Happy New Year! My best wishes for the year ahead. I hope it will bring many exciting house visits.

2026 Diary of Irish Historic Houses (section 482 properties)
To purchase an A5 size 2026 Diary of Historic Houses (opening times and days are not listed so the calendar is for use for recording appointments and not as a reference for opening times) send your postal address to jennifer.baggot@gmail.com along with €20 via this payment button. The calendar of 84 pages includes space for writing your appointments as well as photographs of the historic houses. The price includes postage within Ireland. Postage to U.S. is a further €10 for the A5 size calendar, so I would appreciate a donation toward the postage – you can click on the donation link.
€20.00

donation
Help me to pay the entrance fee to one of the houses on this website. This site is created purely out of love for the subject and I receive no payment so any donation is appreciated!
€15.00
A tour of Lambay Castle is expensive so I don’t think Stephen and I will be going any time soon, so I thought I would publish an entry about it today.
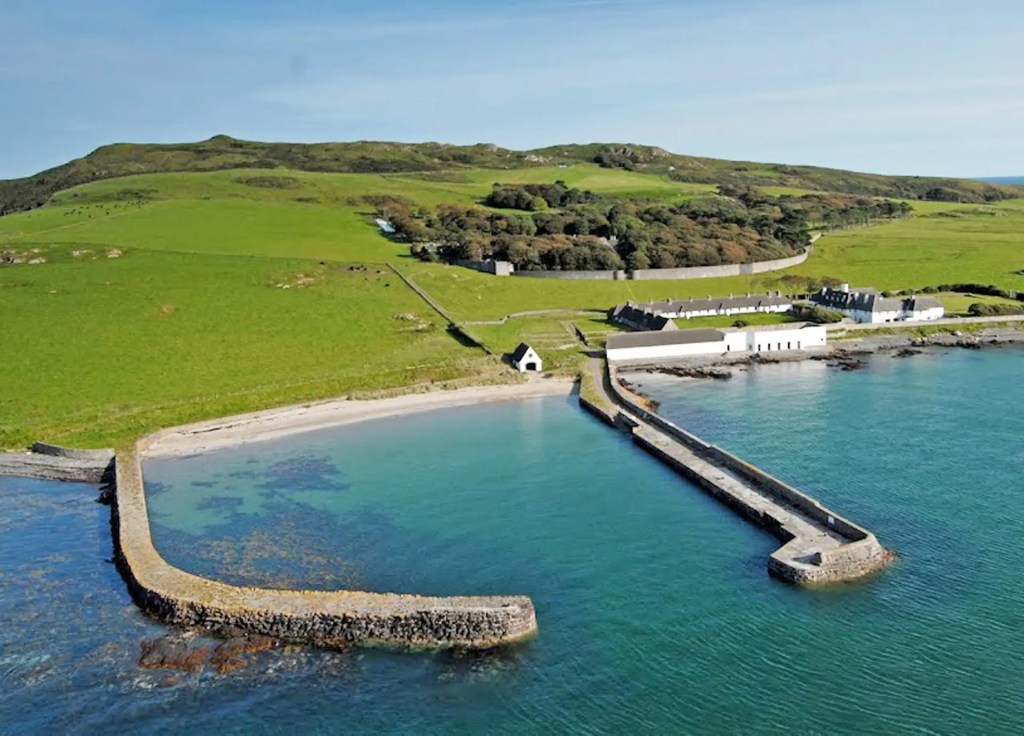


The island is owned and protected today by the Revelstoke Trust and daily management lies in the hands of Alex Baring, 7th Baron Revelstoke, and his family.
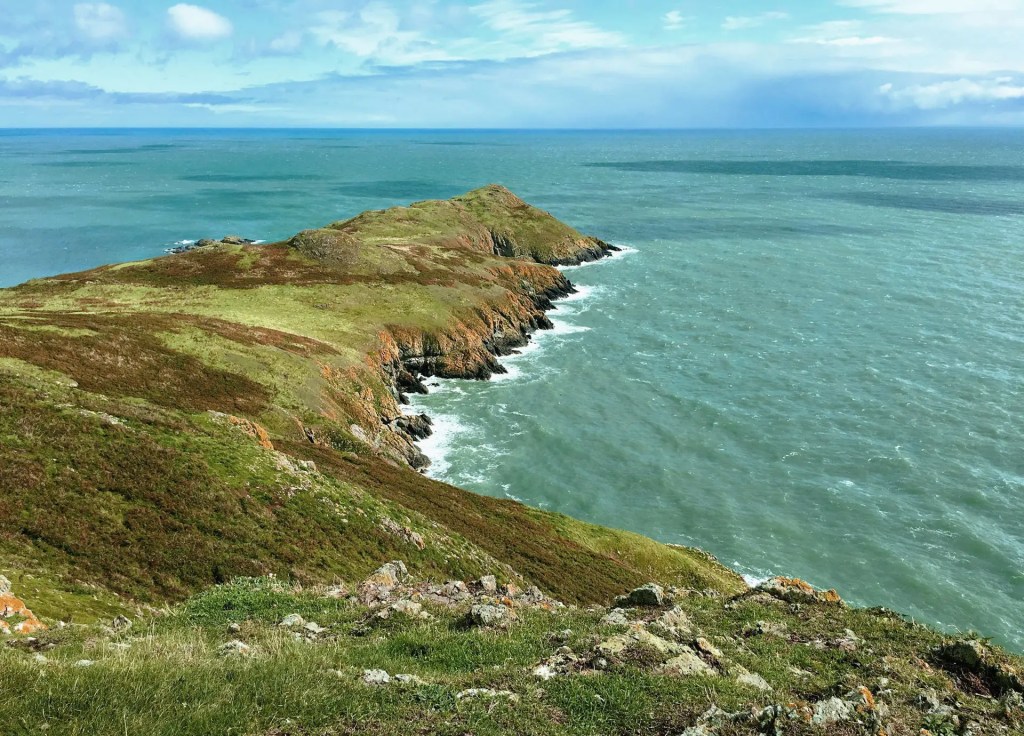
The castle on Lambay Island is privately owned but can be rented for accommodation, and there is other accommodation on the island. One can also visit the island on a day trip but the castle is not open to visitors unless booked in advance on the website.
www.lambayisland.ie
(Tourist Accommodation Facility)
Open for accommodation: April 1- September 30 2026
The website tells us that it the largest island off the east coast of Ireland and the largest privately owned island in North-West Europe. The island is home to seals and puffins, with deer and wallabies that were originally imported. Nesting birds include Fulmars, Guillemots, Herring Gulls, Kittiwakes, Manx Shearwaters and Puffins, while Greylag Geese are common winter visitors.
The island’s farm produces organic meat from sheep, deer and wallabies. Energy on the island is provided by a wind turbine and solar panels, and water is from a natural spring.

The island has an ancient history. The website tells us:
“Its early history is obscure but, like many other small islands, it attracted saints, hermits and pirates. It is thought to be one of the first few places where Viking raiders landed and proofs of its prehistoric history and early modern settlement were found around the harbour which date from the 1st century AD. Excavations also revealed Iron-Age graves dating back to circa 500 BC.”
St. Columba may have established a monastery on the island as early as the sixth century.
In 1181 the island was granted by Prince John (later king) to the Archbishops of Dublin, who received rents and tithes from the island.
To prevent piracy or invasion of the mainland, a license was granted to build a fort in the early 1500s. The structure built may may have formed the core of the castle still surviving when Cecil Baring later purchased the land. John Challoner (d. 1581), who was the first Secretary of State for Ireland, appointed by Queen Elizabeth I in 1560, agreed to build a village, castle and harbour on the island. The website tells us that he set up mines for copper and silver on the island, though it is not clear how successful this was, and bred falcons.
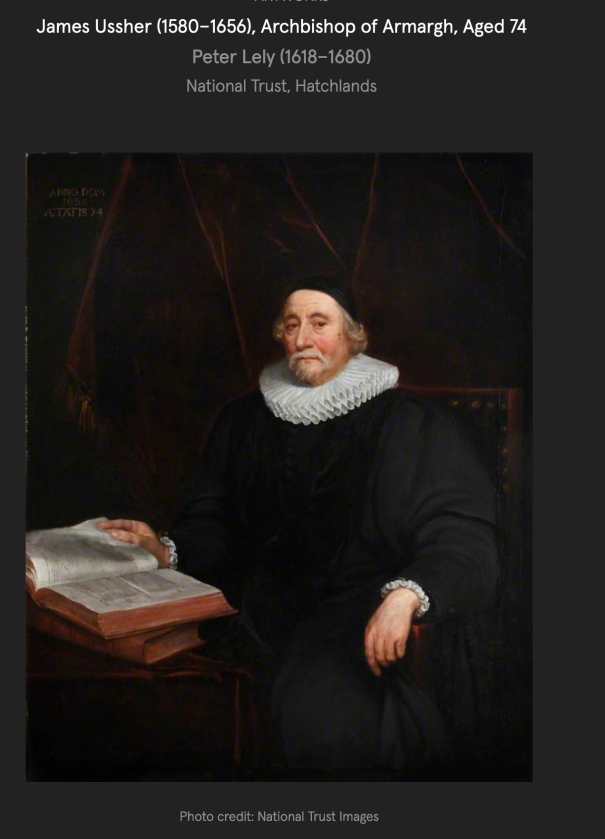
The island passed by marriage to the Ussher family in 1611. James Ussher (1581-1656) is the cleric famous for calculating that the earth was created around 6 pm on 22 October 4004 BC.

Sean O’Reilly tells us in his Irish Houses and Gardens. From the Archives of Country Life (published by Aurum Press Ltd, London, 1998) that:
“Weaver’s first article on an Irish house already showed clearly his concern for disposing of unauthenticated traditions. Among those he corrected was the presumption, promulgated in Samuel Lewis’s Topographical Dictionary of 1837, that the island was granted by Queen Elizabeth to Archbishop James Ussher, a figure famous for dating the creation of the world to 4004 BC on the basis of a chronology of the Old Testament. Weaver pointed out that the island was in fact held by Ussher’s cousin, William. Despite many vicissitudes, Lambay Island remained in possession of the Usshers from 1551 to 1804, from which time no significant work was done on the castle until the arrival of Baring.” [1]
The website tells us that the island was used as a Prisoner of War camp for over 1,000 Irish soldiers during the Williamite war after the Battle of Aughrim.
In 1805 the island was inherited by William Wolseley and in 1814 it was acquired by the family of Richard Wogan Talbot, 2nd Baron Talbot of Malahide. They built a school and a Catholic chapel on the island. The chapel was later renovated by Lutyens to resemble a Doric temple and the school no longer exists.
James Considine sold Portrane House and purchased Lambay in 1888. Count Considine set about developing the island as a hunting estate and was the first man to introduce deer onto the island.

In 1904, Cecil Baring, later the 3rd Baron Revelstoke, and his wife Maude Lorillard bought the island. Baring was a classical scholar and naturalist as well as former director of his family’s New York office of Barings Bank. The website tells us:
”In early 1904, with Maude heavily pregnant, Cecil went to investigate Lambay; he found a small line of cottages occupied by coastguards, a chapel, a walled garden, a dilapidated old fort and a magnificent wealth of wildlife. It was an intoxicating mixture.
”The first task facing the Barings was the repair of the castle and they refitted a heavy lugger, the Shamrock, to carry the necessary materials to the island. The Shamrock (version 3.0) is still in use today as Lambay’s main cargo boat and is used to transport the sheep and cattle as well as bulkier materials and equipment for the off-grid energy system.“
Baring hired Edward Lutyens to renovate the property. The website tells us:
”Lutyens was utterly delighted by Lambay and the couple, and the visit sparked a warm friendship between the three of them that would last throughout their lives. Lutyens extended the Castle masterfully and by 1910 it was a beautiful refuge for Cecil and Maude, surrounded by an impressive circular wall, which Lutyens nicknamed “The Ramparts Against Uncharity“.
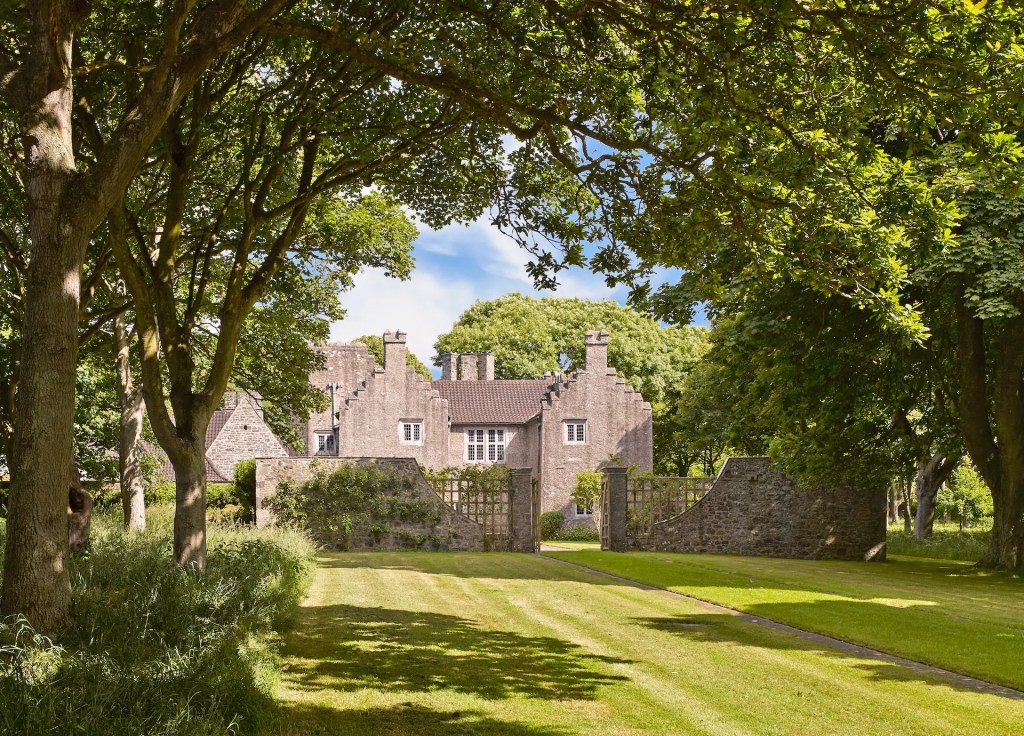

Sean O’Reilly describes the work of Lutyens:
p. 30. “By the time of Lutyen’s arrival much original fabric had deteriorated, and he was required to rebuild in part, though he retained triumphantly the ancient mood. A new service range was necessary, discreetly located off a corner of the castle and set into the ground so as not to dominate the main castle. Lutyens also ensured the prominence of the medieval fabric by deciding not to repeat the leitmotif of the original – the stepped gables – in the new work. Instead he used steep sweeping tiled roofs broken by dormers, gables and stacks.” [1]



The Historic Houses of Ireland website describes the residence:
“Today the three-bay centre of the north-west front, which faces a bastion gateway in the Rampart Wall, is flanked by two full-height projecting bays, each with crow-stepped gables and tall chimneys. Lutyens attached a wing to provide guest accommodation at the northeastern corner and regarded the “link between the two buildings as one of his most brilliant architectural coups” since the castle, which appears single storied on this front, continues to dominate the two-storey wing. The castle and the farm buildings, and the walls of the much enlarged gardens were built in grey-green Lambay stone, with grey pantile roofs, and form a sequence of courts, walled gardens and enclosed yards that give the impression of a small hamlet nestling for protection beneath the castle walls.” [2]
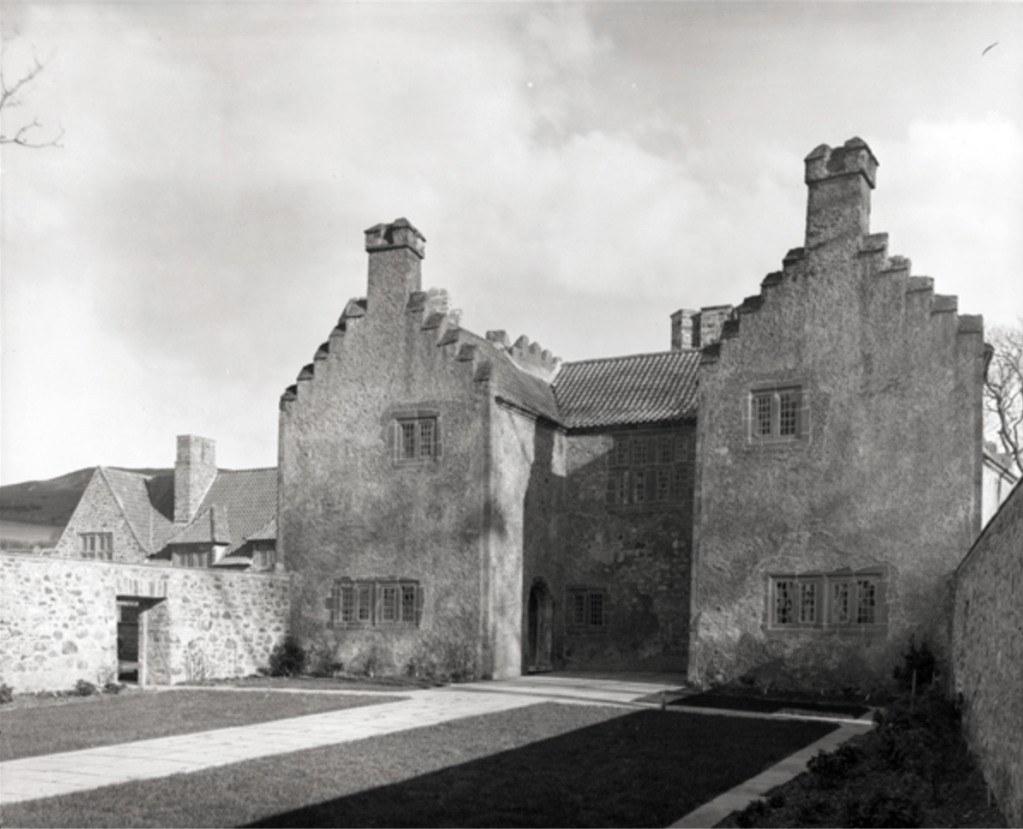

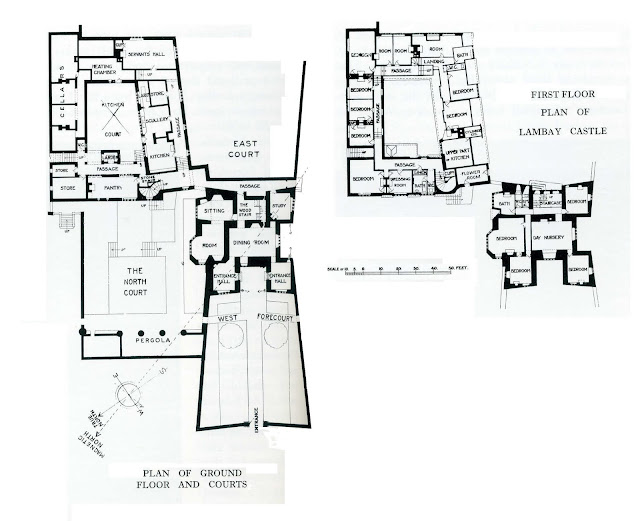
Sean O’Reilly describes Lutyen’s work in more detail:
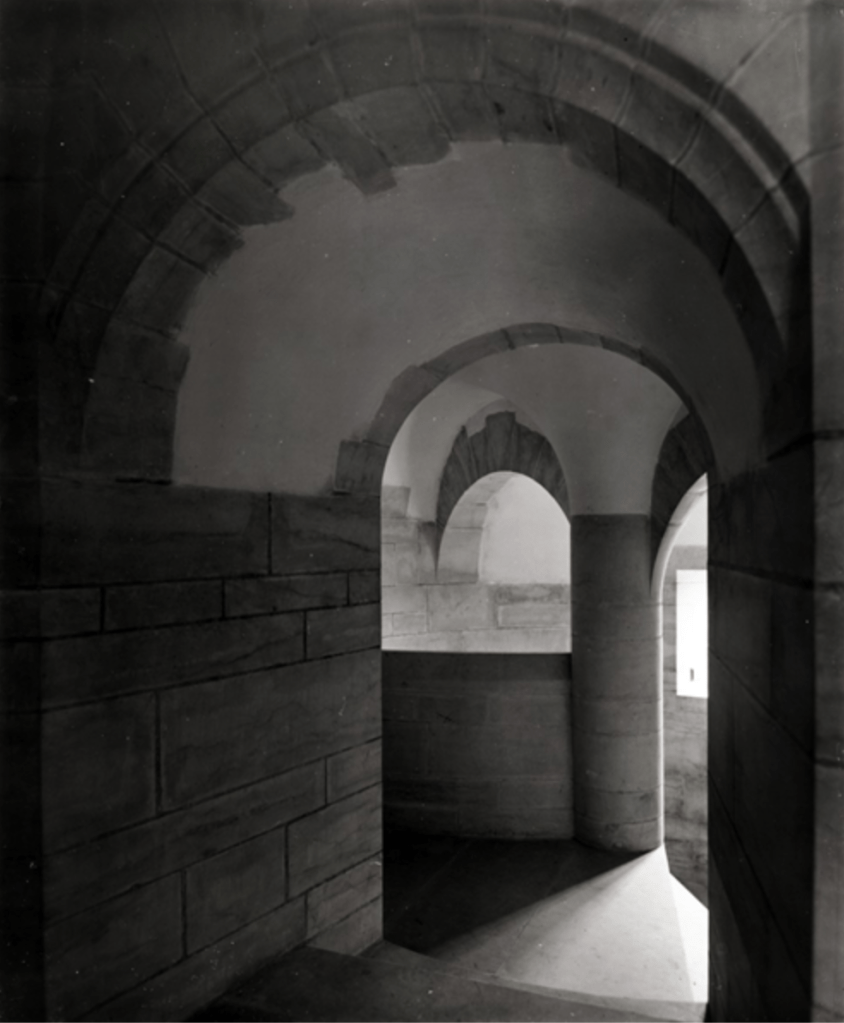
“Lutyens did need to provide suitable facilities within the surviving ruins of the castle, the most basic of these being a staircase. Curiously, the original castle fabric did not possess internal access to the upper floor, so Lutyens inserted his in the space between the bastions at the rear of the building. He linked these two with a sequence of three cross windows broken by the arched doorway leading to the staircase. The new arrangement is a typically imaginative piece of intervention by Lutyens, as it performs a number of functions with appropriate efficiency. It gives access not only to the bedrooms on the upper floor, but also to the raised ground at the rear of the castle, and it connects to the underground service passage to the kitchen wing.
“Reception rooms also needed to be provided inside the ruins, and again it was to Lutyens’s credit that he succeeded in creating an imaginative variety of shapes and spaces without intruding on the individuality of the building. Perhaps most surprising is the provision of two entrance halls, one in each of the corner bastions of the entrance front, and each with its own door. The sitting room, reached only after passing through the central dining room and staircase hall behind, is in the corner adjoining the service wing.
“Due to the need for the reconstruction of this corner Lutyens was more free to open out the architecture, without actually intruding on surviving original fabric. Here he introduced a pointed stone arch linking the section of the room in the original bastion with that part set between the bastions. Lutyens topped this range with a hipped roof – an informal nod to the detailing of the service wing – and square battlements – a more formal bow to the stepping in the original gables, seen across the view of the north court.” [1]

The Historic Houses of Ireland website tells us that the castle is “constructed with small doors and small casements so that the inhabitants seem, on rough days, to be sheltering like monks.” [see 2]
The interior has vaulted ceilings, stone fireplaces and a curved stone staircase, while much of the furniture chosen by Lutyens is still arranged just as he intended.
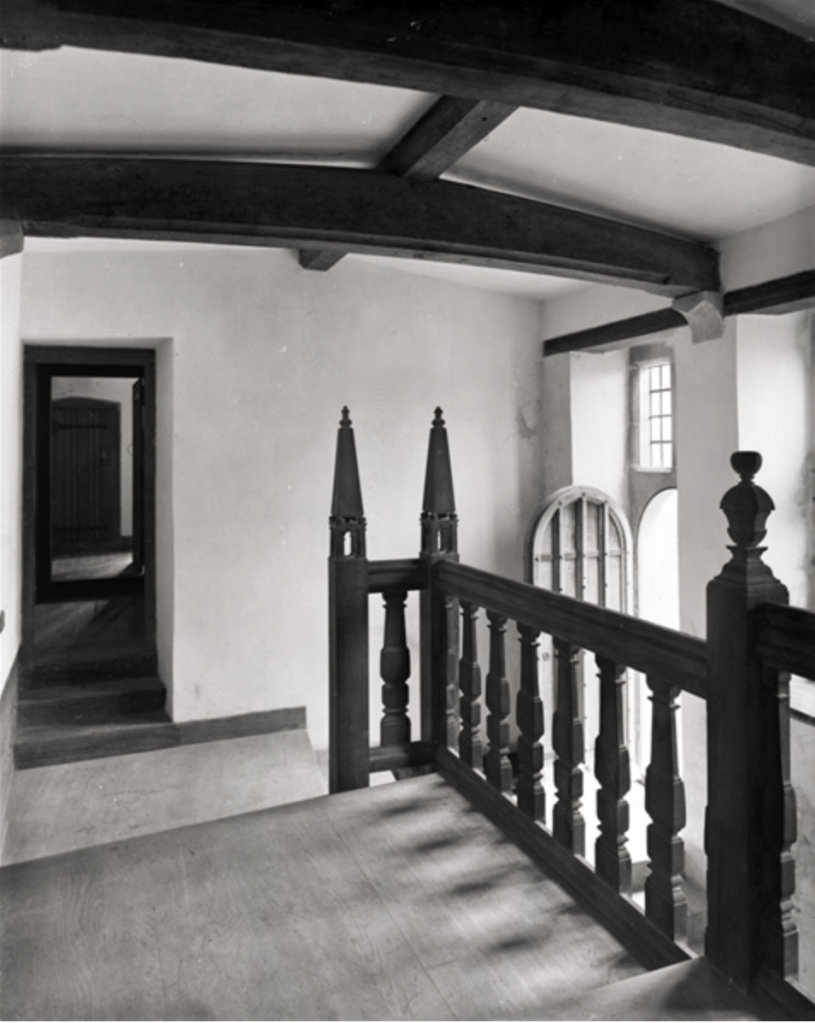






Lutyens also adapted and enlarged a number of other early structures and integrated them into an ingenious coordinated layout for the whole island, combining the farm, gardens and plantations as a single composition, in collaboration with the horticulturalist and garden designer Gertrude Jekyll.

Mark Bence-Jones describes the wall that surrounds the castle and gardens: this wall serves the practical purpose of a wind-break, enabling trees and plants to grow inside it which would not grow outside. [3] He also describes the approach to the castle:
“Lutyens also designed the approach from the harbour, with curved step-like terraces reminiscent of the now-vanished Ripetta in Rome; characteristically, having ascended these Baroque steps, one has to cross an open field to come to the curtain wall, the entrance gaeway not being at first visible; so that there is a wonderful sense of expectancy. Close the the harbour is the White House, a largely single-storey horseshoe-shaped house with high roofs and white harled walls, which Lutyens designed 1930s for Lord Revelstoke’s daughter, Hon Mrs (Arthur) Pollen. On a hill is an old Catholic chapel, with a portico of tapering stone columns and a barrel vaulted ceiling.” [see 3]
The walled kitchen garden pierces the Rampart Wall to the South and there is the mausoleum of the Revelstokes, designed by Lutyens in 1930, on the opposite side of the enclosure. The website tells us:
”Cecil and Maude had 12 blissful years together with their little family on Lambay but alas, in 1922, a still young Maude died of cancer, leaving Cecil with two daughters, Daphne and Calypso, and their little son Rupert. Her body was brought back from London to the island for burial. Lutyens, who was then busy with war memorials and the government buildings of New Delhi, designed a large monument for her grave, set in against the rampart walls and facing towards the Castle. The mausoleum is today one of the most pleasant and peaceful spots on the island. Prefacing Cecil’s epitaph, a beautiful poem about his wife, is the word ‘Quiet’, both an imperative to the reader and a description of the monument’s setting.“
Lutyens also designed the White House overlooking the harbour on the western shores of the island, as a holiday home for the couple’s two daughters and their families. This is now available as visitor accommodation.

The website tells us that Cecil convened a congress to examine the flora and fauna of the island, the findings of which were published in The Irish Naturalist (1907).
“He also tried to introduce new species, including mouflon sheep, chamois goats, kinkajous and rheas. Today, there is a large population of wallabies on Lambay, but these were brought here in the 1980s by Cecil’s son Rupert Revelstoke, who had enjoyed having two pet wallabies in the 1950s.“
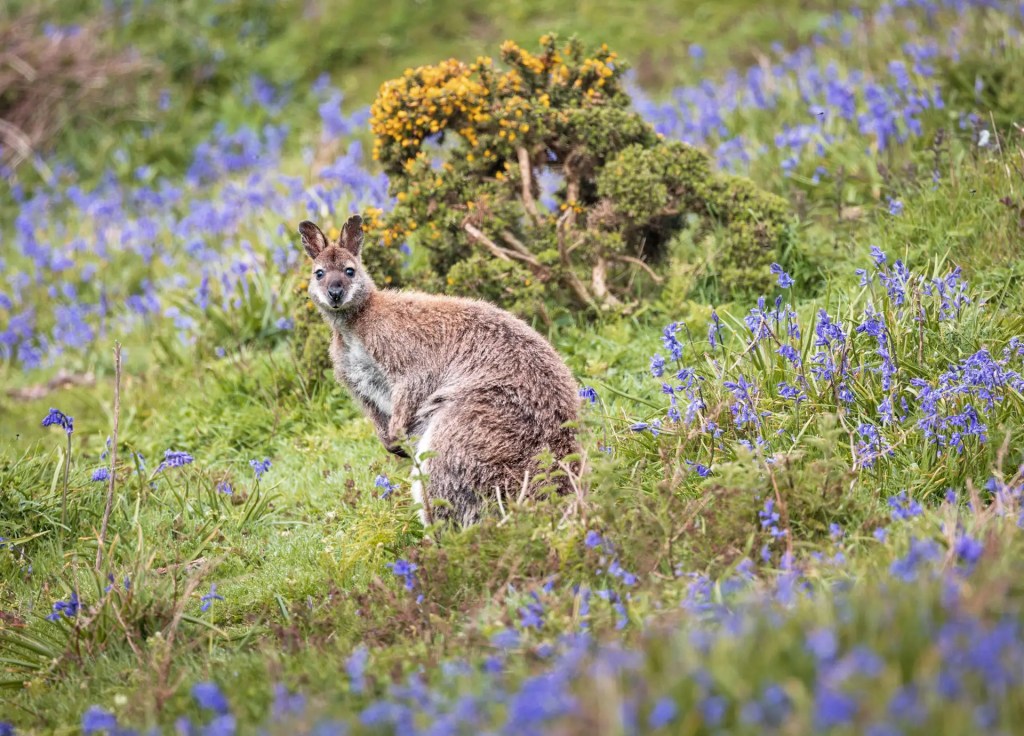

I hope that Stephen and I can visit the island and the castle someday!
[1] Sean O’Reilly Irish Houses and Gardens. From the Archives of Country Life. Published by Aurum Press Ltd, London, 1998.
[2] https://www.ihh.ie/index.cfm/houses/house/name/Lambay%20Castle
[3] Bence-Jones, Mark. A Guide to Irish Country Houses (originally published as Burke’s Guide to Country Houses volume 1 Ireland by Burke’s Peerage Ltd. 1978); Revised edition 1988 Constable and Company Ltd, London.