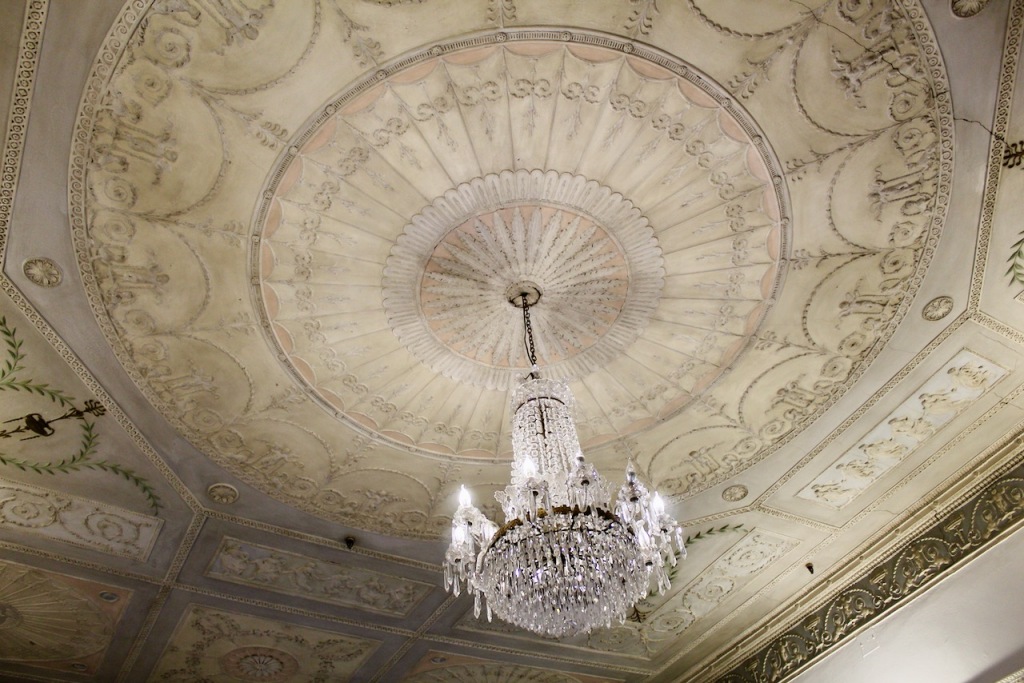
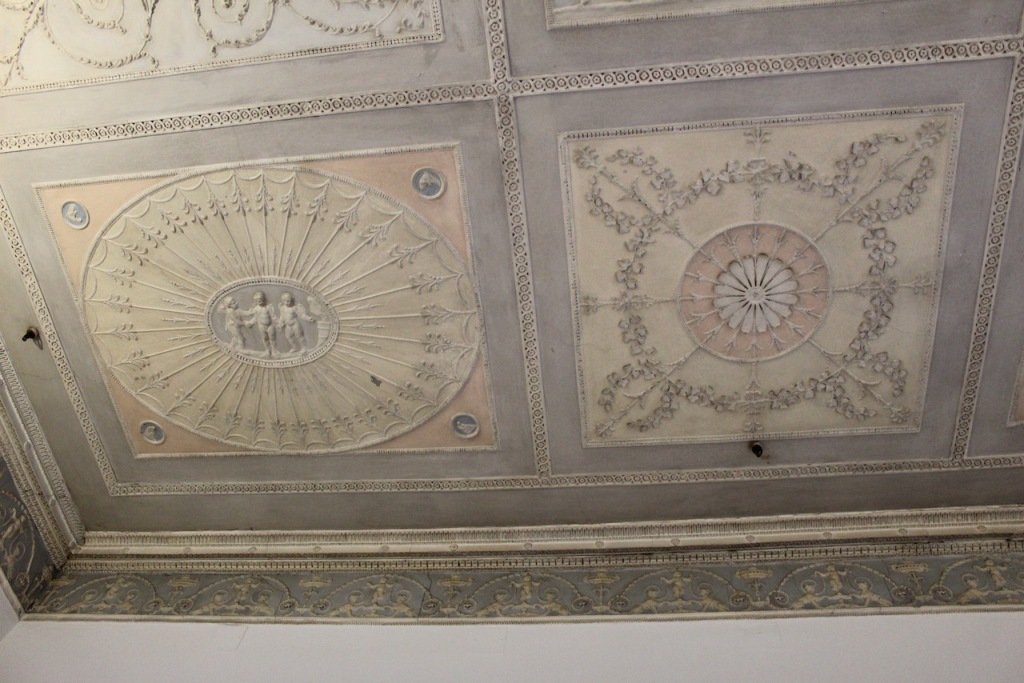
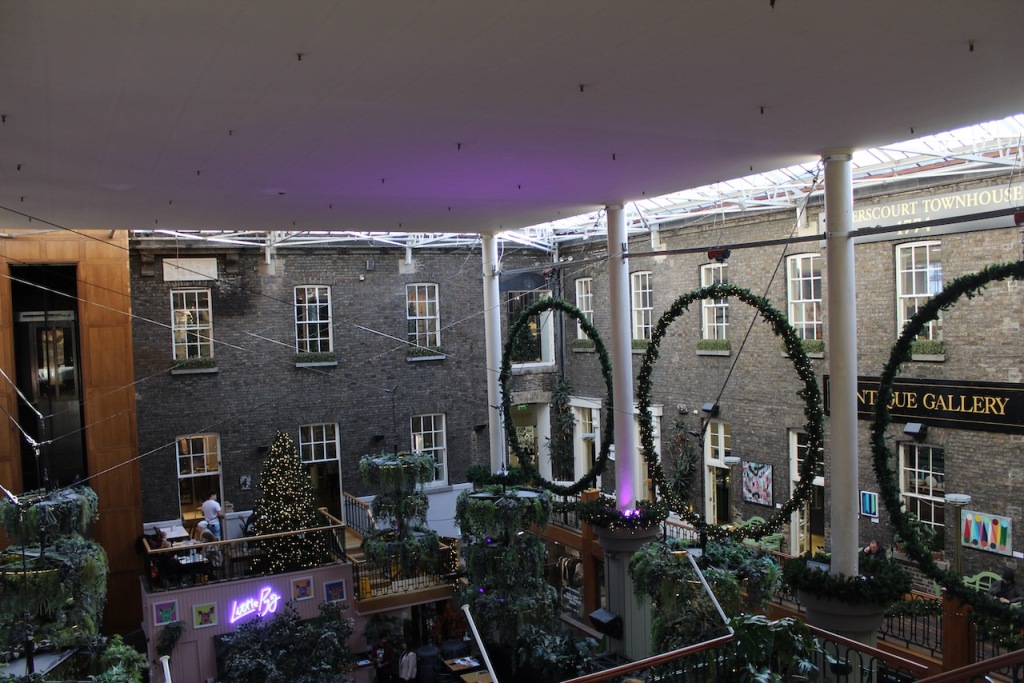
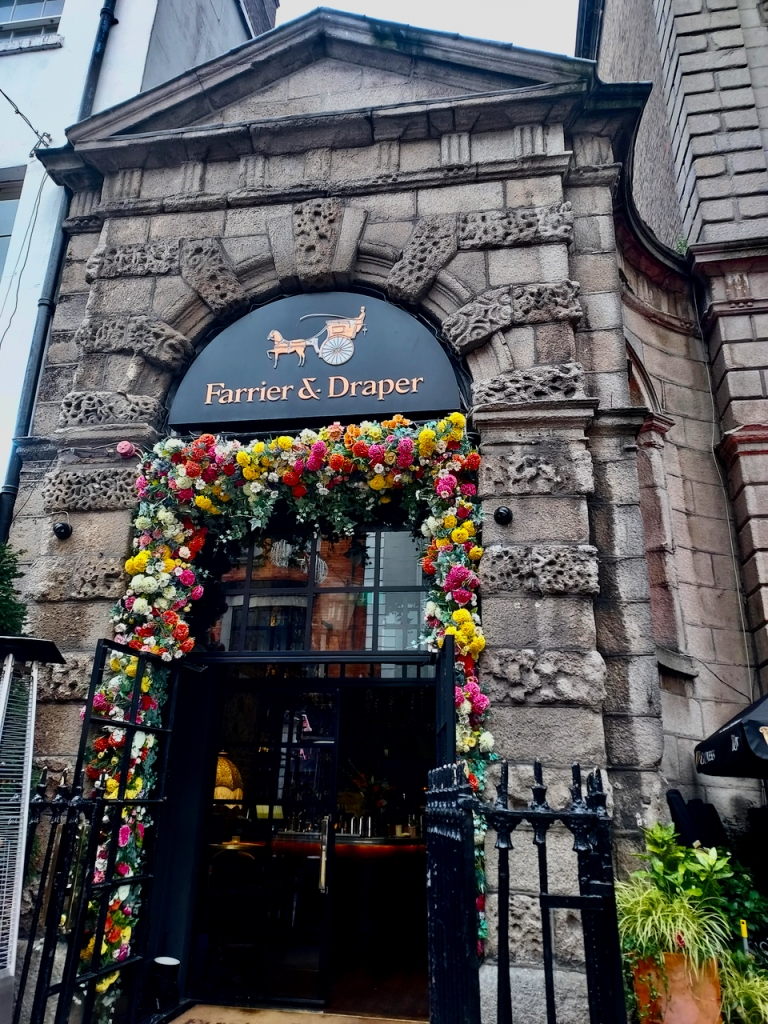
Open in 2026: Jan 12-Dec 22, Jan-Feb, Nov-Dec 10.30am-4pm, Mar-Apr, Sept-Oct, 10am-5pm, May-Aug, 10am-6pm
Fee: adult house €15, tour of house €19, child €7.50, tour of house €10.50, OAP/student €12.50, tour of house €15, family €31.50, tour of house €39.50

donation
Help me to pay the entrance fee to one of the houses on this website. This site is created purely out of love for the subject and I receive no payment so any donation is appreciated!
€15.00
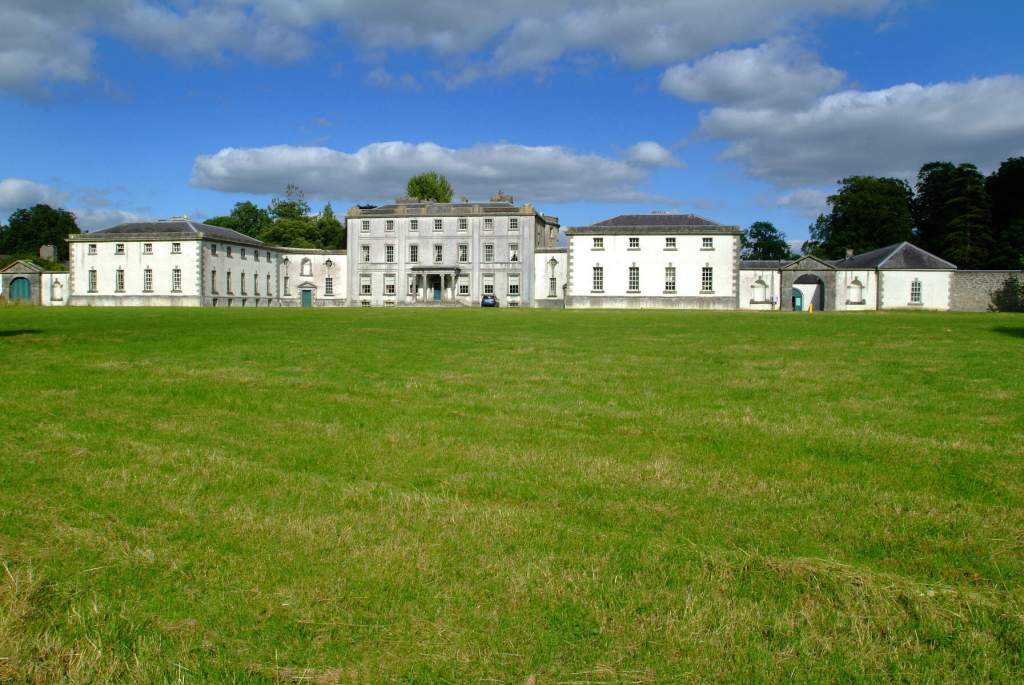
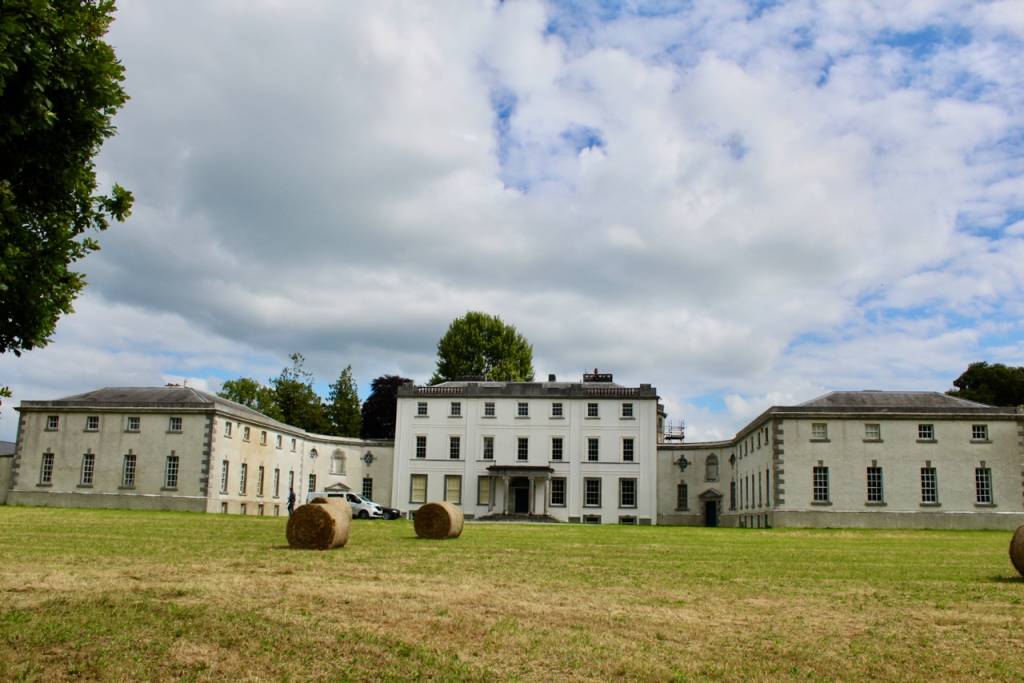


The Archiseek website describes Strokestown Park house as “a substantial house in the Palladian manner of a central block flanked by wings and curved sweeps. The centre block was completed in 1696 but extended around 1730 by Richard Cassels who added the substantial wings. The house was further altered in 1819 by J. Lynn.” [2]

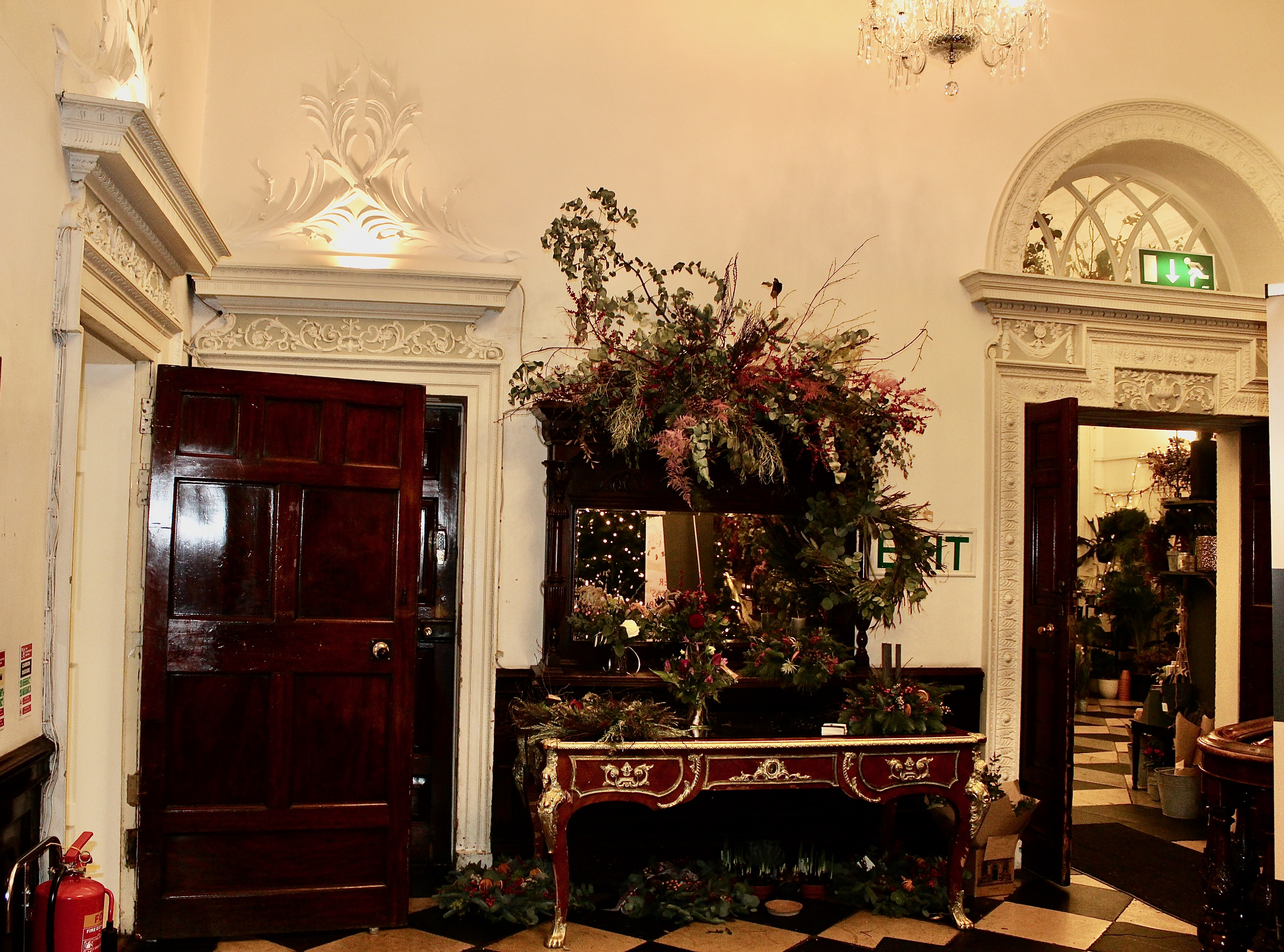
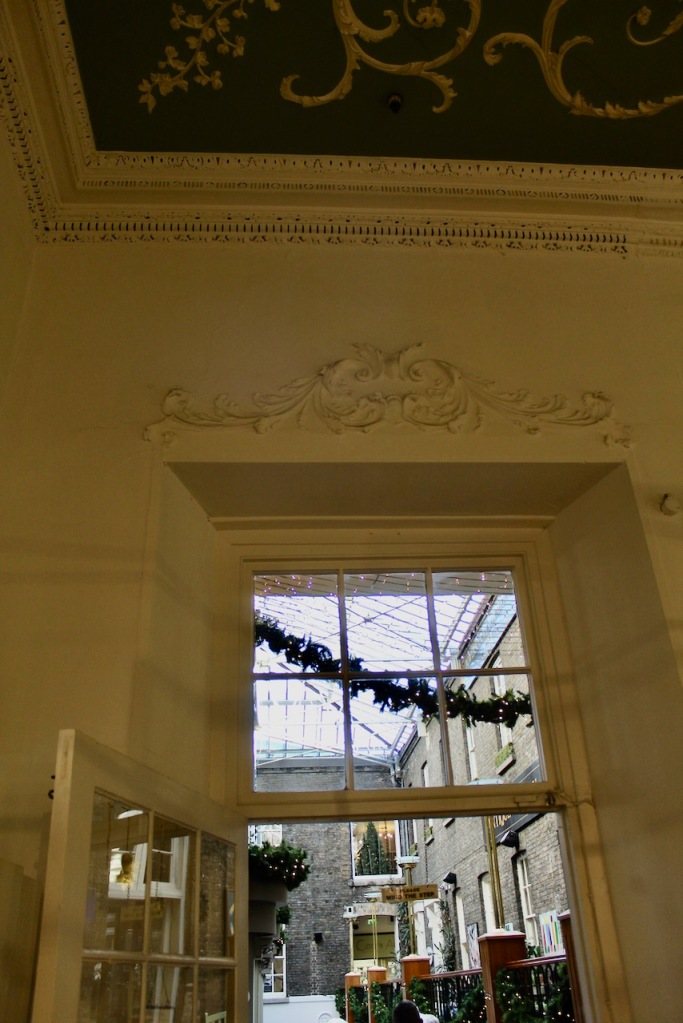
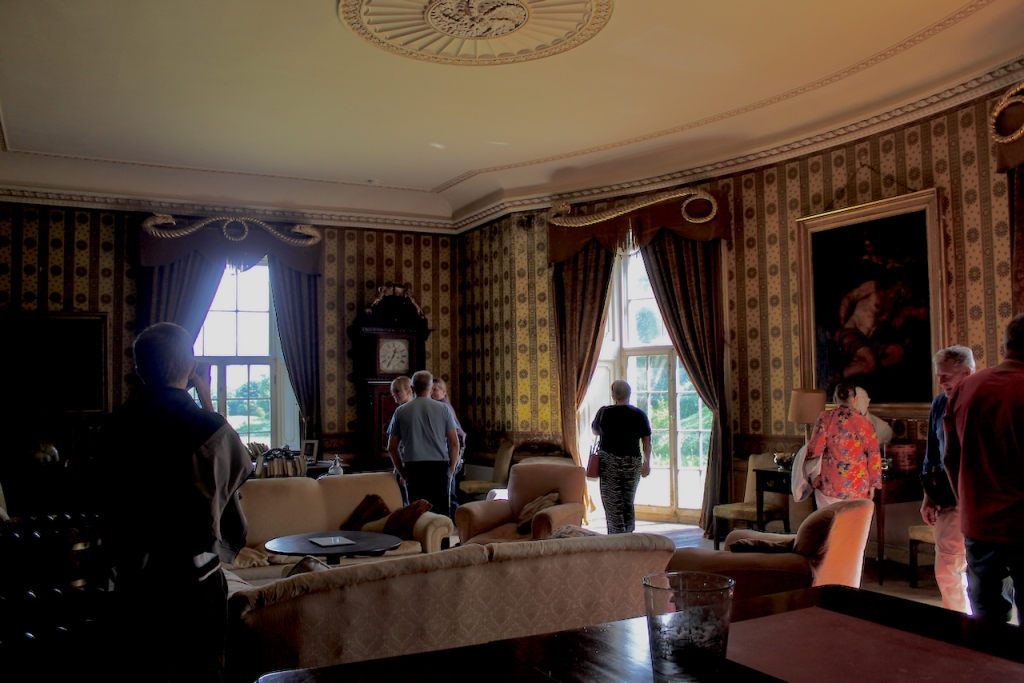
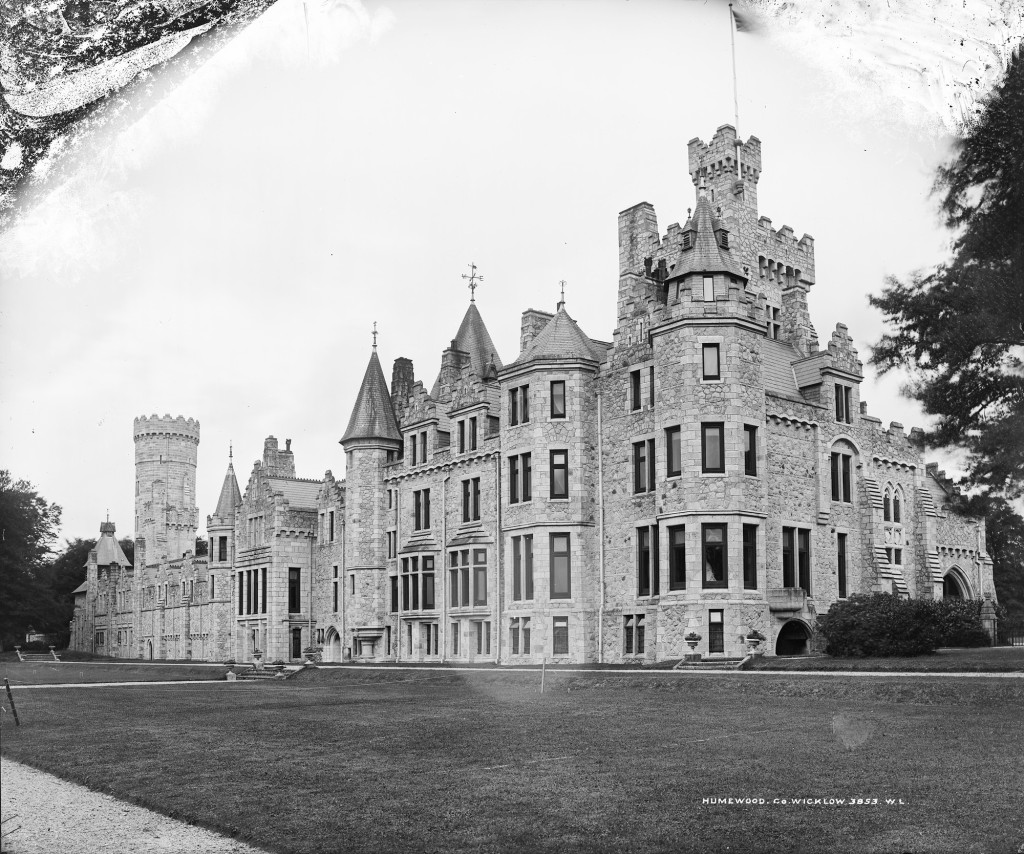
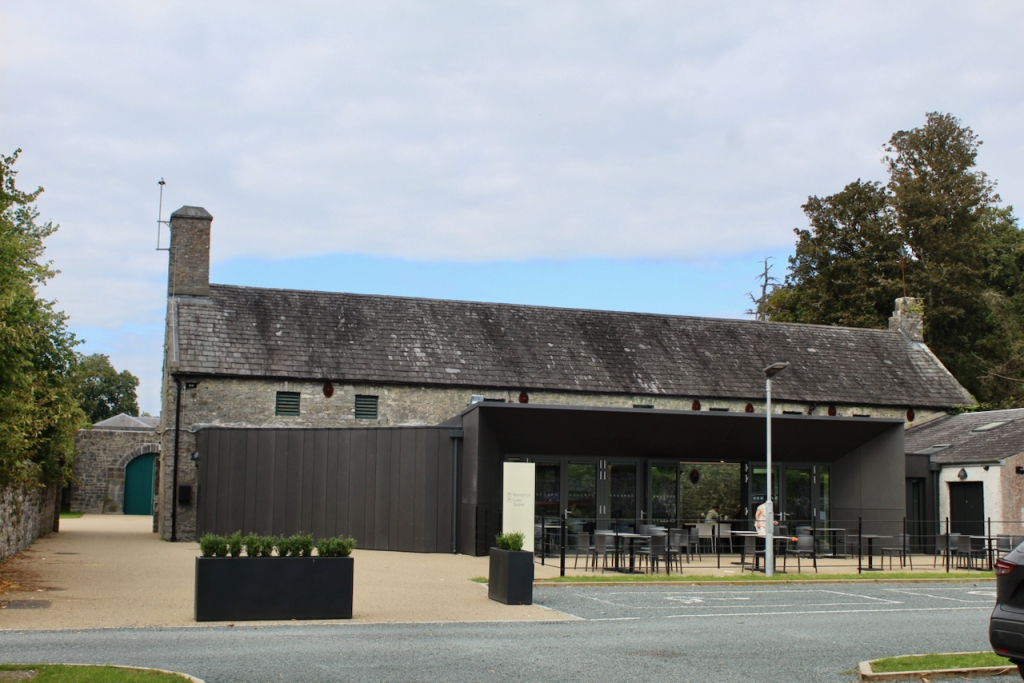
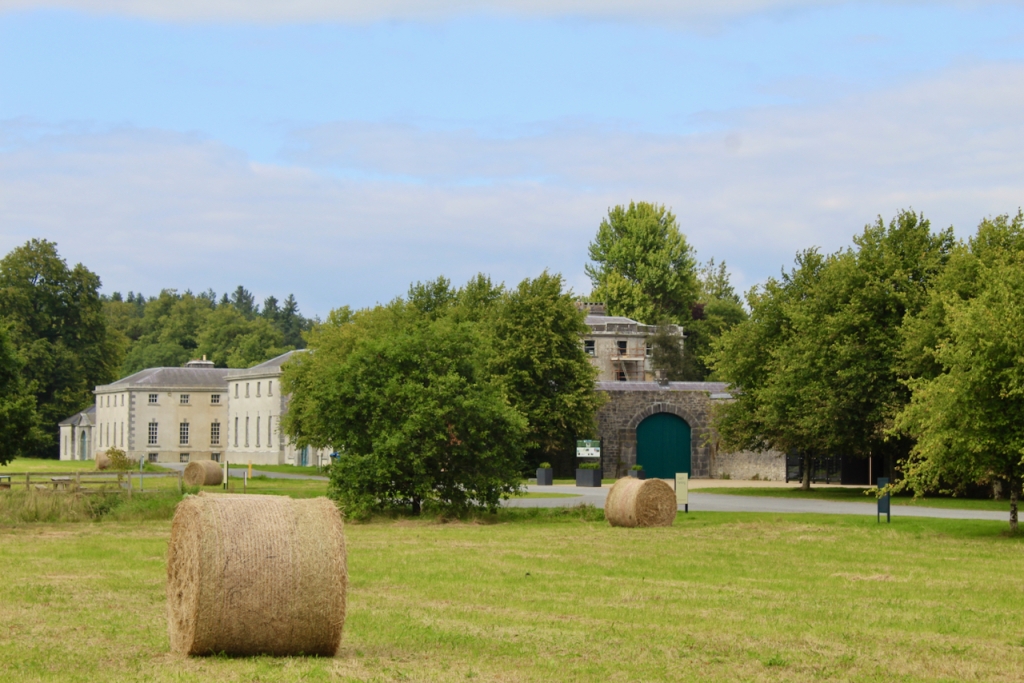
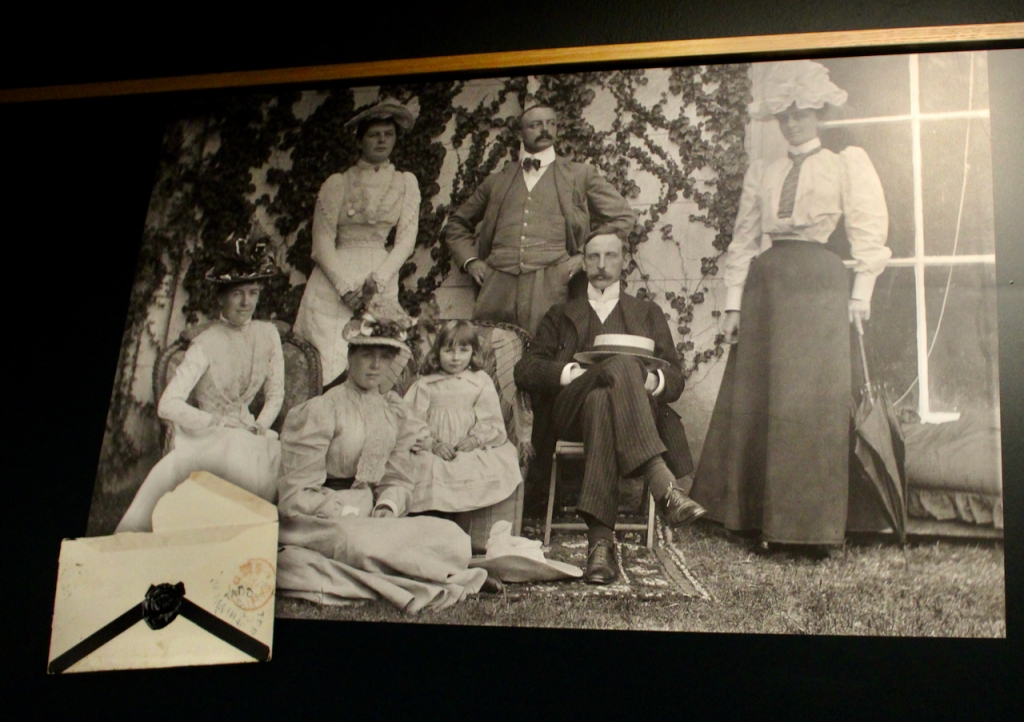
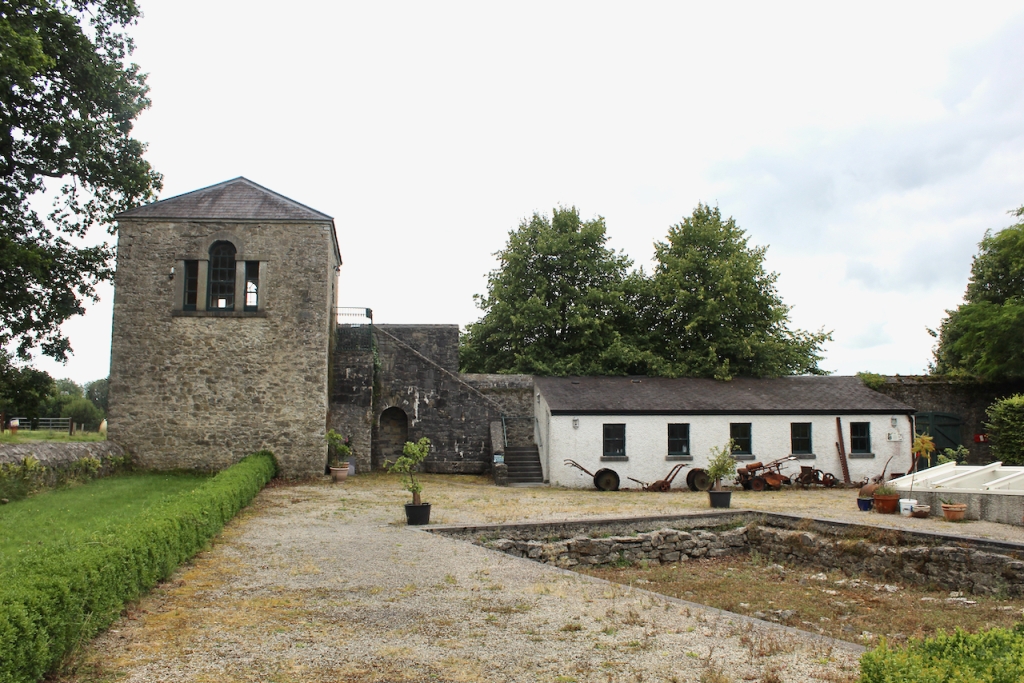
We visited Strokestown Park in County Roscommon during Heritage Week 2022. It houses the excellent National Famine Museum and Archive, which is really worth visiting. It sounds grim, but it is a great exhibition and it tells us so much about people’s lives that it is not a grim museum at all. It also tells us about the Pakenham-Mahons, the family who lived in the impressive Strokestown Park. Strokestown Park was the home of the first landlord to be assassinated during the height of the Great Famine of Ireland the 1840s, and it is therefore ideal for the location of the Famine Museum.
In 1979 Nicholas Hales Pakenham Mahon sold the estate to Westward Garage, founded by Jim Callery. The new owners allowed the last of the Mahon family, Olive and her husband Wilfrid Stuart Hales Pakenham Mahon, to remain living in the house until she moved to a nursing home.
Despite no longer being in the hands of the original owners, the house contains the original furnishings and fittings. The house is unchanged from the time when the Mahons lived there.

The Museum was created when Jim Callery, founder of the Westward Garage which purchased the property, found documents relating to the famine in the family archives. Jim Callery and the Westward Garage carried out a major restoration programme and opened the property to the public. Since 2015, Strokestown Park is cared for by the Irish Heritage Trust, an independent charity. Produce from the original working gardens are grown by volunteers and used in the Strokestown Park Café.
The website tells us that the house is built on the site of the 16th-century castle, home of the O Conor-Roe Gaelic Chieftains. Before being called “Strokestown House” the property was called “Bawn,” in reference to the bawn of the O Conor-Roe castle.
Nicholas Mahon, a captain in King Charles I’s army, was granted Strokestown as a royal deer park in 1653. Later, after pledging allegiance to King Charles II, he received more land. He was High Sheriff of County Roscommon, 1664-76. [3] He received over 3000 acres in 1678. He started to build a house, which was completed after his death in 1680, in 1696. Terence Reeves-Smyth tells us in his book Irish Big Houses that there is a stone by the door which has 1696 carved into it – the stone is now inside the house.
Strokestown Park featured as Building of the Month in December 2015 on the National Inventory of Architectural Heritage, and it tells us about the 1696 house:
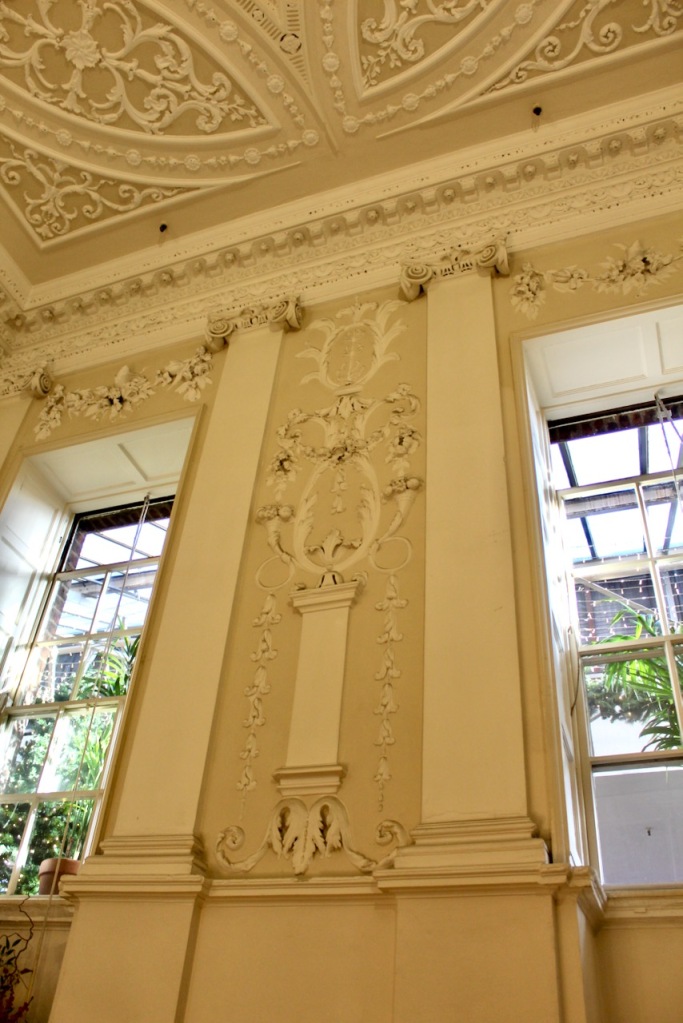
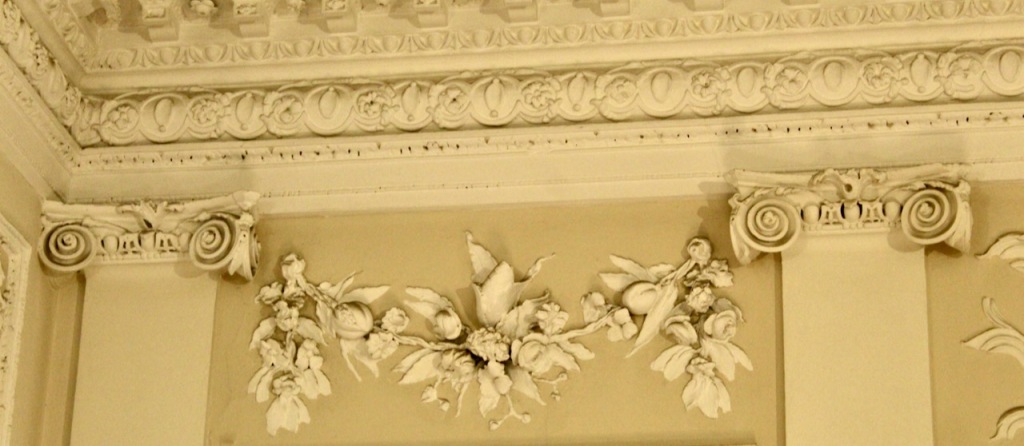
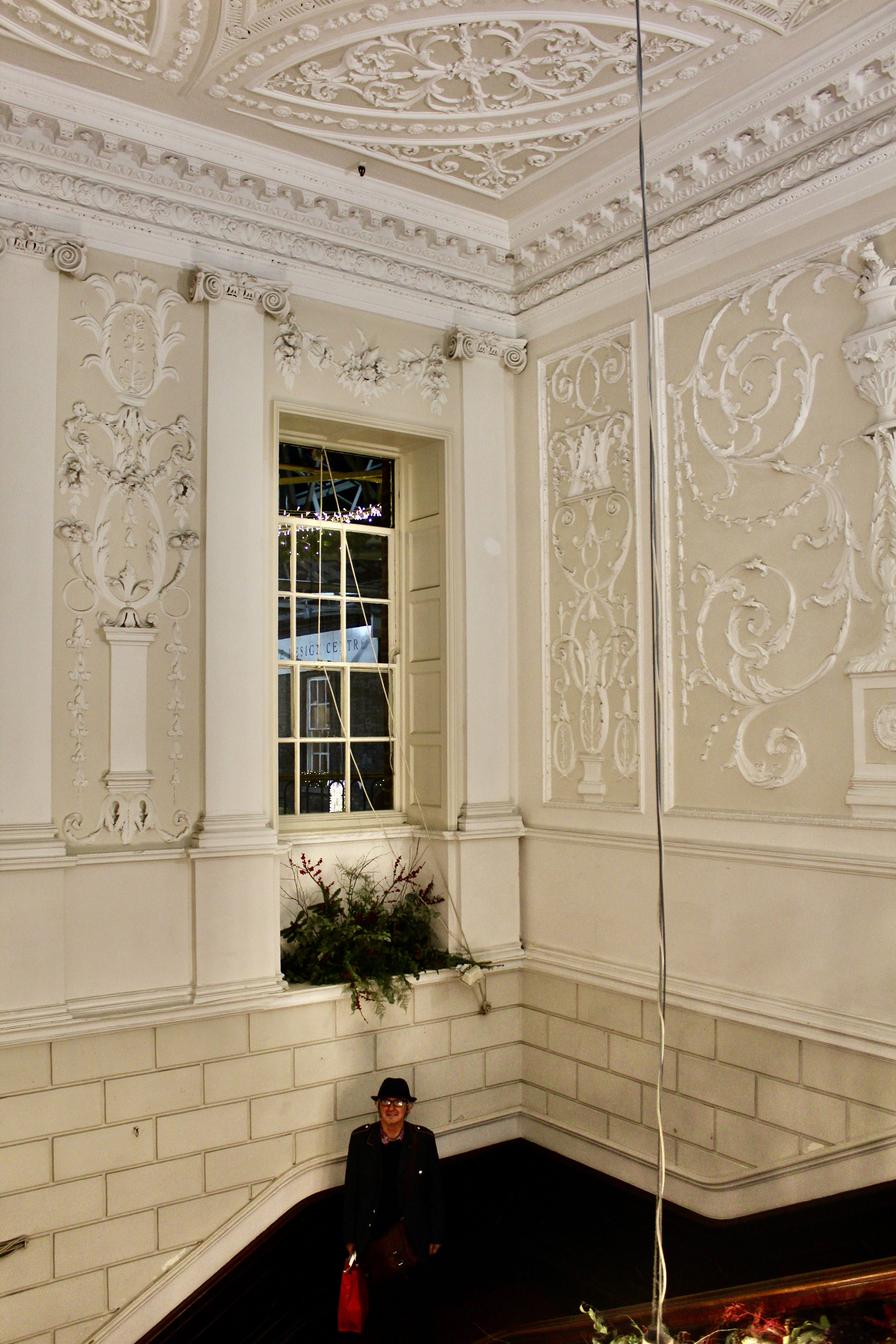
“Evidence of this house survives to the present day at basement level where a panelled still room, previously one of the principal reception rooms, retains a rosette-detailed Jacobean chimneypiece, an egg-and-dart-detailed plasterwork overmantle decorated with fruits and shells, and a compartmentalised ceiling with dentilated moulded plasterwork cornices. Some earlier remains of the castle are also found in the basement where sections of the walls measure almost three metres deep. Memories of the medieval past were carried through into the nineteenth century when the house was still officially called, and was referred to by Isaac Weld (1832) and Samuel Lewis (1837) as “Bawn”.” [4] [5]
Stephen and I were able to see part of the interior of the house, despite the house being closed for restoration work at the time, by joining a Heritage Week talk about a photographic dark room which had been created in the house by one of its residents. Unfortunately we did not get to see the basement or the galleried kitchen.
Captain Nicholas married Magdalena French, daughter of Arthur French of Movilla Castle, County Galway. [6] They had several children. Their son Reverend Peter (d. 1739) became Dean of Elphin and married Catherine, daughter of Paul Gore of Castle Gore, County Mayo (otherwise known as Deel Castle, now a ruin), who was son of Arthur, 1st Baronet Gore, of Newtown Gore, otherwise known as Parkes Castle in Leitrim (see my Office of Public Works in Connaught, Counties Leitrim, Mayo and Roscommon entry).
Another son, Nicholas (c. 1671-1781) married Eleanor Blayney, daughter of Henry Vincent, 5th Baron Blayney of Castle Blayney, County Monaghan.
A daughter, Margaret, married Edward Cooper of Markree Castle, County Sligo (another Section 482 property which we visited).
Strokestown passed via another son, John (d. 1708), who married Eleanor Butler (daughter of Thomas, 3rd Baronet Butler, of Cloughgrenan, Co. Carlow), to their son Thomas (1701-1782). It was Thomas who built on to the 1696 house, to create a residence designed by Richard Cassells, in about 1730.

Terence Reeves-Smyth tells us in his Irish Big Houses that the top storey and balustrade were added probably around 1740 when Richard Castle built the wings for Thomas Mahon. [7]
Richard Castle, or Cassells, (c.1690/95–1751) probably came to Ireland to work for Sir Gustavus Hume to design Castle Hume, Co. Fermanagh. [8] He then worked under Edward Lovett Pearce when Pearce worked on the Parliament Building in Dublin. Pearce died young and Castle succeeded to his practice. The Dictionary of Irish Biography tells us:
“He contributed significantly to the development of Dublin, designing the first imposing town houses in cut stone for the nobility, notably Tyrone House, Marlborough St. (1740–45), built for Marcus Beresford (1694–1793), later earl of Tyrone, and Leinster House, Kildare St. (1745–51), for James Fitzgerald, earl of Kildare, the grandest town house and since the 1920s the seat of Dáil Éireann. His commissions included 85 Stephen’s Green (c.1738), the first stone-fronted house on the Green, latterly part of Newman House; houses in Kildare St., notably Doneraile House (designed c.1743); and Sackville Place...Castle designed many country houses, including Belvedere, Co. Westmeath (designed 1740), which incorporated the ‘Venetian’ window, a common feature of his designs, and Ballyhaise, Co. Cavan (c.1733). By altering and enlarging many houses, he created grand country mansions (often with vaulted stables), notably Powerscourt, Co. Wicklow, with its magnificent Egyptian hall (built 1731×1740; damaged by fire 1974, and since partly restored), Westport House, Co. Mayo (1731–40), and Carton House, Co. Kildare (c.1739–45). Conolly’s Folly at Castletown estate, Co. Kildare (1740), a tall obelisk mounted on multiple arches, is attributed to him. He possibly collaborated with Francis Bindon on Belan House, Co. Kildare, complete with temple and three obelisks (1743), and Russborough, Co. Wicklow (c.1742–55).” [9]
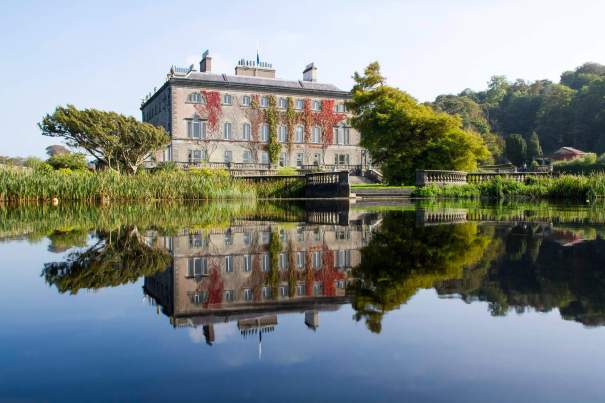
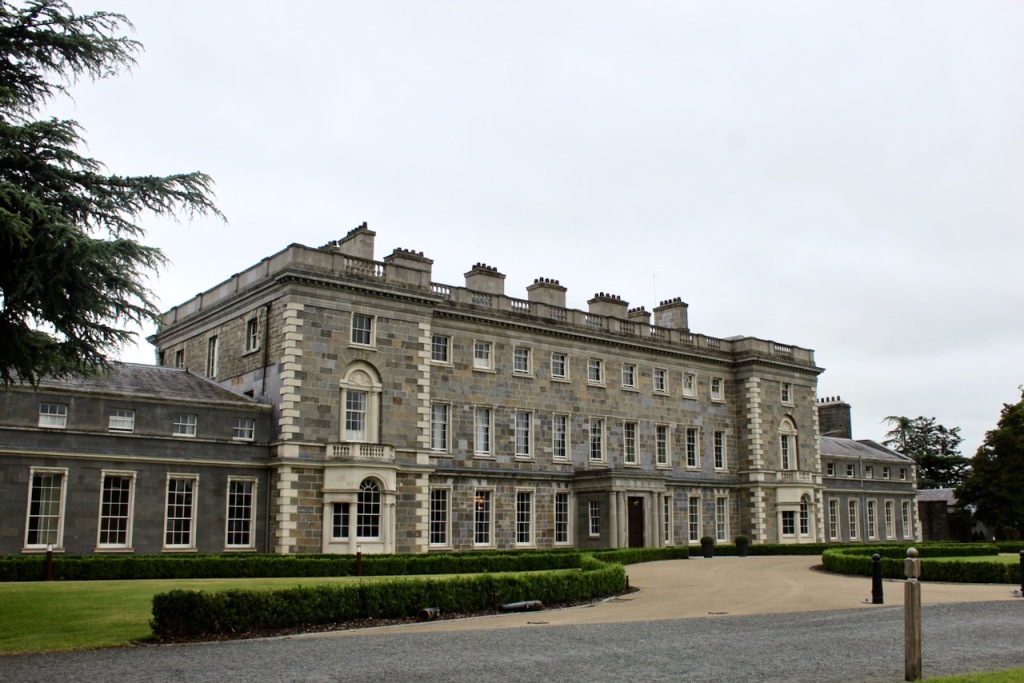
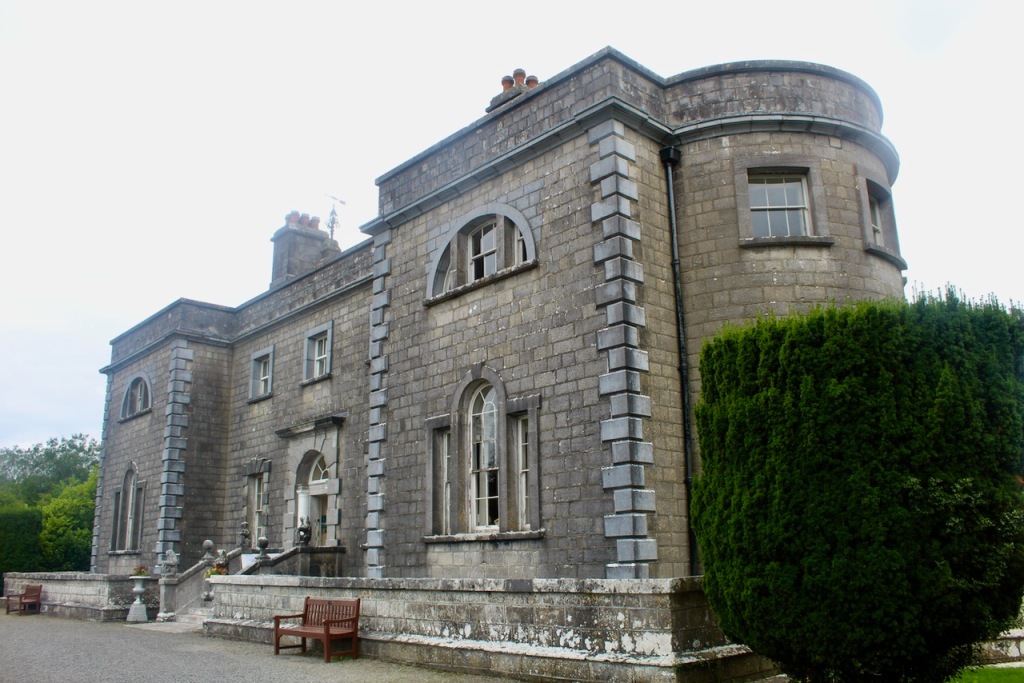
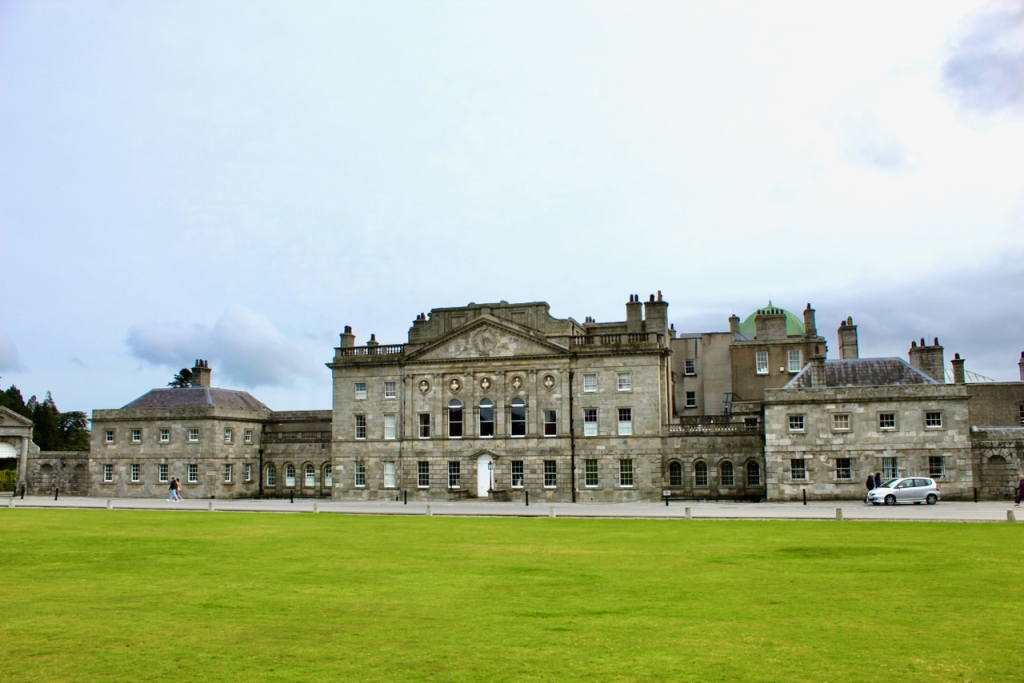
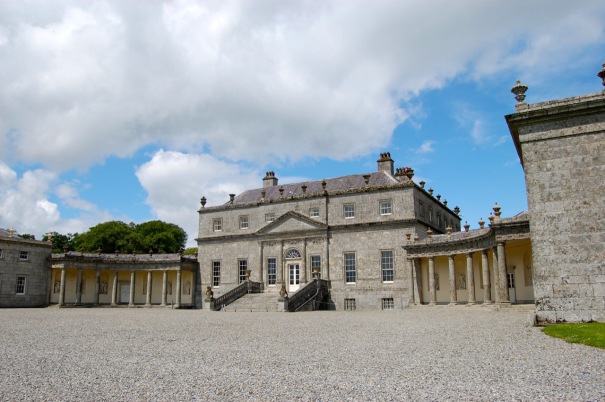










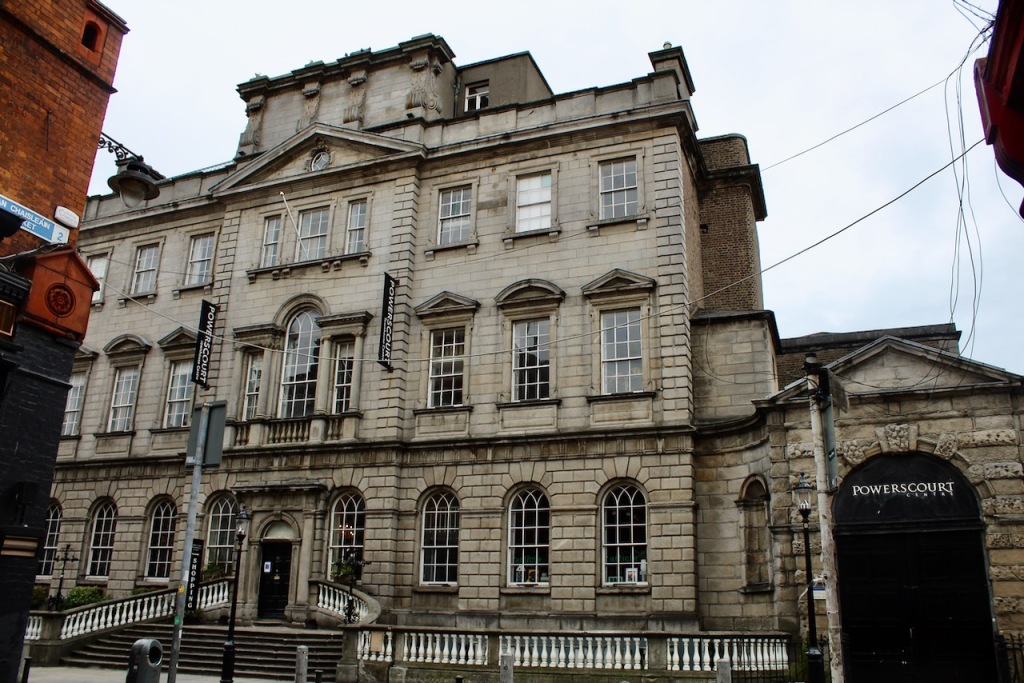
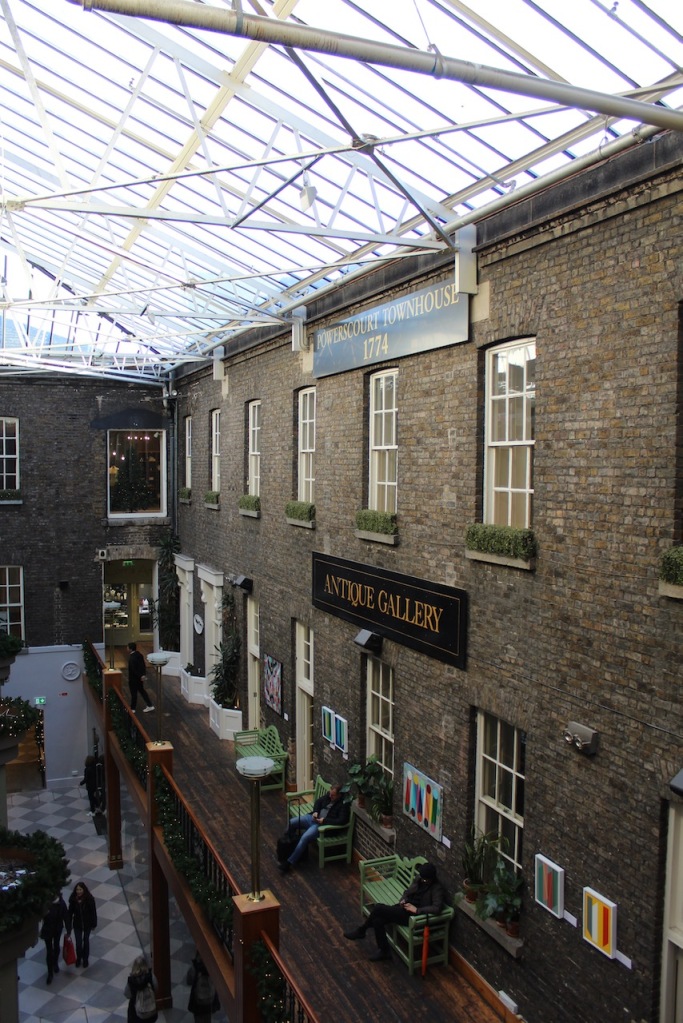
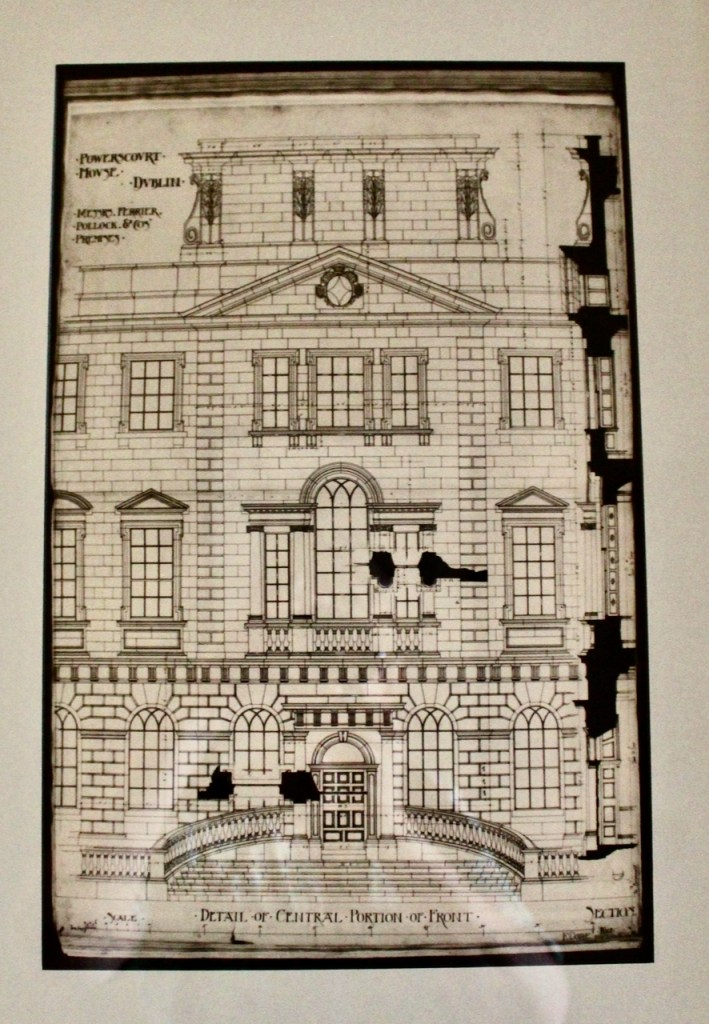
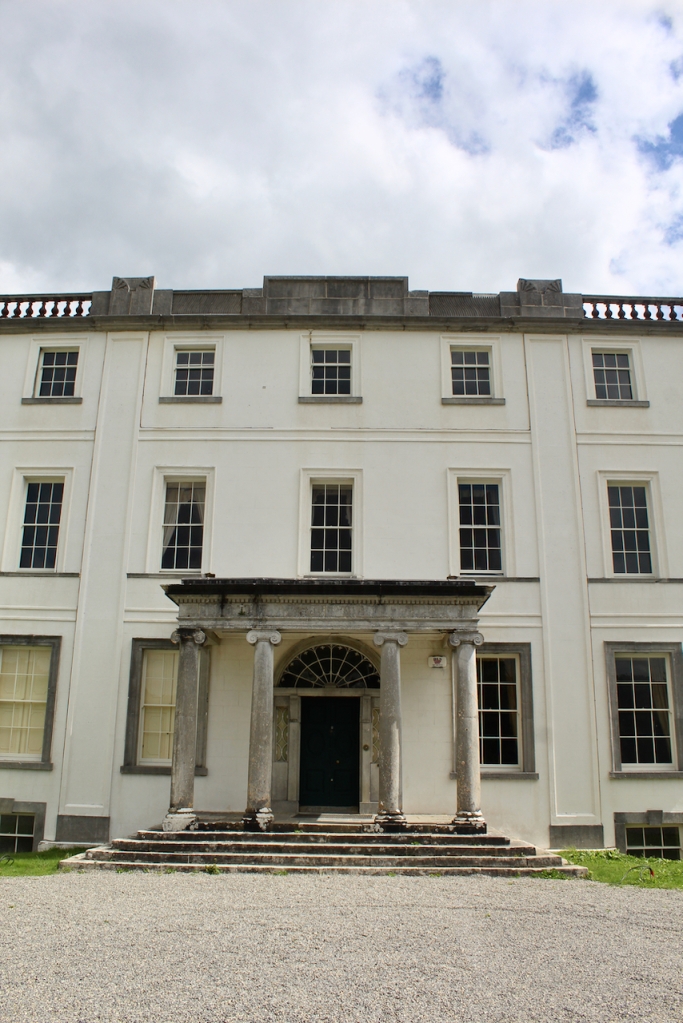
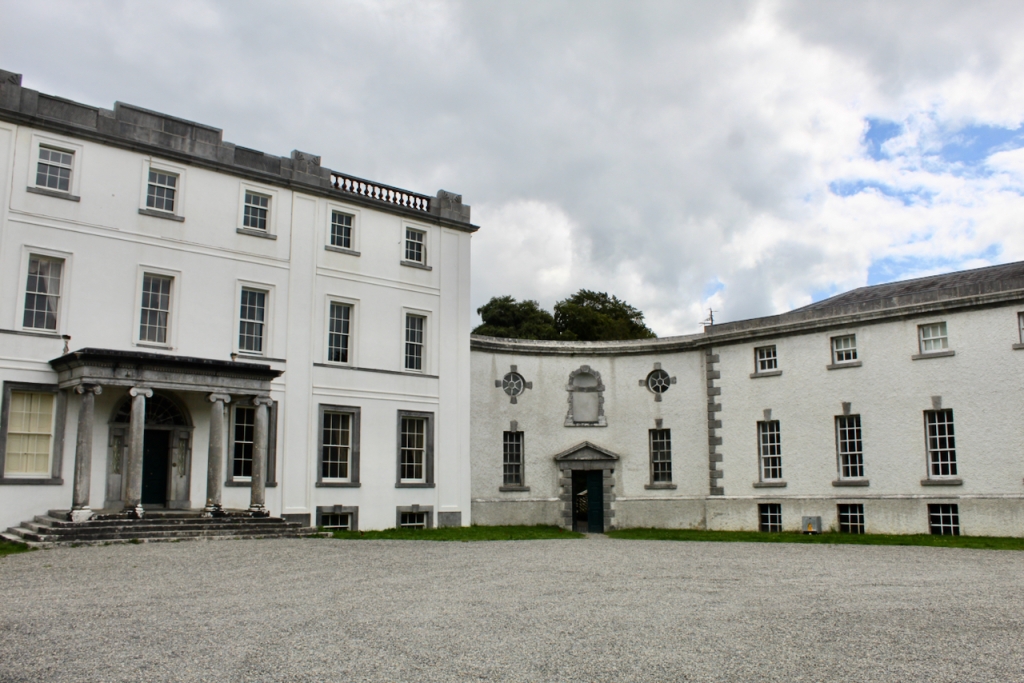
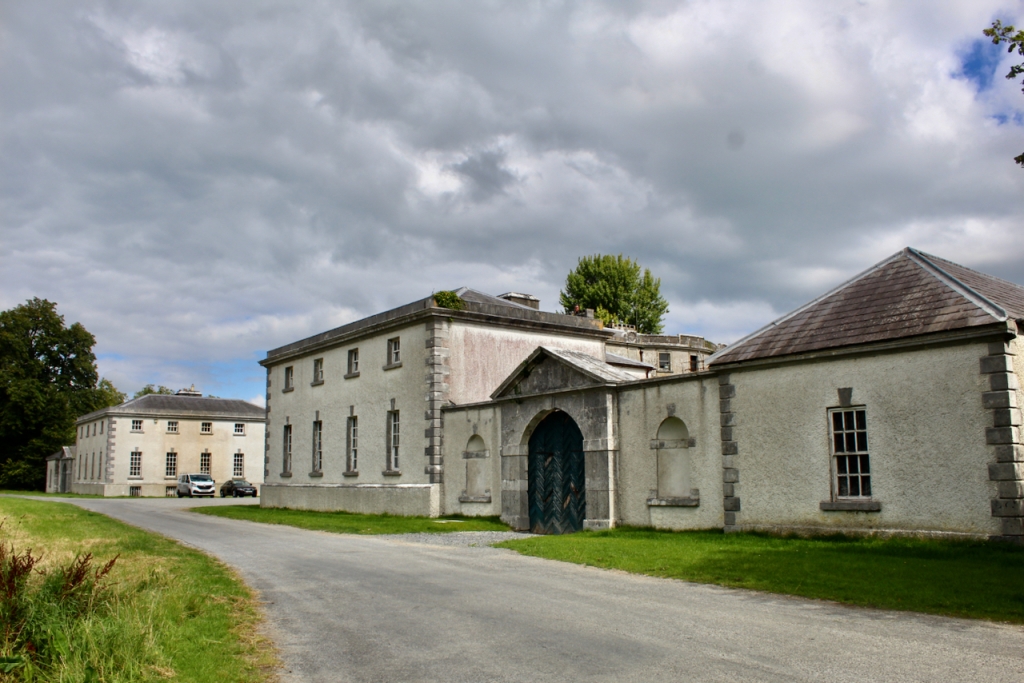
The house has a seven-bay, three-storey over basement central block, with curved curtain walls linking it to flanking pavilions with four-bay principal façades. The centre block front facade has three bays in the centre with giant pilasters either side and two bays beyond on either side. The centre three bays have a central panel on the pediment and the two bays on either side of the pilasters have a balustraded pediment. The front door is set in a tooled stone doorcase with decorative brackets, with an ornate spoked fanlight, and is flanked by traceried sidelights.
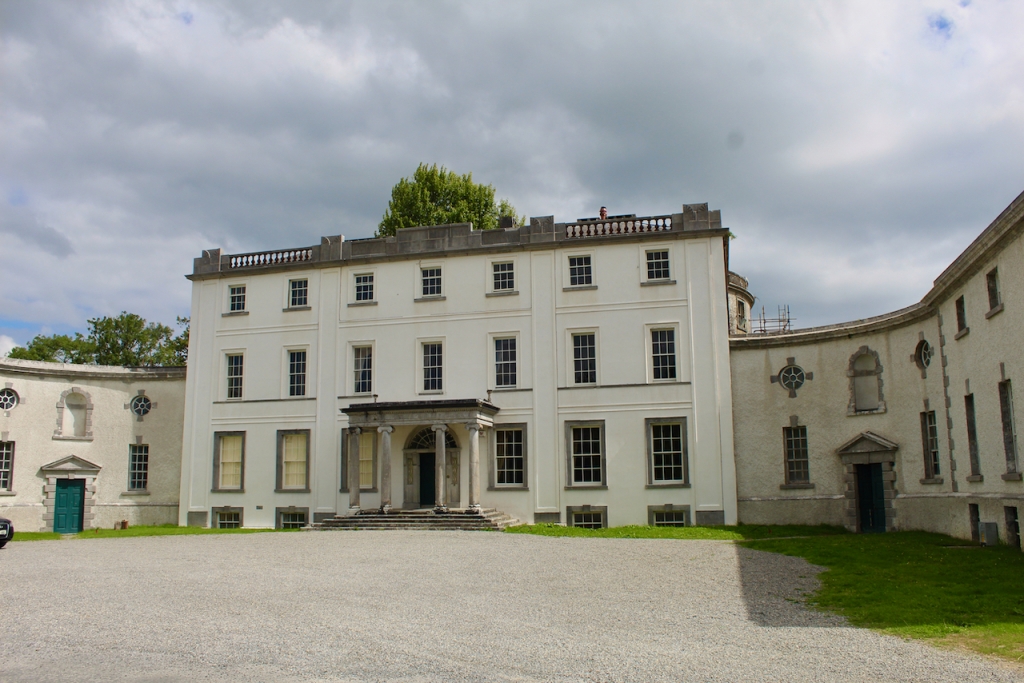

Most of what we see today was designed by Castle, but the house was resurfaced in 1819 and the portico added.
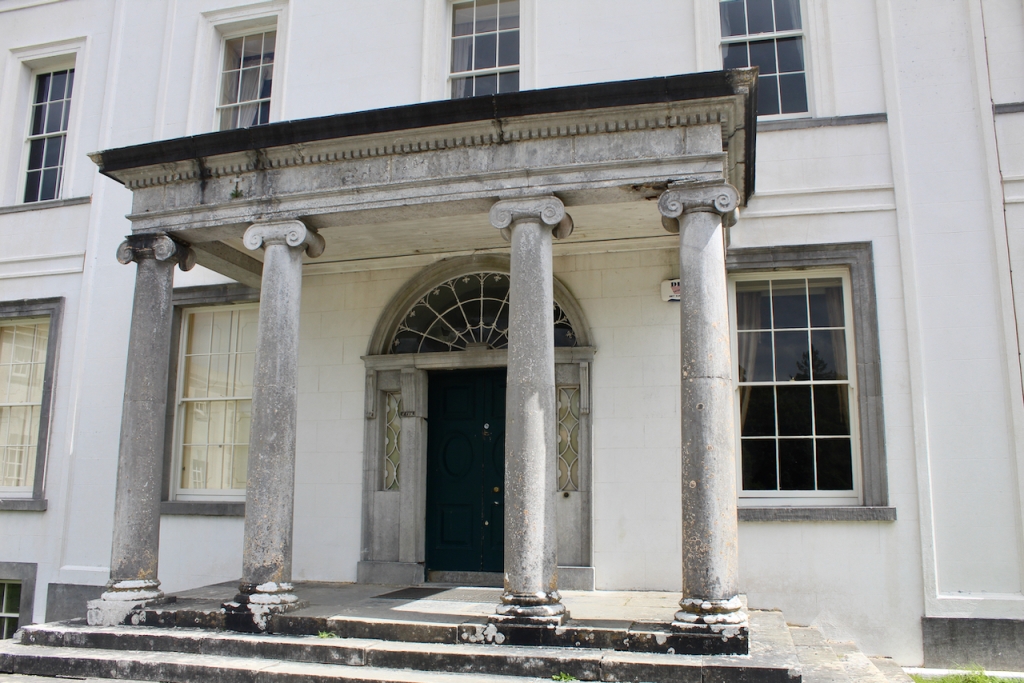
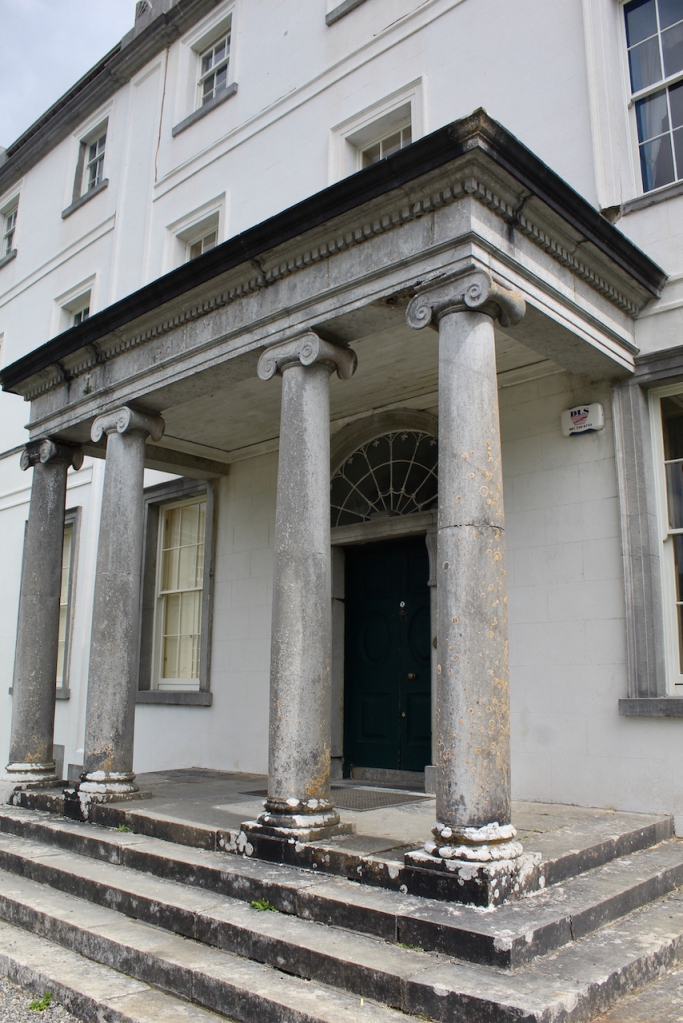



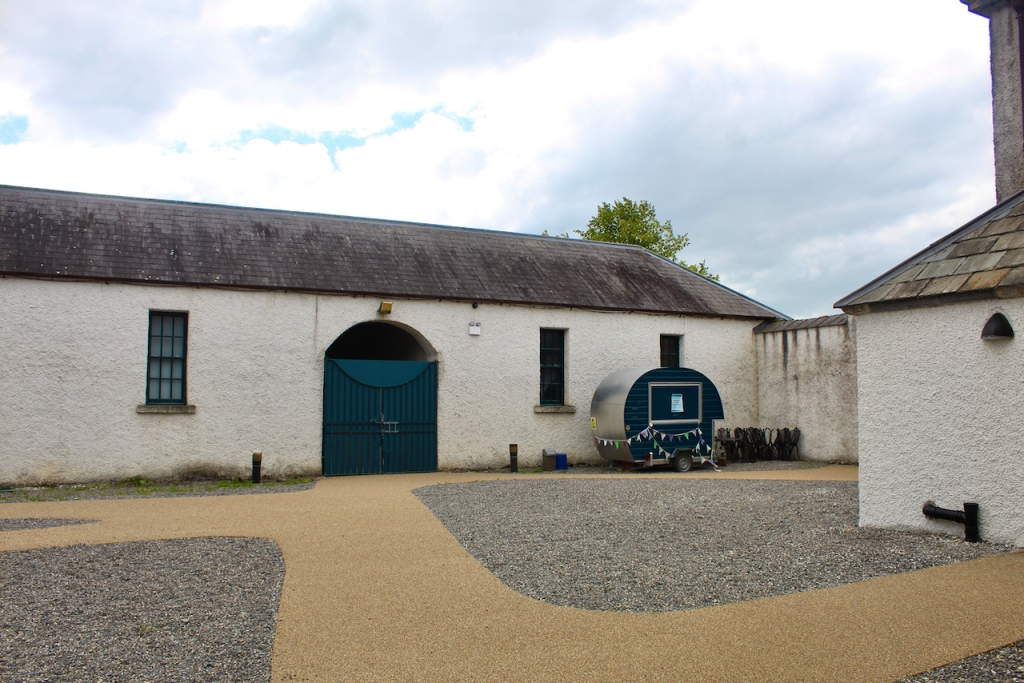
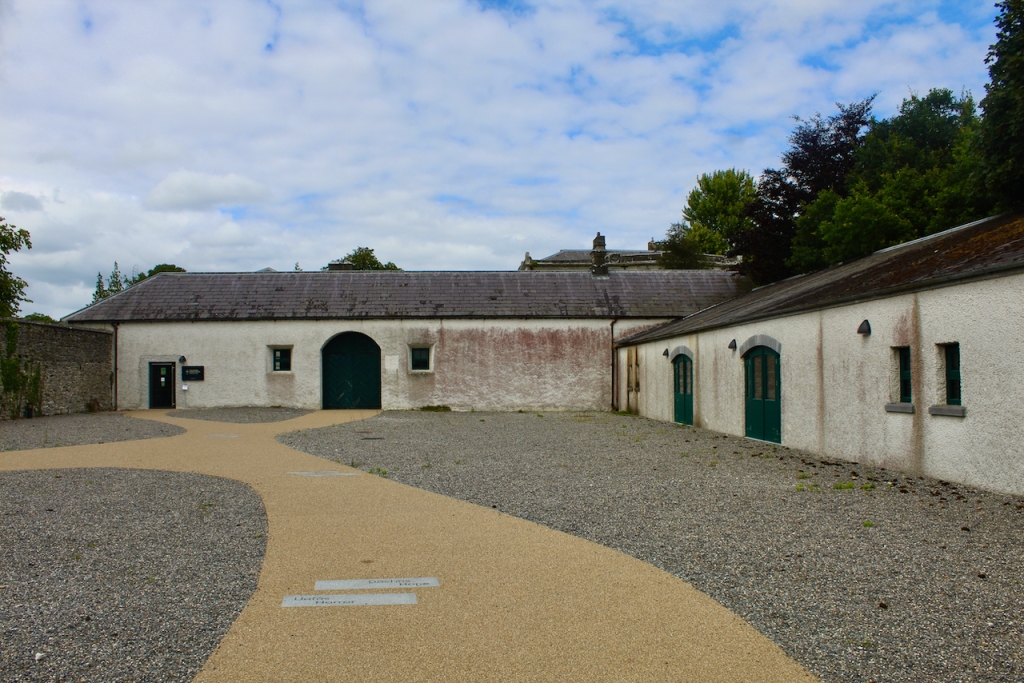
The National Inventory of Architectural Heritage tells us that the pedimented archways to outer walls extending from pavilions give access to stable complex and kitchen yards. [10]
The flanking curtain walls have niches flanked by oculus windows on the upper part with tooled stone surrounds, and a Gibbsean doorcase with pediment over.
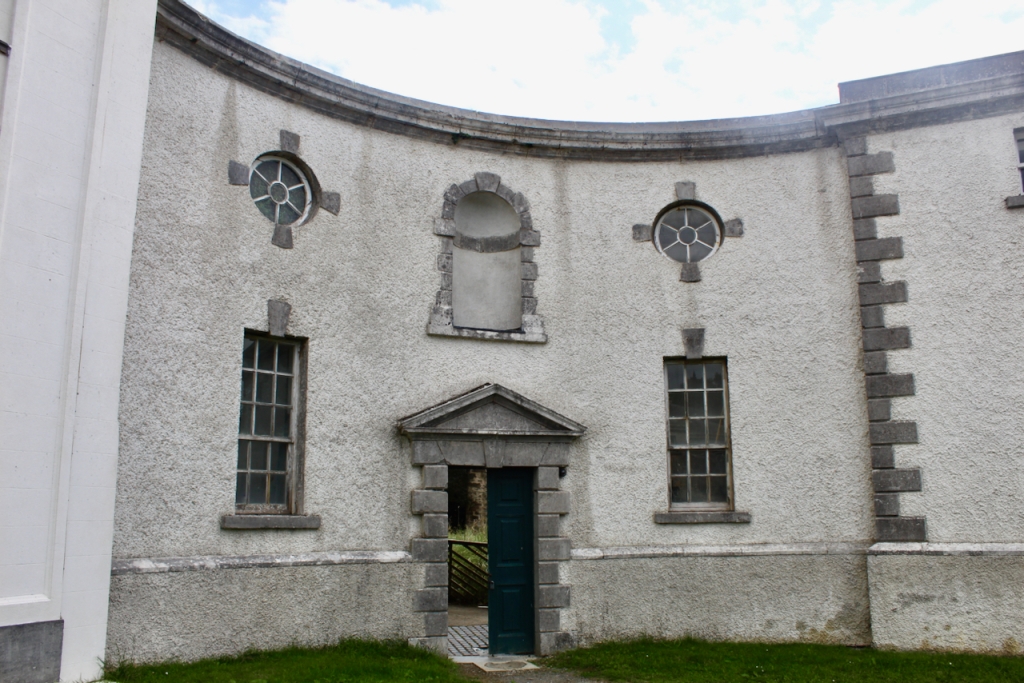
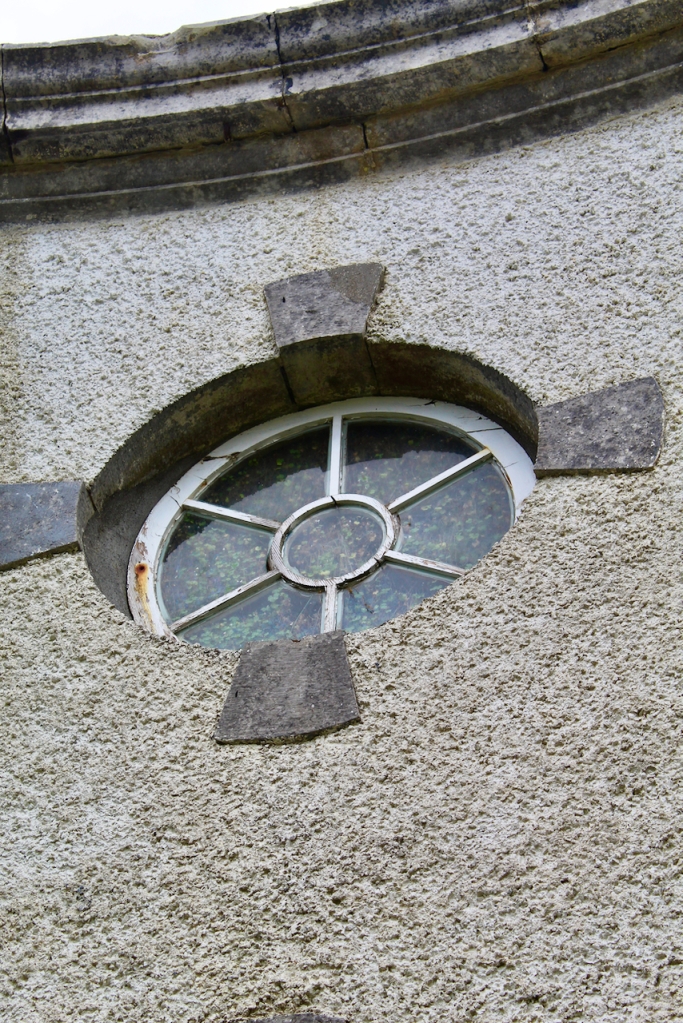




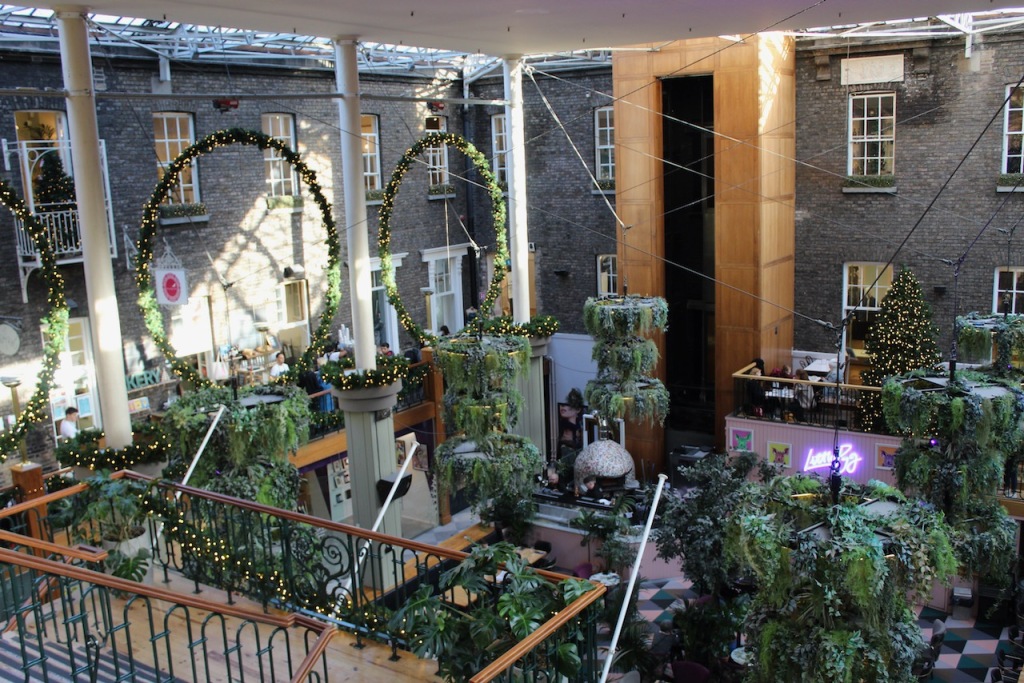
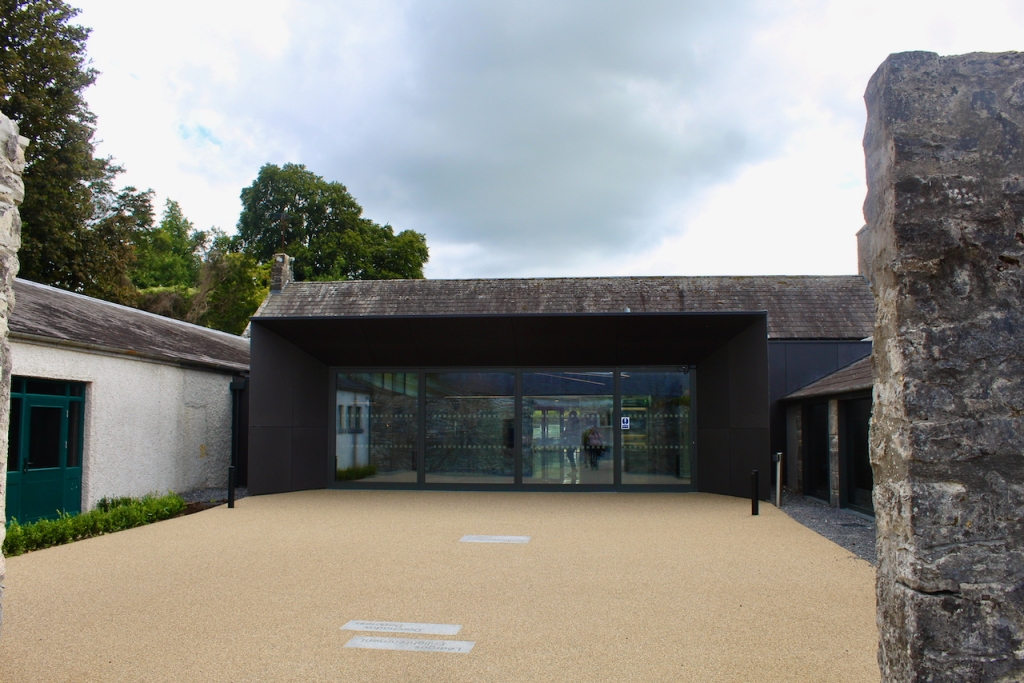
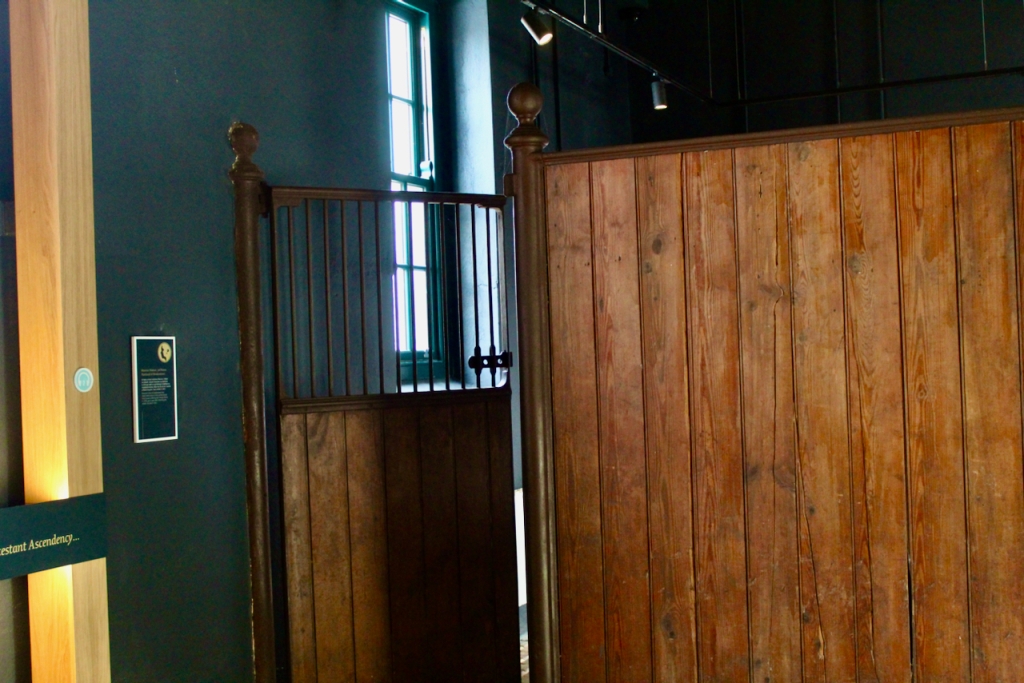
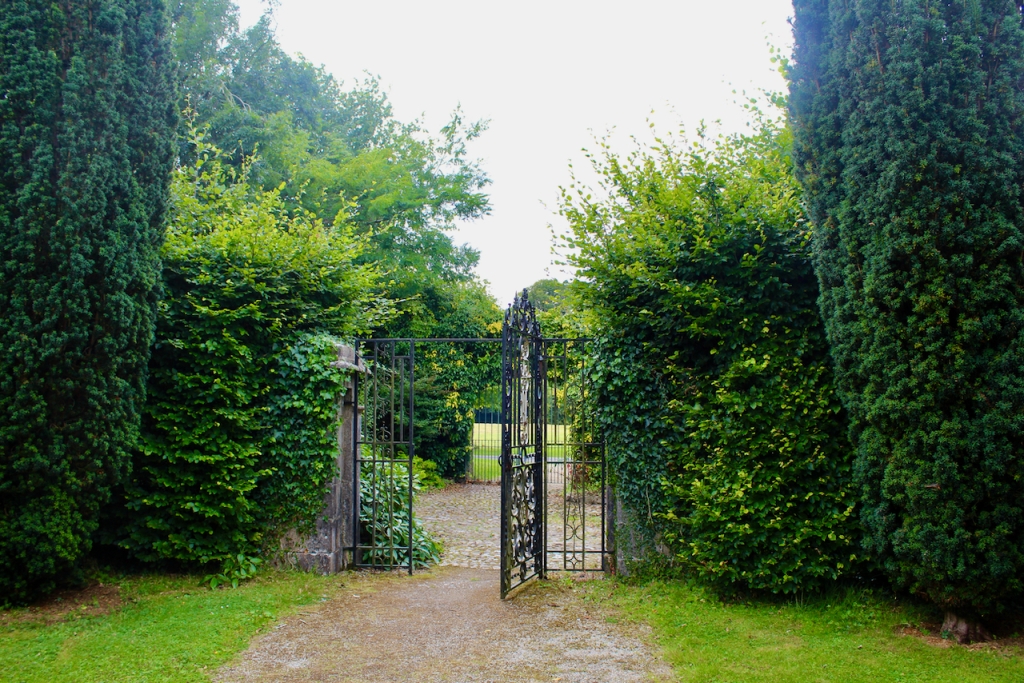
The Famine Museum is located in the stables. One enters via a Visitor Centre to one end of the complex.





In 1735, Thomas married Jane Crosbie, daughter of Maurice, 1st Baron Branden, of Ardfert, County Kerry, MP for County Kerry. Thomas Mahon later became MP, first for the Borough of Roscommon in 1739-1763 then for County Roscommon 1763-82, when he was called the “Father of the House.” [11]
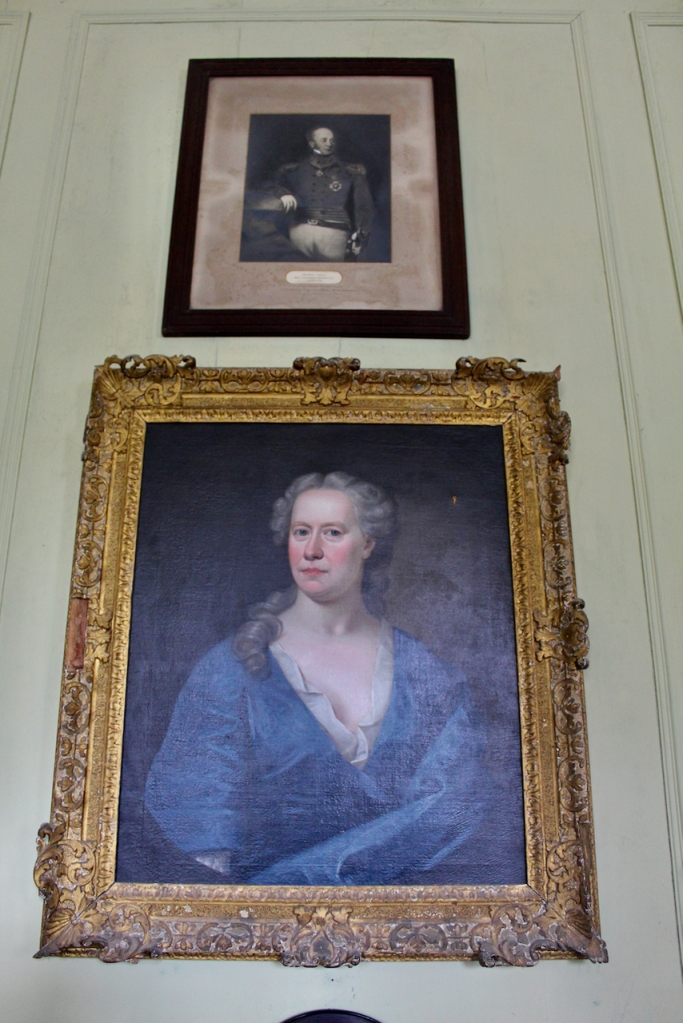

Thomas’s son Maurice (1738-1819), named after Jane’s father, married Catherine, daughter of Stephen Moore, 1st Viscount Mountcashell, in 1765. He inherited when his father died in 1782. He was granted a peerage for his support of the Act of Union, and created 1st Baron Hartland, of Strokestown, Co. Roscommon in 1800.
Terence Reeves-Smyth tells us:
“His son Maurice, who became Baron Hartland upon accepting a Union Peerage in 1800, made further additions and modifications to the house, including the inlaid mahogany doors, chimney-pieces and cornices as well as the library.”

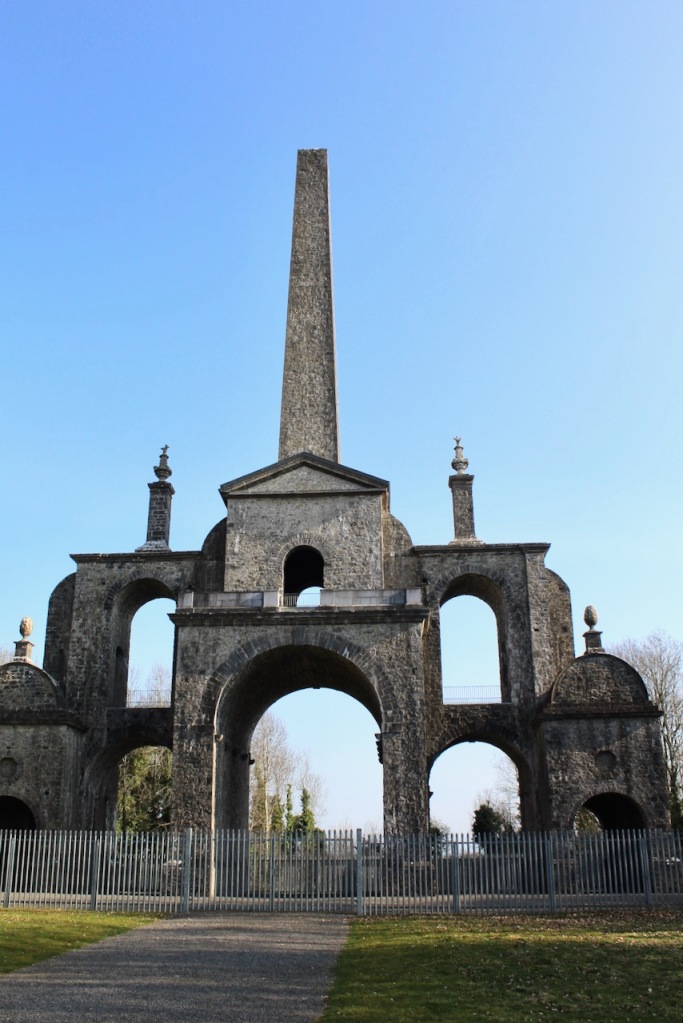
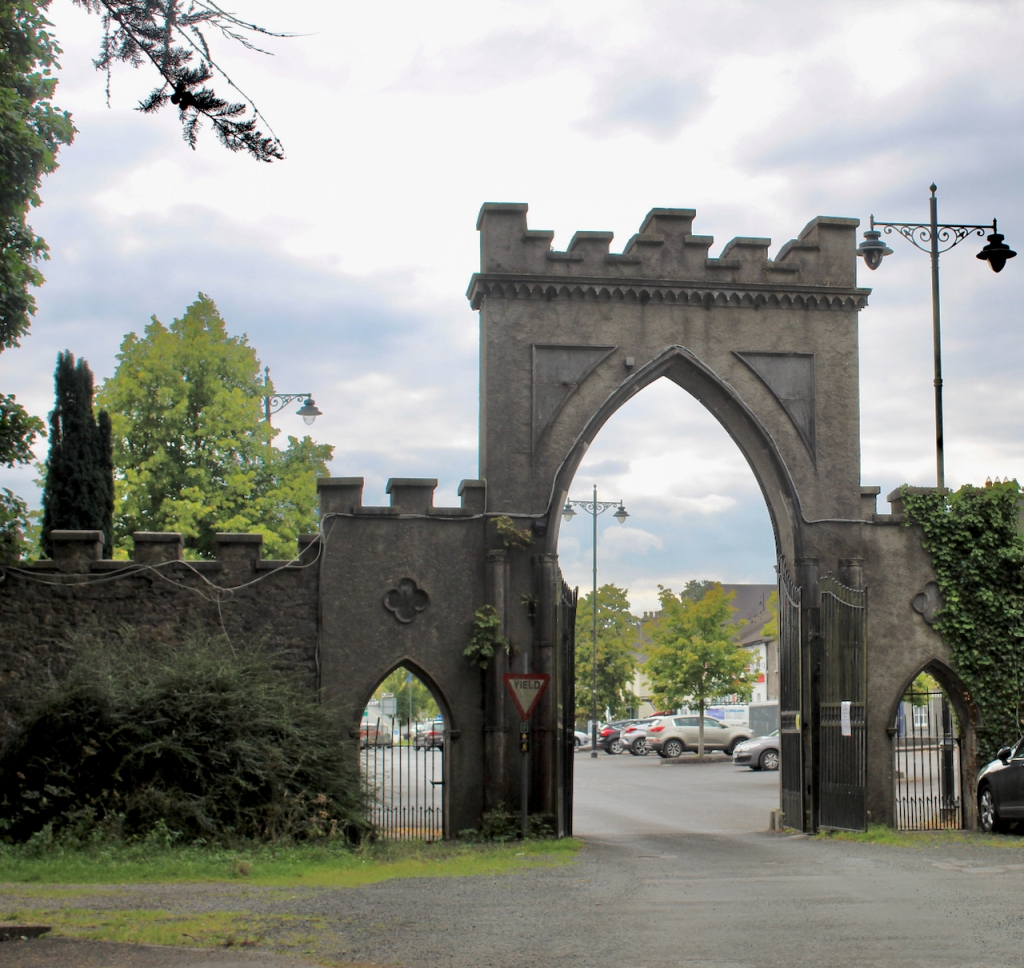
Maurice Mahon also had the main street of Strokestown laid out between 1810 and 1815, and had a tall Georgian Gothic arch erected at the entrance to Strokestown Park, at one end of the main street. At almost one hundred and fifty feet wide, the main thoroughfare, leading up to the gates of the estate, was said to be the widest in Ireland at the time. Apparently Baron Hartland wanted it to be wider than the Ringstrasse in Vienna. [see 12]

Maurice, 1st Baron Hartland had three sons. The first, Thomas (1766-1835) succeeded as 2nd Baron Hartland in 1819. His mother lived another fifteen years after her husband died in 1819, and the museum tells us that receipts for her extravagant spending are kept in the archive.
When Thomas inherited the property in 1819 he hired John Lynn who created the porch, among other renovations. Lynn had served as clerk of works for the building of Rockingham House in County Roscommon, erected in 1810 for Robert, 1st Viscount Lorton to designs by John Nash. We saw pictures of Rockingham House when we visited King House, see my entry. Rockingham House no longer exists. Soon after working in Strokestown, Lynn moved up to Downpatrick, County Down. [13]
Terence Reeves-Smyth continues in Irish Big Houses: “In 1819 Lieutenant General Thomas Mahon, second Lord Hartland, employed the architect J[ohn] Lynn to carry out some more improvements, such as the addition of the porch and giant pilasters to the front. Except for the gardens, few changes were later carried out at Strokestown and it remained the centre of a vast 30,000 acre estate until the present century.”
Thomas the second baron was educated at the Royal School in Armagh, Trinity College Dublin and St. John’s College, Cambridge. He joined the military and became Major in the 24th Light Dragoons. In 1798 he was in command of a garrison in Carlow, where he trapped and killed many rebels. [14] In 1811 he married Catherine Topping, but they did not have any children. He later fought in the Napoleonic wars and in Argentina.
Terence Reeves-Smyth continues:
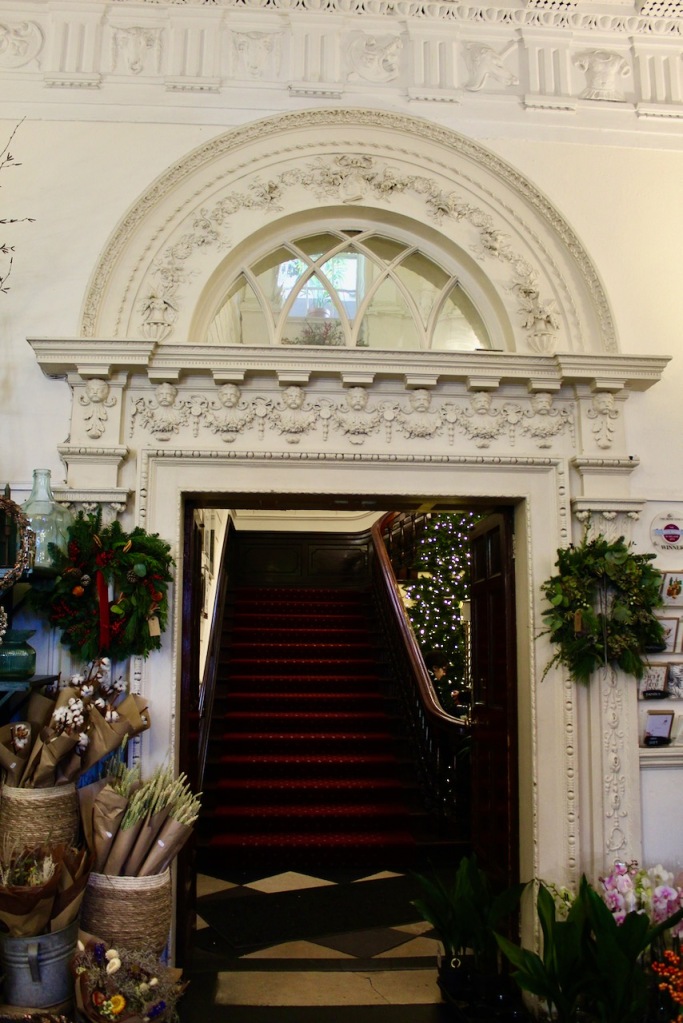
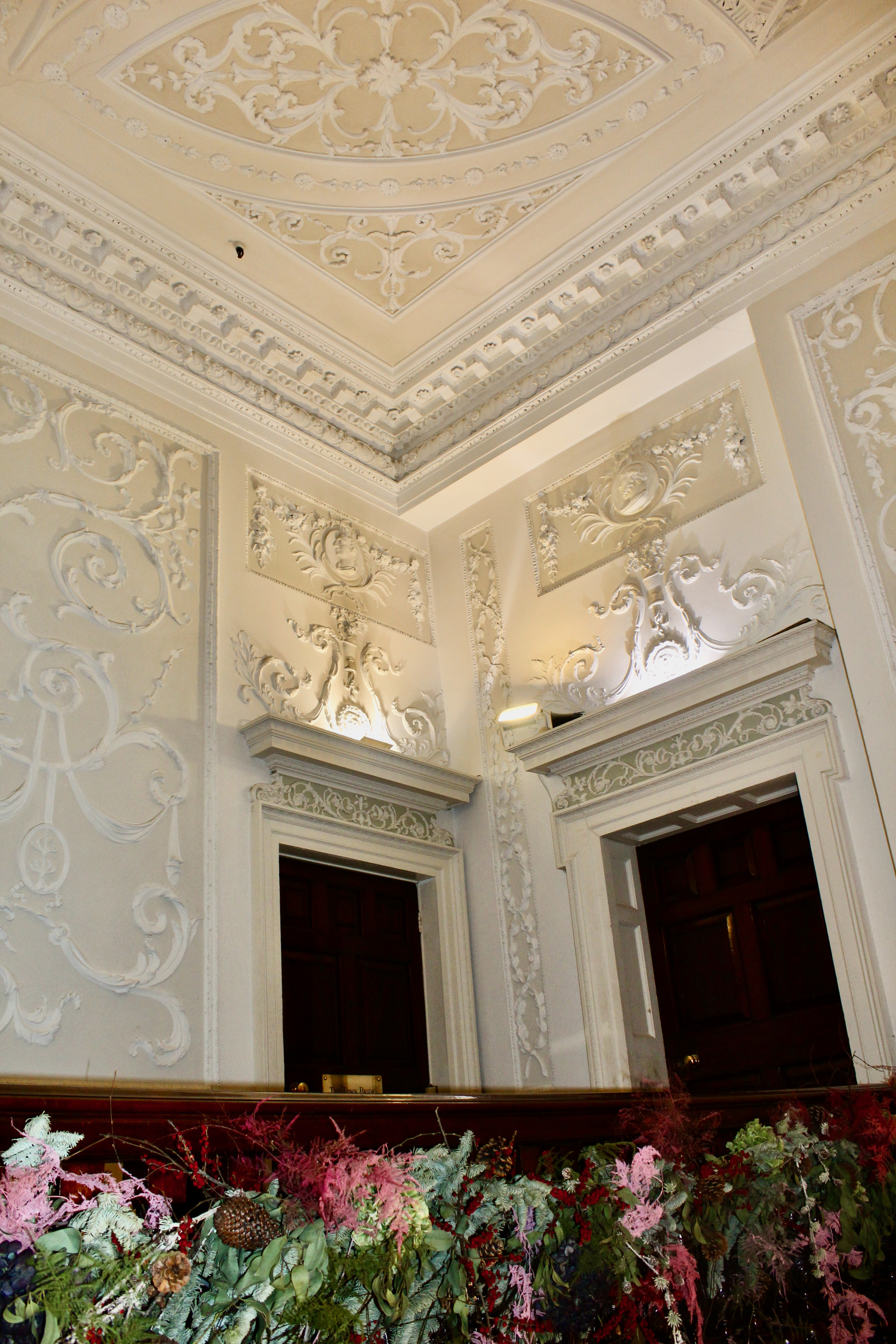
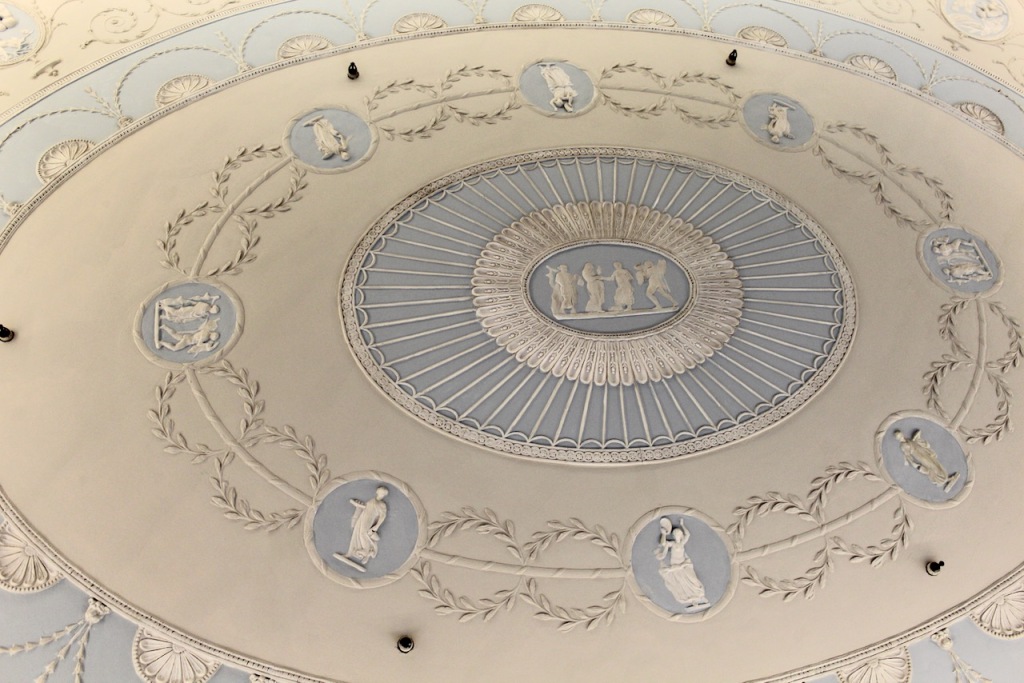
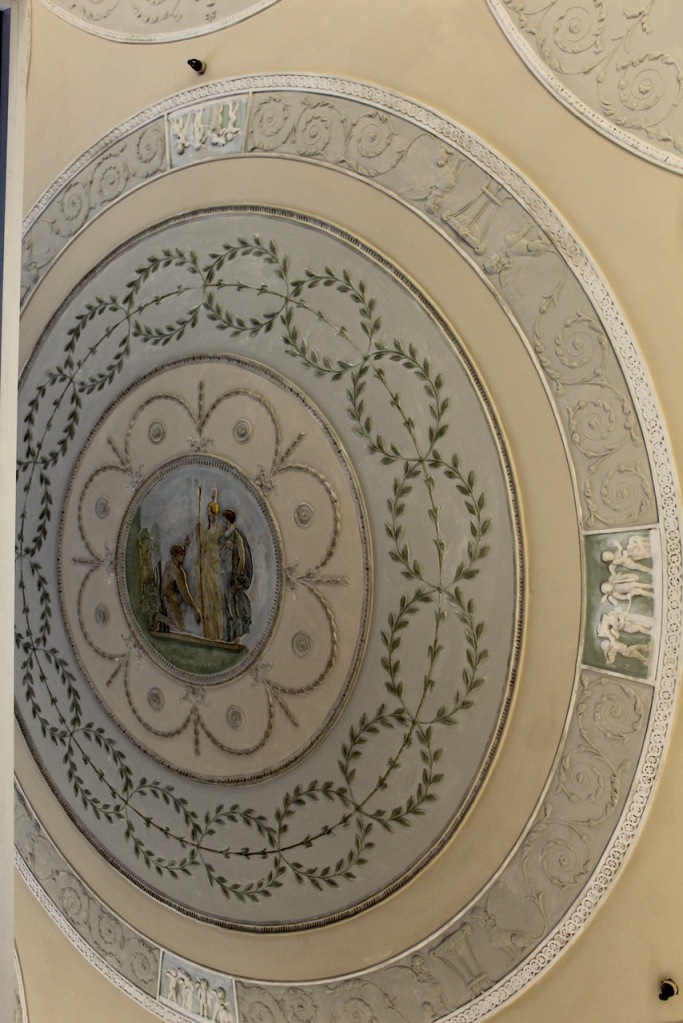
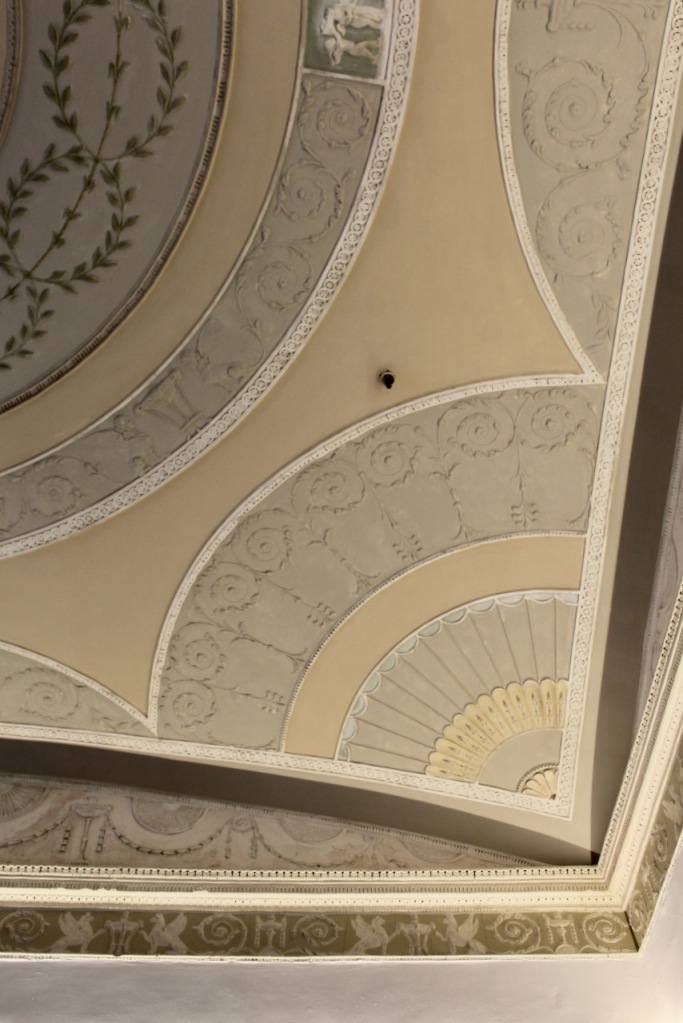
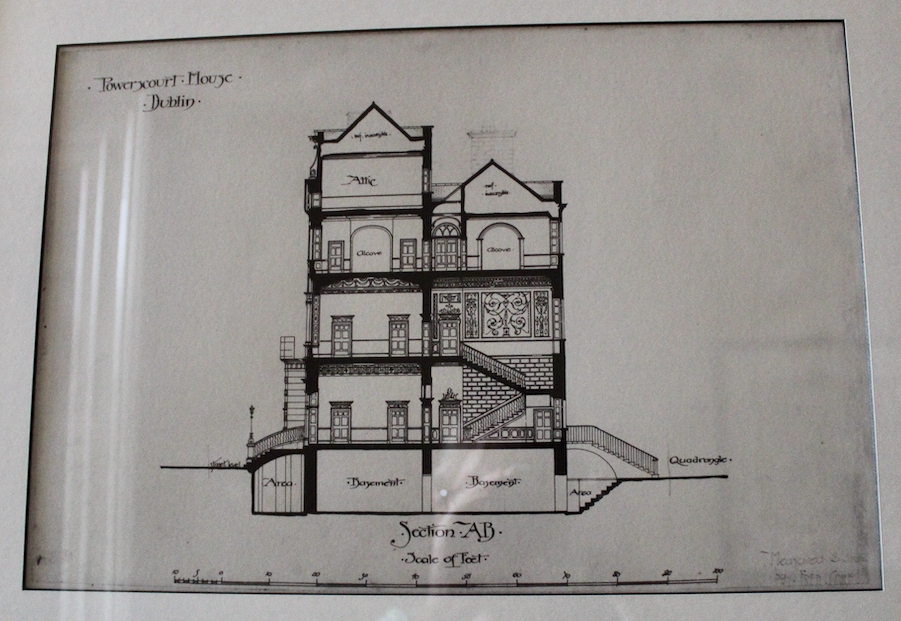
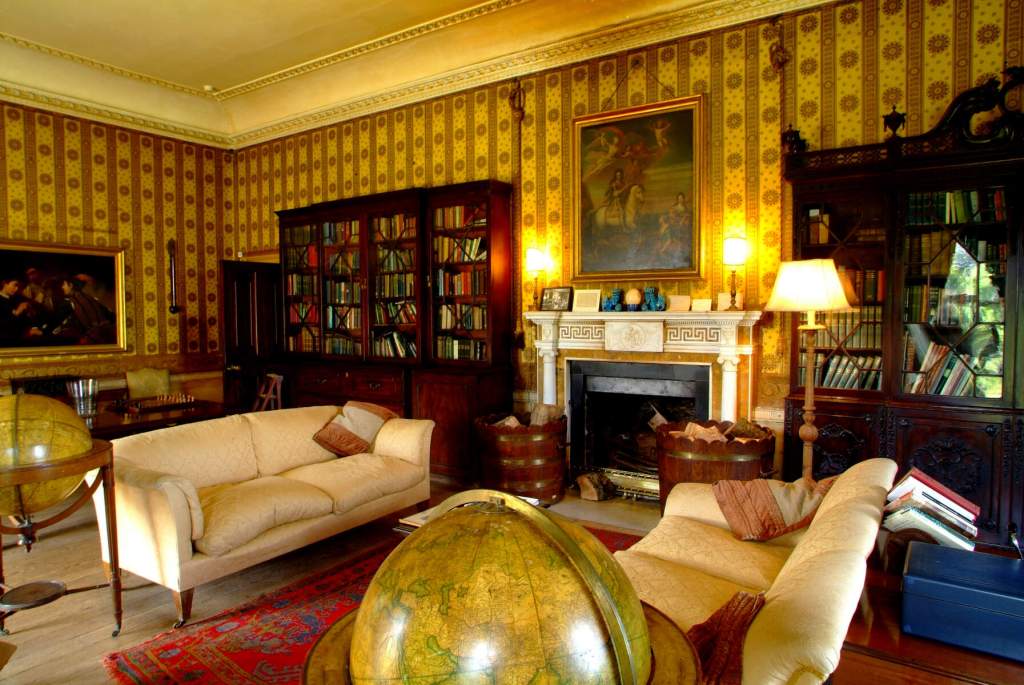
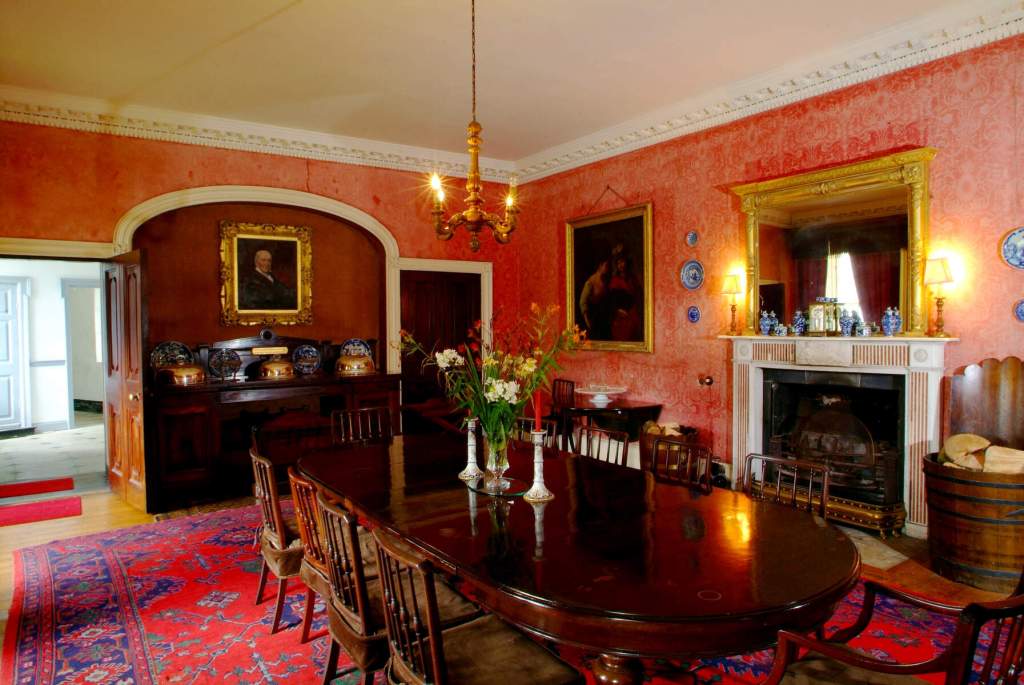
“In contrast to the exterior, the interior is quite intimate, with surprisingly small rooms – a product of the early date of much of the building. Early 18th century wood panelling survives in parts of the house including the main staircase hall, but many rooms were redecorated in regency times, such as the dining room which still has its early 19th century furniture, including a bath-sized turf bucket and pinkish-red damask wallpaper.“
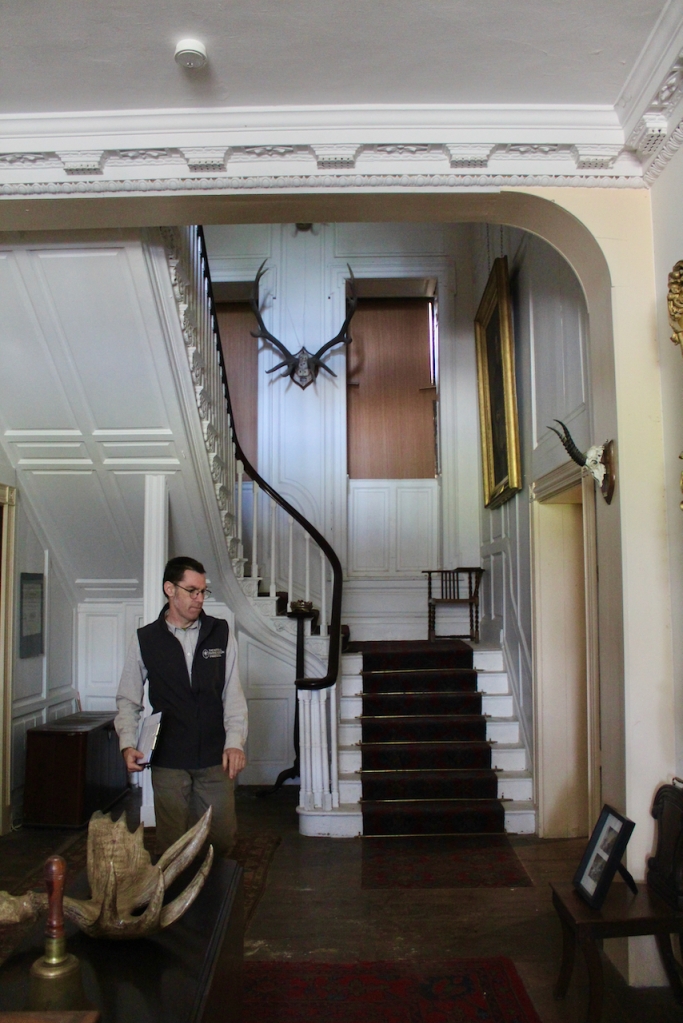
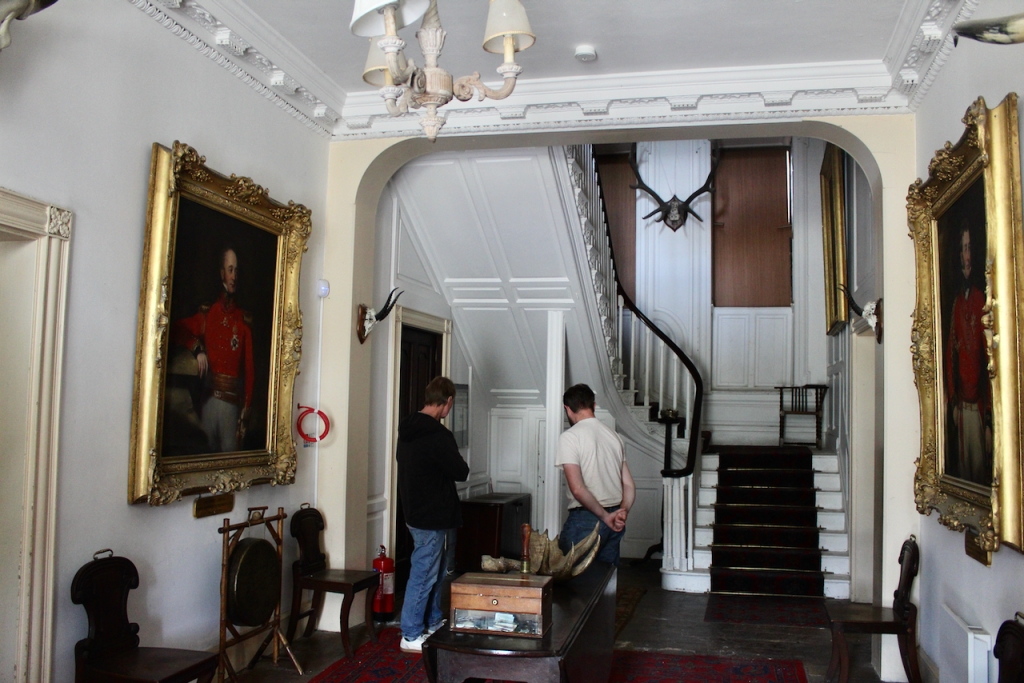
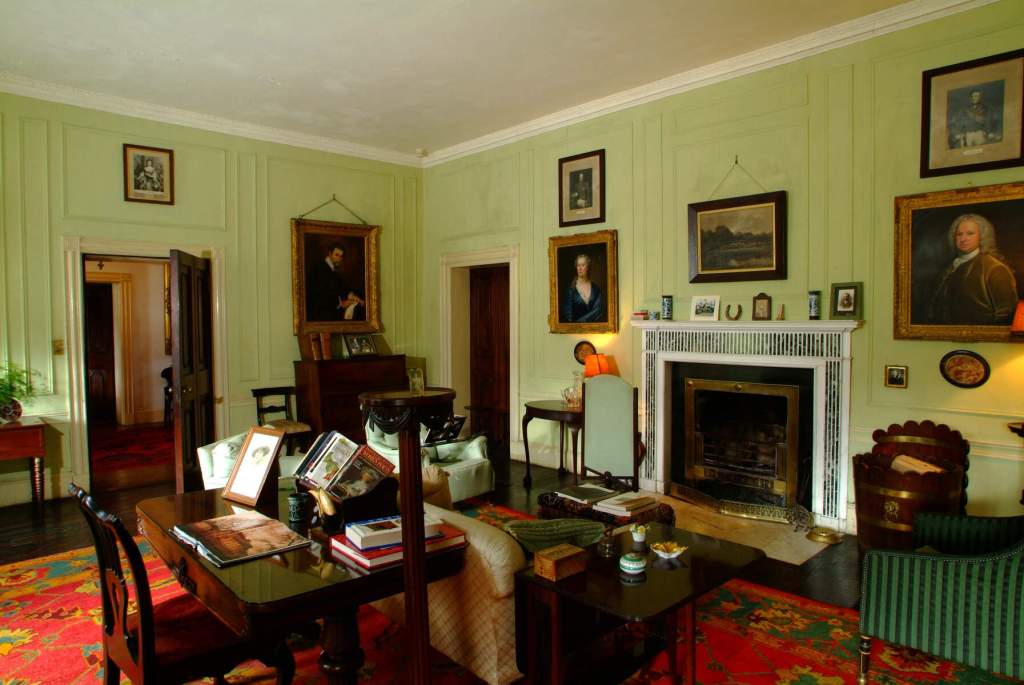
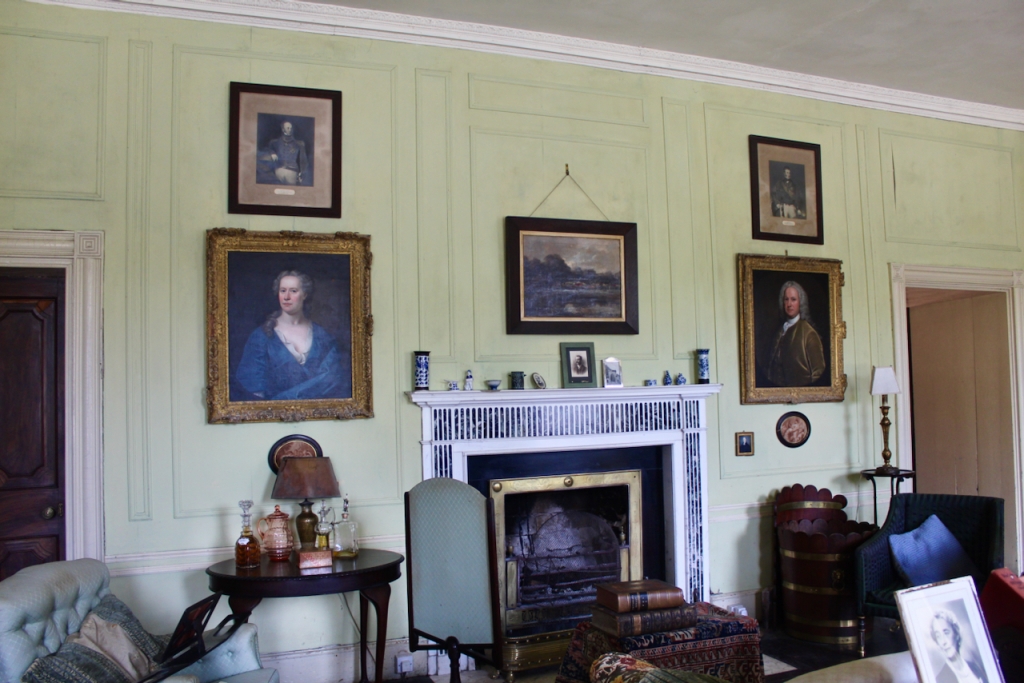
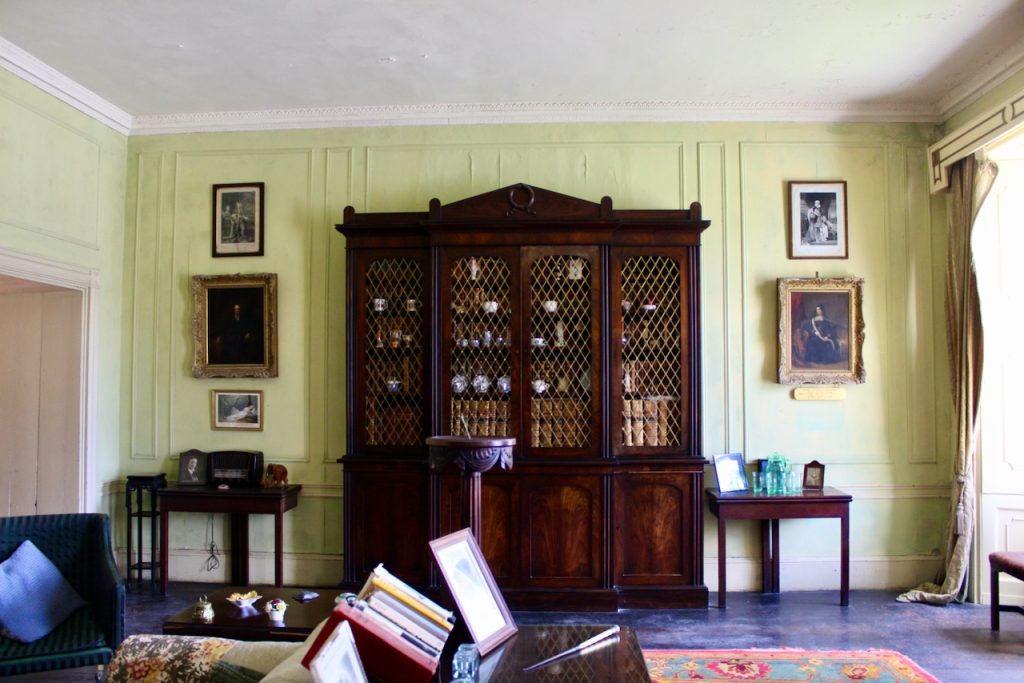








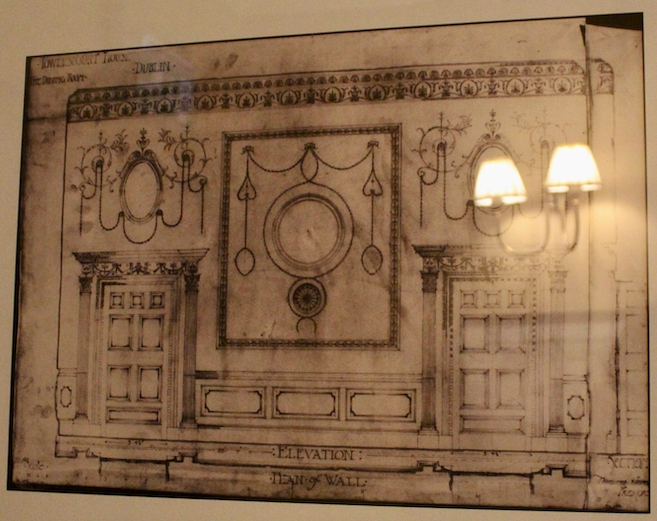
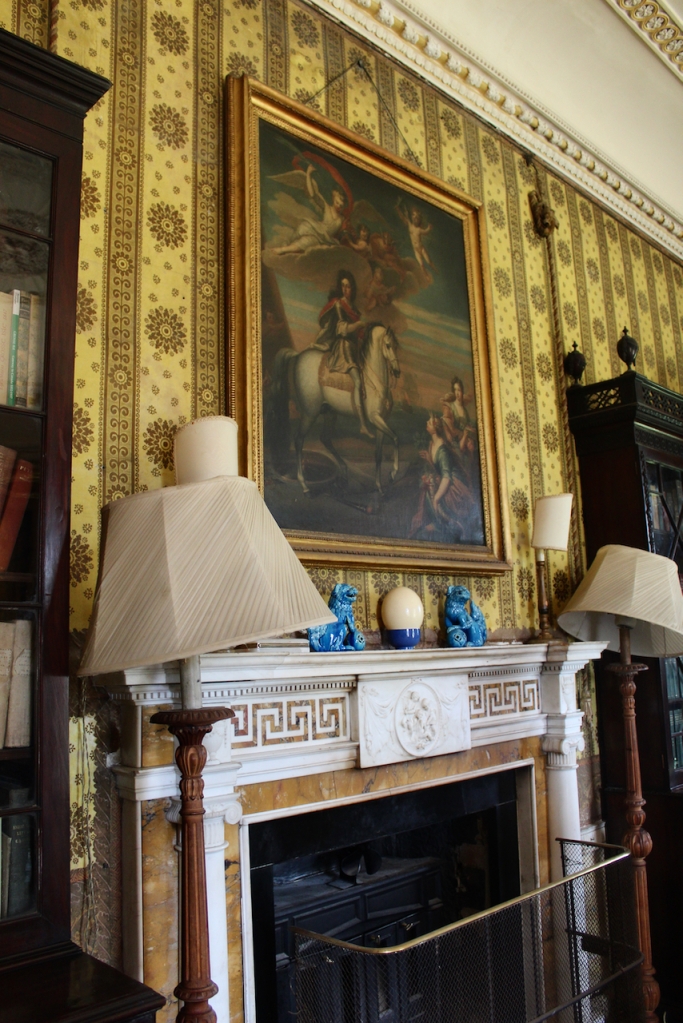
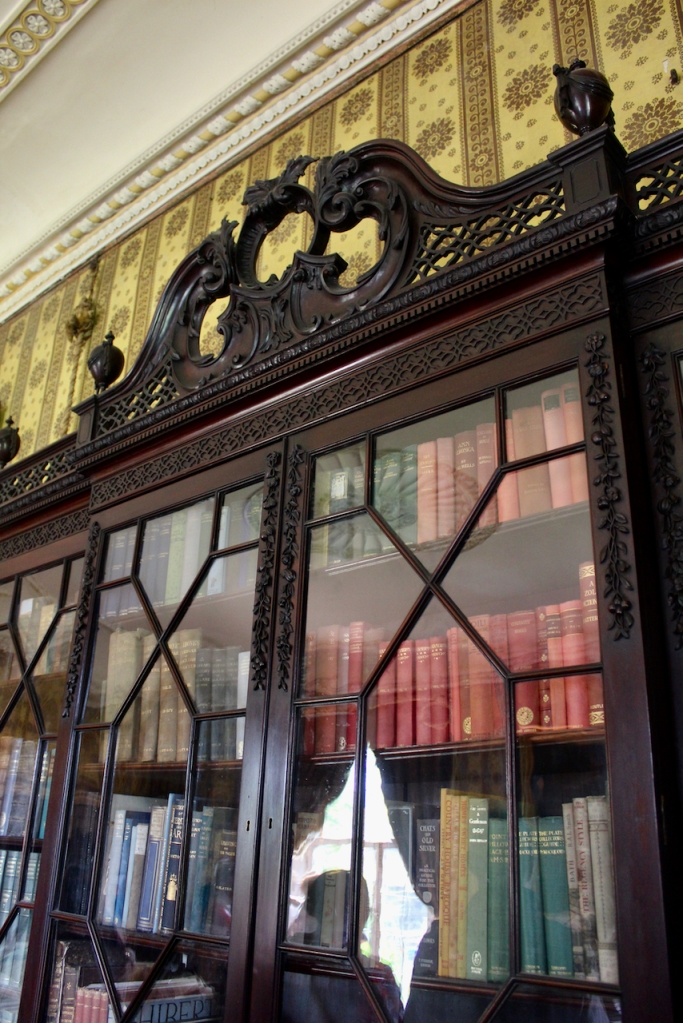
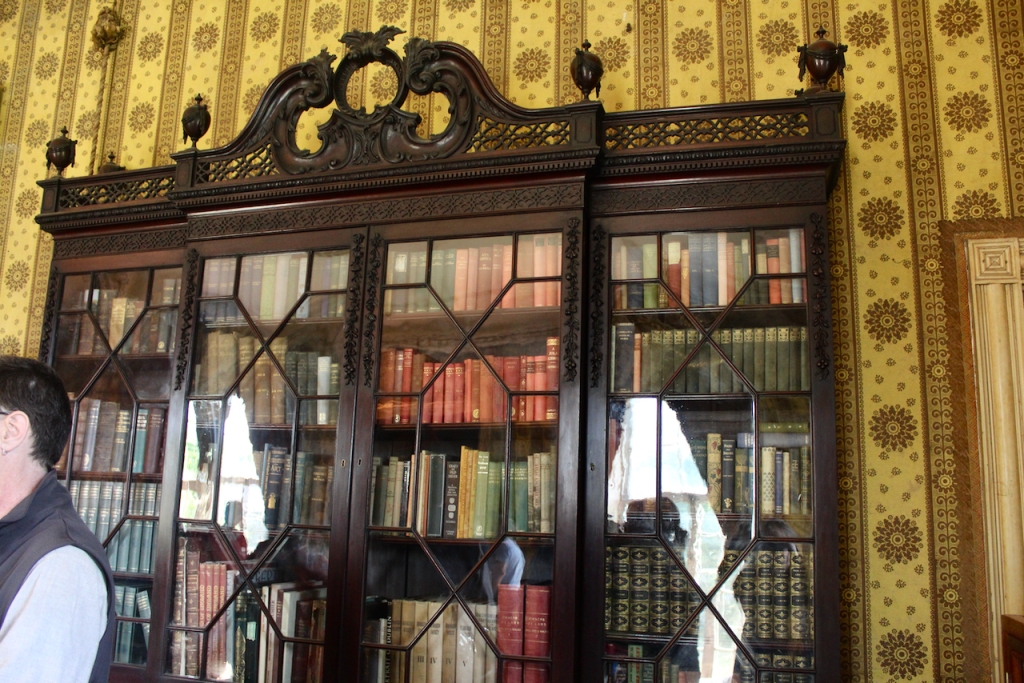
Terence Reeves-Smyth continues: “Regency additions incorporated the study, which also retains its original furnishings, and the smoking room, which was converted into a laboratory and photography darkroom by Henry Pakenham-Mahon, an amateur scientist, in the 1890’s. The finest regency addition is the library at the back, originally built as a ballroom with a bowed wall at one end to accommodate musicians. This contains Chippendale bookcases and beautiful brown and gold wallpaper, made especially for the walls in the early 19th century.“









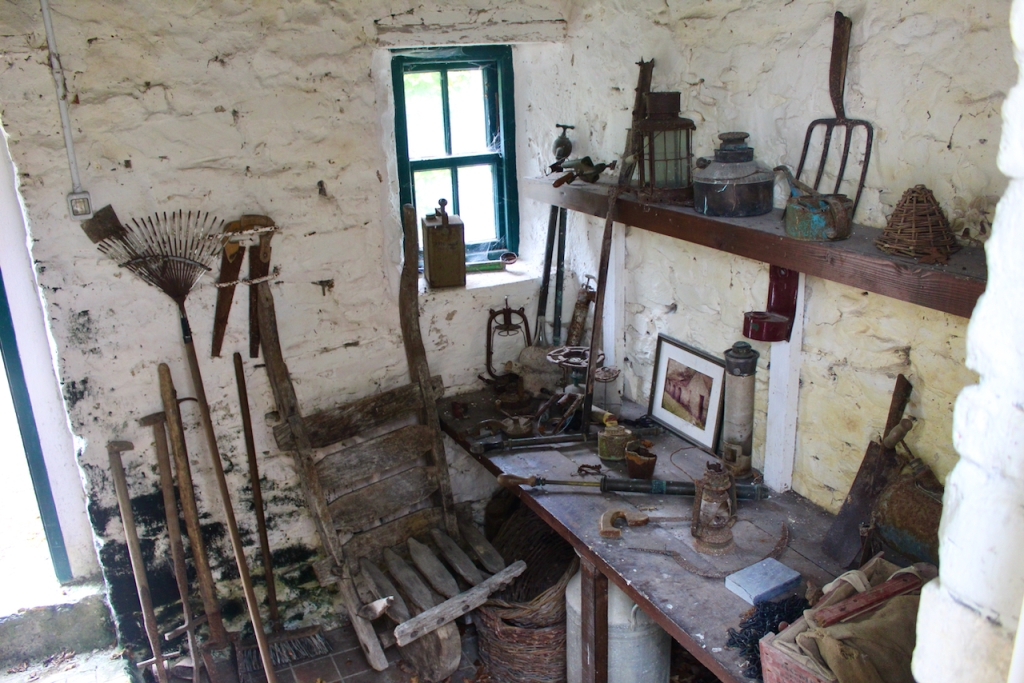
Reeves-Smyth continues, describing the kitchen which we did not see: “The old kitchen in the left wing of the house is approached from the dining room along a curved corridor, past store rooms for kitchen utensils and sporting equipment. Fitted with spits and ovens for baking, roasting and smoking, this kitchen has its original balustraded gallery which crosses the high ceilinged room lengthwise, the only example of its kind to survive in Ireland, especially in houses designed by Richard Castle. These galleries allowed the housekeeper to supervise the affairs below – one tradition has it that menus were dropped from the balcony on Monday mornings with instructions to the cook for the week’s meals.
“The wing to the right of the central block contains magnificent vaulted stables carried on Tuscan columns, similar to stables built by Castle for Carton (1739) and Russborough (1741). An underground passage links these stables to the yard on the north side of the house. The estate office was also in this wing, which meant the tenantry had to come here rather than to an office in the village to pay their rent.“

Maurice Craig tells us in his Irish Country Houses of the Middle Size: p. 21. “The practice of connecting the house with outlying offices by a tunnel seems to be peculiar to Ireland…Strokestown, Bellamont, Castle Coole and Lucan are amongst the Irish examples. In the nature of things, this is a feature of the grander houses, though it has been reported in connection with some of modest size.”
Thomas 2nd Baron married but had no children and his brother Maurice (1772-1845) succeeded as 3rd Baron Hartland when Thomas died in 1835. Maurice had joined the clergy, and was awarded a prebendary (an administrative role) in Tuam Cathedral in 1804.
In 1813 the 3rd Baron Hartland married Jane Isabella Hume of Humewood, County Wicklow, but also had no children and the title became extinct. He had another brother, Stephen, but he predeceased his brothers and had no children. The museum tells us that the 3rd Baron suffered with mental illness, though it does not give us specifics. He was declared insane just a year after he inherited the property in 1835.

The Dictionary of Irish Biography tells us that it was Denis Mahon who brought a motion against Maurice claiming that he was mentally ill and incapable of caring for the estate. Maurice had allowed the lease to lapse for a portion of the estate and stopped collecting rent from the town of Ballykilcline and its surrounding area. This led to an official declaration stating Maurice was a “lunatic.” Denis was named executor of the estate as well as being named Maurice’s legal guardian.
The museum tells us that when he was declared insane in 1836, two cousins battled in the courts to inherit the property: Denis Mahon (1787-1847) and Marcus McCausland.
Marcus McCausland owned the property of Drenagh, Limavady in County Derry (now a wedding venue). His mother was Theodosia Mahon, a sister of the 1st Baron Hartland, who had married Conolly McCausland-Gage. The nine year court case decided in favour of Denis Mahon. As well as the now poorly managed property, he inherited debts.
Denis was the son of a brother of 1st Baron Hartland, Reverend Thomas Mahon (1740-1811). Reverend Thomas married Honoria Kelly, daughter of Denis Kelly of Castle Kelly, County Galway (also called Aughrane Castle, it has been demolished. It was purchased by Bagots in 1910, I’m haven’t found an ancestral link to these Bagots).

It was Denis Mahon who was then murdered during the Famine. The story is told in detail in the Famine Museum. The estate was badly run and tenants let and sublet their parcels of land, hence owned smaller and smaller portions of land to grow their crops.
Reeves-Smyth tells us: “Major Denis Mahon, who succeeded to Strokestown on the death of the third and last Lord Hartland in 1845 was so unpopular a landlord during the famine years that he was shot whilst returning from a meeting of the Roscommon Relief Committee in 1848, apparently on suspicion of chartering unseaworthy ships to transport emigrants from his estate to America. His successors were much better regarded and his great-granddaughter and last owner, Mrs. Olive Hales-Packenham-Mahon, was a much loved figure in this part of Ireland. She died in 1981, leaving a house filled with the trappings of three centuries of unbroken family occupation.“

Captain Denis Mahon chose to help his tenants to leave Ireland. He wanted to reduce his number of tenants. The 1838 Poor Law made a local tax for poor rates. In 1843 the act was amended and introduced new rates, charging landlords a tax for each tenant who had holdings of less than a value of £4. Landlords therefore tried to reduce the number of tenants.



The Famine Museum is introduced by a beautifully handwritten letter by tenants asking not for money or food, but work. The eloquent letter humanises those who were experiencing the poverty of the famine in the 1840s.


Arthur Young writes in his A Tour in Ireland in 1799 that “the poor live on potatoes and milk, it is their regular diet, very little oat bread being used and no flesh meat at all except on Easter Sunday and Christmas day.”



Denis Mahon tried to make the estate pay for itself, to pay off the debts he had inherited. He also tried to take care of his tenants. He had two agents, John Ross Mahon and Thomas Conry. He began relief efforts for his tenants in March 1846. 4000 people were provided with corn on a weekly basis at low or no cost, and after a harsh winter, he distributed free seed to his most needy tenants. He also had a soup kitchen set up.
John Ross Mahon wrote to him that the poor rates would exceed receipts of rent. By 1847 the conditions were worse and there was unrest amongst the tenants. Mahon began to evict tenants and to encourage others to emigrate. The Freeman’s Journal in 1848 states that “The evictions on the estate since Major Mahon had taken over amounted to 3006 people, including the 1,490 who were selected to emigrate.” Fewer than half of those who emigrated survived the trek to Dublin and the journey on the ship.
The building of the month entry in the National Inventory summarises: “Major Mahon, an improving landlord, sought to alleviate the situation by judicious depopulation and in 1847 organised the voluntary emigration of almost one thousand of his tenants to North America. However, a far greater number refused to move and were the subject of evictions involving almost 600 families and 3000 individuals. Returning from an evening meeting in Roscommon, where he had urged the Board of Guardians to keep the workhouse open for needy paupers, Major Mahon was fatally shot on the 2nd of November 1847. Three men were hanged for the murder and two were transported, but the true identity of the assassin or assassins has been debated ever since.”

The Famine Museum tells us that there were secret societies who sought to improve the conditions of the poor. A local one in Roscommon was called the “Molly Maguires.”


The man suspected to be the mastermind of the murder, Andrew Connor, probably escaped to Canada. Police followed to Canada to try to capture him but to no avail. A man named Patrick Hasty was hanged for the murder, along with two others.

Denis’s son Thomas predeceased him, childless, and the house passed to his daughter, Grace Catherine. Earlier in 1847, Grace had married Henry Sandford Pakenham (1823-1893), son of Reverend Henry Pakenham, Dean of St. Patrick’s Cathedral in Dublin, who was from Pakenham Hall in County Westmeath, now called Tullynally (see my entry, it is another Section 482 property which can be visited).
Henry Sandford Pakenham held the office of High Sheriff of County Roscommon in 1830. He was heir to the vast Pakenham and Sandford estates in counties Longford, Westmeath and Roscommon. He legally changed his name to Henry Sandford Pakenham Mahon by Royal Licence in 1847.
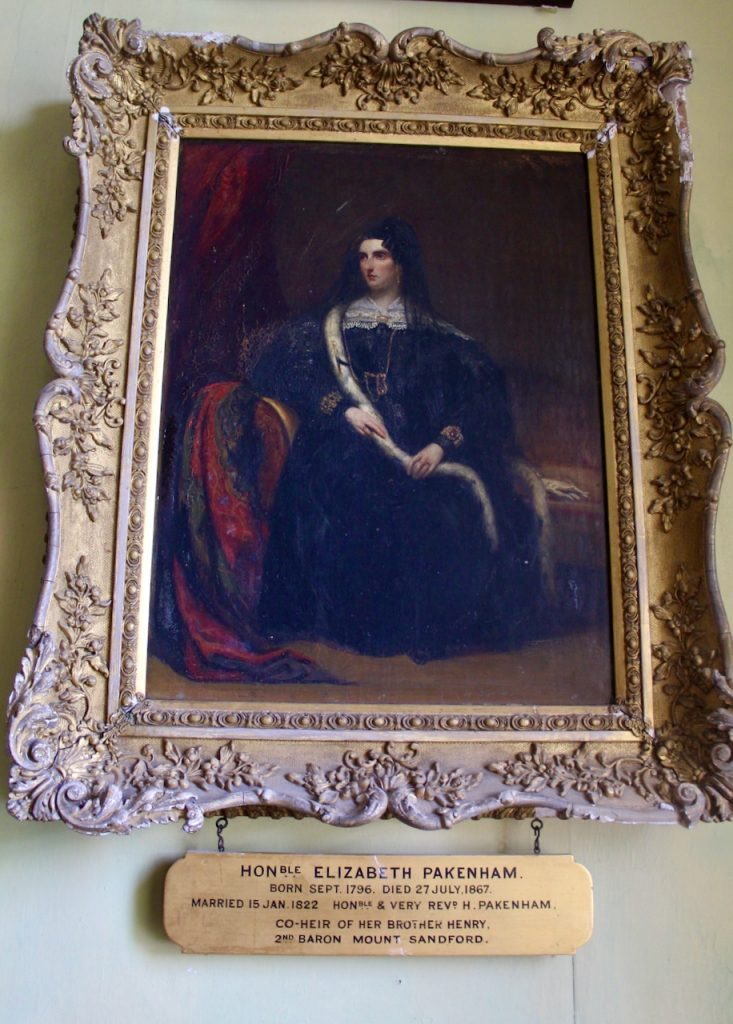
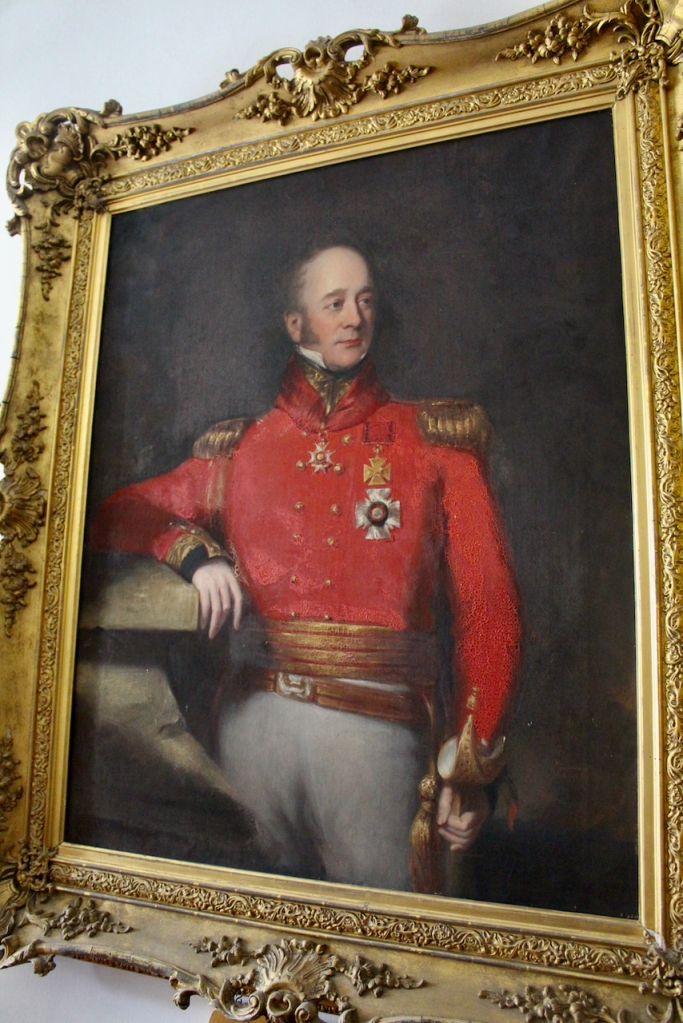
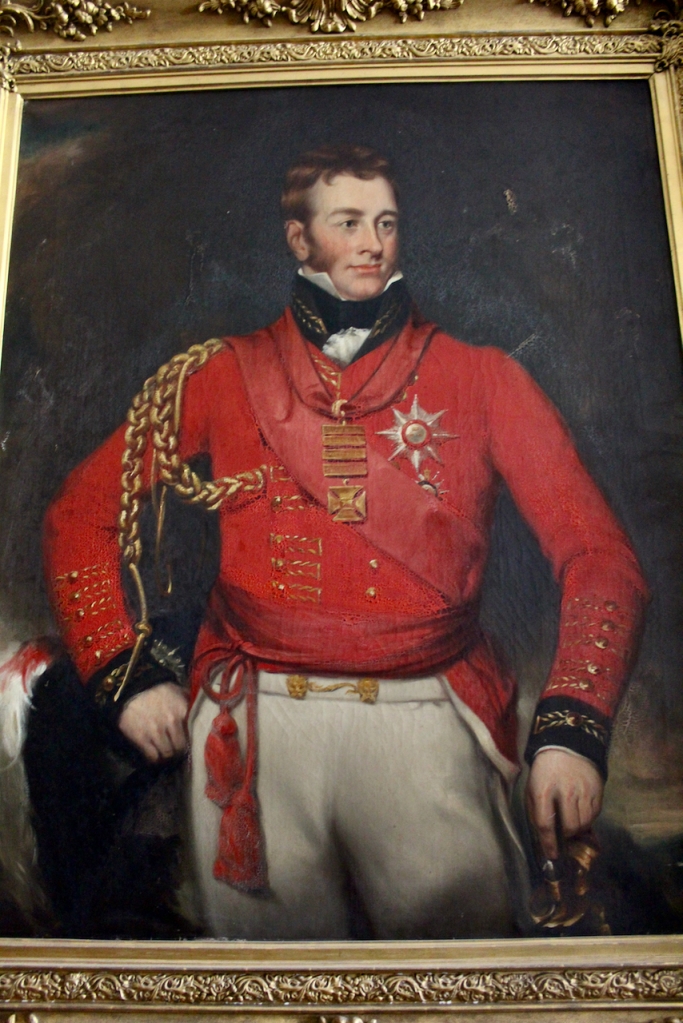



After Denis Mahon was killed his devastated daughter Grace moved to the Isle of Wight with her husband, who continued to manage the estate with the help of his agent.
He and Grace Catherine had several daughters, and a son, Henry Pakenham-Mahon (1851-1922).
Henry moved back to live in Strokestown. He was High Sheriff, Justice of the Peace and Deputy Lieutenant of County Roscommon, following in the footsteps of his father. He married Mary Burrard and Olive, as mentioned by Reeves-Smyth, was their daughter.
Henry Pakenham-Mahon was a keen horticulturalist and his main contribution to the estate was the development of the gardens. The family lived part-time in Strokestown Park and part-time in England. He developed a Pleasure Garden in the walled garden.

He also had an interest in photography, and he built a darkroom in Strokestown House.
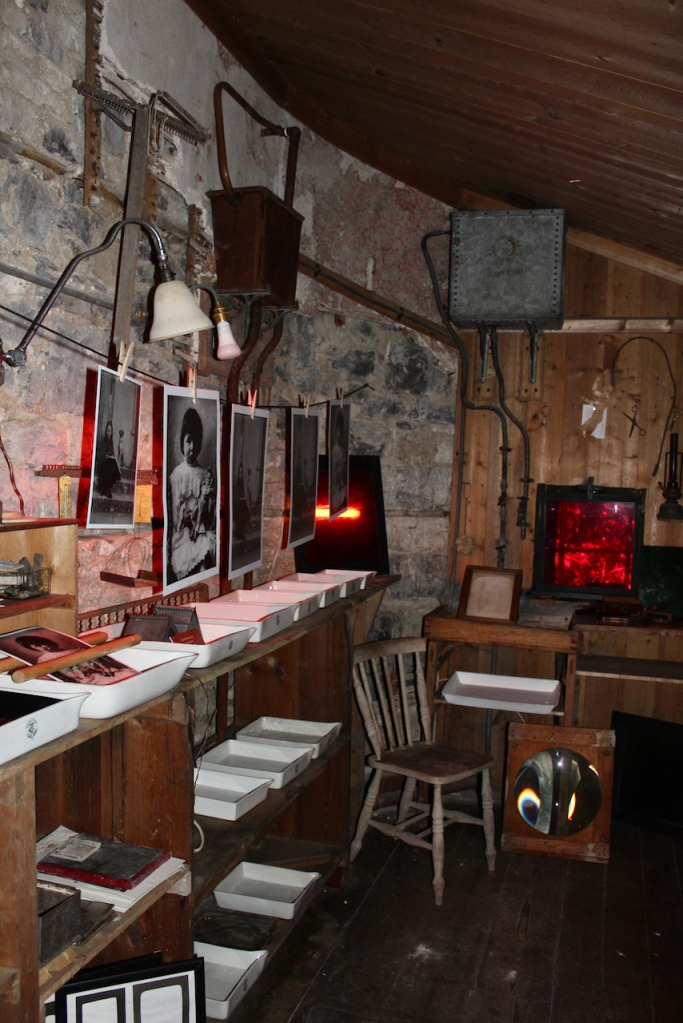
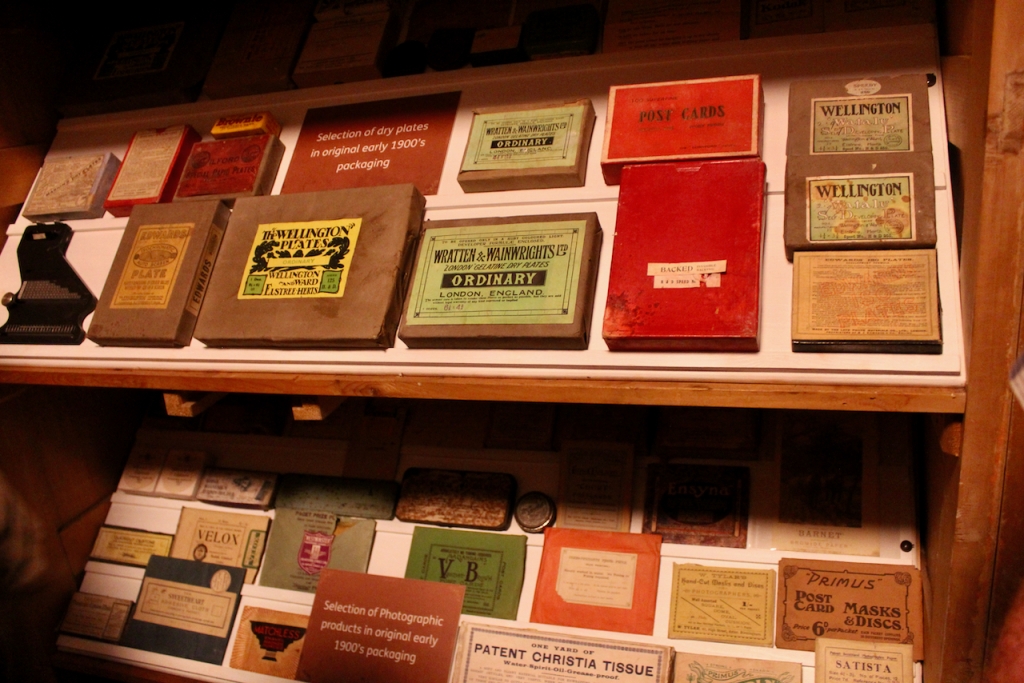
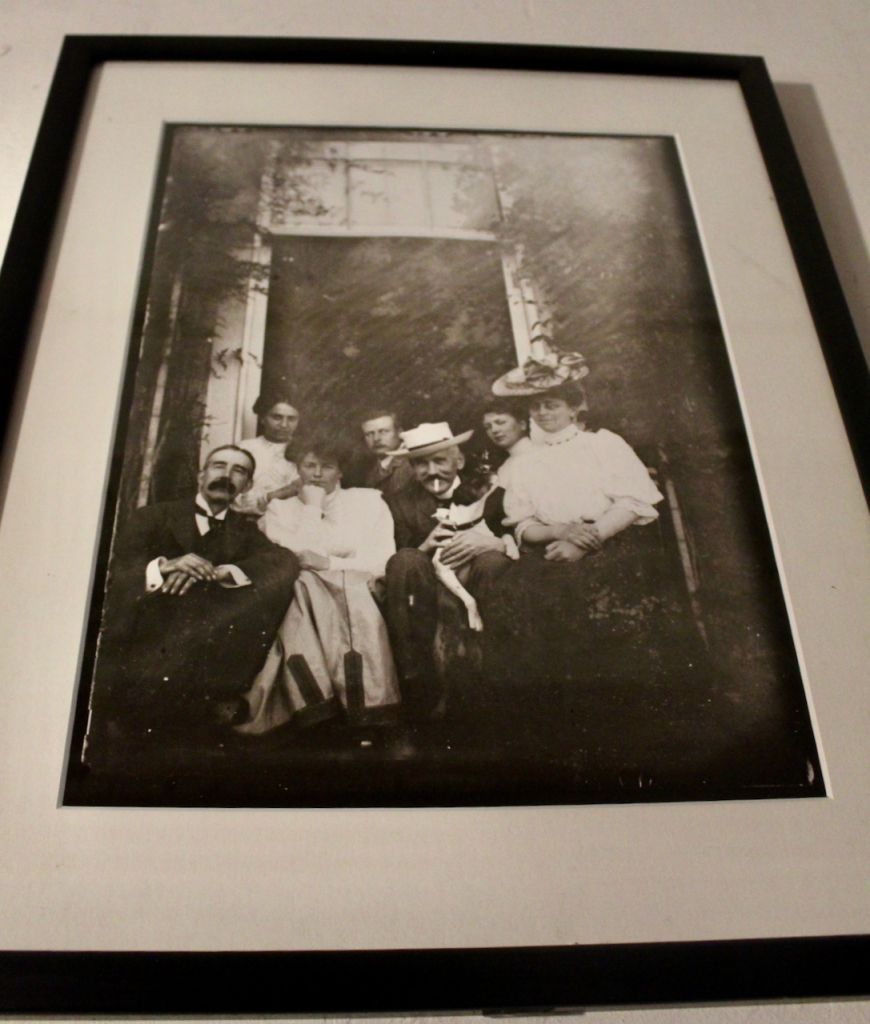







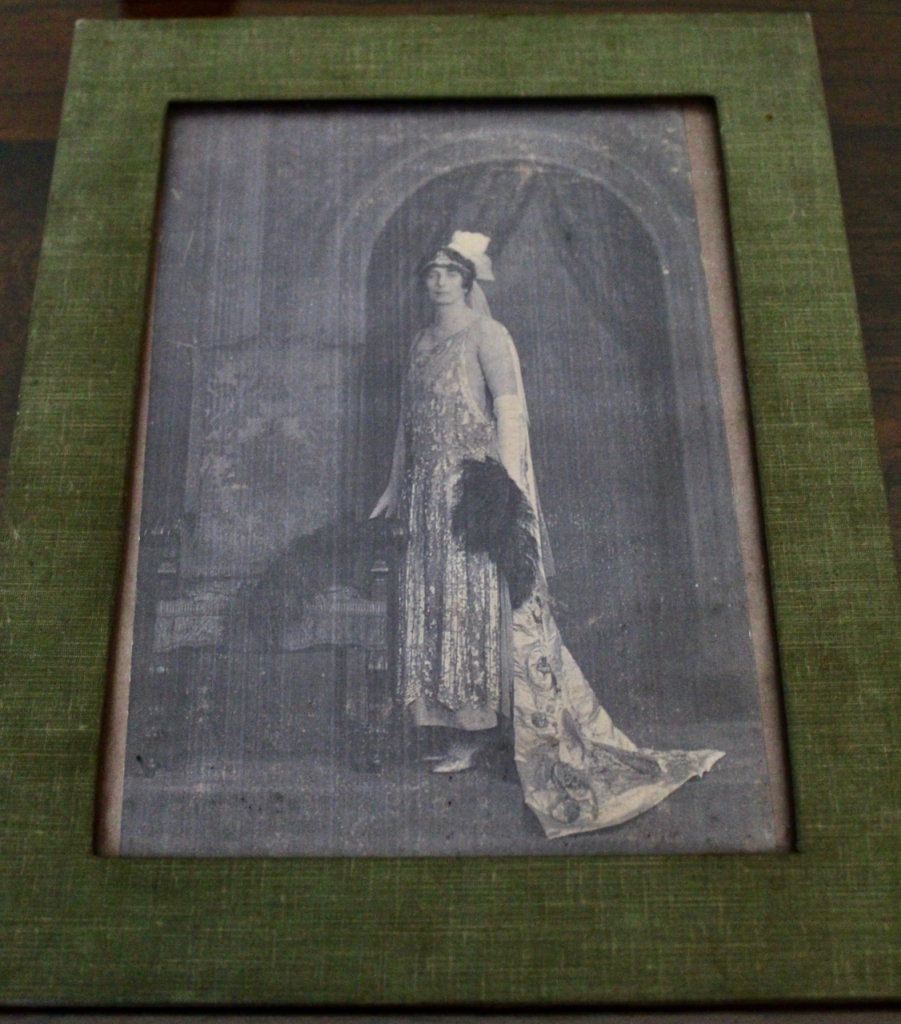
His daughter Olive, born in 1894, first married Captain Edward Charles Stafford-King-Harman, from Rockingham House, County Roscommon, whom we came across in King House. Tragically, he died in the first world war in 1914. They had one daughter, Lettice. If Lettice had been a boy she would have inherited Rockingham. Olive and Lettice returned to live in Strokestown Park.



Olive married again, this time to Wilfrid Stuart Atherstone Hales, who also fought in the first world war, and later, in the second. A British garrison was set up in Strokestown House during the War of Independence. After an ambush nearby, Wilfrid Stuart Hales was sent to investigate, and he and Olive fell in love. On 18 April 1923 his name was legally changed to Wilfrid Stuart Atherstone Hales Pakenham Mahon by Deed Poll. He married Olive in 1921 and he changed his name after the death of her father in 1922. They went on to have several children. It was her son who sold the estate.
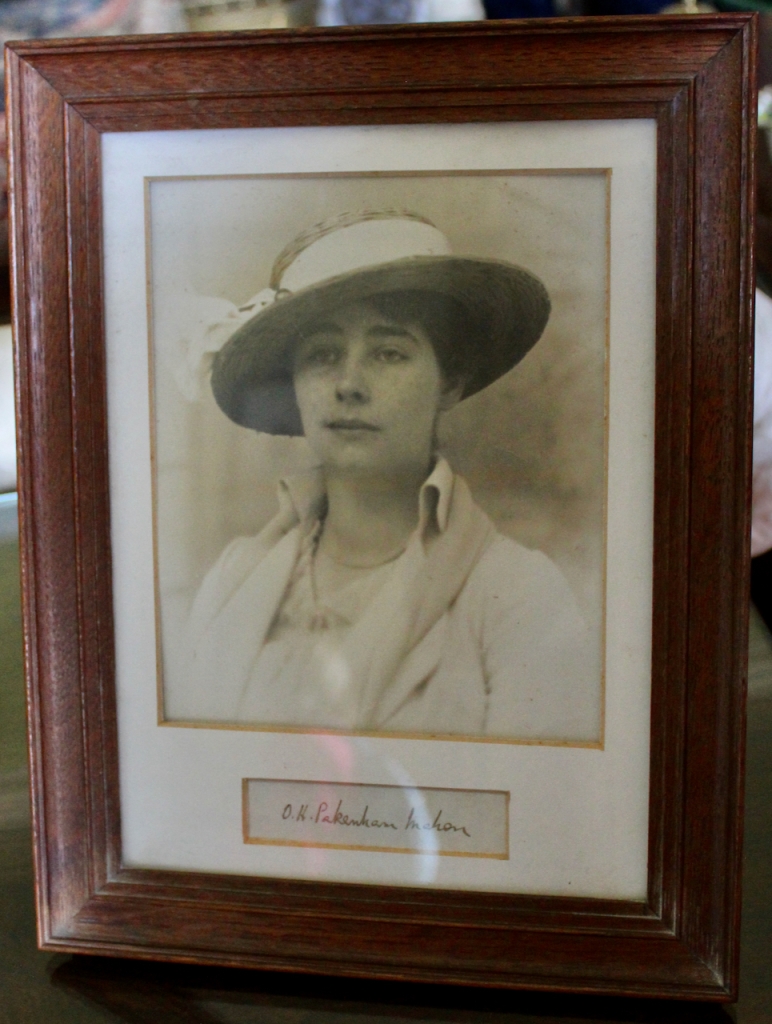


The Pakenham Mahons did not spent much time in Strokestown due to Stuart Hales Pakenham Mahon’s military career, until they returned to live there in the 1950s.
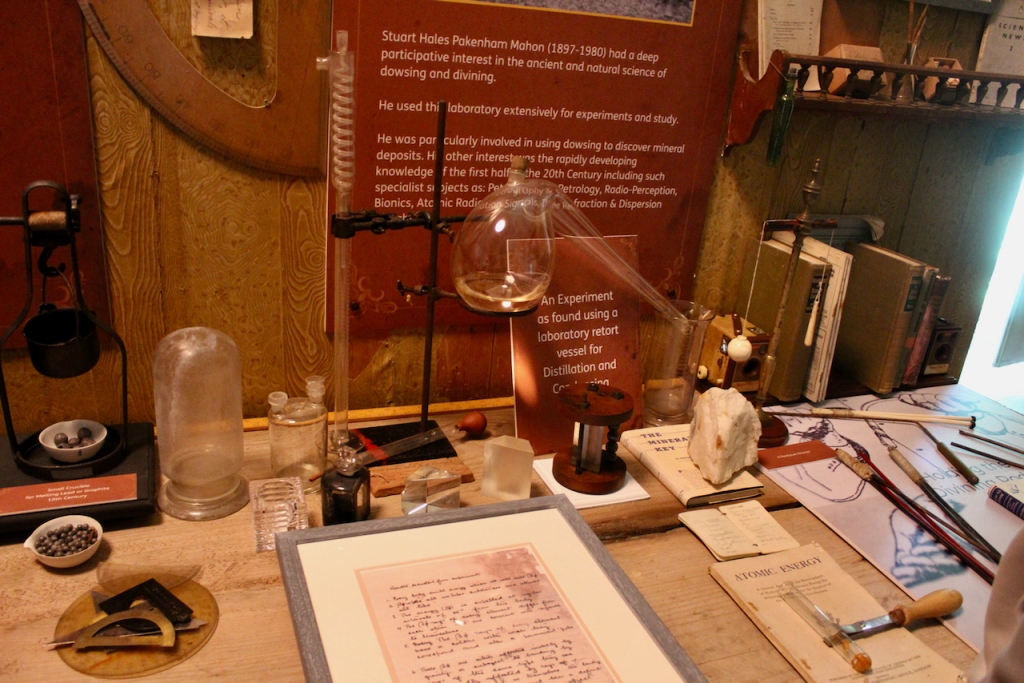
Stuart Hales Pakenham Mahon was interested in finding water and mineral deposits by “dousing,” and the photography display we saw in the house also had information on this topic.

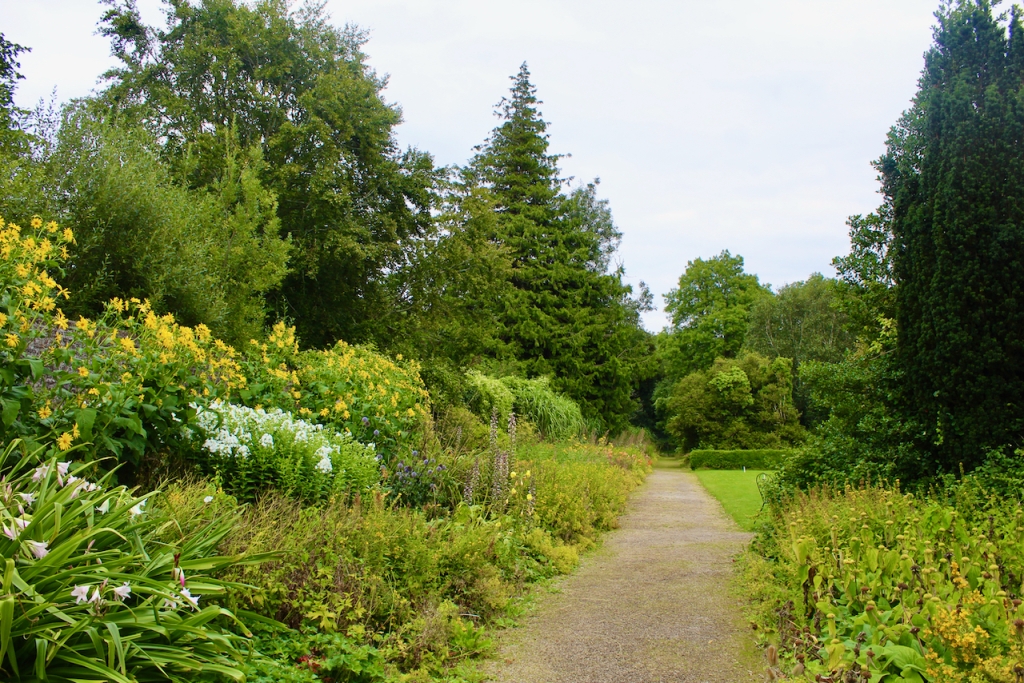
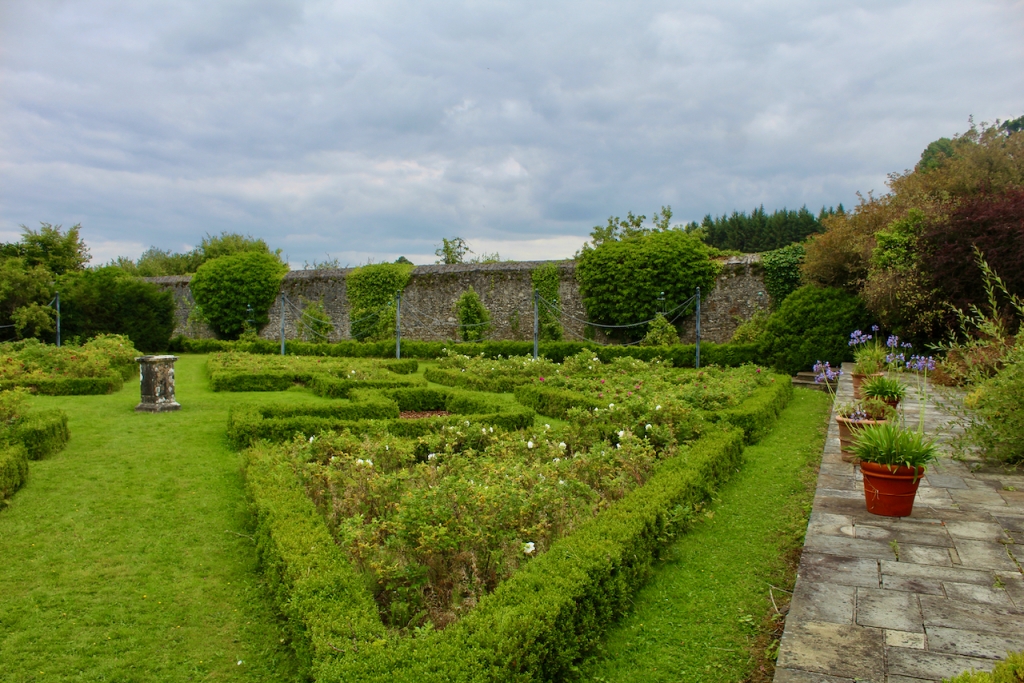
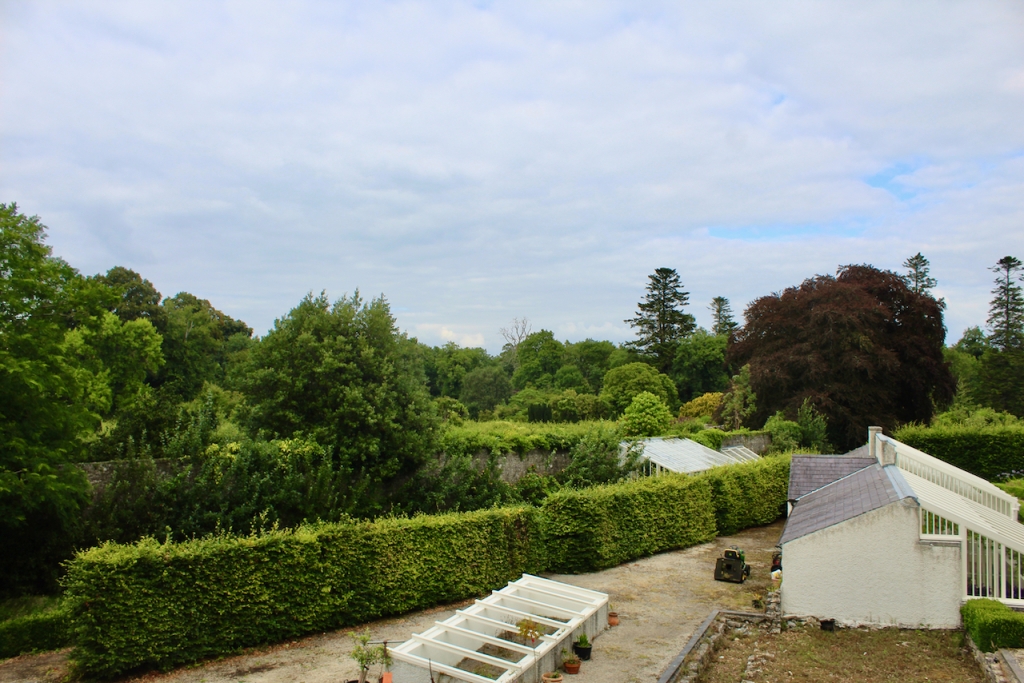
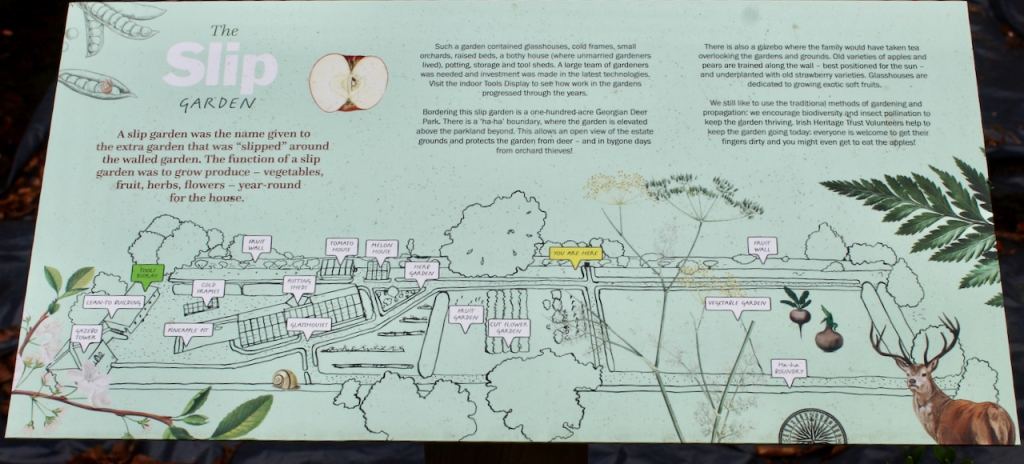
The property has a six acre walled garden and woodlands.
Westward Garage Ltd approached the Pakenham Mahons to buy their land, and terms were agreed. At first the garage only wanted to keep some land and they planned to sell the house, but then Jim Callery found the documents relating to the famine, and had the idea of setting up a famine museum. The company let Olive and her husband remain in the house. Jim Callery employed his cousin Luke Dodd to oversee restoration of the house. [15] In 1987 the house opened to the public, and the Famine Museum opened in 1994. The walled garden opened in 1997, and the herbaceous border is said to be the longest in either Ireland or the UK.



After exploring the Famine Museum we went out to the extensive walled garden.
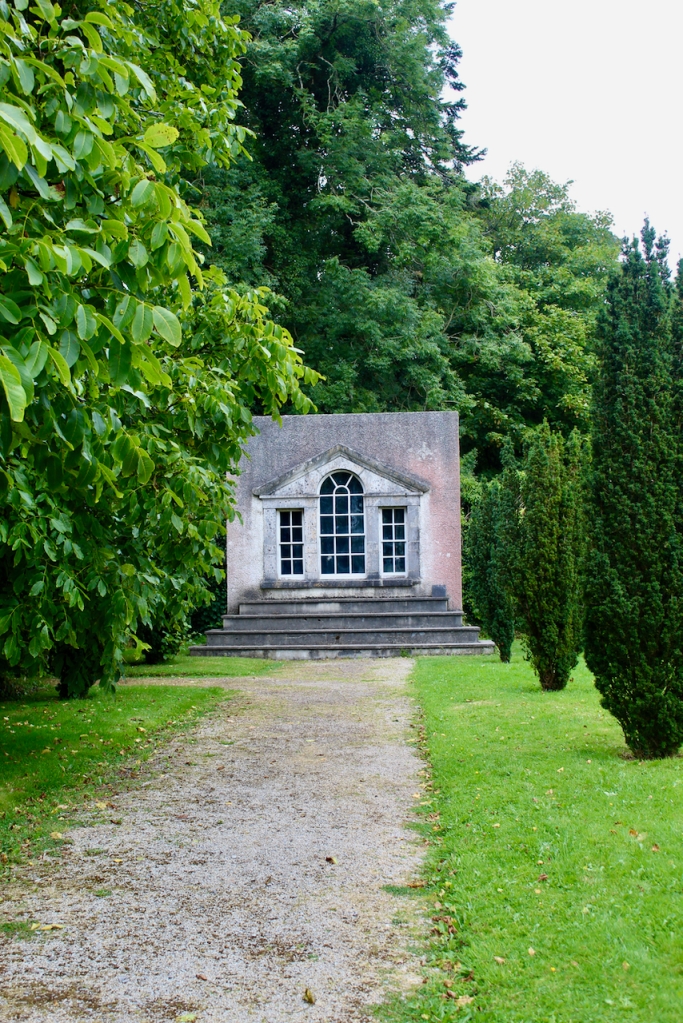
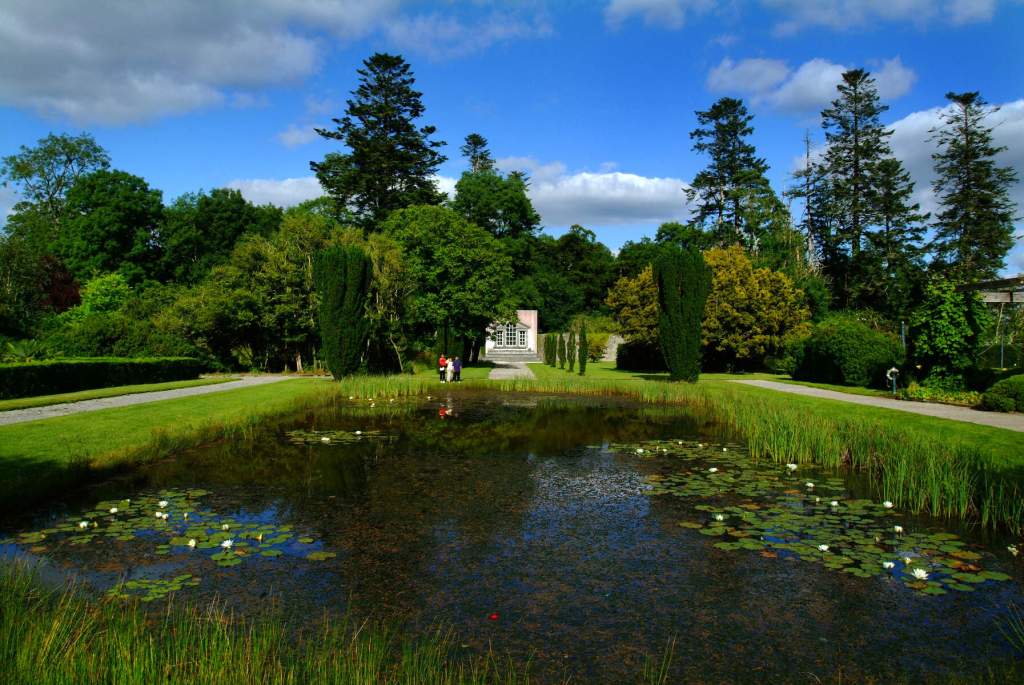
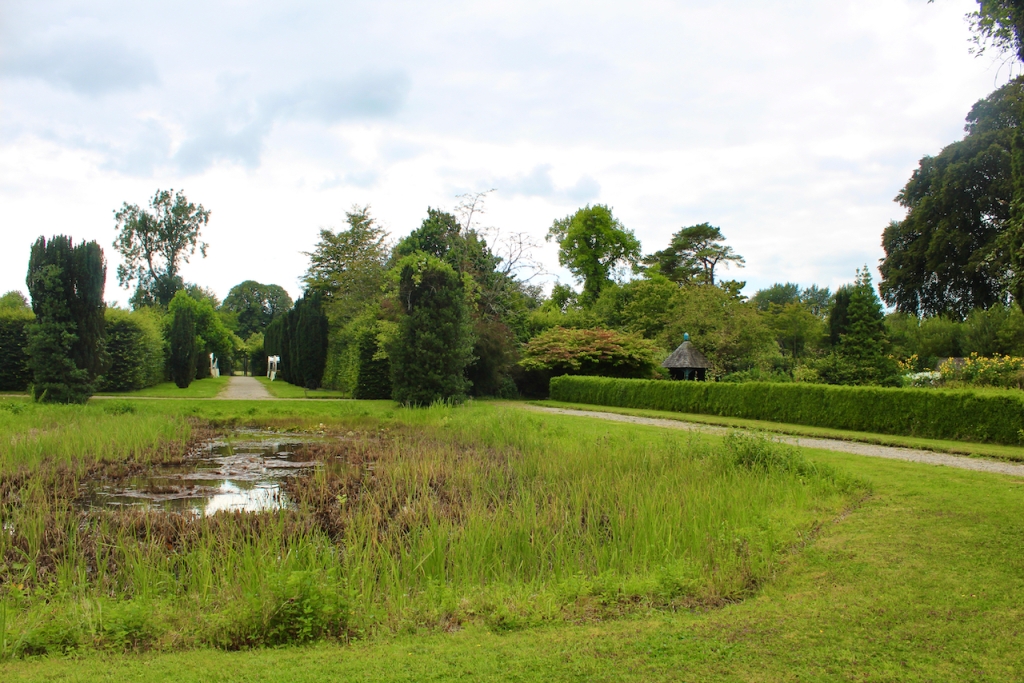
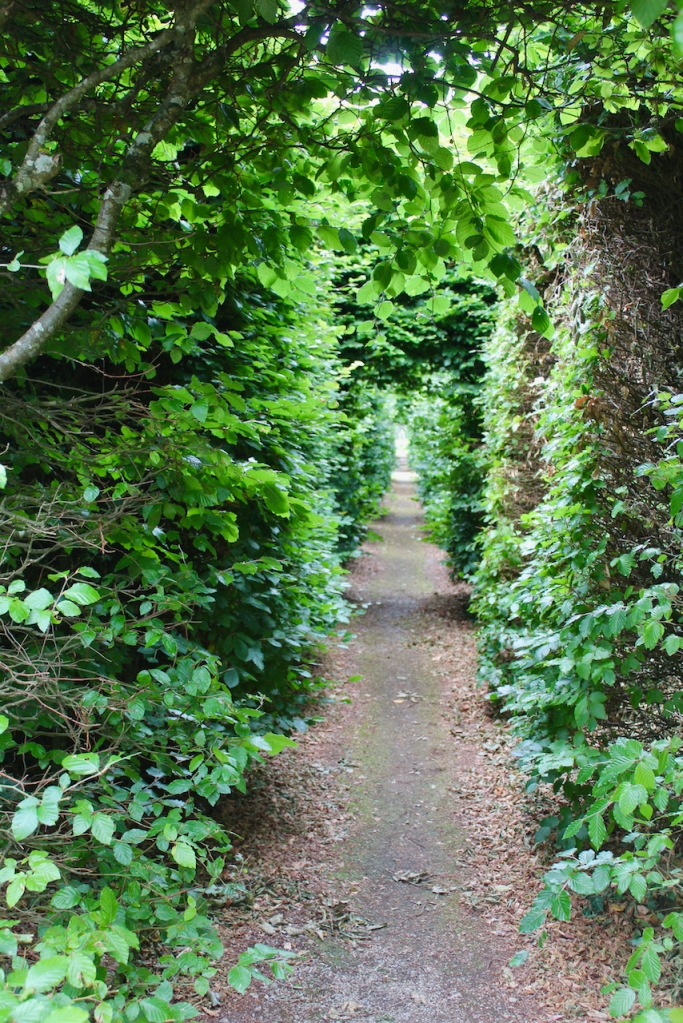















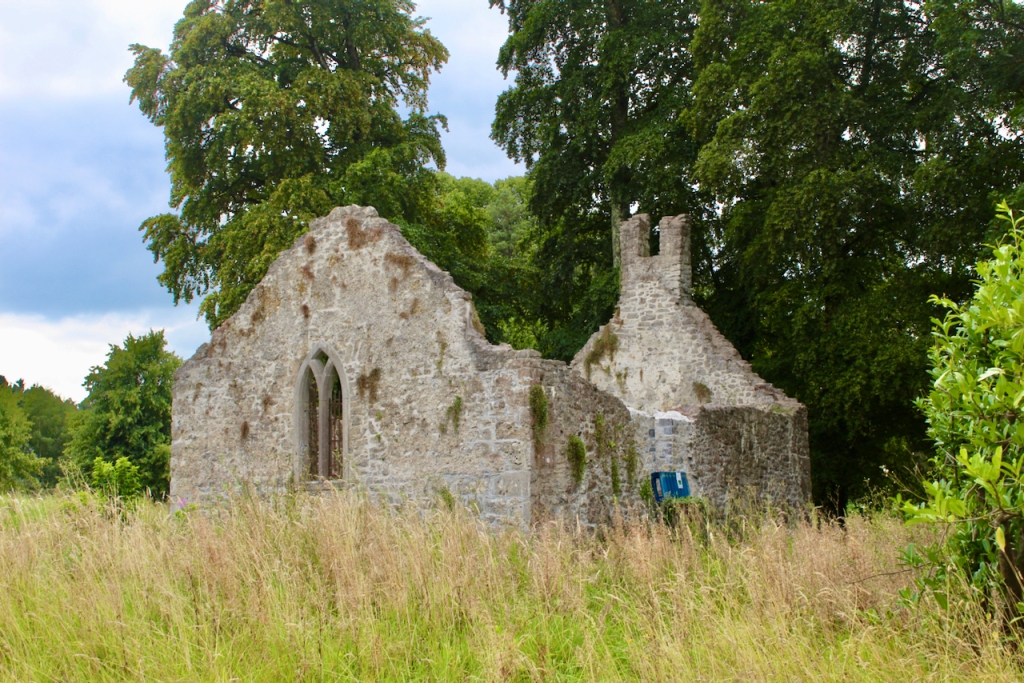
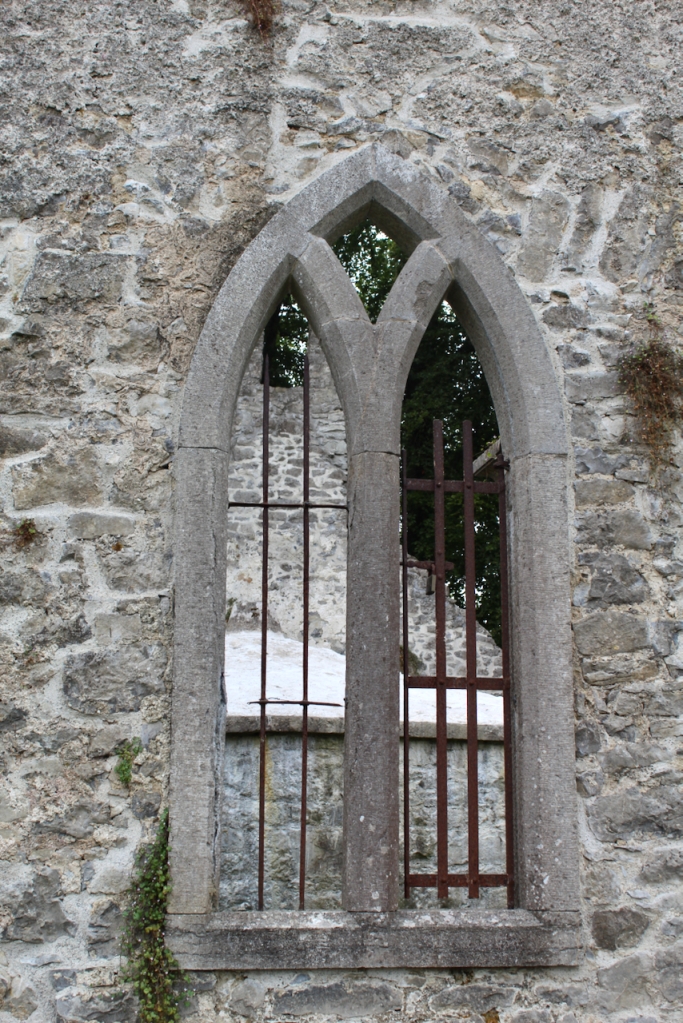
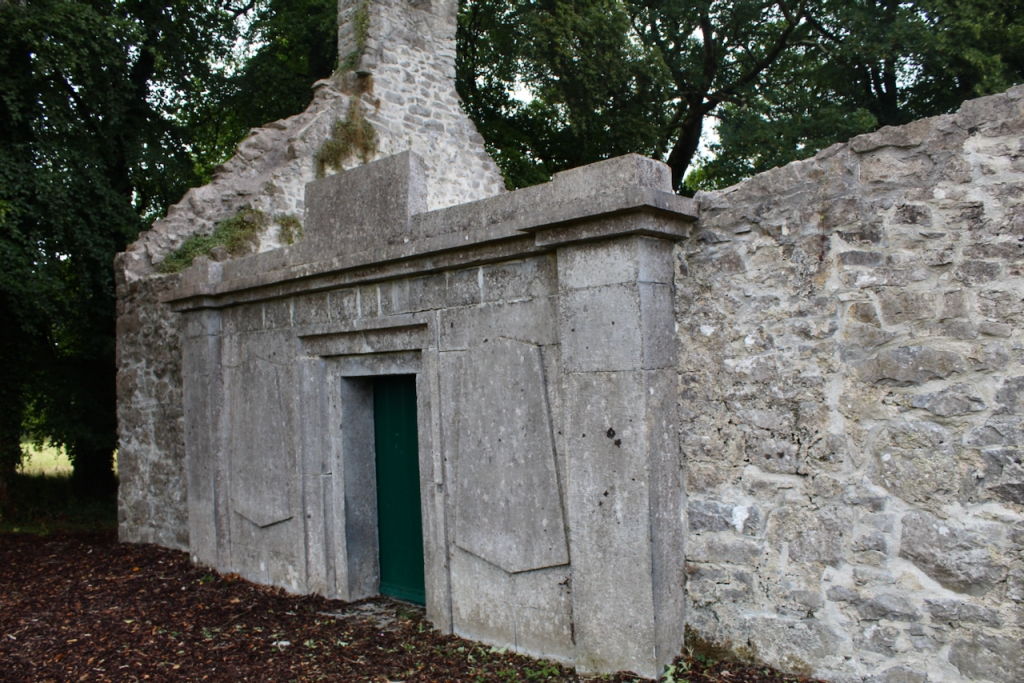
The following day there was a talk about the mausoleum at Strokestown, but we had to move on with our Heritage Week plans. The mausoleum was constructed within an earlier 17th century church and contains a crypt in which members of the Mahon Family were buried. Following years of careful and professional conservation and sympathetic landscaping, this ruin is again accessible and visible to visitors to Strokestown Park.



[1] https://www.irelandscontentpool.com/en
[2] https://www.archiseek.com/2012/1730-strokestown-park-co-roscommon/
[3] http://lordbelmontinnorthernireland.blogspot.com/search/label/County%20Roscommon%20Landowners
[5] You can see the chimney and plaster overmantel on the website of Robert O’Byrne, https://theirishaesthete.com/2014/10/29/getting-to-the-bottom-of-it/
[6] Bernard, Sir Burke, editor, Burke’s genealogical and heraldic history of the landed gentry of Ireland, 4th ed. (London, U.K.: Burkes Peerage Ltd, 1958), page 471. I’m not sure if “Movilla” mentioned here refers to Moyveela townland.
[7] Reeves-Smyth, Terence. Irish Big Houses. Appletree Press Ltd (22 April 2009)
[8] https://www.dia.ie/architects/view/347/CASTLE-RICHARD
[9] https://www.dib.ie/index.php/biography/castle-castles-cassels-cassells-richard-a1552
[10] https://www.buildingsofireland.ie/buildings-search/building/31811028/strokestown-park-house-cloonradoon-strokestown-co-roscommon and Strokestown Park featured as Building of the month in December 2015 https://www.buildingsofireland.ie/building-of-the-month/strokestown-park-house-cloonradoon-td-strokestown-county-roscommon/
[11] http://www.thepeerage.com/p37647.htm#i376469
[12] Bence-Jones, Mark. A Guide to Irish Country Houses (originally published as Burke’s Guide to Country Houses volume 1 Ireland by Burke’s Peerage Ltd. 1978); Revised edition 1988, Constable and Company Ltd, London. Note that Mark Bence-Jones claims that it was the 2nd Baron Hartland who laid out the main street of Strokestown and had the entrance built, but the National Inventory tells us that it was Maurice, 1st Baron Hartland.
[13] https://www.dia.ie/architects/view/3279/LYNN-JOHN%5B1%5D#tab_biography
[14] p. 203. Connolly, Paul. The Landed Estates of County Roscommon. Published by Paul Connolly, 2018.
[15] p. 213, Connolly.
Text © Jennifer Winder-Baggot, www.irishhistorichouses.com