On the map above:
blue: places to visit that are not section 482
purple: section 482 properties
red: accommodation
yellow: less expensive accommodation for two
orange: “whole house rental” i.e. those properties that are only for large group accommodations or weddings, e.g. 10 or more people.
green: gardens to visit
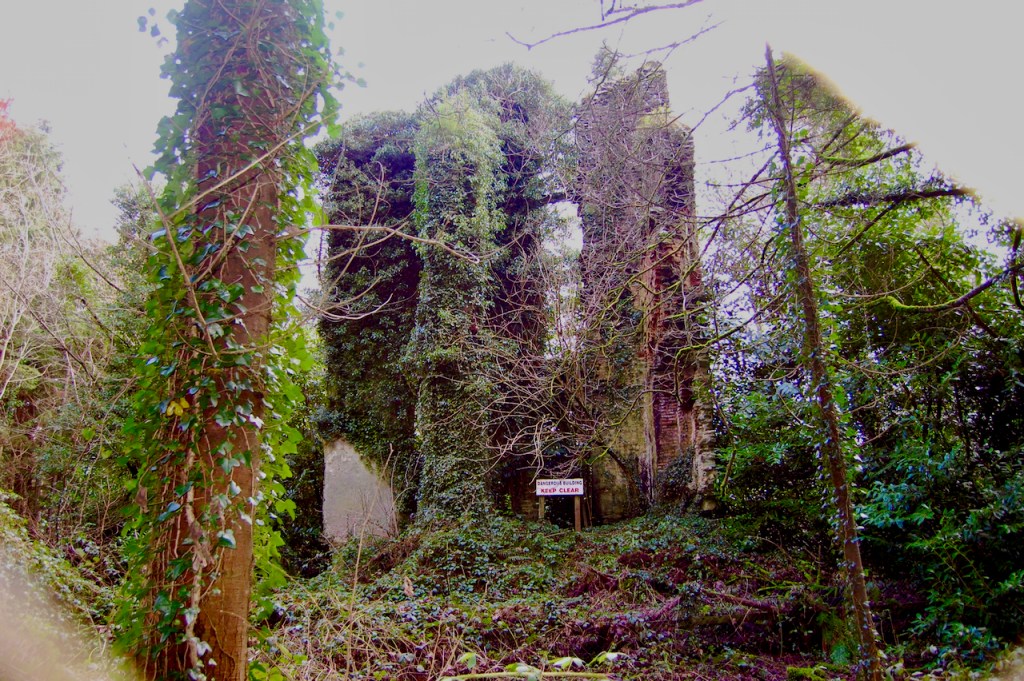
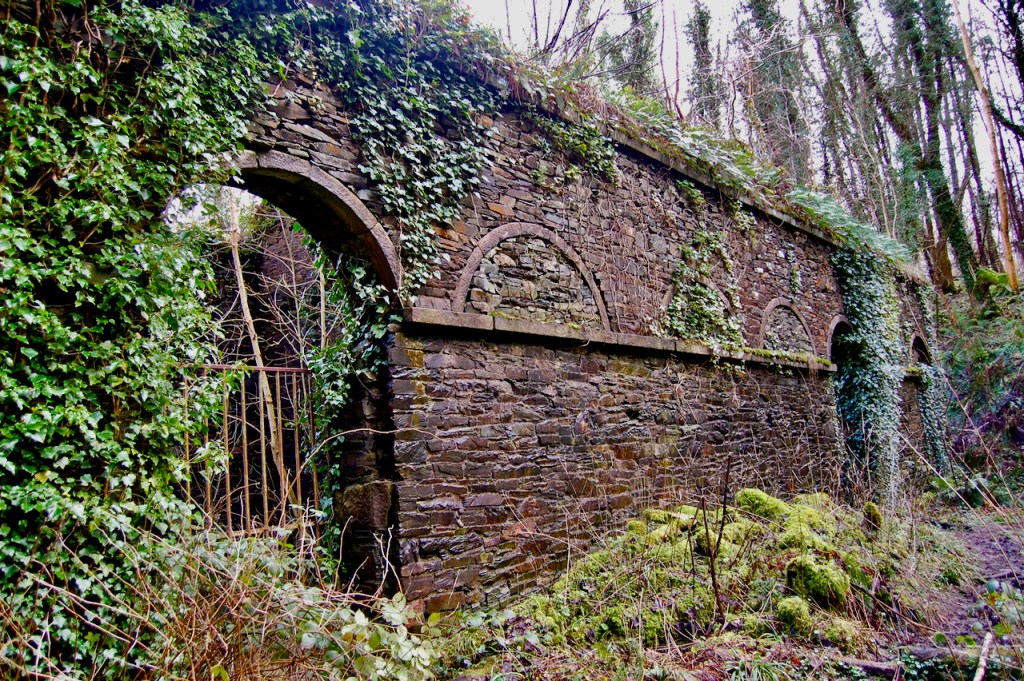
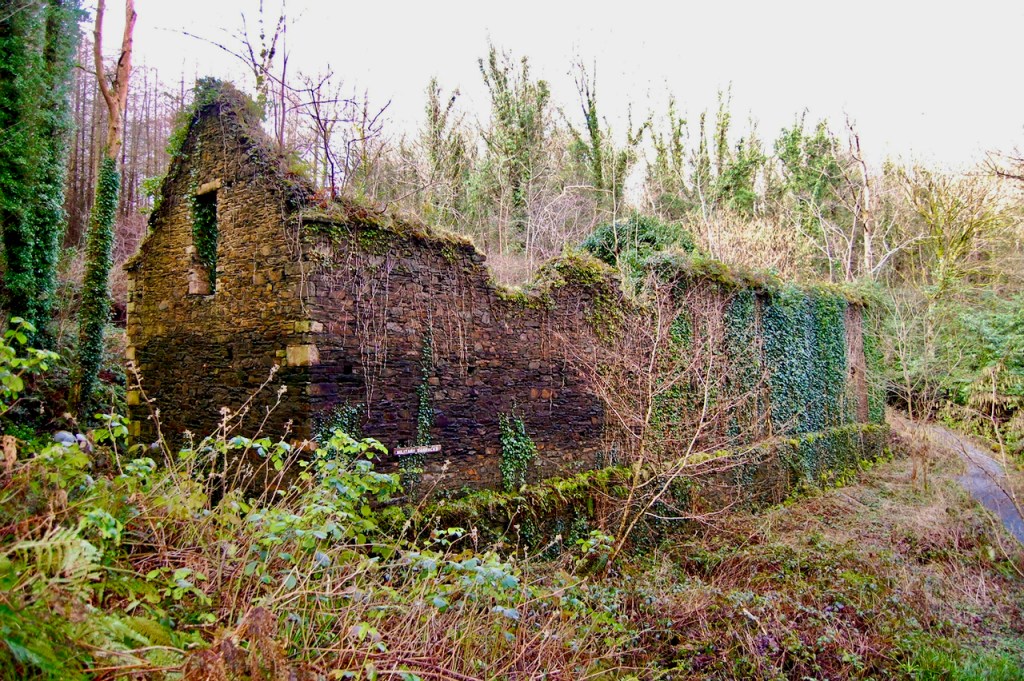
grey: ruins
Carlow, Dublin, Kildare, Kilkenny, Laois, Longford, Louth, Meath, Offaly, Westmeath, Wexford and Wicklow are the counties that make up the Leinster region.
As well as places to visit, I have listed separately places to stay, because some of them are worth visiting – you may be able to visit for afternoon tea or a meal.
For places to stay, I have made a rough estimate of prices at time of publication:
€ = up to approximately €150 per night for two people sharing (in yellow on map);
€€ – up to approx €250 per night for two;
€€€ – over €250 per night for two.
For a full listing of accommodation in big houses in Ireland, see my accommodation page: https://irishhistorichouses.com/accommodation/

donation
Help me to pay the entrance fee to one of the houses on this website. This site is created purely out of love for the subject and I receive no payment so any donation is appreciated!
€10.00
Places to visit in County Louth
1. Barmeath Castle, Dunleer, Drogheda, Co. Louth – section 482
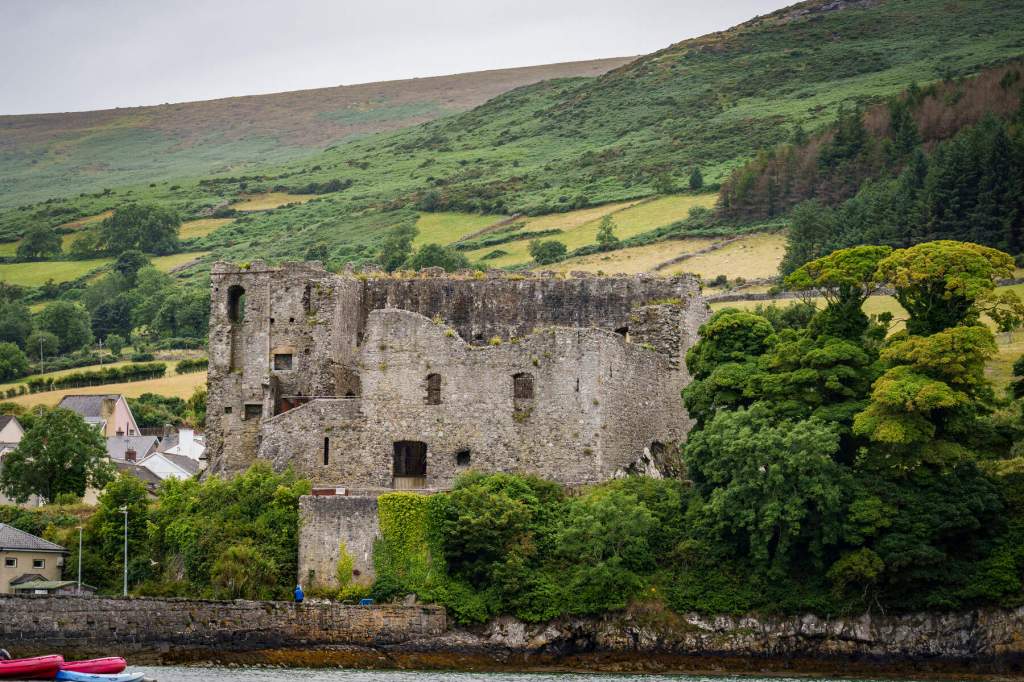
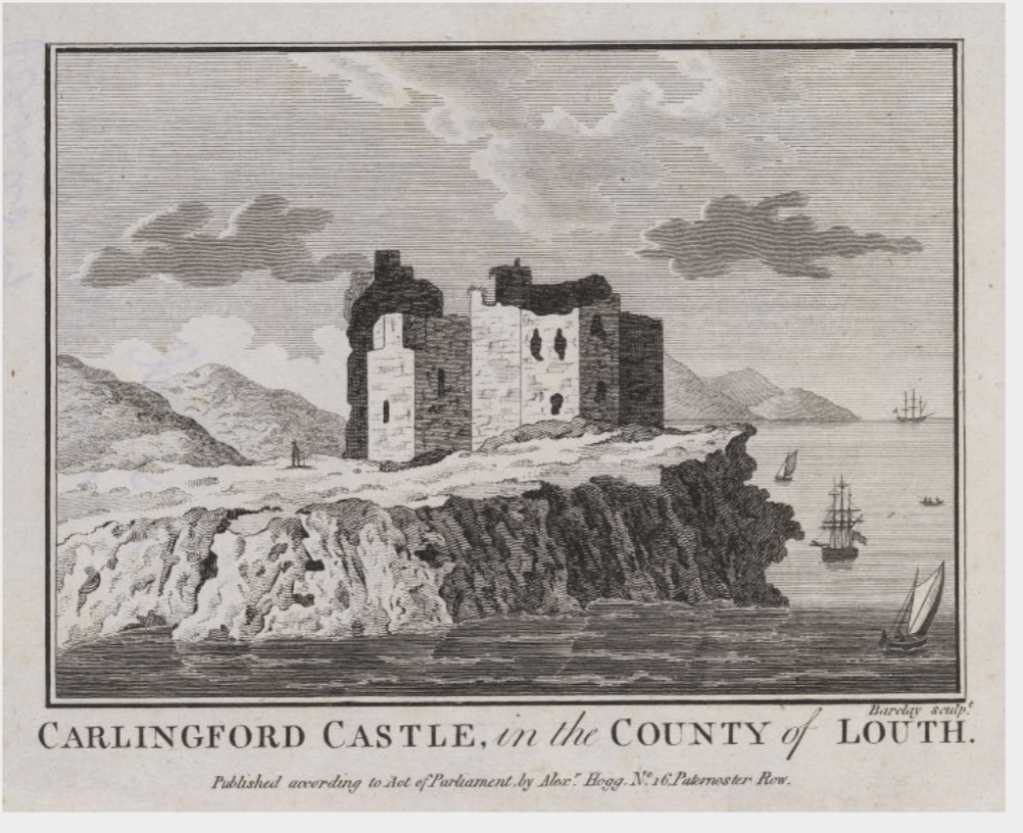
2. Carlingford Castle, County Louth – OPW
3. Castle Bellingham, Co. Louth
4. Collon House, County Louth
5. Killineer House & Garden, Drogheda, Co. Louth – section 482
6. Old Mellifont Abbey, County Louth – OPW
7. Rokeby Hall, Grangebellew, Co. Louth – section 482
Places to stay, County Louth:
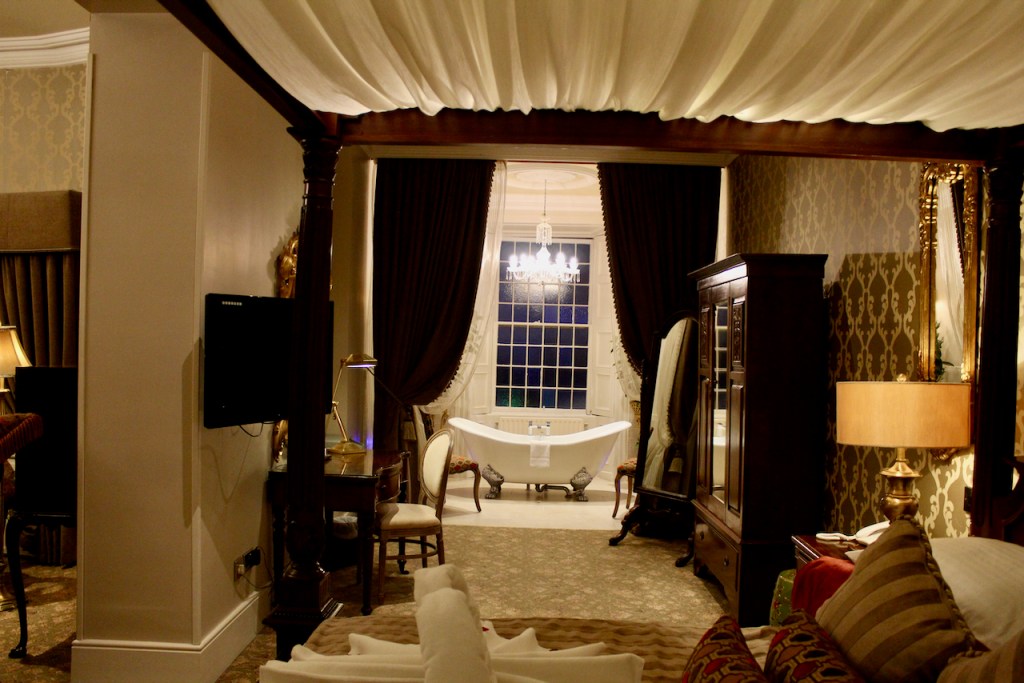
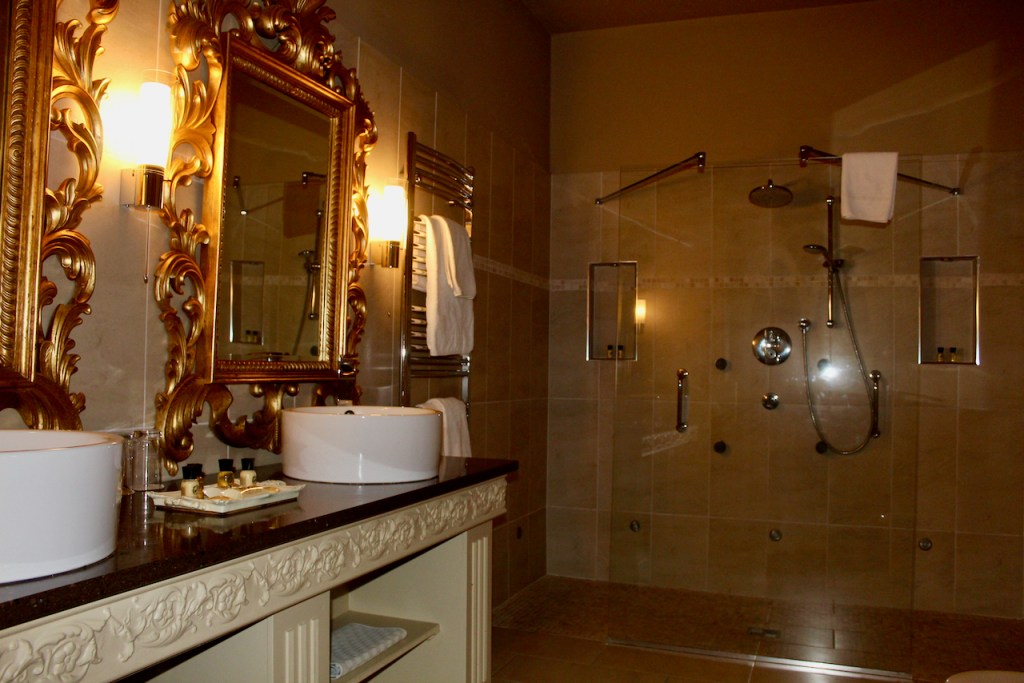
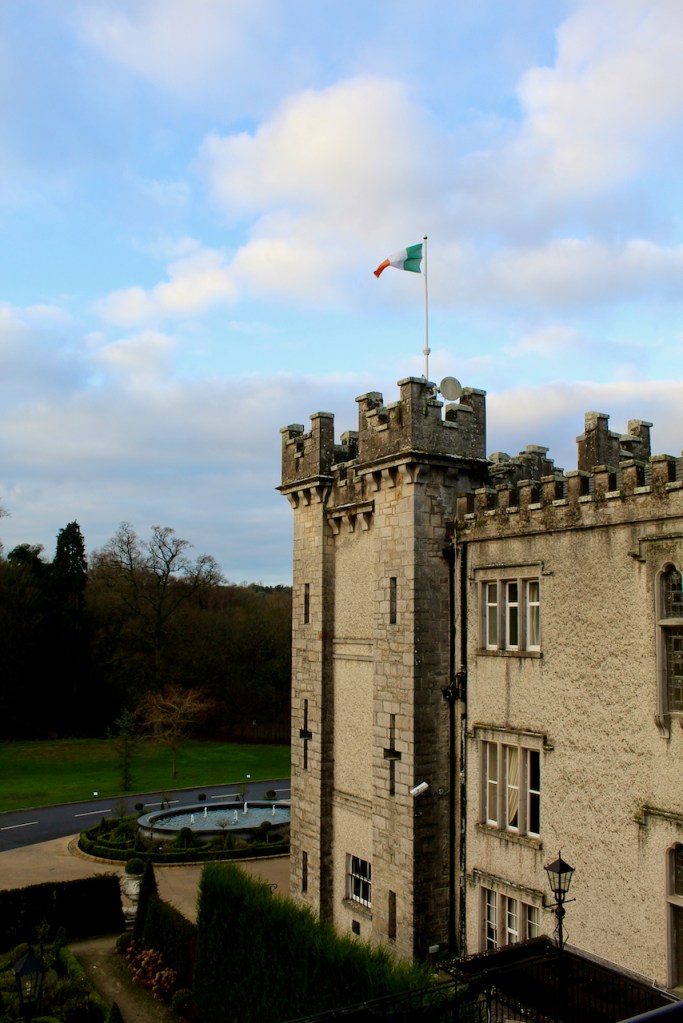
1. Ballymascanlon House, Louth – hotel
2. Collon House, Ardee Street, Collon, Louth [also Oriel Temple] – B&B, plus guided tours
3. Darver Castle, County Louth
4. Ghan House, Co Louth – accommodation
Whole House Rental, County Louth:
1. Barmeath Castle, Dunleer, Drogheda, Co. Louth – section 482, €€€ for two, € for 6-12
2. Bellurgan Park, County Louth
3. Castle Bellingham, Co. Louth – weddings
Places to visit in County Louth
1. Barmeath Castle, Dunleer, Drogheda, Co. Louth A92 P973 – section 482
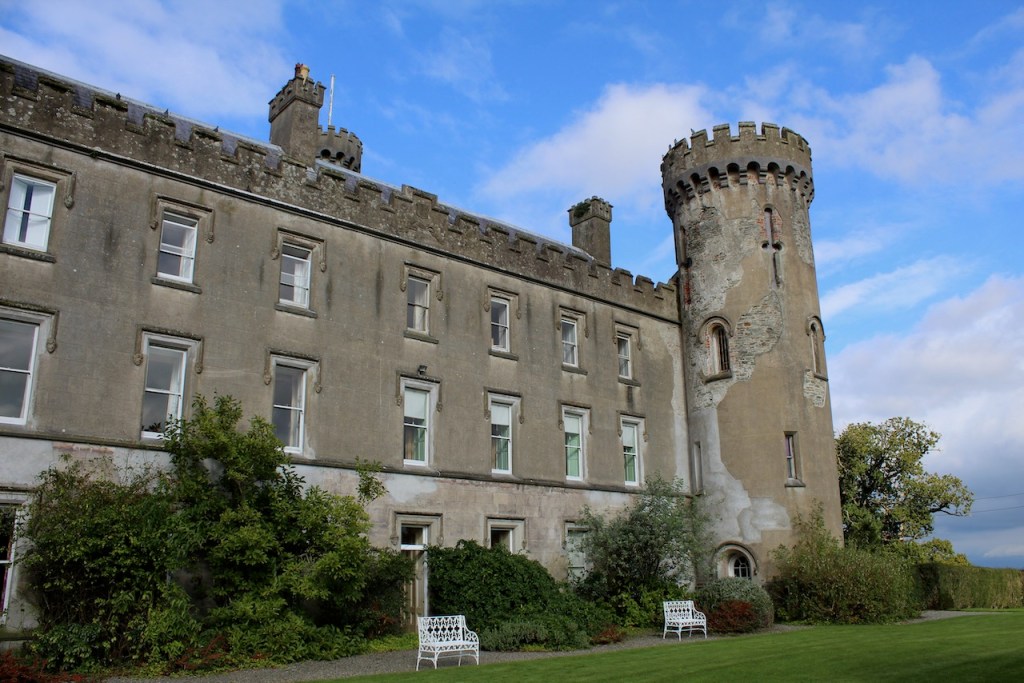

See my entry:
https://irishhistorichouses.com/2020/10/23/barmeath-castle-dunleer-drogheda-county-louth/
Open dates in 2024: May 1-31, June 1-10, Aug 17-25, Oct 1-20, 9am-1pm
Fee: house, adult /OAP/student €5, garden, adult/OAP/student €5, child free
2. Carlingford Castle, County Louth – OPW

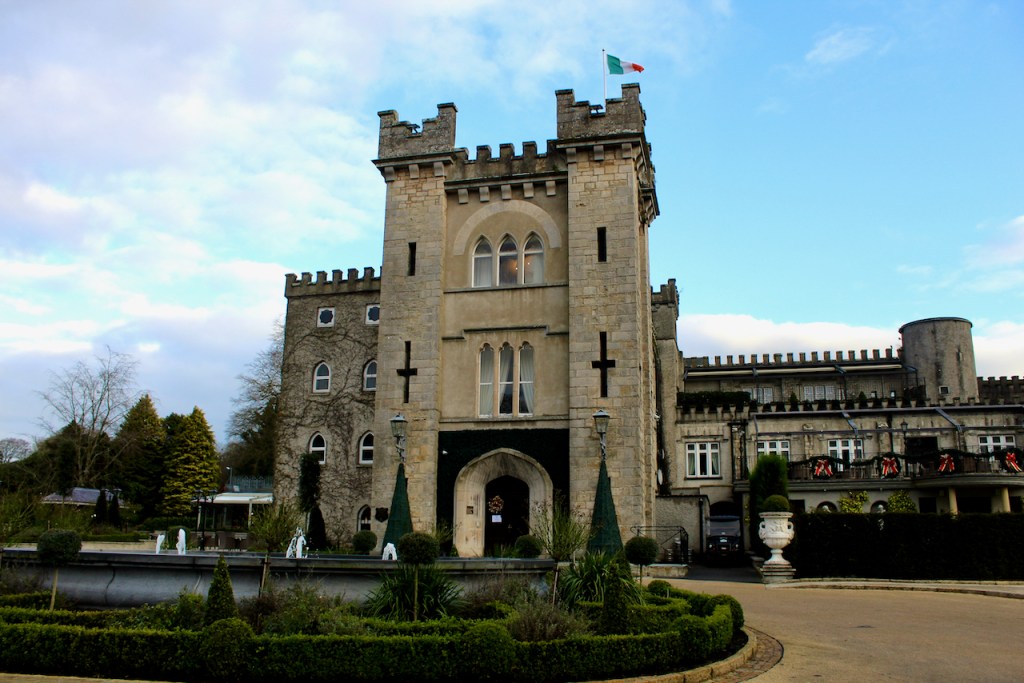
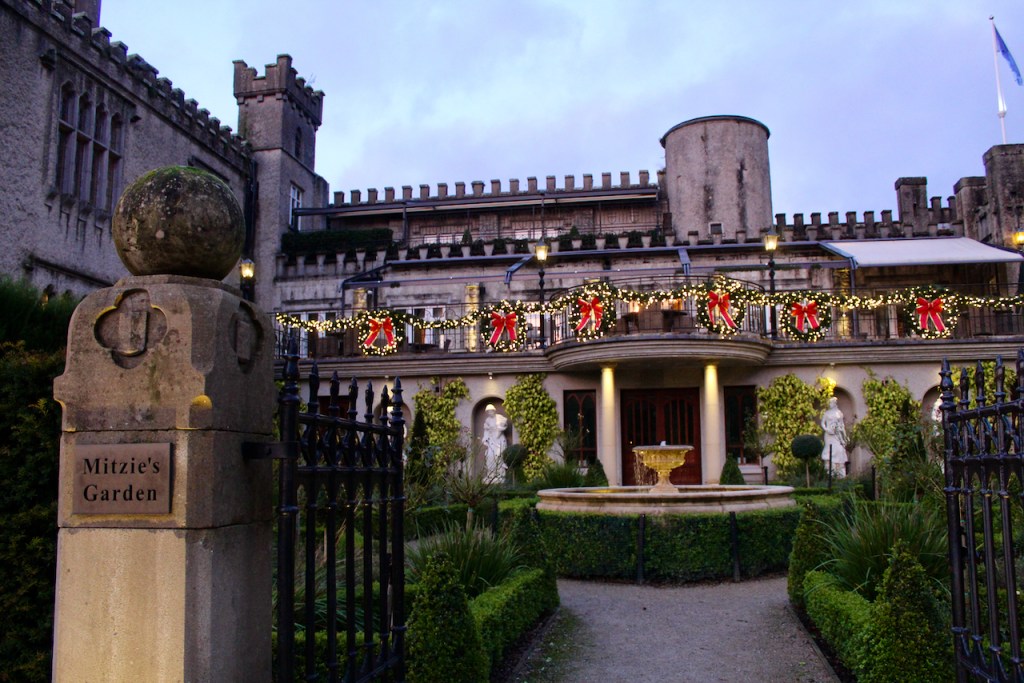
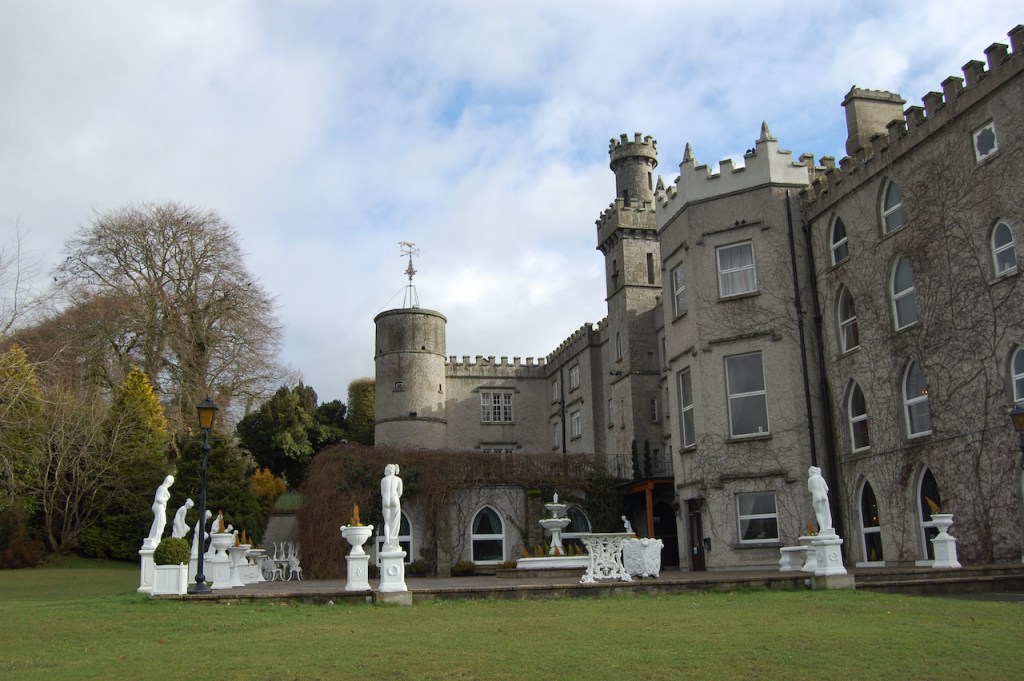
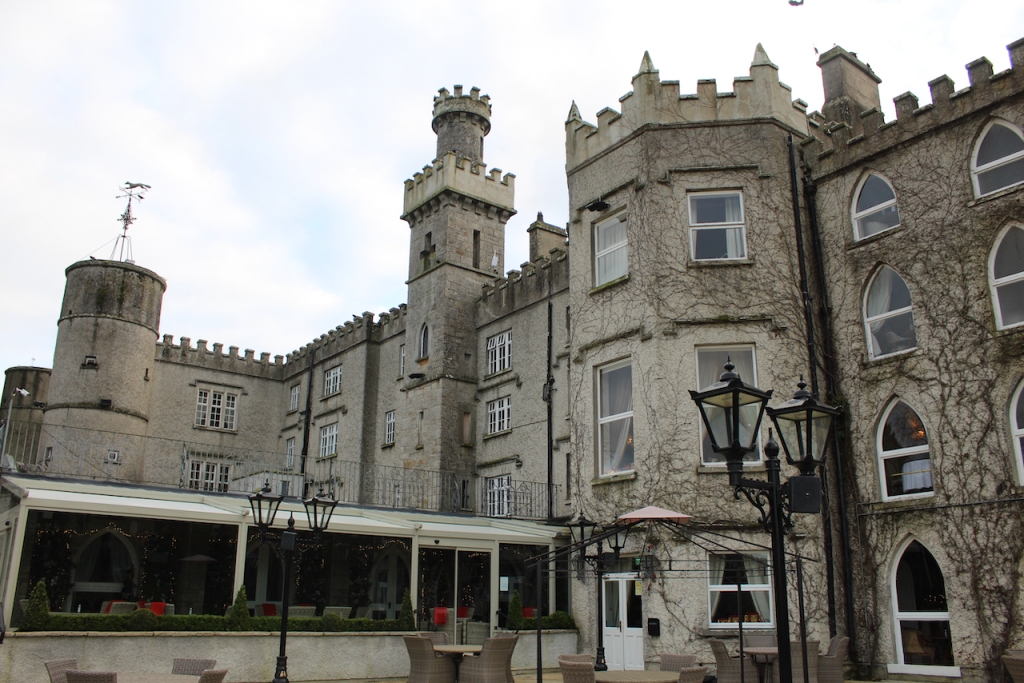
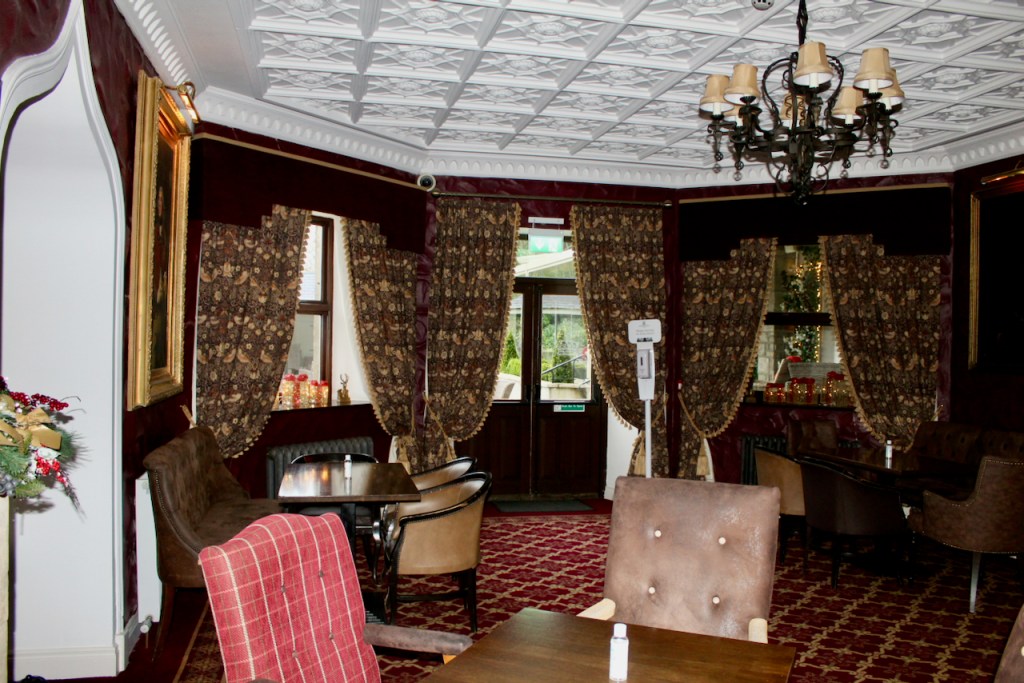
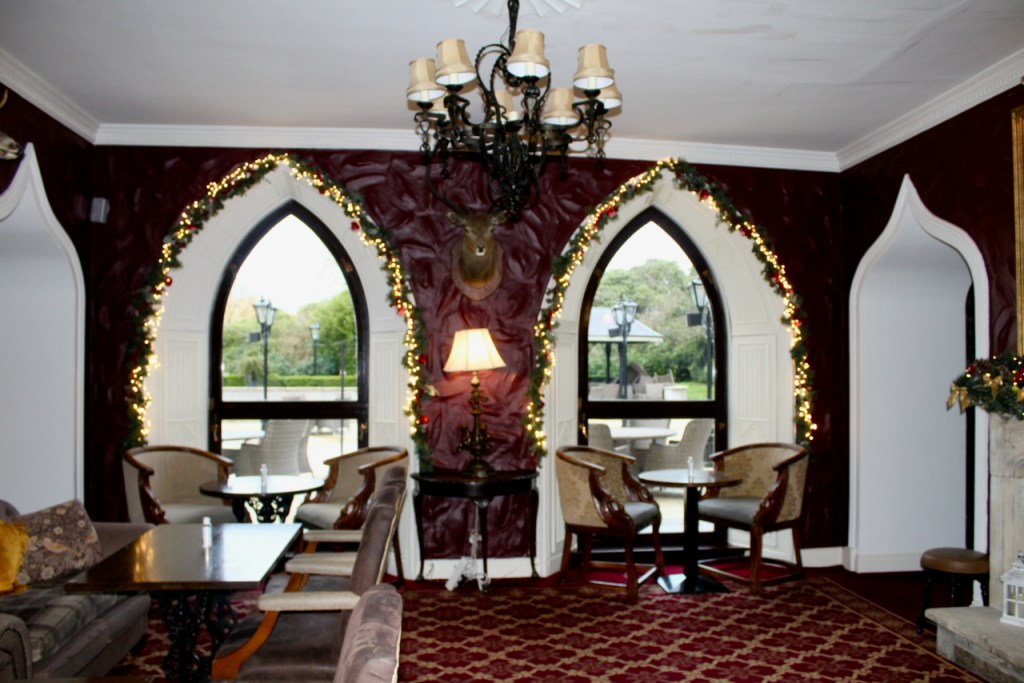
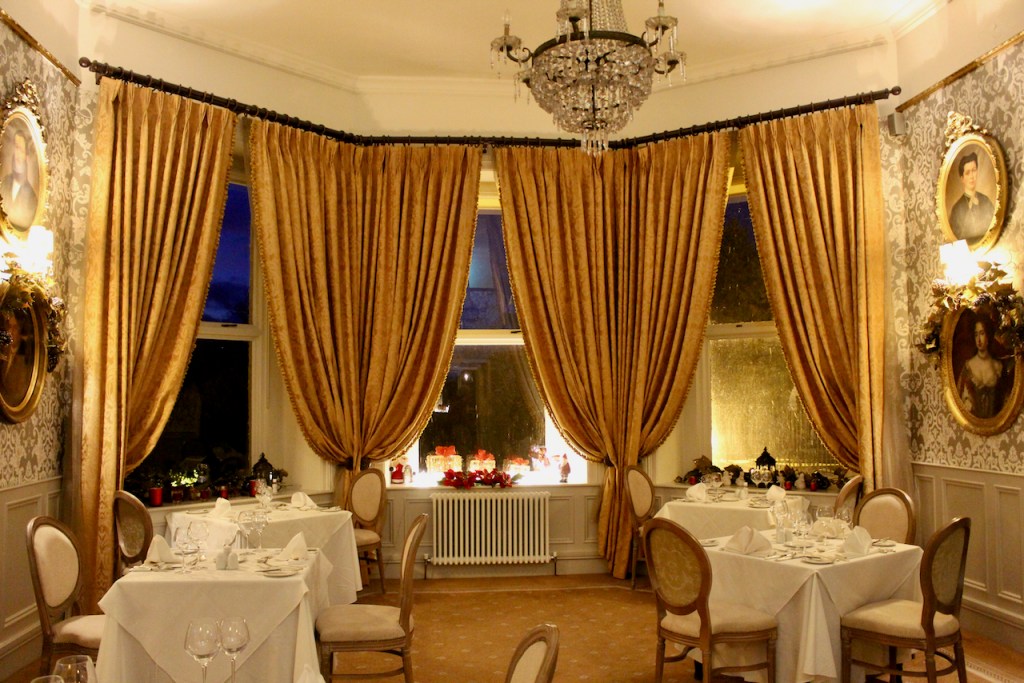
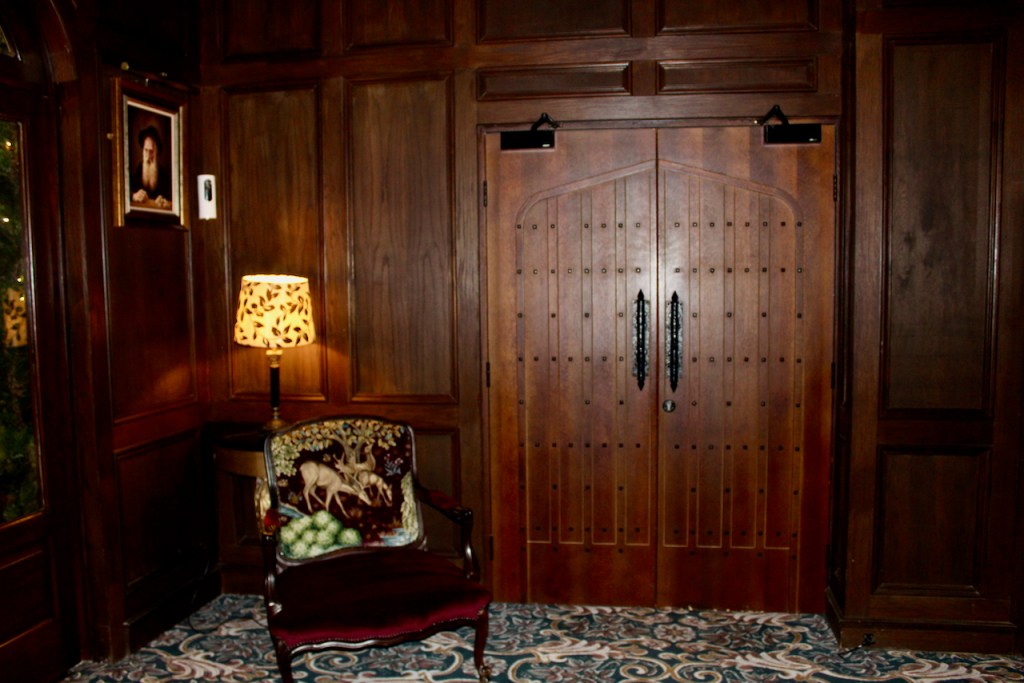
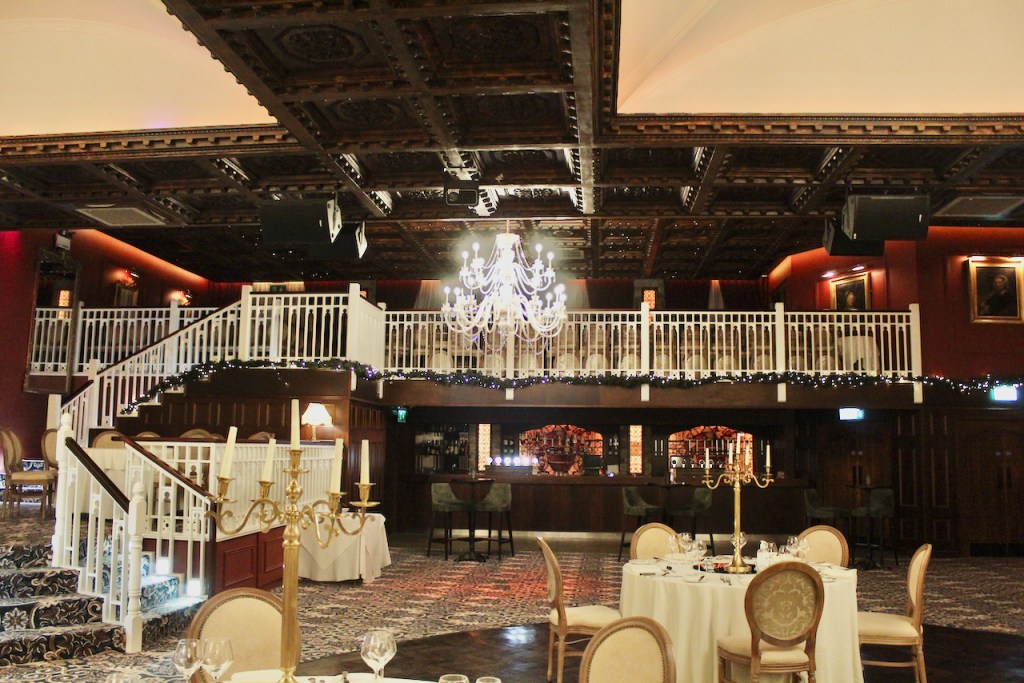
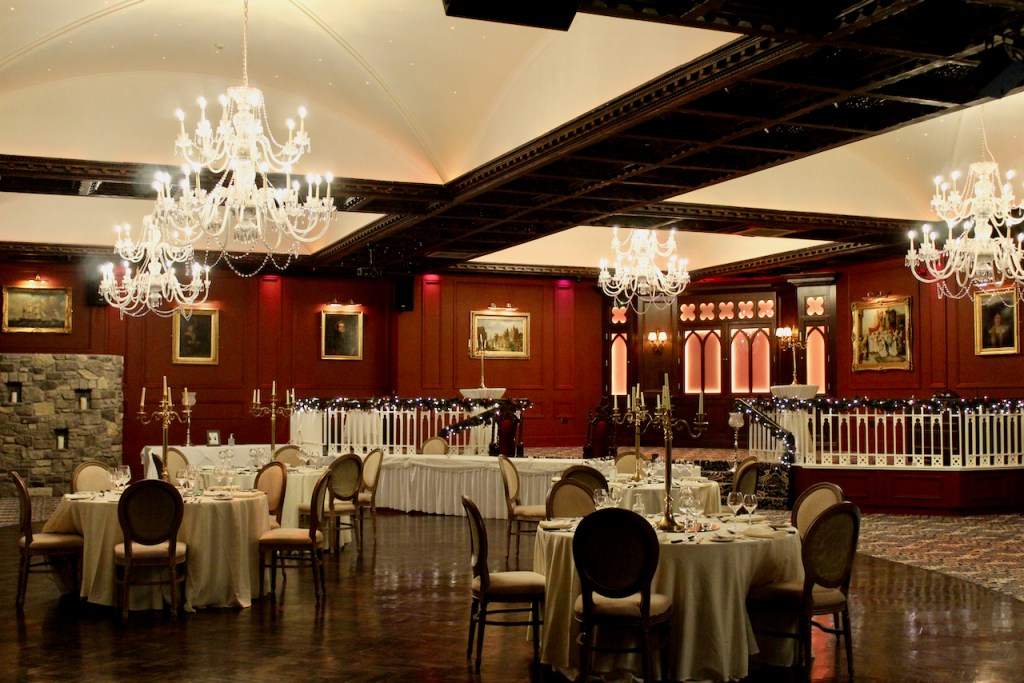
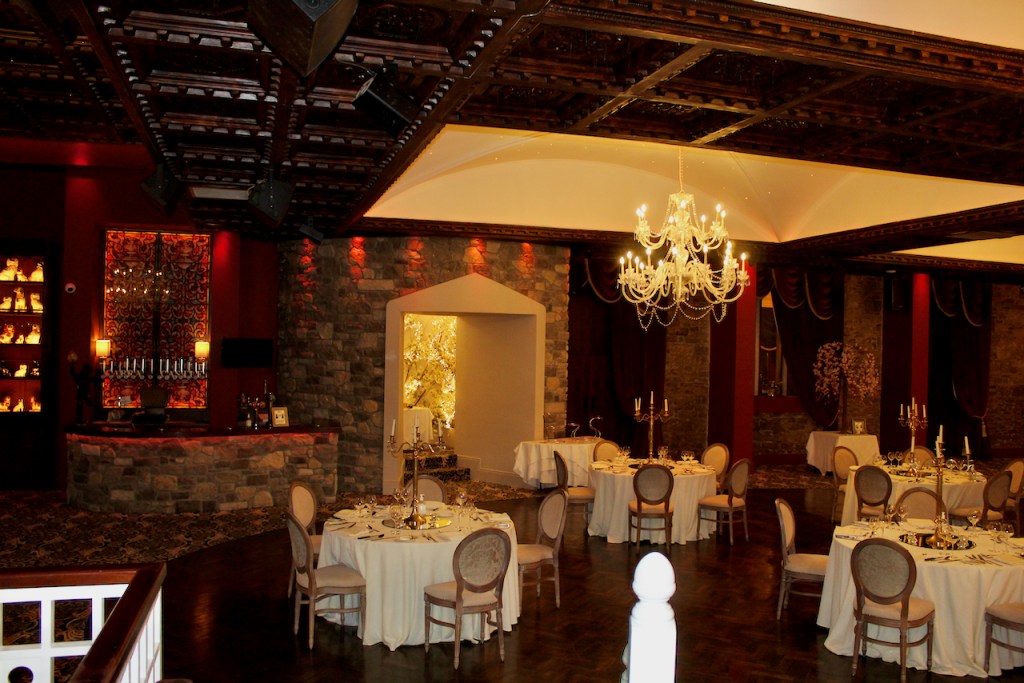
3. Castle Bellingham, Co. Louth – for weddings, and open to public for visits:
Open to the public between the hours of 1pm and 3pm, Monday to Friday for viewing year-round. Please call in advance to ensure there is somebody at the castle to show you around! (Closed December 24, 25 and 26)
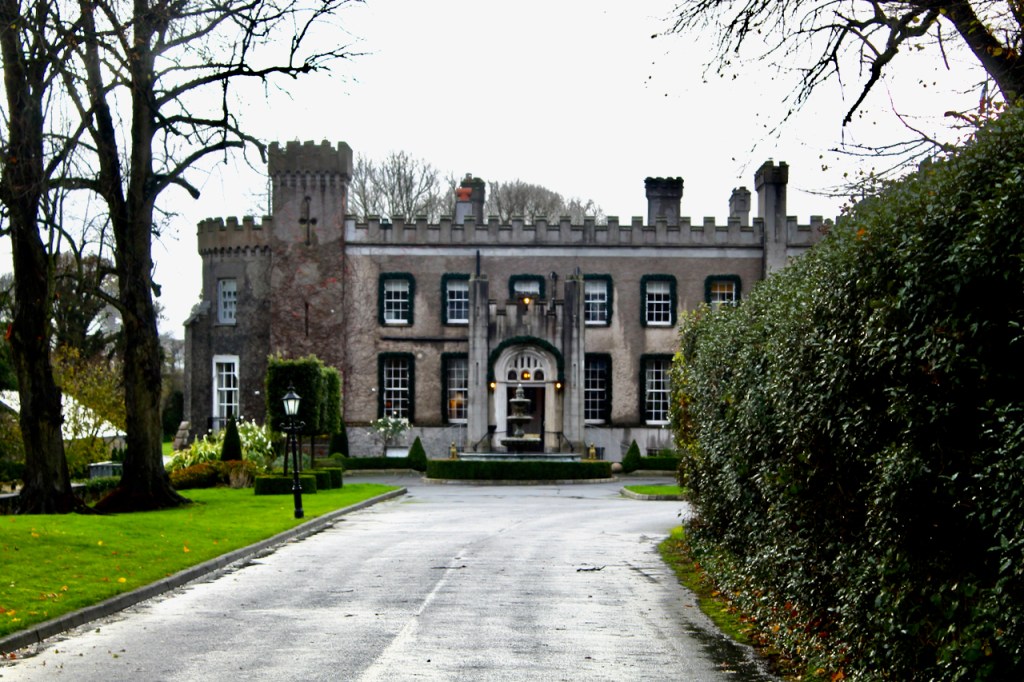

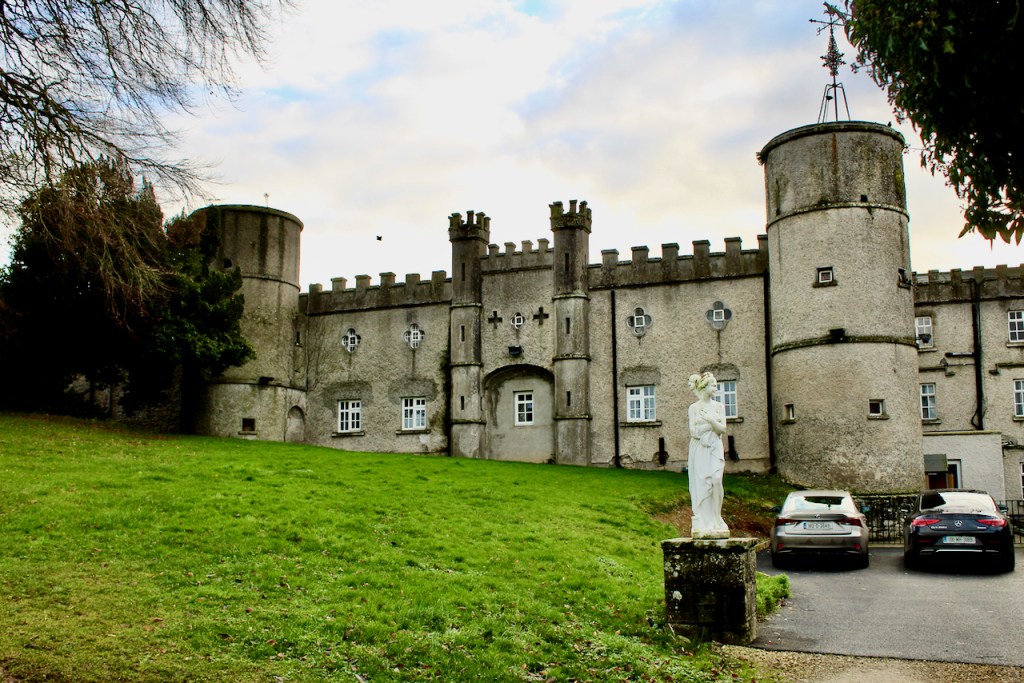
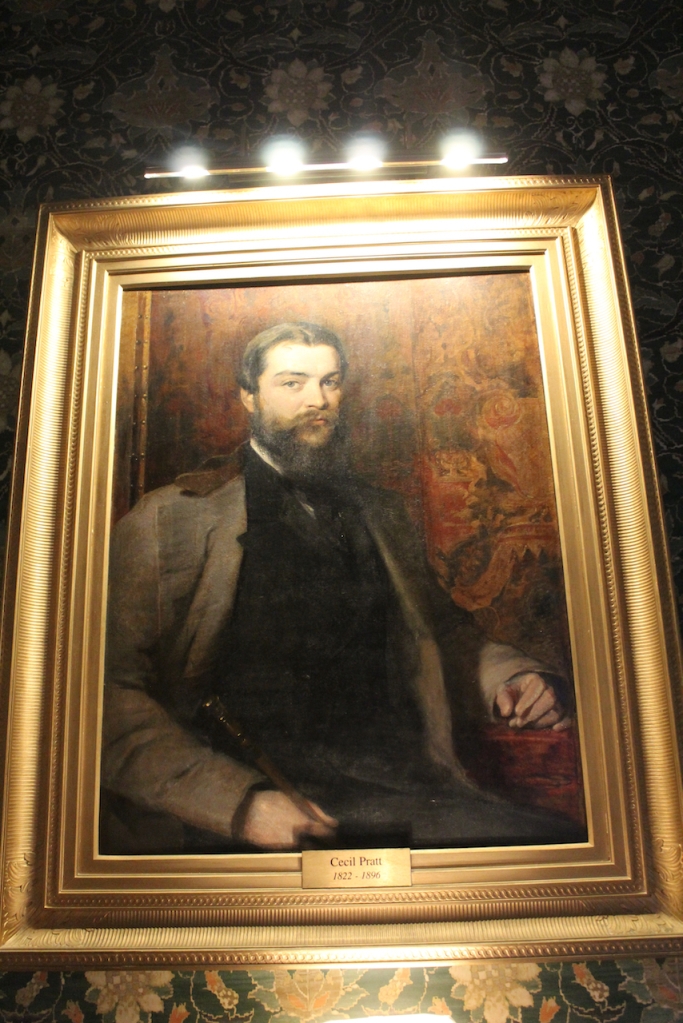
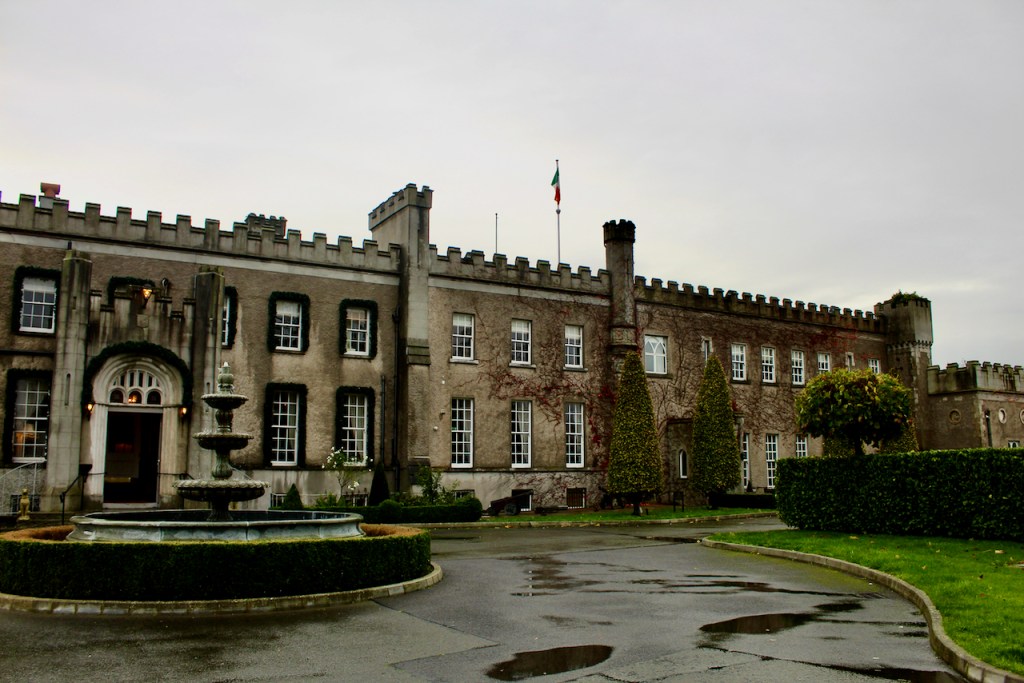
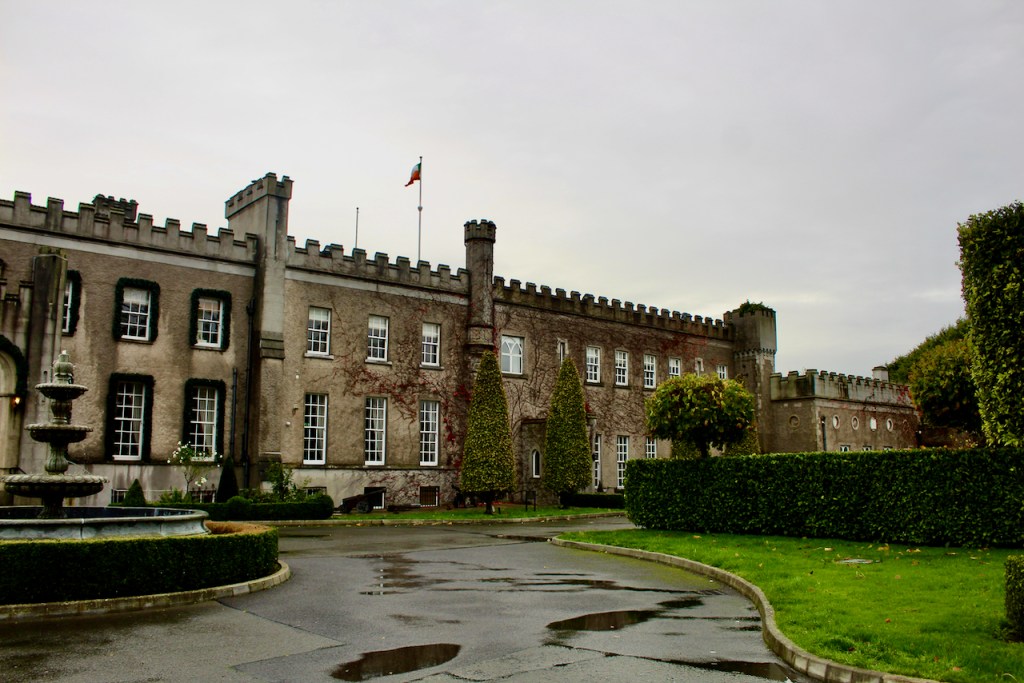
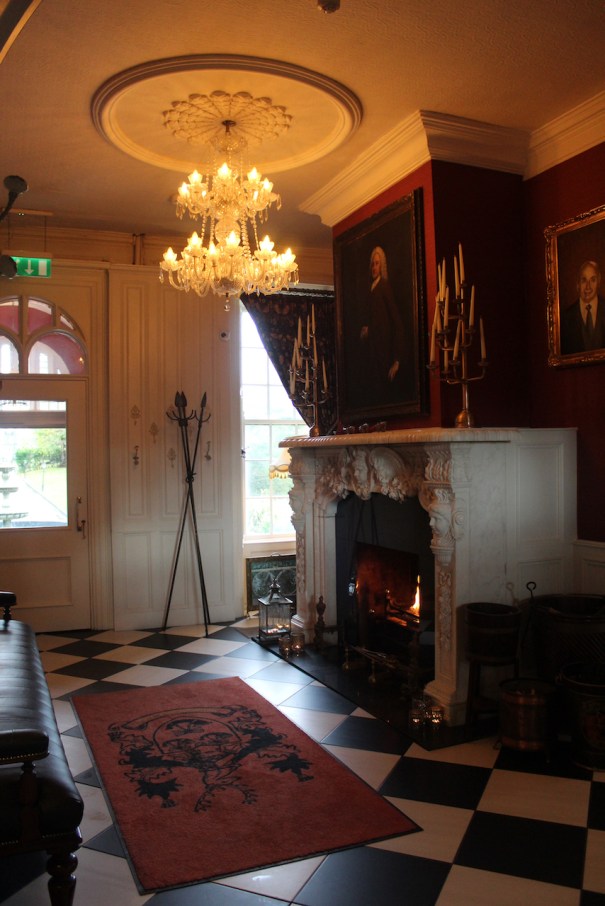
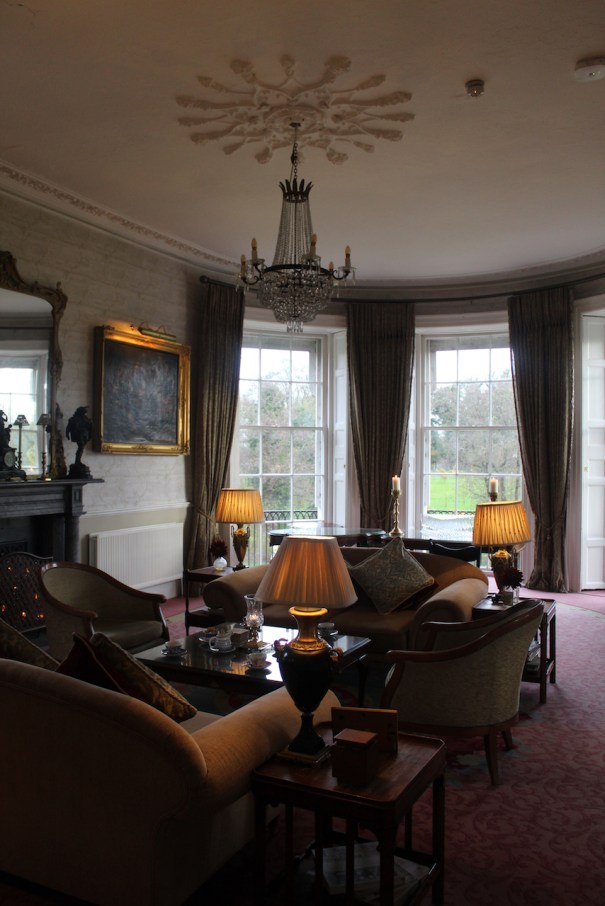
We visited Castle Bellingham in November 2022, and Mr. Corscadden gave us a tour. It’s a beautiful castle venue, for weddings or events, and is sometimes available for accommodation.
It was a rainy November day and the castle is long so I didn’t capture the whole front facade in one shot, so I include to older photograph from the National Inventory of Architectural Heritage.

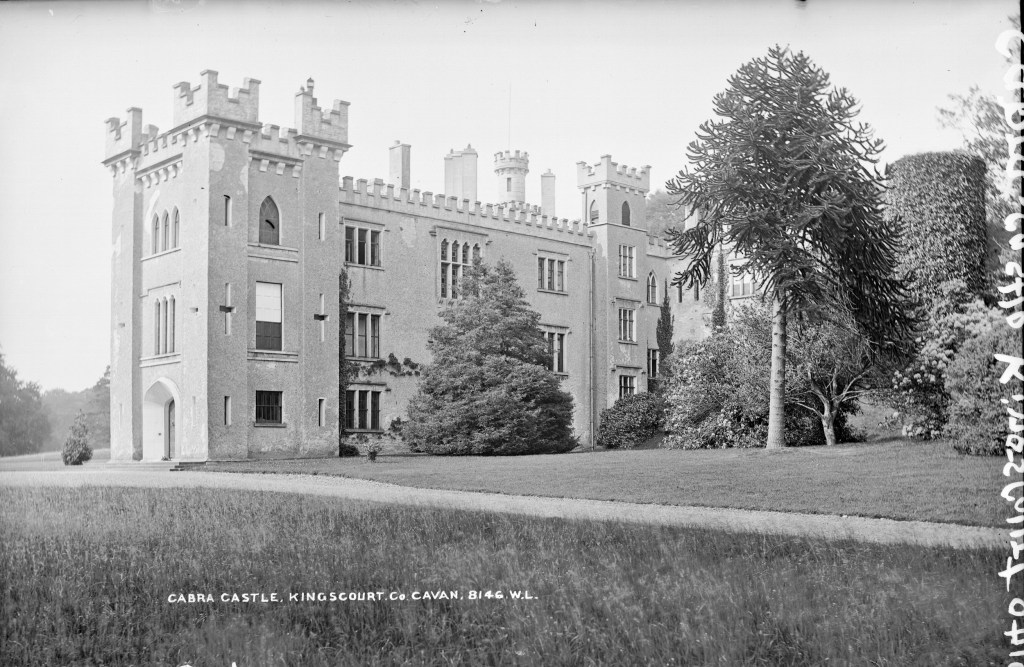
The Castle is owned by the Corscadden family, who also own Cabra Castle in County Cavan, Markree in County Sligo, and the other we have yet to visit, Ballyseede in County Kerry.
https://www.bellinghamcastle.ie
The website tells us:
“At Bellingham Castle, the welcome is warm, the facilities luxurious and the memories, eternal. Nestled in the medieval village of Castlebellingham in County Louth along Ireland’s Ancient East, Bellingham Castle is an elegant and spacious 17th Century authentic Irish Castle available for exclusive hire, to allow you become King or Queen of your very own castle for a truly memorable experience. The Castle opens for overnight stays on select dates throughout the year, but is predominantly a venue for spectacular Weddings, conferences or events.“

“Set at the gateway to the Cooley mountains and on the banks of the glistening River Glyde, Bellingham Castle is the centrepiece of a 17-acre estate that includes a weir and man-made river island where you can create memories that last a lifetime. The opulent 17th Century Irish castle is bursting with rich history, splendour and old-world luxury.
“Fully refurbished, yet retaining all of its character and charm, Bellingham Castle prides itself on elegance and sophistication, intimacy and cosiness, luxury and exclusivity – all just 50 minutes from both Dublin and Belfast.“

“We wanted to create something different at Bellingham Castle, an exquisite combination of a welcoming atmosphere and luxury castle experience. From dreamy and palatial bedrooms, to magnificent reception rooms and meticulously manicured gardens, we ensure each guest enjoys high-quality, bespoke service in an idyllic and inspirational location.“

Mark Bence-Jones writes of Castle Bellingham (1988):
p. 62. “The original castle here, called Gernonstown, which was acquired by Henry Bellingham [1622-1676] mid C17, was burnt by King James’s soldiers before the Battle of the Boyne, when its then owner, Colonel Thomas Bellingham [1645-1721], was fighting for King William. Col Bellingham built a new house 1690/1700 [the National Inventory says 1712] and named it Castle Bellingham; it had a high-pitched roof and is said to have resembled Beaulieu, in the same county. Mrs Delany described it (1745) as “one of the prettiest places I have seen in Ireland.”

“The house was remodelled in later C18, when a third storey was added, and again in early C19, when it was given a battlemented parapet, some turrets and a few other mildly medieval touches. The final result was not so much a castle as a castellated house, with plain Georgian sash windows. The nine bay entrance front, which appears to be only of two storeys owing to the higher ground on this side; the entrance, through a Gothic porch not centrally placed, is, in fact, on the first floor, where the principal rooms are situated. The opposite front, which also just misses being symmetrical – with three bays on one side of a shallow, curving bow and two bays and a turret on the other – also has a curved bow. Simple, pleasant rooms; a small staircase in a narrow hall at right angles to the entrance. Garden with terraces overlooking the river Glyde, formerly adorned with statues brought from Dubber Castle, the seat of another branch of the Bellinghams; vista to shrine of the Virgin Mary, erected by Henry Bellingham, a convert to Catholicism during the later years of the Oxford Movement. Straight avenue aligned on the entrance front of the house, terminated at the opposite end by a castellated gatehouse facing the village green. Having been sold by the Bellinghams ca 1956, Castle Bellingham is now an hotel.” [2]

The website gives a further history of the castle:
“Bellingham Castle served as one of the ancestral homes for the Bellingham family from the 17th Century until the 1950s. The original castle was built around 1660 by Sir Henry Bellingham [1622-1676], who was a cornet in the Army during the Civil War.
“He purchased the lands of Gernonstowne, Co. Louth, from a fellow soldier who had been granted them in lieu of arrears of pay. The purchase was confirmed by King Charles II.
“There is some variation on the spelling of Gernonstowne. On various maps and other documents, it is spelled Gernonstowne, Gernonstown, Gernon’s-Town, Gormanstown, Germanstown, Garlandstown and Garland.
“Irish road signs show the English as Castlebellingham, while the Irish translation still refers to Baile an Ghearlanaigh – or Gernonstown. It was not called Castlebellingham for at least 40 years after the purchase. The name does not appear on any document before the year 1700. Around 1710, it began to appear in journals and other sources as Castlebellingham.
“The castle was occupied by troops and burned down in the autumn of 1689 by King James II, in revenge for Colonel Thomas Bellingham [1645-1721] being a guide for William III, prior to the Battle of the Boyne. It is said that King William’s armies camped the night before the Battle of the Boyne in the grounds of the castle.“
Thomas Bellingham had a son, Henry. The estate passed Henry’s son Henry, but he had no children so when he died in 1755 it passed to his brother Alan Bellingham (1709-1796).
Alan’s son O’Bryen Bellingham (d. 1798) set up a brewery on site around 1770. The website tells us:
The website continues: “Over time, Castlebellingham became an important gathering point in the county. Fairs were held there every year and a church was constructed next door to the castle, along with a graveyard that houses the Bellingham family vault. The Bellinghams became one of the most powerful and influential families in the county; for over 100 years, a Bellingham held the seat in Parliament for County Louth.
“Records also note Castlebellingham for having ‘the best malt liquor’ in Ireland. A brewery was built on site about 1770 and belonged to an O’Bryen Bellingham [d. 1798, a son of Alan Bellingham]. For a number of years, a brewery partnership ran their liquor business. The brewery is still there but now houses the ‘button factory’ or Smallwares Ltd. The brewery was the main supplier of drink to the Boer War troops.“
Alan’s son William married Hester Frances Cholmondeley, daughter of Reverend Robert Cholmondeley and was created 1st Baronet Bellingham, of Castle Bellingham, Co. Louth. He did not have any children and the title passed to his brother Alan’s son, another Alan (1740-1800), who became 2nd Baronet Bellingham of Castle Bellingham, County Louth.
The website continues: “A history of the parish, dated 1908, states that the impressive Calvary standing at the entrance to Bellingham Castle was erected by Sir [Alan] Henry Bellingham [4th Baronet]as a monument to the memory of his first wife, Lady Constance.
“A collection of inset religious panels can be seen on the upper facades of many of the village buildings. These are also a reflection of Sir Henry’s religious sentiments, and they are unique in Ireland. In addition to the many panels, there are biblical quotations cut into the stone window sills of some buildings. North of the castle is a carefully preserved group of ‘widows’ dwellings’, built from charitable motives by Sir Henry.
“In 1905, Bellingham Castle was the venue for the romantic wedding celebrations of Augusta Mary Monica Bellingham, daughter of Sir Alan Bellingham [1846-1921], 4th Baronet to the 4th Marquis of Bute, John Crichton-Stuart.
“The Marquis, who was one of the wealthiest men in the British Isles at the time, spared no expense and treated his bride and guests to a lavish celebration, including chartering the Princess Maud steamer to take their guests and the Isle of Bute pipe band across the Irish Sea to Bellingham Castle for the wedding. As the society event of the year, the wedding attracted worldwide media attention, from California to New Zealand.
“Footage from the wedding celebrations still exists. This remarkable film is believed to be the one of the earliest wedding films in the world. Bellingham Castle is clearly depicted in the footage, together with scenes at nearby Kilsaran Church and the village of Annagassan, from where the wedding party and their guests arrived and departed by steamer.
“Castlebellingham was the ancestral home of the Baronetcy until the late 1950s. The last Bellingham to live there was Brigadier General Sir Edward Bellingham [5th Baronet], born in 1879, who was the last Lord Lieutenant and Guardian of the Rolls (Custos Rotulorum).
“It was purchased by Dermot Meehan in 1958 from the Irish Land Commission for £3,065.00. Mr Meehan spent several years converting the house into a hotel. The Meehan family sold the hotel and 17 acres in 1967 for £30,636.61 to Mr John Keenan and under the Keenan family stewardship, the castle prospered over the following four decades.
“In December 2012, the castle – including the 17 acres – was acquired by the Corscadden family. The family also own Ballyseede Castle in Tralee, Co. Kerry; Cabra Castle, Kingscourt, Co. Cavan, and Markree Castle, Co. Sligo.
“The next chapter in the history of Bellingham Castle has begun, as an exclusive venue for private weddings, civil ceremonies, conferences, meetings and corporate events.
“Bellingham Castle is a building of intrinsic historical and architectural interest and is open to the public between the hours of 1pm and 3pm, Monday to Friday for viewing year-round. Please call in advance to ensure there is somebody at the castle to show you around! (Closed December 24, 25 and 26).“
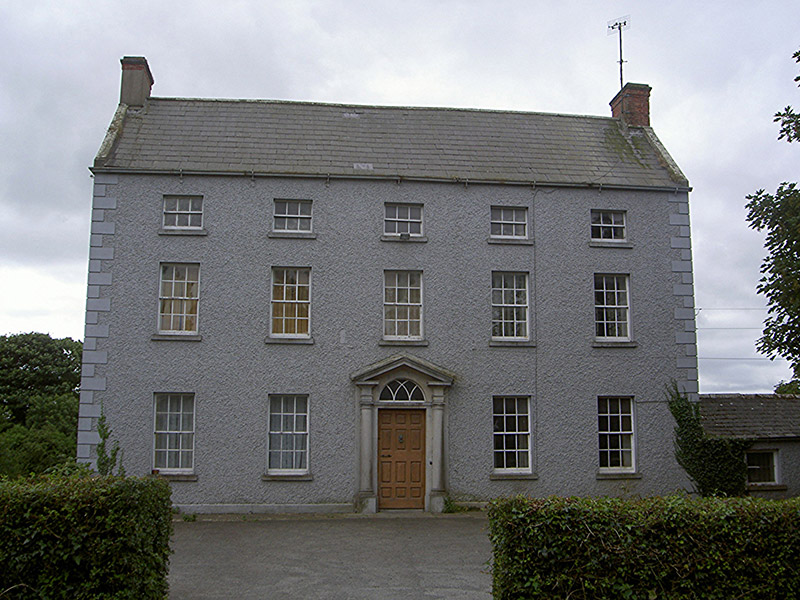
4. Collon House, County Louth

The website tells us:
“Collon House, steeped in history, is full of character and charm; its gracious rooms are exquisitely furnished with period antiques and paintings, retaining the atmosphere of early Georgian living, making this a rare opportunity to experience less than one hour from Dublin City Centre, thirty minutes from Dublin Airport and just five miles from historic Slane.
“Collon House is a perfect location from which to enjoy the wonderful treasures of the Boyne Valley. Bru na Boinne (Newgrange) prehistoric megalithic sites, The Battle of the Boyne visitors centre at Oldbridge, Slane Castle, Old Mellifont Abbey and Monasterboice High Crosses are all less than twenty minutes drive from Collon House.“
The Historic Houses of Ireland (HHI) website tells us:
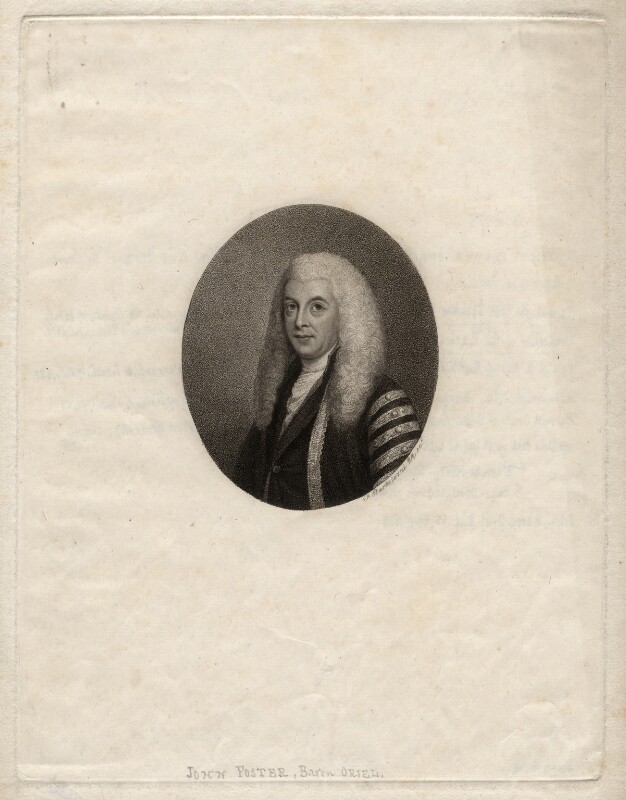
“Anthony Foster [1705-1778], Lord Chief Baron of the Exchequer, purchased the Collon estate in 1740 and chose to build in the centre of the County Louth village, now a market town on the road from Dublin to Derry. His early Georgian house was extended in the 1770s to form a substantial L-shaped dwelling, set back from the street at the central crossroads. The original dwelling is long and low but the later building is taller and more generous in scale with more elaborate interiors and a “handsome half-turn stair” that gives access to the upper floors.” [4]
Anthony Foster married Elizabeth Burgh of Bert House (now called de Burgh Manor, available as a whole house rental, see my entry www.irishhistorichouses.com/2022/04/27/places-to-visit-and-to-stay-leinster-kildare-kilkenny-laois/), County Kildare.
The HHI website continues:
“Anthony’s son John [1740-1828] was elected to the family borough of Dunleer and became the member for Louth in 1768 at the age of twenty-one. Considered ‘the best informed man in the house’ he was briefly Chancellor of the Irish Exchequer before his election as Speaker of the Irish Commons. He held office from 1785 until 1800, when Parliament was dissolved for ever under the Act of Union, a measure which Foster had strenuously opposed. As Speaker he pronounced the final words at the closing session, choosing to retain his official mace ‘for future contingencies’. Mr. Speaker Foster was returned to Westminster after the Union and was finally rewarded with a UK peerage in 1821 (his wife had previously been granted two Irish titles) after an illustrious political career that spanned more than sixty years.
“In ‘A Tour of Ireland‘ published in 1780, the agronomist Arthur Young mentions Foster whose improvements on the Collon estate “were of a magnitude that I have never heard of before.” These included Oriel Temple, an elaborate and chastely classical lakeside folly, which was subsequently enlarged to form the principal family seat. Foster’s son Thomas married an heiress, Harriet Skeffington, and the family moved to Antrim Castle when she succeeded as Viscountess Massereene.”
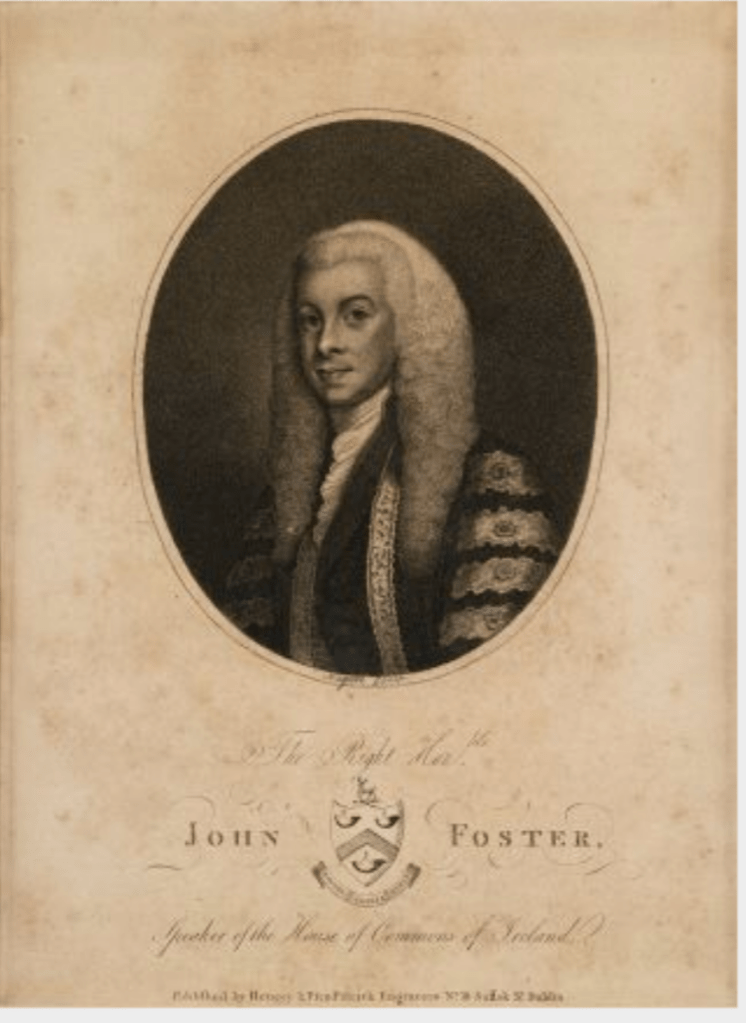

For more about the Foster family see my Cabra Castle entry, www.irishhistorichouses.com/2021/03/28/cabra-castle-kingscourt-county-cavan/
The HHI website continues: “Collon House has been altered over the intervening years but the building retains many fine Georgian interiors, now greatly enhanced by sympathetic restoration, fine furniture, glass, porcelain, pictures and objects. Their rich decoration makes a striking contrast with the plain exterior.
“The gardens have also been restored with inspired and authentic planting. The entrance overlooks a sunken garden with an intricate box parterre, while the herbaceous border in the ornamental garden leads to a classical summer house in the Grecian style.” [4]

The National Inventory tells us it is a: “Corner-sited attached five-bay three-storey house, built c. 1770. Rectangular-plan, extended by two-bays into two-storey terrace to east, three-bay two-storey wing to north, extended former mews buildings surrounding courtyard to north, single-storey flat-roofed entrance porch to west elevation…This imposing house, the principal home of the Foster family, at the heart of Collon, has historical associations with John Foster, the last man to speak in the Irish House of Commons. It contains many details of interest, such as stone window dressings. Its prominence at the heart of the village is of intrinsic importance to the architectural heritage of Collon.” (see [3])
5. Killineer House & Garden, Drogheda, Co. Louth A92 P8K7 – section 482
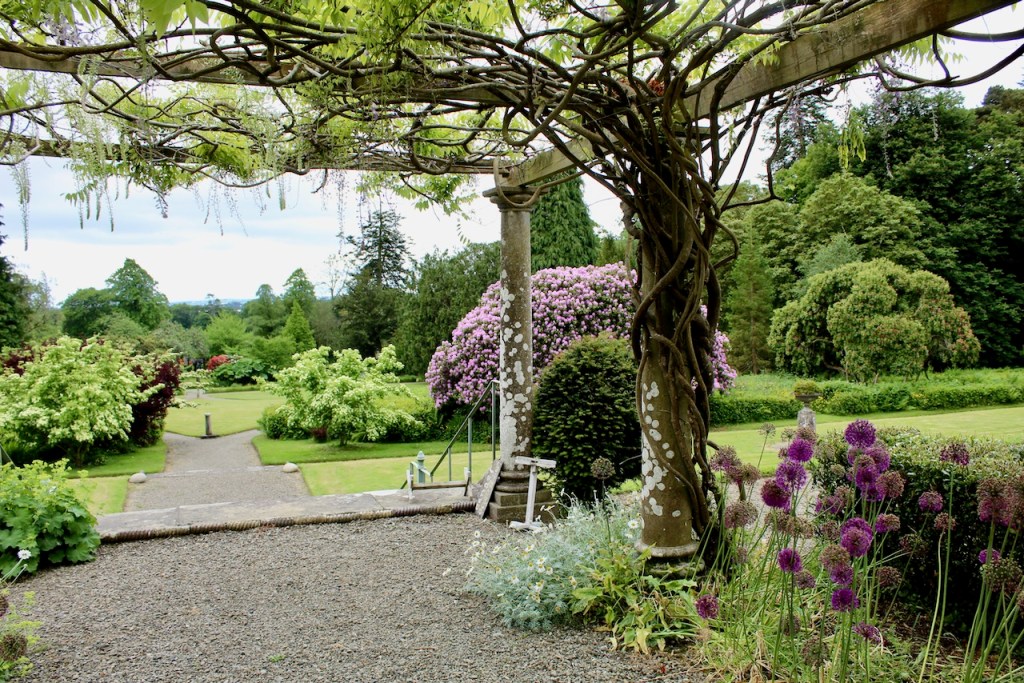

See my entry:
https://irishhistorichouses.com/2021/08/10/killineer-house-county-louth/
www.killineerhouse.ie
Open dates in 2024: Feb 1-20, May 1-31, Aug 17-25, 9am-1pm
Fee: adult/OAP/child/student, house: €4, garden €6
6. Old Mellifont Abbey, County Louth – OPW
7. Rokeby Hall, Grangebellew, Co. Louth – section 482
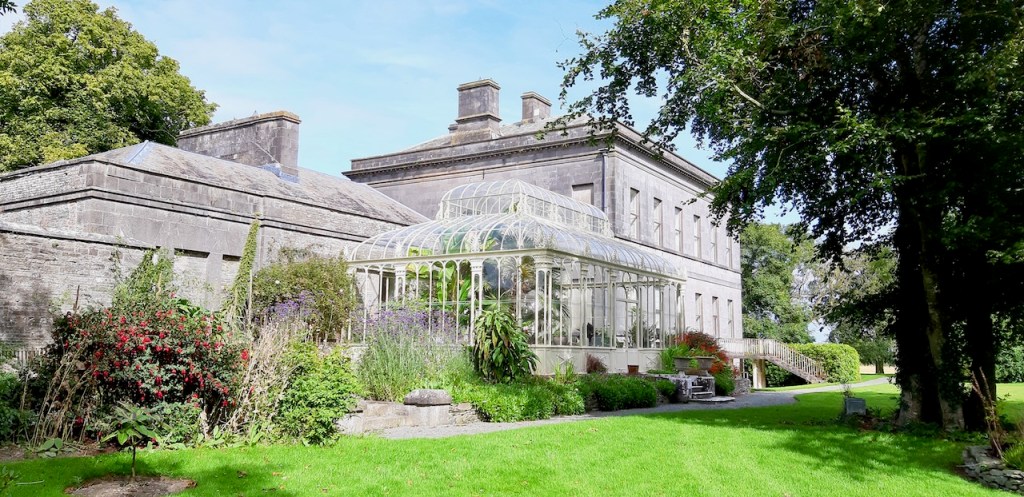

See my entry:
https://irishhistorichouses.com/2020/08/17/rokeby-hall-grangebellew-county-louth/
www.rokeby.ie
Open dates in 2024: May 1-31, Mon-Sat, Aug 17-25, Sept 1-30, Mon-Sat, 10am-2pm
Fee: adult/OAP €10, child/student €5
Places to stay, County Louth:
1. Ballymascanlon House, Louth – hotel
https://www.ballymascanlon.com
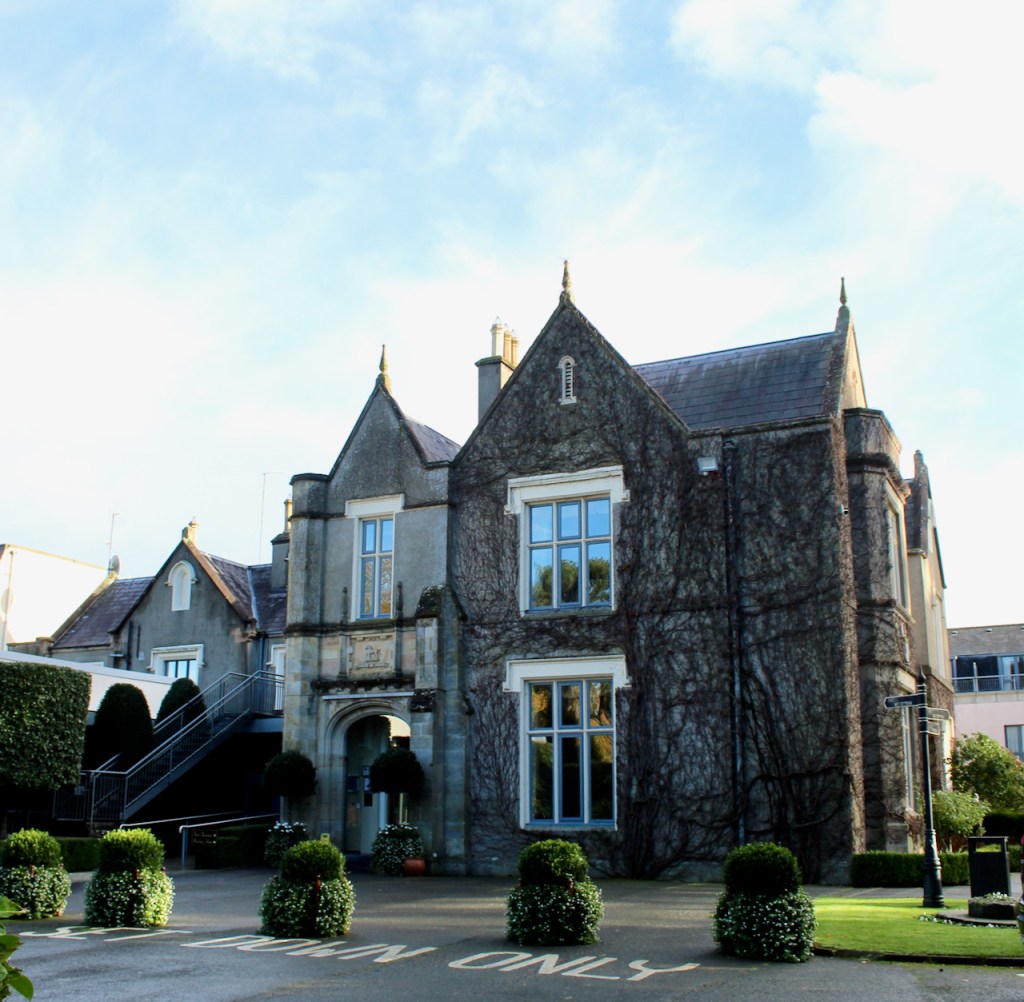

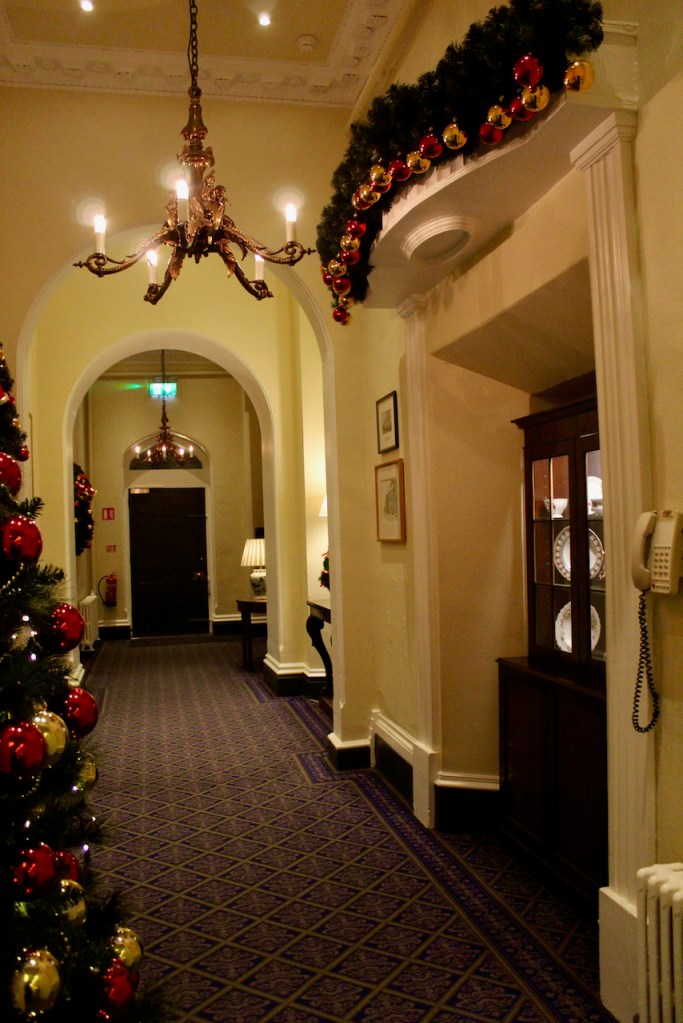
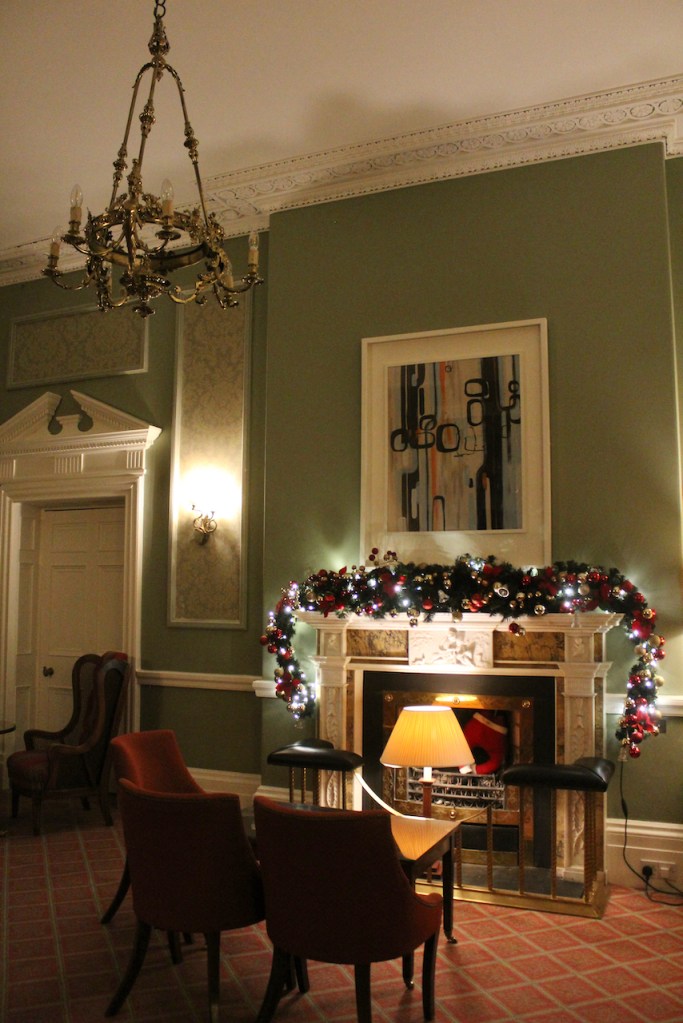
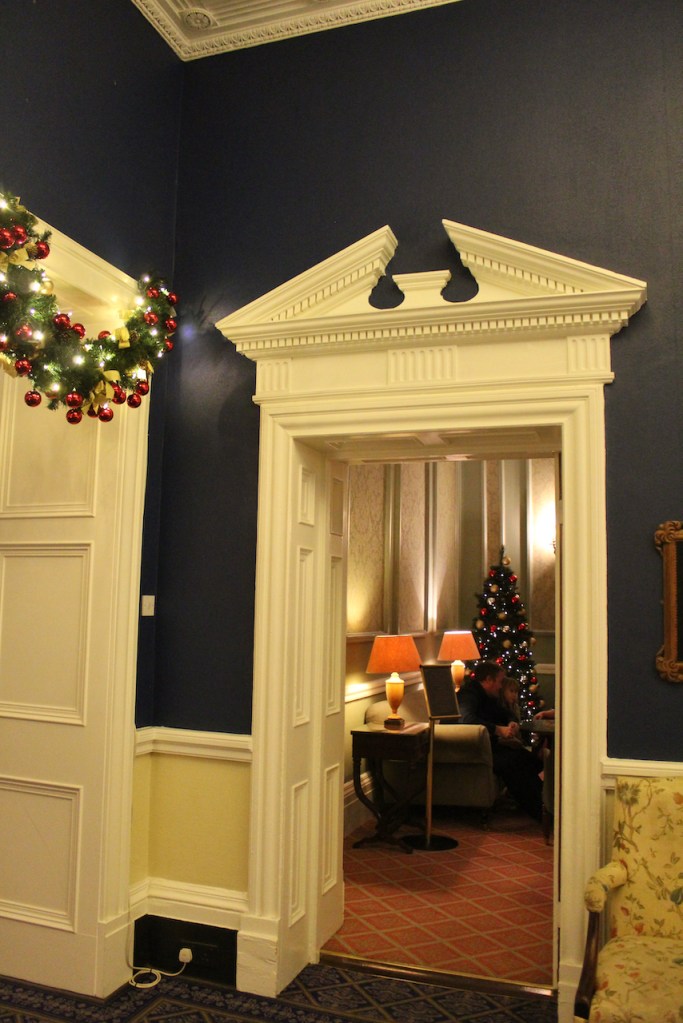
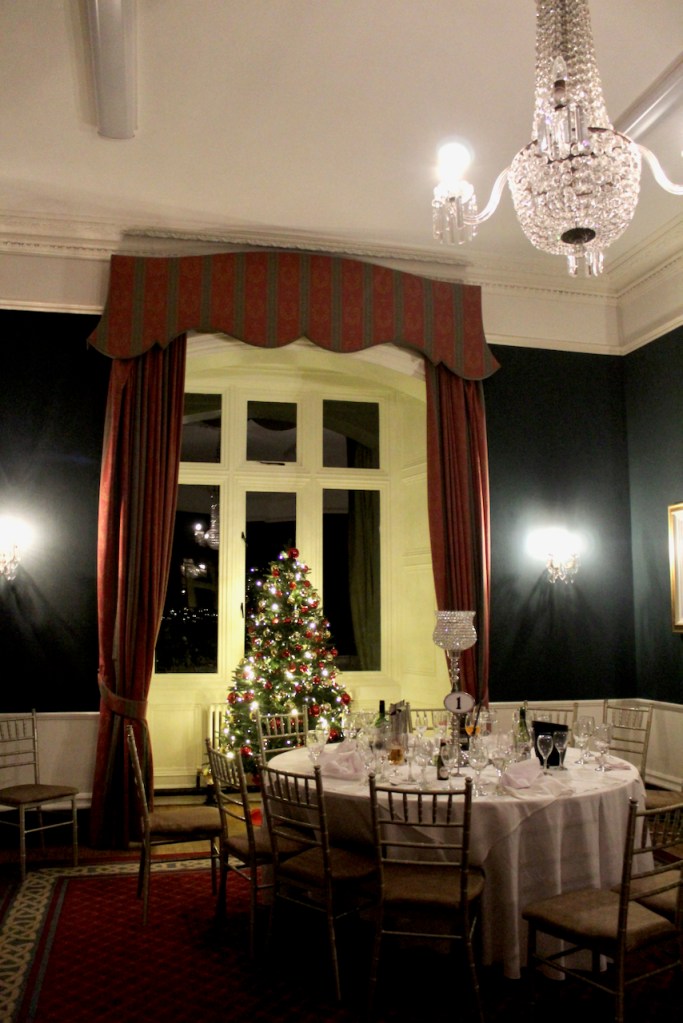
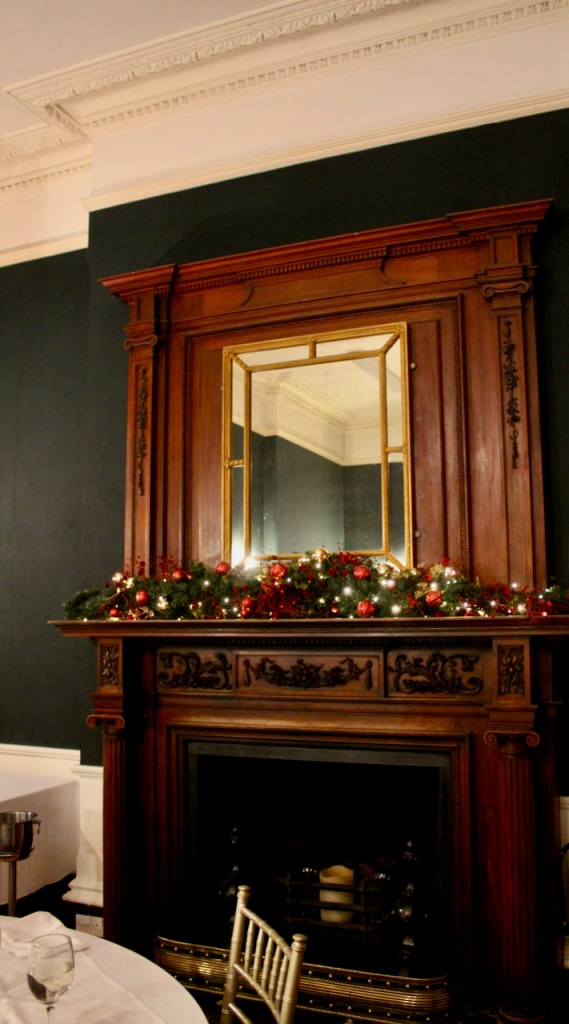
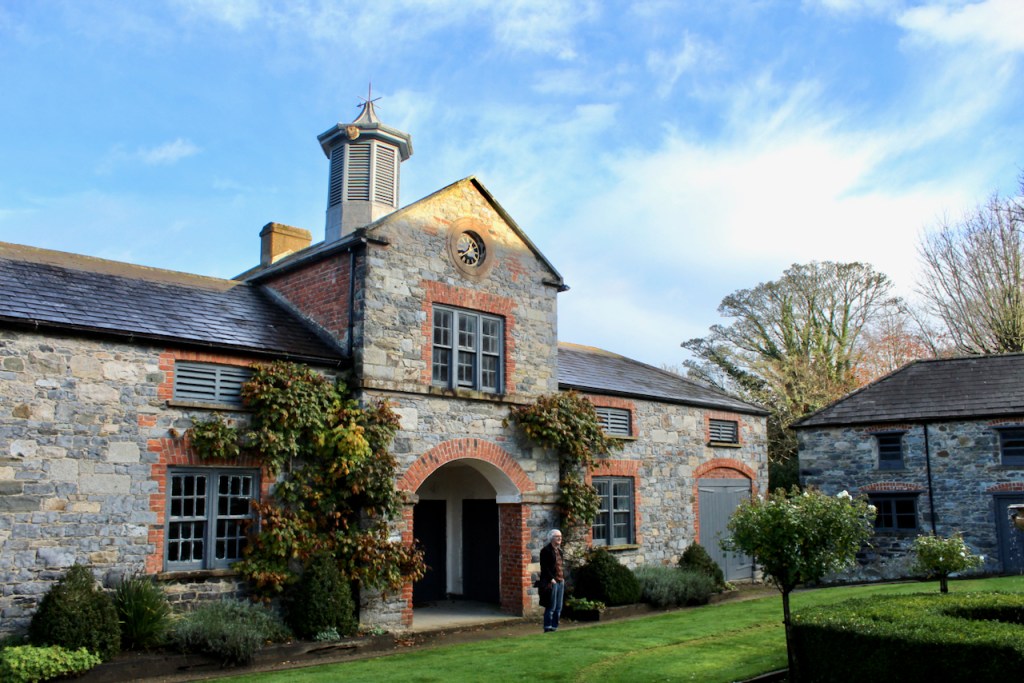
We treated ourselves to a stay in Ballymascanlon House hotel in November 2022.
The website tells us: “The Ballymascanlon House is set on 130 acres of beautiful parkland, this impressive Victorian House forms the heart of this Hotel. It is one of the most remarkable historical estates in Ireland dating back to 833 A.D. Steeped in history, Ballymascanlon estate is located in Ireland’s North East on the Cooley Peninsula in close proximity to the Irish Sea and Mourne Mountains. Less than 1 hour from Dublin and Belfast, and 20 minutes from the medieval town of Carlingford. We are delighted to welcome you to our beautiful luxurious venue, ideal for both Business and Leisure.”
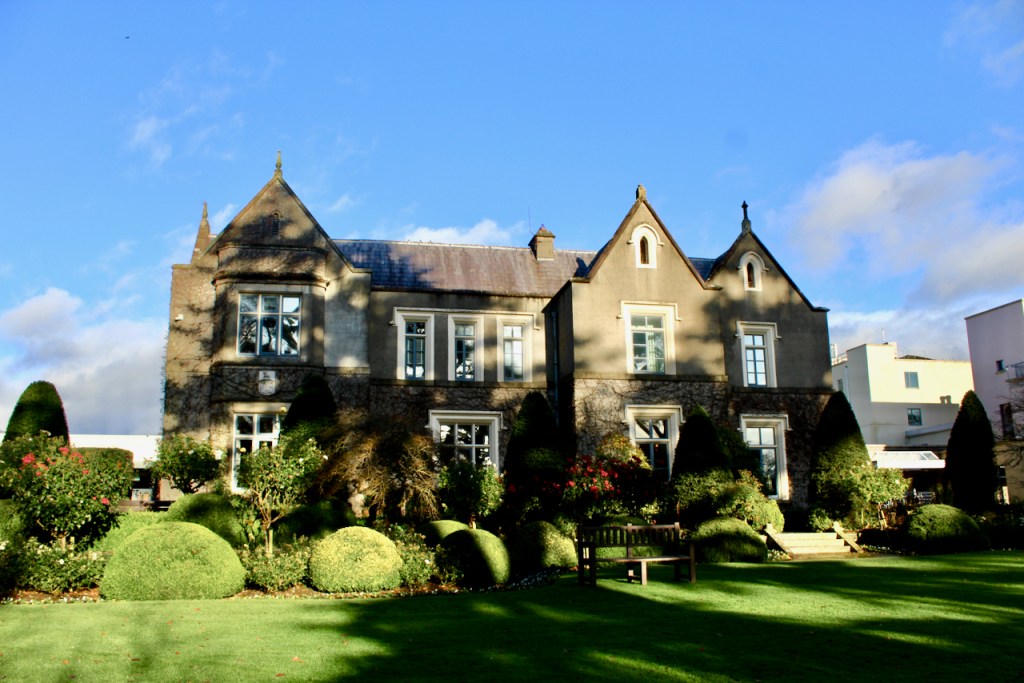

Ballymascanlon means the town of the son of Scanlan, and was part of the ancient Sept of Scanlan. I noticed that locals call it “Ballymac” and it would seem the “mac” would be correct if it’s “son of” though the name now skips that “c” – it’s not named “Ballymac scanlan” any longer. A document in the front hall tells us of its history. The area is full of ancient archaeological features including the Proleek Dolmen which dates to approximately 4000 BC. The information tells us that a chieftain, MacScanlan, expelled a Danish incursion into the area, before the Anglo-Normans came to Ireland.
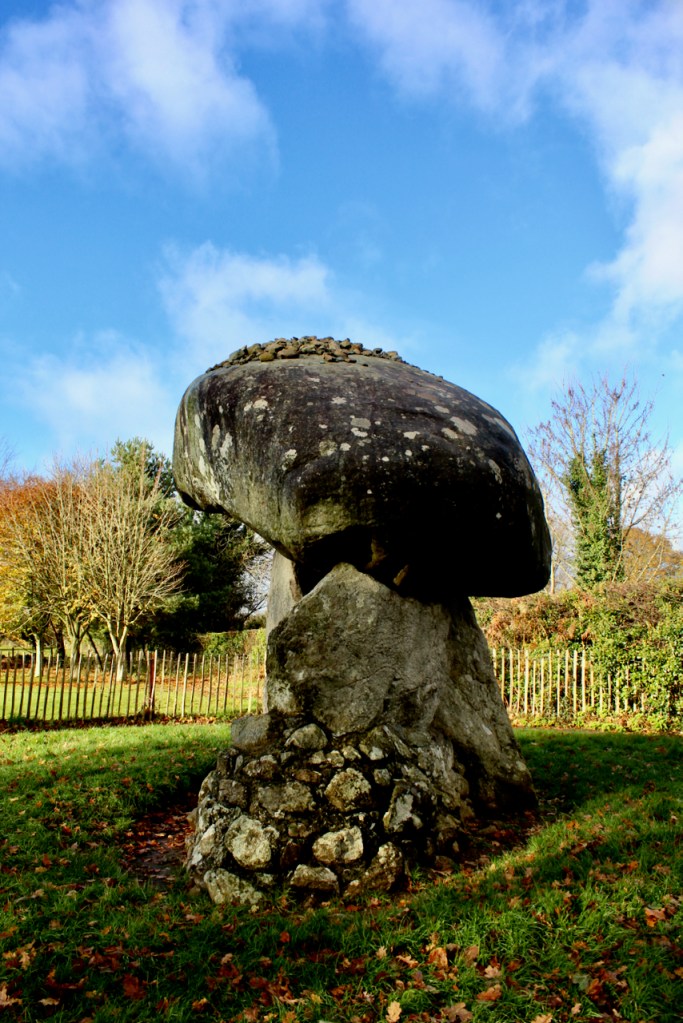
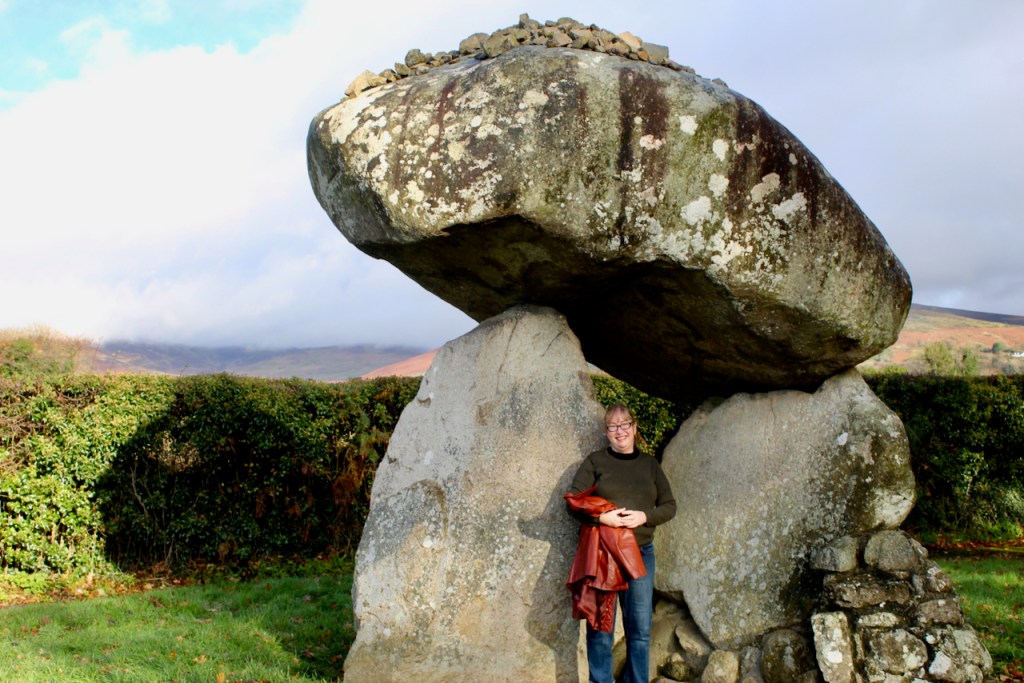
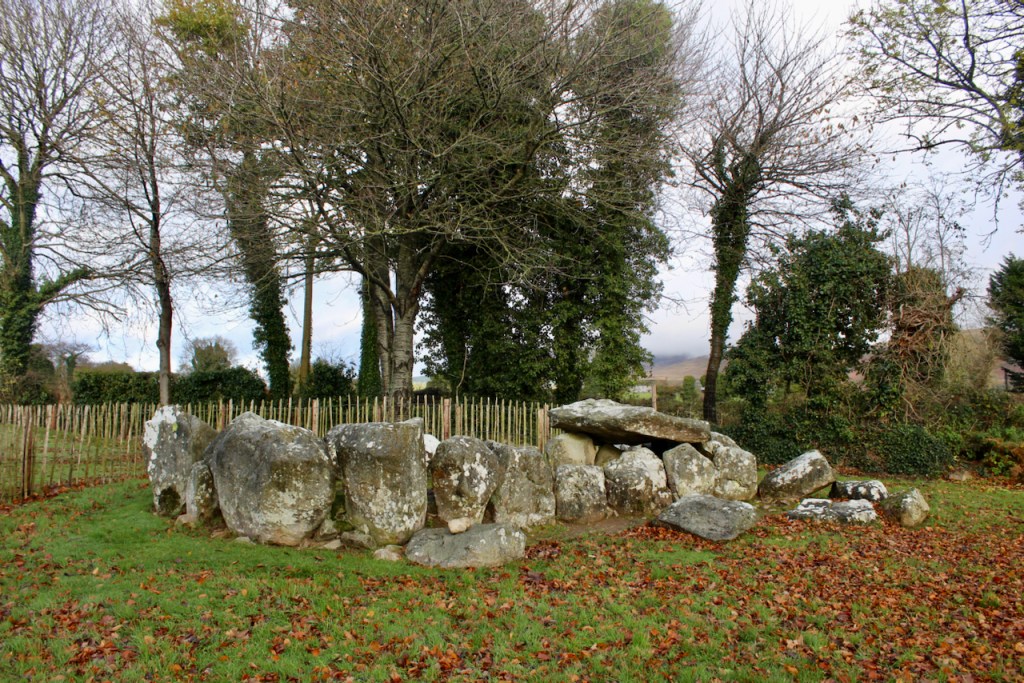





When the Anglo-Normans came, Hugh de Lacy gave this area to the Cistercian Mellifont Abbey. After the dissolution of the monastery by King Henry VIII the land was given to Edward Moore (1540-1601), ancestor of the Marquess of Drogheda.
The document also tells us that the Duke of Schomberg camped here before the Battle of the Boyne, and that a field hospital was set up. Later the Irish Volunteer branch, the Ballymascanlon Rangers, were led by Robert MacNeale of Ballymascanlon, father of James Wolf MacNeil, who built the building we see today.
Ballymascanlon House is a multiple-bay two-storey over basement with attic Tudor-Revival house, built in 1863 for James Wolfe MacNeil, incorporating fabric of earlier building which had been built for Frederick Foster, with gables, mullioned windows, hood-mouldings and a recessed doorway. [5] MacNeil owned the nearby corn mills. There may be been a house previously located on the site, David Hicks tells us in Irish County Houses, A Chronicle of Change. [6]
Hicks tells us that the house was sold and further improved by architect P.J. Byrne for Frederick Foster. The red brick gate lodge was added at this time. Frederick Foster (1799-1888) married Isabella Vere. He was the son of John William Foster (1745-1809). Frederick had no children. His sister Louisa Jane married Thomas Span Plunkett, 2nd Baron Plunket of Newton.
Further building works were carried out in 1904 and 1919 for Katherine Plunkett, daughter of Louisa Jane and Thomas Span Plunkett, who then owned the house. The house has high pitched gables and projecting bays. The Plunkett coat of arms over the front door depicts and horse and the Plunkett motto, Festina Lente, or Make Haste Slowly.
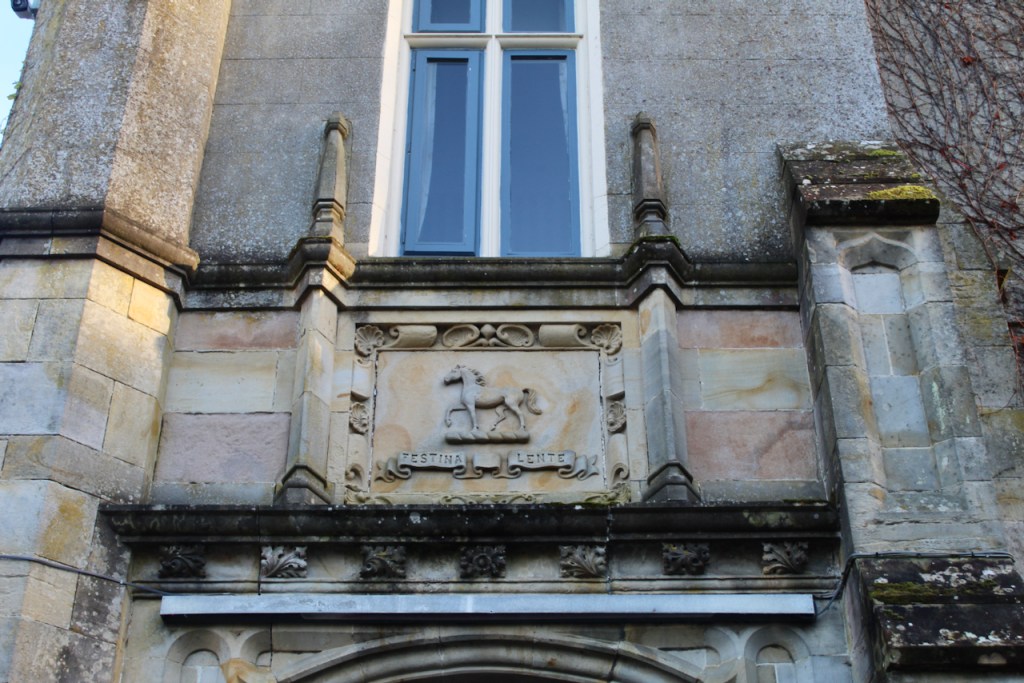


Hicks continues his description:
“Inside, a spine corridor leads past the various reception rooms that overlook the gardens through mullioned windows. This corridor provided ample space for family portraits and landscapes that once decorated the walls. One of the most interesting features of the interior is the glazed dome that provides light to the inner hall at the centre of the house where the hotel reception is. The various reception rooms of the house are tastefully decorated and have retained much of their old world charm.“
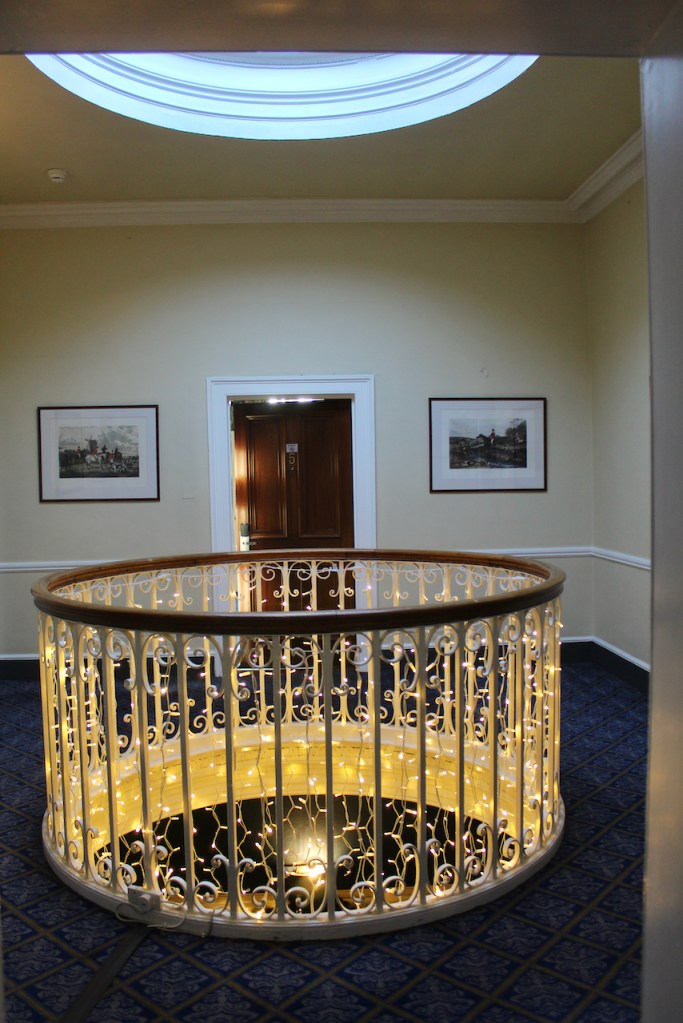










The house was offered for sale in 1943 and purchased by George Noble Plunkett, a Papal court who received his title from Pope Leo XIII for donating money to Catholic charities. He was the father of Joseph Mary Plunkett, one of the signatories of the Proclamation of the Irish Republic, who was executed for his part in the 1916 Rising.
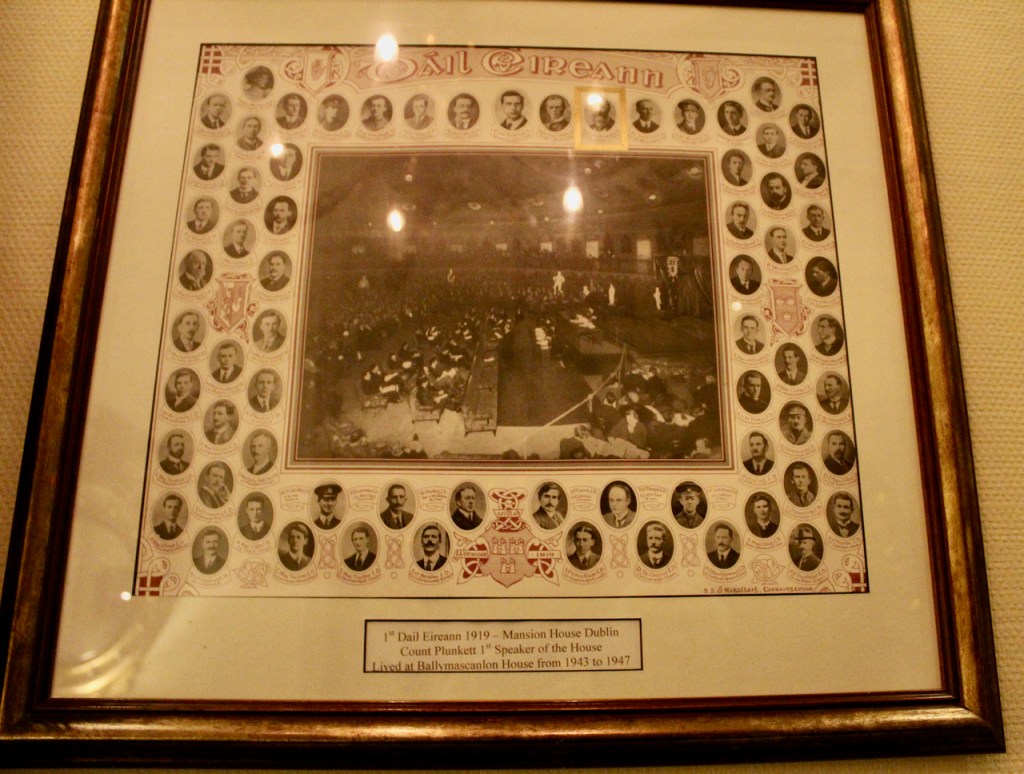

George Noble Plunkett and his wife Josephine Cranny were children of Pat Plunkett and Pat Cranny, two successful property developers who built many of the red brick Victorian houses in Dublin. Count Plunkett began his professional life as the director of the National Museum. After his son was killed he entered politics. After his wife died, he sold the house to the Quinn family, who turned it into a hotel.
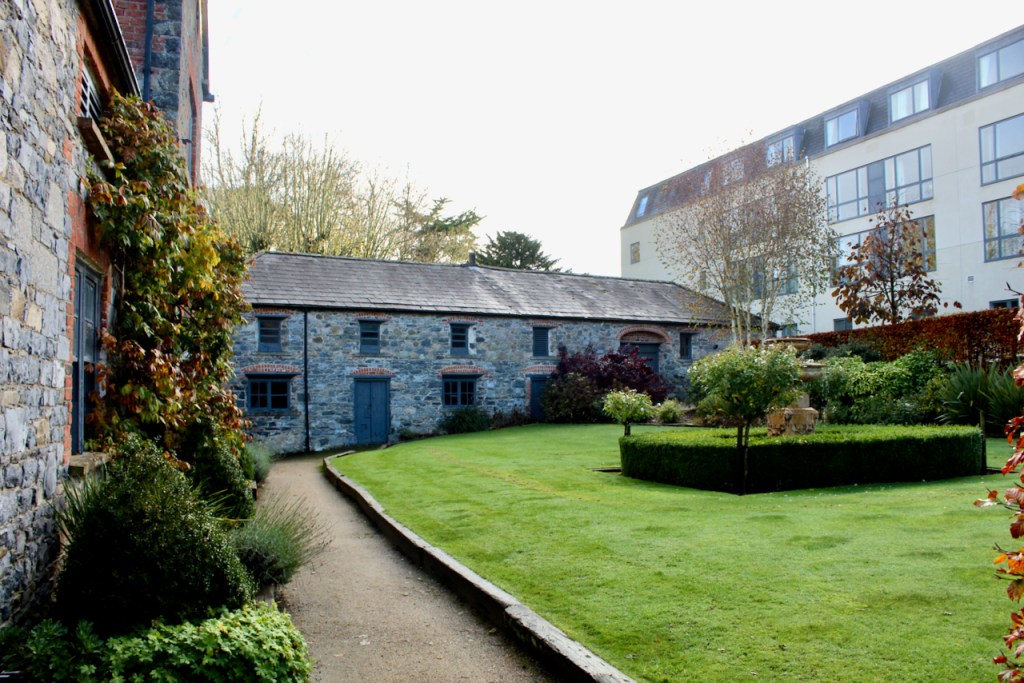
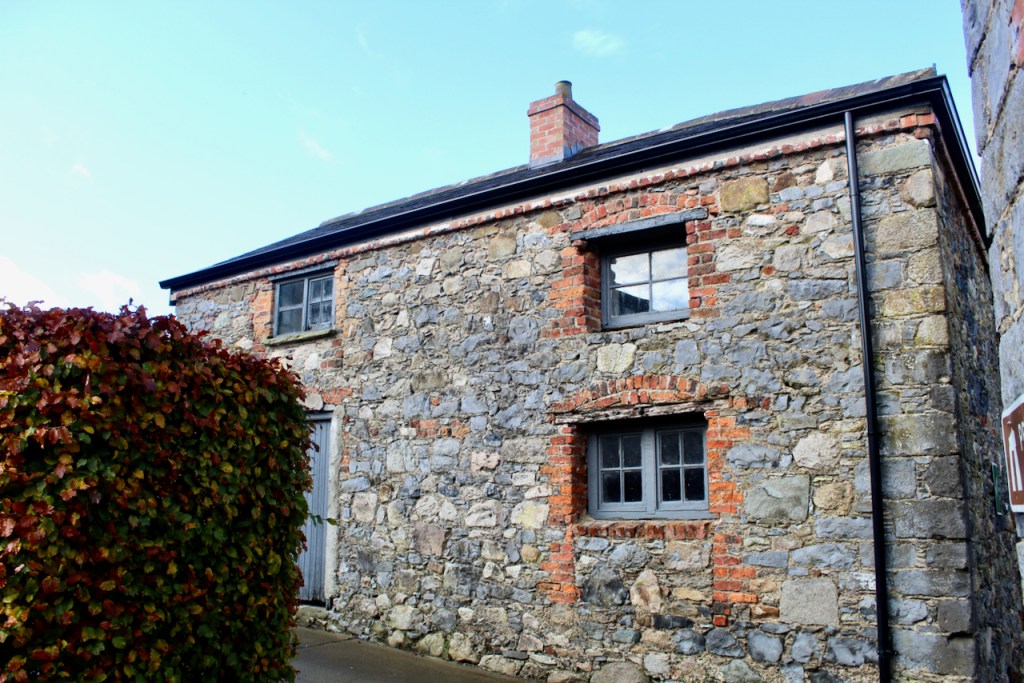








2. Collon House, Ardee Street, Collon, Louth – see above
3. Darver Castle, County Louth
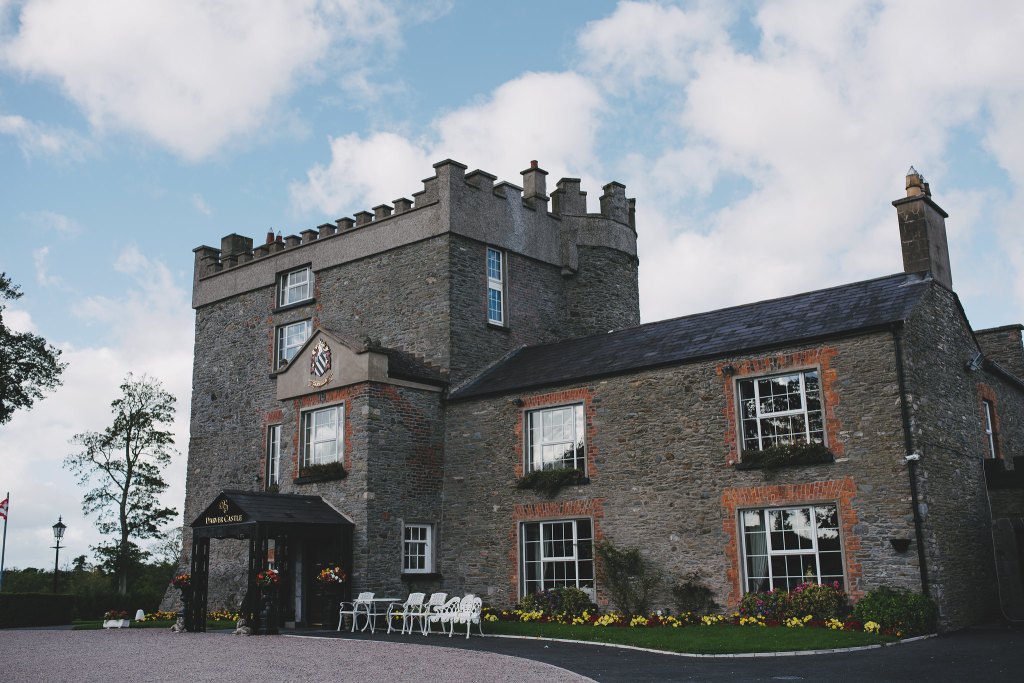

https://www.darvercastle.ie/home/
The website tells us:
“The Castle, dating from the 15th century is situated in a fine parkland setting and surrounded by mature trees. The courtyard, approached through a medieval arched gateway has lofted stone faced buildings while the outer yard has very impressive stone faced buildings with stabling for 20 horses. Also included is an outdoor manège, partly walled garden and orchard. The lands, all in old pasture, have excellent road frontage and are renowned for their fattening qualities.In the early 12th Century a man named Patrick Babe was given 500 acres of land in the parish of Derver by King James II. He built a castle for himself and his family to live in on the grounds formerly owned by the church. The castle was built on the north side of the hill north of the cave and on the edge of the deep slope that led to the banks of two rivers, which provided fish and eels for the family food.The rivers acted as security from the enemy advancing from the north. With a large yard wall to the east 12 feet high and 20 acres of woodland to the west helped keep the enemy out. But a problem arose on the southside of the hill as it sloped to a deep valley and joined the high hill of newtown Darver. As the top of this hill is just 4 feet higher than the level of the top of the castle. So the soldiers were unable to see the enemy approaching from the south. Patrick Babe had a round tower built on the very top of the hill and placed soldiers into this garrison which gave them a clear view for 40 miles away so no enemy ever got near Darver Castle Estate during all the wars.
“The church was never reached by Cromwell because of the protection from the hilltower. When the wars were over, Patrick Babe had wings put on the front of the tower and converted it into a windmill, and used it to ground corn for himself and his tenants. This continued for 150 years until large mills were built on the edge of the rivers, powered by the water, so that the use of the towermill ended and it was later demolished and the land around made arable. The hill is still known as windmill hill. 12thC Patrick Babe built the castle. Later he built 14 tenant houses. 1385 John Babe was given the advocasy of the church 1655 The Babes rented the castle to Abraham Ball. He died in 1742. 1740 James Babe sold the castle and 500 acres of land to Richard Fiscall Dublin for $4,000 1777 According to a survey done by Taylor and Skinner. The castle was idle. 1789 John Booth bought the castle. He died in 1840. 1840 Joseph Booth appears. He added the new wing and porch. 1857 John Filgate Booth died there. 1890 Frances Rutherford died there. 1894 Elizabeth Booth died there. 1906 Charles Rutherford died there. 1921 Zane Booth died there. 1980 John Booth died there. 1993 McCormack family took over and shortly afterwards Aidan and his wife Mary took ownership. Through a lot of hard-work and love for the castle, they have transformed it into the castle wedding venue it is today. The Carville family still continue to care for the castle, with improvements happening endlessly.“
4. Ghan House, Co Louth
The National Inventory tells us: “Built in 1727 by William Stannus, this building, with its unadorned façade and finely-balanced elegant classical proportions, is a handsome representative of architectural developments during the Georgian era. It retains a large amount of original and early fabric, including handsome boundary walls, corner tower and carriage arch.”
Whole House Rental, County Louth:
1. Barmeath Castle, Dunleer, Drogheda, Co. Louth – section 482, see above, €€€ for two, € for 6-12
2. Bellingham Castle, Co. Louth – for weddings, and open to public for visits
https://www.bellinghamcastle.ie
See above
3. Bellurgan Park, County Louth
[2] Bence-Jones, Mark. A Guide to Irish Country Houses (originally published as Burke’s Guide to Country Houses volume 1 Ireland by Burke’s Peerage Ltd. 1978); Revised edition 1988 Constable and Company Ltd, London.
[4] https://www.ihh.ie/index.cfm/houses/house/name/Collon%20House
[6] p. 147. Hicks, David. Irish County Houses: Chronicle of Change. Collins Press, Cork, 2012.
Text © Jennifer Winder-Baggot, www.irishhistorichouses.com



















































































































