On the map above:
blue: places to visit that are not section 482
purple: section 482 properties
red: accommodation
yellow: less expensive accommodation for two
orange: “whole house rental” i.e. those properties that are only for large group accommodations or weddings, e.g. 10 or more people.
green: gardens to visit
grey: ruins

donation
Help me to pay the entrance fee to one of the houses on this website. This site is created purely out of love for the subject and I receive no payment so any donation is appreciated!
€15.00
The province of Ulster contains counties Antrim, Armagh, Cavan, Derry, Donegal, Down, Fermanagh, Monaghan and Tyrone.
Down:
1. Audley’s Castle, County Down
2. Bangor Castle Park, County Down
3. Castle Ward, County Down
4. Dundrum Castle, County Down
5. Hillsborough Castle, County Down
6. Montalto Estate, County Down
7. Mount Stewart, County Down
8. Newry and Mourne Museum, Bagenal’s Castle, County Down
9. Portaferry Castle, County Down
Places to stay, County Down
1. Barr Hall Barns, Portaferry, County Down – self-catering accommodation
2. Castle Ward, County Down – accommodation in Potter’s Cottage in farmyard and Castle Ward bunkhouse
3. Culloden, County Down – hotel
4. Florida Manor, 22 Florida Road, Killinchy, Newtownards, Co Down, BT23 6RT Northern Ireland – self-catering accommodation
5. Helen’s Tower, Bangor, County Down: Irish Landmark accommodation
6. Kiltariff Hall, County Down – B&B
7. Narrow Water Castle, apartment, Newry Road, Warrenpoint, Down, Northern Ireland, BT34 3LE – self catering apartment
8. The Old Inn, Bangor, County Down
9. Slieve Donard hotel and spa, County Down
10. St John’s Point Lighthouse Sloop, Killough, County Down – Irish Landmark accommodation
11. Tullymurry House, Tullymurry road, Donaghmore, Newry, County Down – Irish Landmark accommodation
12. Tyrella, Downpatrick, County Down, BT30 8SU – accommodation
Whole house County Down
1. Ballydugan House, County Down (weddings)
2. Drenagh Estate and Gardens, County Down (weddings)
3. Tullyveery House, County Down – whole house holiday rental

donation
Help me to pay the entrance fee to one of the houses on this website. This site is created purely out of love for the subject and I receive no payment so any donation is appreciated!
€15.00
Places to visit in County Down:
1. Audley’s Castle, Castle Ward, County Down
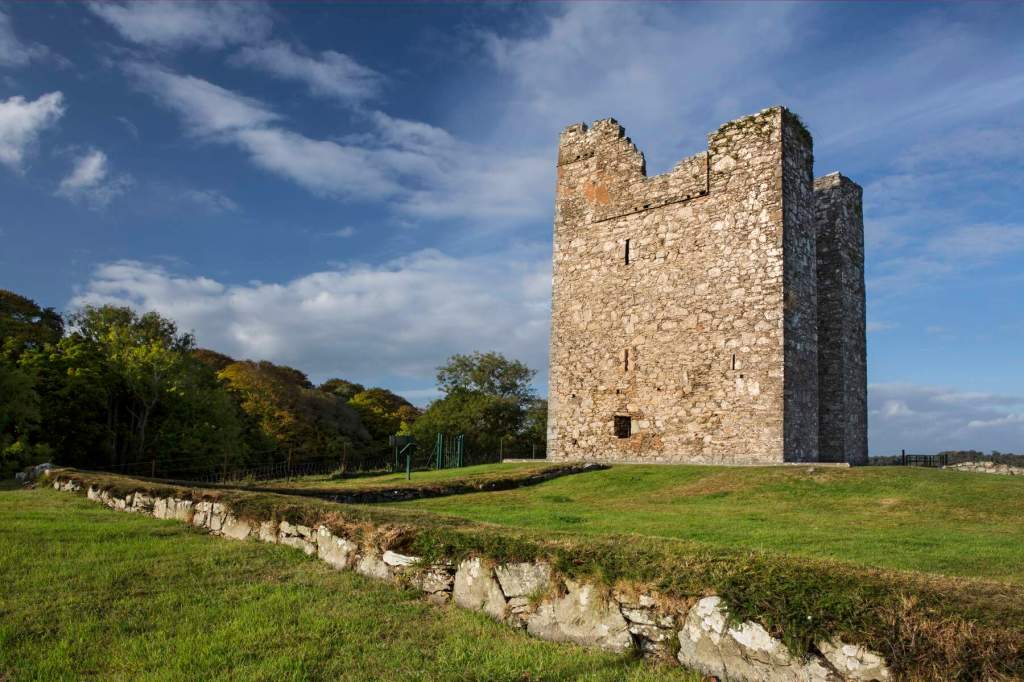

https://discovernorthernireland.com/things-to-do/audleys-castle-p707501
“The castle is named after its late 16th-century owners, the Audleys, an Anglo-Norman family who held land in the area in the 13th century, It was sold, with the surrounding estate, to the Ward family in 1646 and used in 1738 as an eye-catching focus of the long vista along Castle Ward’s artificial lake, Temple Water.
The site comprises of a number of paths to allow you to get to the Castle.“
2. Bangor Castle Park, County Down
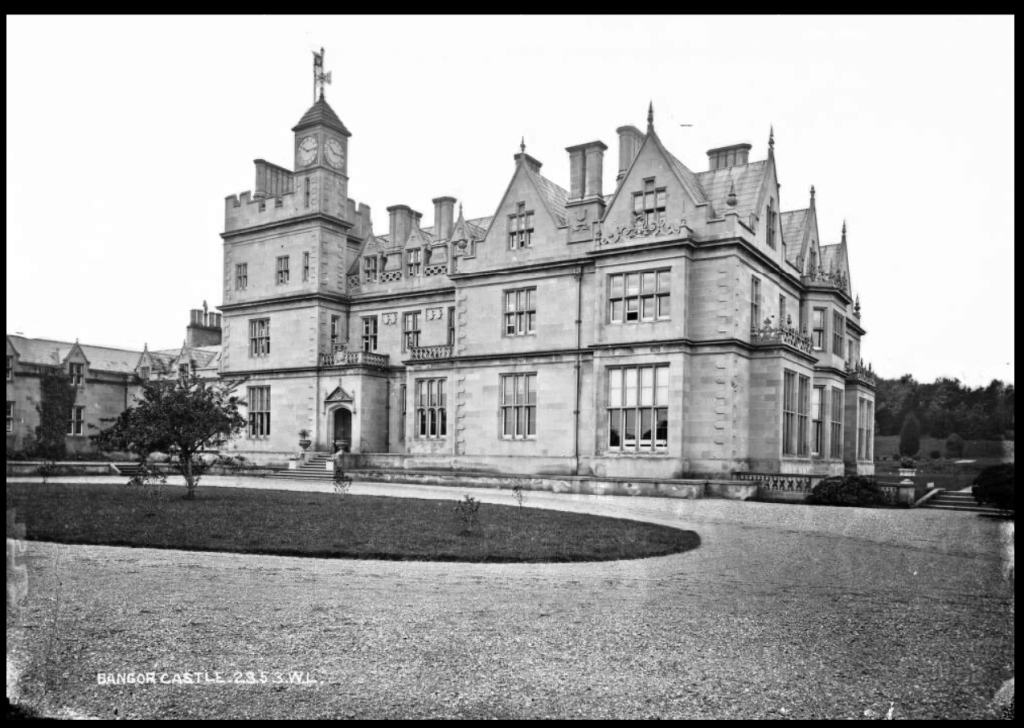

https://discovernorthernireland.com/things-to-do/bangor-castle-town-hall-p676451
“This impressive building was built for the Hon Robert Edward Ward [1818-1904] and his family in 1852. It is presently the headquarters of Ards and North Down Borough Council who use the mansions spectacular grand salon as the council chamber. The building is situated in the grounds of Castle Park alongside North Down Museum and is just a short walk from Bangor Castle Walled Garden.
“CS Lewis visited North Down on many occasions throughout his life and regularly returned to the area. He enjoyed the beautiful view over Belfast Lough from the grounds of Bangor Castle. As Lewis himself once said “Heaven is Oxford lifted and placed in the middle of County Down”.

Mark Bence-Jones writes in his A Guide to Irish Country Houses (1988):
p. 30. “(Ward, sub Bangor, V/PB; Bingham, Clanmorris, B/PB) An Elizabethan-Revival and Baronial mansion by William Burn, built 1847 for Robert Ward, a descendant of 1st Viscount Bangor. Mullioned windows; oriels created with strapwork; rather steep gables with finials. At one end, a battlemented tower with a pyramidal-roofed clock turret. Partly curved quoins, very characteristic of Burn. Inherited by Robert Ward’s daughter and heiress, Matilda Catherine, wife of 5th Lord Clanmorris [John George Barry Bingham, 5th Baron Clanmorris of Newbrook, County Mayo]. Featured in Peers and Plebs by Madeleine Bingham. Now owned by the town of Bangor.”
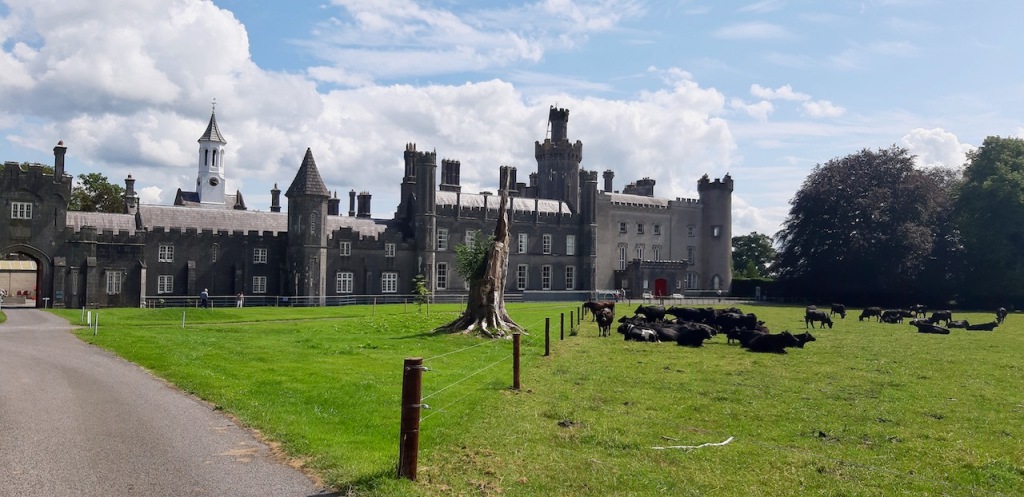
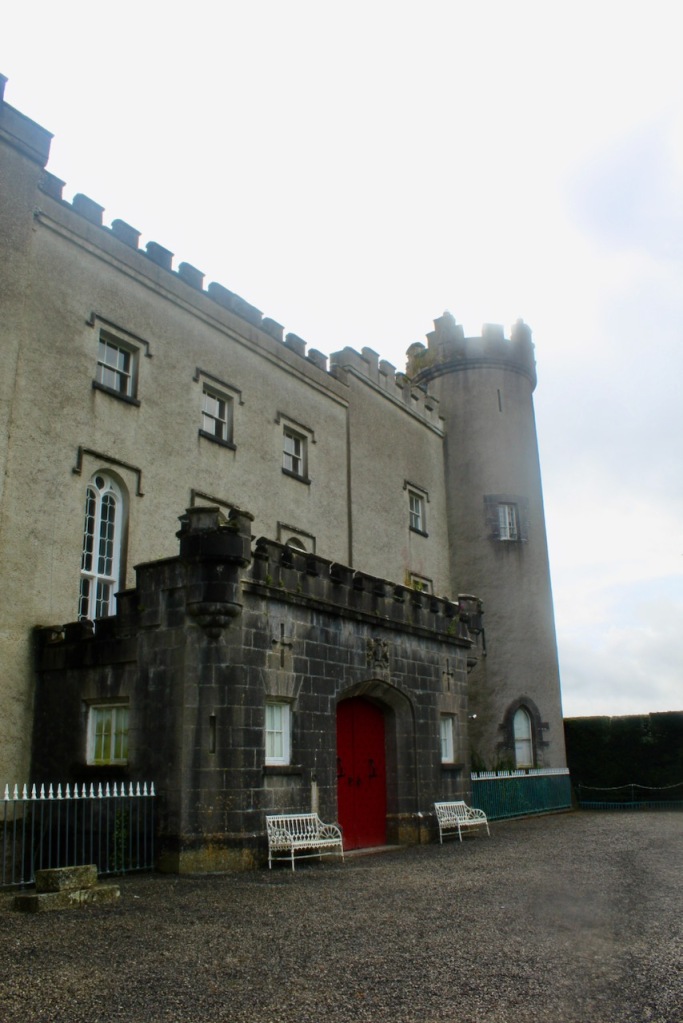
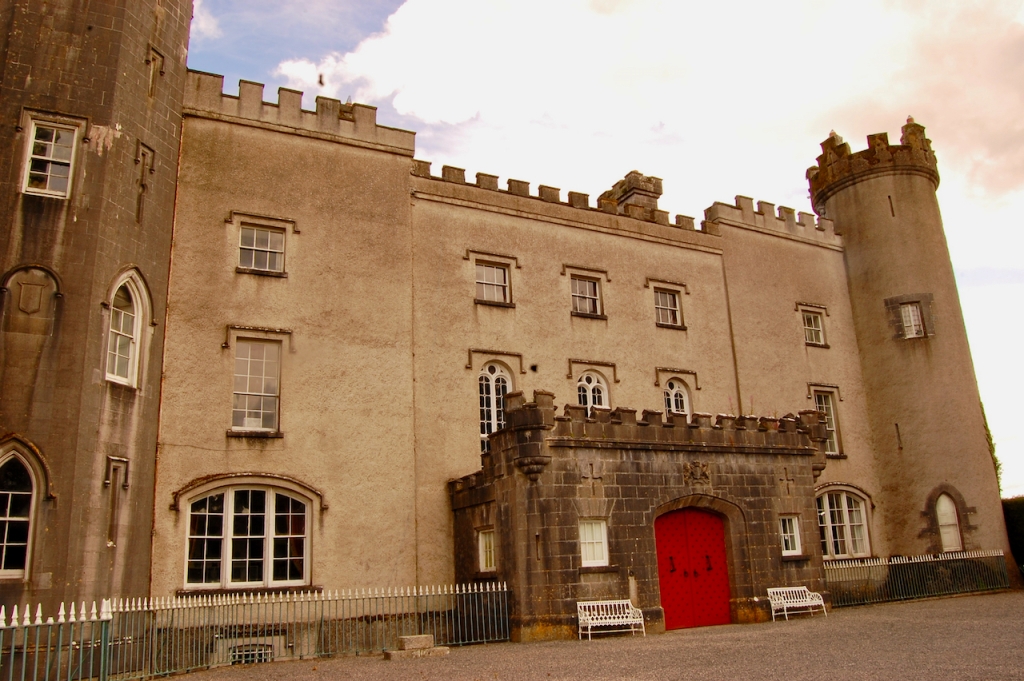
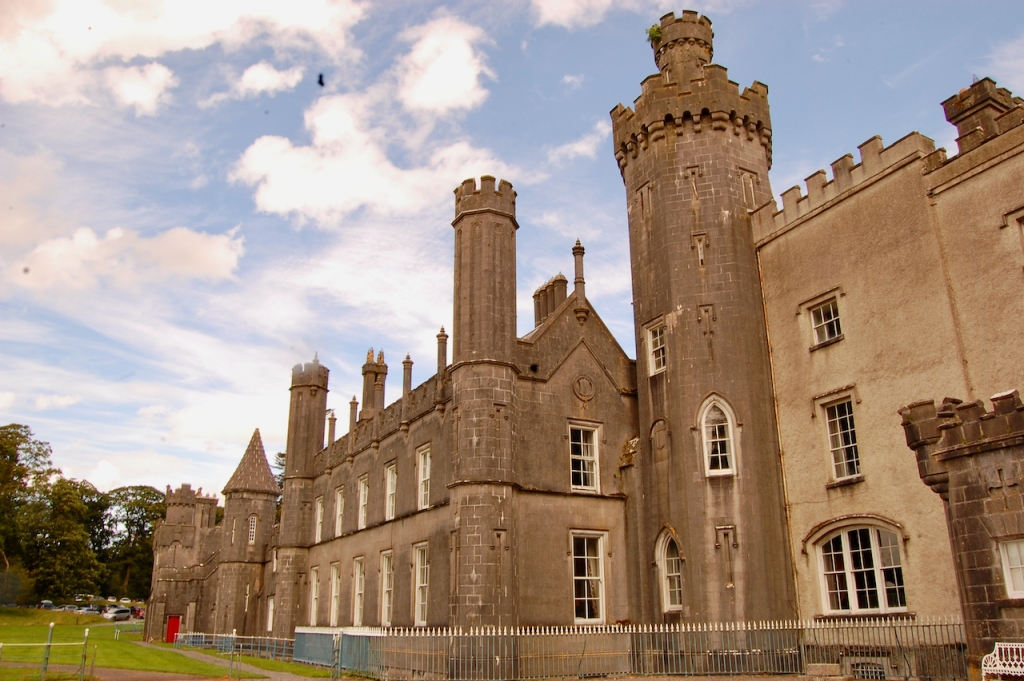
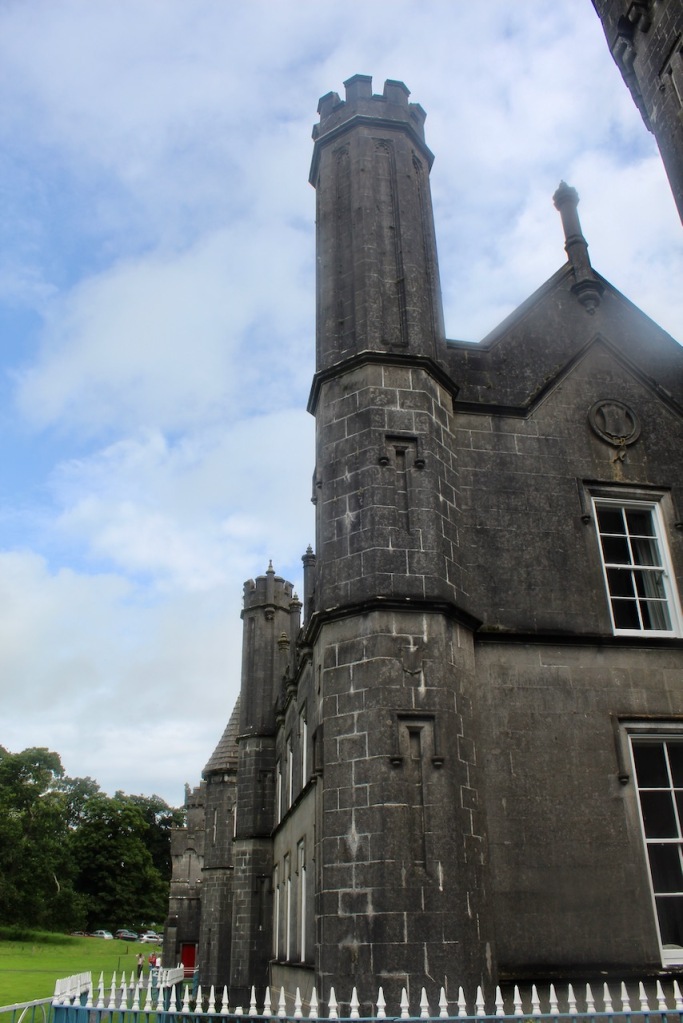
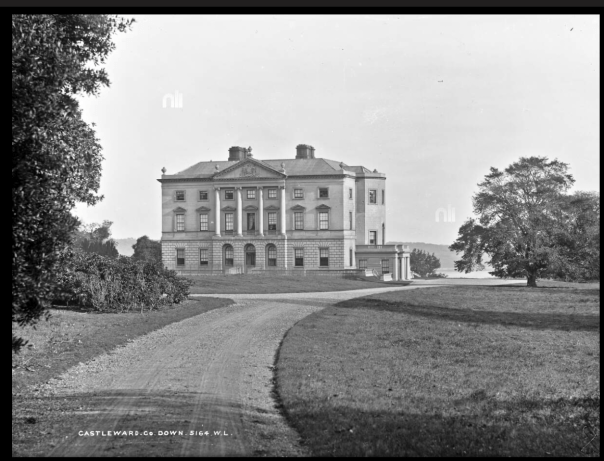
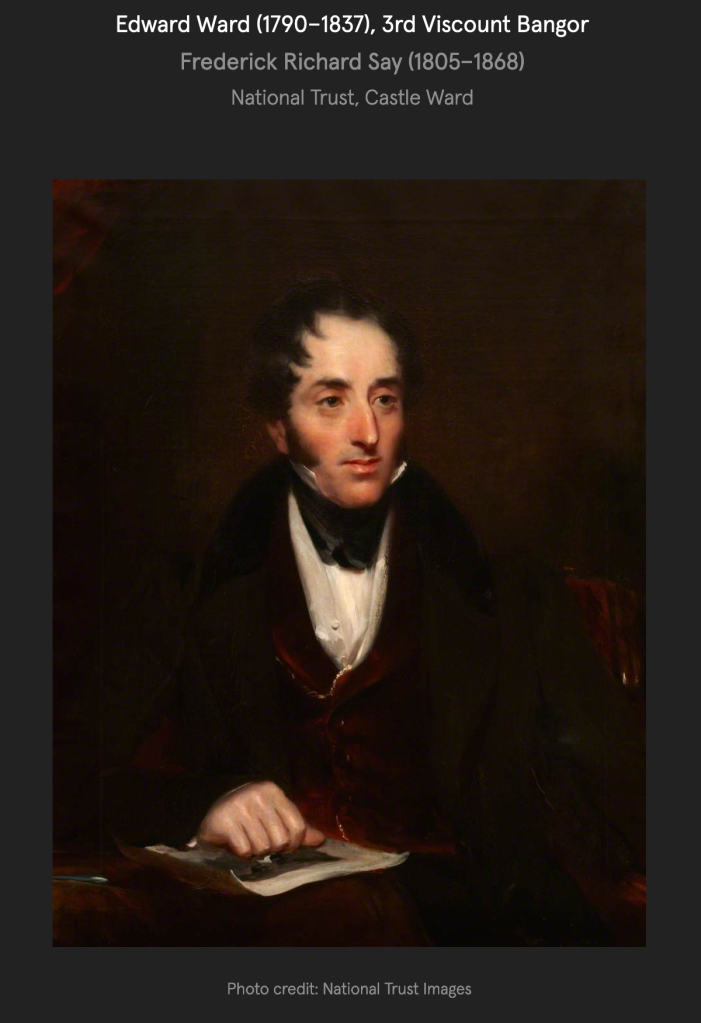
3. Castle Ward, County Down

https://discovernorthernireland.com/things-to-do/castle-ward-p675331 and https://www.nationaltrust.org.uk/castle-ward
The National Trust website tells us:
“The current Castle Ward is a particularly unusual building, famed for having been built with two completely different architectural styles, both inside and out.
“One half is built in the classical Palladian style, with the other half which faces out across Strangford lough built in the more elaborate Gothick style.



“The story told for the reason behind this unusual decorative scheme is that the original builder of the house, Bernard Ward, 1st Viscount Bangor, did not agree with his wife Lady Anne [Anne Bligh (1718-1789, daughter of John Blight 1st Earl of Darnley] on the décor. Bernard was more classical in taste with Lady Anne prefering the fashionable Gothick style, leading them to split the house down the middle. This story is compounded by the fact that they separated not long after the house was finished with Anne leaving Castle Ward for good. This hint of scandal has carried this story through the years, but let us consider instead that Anne and Bernard set out to build the house exactly as it is – not a marriage of compromise, but a triumph of collaboration.
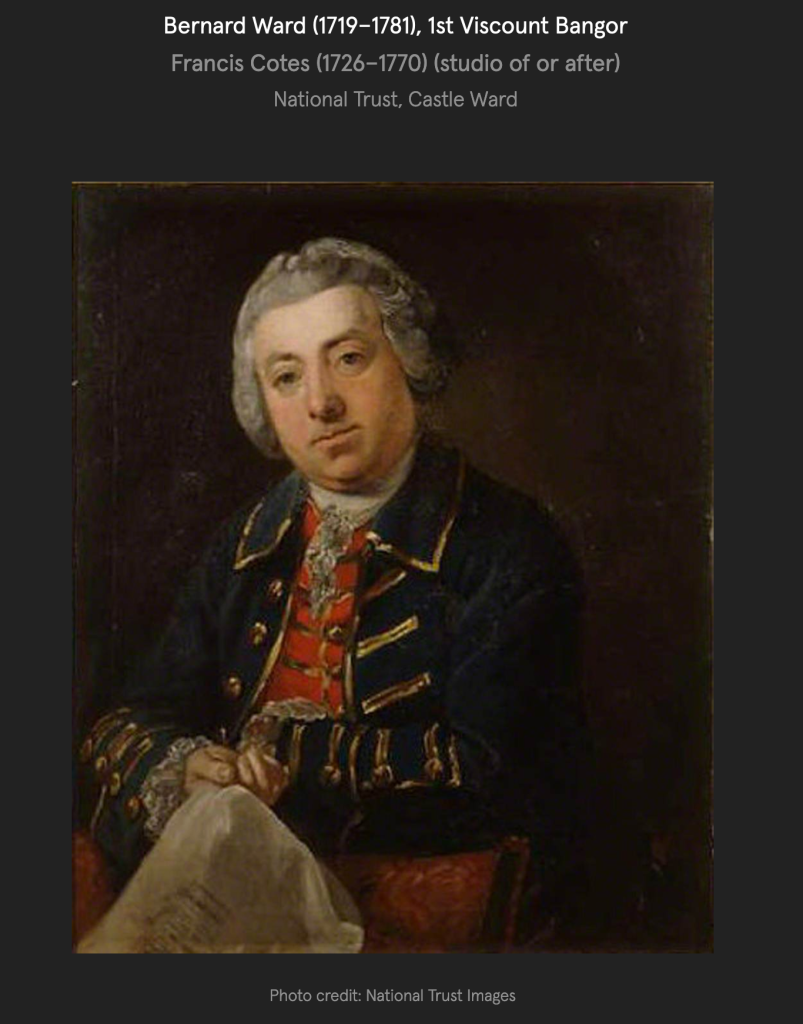


“When Bernard and Lady Anne inherited the estate in 1759 they set about building themselves a fine new house, one which would be symbolic of their union and exist as a statement of the Ward family’s bold and forward-thinking place in the world. Castle Ward was completed in 1766 and by 1781 they had been created Viscount and Viscountess Bangor in the Peerage of Ireland.
“Lady Anne’s grandfather was the nephew of the Duchess of York – wife of King James II, and a first cousin of Queen Anne. This royal ancestry shows itself in the choice of the Gothick style. The ceiling in the Morning Room is copied from the Henry VII Chapel in Westminster Abbey where Anne’s maternal family were permitted to be buried due to their royal blood. Rather than the house becoming known as an architectural monstrosity, the couple aimed for it to be a masterpiece, striving against convention and rooting the Ward family as bold, modern thinkers with an impressive past.
“The unusual combination of styles has long been a point of joy or novelty for guests, having a ‘marmite’ appeal. On a visit to Castle Ward, writer and poet John Betjeman referred to the ceiling in the Boudoir as “like sitting under a cow’s udder”, and the comment has stuck. Others comment on the otherworldly feeling created in the exotic grandeur of the Gothick side.
“Please check the homepage for opening times of the mansion house before planning your visit, as they may change seasonally. There is no need to book your visit in advance.“
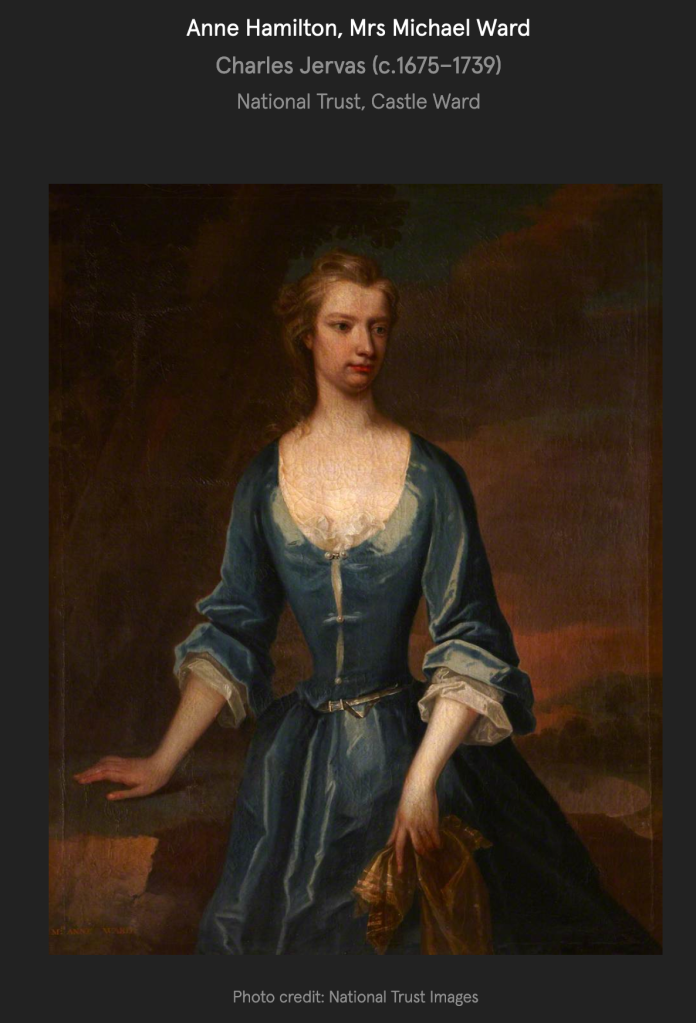




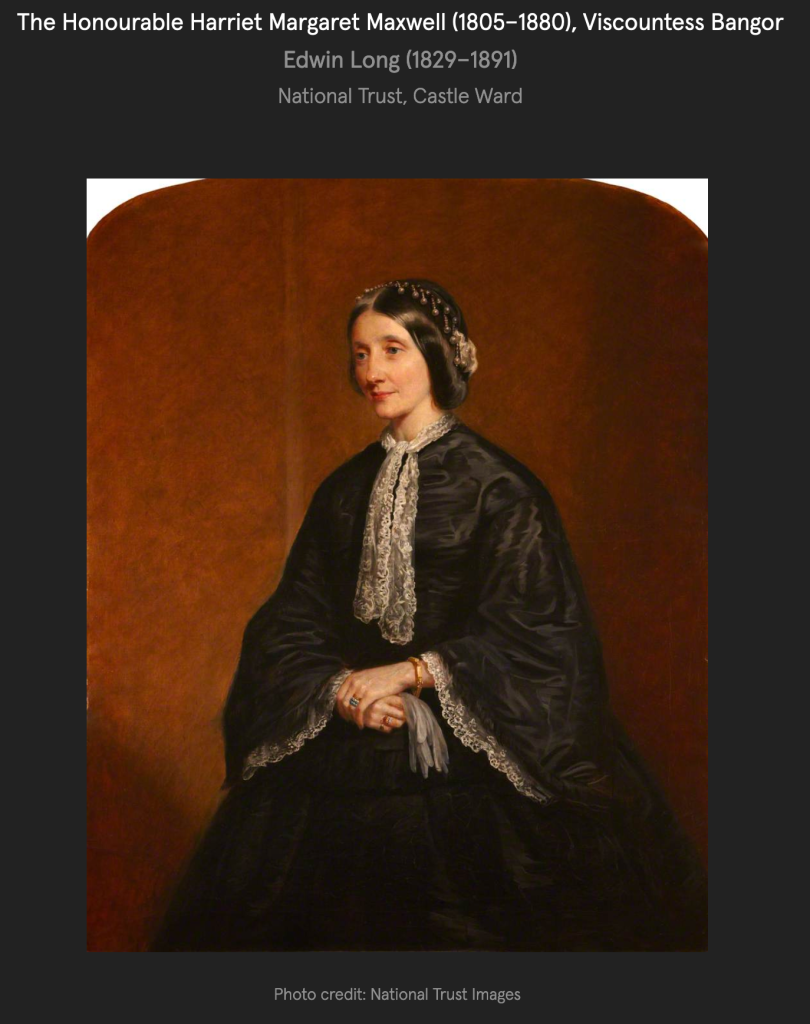
The website also tells us more about owner Anne Ward:
“Castle Ward – the story of a warring couple, divided in opinion and styles leading to a house with two sides. Perhaps the story is a little more complicated – here we delve deeper into the background of Lady Anne Bligh, co-architect of Castle Ward.
“Given that Lady Anne Ward was co-creator of the dichotomous style of Castle Ward, it is surprising how few of her possessions or papers are left in the collection. Hers’ remains a hidden history. Having left Castle Ward and her husband Bernard in 1770 shortly after the completion of the house, she has become a symbol of mystery and speculation, made notorious and unusual because of her independence of mind and spirit.“Given that Lady Anne Ward was co-creator of the dichotomous style of Castle Ward, it is surprising how few of her possessions or papers are left in the collection. Hers’ remains a hidden history. Having left Castle Ward and her husband Bernard in 1770 shortly after the completion of the house, she has become a symbol of mystery and speculation, made notorious and unusual because of her independence of mind and spirit.
“The public expression of her personal tastes in the Gothick style at Castle Ward, clashed dramatically with her husband’s preferred classical style, and this has resulted in the condemnation of Lady Ann as unusual. History has found it difficult to understand the architectural choice that was reached by Lady Anne and Bernard, seeming as a legacy to their failed marriage. Whilst Bernard is remembered as the maker of the classical side of the house, symbolically representing reason, balance and order, Lady Anne in contrast represents an ‘otherness’ which she expressed in Gothick architecture – seemingly conveying her fantastical, whimsical and unconventional personality.
“The Royal blood from her maternal grandparents gave Lady Anne the hauteur and confidence to do as she pleased. Her grandfather, the Earl of Clarendon was the nephew of the Duchess of York, wife of James II, and a first cousin of Queen Anne. Queen Anne was her mother Theodosia’s Godmother, and as such Theodosia was allowed to marry in Westminster Abbey. This was something Lady Ann was keen to highlight in her choice of architecture at Castle Ward, even copying the plasterwork from the Henry VII Chapel and recreating it in the Morning Room as a reminder of her royal connections.
“The Earl of Clarendon also prompted perception of the family as “eccentric” by accounts of them acting out their role as Colonial Governor of New York dressed in articles of women’s clothing which challenged social boundaries of the period. Historians have been unable to confirm the accuracy of these accounts nor the motivations behind the Earl’s alleged presentation of gender non-conformity. Whatever the accuracy or reason, contemporaries condemned the Earl and considered it to be a sign of ‘great insanity’, however the Earl remained protected and often handsomely rewarded by their cousin Queen Anne. This connection provided crucial protection from critics.
“Elizabeth Hastings, Countess of Moira who knew the family decribed them as having ‘an hereditary malady’. Members were noted as experiencing varied mental health issues. Lady Anne was accused of having ‘a shade of derangement in her intellects’. Her brother, Lord Darnley, was convinced he was a teapot and was reluctant to engage in sexual activity lest ‘his spout would come off in the night’; Lady Anne’s son Nicholas was declared ‘a lunatic’ in 1785 but details about this are scant.
“Lady Anne’s relationship with a woman, prior to her two marriages [she was previously married to Robert Hawkins-Magill of Gill Hall, County Down], has also been the source of popular speculation and of academic debate. At 21, Lady Anne embarked on a six year relationship with Letitia Bushe, a woman considered much inferior in status and wealth, but much more experienced in the world with a great intellect and close friend of Mrs Delany. From the surviving correspondence of Letitia Bushe, it is clear that she was besotted with Lady Anne who was some fifteen years her junior, writing in 1740:
‘This Day twelvemonth was the Day I first stay’d with you, the night of which you may remember pass’d very oddly. I cannot forget how I pity’d you and how by that soft road you led me on to love you… that first Sunday at Bray, when you were dressing and I lay down on your Bed – ‘twas then I took first a notion to you’.
“Academic research has suggested that this instance of same-sex love and desire provided Lady Anne with ‘an alternative outlet for emotional needs and energies, free of the complex web of economic and social considerations that surrounded relations between men and women of the propertied classes’ at this time.
“Sadly none of Lady Anne’s correspondence to Letitia Bushe survives – in true Lady Anne style she remains an enigma, true to herself regardless of tastes or conventions, and a symbol of ‘the three-dimensional complexity of human life’.“
Mark Bence-Jones writes in his A Guide to Irish Country Houses (1988):
p.78. Castleward: “Ward, Bangor, V/PB) A grand mid-C18 house of three storeys over basement and seven bays; built 1760/73 by Bernard Ward (afterwards 1st Viscount Bangor), and his wife, Lady Anne, daughter of 1st Earl of Darnley, to replace an earlier house. Probably by an English architect; and faced in Bath stone, brought over from Bristol in Mr Ward’s own ships. It seems that the Wards could not agree on the style of their new house; he wanted it to be Classical; but she was of what Mrs Delany called “whimsical” taste and favoured the fashionable new Strawberry Hill Gothic. The result was a compromise. The entrance front was made Classical, with central feature of a pediment and four engaged Ionic columns rising through the two upper storeys, the bottom storey being rusticated and treated as a basement. The garden front, facing over Strangford Lough, was made Gothic, with a battlemented parapet, pinnacles in the centre, and pointed windows in all its three storeys and seven bays – lancet in the central breakfront, ogee on the other side. All the windows have delightful Strawberry Hill Gothic astragals. This front of Castleward, and Moore Abbey, Co Kildare, are the only two surviving examples of mid-C18 Gothic in major Irish country houses which are not old castles remodelled. The interior of Castleward is remarkable in that the rooms on the Classical side of the house are Classical and those on the Gothic side Gothic; thus the hall – now the music room – has a Doric frieze and a screen of Doric columns; whereas the saloon has a ceiling of fretting and quatrefoils, pointed doors and a Gothic chimneypiece. The dining room, with its grained plaster panelling, is Classical and the sitting room is Gothic with spectacular plaster fan vaulting. Mr Ward, however, managed to be one up on his wife in that the staircase, which is in the middle of the house, is Classical; lit by a Venetian window in one of the end bows. If we believe Lady Anne, this was not the only time when he got his own way at her expense, for, having left him, as it turned out, for good, she wrote accusing him of bullying her. In C19, a porch was added to one of the end bows of the house, making a new entrance under the staircase; so that the hall became the music room. In the grounds there is a four storey tower-house, built at the end of C16 by Nicholas Ward; also a temple modelled on Palladio’s Redentore, dating from ante 1755; it stands on a hill, overlooking an early C18 artificial lake, or canal. On the death of 6th Viscount, 1950, Castleward was handed over in part payment of death duties to the Northern Ireland Government, who gave it, with an endowment, to the National Trust. The house and garden are now open to the public, and the Trust has set up various projects in different parts of the estate.”




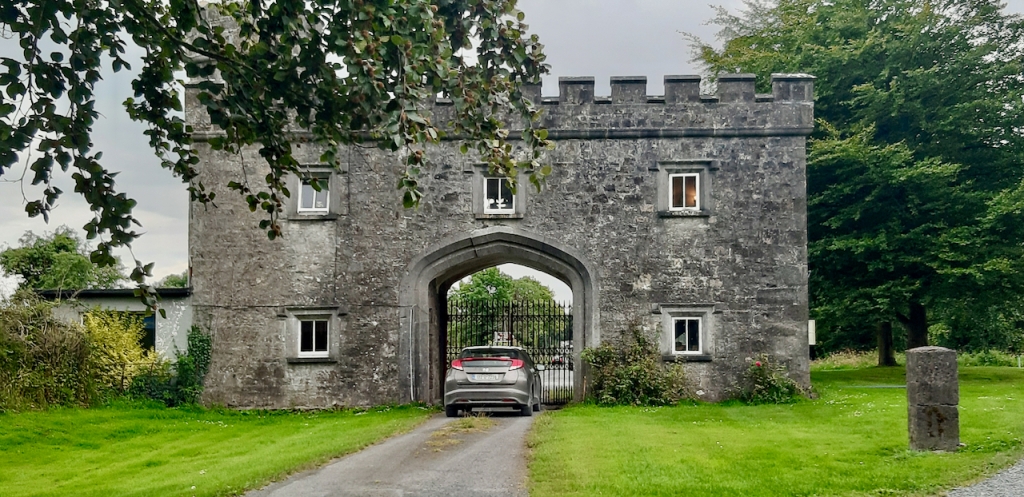
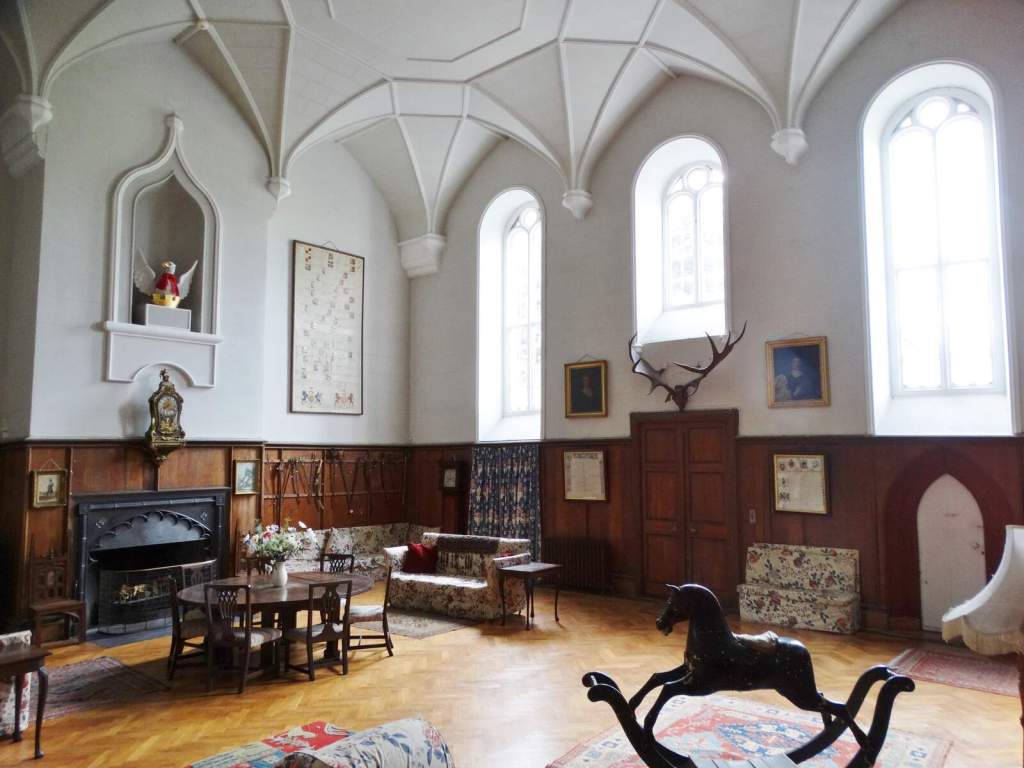
4. Dundrum Castle, County Down – ruins
https://discovernorthernireland.com/things-to-do

5. Hillsborough Castle, County Down
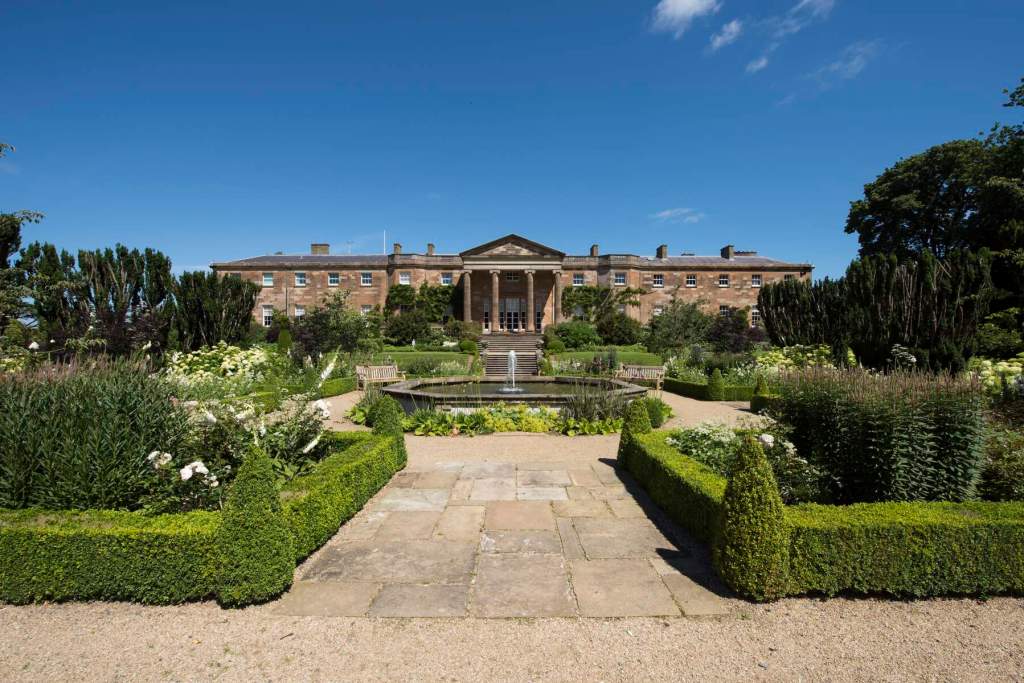

https://www.hrp.org.uk/hillsborough-castle
“Hillsborough Castle has been a grand family home and is now the official home of the Secretary of State for Northern Ireland, and a royal residence. Members of the Royal Family stay at Hillsborough when visiting Northern Ireland.
“Viewed by some as a politically neutral venue, Hillsborough has played an important role in the Peace Process in Northern Ireland since the 1980s.
“In 2014, Historic Royal Palaces took over the running of Hillsborough Castle and Gardens and began an ambitious project to restore the house and gardens to its former glory.
“Hillsborough, originally the settlement of Cromlyn (meaning Crooked Glen) in mid-Down, became part of the Hill family estates in the early 1600s. Moyses Hill, the landless second son of an English West Country family, joined the army to seek his fortune in Ireland, where he supported the Earl of Essex, a military leader sent by Elizabeth I.
“At this time, the land was still in the hands of Irish chiefs of the Magennis family. But the defeat of Irish chieftain Hugh O’Neill in 1603 opened the way for men such as Moyses Hill to establish themselves as landowners in Ireland. The Hills bought some 5,000 acres of land, then gradually added to this over the next 20 years until the whole area around the present Hillsborough had passed from the Magennises to the Hills.
“Successive generations of this ambitious family began to rise, politically and socially, in Ireland. Within 50 years they were one of the most prominent landowning families in the area; their estates stretched for over 130 miles from Larne, north of Belfast to Dun Laoghaire, south of Dublin, around 115, 000 acres in total.
“Wills Hill was the first Marquess of Downshire and his diplomatic skills as a courtier cemented the family’s position in society.

“From 1768-72 he held the post of Secretary of State for the Colonies. He had grown very powerful in government and served the royal family, for which he was awarded his title in 1789.
“Wills Hill famously hosted American founding father Benjamin Franklin, but contrary to popular myth, when they met at Hillsborough in 1771, the two men got along well together.
“Wills Hill built not only this house but also the Courthouse in The Square. He also built the terraces around The Square and other buildings in the town.
“Hillsborough is unusual for an Irish Big House as it is not a country house around which a town grew; rather it was built as a townhouse, forming one side of a neat Georgian square.
“The road to Moira once passed directly below the windows, and opposite the house were a variety of shops, houses and the Quaker Meeting House.
“The 3rd and 4th Marquesses, also commissioned a lot of work on the house, giving it the outward appearance it has today.
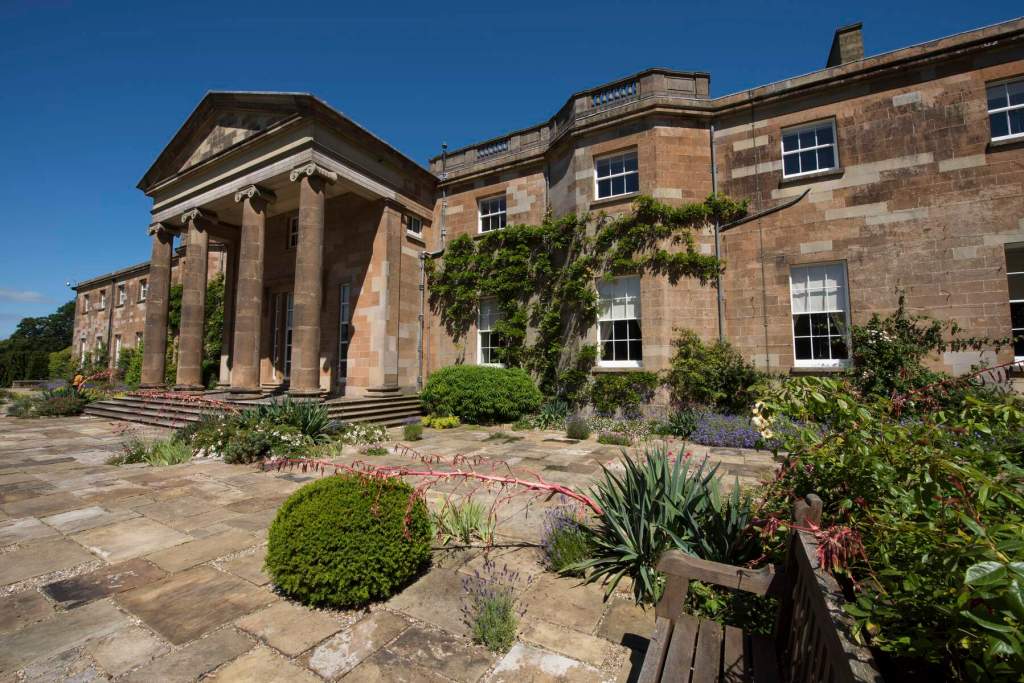

“When the house was being altered in the 1840s, the family decided to expand the gardens and so rebuilt the road, houses and Quaker Meeting House all further away. The old road was absorbed into the landscaping of the gardens, and the south side of the house was opened out to allow views of the ‘picturesque’ gardens.
“Successive generations of the Hill family enjoyed the house as a family home, renovating and redecorating in the latest styles and improving the gardens.
“However, by the end of the 19th century they were spending more time on their estate in England, at Easthampstead Park in Berkshire or their seaside home at Murlough House in County Down. The sixth Marquess’ uncle and guardian, Lord Arthur Hill remained at Hillsborough Castle to look after his nephew’s estate. The family first rented out Hillsborough in 1909, then sold it completely in 1925.
“It was bought by the British government, for around £24,000 (equivalent to £1.3m today) to be the residence of the Governor of Northern Ireland.
“Following Partition in 1921, Governors were appointed to represent the monarch in Northern Ireland, replacing the Lord-Lieutenant of Ireland who had previously lived at Dublin Castle. The house became known as Government House, remaining the official residence of the Governors for over 50 years.”
Mark Bence-Jones writes in his A Guide to Irish Country Houses (1988):
p. 152. “(Hill, Downshire, M/PB; Dixon, Glentoran, B/PB) A large, rambling, two storey late-Georgian mansion of a warm, golden-orange ashlar; its elevations rather long for their height. It appears to incorporate a much smaller house of ca 1760, but was mostly built later in C18, to the design of R.F. Brettingham, by Wills Hill, 1st Marquess of Downshire, a prominent member of Lord North’s Cabinet at the time of the American War. The work was not completed until 1797, four years after 1st Marquess’s death. In 1830s and 1840s, the house was enlarged and remodelled, to the design of Thomas Duff, of Newry, and William Sands. The pedimented portico of four giant Ionic columns in the middle of the long seventeen bay garden front – originally the entrance front – which is the principal exterior feature, dates from this period; as does the present appearance of the pedimented front adjoining to the left, with its asymmetrical projecting ends; as well as the treatment of the elevations of the two ranges at right angles to each other which form two sides of the entrance forecourt; one of them having a rather shallow single-storey portico of four pairs of coupled Ionic columns. The forecourt, with its magnificent mid-C18 wrought iron gates and railings, brought here 1936 from Rich Hill, Co Armagh, is on one side of the main square of the charming little town of Hillsborough, which is reminiscent of the Schlossplatz in a small German capital. Although the house backs onto a sizeable demesne, with a lake, the park is on the opposite side of the town. Its chief feature is Hillsborough Fort, a star-shaped fort built by Col Arthur Hill ca 1650. The gatehouse of the fort was rebuilt most delightfully in the Gothic taste ca 1758, perhaps to the design of Sanderson Miller himself. Hillsborough Castle became the official residence of the Governor of Northern Ireland 1925, and consequently became known as Government House; from then, until 1973, when the post of Governor was abolished, it was occupied by successive Governors (all PB); namely, 3rd Duke of Abercorn, 4th Earl Granville, 2nd Lord Wakehurst, Lord Erskine of Rerrick, and Lord Grey of Naunton; during this period, the house was frequently visited by members of the British Royal Family. In 1934 the house was seriously damaged by fire, and in the subsequent rebuilding the principal rooms were done up in a more palatial style, with elaborate plasterwork. The future of the house is now uncertain.”
6. Montalto Estate, County Down
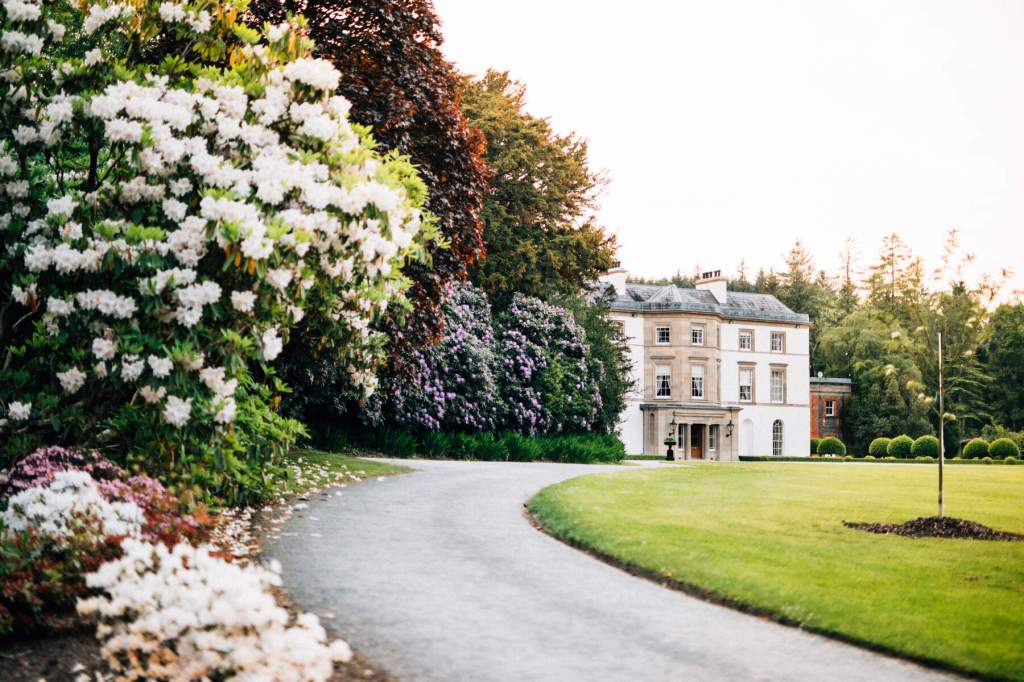

https://discovernorthernireland.com/things-to-do/montalto-estate-p728301
“For the first time in its history, this mystical and enchanting estate, set in magnificent natural surroundings, is open to visit.
“Nestled in the picturesque County Down countryside, Montalto is a privately-owned demesne steeped in history dating back to the 1600s. It is famously the site of ‘The Battle of Ballynahinch’ which took place during the Irish rebellion in 1798. It is also home to an exotic plant collection initially created by ‘The Father of Irish Gardening’, Sir Arthur Rawdon.
“Montalto Estate aims to reconnect visitors with nature through access to a range of captivating gardens and beautiful walks and trails. The visitor experience includes: public access to the estate’s beautiful gardens along with unique and surprising garden features; historic walks and trails; and an exciting play area where children can explore, learn and wonder at their natural surroundings. A purpose built centre, designed in keeping with the look and feel of the estate, includes a welcome area featuring interpretation of the estate’s history; a stylish café offering flavoursome and beautifully presented food; and a shop that offers a mix of estate produce, local craft products and many other unique and exceptionally designed items.
“The beautiful gardens include an Alpine Garden, a Winter Garden, a Cutting Garden, a Walled Garden, a Formal Garden and the Orchard situated within a wildflower meadow. Both the Winter Garden and Alpine Garden will always be accessible whilst the other gardens will be accessible whenever possible as they are working gardens. Four champion trees are located around the lake and the pinetum and over the past three years over 30,000 trees have been planted here.
“Active families will enjoy the Woodland Trail and low wood. The impressive purpose built tree house, which was handcrafted onsite, features rope bridges, monkey bars and treetop views kids of all ages will enjoy. Mini explorers can enjoy the smaller tree house and natural play area. Everything within this area has been designed to fuel the imagination through exploration and discovery.
“For tranquil and picturesque walks you can enjoy the stunning views of The Lake Walk and The Garden Walk. Catch a glimpse of some of the wonderful wildlife that calls Montalto Estate their home or simply take in the beautiful seasonal displays and reconnect with nature.”
The website tells us:
“Montalto, nestled beautifully in the heart of the picturesque Co. Down countryside, is a privately-owned demesne which dates back to the early 1600s.
“In pre-plantation times the estate was originally owned by Patrick McCartan. However, due to his involvement in the 1641 Rebellion, his Ballynahinch lands were confiscated, and in 1657 the townland was purchased by Sir George Rawdon [and Patrick McCartan was executed]. Circa 1765, his descendant Sir John Rawdon – First Earl of Moira [1720-1793] – built a mansion property on the estate: this is the house that we now know as Montalto House.
“Sir John’s ancestor, Sir Arthur Rawdon – The Father of Irish Gardening – had earlier amassed a large collection of exotic foreign plants at Moira Castle. Many of Sir Arthur’s plants were transferred to Montalto when his grandson Sir John moved onto the estate.
“During the Battle of Ballynahinch (part of the 1798 Rebellion), rebels occupying Montalto House are attacked by the militia. The mansion sustains some fire and artillery damage. Francis Rawdon-Hastings – 2nd Earl of Moira and Montalto resident – is a respected British military officer during the American War of Independence. He is a close friend of the Prince Regent, later King George IV. For ten years he is Governor General of India, carrying huge military and political responsibilities. He sells the Montalto Estate soon after the 1798 Rebellion and later becomes 1st Marquess of Hastings in 1816.“
John Rawdon 1st Earl of Moira married three times: first to Helena Perceval, daughter of John Perceval 1st Earl of Egmont, Co. Cork; next to Anne Hill, daughter of 1st Viscount Hillsborough, and finally to Elizabeth, daughter of Theophilus Hastings, 9th Earl of Huntingdon, England. His heir is Francis Rawdon-Hastings, 1st Marquess of Hastings.

“In 1803 David Ker of Portavo purchased the estate. In 1910 Richard – the last of the Kers to reside at Montalto – is finally forced to sell the estate. In 1912 Arthur, [Arthur Vesey Meade] 5th Earl of Clanwilliam [County Tipperary], purchases Montalto for £20,000.
“The Earl fights in the Boer War (where he is badly wounded), and with the Guards in France in WW1. His wife Lady Muriel cares for wounded Allied officers during their convalescence at Montalto.
“In 1979 the house is purchased by the Hogg Corry Partnership. In 1988 Corry withdraws. In 1995 it is purchased by the Wilson family. Working with local architects Hobart and Heron, as well as John O’Connell – a leading conservation architect from Dublin, specialising in Georgian architecture – they set about a programme of works to restore the house, grounds, and outbuildings to their former glory.
“The estate has been almost exclusively, a family home since Lord Moira built the first house here. Nowadays Montalto offers visitors the use of 400 acres of rolling Irish countryside, which includes wonderful trails and gardens and a chance to explore this historic demesne and reconnect with nature.“”The estate has been almost exclusively, a family home since Lord Moira built the first house here. Nowadays Montalto offers visitors the use of 400 acres of rolling Irish countryside, which includes wonderful trails and gardens and a chance to explore this historic demesne and reconnect with nature.“
Mark Bence-Jones writes in his A Guide to Irish Country Houses (1988):
p. 209. “(Rawdon, Moira, E/DEP; Ker/IFR; Meade, Clanwilliam, E/PB) A large and dignified three storey house of late-Georgian aspet; which, in fact, was built mid-C18 as a two storey house by Sir John Rawdon, 1st Earl of Moira, who probably brought the stuccodore who was working for him at Moira House in Dublin to execute the plasterwork here; for the ceiling which survives in the room known as the Lady’s Sitting Room is pre-1765 and of the very highest quality, closely resembling the work of Robert West; with birds, grapes, roses and arabesques in high relief. There is also a triple niche of plasterwork at one end of the room; though the central relief of a fox riding in a curricle drawn by a cock is much less sophisticated than the rest of the plasterwork and was probably done by a local man. 2nd Earl, afterwards 1st Marquess of Hastings, who distinguished himself as a soldier in the American War of Independence, and was subsequently Governor-General of India, sold Montalto 1802 to David Ker, who enlarged the windows of the house, in accordance with the prevailing fashion. In 1837, D.G. Ker enlarged the house by carrying out what one would imagine to be a most difficult, not to say hazardous operation; he excavated the rock under the house and round the foundations, thus forming a new lower ground floor; the structure being supported by numerous arches and pillars. It was more than just digging out a basement, as has been done at one or two other houses in Ulster; for the new ground floor is much higher than any basement would be; the operation made the house fully three storeyed. Entrance front of two bays on either side of a central three sided bow; the front also having end bows. Shallow Doric porch at foot of centre bow. Ground floor windows round-headed; those above rectangular, with plain entablatures over the windows of the original ground floor, now the piano nobile. Parapeted roof. The right hand side of the house is of ten bays, plus the end bow of the front; with a pilastered triple window immediately to the right of the bow in the piano nobile, balanced by another at the far end of the elevation. The left-hand side of the house is only of three bays and the bow, with a single triple window’ the elevation being prolonged by a two storey wing with round-headed windows. Various additions were built at the back of the house and at the sides during the course of C19; a ballroom being added by D.S. Ker, grandson of the David Ker who bought the estate. In 1837 ground floor there is an imposing entrance hall, with eight paired Doric columns, flanked by a library and a dining room. A double staircase leads up to the piano nobile, where there is a long gallery running the full width of the house, which may have been the original entrance hall. Also on the piano nobile is the sitting room with the splendid C18 plasterwork. Montalto was bought ca 1910 by 5th Earl of Clanwilliam, whose bridge refused to live at Gill Hall, the family seat a few miles to the west, because of the ghosts there. In 1952, the ballroom and a service wing at the back were demolished.”
7. Mount Stewart, County Down
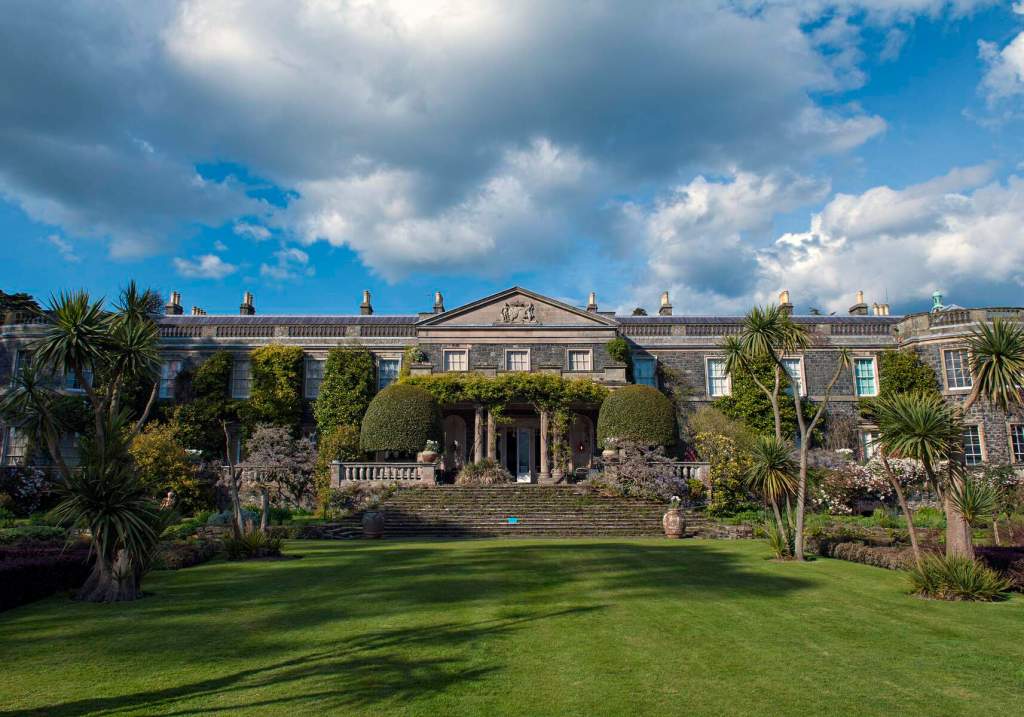

https://discovernorthernireland.com/things-to-do/mount-stewart-p675341 and https://www.nationaltrust.org.uk/mount-stewart
See my entry https://irishhistorichouses.com/2024/06/06/mount-stewart-county-down-northern-ireland-a-national-trust-property/
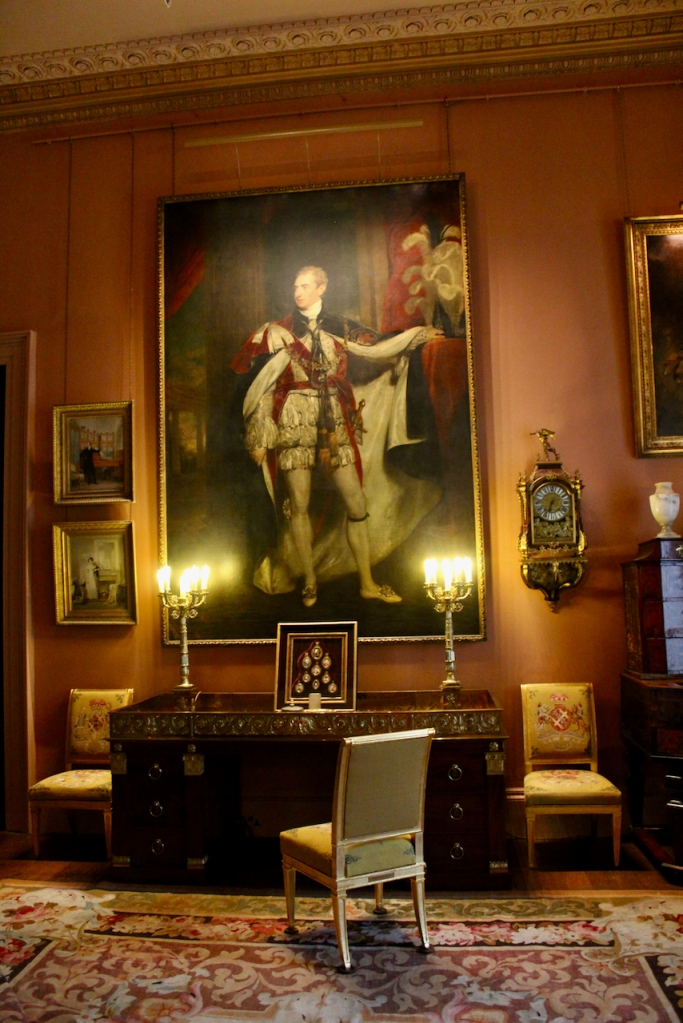
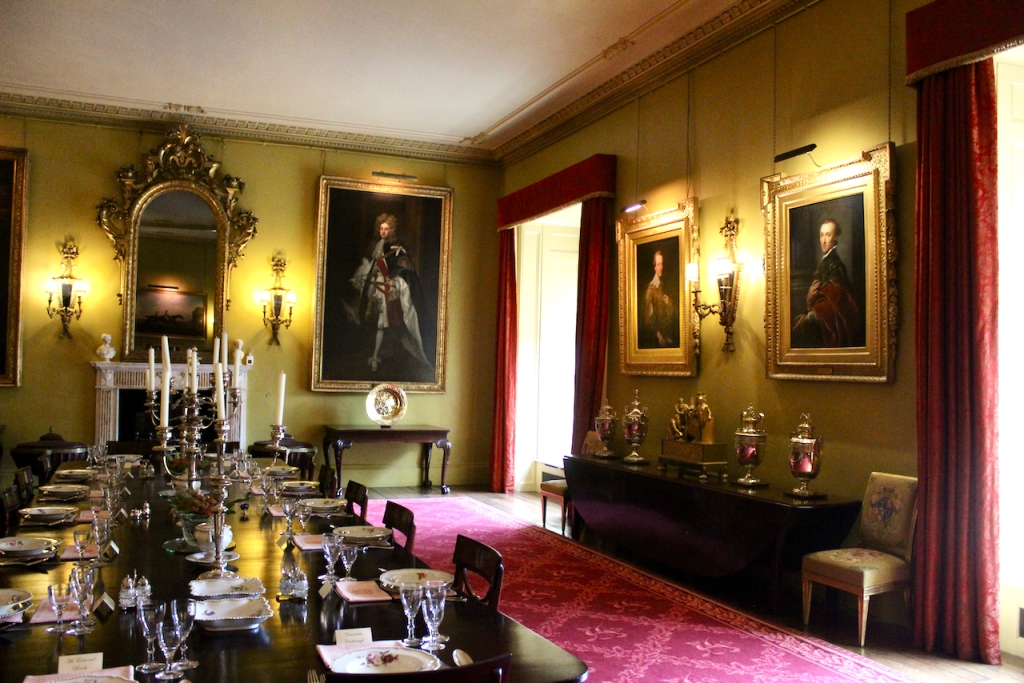
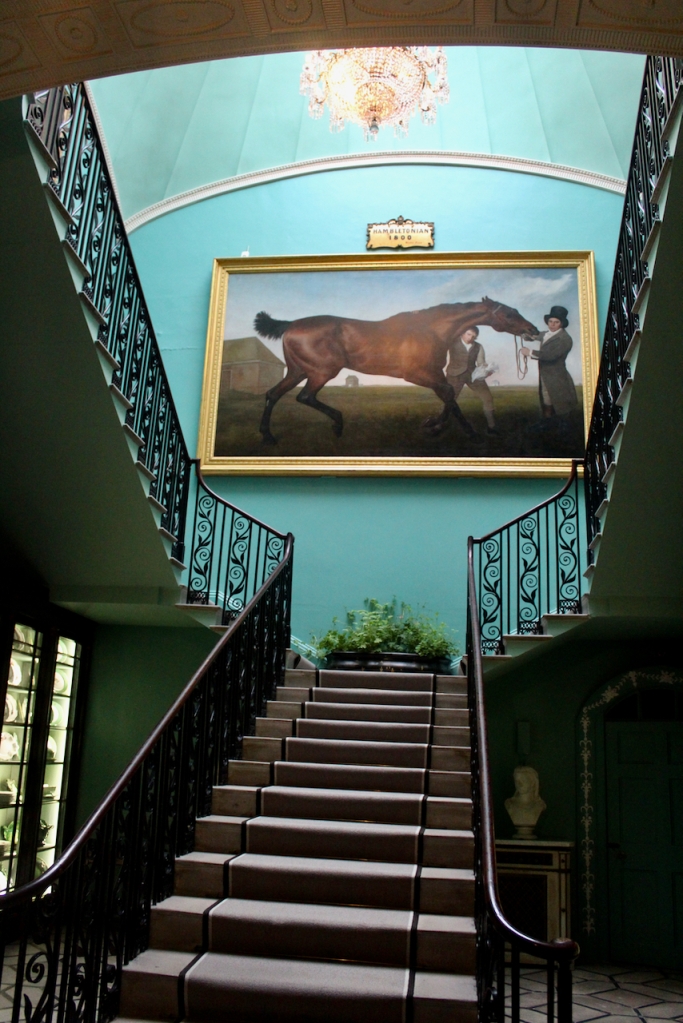
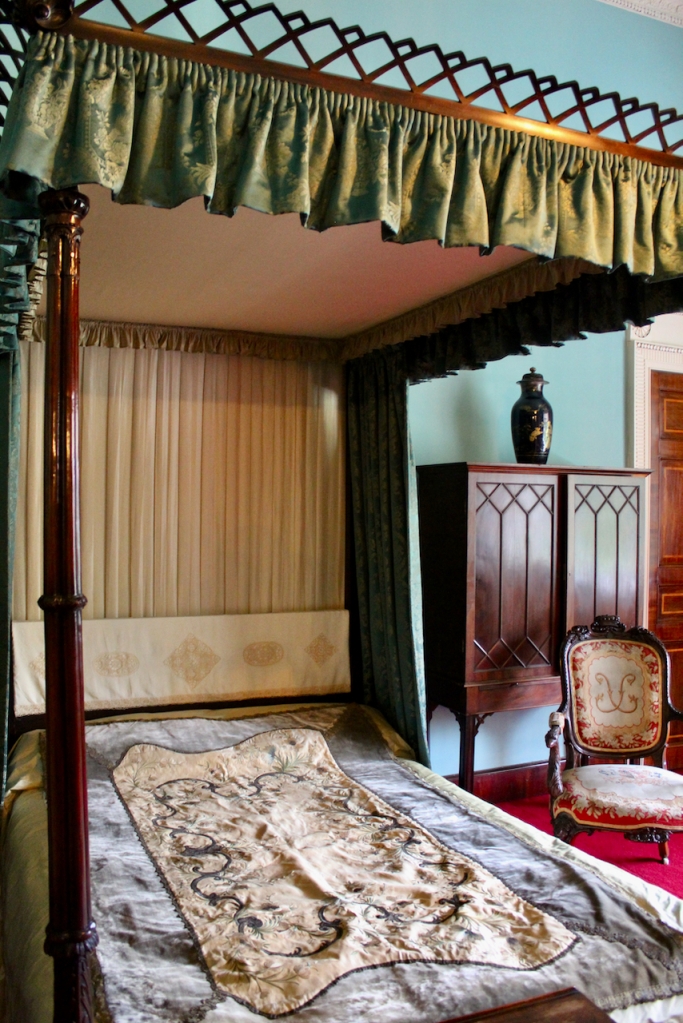
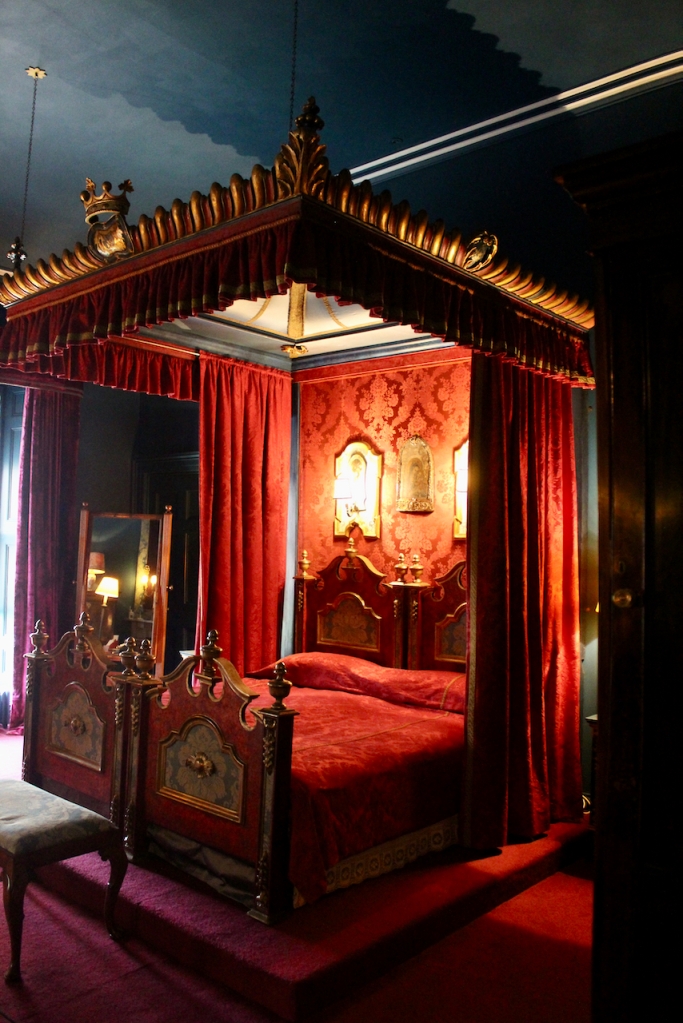






With twin painted and gilt panelled heads and ends inset with shaped reserves of blue brocade and surmounted by carved and gilt scrolls with turned vase shaped finials, the backboard covered in red figured silk damask, the side curtains of the same material, trimmed galloon. The domed canopy covered in blue silk trimmed with galloon and appliqued gilt carvings, the front and sides carved with gadrooning and leafage, centering on an armorial panel surmounted by a coronet, the whole raised on a plinth as per Londonderry House image of a figured walnut plinth, with box spring mattress, hair overlay and bedding. The bed was Lady Londonderry’s when she was in Londonderry House and was brought here in 1961 Lady Mairi slept in it in Londonderry House and Lady Rose was born in it in 1943, at Londonderry House. Photograph © Jennifer Winder-Baggot, www.irishhistorichouses.com
8. Newry and Mourne Museum, Bagenal’s Castle, County Down
https://discovernorthernireland.com/things-to-do/newry-and-mourne-museum-bagenals-castle-p690251

The Discover Northern Ireland website tells us:
“Bagenal’s Castle is a sixteenth century fortified house and adjoining nineteenth century warehouse. It houses Newry and Mourne Museum and Newry Visitor Information Centre.
“During restoration work on the Castle many original features were uncovered including fireplaces, windows, doorways, gun loops and a bread oven. These have been interpreted for the visitor and drawings were commissioned to illustrate how the various living quarters of the castle would have functioned in the sixteenth century. Highlights include a restored Banqueting Room which is used throughout the year for seasonal and family events.“During restoration work on the Castle many original features were uncovered including fireplaces, windows, doorways, gun loops and a bread oven. These have been interpreted for the visitor and drawings were commissioned to illustrate how the various living quarters of the castle would have functioned in the sixteenth century. Highlights include a restored Banqueting Room which is used throughout the year for seasonal and family events.
“The Museum’s diverse collections include material relating to prehistory, Newry’s Cistercian foundations, Ulster’s Gaelic order and the relationship with the English Crown; the building of a merchant town and the first summit level canal in the British Isles. You can also discover the history of the ‘Gap of the North’, the historic mountain pass between Ulster and Leinster located to the south of Newry. One of the key main exhibitions, ‘A Border Town’s Experience of the 20th Century’, examines local attitudes to major political and economic events of the 20th century. There are also permanent exhibitions on farming, fishing and folklore in the Mournes and South Armagh.”
9. Portaferry Castle, County Down
https://discovernorthernireland.com/things-to-do/portaferry-castle-p676311
The website tells us:
“Portaferry Castle is a 16th-century tower-house, built by the Savage family and prominently located on the slope overlooking Portaferry harbour within sight of Strangford and Audley’s Castles across the water. Simpler than the earlier ‘gatehouse’ tower house, it is square in plan with one projecting tower to the south where a turret rises an extra storey and contains the entrance and stair from ground floor to first floor.
There are three storeys and an attic, and like early tower-houses it has spiral stairs. However, like some later tower houses it lacks a stone vault as all floors were originally made of wood.
***THE CASTLE IS CURRENTLY CLOSED FOR REPAIRS AND WILL NOT OPEN THIS YEAR”
Places to stay, County Down
1. Barr Hall Barns, Portaferry, County Down – self catering
https://www.barrhallbarns.co.uk/
The website tells us:
“Barr Hall Barns are 18th Century period cottages in an outstanding tranquil location with panoramic views across Strangford Lough to the Mourne Mountains.
We are based just outside the seaside village of Portaferry, at the very southern tip of the Ards Peninsula, overlooking Barr Hall Bay which is protected by the National Trust.
With idyllic walking routes right at our doorstep, come escape to an area of natural outstanding beauty and enter the truly magical setting of Barr Hall Barns.“
2. Castle Ward, County Down – cottage hliday rental
Potter’s Cottage in farmyard:
https://www.nationaltrust.org.uk/holidays/the-potters-cottage-northern-ireland
and Castle Ward bunkhouse: https://www.nationaltrust.org.uk/holidays/castle-ward-bunkhouse-northern-ireland
Sleeps 14 people.
3. Culloden, County Down – hotel

4. Florida Manor, 22 Florida Road, Killinchy, Newtownards, Co Down, BT23 6RT Northern Ireland – self-catering
http://www.floridamanorni.com/cgi-bin/greeting?instanceID=1
and Florida Manor Gambles Patch, Hollow View and Meadow Green.
The website tells us: “Dating back to 1676, Florida Manor, an original Irish Georgian Estate has undergone sympathetic refurbishment. Within the estates original stone perimeter wall lies 200 acres of extensive landscaped grasslands, private lakes, walkways and bridal paths.“
Mark Bence-Jones writes in his A Guide to Irish Country Houses (1988):
p. 297. “(Gordon/IFR) A C18 house consisting of a three storey principal block with a recessed centre, linked to lower wings by curved sweeps with balustrades and pilasters. Projecting enclosed porch, also balustraded and with Ionic columns. quoins. Originally the seat of the Crawfords; passed by marriage to the Gordons C18. The house became ruinous in the present century but has been restored as two dwellings.”
5. Helen’s Tower, Bangor, County Down – Irish Landmark accommodation
https://www.irishlandmark.com/property/helens-tower/
“A tower with pepper-pot bartizans rising from a hill at the southern end of the demesne, completed 1862 to a design by William Burn. It was built in honour of his mother, Helen, Lady Dufferin, one of three beautiful and lively sisters who were the granddaughters of Richard Brinsley Sheridan; in a room near the top of the tower, lined with delicate Gothic woodwork, the walls are adorned with poems on bronze tablets expressing the love between mother and son; including a poem written specially for Lord Dufferin by Tennyson:
Helen’s Tower here I stand
Dominant over sea and land
Son’s love built me, and I hold
Mother’s love in lettered gold.”
And see Robert O’Byrne’s entry about it at https://theirishaesthete.com/2022/09/05/helens-tower/

6. Kiltariff Hall, County Down – B&B
https://www.kiltariffhall.co.uk
The website tells us: “Kiltariff Hall is a Victorian Country House on the outskirts of the small market town of Rathfriland. Built by our great-grandfather William Fegan in 1888, the house is set at the end of a short drive and is surrounded by mature oak, sycamore and pine trees. It is run myself, Catherine and my sister Shelagh who grew up in Kiltariff when it was a working farm. We are both passionate and knowledgeable about the Mourne area and believe that providing good locally produced food is key to ensuring guests enjoy their stay.“
7. Narrow Water Castle, apartment, Newry Road, Warrenpoint, Down, Northern Ireland, BT34 3LE – self catering
http://narrowwatercastle.co.uk
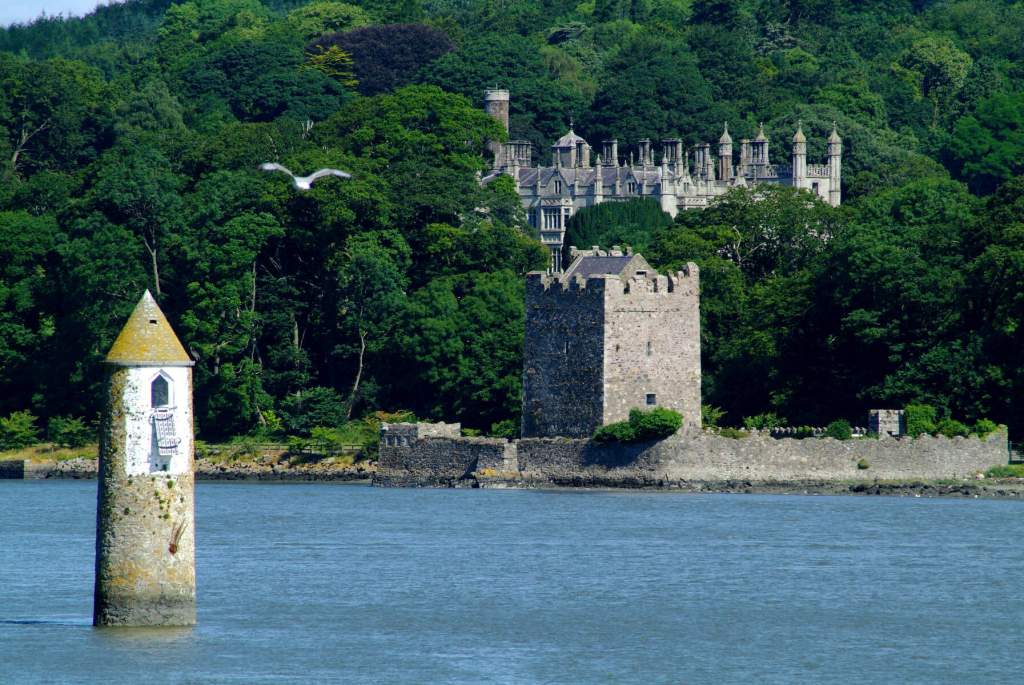

The website tells us:
“Narrow Water Castle is the private home of the Hall family who have lived at Narrow Water since 1670, originally in the Old Narrow Water Keep situated on the shoreline of Carlingford Lough which is now a national monument.
As a private home the castle is not open for public admission. It does however occasionally open its doors for weddings and exclusive events.
In 1816 construction began on the new Castle by Thomas Duff, a well-known Newry architect who also designed the Cathedrals in Newry, Armagh and Dundalk. The Elizabethan revival style castle is made from local granite and built next to the existing house, Mount Hall (1680). It was completed in 1836.
The self catering apartments are located in the original hub of the castle (Mount Hall), dating back to 1680. Mount Hall joins the Elizabethan revival part of the castle to the courtyard.“
Number 2: The apartment opens into an elegant open plan, living room and dining room with open fire. We have used several antique pieces of furniture to hint of times gone by. We are happy to provide logs if our guests wish to use the fire.
There are two spacious, beautifully furnished bedrooms, one of which is en-suite.
Number 6: This 2 bedroom luxury apartment is the perfect place to escape and unwind. Both bedrooms are en-suite. There is a grand open plan living /dining area with a unique feature skylight and exposed beams. The living area is adorned with antique furniture has a wood burning stove for cosy nights by the fire. The modern kitchen is fully equipped and the dining area seats six comfortably. A quality sofa bed allows this apartment to accommodate up to six guests. This apartment is on the first floor with access via the original stone staircase dating to the 1680s
8. The Old Inn, Bangor, County Down
Established in 1614!
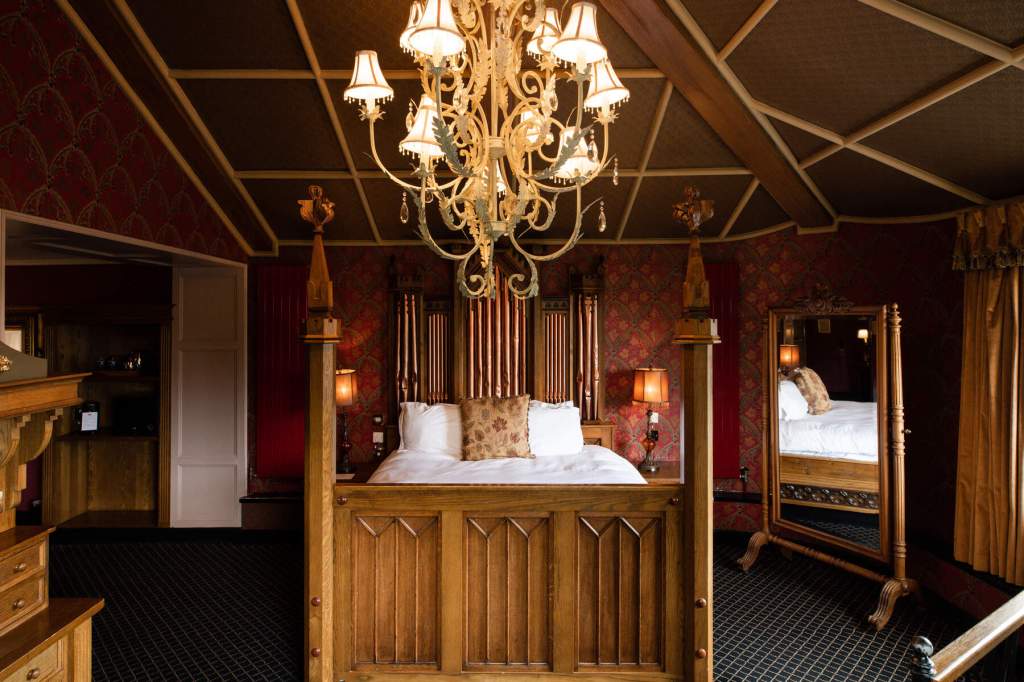

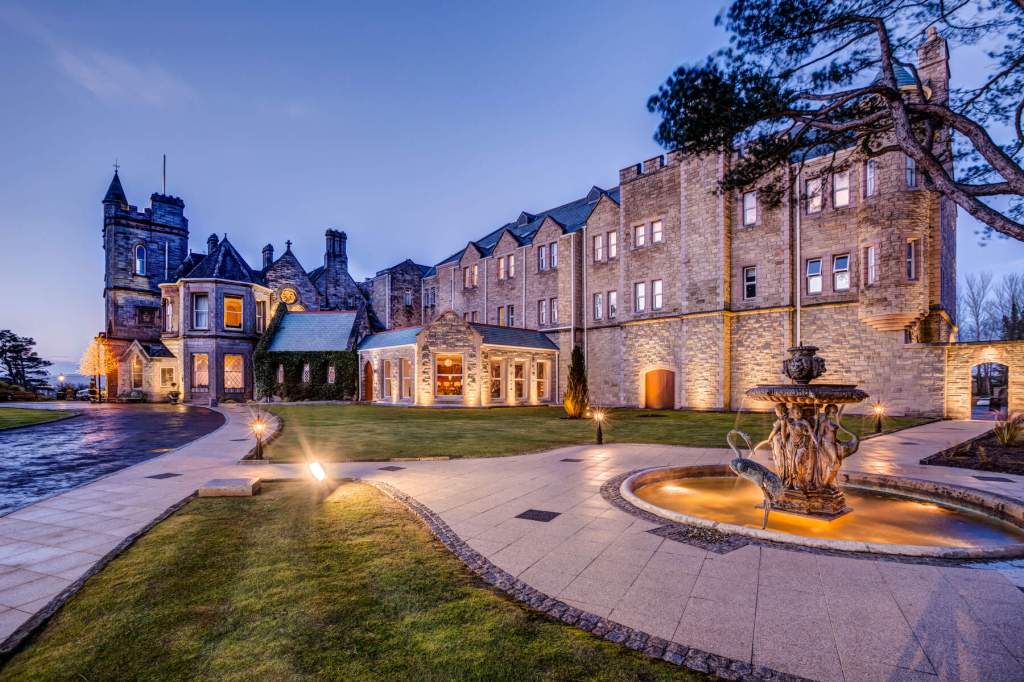
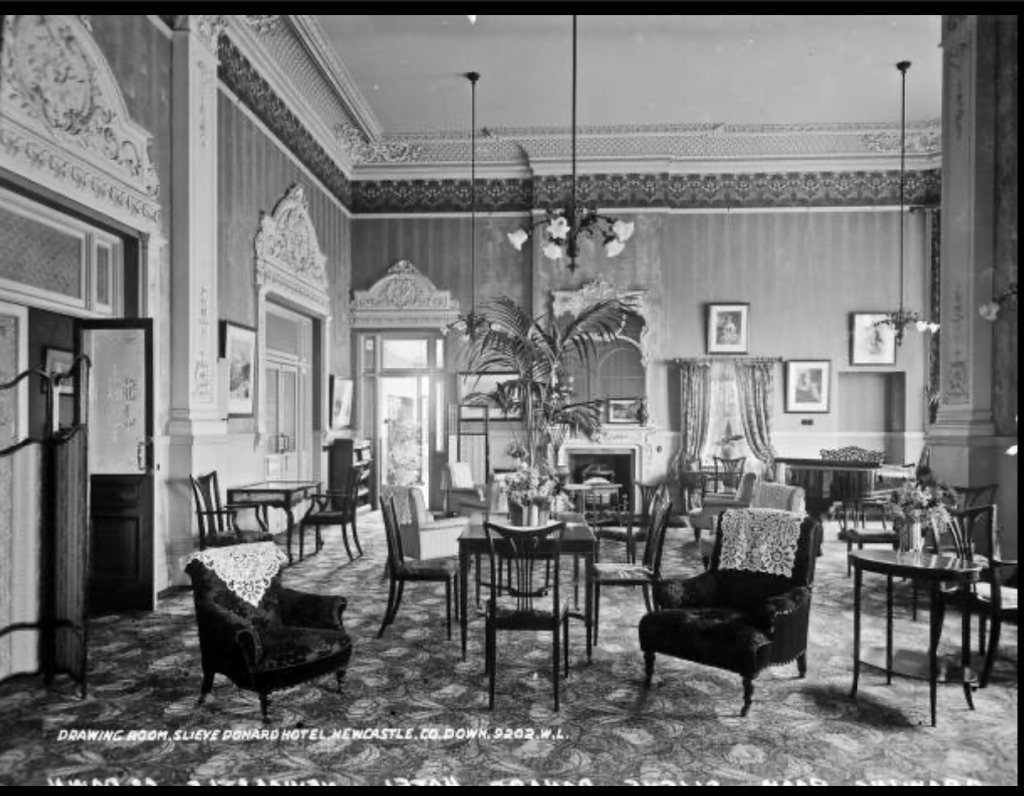
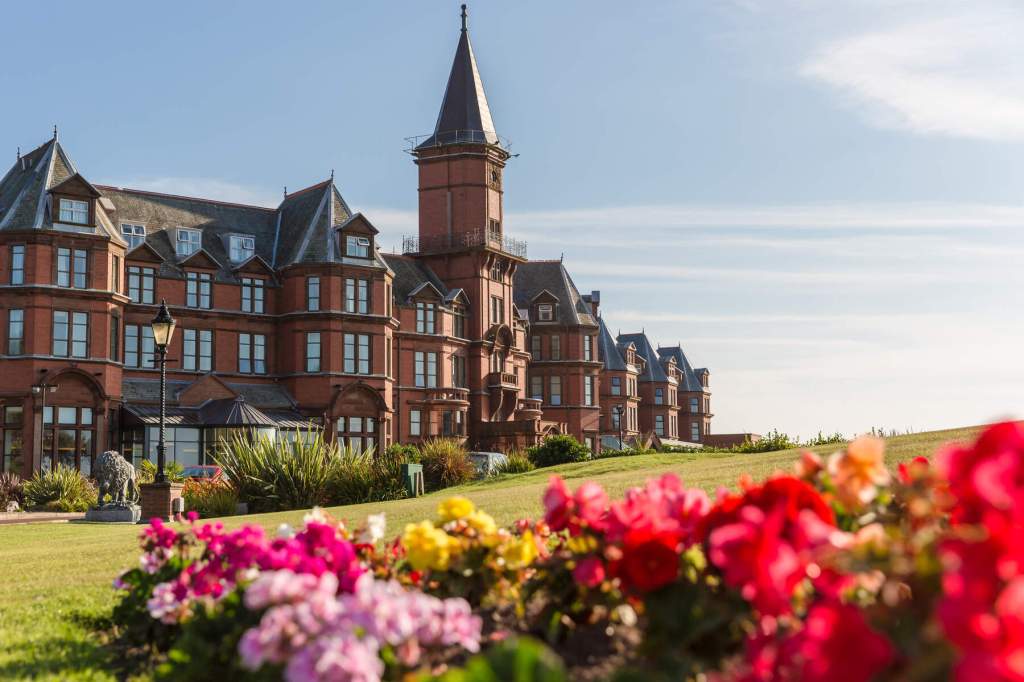
9. Slieve Donard hotel and spa, County Down €€
https://www.slievedonardhotel.com
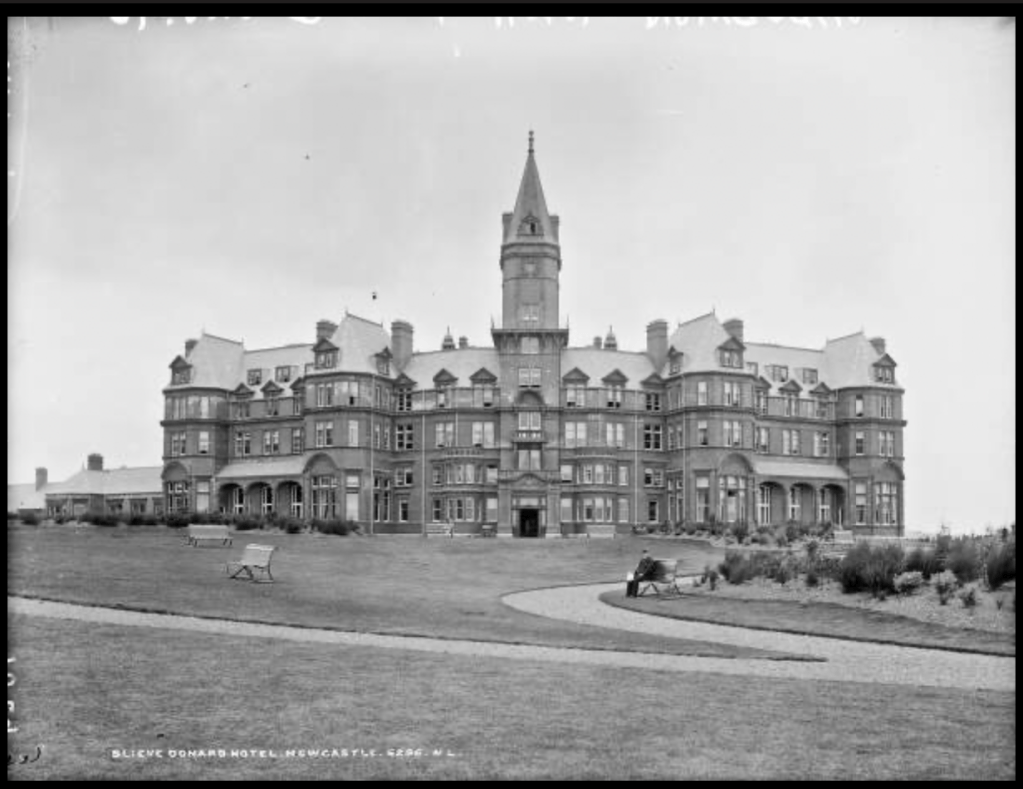

The website tells us: “Slieve Donard was originally built by the Belfast and County Down Railway as an ‘end of the line’ luxury holiday destination. Construction started in 1896 and was completed and officially opened on 24th June 1898 at the cost of £44,000. It was one of the most majestic hotels of its time and was almost self-sufficient with its own bakery, vegetable gardens, pigs, laundry and innovatively a power plant, which also provided electricity for the railway station.
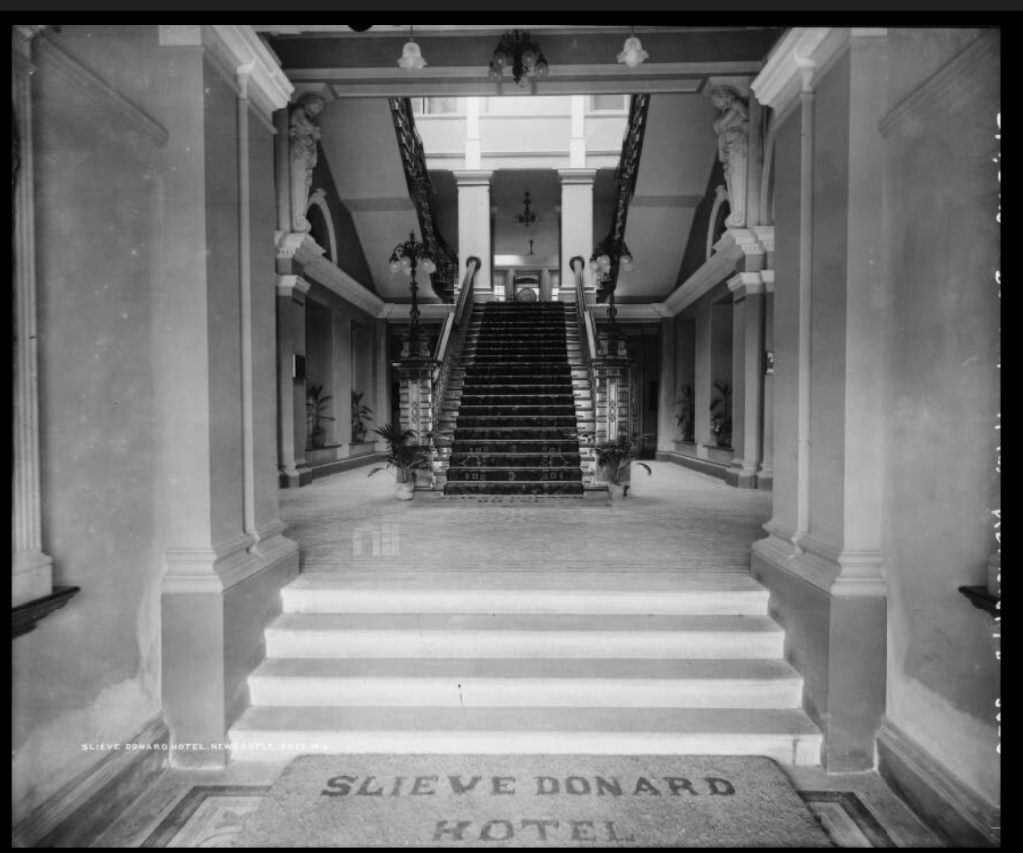
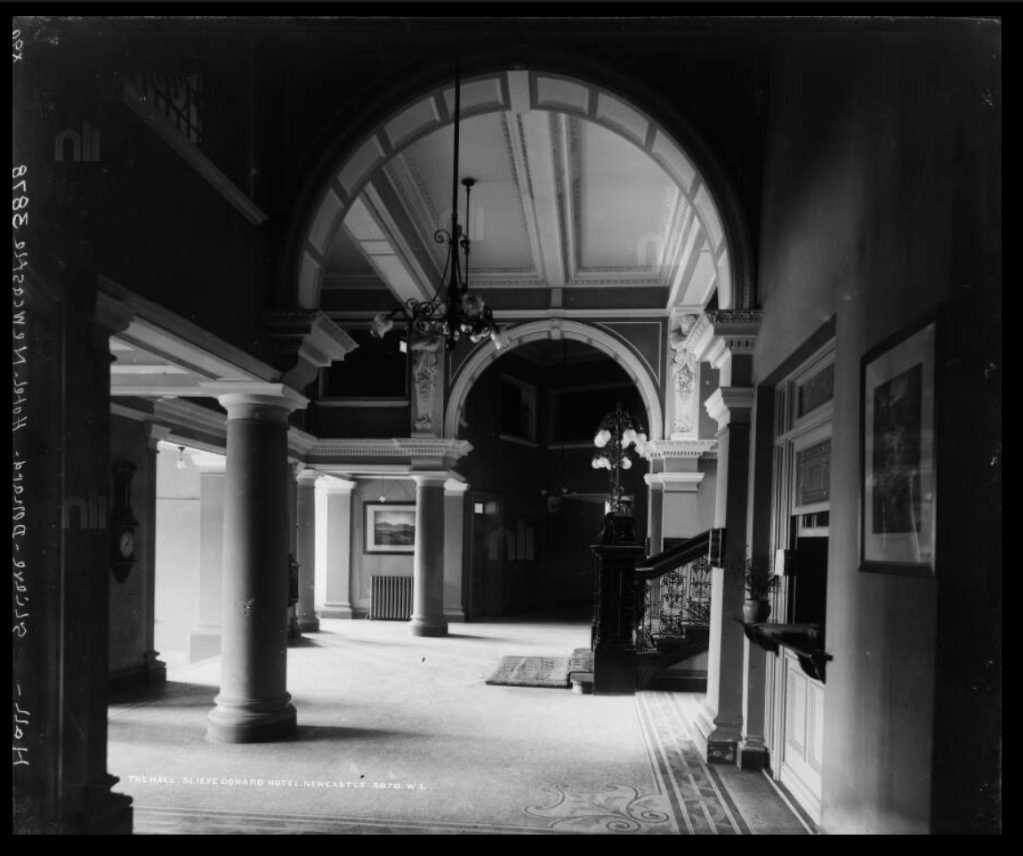


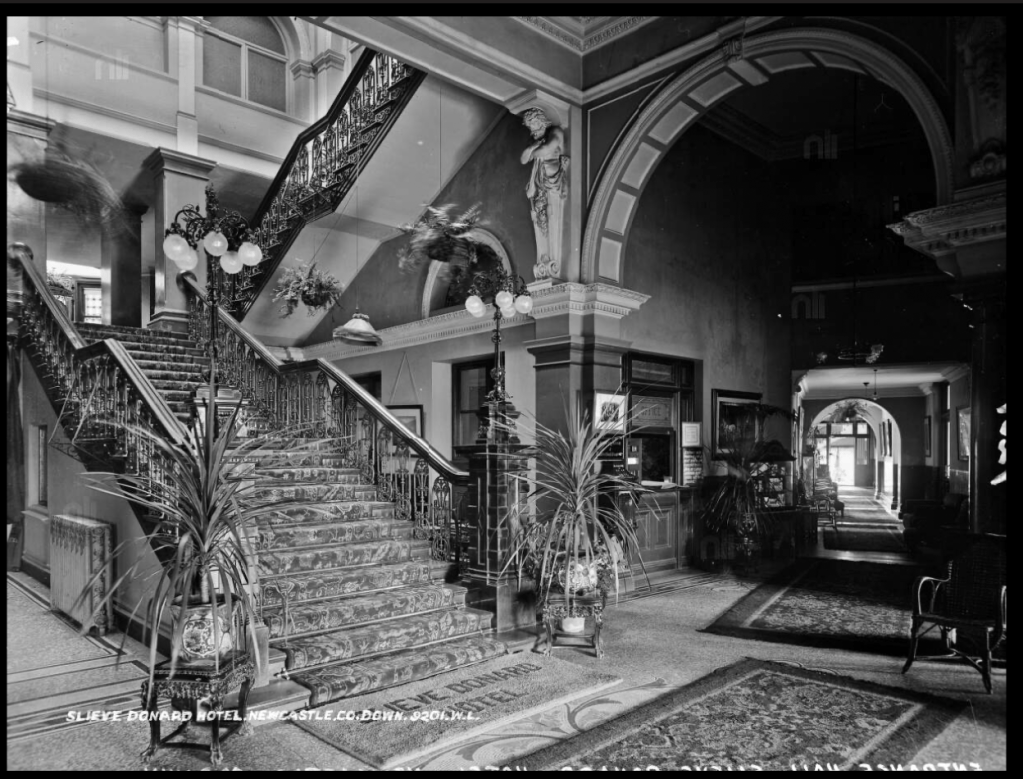
Slieve Donard typified the idea of Victorian grandeur and luxury with its Drawing Room, Grand Coffee Room, Reading and Writing Room, Smoking Room, Billiard Room and Hairdressing Rooms—you can’t help but conjure up scenes of great style and decadence. ‘One could even partake of seawater baths, douche, spray, needle and Turkish baths all provided by an electric pump straight from the sea.
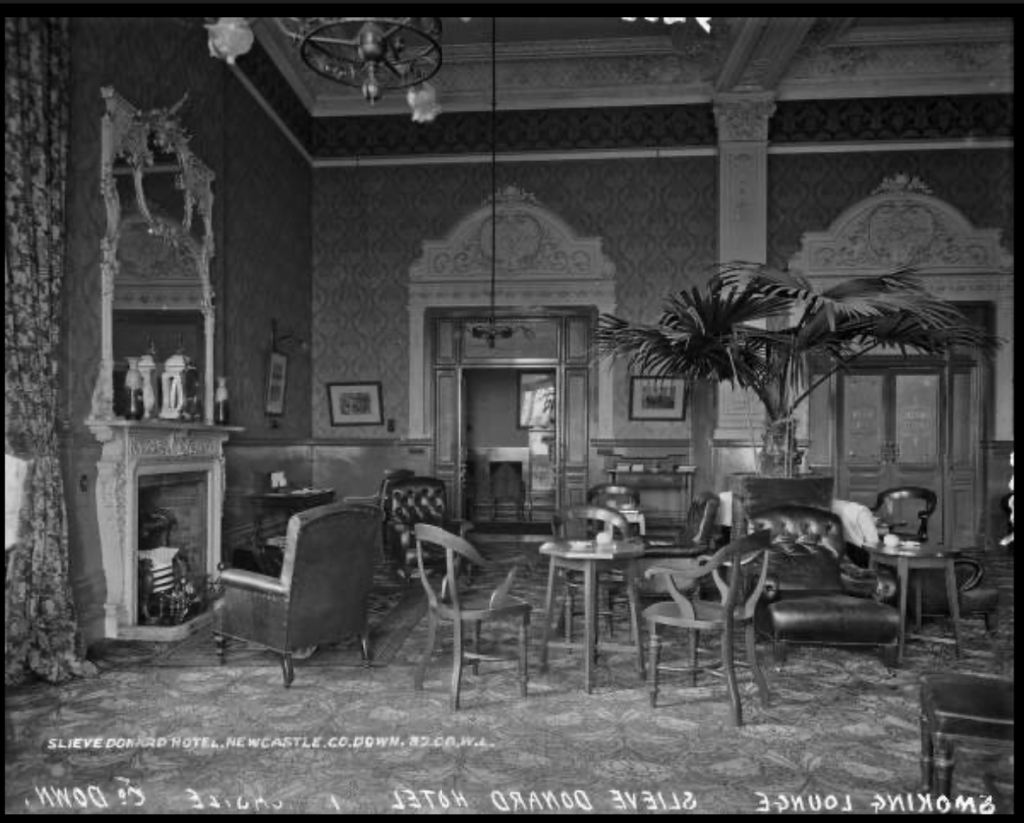
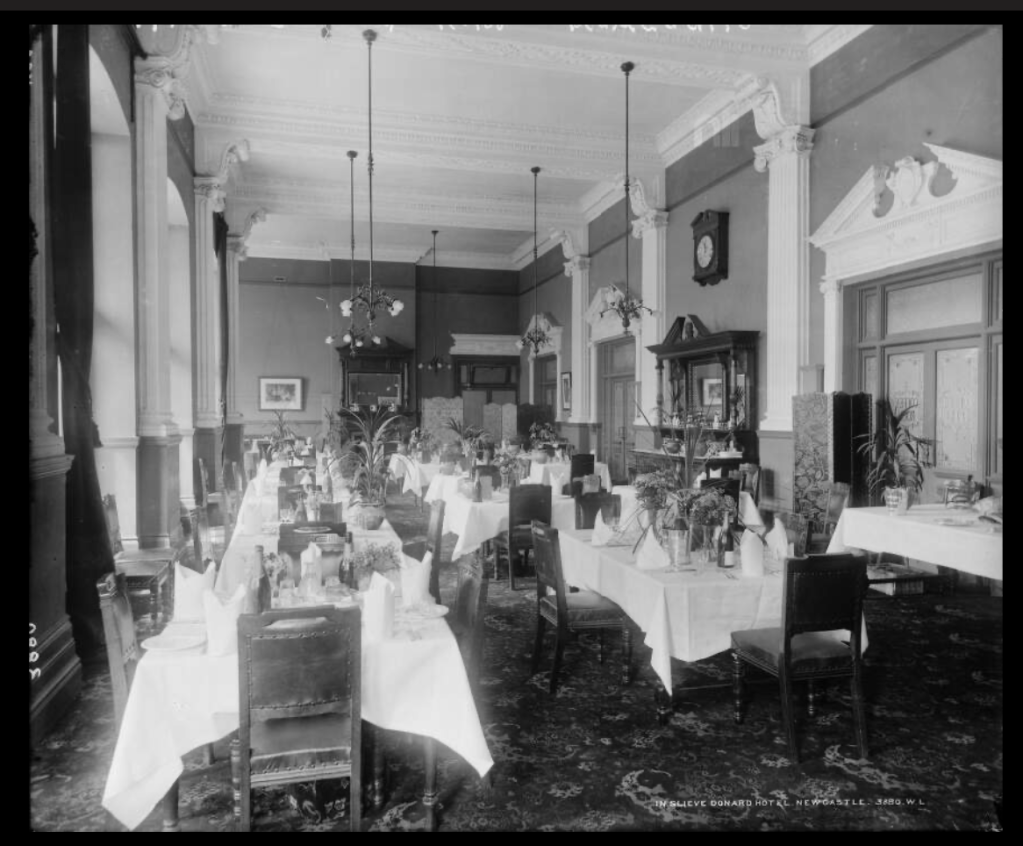
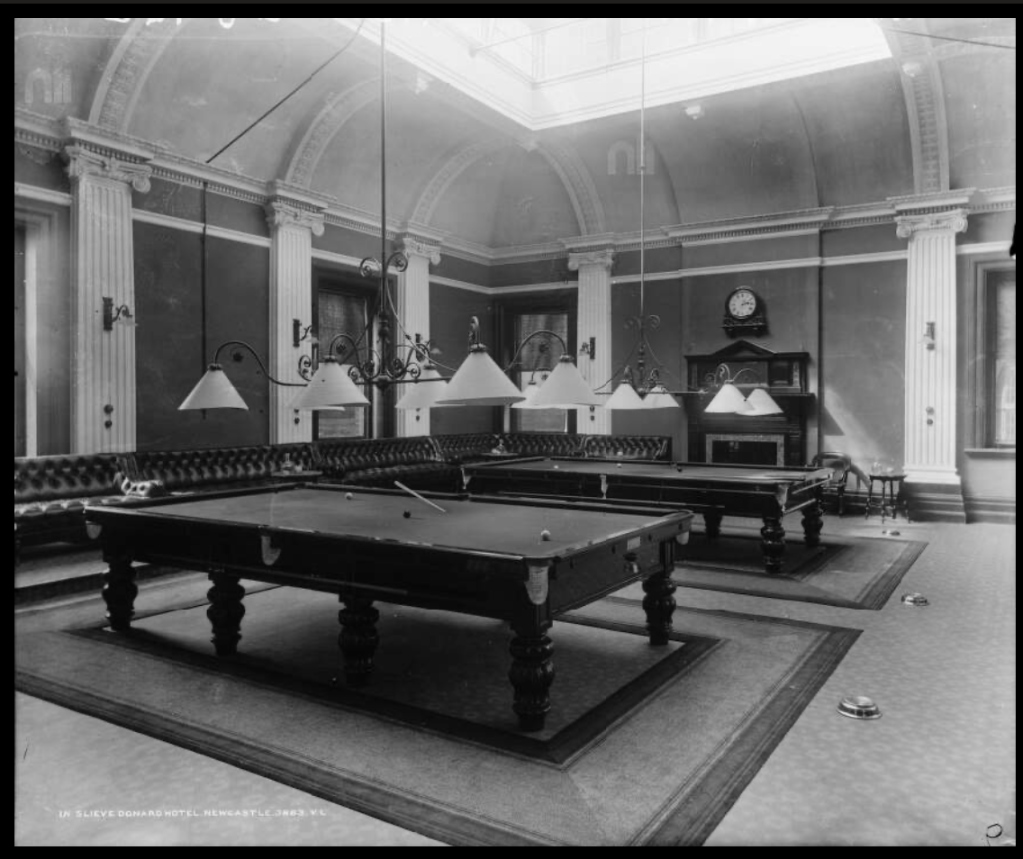




In 2021, Adventurous Journeys (AJ) Capital Partners acquired Slieve Donard Resort and Spa, which will become the first Marine & Lawn Hotels & Resorts property in Northern Ireland and the fourth hotel in the collection.“

9. St John’s Point Lighthouse Sloop, Killough, County Down – Irish Landmark accommodation
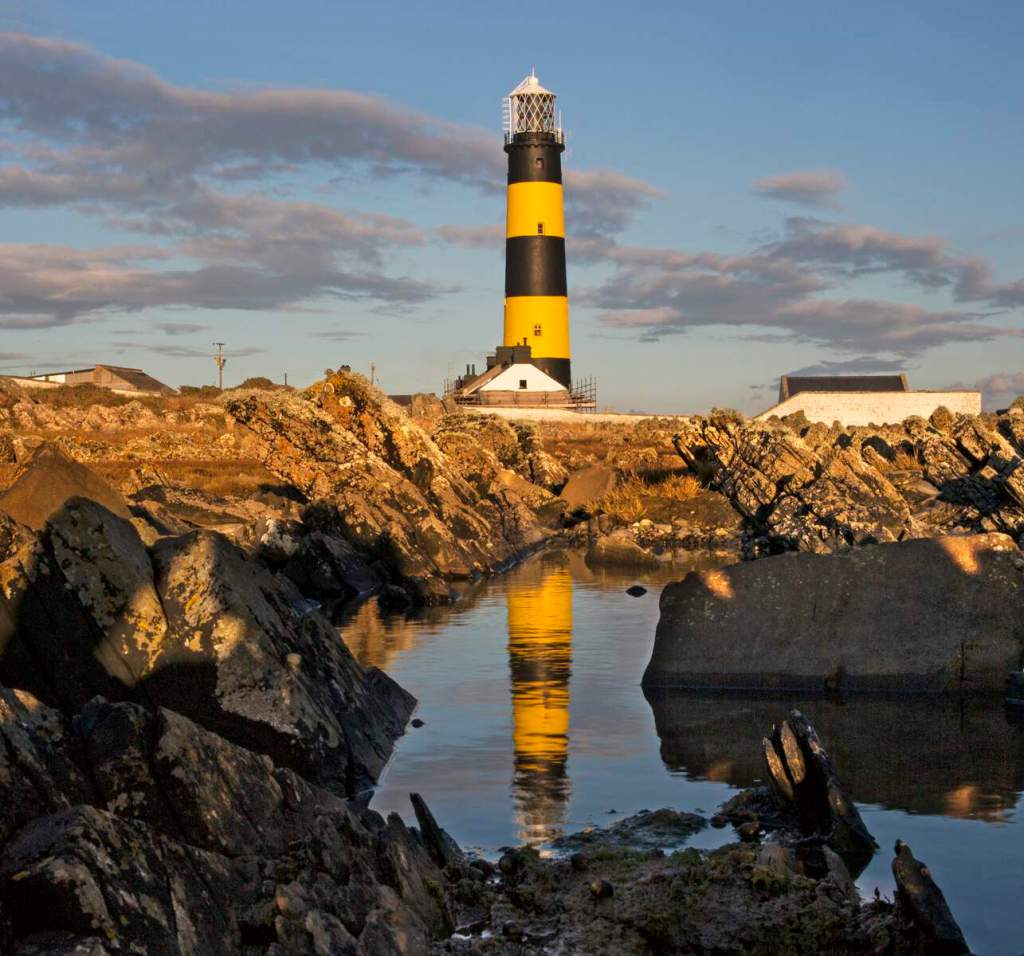

JP Ketch and JP Sloop. Each sleeps four people, From £328 for 2 nights.
10. Tullymurry House, Tullymurry road, Donaghmore, Newry, County Down – Irish Landmark accommodation
“This fabulous period home is a historic Irish country farm house. Set on wonderful gardens including an orchard, Tullymurry House is an ideal base for golf, fishing, hiking, walking, beach, and other outdoor pursuits.“
11. Tyrella, Downpatrick, County Down, BT30 8SU – B&B accommodation
https://www.tyrellahouse.com/the-rooms
The website tells us:
“Tyrella House is a luxury B&B and wedding venue located in the heart of picturesque County Down, with its necklace of pretty fishing villages. A fine 18th century house surrounded by glorious wooded parkland with its own private beach just a short walk from the house, Tyrella offers a tranquil and relaxing getaway.
Tyrella House has been owned by the Corbett family for over 60 years, and was bought by John Corbett after the Second World War to train race horses.
His son, David Corbett began running B&B in the 1990s, which continues to this day. In 2020, the day to day running of the B&B was taken over by his son, John and his wife Hannah.“
Whole house County Down
1. Ballydugan House, County Down (weddings)
“At Ballydugan we can provide accommodation and an oasis of relative calm for the Bride’s immediate family. Also if absolute adherence to tradition is important then we have Ballymote Country House nearby, where we can ensure that the paths of the Bride and Groom will not cross prior to the wedding.“
2. Drenagh Estate and Gardens, County Down (wedding venue)
It tells us “Nestled in beautiful parkland and surrounded by our gardens, you will find our grand Georgian Mansion House which is perfect for weddings, family get togethers, corporate events and much more.“
The website tells us the history of the McCausland family who own the property:
“The family name McCausland goes back more than 900 years to an O’Cahan named Anselan, son of Kyan, King of Ulster. Anselan was forced to leave Ireland in about 1016 on account of his share in a ‘memorable stratagem where he and other young Irishmen dressed in women’s attire surprised and slaughtered their Danish oppressors’ (The Vikings). When Malcolm II of Scotland heard of Anselans feats he invited him to become his Master of Arms and ‘bestowed ample lands upon him in The Lennox’.
Twelve generations later, in the 1540s, his descendant Baron Alexander McAuslane returned to Ulster with his brother Andrew and settled in the Strabane area. The first McCausland to live at Drenagh (then called Fruithill) was Robert McCausland, Alexander’s grandson. Robert was bequeathed the Estates when he married the daughter of William Conolly, a wealthy self-made man and speaker of the Irish Parliament. [I don’t think this can be correct as William Conolly didn’t have a daughter]
Robert named his first son Conolly in reverence to his father-in-law; the name is still used in alternate generations to this day. A large painting of Robert and his family now hangs in the dining room at Drenagh. The first Conolly married the heiress Elizabeth Gage from Bellarena (five miles up the coast) and had a son, Conolly, who also formed another lucrative union with Theodosia Mahon from Strokestown House, Co. Roscommon [see my entry on Strokestown].
It was their son Marcus McCausland (1787-1862) who was responsible for commissioning Sir Charles Lanyon to build the present house. The former house (Fruithill) can be seen through a window painted in the portrait of Robert McCausland and his family. Marcus and his wife, Marianne, nee Tyndall from The Fort at Bristol, produced an heir Conolly Thomas(1828-1902). A delightful portrait of him dressed in his Eton cricketing clothes also hangs in the dining room at Drenagh.
Conolly Thomas’s son Maurice Marcus lived through both the best and worst of times at Drenagh as in 1902, through the Irish Land Acts; the Government compulsorily purchased 75% of the Estate. Drenagh was lucky; many Irish Estates were taken off their owners in their entirety. Some say this was no bad thing, as landlords the Irish landed gentry could be brutal in their treatment of their tenantry, indeed some were burnt out before they could be bought out.
Conolly Robert, Maurice’s son, fought in the 2nd World War and was so profoundly affected by what he experienced that he changed his Faith to Catholicism. This he did despite knowing he had signed a codicil to his fathers will barring him from inheriting should he become a Catholic. The will was contested but it was found that although the codicil applied to Conolly Robert, it did not do so to any of his direct descendants. So, on his death in 1968, his son Marcus inherited Drenagh.
Sadly four years later in 1972 Marcus was shot dead by the IRA.
Currently Marcus’s son Conolly Patrick lives at Drenagh.“
3. Tullyveery House, County Down – holiday rental and weddings
The website tells us:
“Tullyveery House is an exclusive and intimate wedding and private events venue nestled in the rolling drumlins of County Down, convenient to Belfast. The family-owned Georgian House and Victorian courtyard area surrounded by mature private grounds and gardens provide a stunning rural backdrop overlooking the Mourne Mountains.
Tullyveery House remains a family home and working farm. The Georgian house, built between 1825 and 1828, was extended between 1867 and 1890.
Thomas Heron (1711-1776), one of the grandsons of a trio of brothers, decided in 1752 to move from his home at Killinchy and rent land and a house in Tullyveery townland, near Killyleagh.
Surviving farm survey maps made in 1760 show a dwelling and a farm of over 100 acres, the majority of which was let out to under-tenants. The family continued to expand and prosper, by growing flax and having it spun into thread in the local area, prior to carting to Belfast.
Thomas had a son, Francis (1750-1810), who was raised at Tullyveery, decided to move his household to an existing and somewhat better quality house at Ardigon townland, about a mile away, leaving Tullyveery as the ‘junior’ house. The Tullyveery freehold was subsequently bought in 1804.
Thomas’s son, James (1785-1839), inherited Tullyveery in 1816 and, as a 31 year old bachelor, then built between 1825-1828 the Georgian house that stands there today. In 1866-1867, his son, also called James, eventually demolished the remains of the single-story thatched house and used the square-cut stone masonry to face the existing courtyard buildings, now being used today to host weddings and events. A large three-story Victorian rear extension was finally added in the 1890s.
More recently, in 1973, the custodianship of Tullyveery passed to Colin Heron, from his father. Colin’s career resulted in him spending extended periods of time away from Tullyveery during which Michael, Colin’s brother, maintained the house and grounds, and operated a working farm. Colin returned to live in Tullyveery permanently in 2000. In 2012 he decided to diversify from farming. After much research and consideration, he decided to offer a private alternative to a hotel wedding and opened the home and grounds to couples for weddings and events. Colin also worked with TV’s Apprentice Nick Hewer as he travelled around Northern Ireland helping farms diversify on the BBC programme ‘The Farm Fixer’, which spurred him on to pursue this new path for Tullyveery.
In 2019 the custodianship of Tullyveery was passed down to the next generation and Charles (Colin’s nephew) is looking forward to taking Tullyveery from strength to strength. However, the vision for, and philosophy of, Tullyveery has not changed and you can be assured of the same high standards, seamless weddings and memorable parties that Tullyveery has become renowned for.
The latest project at Tullyveery has been to convert our private Orchard Garden into a space suitable for ceremonies, receptions and parties. Charles remembers sneaking into the Orchard as a child to ‘steal’ apples and to go into the fruit cage to pick fresh raspberries and gooseberries. It is fantastic to now be able to share this space with our guests while also adding a much needed covered garden area to the list of spaces available.
[1] Ireland’s Content Pool, https://www.irelandscontentpool.com/en
Text © Jennifer Winder-Baggot, www.irishhistorichouses.com