected house. Millbrook is still in the process of being restored to its former state.” [5]
See also the entry by Robert O’Byrne, https://theirishaesthete.com/tag/millbrook/
14. Moone Abbey House & Tower, Moone Abbey, Moone, Co. Kildare R14 XA40 – section 482
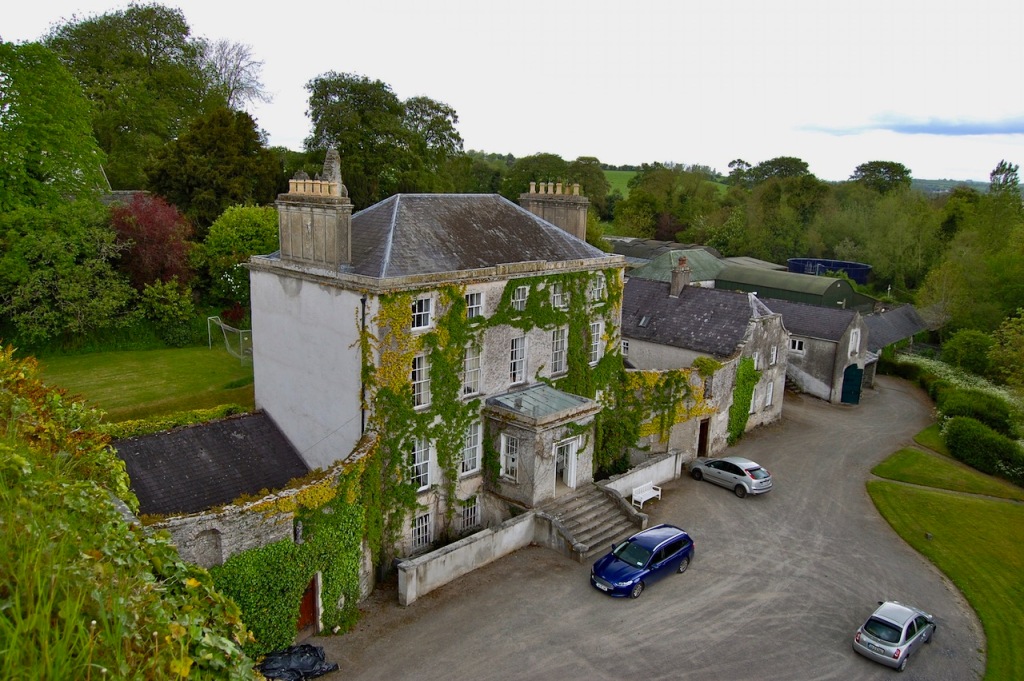

https://irishhistorichouses.com/2020/06/13/moone-abbey-house-and-tower-moone-county-kildare/
Open dates in 2024: May 1-31, Aug 17-25, Sept 1-20, 12 noon- 4pm
Fee: adult €8, OAP/student/child €4
15. Moyglare Glebe, Moyglare, Maynooth, Co. Kildare – section 482
Open dates in 2024: Jan 2-26, 29, May 1-31, Aug 17-25, 8.30am-12.30pm
Fee: adult €6, OAP/student/child €3
16. Steam Museum Lodge Park Heritage Centre, Lodge Park, Straffan, Co. Kildare – section 482
www.steam-museum.com
Open dates in 2024: Apr 30, May 4-6, 11-12, 18-19, 25-26, June 1-3, 7-9, 14-16, 21-23, 28-30, July 5-7, 12-14, 19-21, 26-28, Aug 2-5, 9-11, 16-25, 31, Sept 1, 7-8, 14-15, 21-22, 28-29, 1pm-5pm
Fee: Garden and Museum, adult Fri/Sat, €12, Sun €15 steam, child/OAP/student €6, family €25, scenic railway €5 when open

The Historic Houses of Ireland website tells us about Lodge Park:
“Lodge Park, overlooking a fine stretch of the River Liffey, was built by Hugh Henry who had married his cousin, Lady Anne Leeson from Russborough [daughter of Joseph Leeson 1st Earl of Milltown]. Completed in about 1776, the centre block forms the core of an unusual composition with curved quadrants leading to a pair of two-storey wings, both attached to two further pavilions by curtain walls to form a unique elongated ensemble of five interconnected buildings, “perhaps the most extreme example of the Irish Palladian style.”
“Henry’s father was the merchant banker Hugh Henry, who had purchased the entire Straffan estate with 7,000 acres. Lodge Park was long thought to be the last building by Nathaniel Clements, who died in 1777, but has now been attributed to John Ensor. The hipped roof is surrounded by a granite-topped parapet, and the walls are finished in rough cast, with ashlar block quoins and granite window surrounds with detailing. It is Ireland’s best exampe of concatenation, having curtain walls attached to the main house, leading to two pavilions, attached by two gateways to two further buildings. Hugh’s son Arthur built the Victorian walled garden, now beautifully restored and open to the public, as well as the fine gate lodge. The house was bought by the Guinness family in 1948.
The walled garden has been beautifully restored while a disused Victorian church has been re-erected in the grounds to house a magnificent Steam Museum with early inventor’s models, scientific engineering models and historic works of mechanical art. The Power Hall displays six huge stationary steam engines, which are run on special occasions.” https://www.ihh.ie/index.cfm/houses/house/name/Lodge%20Park
17. Templemills House, Newtown Road, Celbridge, Co. Kildare W23 YK26
Open dates in 2024: Jan 14-26, Feb 3-9, May 1-31, Aug 17-25, 9am-1pm
Fee: adult €12, student/OAP €8, child free
Places to stay, County Kildare:
1. Balyna, Moyvalley, Co Kildare – weddings, accommodation
Now called Moyvalley Hotel. https://www.moyvalley.com/aboutus.html
The website tells us:
“Balyna House lies to the south of Moyvalley Bridge over the Grand Canal, about half way between Enfield and Kinnegad on the old Dublin — Galway road. The house lies in the centre of the estates 500 acres. Balyna Estate was granted in 1574 by Queen Elizabeth I to the O’Moore family because they had lost their land in Laois and were reinstated in Balyna.
“Major Ambrose O’Ferrall married Letitia More in 1796. Their eldest son Richard More O’Ferrall was born in 1797. [ I don’t think this is correct. I believe that Letitia More married Richard O’Ferrall (1729-1790) and that their son was Ambrose More O’Ferrall who married Ann Baggot daughter of John Baggot of Castle Baggot, Rathcoole. Richard More O’Ferrall (1797-1880) was their son]. He is reputed for having been responsible for the erection of the Celtic cross which now stands to the rear of the house. It is said that this Cross, along with another was transported from Europe, the two being encased in wooden crates and towed behind the ship on a barge. Legend has it that one was lost at sea, but its twin survives to this day.“
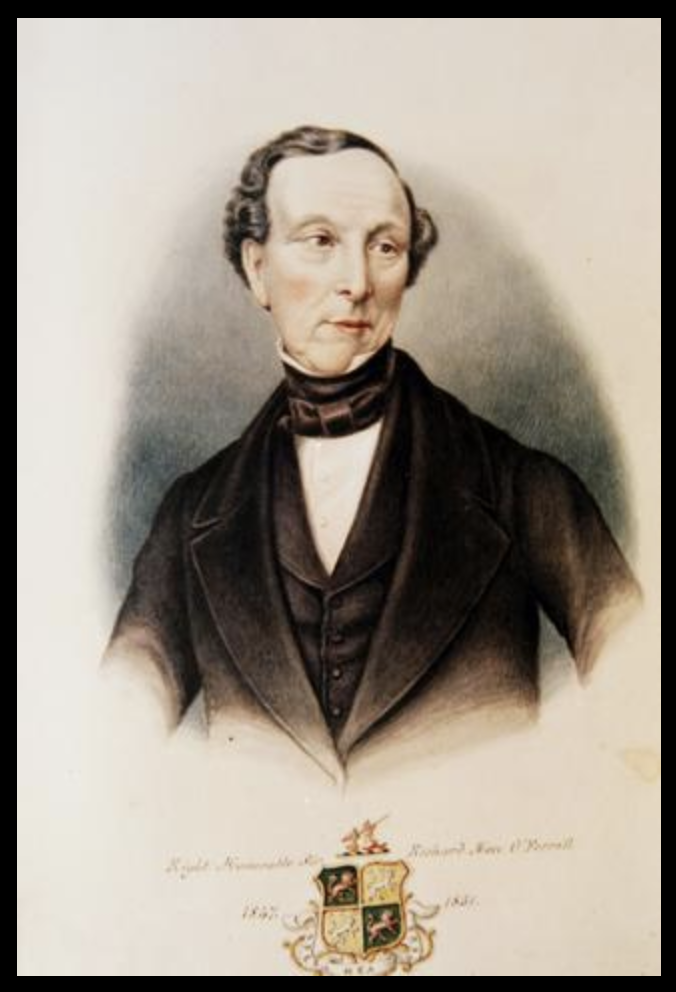


Mark Bence-Jones writes (1988):
p. 30. [More O’Ferrall] “The ancestral home of the O’More family, the land having been granted to them by Eliz I as a small compensation for their forfeited territories in Laois… A new house was built 1815, which was burnt 1878; this was replaced by the present house, built 1880s. It is slightly Italianate, with a Mansard roof carried on a bracket cornice; of 2 storeys with a dormered attic. Entrance front with two 3 sided bows and a single-storey Ionic portico, 5 by garden front with pediment, the windows on either side being larger than those in the centre. Imposing staircase with handrail of decorative ironwork; ceiling of staircase hall has modillion cornice. Chapel in garden. Sold 1960s, subsequently owned by Bewleys Oriental Cafe Ltd” [6]
The website continues: “The first real record of any house dates from 1815 when Ambrose built a large mansion. That Georgian house was burned down and replaced in the 1880’s by the present Italianate mansion.
“The estate was a refuge for bishops and priests for centuries and Dr. Forstall, Bishop of Kildare, ordained priests here in the year 1678 — 1680. For this loyalty, the family was granted Papal permission to build a private Chapel on the estate (located to the rear of the house) and up to approximately 1914 Sunday Mass was offered. It was only used intermittently after that, with the last occasion being in the summer of 1959.
“The estate remained in the More O’Ferrall family until May 1960 when it was sold to the Bewley family (of Café fame). The wonderful milk and cream in the Cafes came from the pedigree Jersey herd at Balyna. In 1984 the estate was sold to Justin Keating; it was sold again in 1990-1991 to George Grant. Moyvalley was developed into a Hotel & Golf Resort in 2007.
“Balyna House consists of 10 luxurious ensuite bedrooms, 3 reception rooms to cater for up to 100 guests, Balyna Bar and Cellar Bar. The house is available exclusively for private events and weddings.
“In 2014 the resort was purchased by the late Oliver Brady (well-known horse trainer from Co. Monaghan) with his business partner a well know entrepreneur Rita Shah owner of Shabra Recycling Plastic’s Group, Thai business woman Jane Tripipatkul and her son Mark McCarthy who are based in London.
“It is likely that several Irish and European military campaigns were discussed and argued over at Balyna, as apart from the fierce-some O’More’s and the well documented Irish battles in which they took part, several later generations saw service in European armies. All three sons of Richard and Letitia O’Ferrall saw service abroad. The eldest, Ambrose, and his youngest brother, Charles, rose to the rank of Major in the Royal Sardinian Army, while the middle brother, James attained the rank of Major General in the Austrian Hohenzollern Army.“
Incidentally, there was a Bagot family of “Castle Baggot” in Rathcoole, and neither son had children so all the Bagot property, which included land around Smithfield in Dublin and extensive property in County Carlow, passed to the daughter, Ann, who married the above-mentioned Ambrose More O’Ferrall.
“As a digression, it is worth noting that Rory O’ More’s eldest daughter, Anne, married Patrick Sarsfield, 1st Earl of Lucan and famous military leader. His father in law was the man behind the Irish Rebellion of 1641.
“King James had adopted the policy of remodelling the Irish army so as to turn it from a Protestant-led force to a Roman Catholic led one, and Sarsfield, whose family were Roman Catholics, was selected to assist in this reorganisation. Colonel Sarsfield went to Ireland with Richard Talbot, 1st Earl of Tyrconnell , who was appointed commander-in-chief by the king.“
2. Barberstown Castle, Kildare – hotel

Mark Bence-Jones writes (1988): p. 31. “A tower-house with a long plain 2 storey wing attached. In 1814, the residence of Jos Atkinson, in 1837, of Capt Robinson.”
The website gives a timeline:
“1288: Nicholas Barby built the original Castle towards the end of the 13th Century on the land which was originally owned by the Great Norman family the Fitzgerald’s.
“1310: The Castle was built as a fortress to protect the village and people of Barberstown from the attack of the rebellious Ui Faolain tribesmen who tried to burn the town (among others) in 1310. It has traditionally found itself in the middle of political struggle and local wars which generally resulted in change of ownership.
“Retaining Ownership: Some of its previous owners have gone to extreme lengths to retain ownership. Just how far some went is illustrated by the story of the body that is said to be interred in the tower of the Castle Keep (the original part of the Castle). His fate can be explained by reading the lease on the Castle at the time in which was written that the lease would expire when he was buried underground (ie. his death). The ending of a lease normally resulted in an increase in rent so after the man’s death he was buried in the tower above the earth which ensured the family continued to hold the lease to the Castle!
“The walls of the Castle Keep walls slope inwards so as to prevent an enemy getting out of range by closing up to the building. Ironically however the rooms on the upper floors of the Castle are larger than those on the ground level as their walls are somewhat thinner.
“Penal Times: The neighbouring village of Straffan is named after St. Straffan, one of the early sixth century missionaries. Its close linkages with the local town and people were proven when an underground tunnel from the Church in Straffan to the Castle was found in 1996 during renovations. A ‘Priest’s Hole’ can be also found in the Castle which was originally made to protect the priests of the town during Penal Times.
“1630: William Sutton of one of the most important families in the area owned the property. The population of Barberstown at the time was 36!
“1689: Lord Kingston [I’m not sure who they mean here – Robert King (d. 1693) was the 2nd Baron of Kingston at the time] had his ownership confiscated by Earl of Tyrconnell after the accession to power of James 11 of England. It was around this time that it fell into the less glamorous hands of the Commissioners of the Revenue who let it out to a Roger Kelly for £102 annual rent in the late 1600s.
“1703: It was purchased by Bartholomew Van Homreigh in 1703 for £1,033 the sixth owner in six years. At the time the property was 335 acres. Van Homreigh had been mayor of Dublin in 1697 and his greatest ‘claim to fame’ lies in the fact that he was the father of Vanessa of whom Swift wrote so passionately about. He sold it to the Henrys who were prone to excessive spending at the time….
“1830: The Henry’s had no option but to sell it to Mr. Hugh Barton [1766-1854] who completed the last wing of the house in the 1830s which added to the present day unique architectural status of Barberstown. He is also famed for constructing Straffan House known today at the K-Club.
“1900: As the property became too expensive to retain as a residence, the Huddlestons who owned Barberstown Castle in the 1900s sold it to Mrs. Norah Devlin who converted it into a hotel in 1971. Barberstown was one of the first great Irish country houses to display its splendour to the outside world when it opened as a hotel in 1971. It has maintained the elegance of design over the centuries by sympathetically blending its Victorian and Elizabethan extensions with the original Castle Keep.
“1979: The acclaimed Musician, Singer, Songwriter & Record Producer Mr. Eric Clapton CBE purchased the property in 1979 and lived in the property until 1987. Music sessions took place in the Green Room and original Castle Keep during the time Eric lived here with many famous Rockstars from all over the world coming here to stay.
“1987 to Present Day: Upon purchasing Barberstown Castle from Eric Clapton in 1987, this beautiful historic house has since been transformed from a 10-bedroom property with three bathrooms to a 55-bedroom Failte Ireland approved 4 Star Hotel. They are a proud member of Ireland’s Blue Book of properties and Historic Hotels of Europe.
“Since 1288 Barberstown has had 37 owners all of whom had the foresight to protect its heritage and character. Look out for the names of all the owners of Barberstown Castle painted on the bedroom doors of the hotel!“
3. Batty Langley Lodge, Celbridge, County Kildare €€
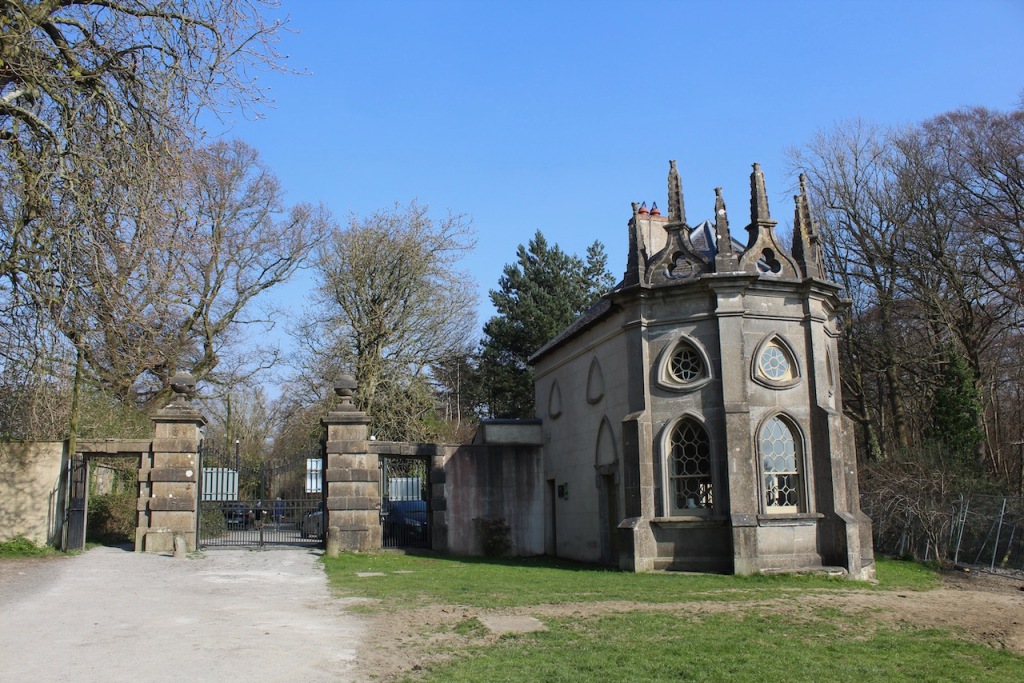

One of the entrances to the Castletown demesne has a Gothic lodge, from a design published by Batty Langley (1696-1751) 1741. Batty Langley was an English garden designer who produced a number of engraved “Gothick” designs for garden buildings and seats. He was named “Batty” after his father’s patron, David Batty. He also published a wide range of architectural books.
4. Burtown House holiday cottages – see above
5. Carton House, Kildare – open to public, hotel

The website tells us that the name ‘Carton’ comes from the old Irish name ‘Baile an Cairthe’ or Land of the Pillar Stone.
Mark Bence-Jones writes of Carton (1988):
p. 60. “(Talbot de Malahide, B/PB; Fitzgerald, Leinster, D/PB; Nall-Cain, sub Brocket, P/BP) The lands of Carton always belonged to the Fitzgeralds, Earls of Kildare, whose chief castle was nearby, at Maynooth; in C17, however, they were leased to a junior branch of the Talbots of Malahide, who built the original house there.”
The Carton website tells us that the lands of Carton first came into the ownership of the FitzGerald family shortly after Maurice FitzGerald (d. 1176) played an active role in the capture of Dublin by the Normans in 1170 and was rewarded by being appointed Lord of Maynooth, an area covering townlands which include what is now Carton. The website goes on to tell us:
“His son became Baron Offaly in 1205 [Gerald FitzMaurice FitzGerald, d. 1203] and his descendant John FitzGerald [5th Baron Offaly, d. 1316], became Earl of Kildare in 1315. Under the eighth earl, [Gerald FitzGerald (1455-1513)] the FitzGerald family reached pre-eminence as the virtual rulers of Ireland between 1477 and 1513.
However, the eighth earl’s grandson, the eloquently titled Silken Thomas [the 10th Earl of Kildare] was executed in 1537, with his five uncles, for leading an uprising against the English. Although the FitzGeralds subsequently regained their land and titles, they did not regain their position at the English Court until the 18th century when Robert, the 19th Earl of Kildare, became a noted statesman.“
It surprises me that after Silken Thomas’s rebellion that his brother was restored to the title and became the 11th Earl on 23 February 1568/69, restored by Act of Parliament, about thirty years after his brother was executed.
It was William Talbot, Recorder of the city of Dublin, who leased the lands from Gerald FitzGerald, 14th Earl of Kildare (1547-1612). William Talbot was created 1st Baronet Talbot, of Carton, Co. Kildare on 4 February 1622/23. He was MP for Kildare in 1613-1615. He built a house at Carton. His son Richard was created 1st Duke of Tyrconnell in 1689 by King James II, after he had been James’s Groom of the Bedchamber. He fought in the Battle of the Boyne and was loyal to the Stuarts, so was stripped of his honours when William of Orange (William III) came to power.
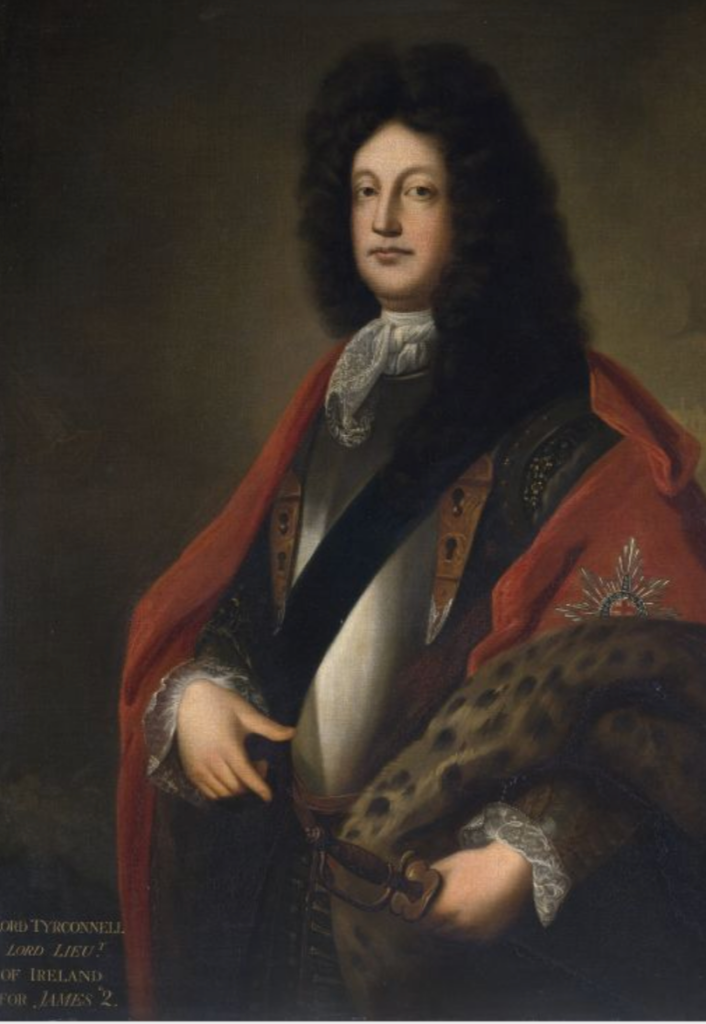


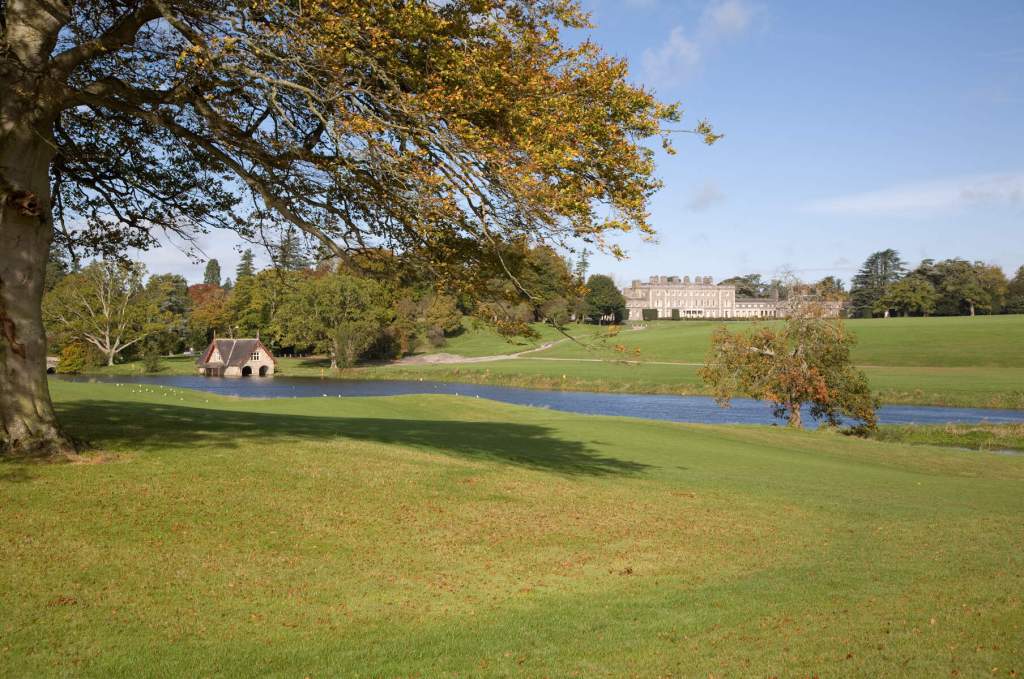
Mark Bence-Jones continues: “After the attainder of Richard Talbot, Duke of Tyrconnell, James II’s Lord Deputy of Ireland, Carton was forfeited to the crown and sold 1703 to Major-Gen Richard Ingoldsby, Master-General of the Ordnance and a Lord Justice of Ireland; who added a two storey nine bay pedimented front to the old house, with wings joined to the main block by curved sweeps, in the Palladian manner. In 1739 Thomas Ingoldsby sold the reversion of the lease back to 19th Earl of Kildare [Robert FitzGerald (1675-1744)], who decided to make Carton his principal seat and employed Richard Castle to enlarge and improve the house.“
Richard Ingoldsby (c.1664/5–1712) was the son of George, who came to Ireland with the Cromwellian army in 1651 and became a prominent landowner in Limerick. Richard fought in the Williamite army. The Dictionary of Irish Biography tells us that Richard Ingoldsby purchased Carton House and demesne in Co. Kildare for £1,800 in 1703 from the Talbot family. He also owned a town house in Mary St., Dublin. He married Frances, daughter of Col. James Naper of Co. Meath; they had at least one son, Henry Ingoldsby (d. 1731). Henry lived the high life in London and Carton had to be sold to pay his debts in 1738, and he sold it back to Robert Fitzgerald the 19th Earl of Kildare.
Robert FitzGerald the 19th Earl of Kildare married Mary O’Brien, daughter of William, 3rd Earl of Inchiquin.
Bence-Jones continues: “Castle’s rebuilding obliterated all traces of the earlier house, except for a cornice on what is now the entrance front and the unusually thick interior walls. He added a storey, and lengthened the house by adding a projecting bay at either end; he also refaced it. He gave the entrance front a pediment, like its predecessor; but the general effect of the three storey 11 bay front, which has a Venetian window in the middle storey of each of its end bays, is one of massive plainness. As before, the house was joined to flanking office wings; but instead of simple curved sweeps, there were now curved colonnades.”


The Archiseek website tells us:
“In 1739, the 19th Earl of Kildare employed Richard Castle to build the existing house replacing an earlier building. Castle (originally Cassels) was responsible for many of the great Irish houses, including Summerhill, Westport, Powerscourt House and in 1745, Leinster House, which he also built for the FitzGeralds.“


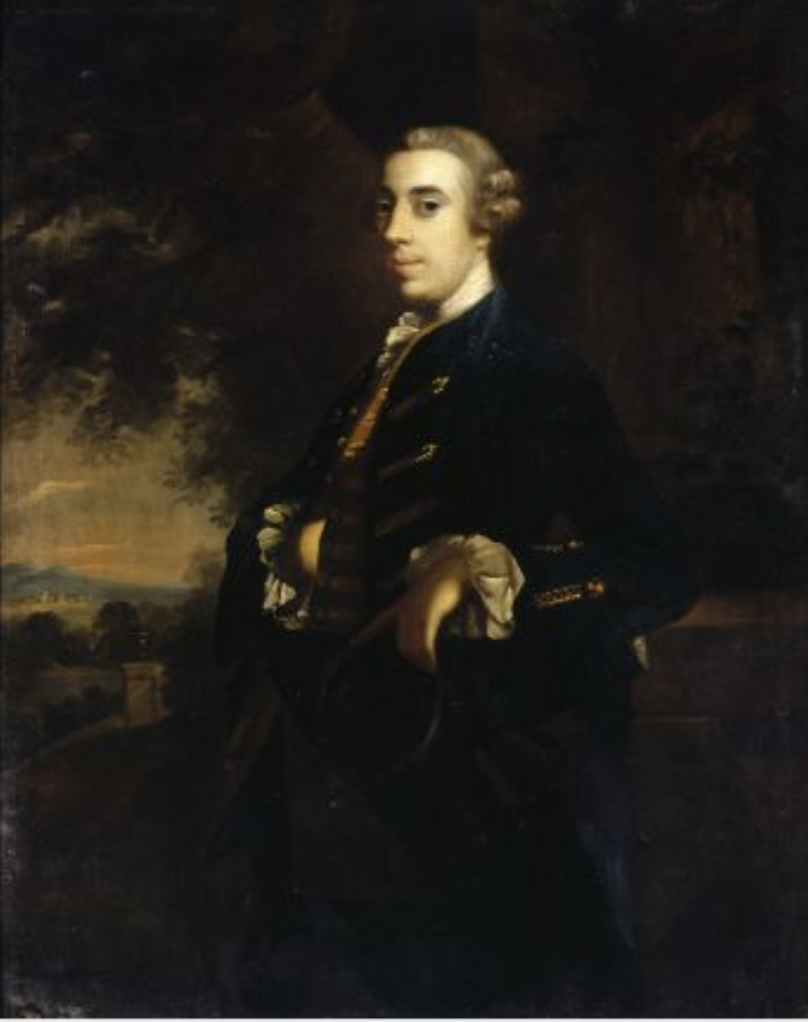
There is a projecting bay on either side of the garden front facade with a Venetian window in the middle storey of either projecting bay. According to Mark Bence-Jones, these were designed by Richard Castle. The flanking wings were joined initially by curved colonnades, later replaced by straight connecting links.
Mark Bence-Jones continues: “The work was completed after the death of 19th Earl for his son [James (1722-1773)], 20th Earl, who later became 1st Duke of Leinster and was the husband of the beautiful Emily, Duchess of Leinster [Emily Lennox, daughter of the 2nd Duke of Richmond] and the father of Lord Edward Fitzgerald, the United Irish Leader.”
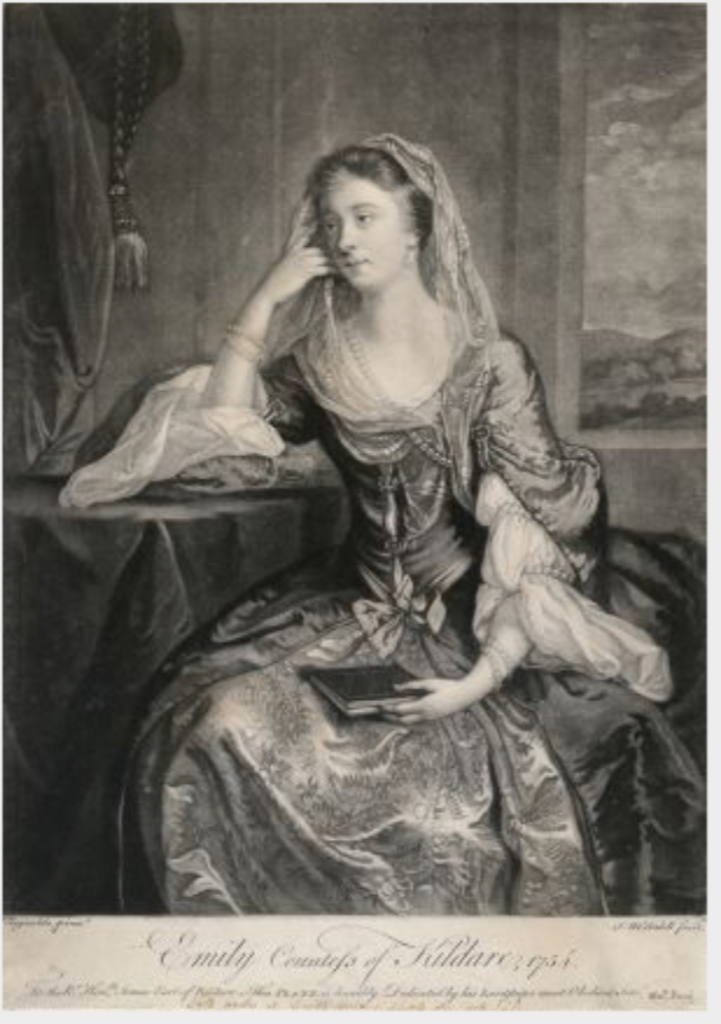


They certainly were a rebellious family! It is said that this saved the house from being burnt by Irish rebels in 1920s, as a portrait of Edward Fitzgerald the United Irishman was shown to the would-be arsonists. Emily Lennox’s sister, Louisa, married Thomas Conolly and lived across the parkland in Castletown House. Stella Tillyard writes of the life and times of the sisters, Emily and Louisa and it was made into a mini series for the BBC, entitled “The Aristocrats” which was filmed on site at Carton House. I’d love to read the book and see the movie! She also wrote about Edward FitzGerald.


Mark Bence-Jones continues: “3rd Duke, Lord Edward’s nephew, [Augustus Frederick Fitzgerald (1791-1874)] employed Sir Richard Morrison to enlarge and remodel the house ca 1815, having sold Leinster House in Dublin. Morrison replaced the curved colonnades with straight connecting links containing additional rooms behind colonnades of coupled Doric columns, so as to form a longer enfilade along what was now the garden front; for he moved the entrance to the other front [the north side], which is also of 11 bays with projecting end bays, but has no pediment. The former music room on this side of the house became the hall; it is unassuming for the hall of so important a house, with plain Doric columns at each end. On one side is a staircase hall by Morrison, again very unassuming; indeed, with the exception of the great dining room, Morrison’s interiors at Carton lack his customary neo-Classical opulence.”
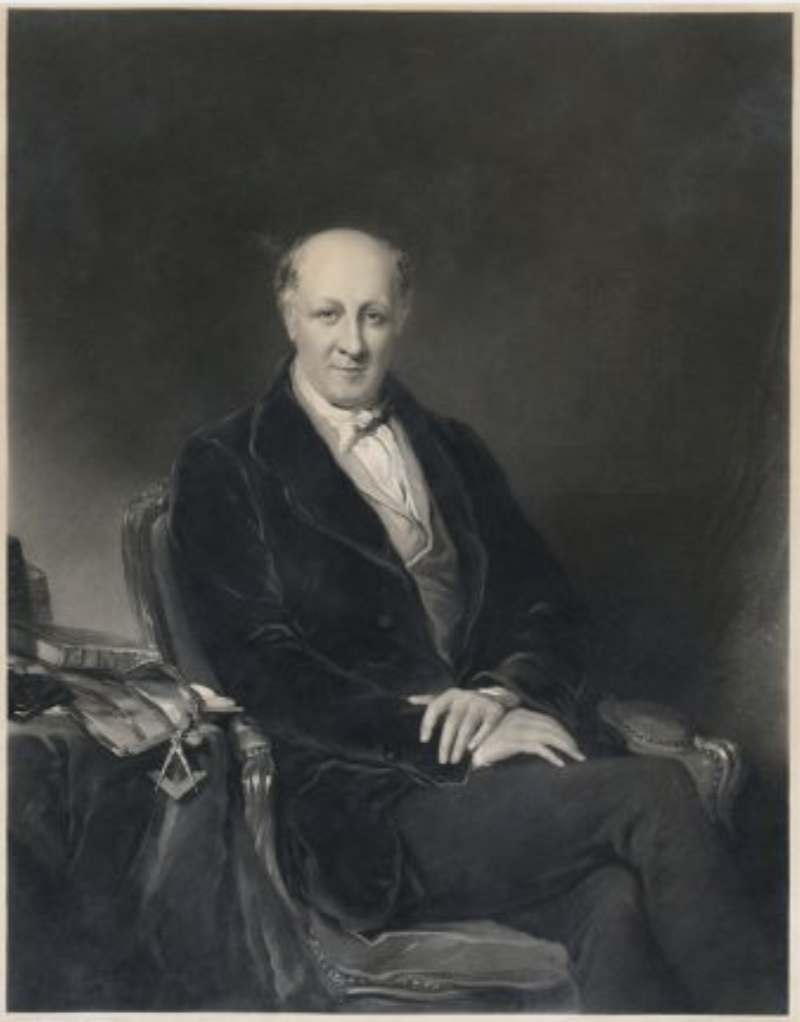

Archiseek continues: “Carton remained in the control of the FitzGeralds until the early 1920s when the 7th Duke sold the estate and house to pay off gambling debts of £67,500. In 2000, Carton was redeveloped as a “premier golf resort and hotel”. A hotel was added to the main house, and the estate’s eighteenth-century grounds and landscaping were converted into two golf courses.” [8]



Mark Bence-Jones continues: “Beyond the staircase, on the ground floor, is the Chinese bedroom, where Queen Victoria slept when she stayed here; it remains as it was when decorated 1759, with Chinese paper and a Chinese Chippendale giltwood overmantel. The other surviving mid-C18 interior is the saloon, originally the dining room, in the garden front, dating from 1739 and one of the most beautiful rooms in Ireland. It rises through two storeys and has a deeply coved ceiling of Baroque plasterwork by the Francini brothers representing “the Courtship of the Gods”; the plasterwork, like the decoration on the walls, being picked out in gilt. At one end of the room is an organ installed 1857, its elaborate Baroque case designed by Lord Gerald Fitzgerald [1821-1886], a son of the 3rd Duke.“
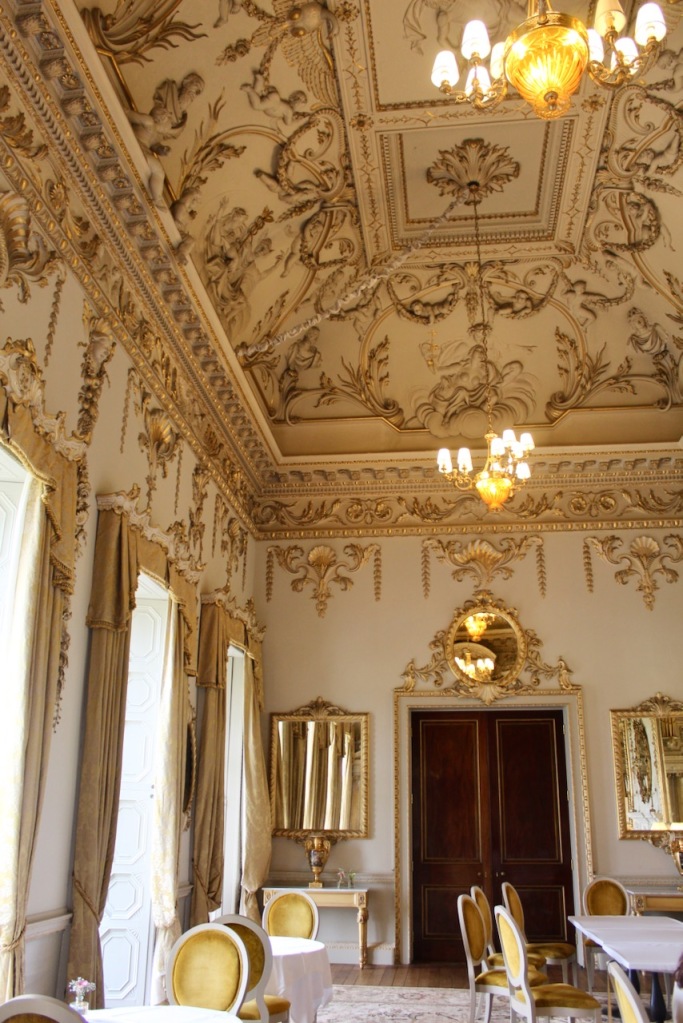
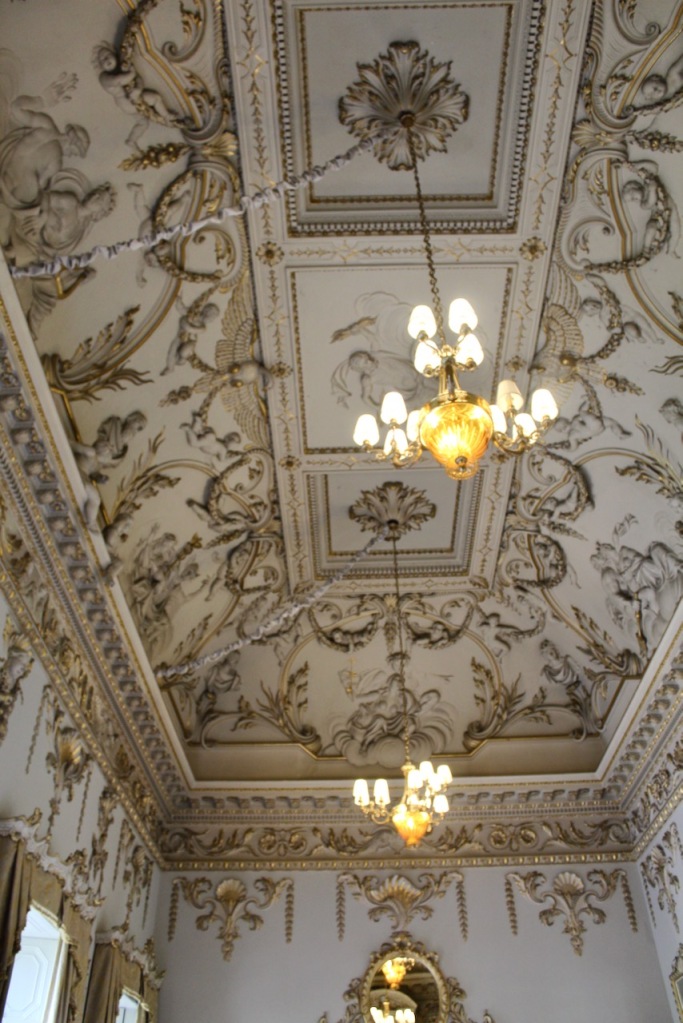
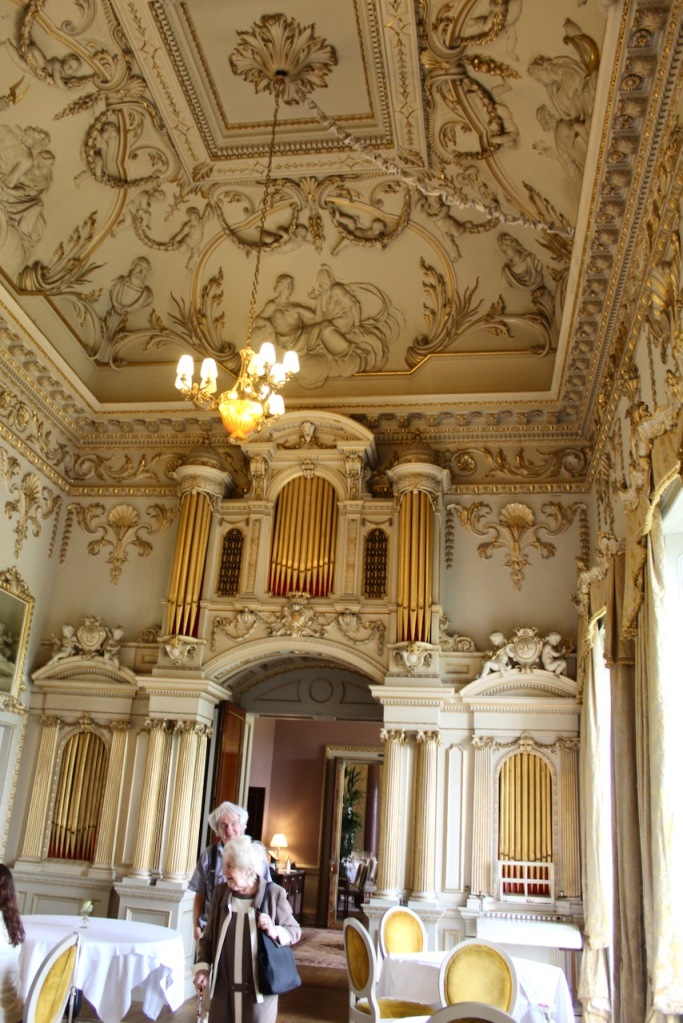
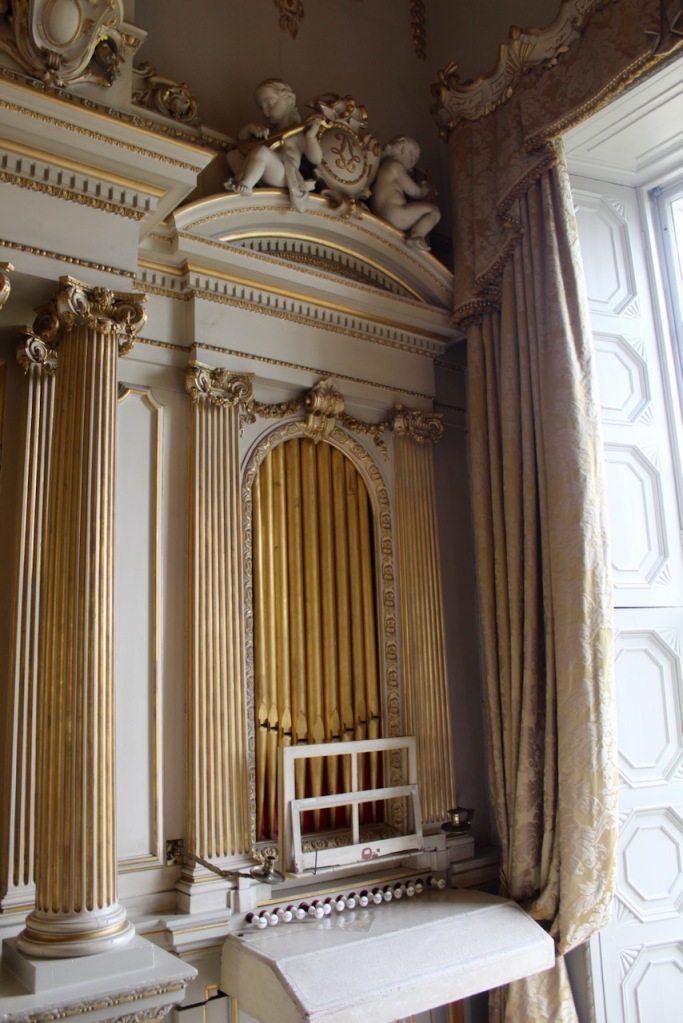
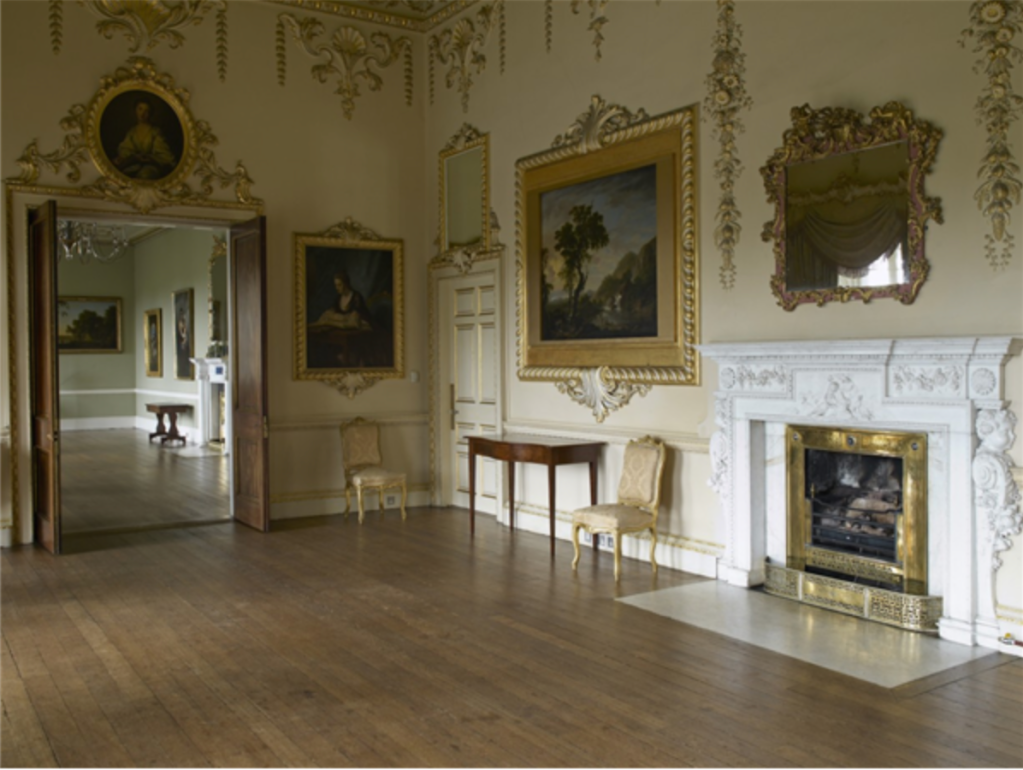
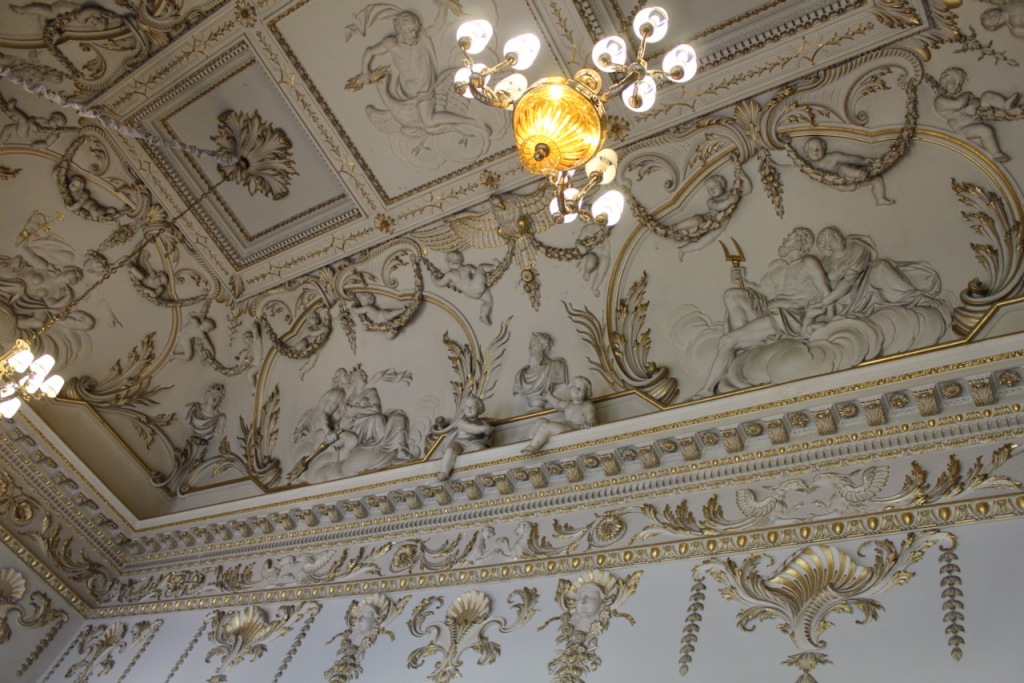








“The door at this end of the saloon leads, by way of an anteroom, to Morrison’s great dining room, which has a screen of Corinthian columns at each end and a barrel-vaulted ceiling covered in interlocking circles of oak leaves and vine leaves.
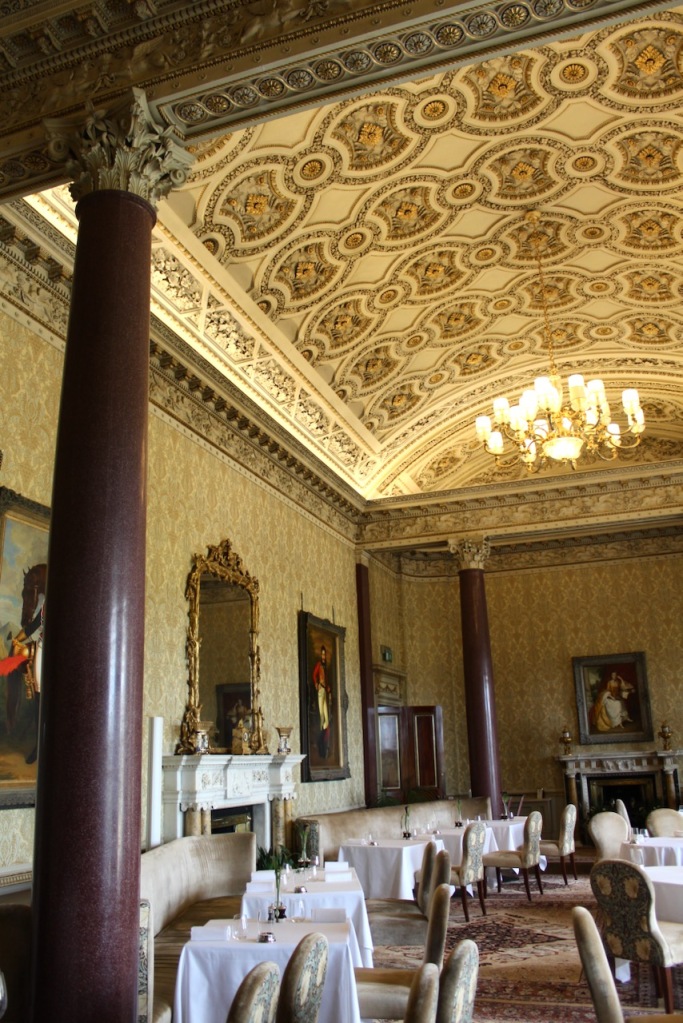
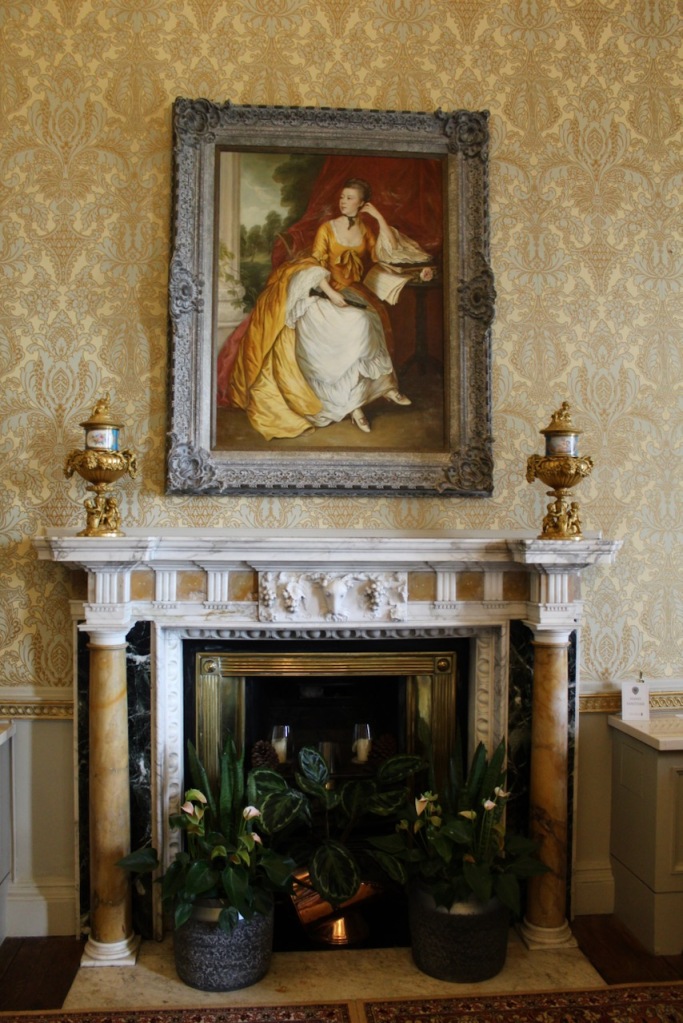
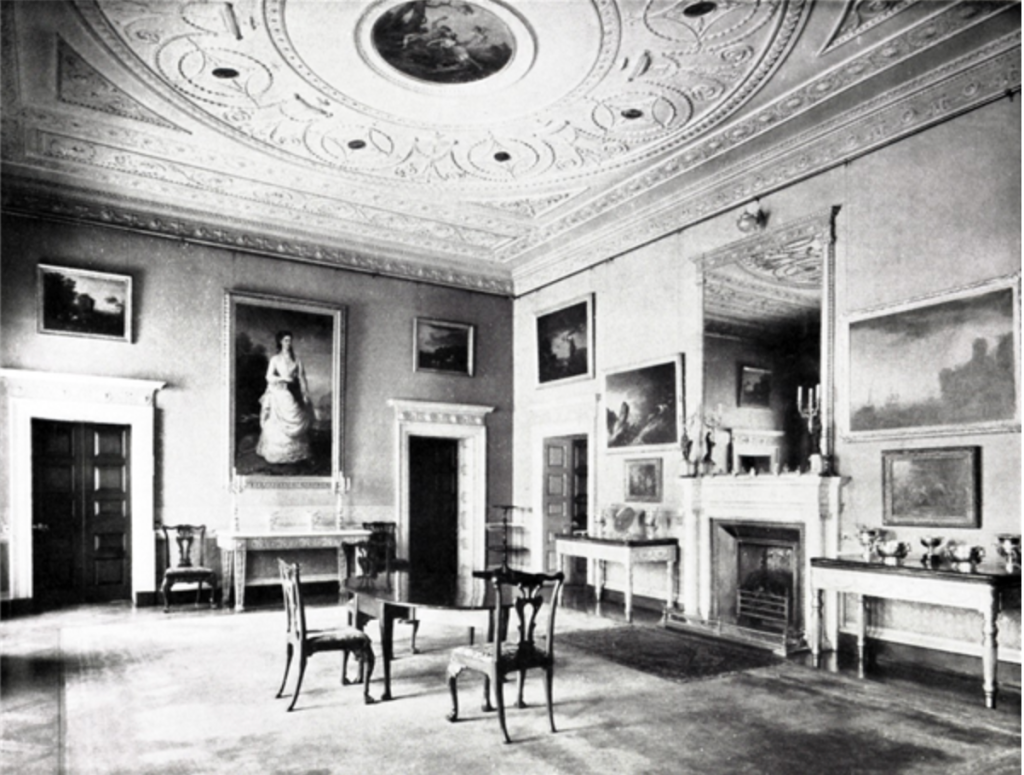






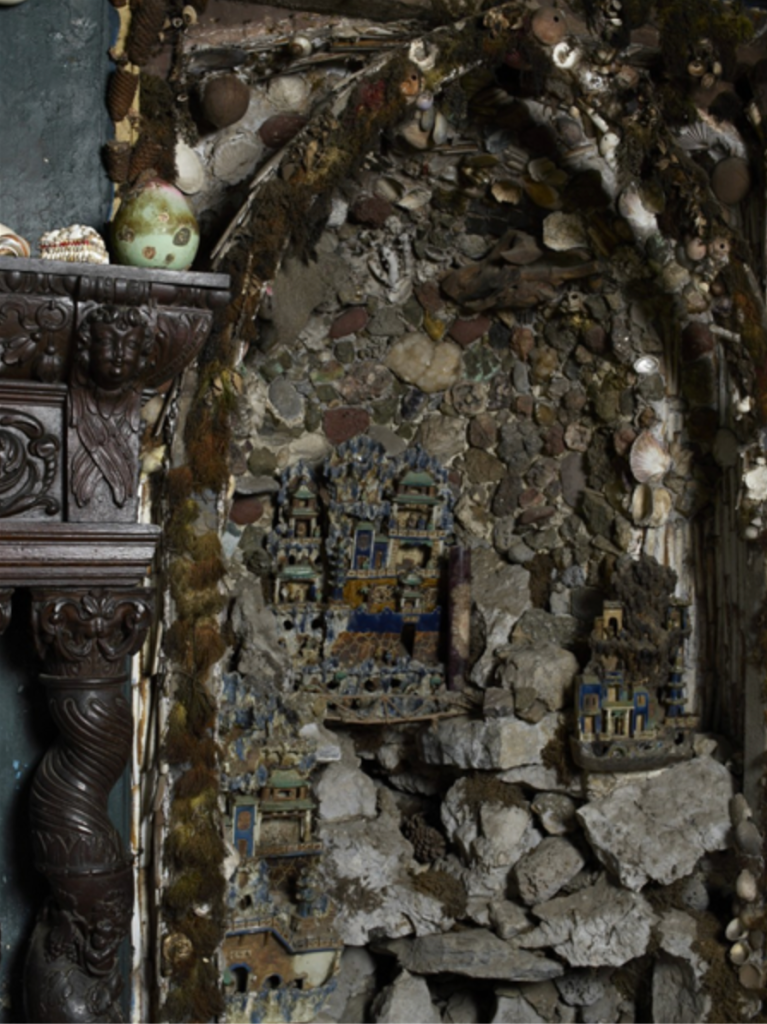
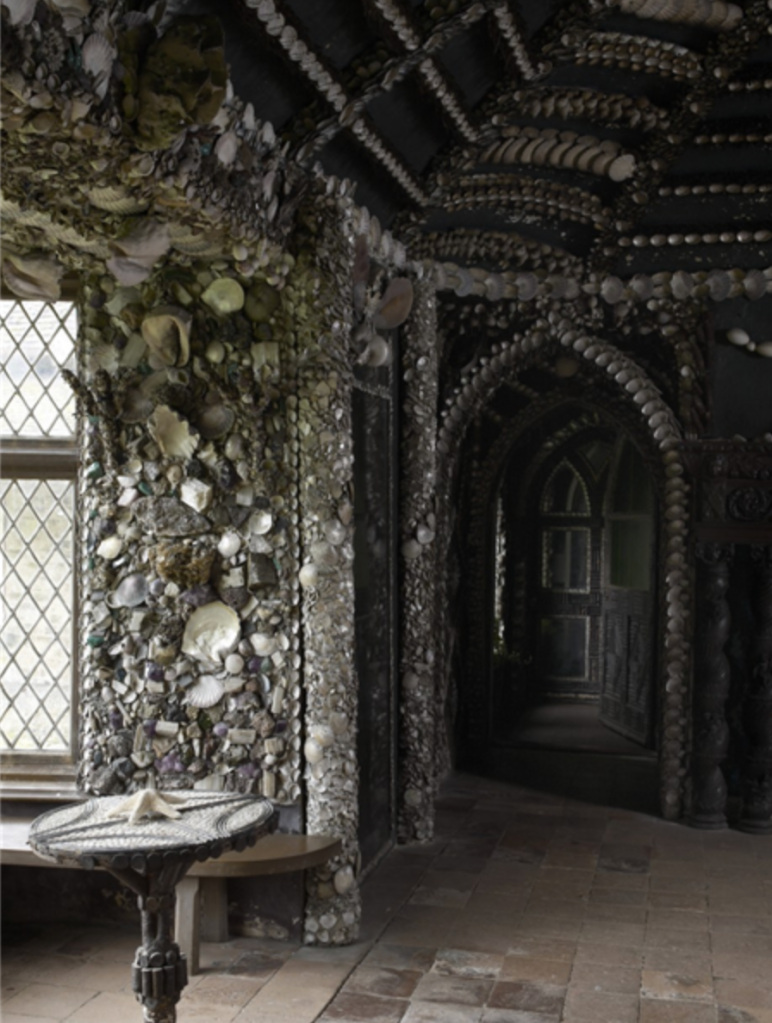
“The demesne of Carton is a great C18 landscape park, largely created by 1st Duke and Emily Duchess; “Capability” Brown was consulted, but professed himself too busy to come to Ireland. By means of a series of dams, a stream has been widened into a lake and a broad serpentine river; there is a bridge by Thomas Ivory, built 1763, an ornamental dairy of ca 1770 and a shell house. Various improvements were carried out to the gardens toward the end of C19 by Hermione, wife of 5th Duke, who was as famous a beauty in her day as Emily Duchess was in hers; she was also the last Duchess of Leinster to reign at Carton, for her eldest son, 6th Duke, died young and unmarried, and her youngest son, 7th Duke, was unable to live here having, as a young man, signed away his expectations to the “50 Shilling Tailor” Sir Henry Mallaby-Deeley, in return for ready money and an annuity. As a result of this unhappy transaction, Carton had eventually to be sold. It was bought 1949 by 2nd Lord Brocket, and afterwards became the home of his younger son, Hon David Nall-Cain, who opened it to the public. It was sold once again in 1977.”
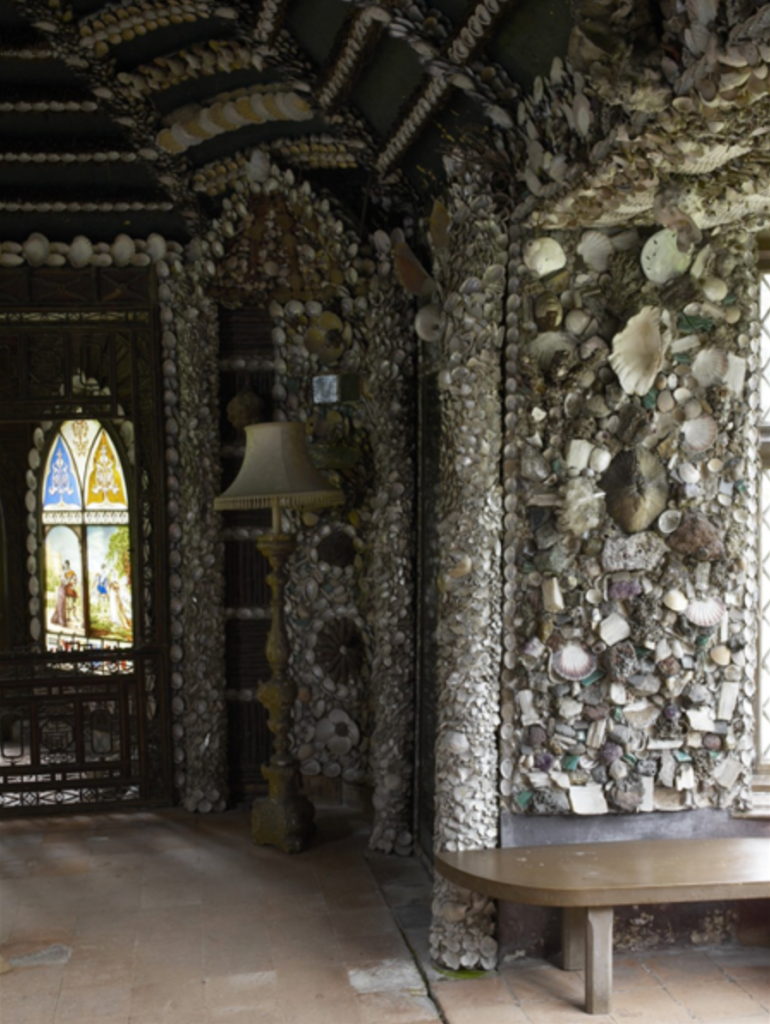




6. Castletown Gate Lodge, Celbridge, County Kildare € for 3

7. Castletown Round House, Celbridge, County Kildare: Irish Landmark € for 3-6
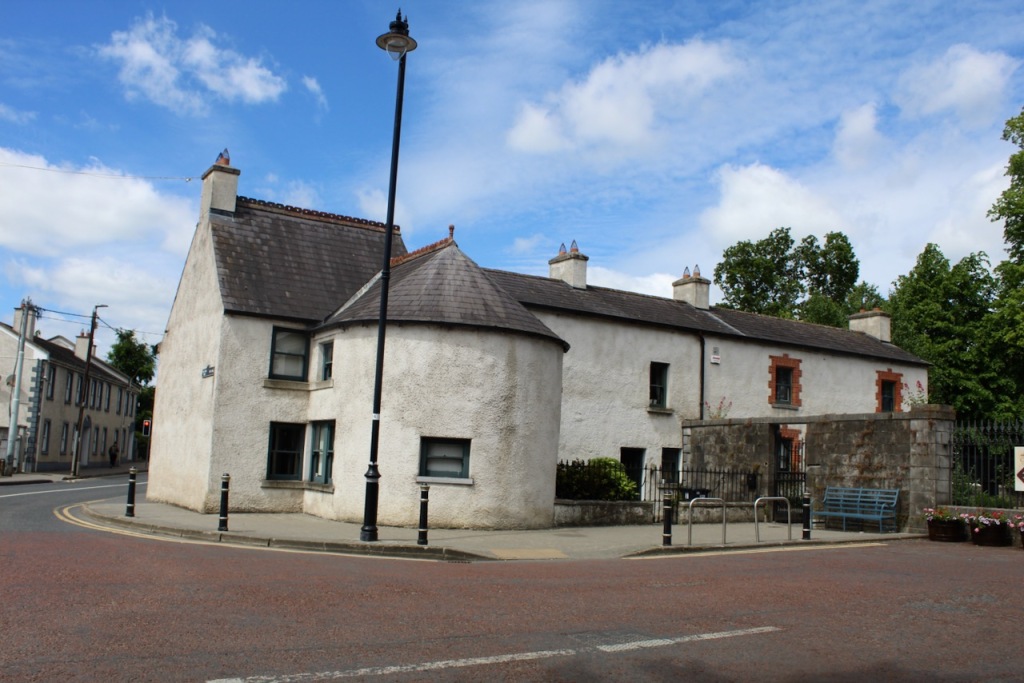

https://www.irishlandmark.com/property/castletown-round-house/
8. The Cliff at Lyons, County Kildare
Robert O’Byrne writes about the Cliff at Lyons:
“The Village at Lyons, County Kildare is often described as a restoration but to be frank it is more a recreation. By the time the late Tony Ryan bought the estate in 1996, the buildings beside the Grand Canal, which had once included a forge, mill and dwelling houses, were in a state of almost total ruin. Therefore the work undertaken here in the years prior to his death in 2007 involved a great deal of architectural salvage, much of it brought from France, although some Irish elements were incorporated such as a mid-19th century conservatory designed by Richard Turner, originally constructed for Ballynegall, County Westmeath. Today the place primarily operates as a wedding venue, providing an alluring stage set for photographs but bearing little resemblance to what originally stood here.”[9]

Mark Bence-Jones writes of Lyons:
p. 196. “(Alymer/IFR; Lawless, Cloncurry, B/PB1929; Winn, sub St. Oswalds, B/PB) Originally the seat of the Aylmer family. Sold 1796 by Michael Aylmer to Nicholas Lawless,the 1st Lord Cloncurry, son of a wealthy blanket manufacturer, who had a new house built in 1797, to the design of an architect named Grace.
“Three storey block with a curved bow on either side of its entrance front, joined to two-storey wings by curved sweeps. About 1801, shortly after his release from the Tower of London, where he had been imprisoned for two years on account of his advanced political views and friendship wiht some of the United Irishmen, the 2nd Lord Cloncurry hired Richard Morrison to undertake improvements and alterations to his father’s house, work continuing till 1805.
“During this period, Lord Cloncurry was in Italy, collecting antiques and modern sculpture for the house; he also acquired three antique columns of red Egyptian granite from the Golden House of Nero, afterwards at the Palazzo Farnese, which were used as three of the four columns in a single-storey portico at Lyons, with a triangular pediment surmounted by a free-standing coat-of-arms.The other notable alteration made to the exterior of the house at this time was the substitution of straight colonnades for the curved sweeps linking the main block to the winds, a change similar to that which Morrison made a few years later at Carton. Also the main block and wings were faced with rusticated ashlar up to the height of one storey on the entrnace front. The hall was given a frieze of ox-skulls and tripods based on the Temple of Fortuna Virilis in Rome, doorcases with fluted entablatures and overdoor panels with classical reliefs; a pair of free-standing antique marble Corinthian columns were set against one wall, and vaarous items from Lord Cloncurry’s collection fo sculpture disposed around the other walls. The walls of the dining room and music rom were painted with Irish waterfalls – and other enchanting decoration by Gaspare Gabrielli, an artist brought by Lord Cloncurry from Rome. The bow-ended dining room was also decorated with a wall painting, of Dublin Bay; and was adorned with reliefs of the story of Daedalus.”

Bence-Jones continues: “The seven-bay garden front was left fairly plain, but before it a vast formal garden was laid out, with abundant statuary and urns and an antique column supporting a statue of Venus half way along the broad central walk leading from the house to what is the largest artificial lake in Ireland. Beyond the lake rises the wooded Hill of Lyons.
“The Grand Canal passes along one side of the demesne, and there is a handsome Georgian range of buildings beside it which would have been Lord Cloncurry’s private canal station. A daughter of 3rd Lord Cloncurry was Emily Lawless, the poet, a prominent figure in the Irish Revival of the early yars of the present century. Her niece, Hon Kathleen Lawless, bequeathed the Lyons estate to a cousin, Mr G M V Winn, who sold it about 1962 to University College, Dublin, which has erected a handsome pedimented arch from Browne’s Hill, Co Carlow at one of the entrances to the demesne.”
Art Kavanagh’s book on the Landed Gentry and Aristocracy: Meath, volume 1, tells us more about the Aylmers of Balrath. During the reign of Henry VI, Richard Aylmer of Lyons was a Keeper of the Peace for both Dublin and Kildare. He was in charge of protecting the settler community from attack by the neighbouring O’Toole and O’Byrne septs. The family rose to become one of the most prominent families in Meath and Kildare and key figures in the Dublin administration. Before the end of the 16th century they had established two independent branches at Donadea in Kildare and Dollardstown in County Meath.
The first Aylmer of real significance, Art Kavanagh tells us, was John Aylmer (c. 1359 – c. 1415) who married Helen Tyrell of Lyons, an heiress, at the end of the 14th century, and so the family acquired Lyons. [p. 1, Kavanagh, published by Irish Family Names, Dublin 4, 2005]
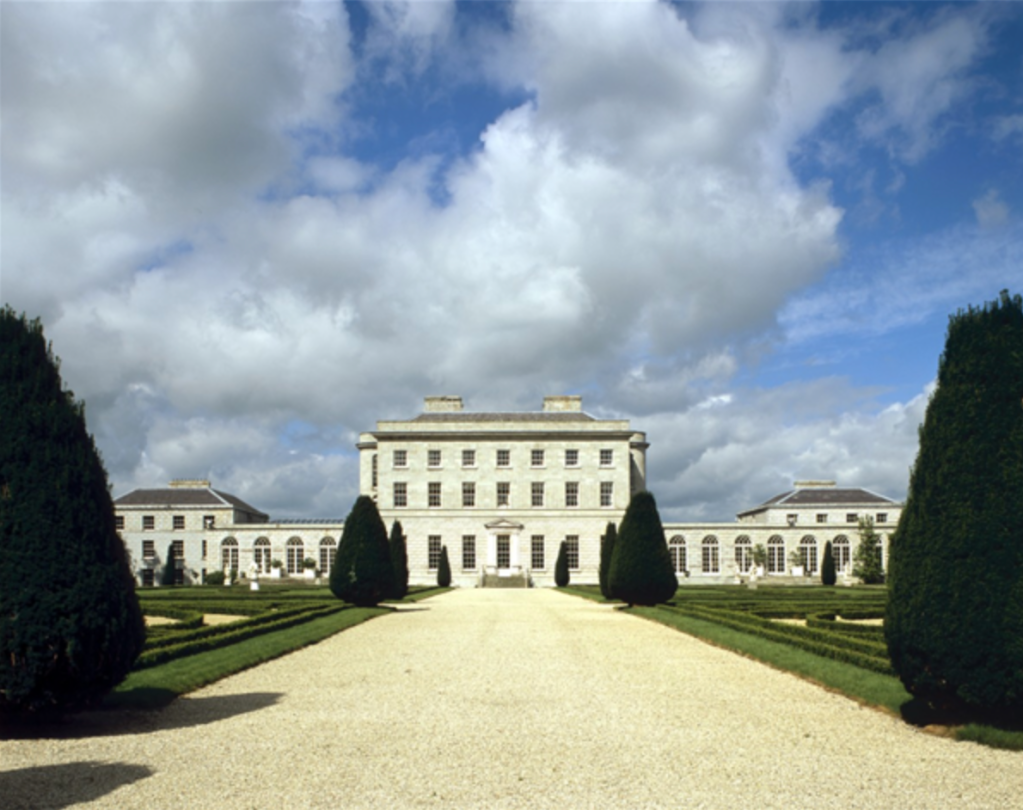
9. The K Club, Straffan House, County Kildare

The Straffan estate formed part of the original land grant bestowed upon Maurice Fitzgerald by Strongbow for his role in the Anglo-Norman invasion of 1169. In 1679, the property was purchased by Richard Talbot, the Duke of Tyrconnell who commanded the Jacobite army in Ireland during the war between James II and William of Orange. Tyrconnell’s estates were forfeited to the crown in the wake of the Williamite victory. In about 1710, the property was purchased by Hugh Henry, a prosperous merchant banker, who also owned Lodge Park. He married Anne Leeson, a sister of Joseph Leeson, 1st Earl of Milltown. Straffan passed to their son, Joseph, who travelled in Europe and collected art. In April 1764 he married Lady Catherine Rawdon, eldest daughter of the 1st Earl of Moira.
Their son John Joseph (1777-1846) married Lady Emily Fitzgerald, the 23-year-old daughter of the 2nd Duke of Leinster. He was an extravagant spender and had to sell Straffan in 1831.
Hugh Barton (1766-1854) acquired Straffan House from the Henry family in 1831 and his descendents remained there until the 1960s. The Barton family were part of the Barton & Guestier winemakers. Hugh soon commissioned Dublin architect, Frederick Darley, to build a new house, based on Madame Dubarry’s great Château at Louveciennes to the west of Paris. [10] The house passed through many hands subsequently.
Mark Bence-Jones writes of Straffan House (1988):
p. 266. “(Barton/IFR) An imposing C19 house in a style combining Italianate and French chateau. Main block of two storeys with an attic of pedimented dormers in a mansard roof; seven bay entrance front, the centre bay breking forward and having a tripartite window above a single-storey balustraded Corinthian portico. Entablatures on console brackets over ground-floor windows; triangular pediments over windows above and segmental pediment of central window. Decorated band between storeys; balustraded roof parapet; chimneystacks with recessed panels and tooth decoration. The main block prolonged at one side by a lower two storey wing, from which rises a tall and slender campanile tower, with two tiers of open belvederes. Formal garden with elaborate Victorian fountain. Capt F.B. Barton sold Straffan ca 1949 to John Ellis. It was subsequently the home of Kevin McClory, the film producer, and later owned by Mr Patrick Gallagher, who restored the main block to its original size.”
10. Kilkea Castle, Castledermot, Kildare – hotel

Mark Bence-Jones writes (1988):
p. 167. “(Fitzgerald, Leinster, D/PB) A medieval castle of the FitzGeralds, Earls of Kildare, especially associated with C16 11th Earl of Kildare, the most famous “wizard Earl.” [Gerald (1525-1585)] After Carton became the family seat in C18, it was leased to a succession of tenants; one of them being the Dublin silk merchant, Thomas Reynolds, friend of Lord Edward Fitzgerald through whom he became a United Irishman, only to turn informer when he realised the full aims of the movement. His role as informer did not prevent the unhappy Reynolds from having the castle, which he had only recently done up in fine style, sacked by the military; who tored up the floorboards and tore down the panelling on the pretext of searching for arms. Subsequent tenants caused yet more damage and there was a serious fire 1849; after which the third Duke of Leinster resumed possession of the castle and restored and enlarged it as a dower-house for his family. The work was sympathetically done, so that the tall grey castle keeps its air of medieval strength with its bartizans and its massively battered stone walls; though its battlements and its rather too regularly placed trefoil headed windows are obviously C19. AT one side of the caslte a long, low, gabled office range was added, in a restrained Tudor Revival style. The interior is entirely of 1849, for the lofty top storey, where the principal rooms were originally situated, was divided to provide a storey extra. The ceilings are mostly beamed, with corbels bearing the Leinster saltire. In 1880s the beautiful Hermione, Duchess of Leinster (then Marchioness of Kildare) lived here with her amiable but not very inspiring husband [Gerald the 5th Duke of Leinster]; finding the life not much to her taste, she composed the couplet “Kilkea Castle and Lord Kildare/are more than any woman can bear.” After the sale of Carton 1949, Kilkea became the seat of the 8th and Present Duke of Leinster (then Marquess of Kildare), but it was sold ca 1960 and is now an hotel.”
11. Leixlip Manor hotel (formerly Liffey Valley House hotel, formerly St. Catherine’s Park), Leixlip, Co Kildare
http://www.leixlipmanorhotel.ie/about-us/the-manor-kildare
The house that stood before the current Manor House was taller and was tenanted by the Earl of Lanesborough. Then in 1792, it was occupied by David La Touche, of the Huguenot banking family. It shortly thereafter burned to the ground and in around 1798 a new house, also called St Catherine’s Park, was built in the same townland to the design of Francis Johnston; it is now Leixlip Manor Hotel & Gardens.
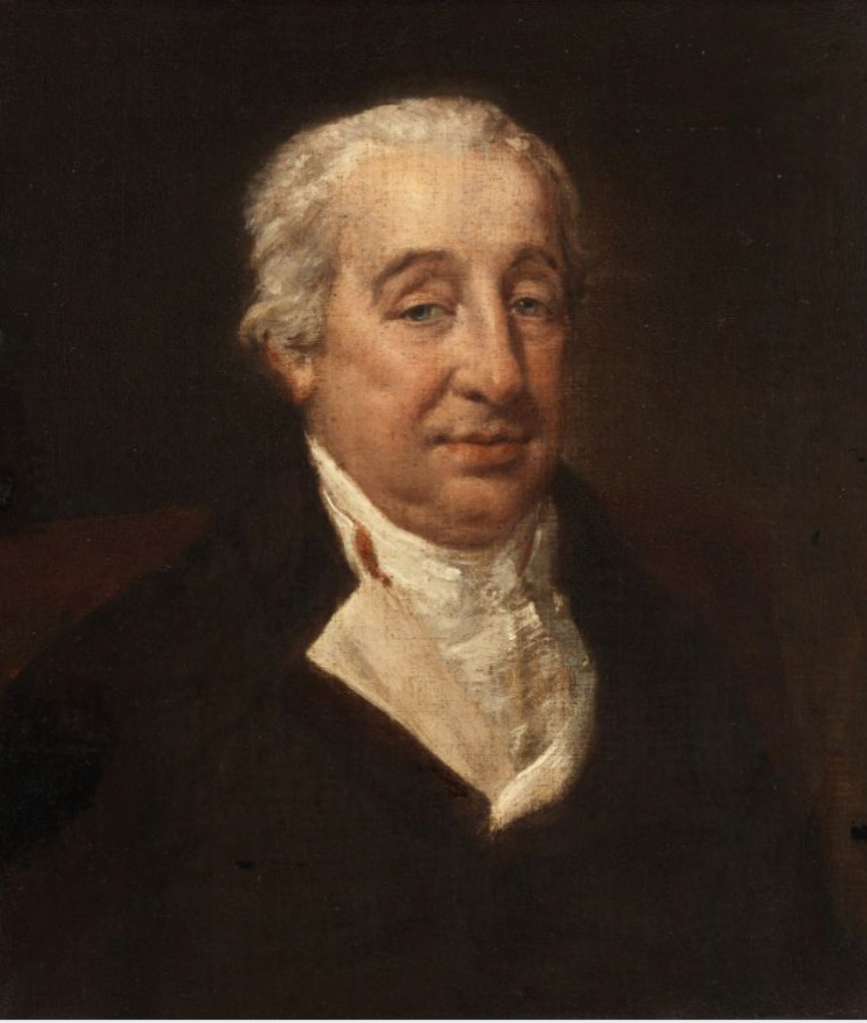

12. Martinstown House, Kilcullen, Co Kildare – accommodation

http://martinstownhouse.com/wordpress/
featured in Great Irish Houses. Forewards by Desmond FitzGerald, Desmond Guinness. IMAGE Publications, 2008.
p. 232. “Martinstown House is one of the finest cottage ornee style buildings in Ireland today. Originally part of the huge estates of the Dukes of Leinster, this fine house was commissioned by Robert Burrowes [d. 1850, son of Kildare Dixon Borrowes, 5th Baronet] and completed by the Burrowes family between 1832 and 1840, when decorative effects such as thatched roofs, undressed stonework and verandahs made of free growing branches were being incorporated into rural Irish dwellings. While experts feel the house was built in 1833, it may have been started years earlier, with many of the outbuildings including stables and also the walled gardens dating to some time between 1815 and 1820.” The book’s authors add that Decimus Burton was involved in the creation of this house.
See also Robert O’Byrne’s entry, which has lovely pictures: https://theirishaesthete.com/2022/03/07/martinstown/
13. Moone Abbey, County Kildare holiday cottages – see above
Whole house accommodation in County Kildare:
1. de Burgh Manor (or Bert), Kilberry, County Kildare – whole house accommodation

“Beautiful self catering, Georgian Manor centrally located in the hearth of Kildare in a very private setting. De Burgh Manor comprises of 15 bedrooms all ensuite. The ground floor consists of a double reception room, drawing room, dining room, bar, library , breakfast room and kitchen. Situated on c. 6 acres of grounds overlooking the River Barrow.“
The website also tells us about the history:
“De Burgh Manor was built circa 1709 [the National Inventory says it was built around 1780] by Thomas Burgh [1670-1730] of Oldtown [built ca 1709 by Thomas Burgh (1670-1730), MP, Engineer and Surveyor-General for Ireland, to his own design. The centre block was burned 1950s. A house has now been made out of one of the wings. He also designed Kildrought house, a Section 482 property] for his brother William Burgh later known as Captain William De Burgh and who became Comptroller and Auditor General for Ireland. Thomas Burgh was Barracks Overseer for Ireland from 1701 and was also responsible for [building] – the Library at Trinity College Dublin, Collins Barracks Dublin – now a museum – and Dr Steeven Hospital Dublin.
“William De Burgh was born in 1667 and had a son, Thomas, and a daughter, Elisabeth. Thomas, born in 1696, eventually became a Member of Parliament for Lanesboro, Co. Longford. Freeman of Athy Borough and Sovereign of Athy, in 1755 he married Lady Ann Downes, daughter of the Bishop of Cork & Ross. Her mother was a sister to Robert Earl of Kildare. Her brother, Robert Downes, was the last MP for Kildare in 1749 and was Sovereign of Athy.
“Thomas had two sons, William and Ulysses [Ulysses was actually the grandson of Thomas, son of another Thomas]. William born in 1741 went on to represent Athy as an MP in Parliament between 1768 and 1776. A monument to his memory by Sculptor Sir Richard Westmacott, a statue of faith, which depicts him with a book in one hand and a scroll in the other and stands in York Minster. He wrote two books on religion and faith.
“Ulysses, born in 1788 succeeded to the title of Lord Downes [2nd Baron Downes of Aghanville] on the death of his cousin William Downes who was made Lord Chief Justice in 1803 and created Lord Downes on his retirement in 1822. It was Ulysses De Burgh who presented the Town Hall Clock to Athy in 1846 and it was he who had the wings added to Bert House. [Mark Bence-Jones writes of Bert: “enlarged early in C19 by the addition of two storey Classical overlapping wings, of the same height as the centre block; which is of three storeys over basement with two seven bay fronts.”]
“Ulysses’ daughter Charlotte was the last of the De Burgh’s to call Bert House home with her husband Lt. General James Colbourne [2nd Baron Seaton of Seaton, co. Devon]. Charlotte and James came to Bert House in 1863 as Lord and Lady Seaton after the death of Lord Downes. It was sold by them in 1909 to Lady Geoghegan who then sold it onto her cousin, Major Quirke.“
2. Firmount, Clane, County Kildare – whole house or weddings
https://www.firmounthouse.com/
The website tells us:
“Firmount House is a unique and stunning venue just outside Clane in County Kildare, only 40minutes from Dublin city centre. Lovingly restored by the owners, the house is known for flexibility and creativity and is now open for weddings, private parties, film shoots, yoga retreats and corporate events. Enjoy visiting the Firmount website and see for yourself the lifelong journey these restoration warriors have taken to provide you with the perfect location in a wonderful, natural setting.
“This fabulous house consists of a sitting room, breakfast room and dining room downstairs reached from a large hallway, alongside a commercial kitchen and butlers pantry. The first floor consists of seven large and sumptuous bedrooms – five doubles and two twin rooms with plenty of room for two travel cots which are also provided. There are also six bathrooms. Heated by oil fired radiators, there are also two stoves in the main entertaining space.
“Firmount House has a colourful history dating from the 13th century when there was reputed to be a fortified house on the current site. The Down Survey of 1655 seems to show a house on the land (then known as Keapock). In the 18th century the house was owned by the Warburtons and sat on extensive grounds. The story of the current house really begins in 1878 when Hugh Henry Snr having married his cousin Emily Henry (of Lodge Park, site of the current K-club) bought Firmount house and renovated it extensively. It seems he took what was a Georgian house, wrapped it in concrete (one of the first houses of it’s kind) and added a Victorian wing to the South.
“The estate consisted of 409 acres at that point. Hugh Henry’s son, imaginatively named Hugh Jr, inherited the house in 1888 and lived there until 1917. It is rumoured that his wife, Eileen, had nightmares of the house going down in flames – although given it was made of concrete, we think she would have been ok. The house became a WWI hospital in 1917 and 390 soldiers were treated there until 1919, with no deaths registered – thank goodness for that. However the next decades were not so lucky for the house. In 1929 the house was bought by Kildare County Council and turned into a TB sanatorium. It ran as such until 1961. There are local stories of movies being run in the ballroom for patients with the now Mayor of Clane, at the projector. And of patients sitting on the elevated banks at the very front of the house on the roadside, watching life on the road go by but being unable to participate. 1964 brought the purchase of the house by the Department of Defence who ran it as a Control Centre for Nuclear Tracking and named it Section Seven Regional Control.
“Here things get really interesting as the basement of the house was intended to house senior officials, media and communications personel in the event of nuclear fall out. It is rumoured the Taoiseach (Irish prime-minister) was supposed to have a bunker on site and the house can still be found on Russian nuclear maps! This picture shows one of the several signs found in the house. The downside of government and county council ownership is that many original period features were lost through ignorance, neglect and the reinforcement of windows, floors, porticos and doors with concrete.
“The current “madthings” bought the house in 2012 with the aim of slowly bringing Firmount house back to life, window by window and floor by floor aswell as bringing Firmount forward into a gathering place with a welcome for all.“
3. Griesemount House, County Kildare, whole house rentals – see above
[1] https://www.ihh.ie/index.cfm/houses/house/name/Burtown%20House
[2] http://lordbelmontinnorthernireland.blogspot.com/search/label/County%20Kildare%20Landowners
[3] https://www.ihh.ie/index.cfm/houses/house/name/Griesemount%20House
[5] https://www.ihh.ie/index.cfm/houses/house/name/Millbrook%20House
[6] Bence-Jones, Mark. A Guide to Irish Country Houses (originally published as Burke’s Guide to Country Houses volume 1 Ireland by Burke’s Peerage Ltd. 1978); Revised edition 1988 Constable and Company Ltd, London.
[7] https://www.irelandscontentpool.com/en
[8] https://archiseek.com/2014/carton-maynooth-co-kildare/
[9] https://theirishaesthete.com/2020/01/08/a-stage-set/
[10] http://www.turtlebunbury.com/history/history_family/hist_family_barton.html