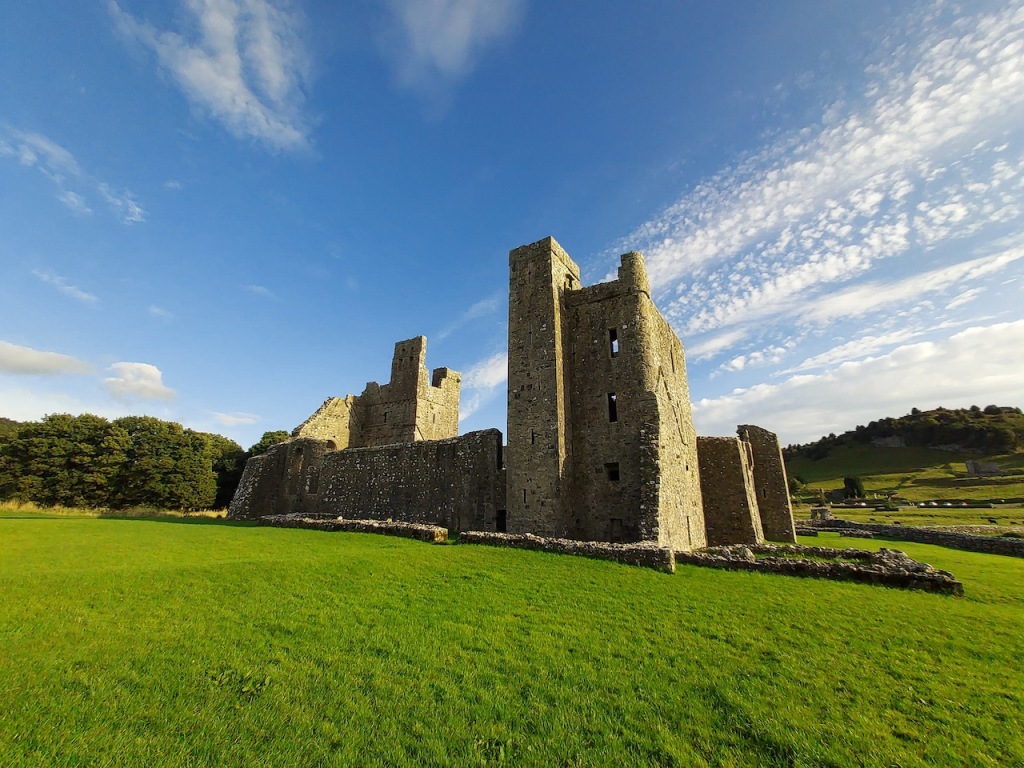
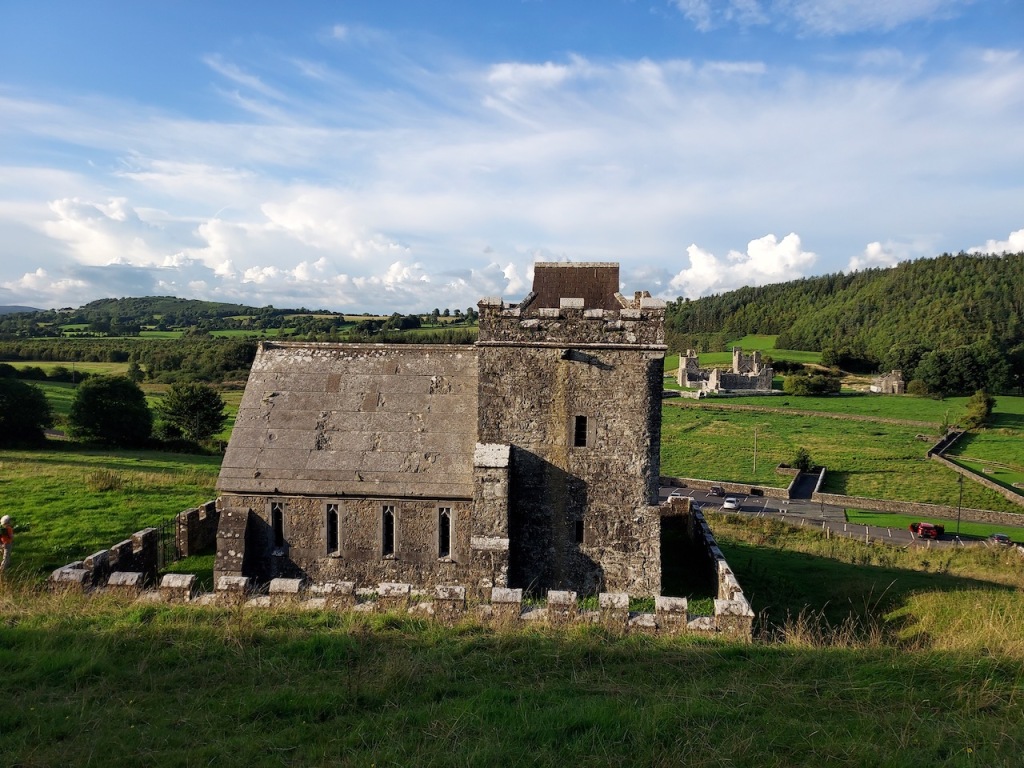
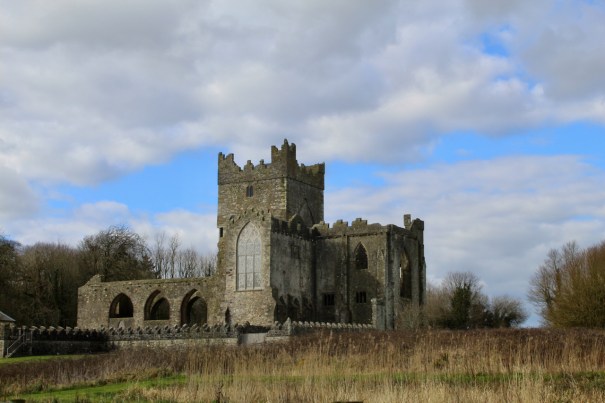
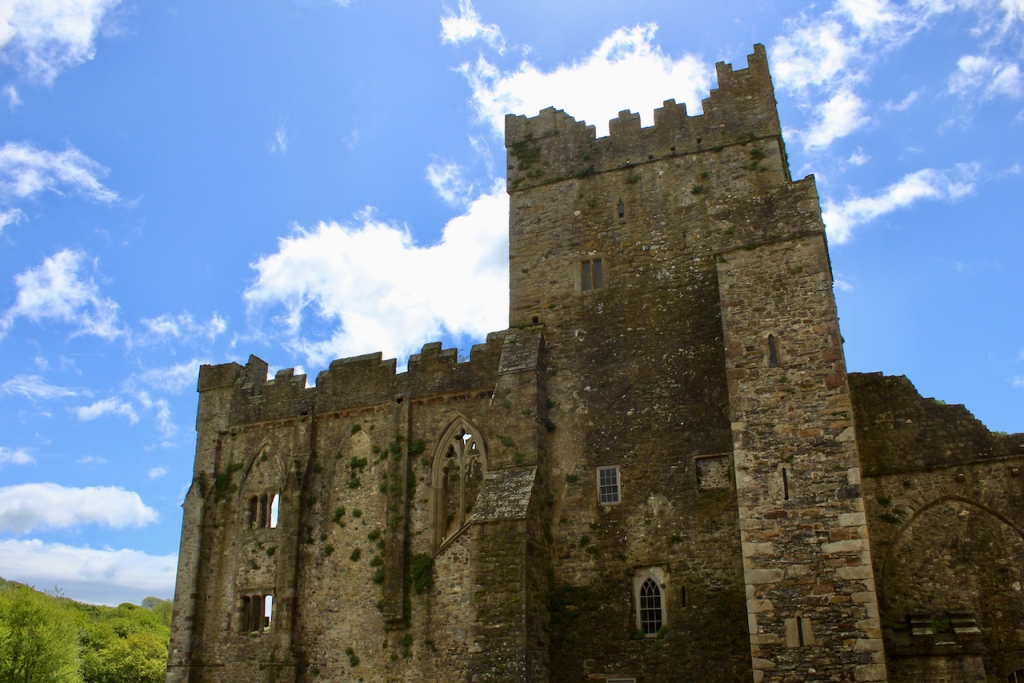
Tintern Abbey, County Wexford

General information: 051 562650, tinternabbey@opw.ie

donation
Help me to pay the entrance fee to one of the houses on this website. This site is created purely out of love for the subject and I receive no payment so any donation is appreciated!
€15.00
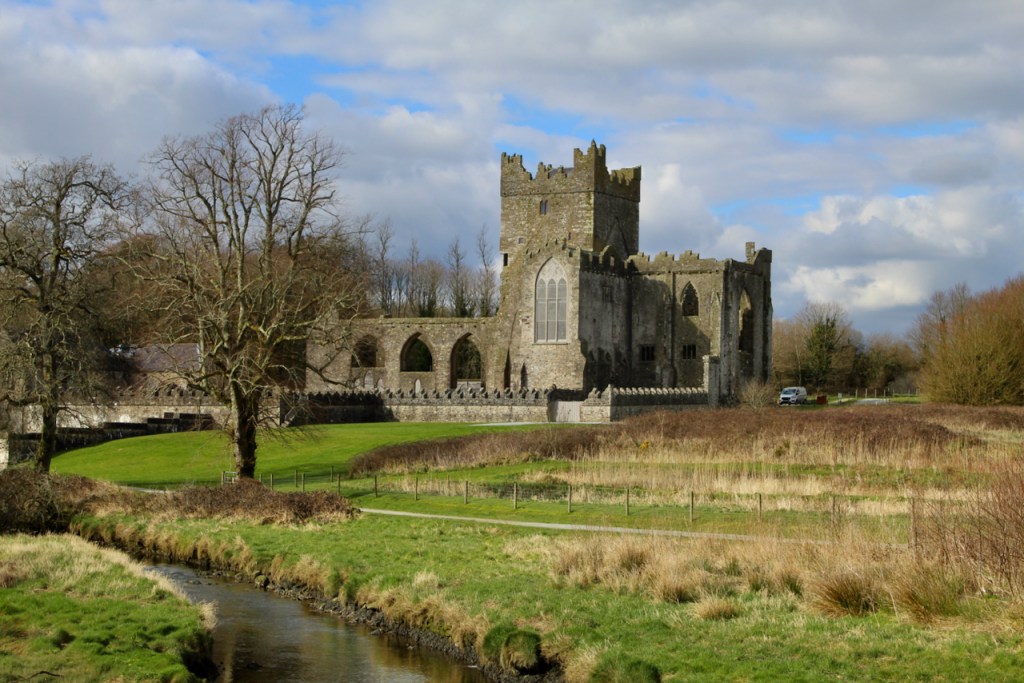
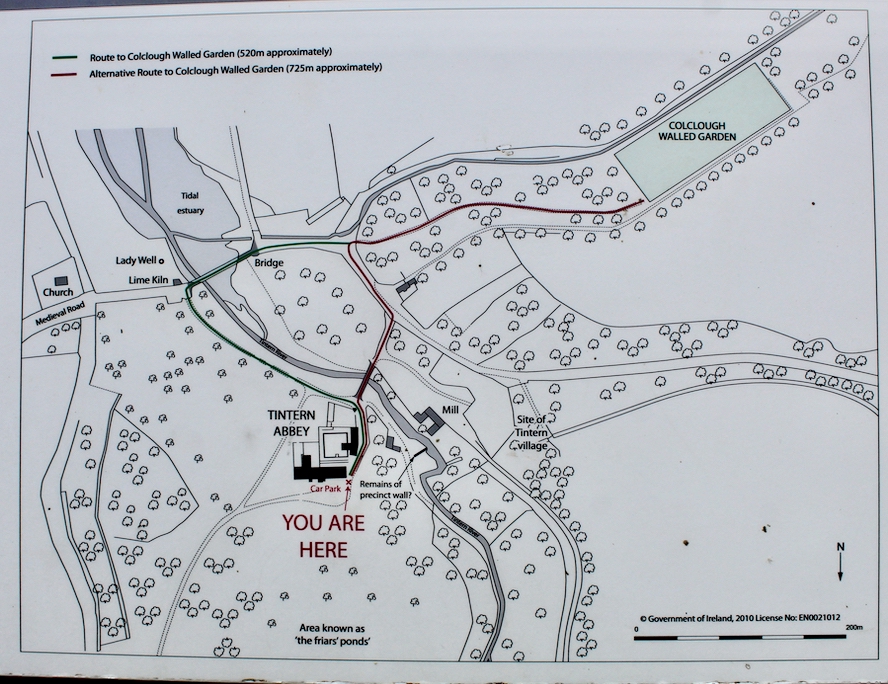
We visited Tintern Abbey when we were in Wexford in May 2023. We visited again recently as it had rained on our previous visit and we didn’t get to to go to Colclough walled garden, so we made a beeline for the walled garden on our second visit.
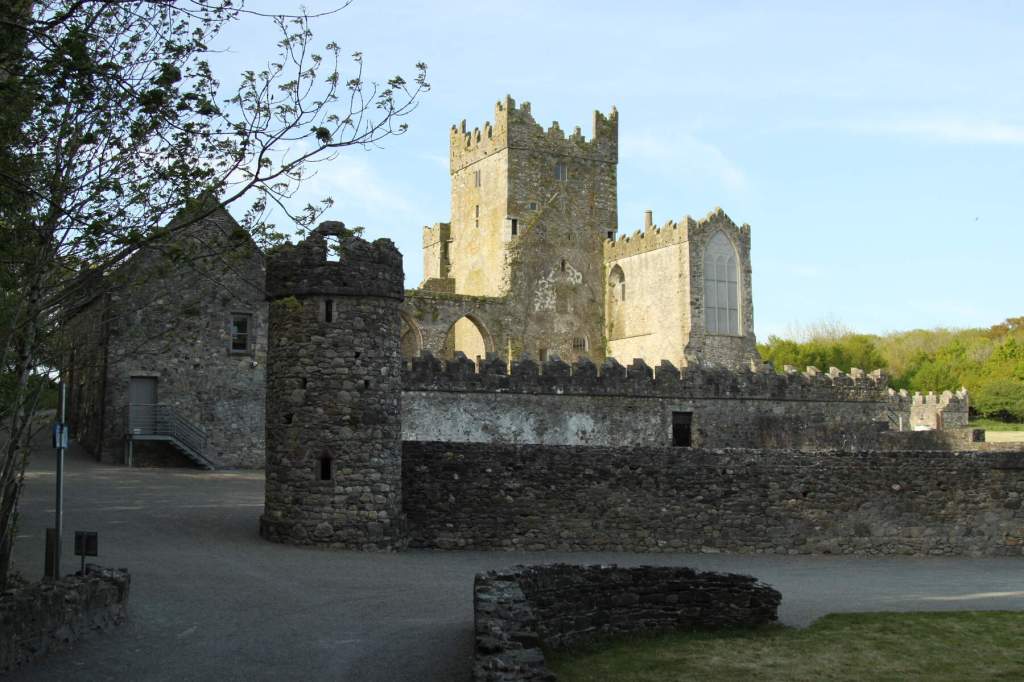


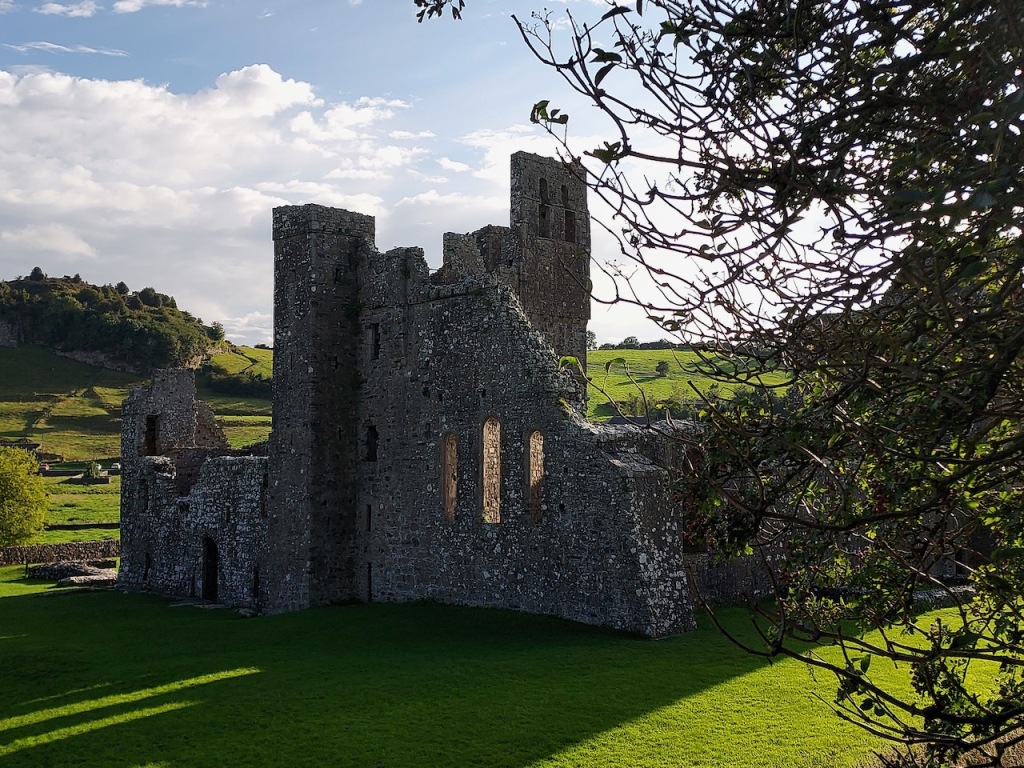
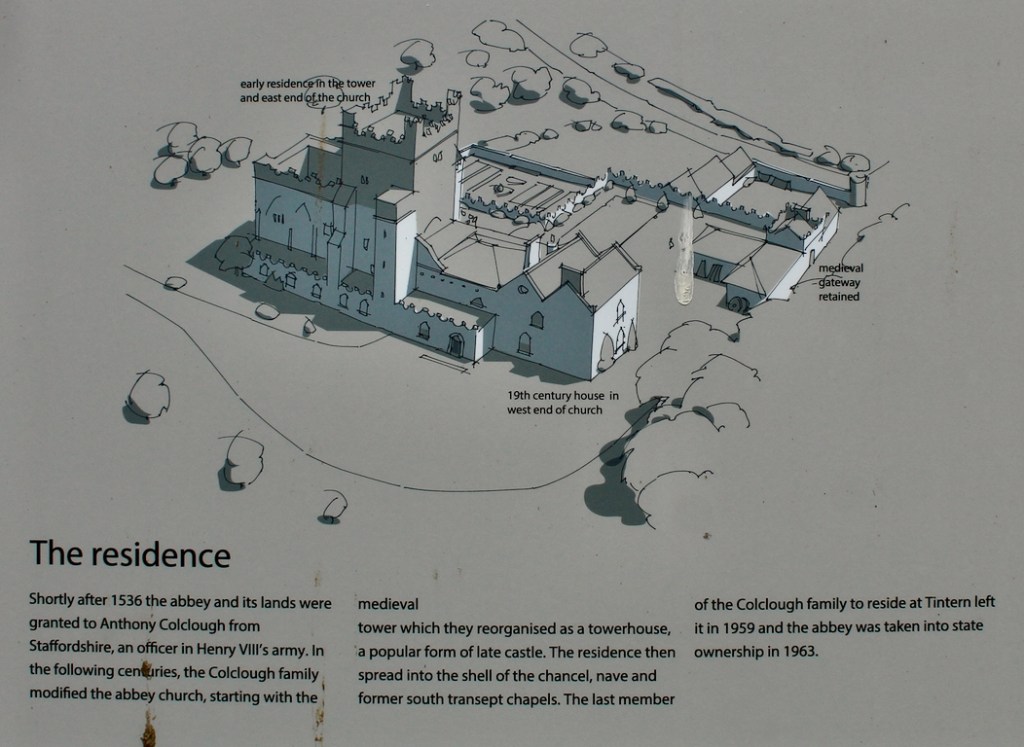
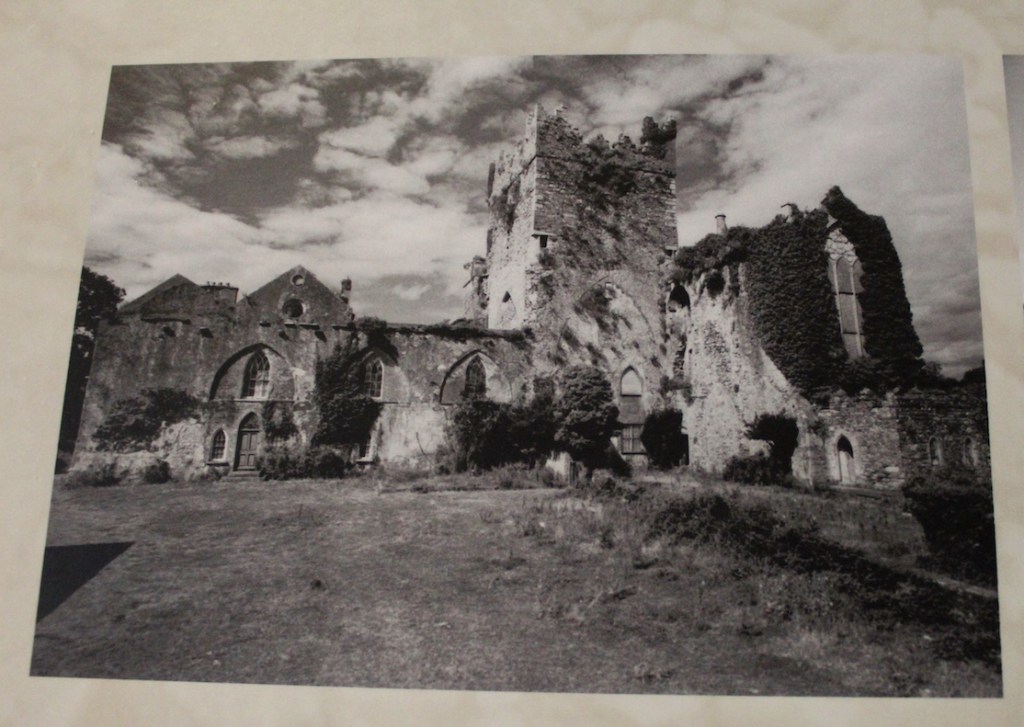
The Abbey was converted into a residence after the Dissolution of the Monasteries in King Henry VIII’s time. When the Abbey was gifted to the state, the Irish Board of Works immediately demolished the residence, so that the building was left a ruin. It was only two decades later that the Board of Works began to conserve the property.

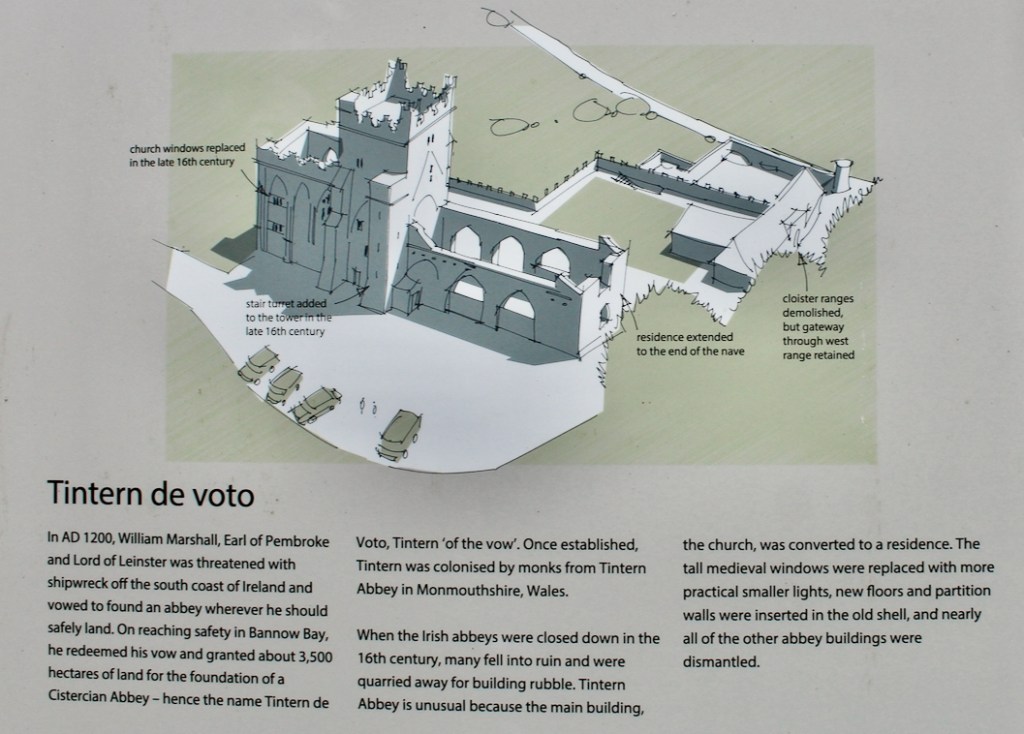
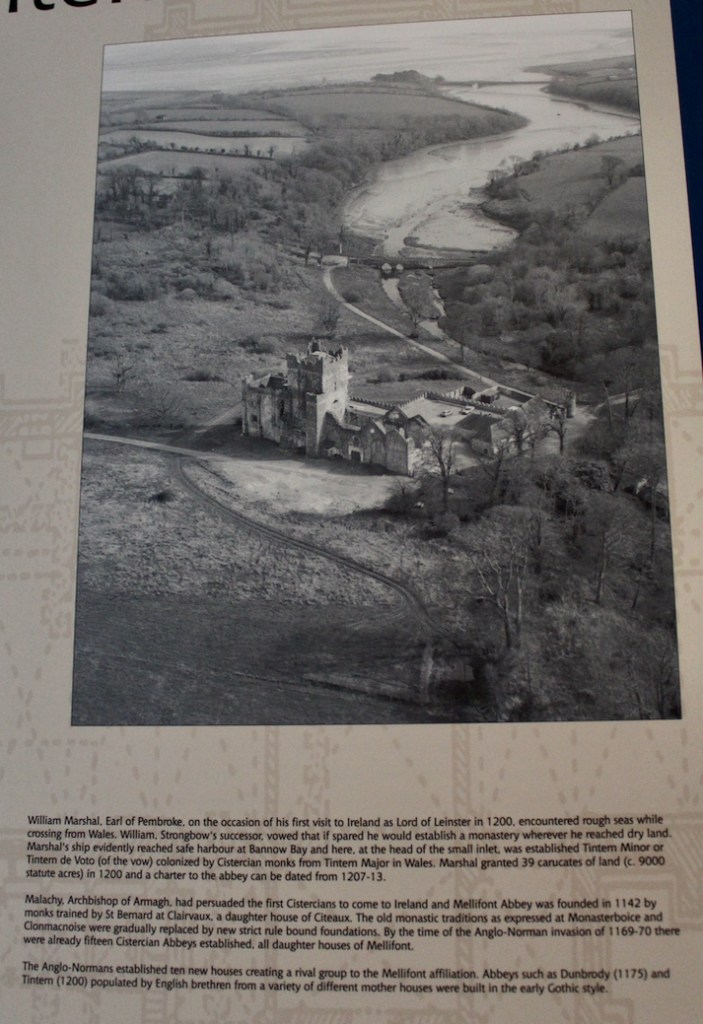
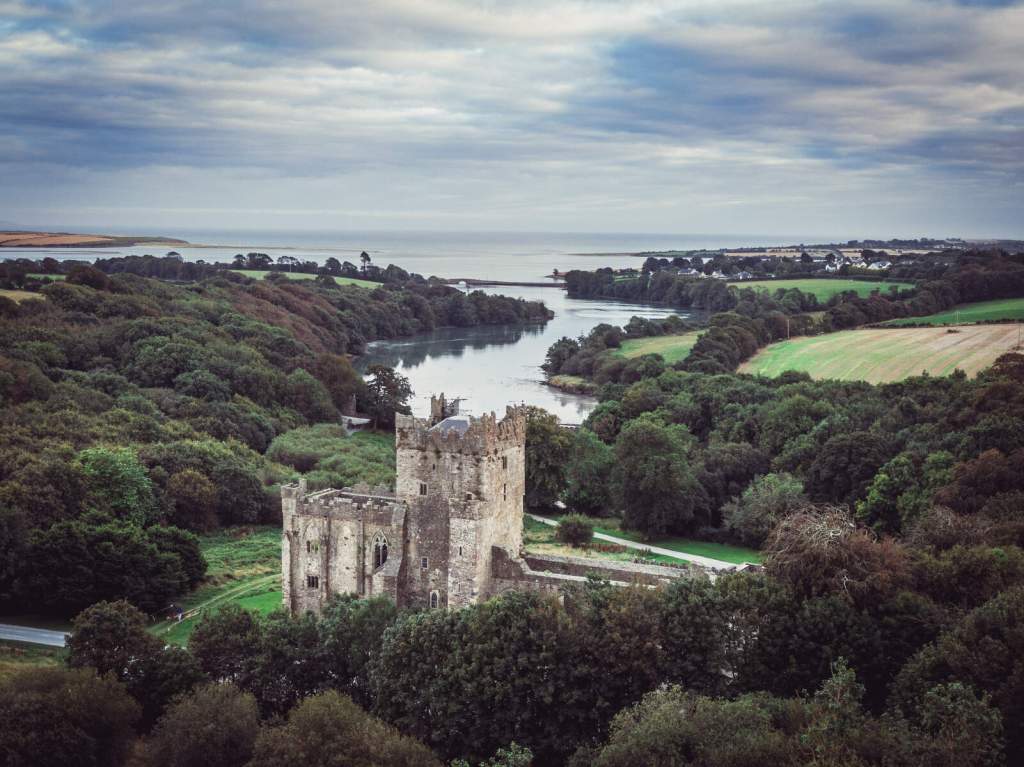
The OPW website https://heritageireland.ie/visit/places-to-visit/tintern-abbey/ tells us that the Abbey was founded as a Cistercian monastery around the year 1200 by William Marshall, 1st Earl of Pembroke, who became Lord of Leinster as he married Isabella de Clare, the daughter of “Strongbow,” Richard de Clare, 2nd Earl of Pembroke. Marshall vowed to create an abbey wherever he could safely land in Ireland during a storm, and he landed in Bannow Bay. Tintern Abbey is located at the head of a small inlet of the sea, next to a stream that provided fresh water. The Abbey was founded as a “daughter house” of Tintern Abbey in Wales, made famous by poet William Wordsworth. To distinguish it from the Welsh abbey, Wexford’s Abbey was also called “Tintern de Voto” meaning “of the vow.”


After the dissolution of the monasteries by Thomas Cromwell and King Henry VIII, Tintern Abbey was granted to a soldier, Anthony Colclough (d. 1584).
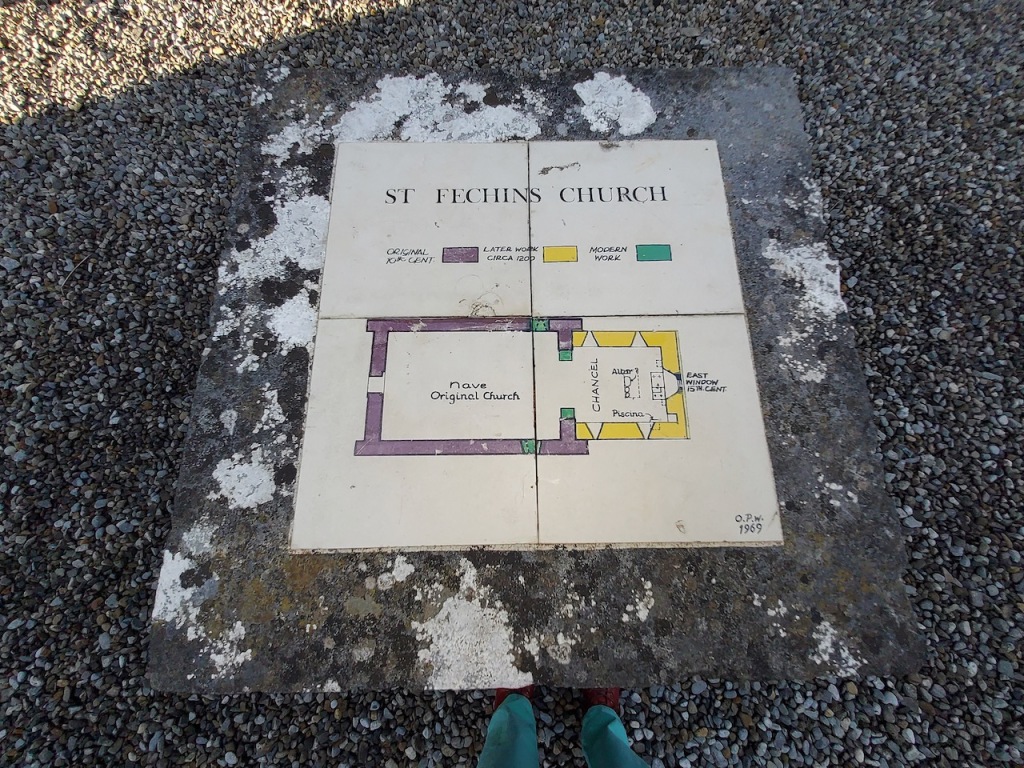
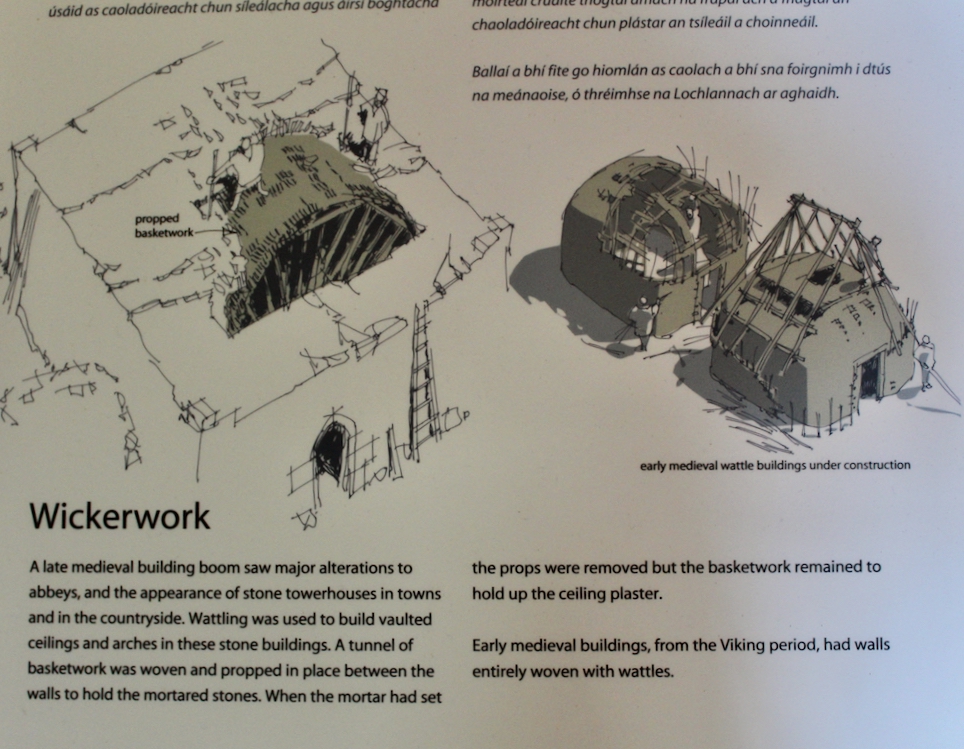
Information boards tell us about the history of the Abbey and the Cistercian Order, which was based on a strict interpretation of Benedictine rule. The monks would have lived according to a spartan routine of prayer and manual labour. Most of the difficult tasks were carried out by lay brothers. The practice of having lay brothers began because initially the monks wanted to cut themselves off from the outside world and did not allow lay people on their land. However, they needed labourers, so the lay ministry was formed. Some of these lay brothers may have lived nearby in Rathumney Hall, or Castle, now a ruin. Lay brothers often lived in out-farms or “granges,” which would have their own hall, dormitory, kitchen and chapel, and the brothers would then join the monks at the Abbey at weekends.



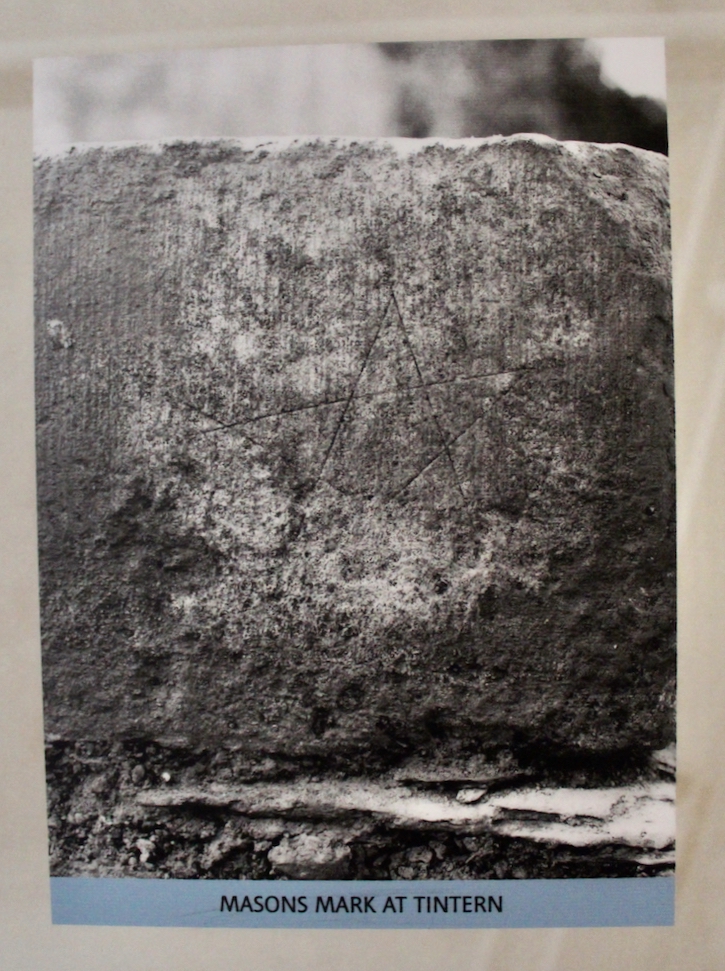
Information boards tell us of the various phases of the Abbey. It would have been built first by lay monks, and later by the mid 1200s, by professional masons.



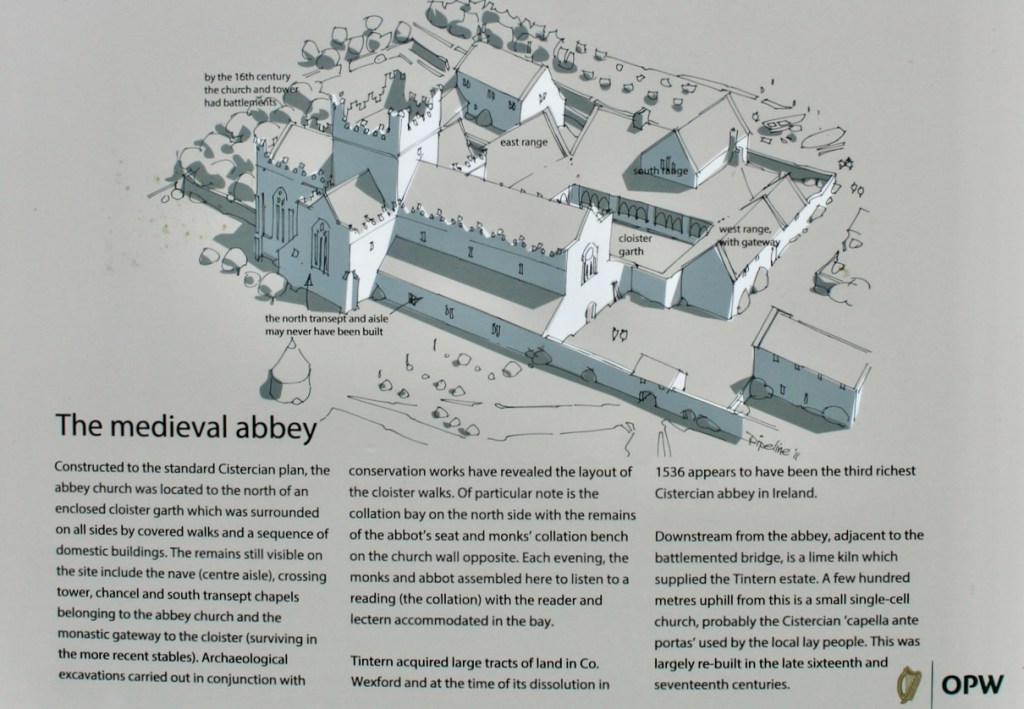
Cistercian simplicity was reflected in their buildings, of strong form and good building techniques. In 1140, Malachy, Bishop of Down, visited Bernard of Clairvaux. Bernard sent helped to establish the Cistercian monastery in Mellifont, County Louth, and by 1169 Ireland had fourteen Cistercian settlements. The Anglo Normans established a further ten in the fifty years after 1169, including Dunbrody Abbey, another Cistercian monastery near Tintern Abbey.
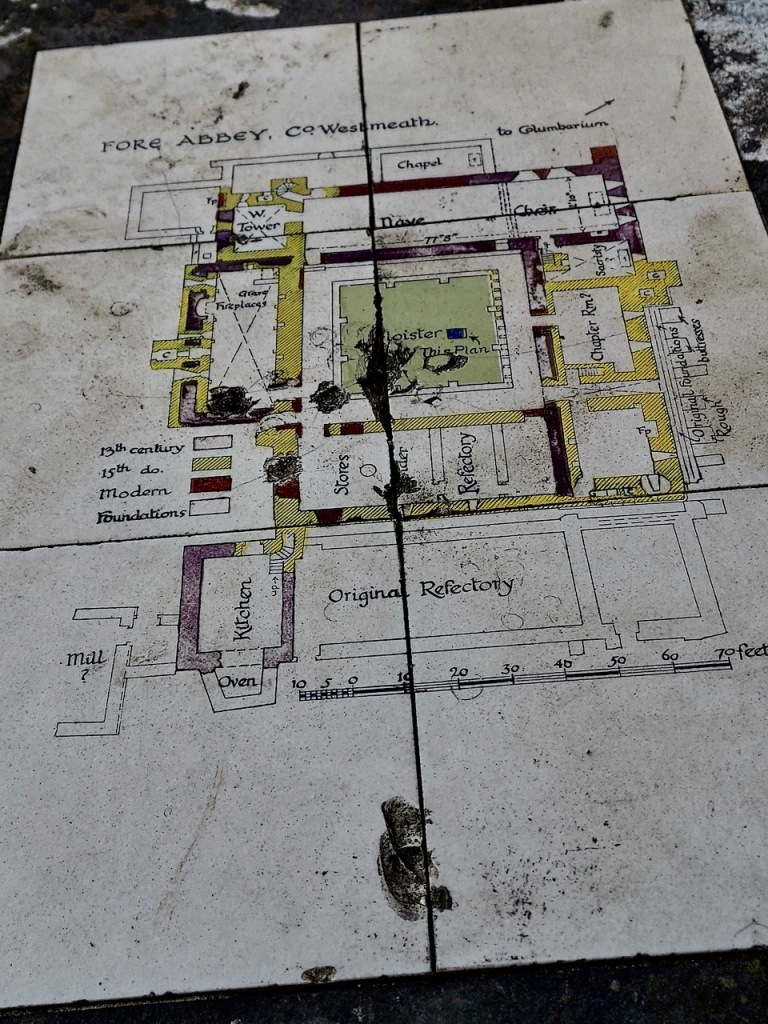
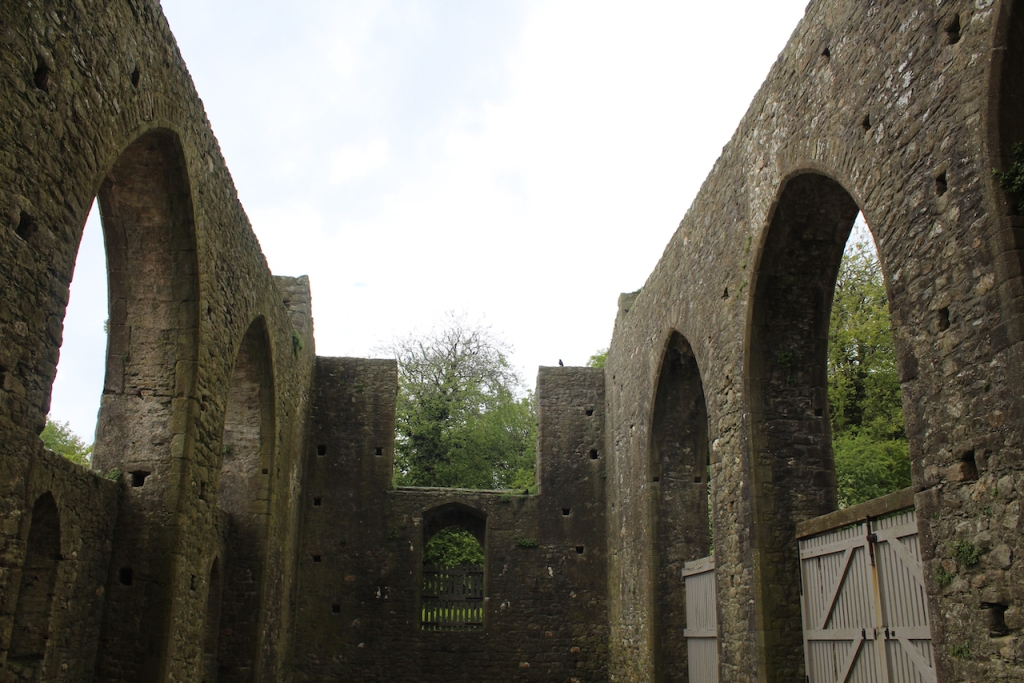
The Cistercians built according to well-established convention. The churches consisted of an aisled nave and presbytery with north and south transepts. A tower was not a usual feature. The cloister was south of the church and was surrounded by buildings such as the infirmary, dormitory, kitchen, guest house and scriptorium.






The monks were interested in farming and adopted the latest methods.


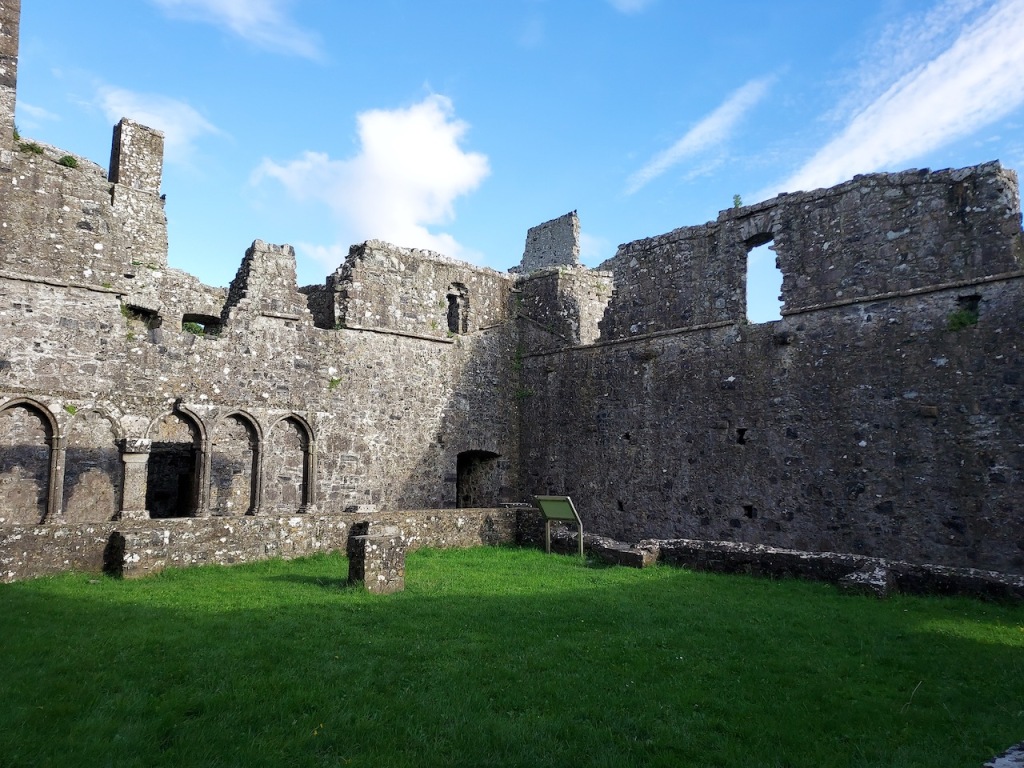
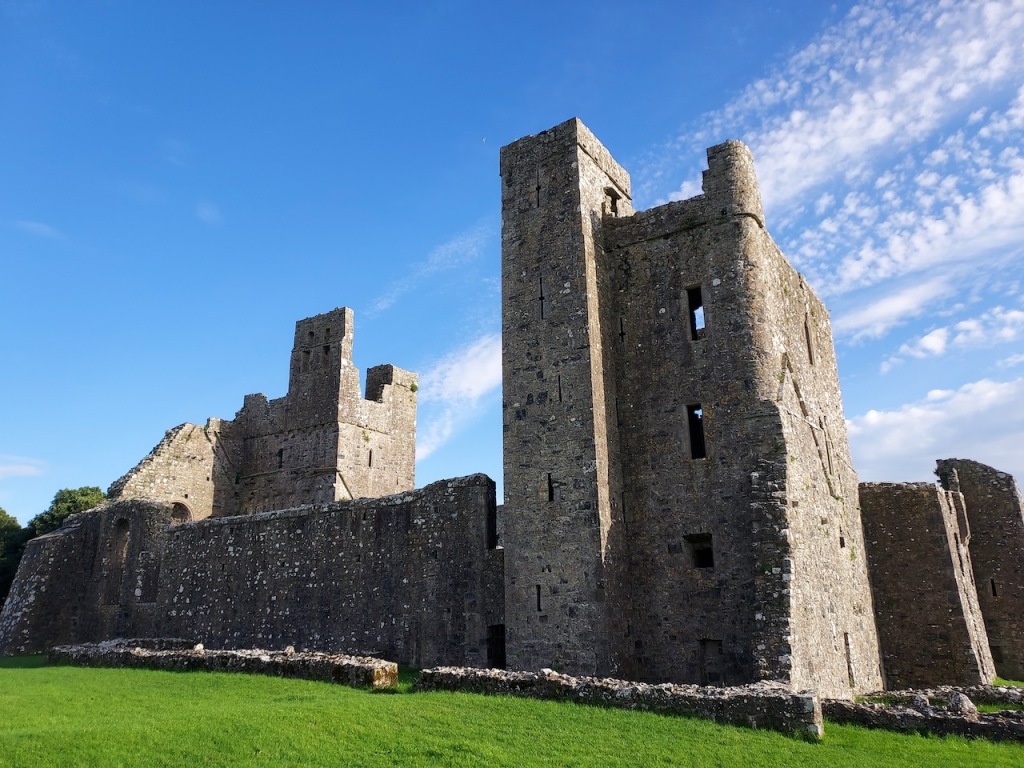
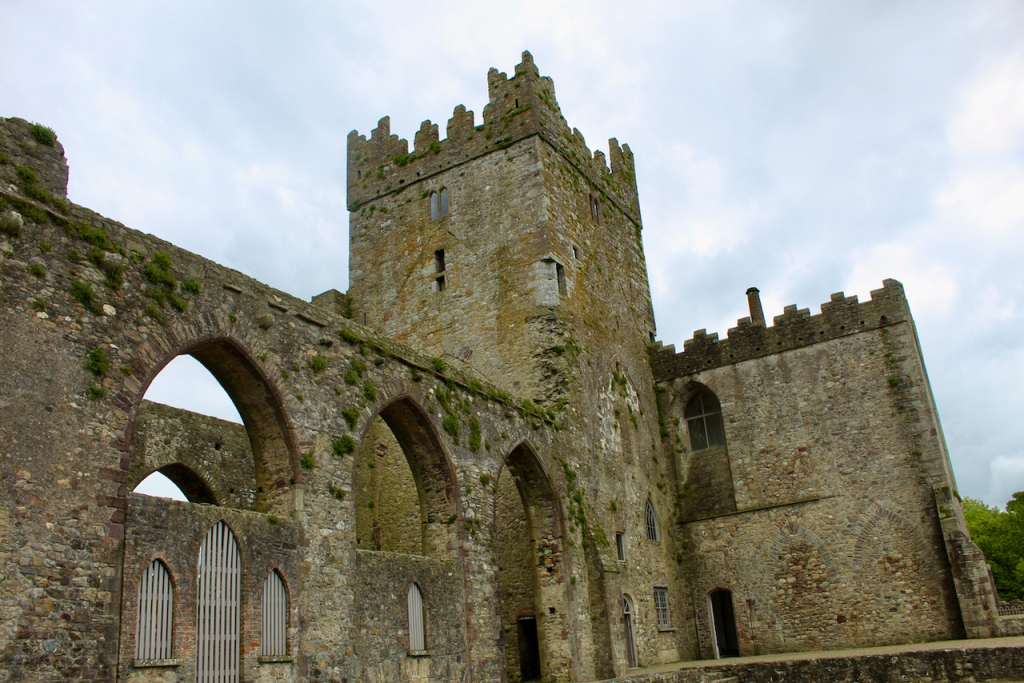
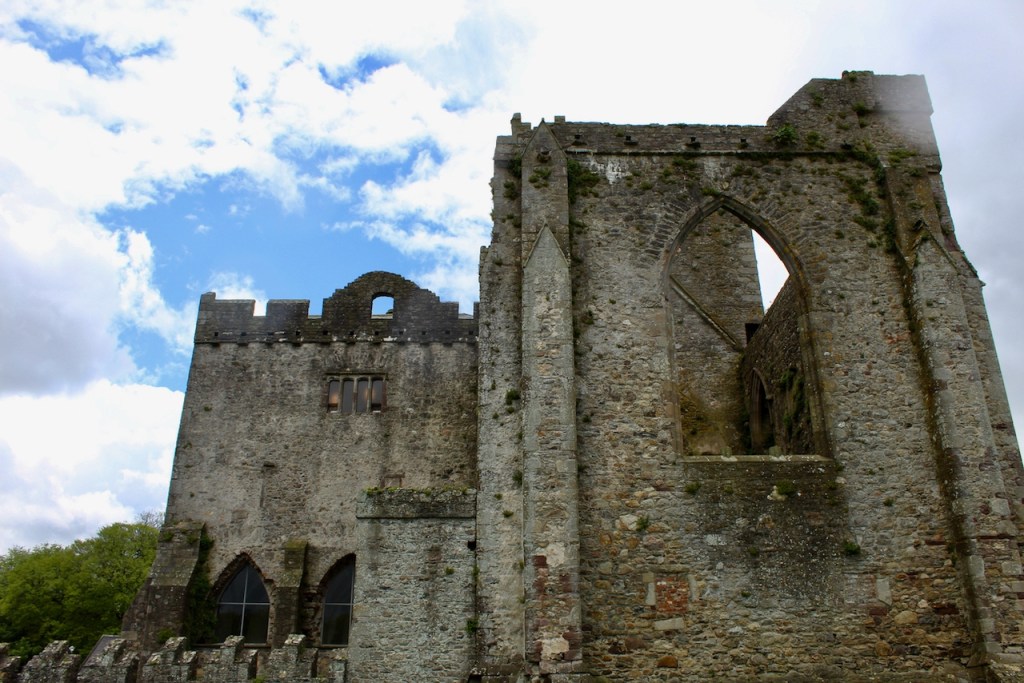
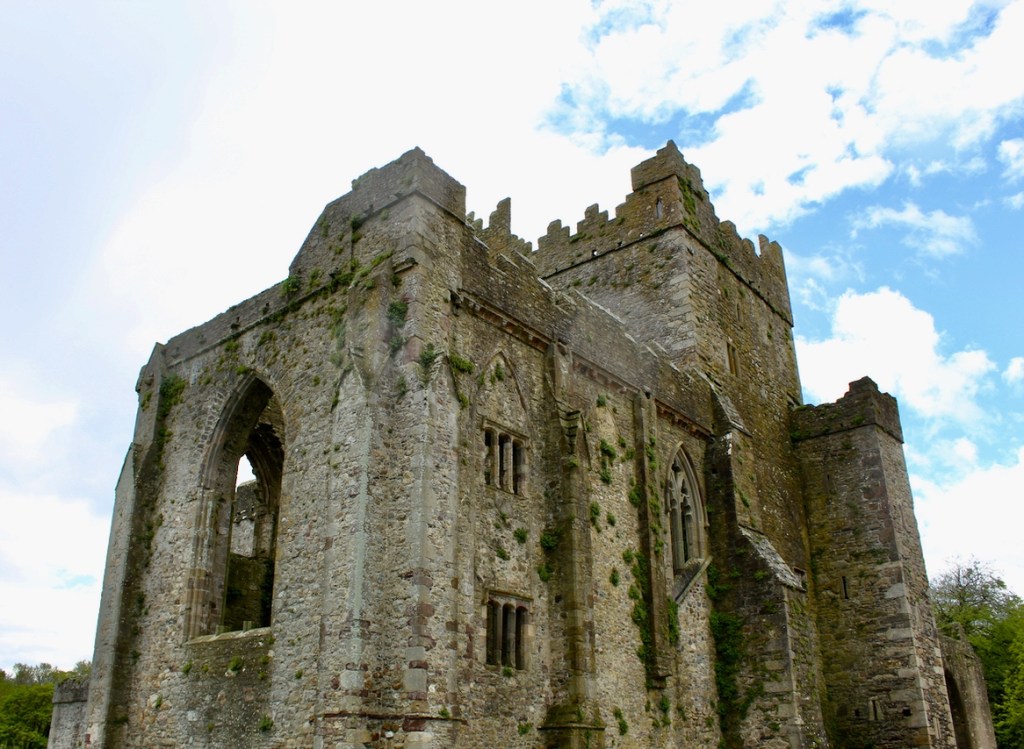
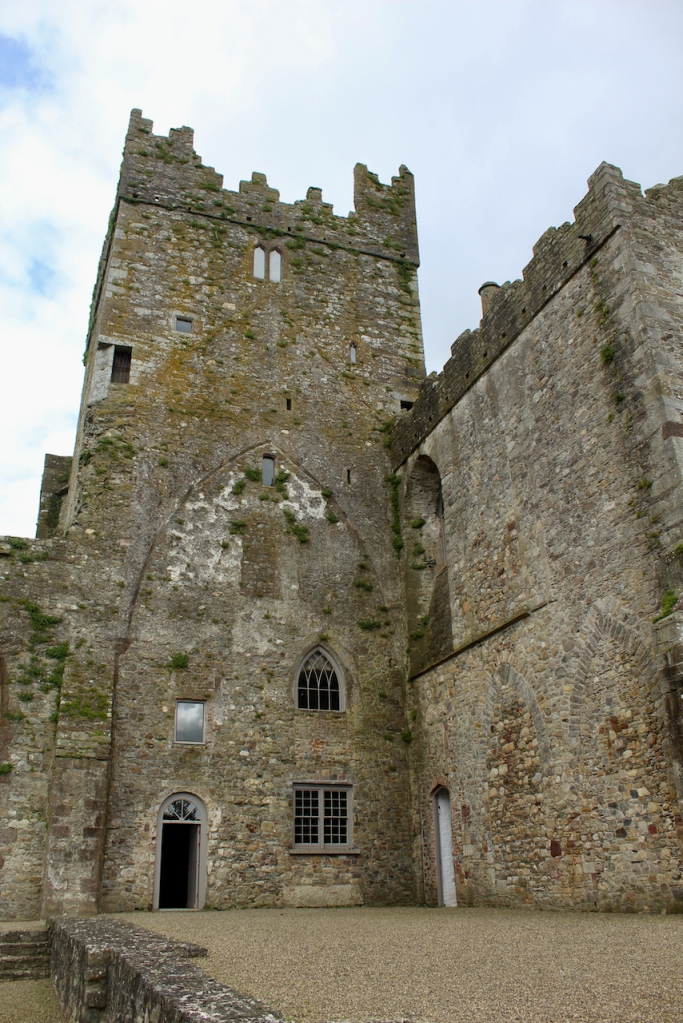
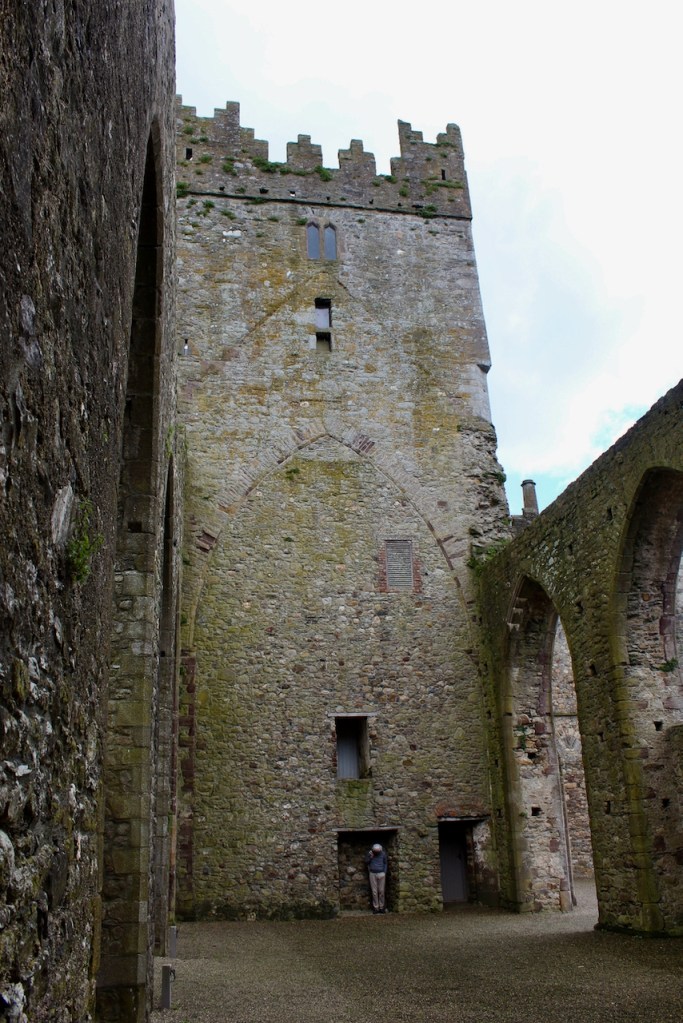
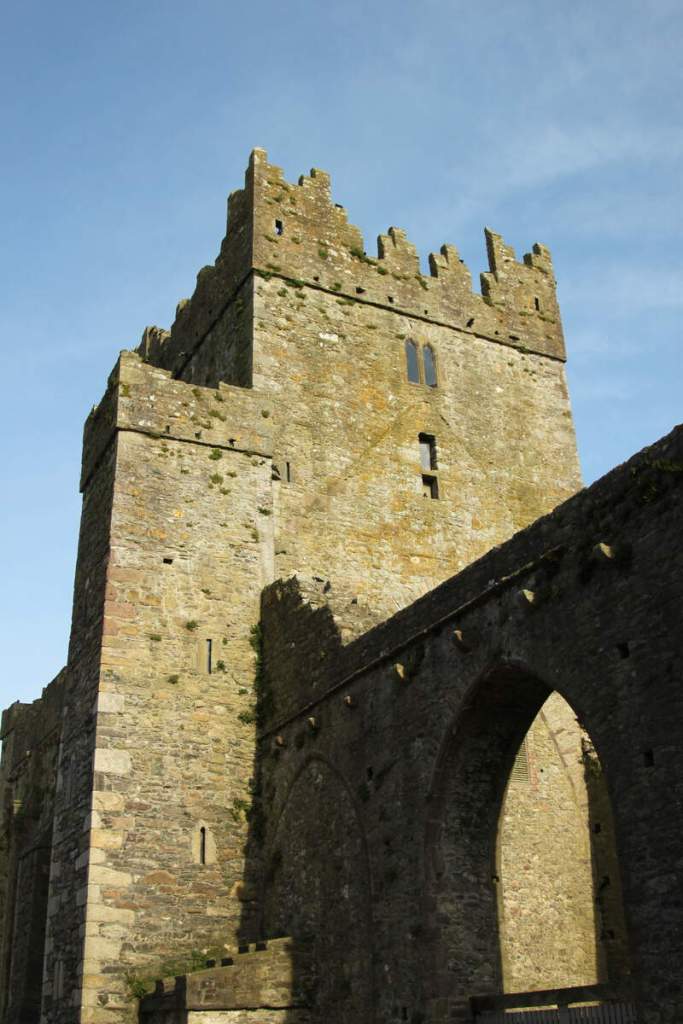
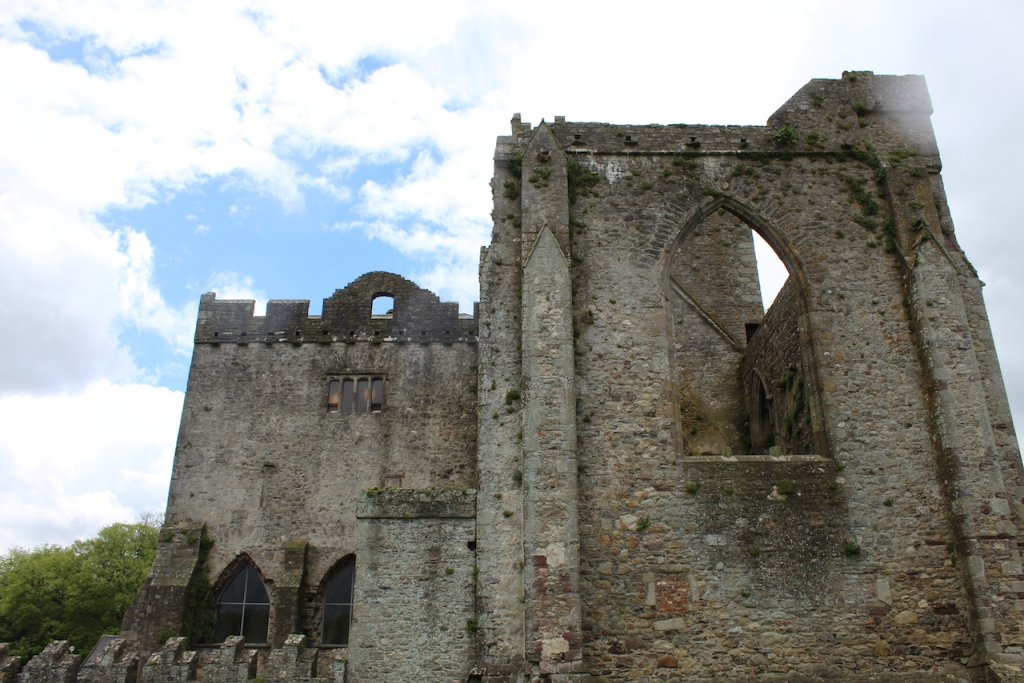
The nave, chancel, tower, chapel and cloister still stand. The nave has lost its aisles and clerestory, but still has three bays of plain arches.
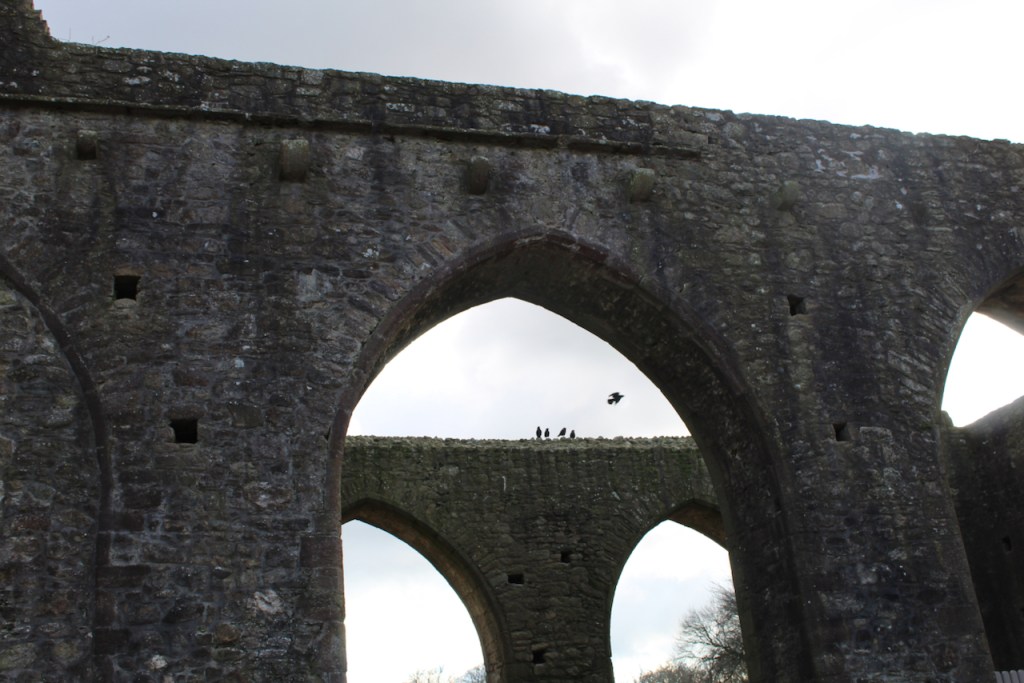





Sculpture was not encouraged in Cistercian buildings but Tintern has a few fine surviving examples. A carved corbel table remains, which contains twenty four carved heads, some human, some monstrous.
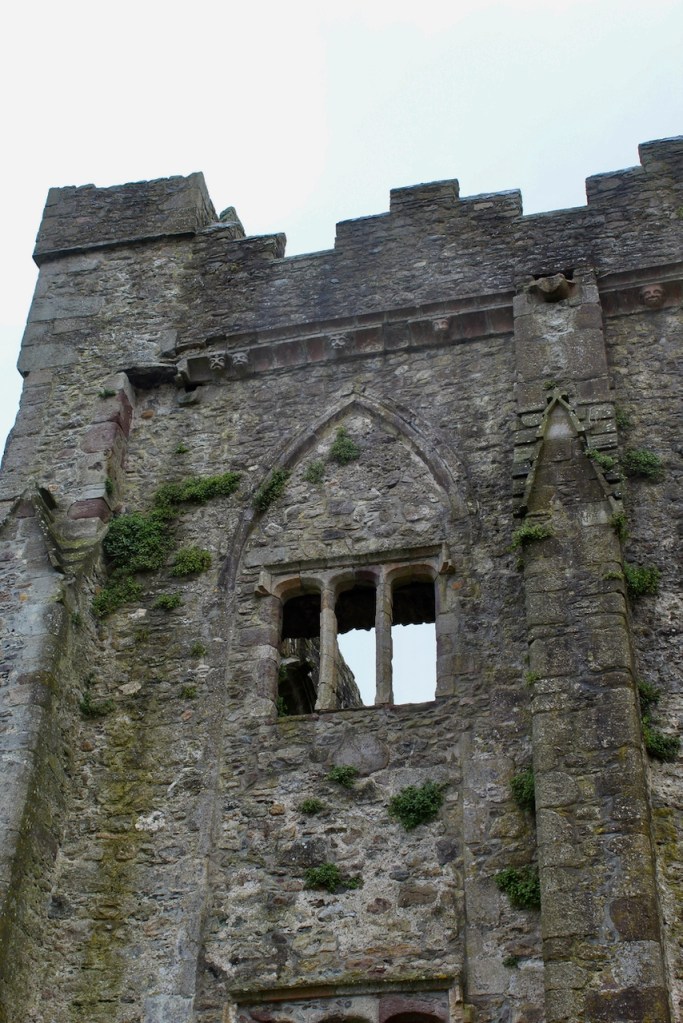
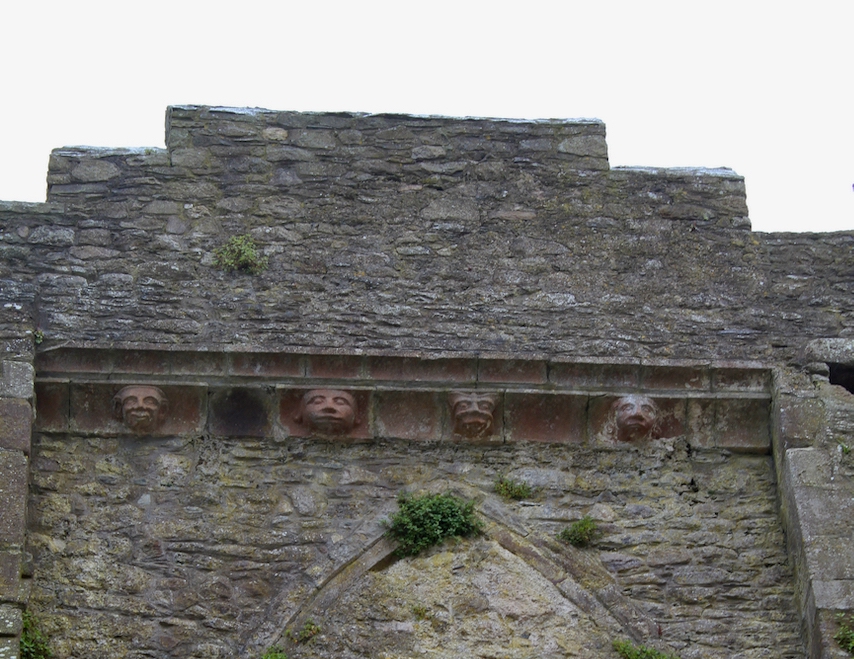
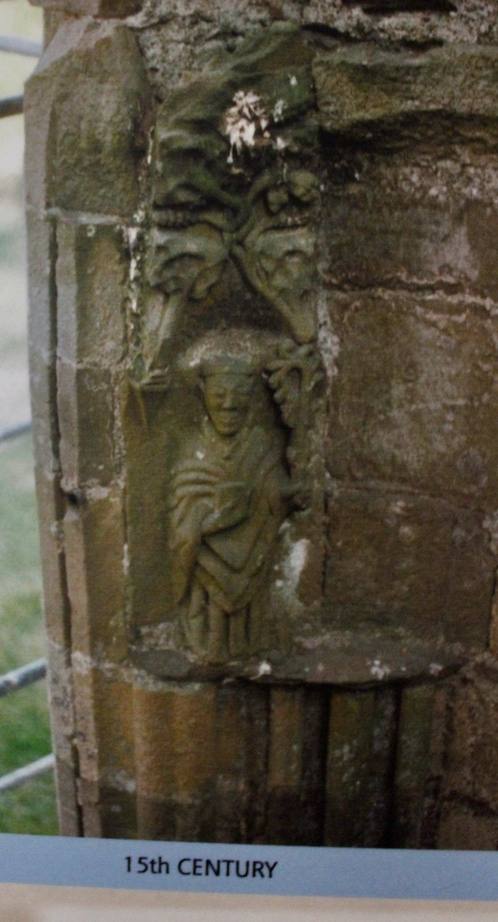




In the 16th century the old abbey was granted to the Colclough family (pronounced Coakley) and soon after the church was partly converted into living quarters and further adapted over the centuries. The Colcloughs occupied the abbey from the sixteenth century until the mid-twentieth.


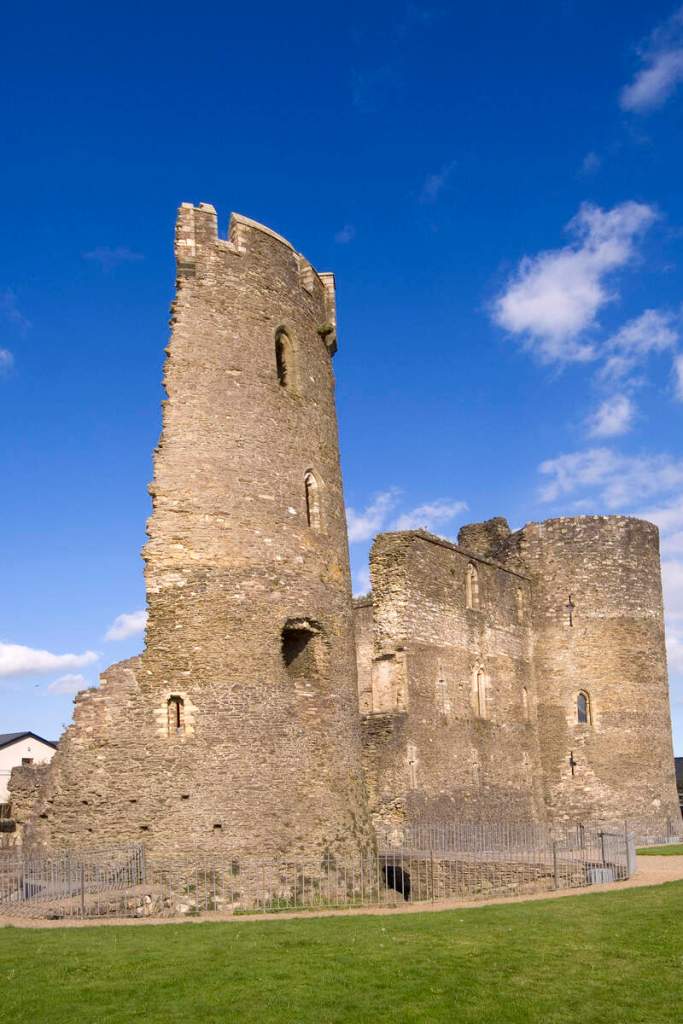
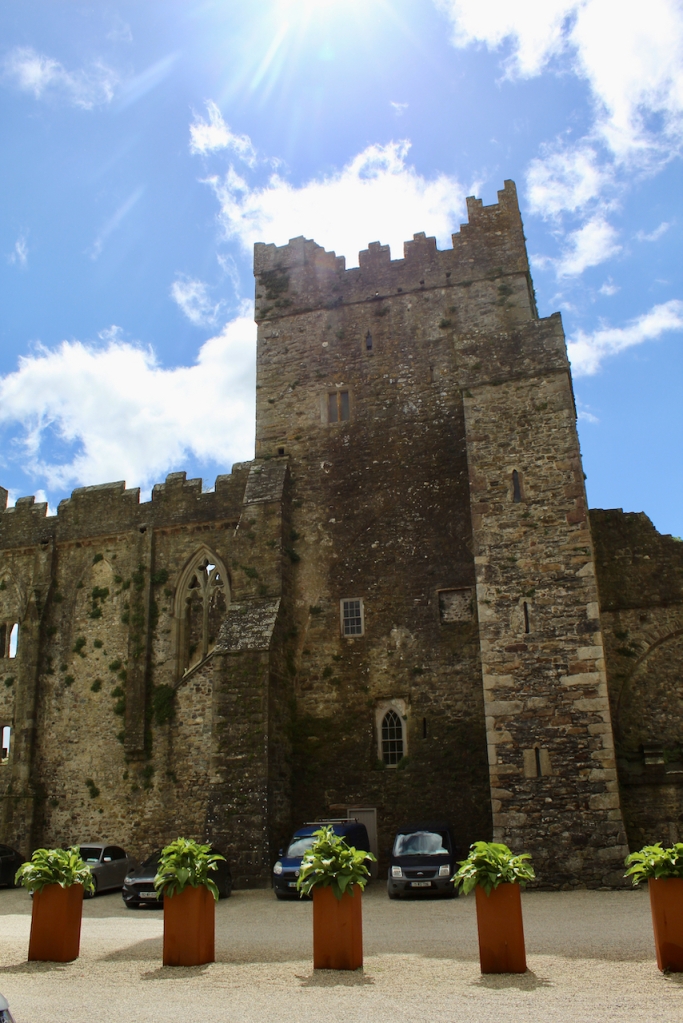
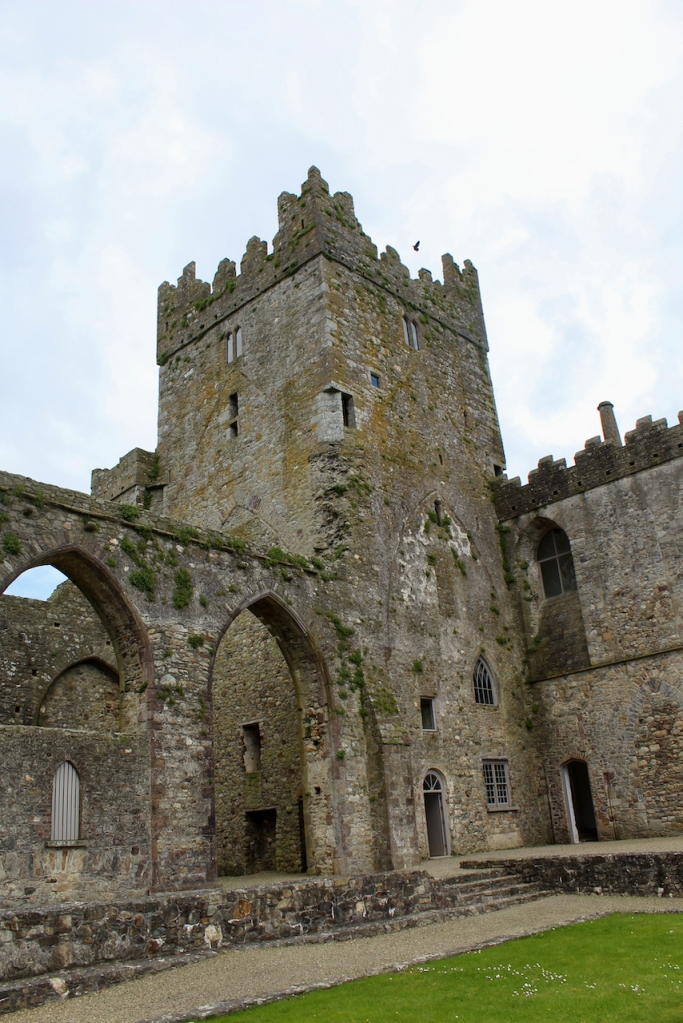
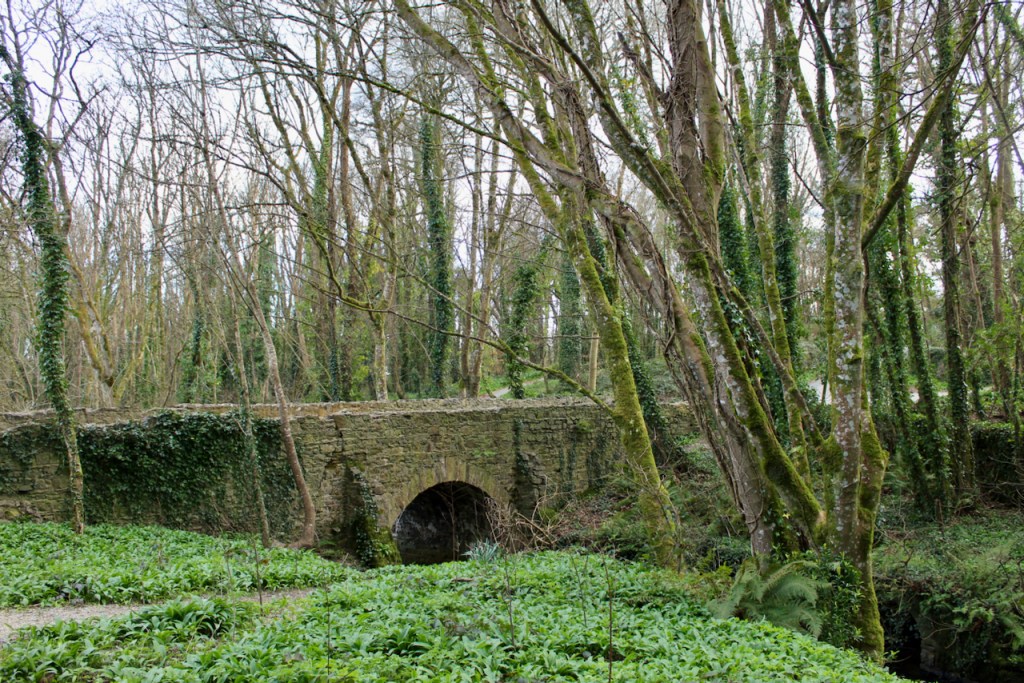
A chapter by Sean Clooney about Tintern Abbey in Tintern Abbey County Wexford, Cistercians and Colcloughs, Eight Centuries of Occupation, 1st Edition edited by Kevin Whelan, 2nd Edition edited by Anne Finn, tells us that Anthony Colclough, much like King Henry VIII, divorced his first wife! He divorced Thomasine Sutton in 1547 and married Clare Agard. He converted the tower of the abbey into a fortified tower house. A fire in 1562 had destroyed many of the other buildings. He also built the unique fortified bridge nearby.
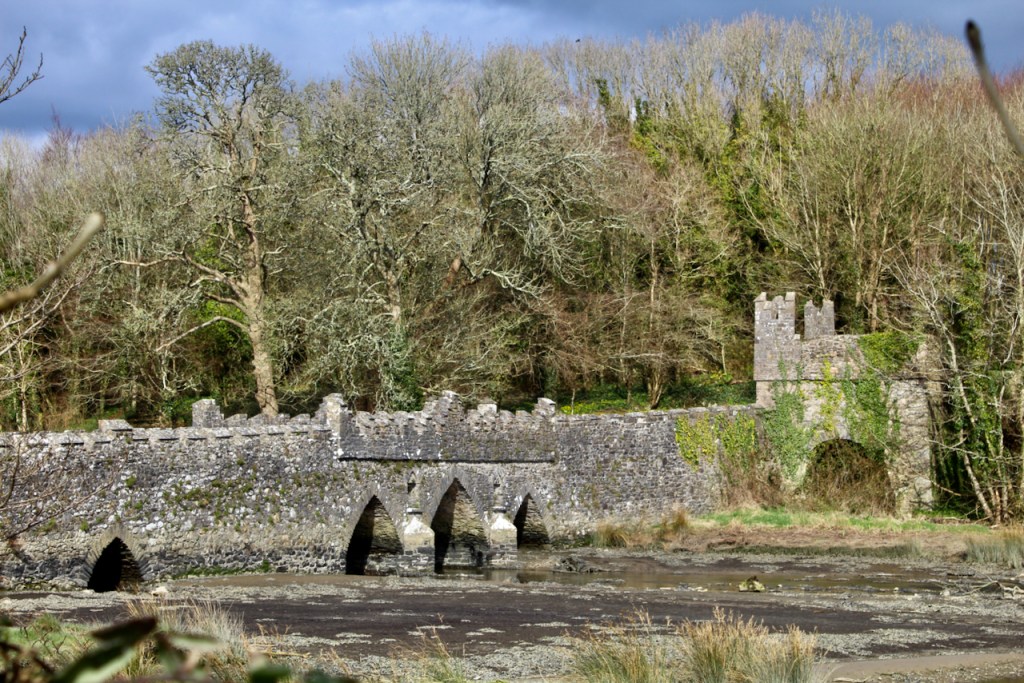
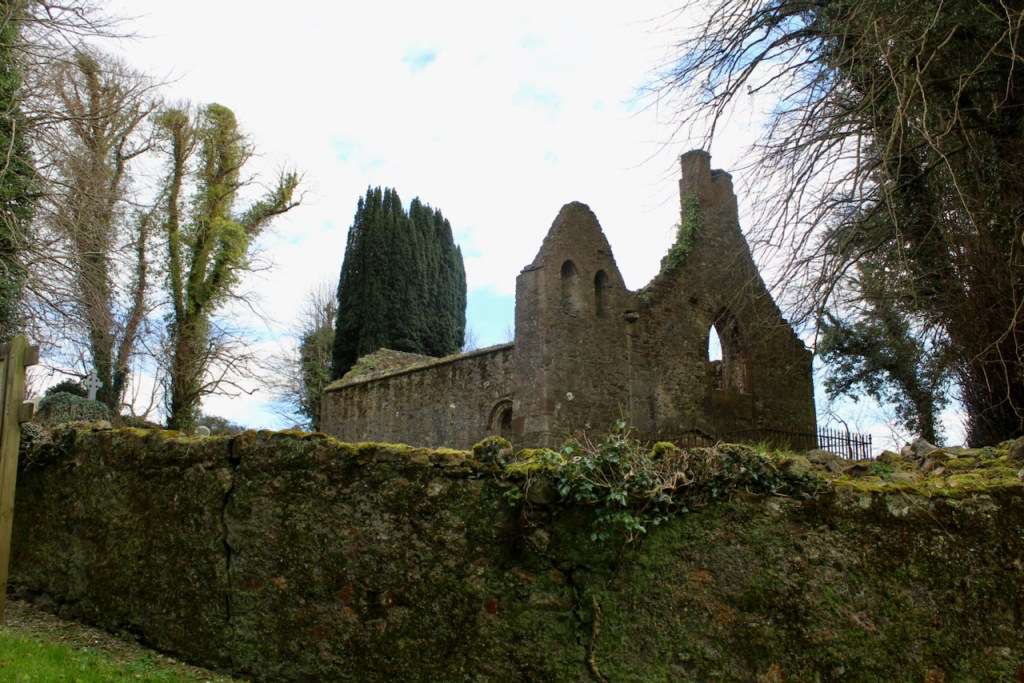



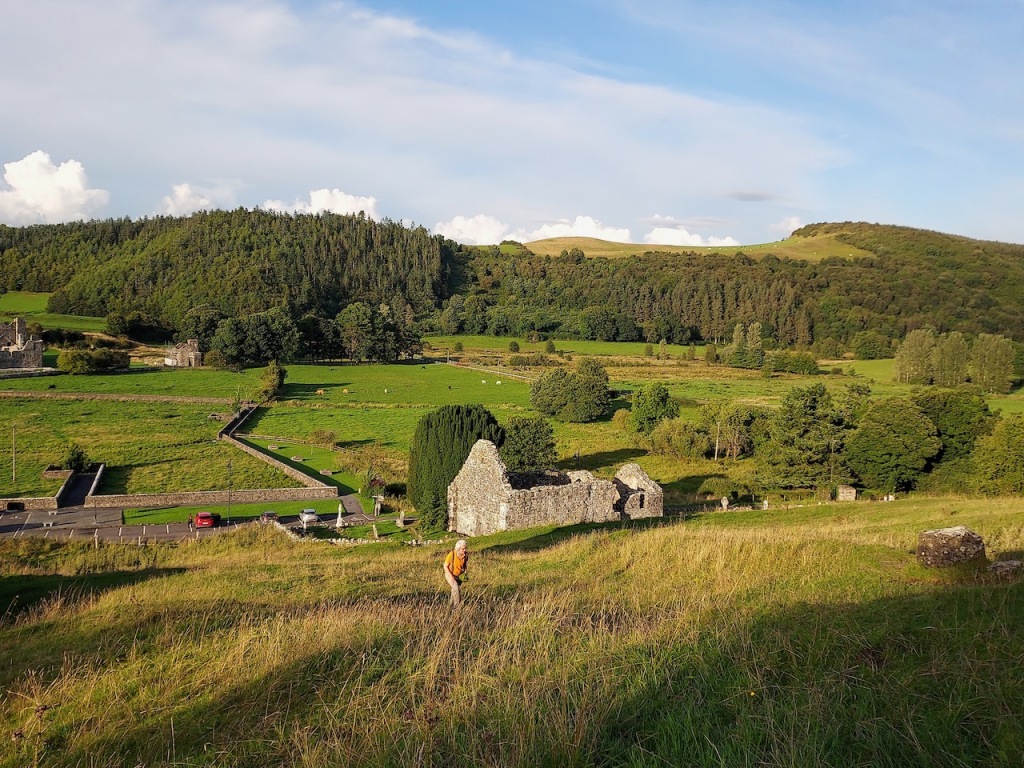
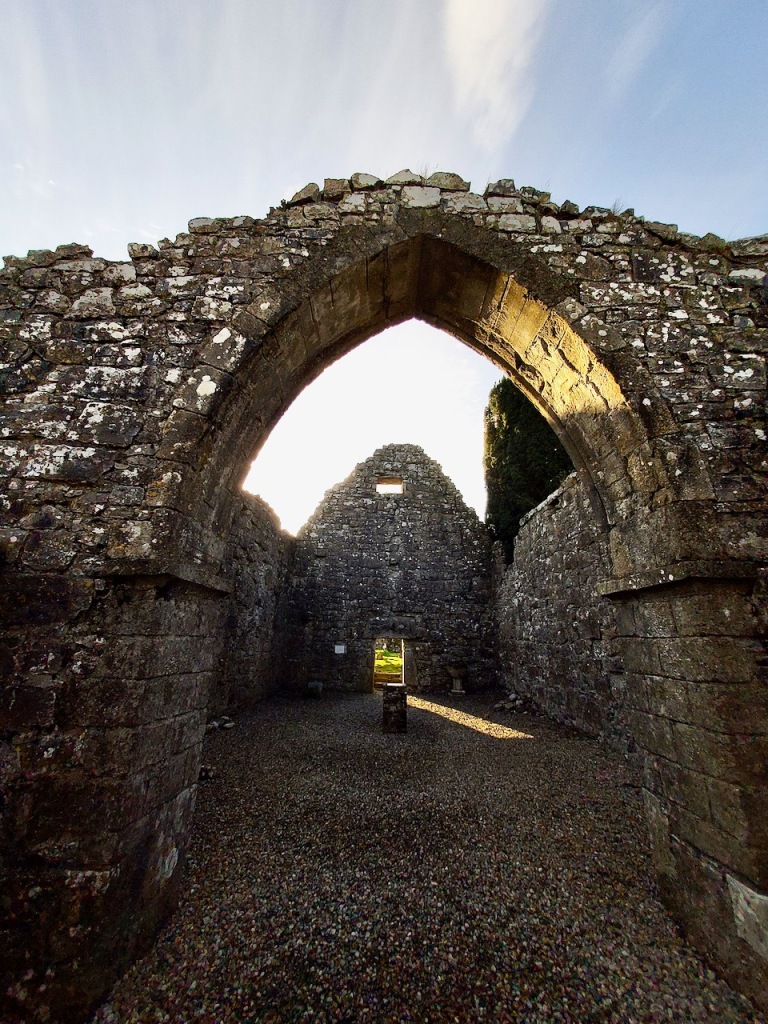
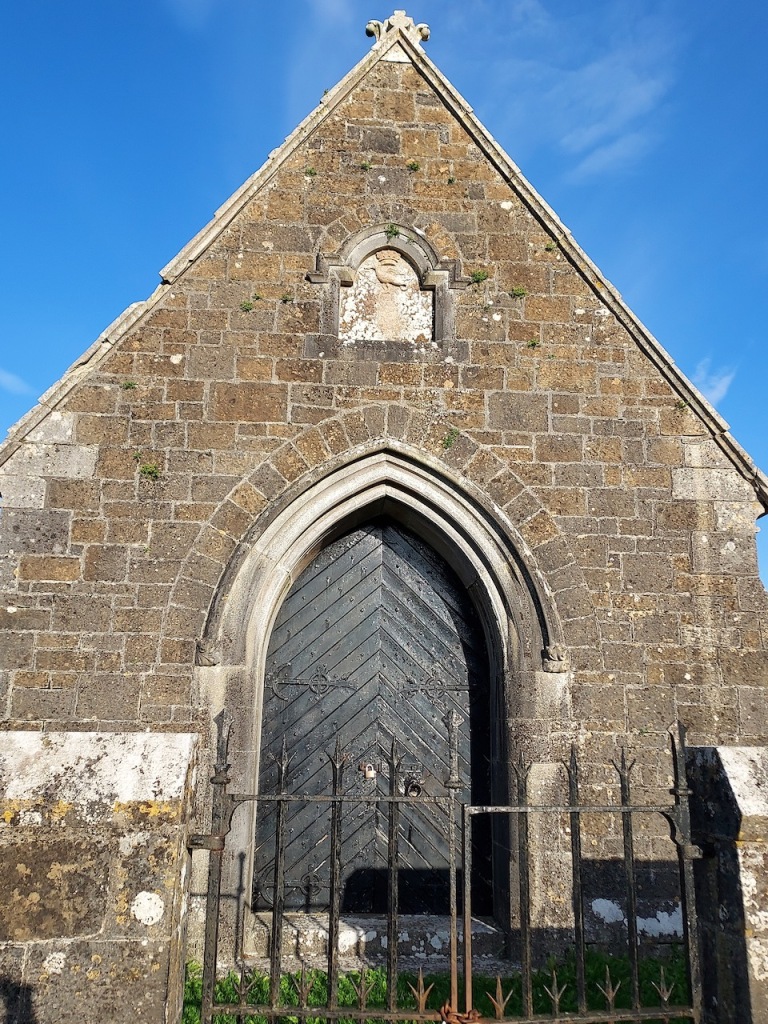
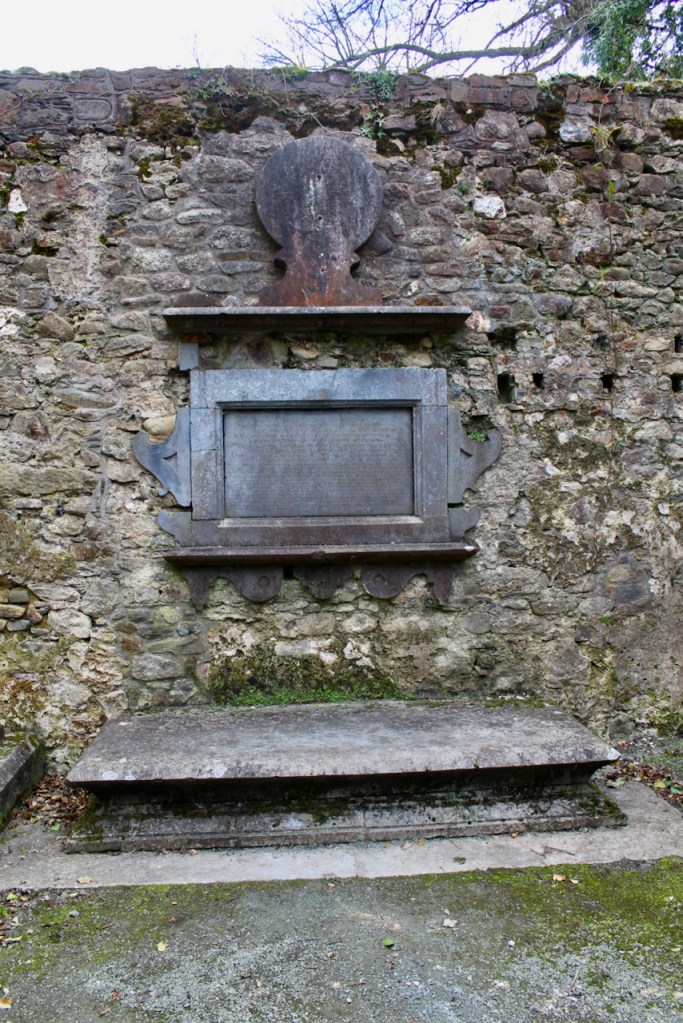
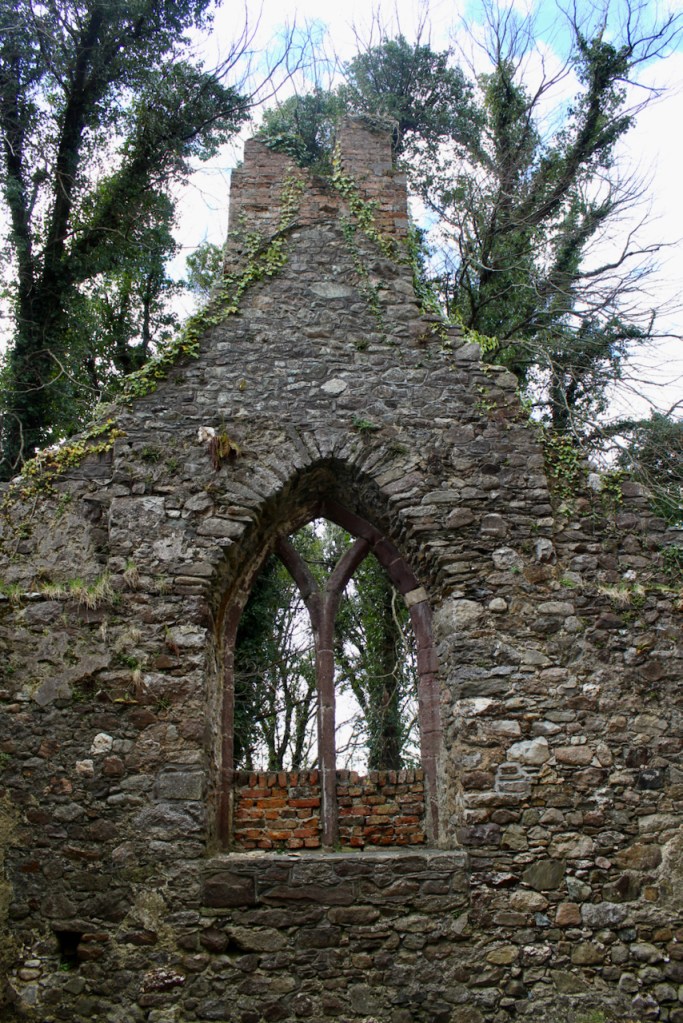
He is buried in the small ruined church a few hundred metres south east of the abbey. The plaque in this church reads:
“Here lieth the body Syr Anthony Colclought Knight, eldest sune of Richard Colclought of Wolstanton in Stafordshire Esquier who came first into this land in the 34 yere of Henry the 8 and then was Captayn of the Pensioners in which place and others of greater charge he continued a most faythful serviter during the life of Edward the VI and Queen Mary and until the XXVI yer of our most noble Queen Elisabeth and then died the IX of December 1584. He left his wife, Clare Agare, daughter of Thomas Agare Esquier 7 sonns, Frances, Ratlife, Anthony, Syr Thomas Colclough, Knight, John, Matew, Lenard and 5 doghters, Jaqnet who married to Nicholas Walsh Esquier of the Priveie Counsayle and one of the Justice of the Kings Bench in Ireland; Fraunc married to William Smethwike of Smethwik in Cheshier; Clare married to William Snead of Brodwal in Stafordshire Esquier; Elinor died iunge.”





Anthony’s son Thomas continued to develop Tintern, and is said to have established oyster beds in Bannow Bay. He married, first, Martha Loftus, daughter of Adam Loftus, Protestant Archbishop of Dublin. Their son Adam was raised to the baronetcy as 1st Baronet of Tintern Abbey. Thomas’s second wife, Eleanor Bagenal, was Catholic. After her husband’s death, she married Lucas Plunkett, 1st Earl of Fingall. Thomas’s son by his second marriage inherited lands at Duffry, where Duffry Hall was built by his grandson Patrick Colclough (d. 1691).

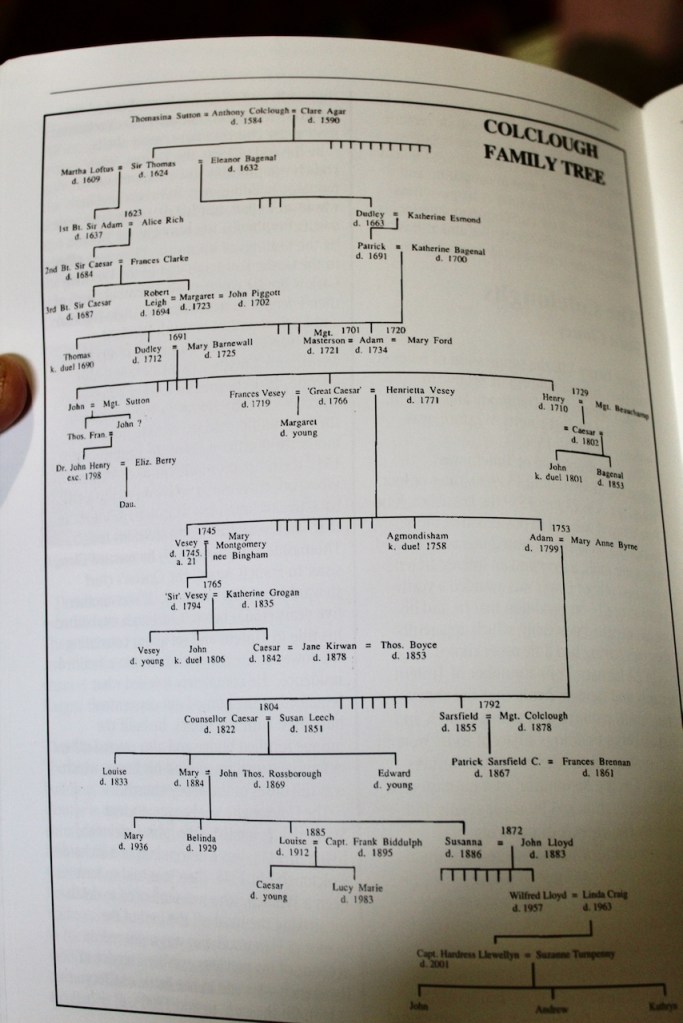
During the 1641 rebellion 200 local Protestant people took refuge in Tintern which was garrisoned by forty soldiers from Duncannon Fort situated nearby. At that time Tintern would have been inhabited by the 2nd Baronet, Caesar Colclough (d. 1684). Shortly afterwards the Catholic branch of the family laid siege to the Protestant branch who were in residence in Tintern Abbey. [2]
The Catholic branch who took control of the abbey following a two-week siege included Dudley Colclough (1613-1663), who had married Katherine Esmonde of Johnstown Castle, and his two brothers John and Anthony (who married Mary Esmonde from Johnstown Castle). Following Oliver Cromwell’s arrival in 1649 Dudley was banished to Connaught and he ultimately died in exile in France.
The 3rd Baronet of Tintern Abbey, Caesar (1650-1687) had no heir so the title expired and the lands passed to his sister Margaret. She married firstly, in 1673, Robert Leigh, of Rosegarland, who thereupon assumed the surname of Colclough; and secondly, in 1696, John Pigott, of Kilfinney, County Limerick, who also assumed the surname of Colclough.
Caesar Colclough (d. 1766), known as “Great Caesar,” great-grandson of Catholic Dudley who had rebelled in 1641, united the properties. His grandfather, Patrick Colclough of Duffry Hall, married Katherine Bagenal of Dunleckney, County Carlow. Patrick Colclough was Catholic and very active in the Jacobite cause and was attainted of High Treason and outlawed by King William III but he died in 1691, before the attainder passed into law, so his eldest son was able to inherit his estates. His son Dudley (d. 1712) was brought up in the Protestant faith. [3] He married Mary Barnewall, granddaughter of Nicholas Barnewall, 1st Viscount Barnewall of Kingsland. The Great Caesar was their son.
The “Great Caesar” was a great sportsman and generous landlord. He brought a team of men to play hurling in front of King George. The team wore a yellow sash to distinguish them from the opposition, and the king or queen called out, “Come on the yellow bellies!” and from then on, Wexford men are called “yellow bellies.”
Caesar’s second wife, Henrietta Vesey, was the great-granddaughter of King Charles II, granddaughter of Mary Walters de Crofts, illegitimate daughter of Charles II.
Upon the Great Caesar’s death in 1766, the Tintern estates passed to his grandson Vesey, and the Duffry estates passed to his younger son Adam. Vesey Colclough (1745-1794) married Catherine Grogan of Johnstown Castle in County Wexford. It was not a happy marriage and they separated, but Vesey remained in Tintern and transformed the chancel of the abbey into a residence. He was extravagant in his lifestyle, however, and his son John had to extricate himself from debt accrued.
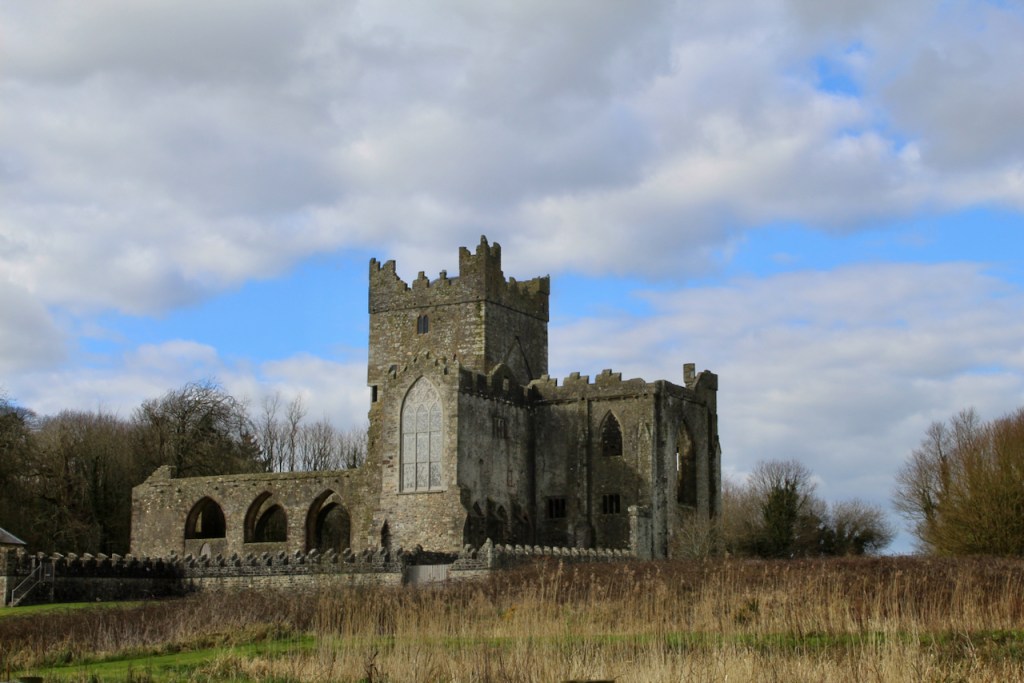


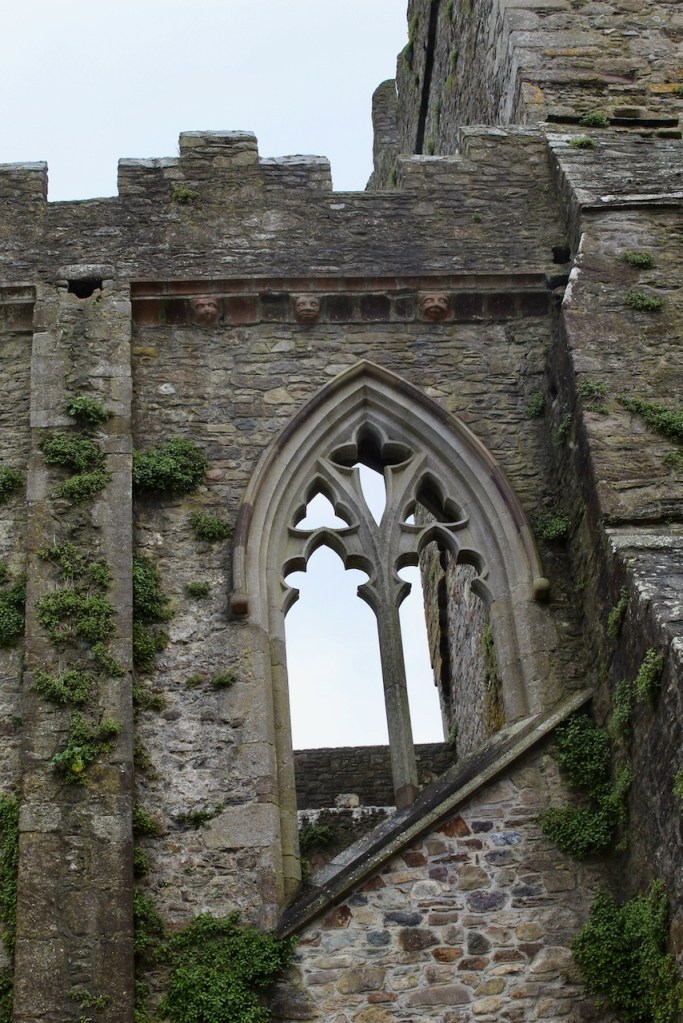
John did more renovations of the abbey, constructing a second storey over the south transept aisle, which was known as the Lady Chapel. The lower storey held a kitchen and above, a library, wiht a massive Gothic window facing the sea.
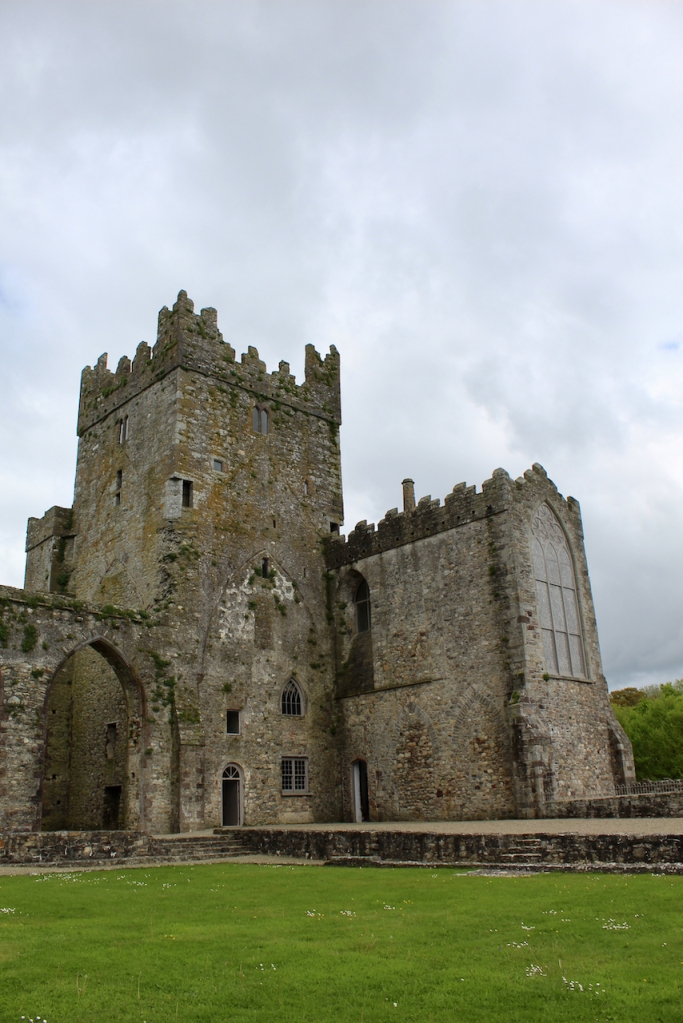
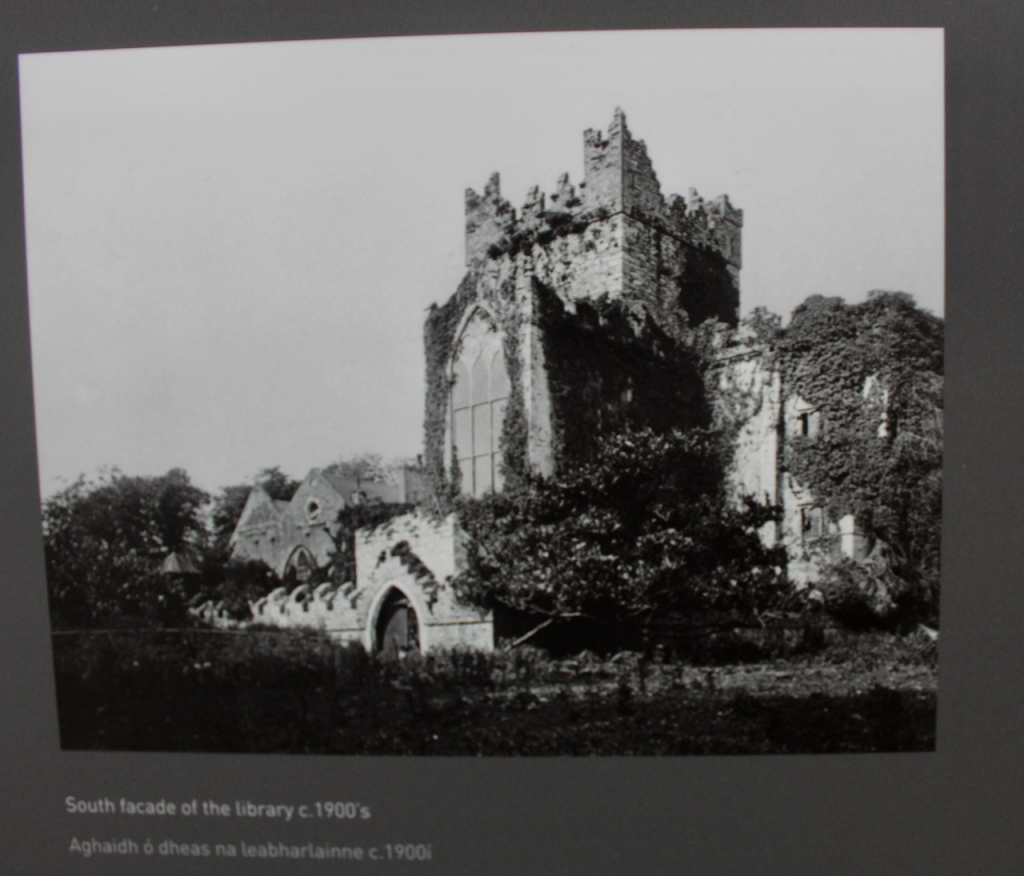
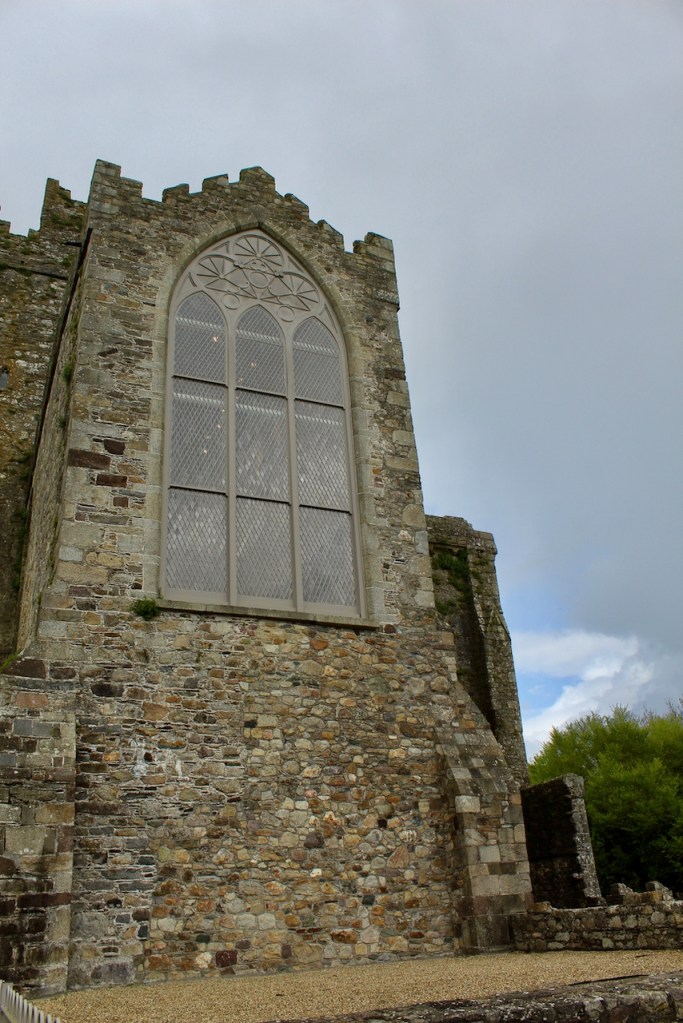
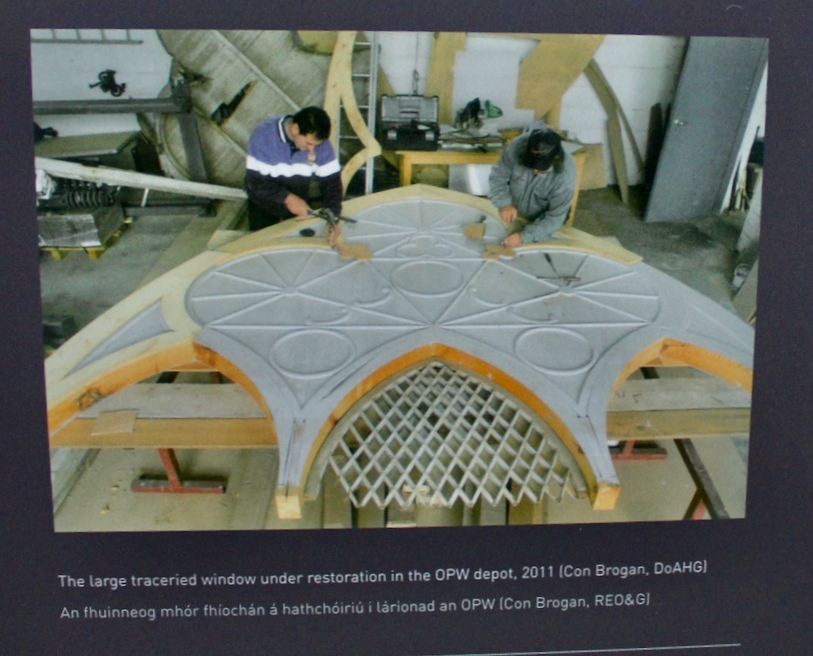
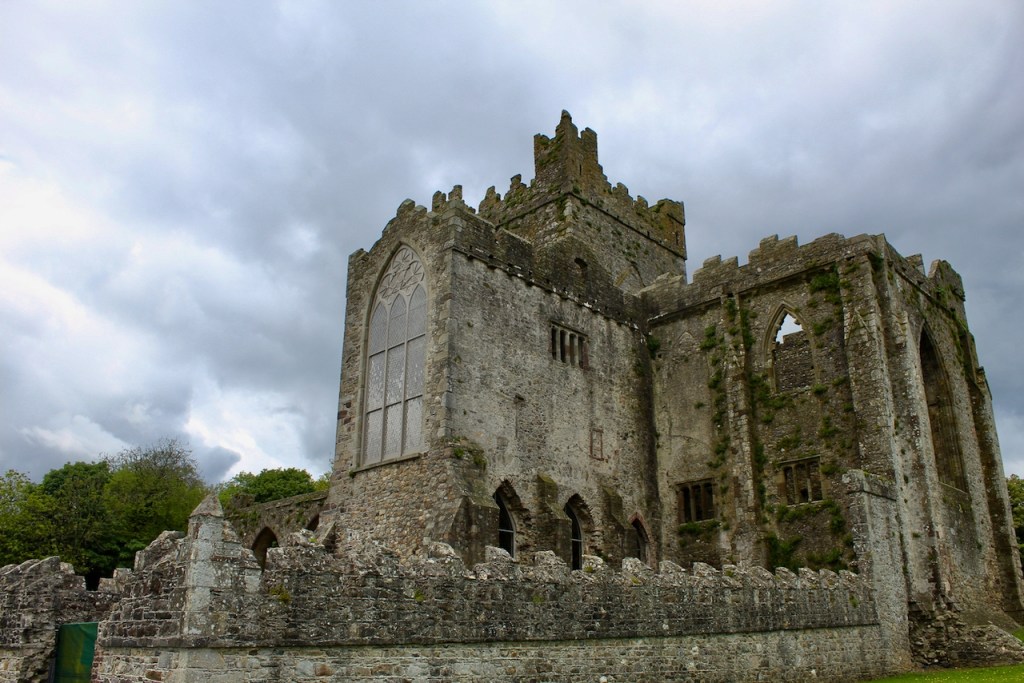






However, when John was standing for election he was shot dead in a duel in 1807 by William Alcock of Wilton Castle in County Wexford, an opponent in the election. Alcock was acquitted by a jury of his peers, but his mental health deteriorated.
Four Colcloughs died in duels. Thomas of Duffrey Hall was killed in a duel in 1690. Agmondisham, son of “Great Caesar,” was killed in a duel in 1758, and John Colclough of St. Kieran’s was killed in 1801 by Henry Loftus Tottenham of Loftus Hall, far down on the Hook Peninsula (a property that is again advertised for sale).
Tintern passed to John’s brother, another Caesar Colclough (1766-1843). He and his wife Jane Kirwan had no children, and some suspected his wife of killing him. She went on to marry Thomas Boyce. Her right to the property was challenged by the Colclough family. So many court cases were instigated that it has been said that it was one of the inspirations for Dickens’ “Jarndice vs Jarndice” in Bleak House.
Adam, the son of “Great Caesar” who inherited Duffry, had a son, Caesar, who died in 1822. He was Chief Justice of Prince Edward Island in Canada. It was his daughter, Mary, who married John Thomas Rossborough, who eventually gained ownership. Her husband took the name Colclough.
The Colclough family lived there until 1958, when it was presented to the state by Lucy Biddulph-Colclough.
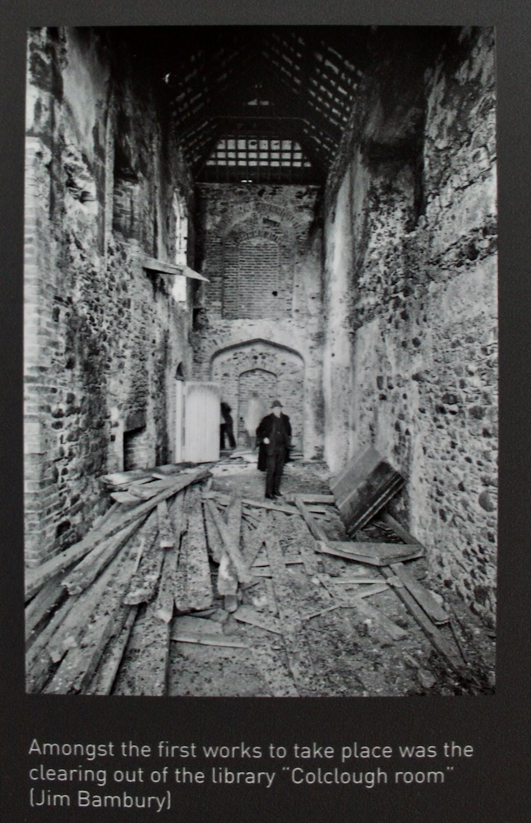
The Board of Works that took on care of Tintern Abbey dismantled the residential part of the building: floors, doors and windows were taken out, the roof was taken off, and materials were sold by auction. It was only twenty years later that the Board of Work returned to preserve the abbey.
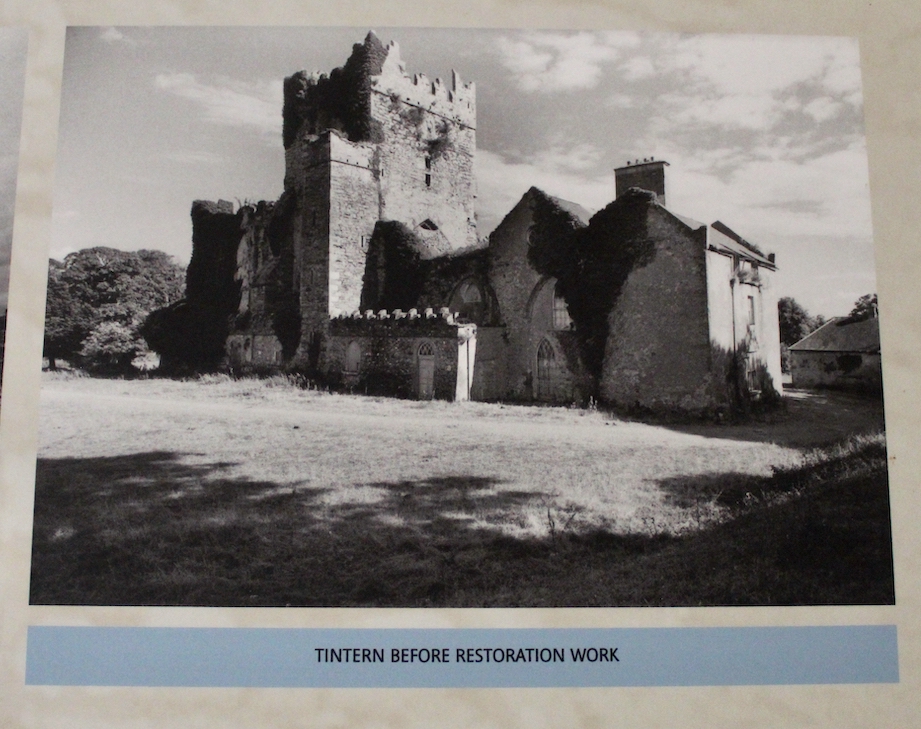
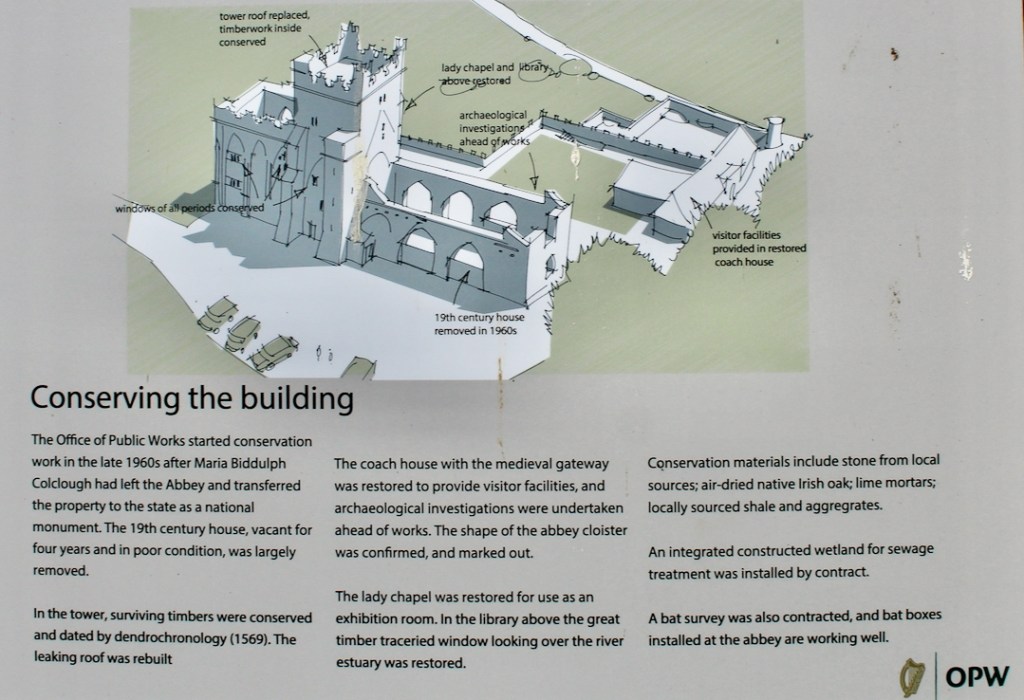


When it was being restored, the roof of the tower was rebuilt. The coach house with the medieval gateway was restored to provide visitor facilities.

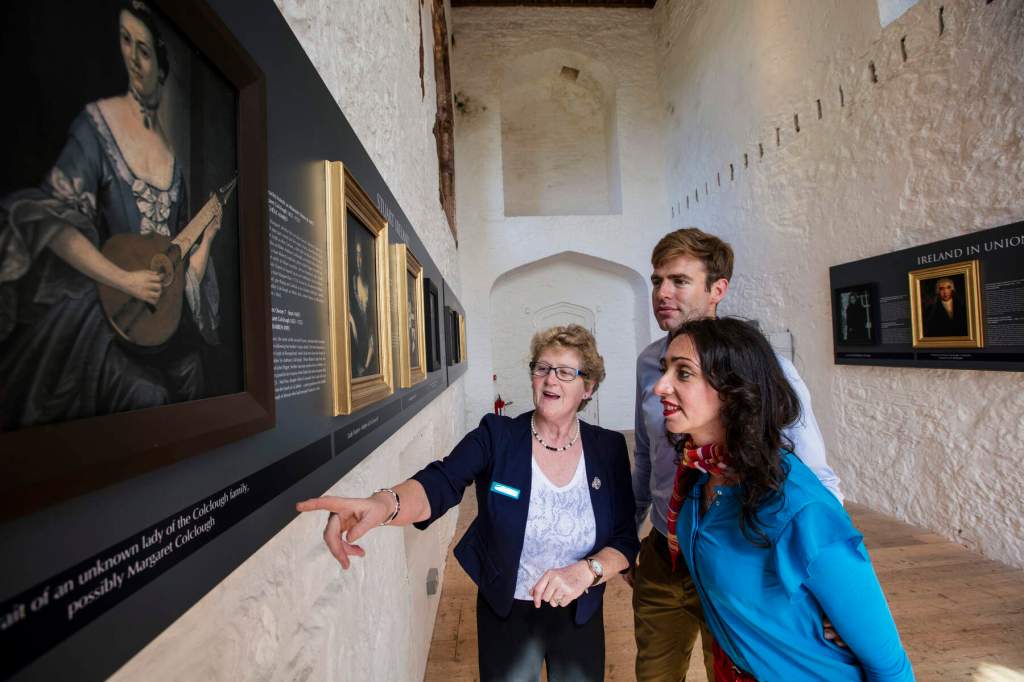
The Lady Chapel was restored for use as an exhibition room.
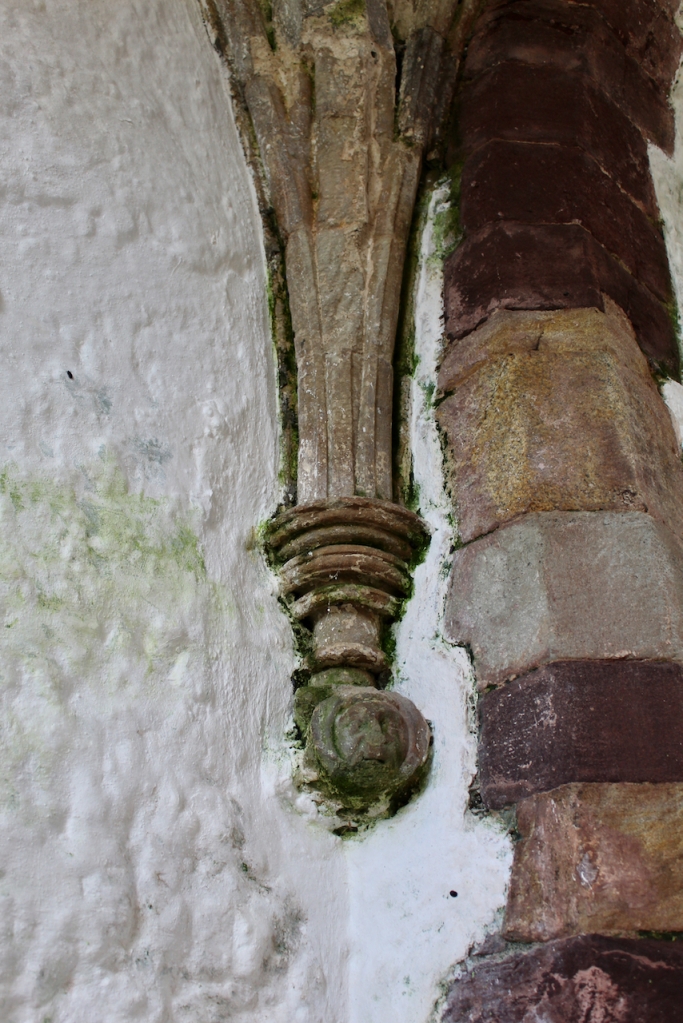
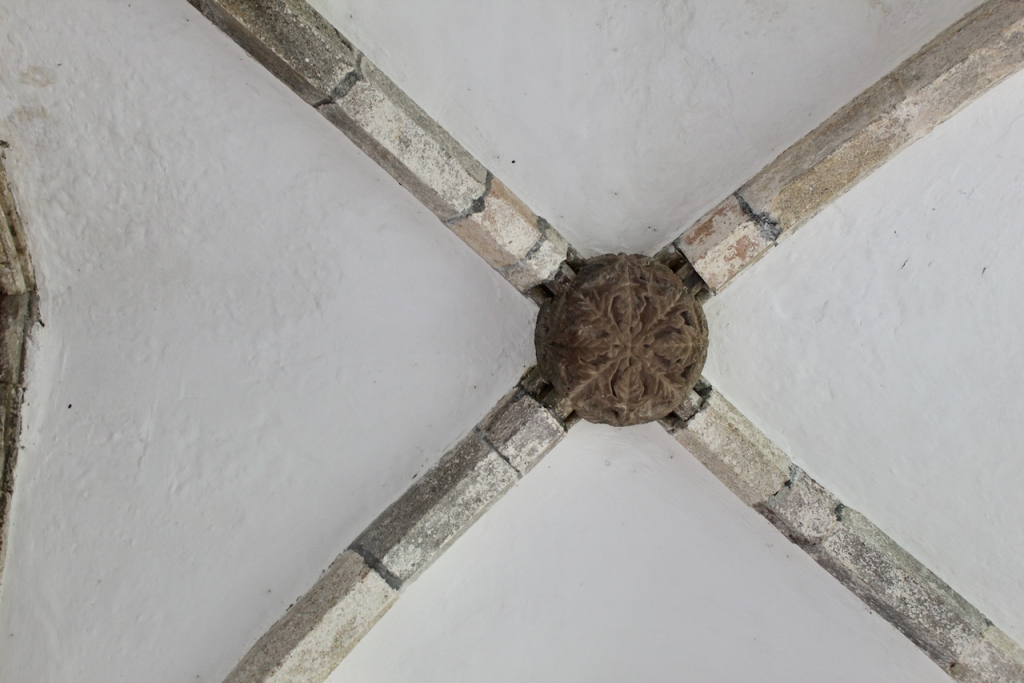




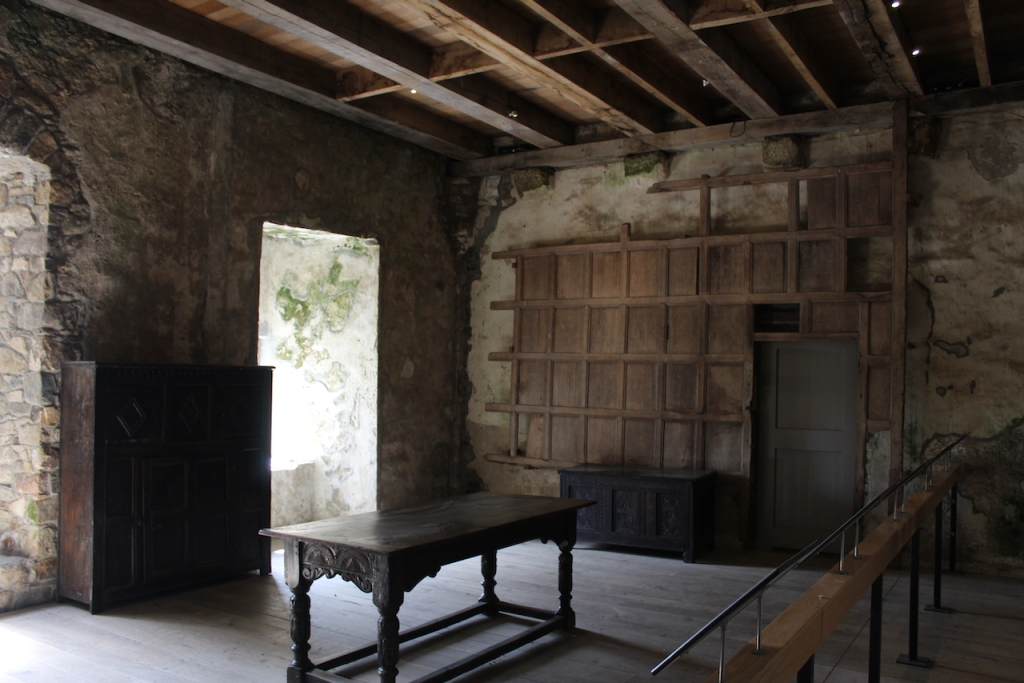
When the Abbey was converted into a residence, new flooring was added and the tower house was divided into rooms with wattle and daub timber frame screen walls and oak panelling fixed to the masonry walls. What remains of the oak panelling has been conserved and is now located on the first floor of the Crossing Tower. Dendrochronology dates the timbers to 1600-1620. It was known as “wainscotting.” It added warmth to the room.
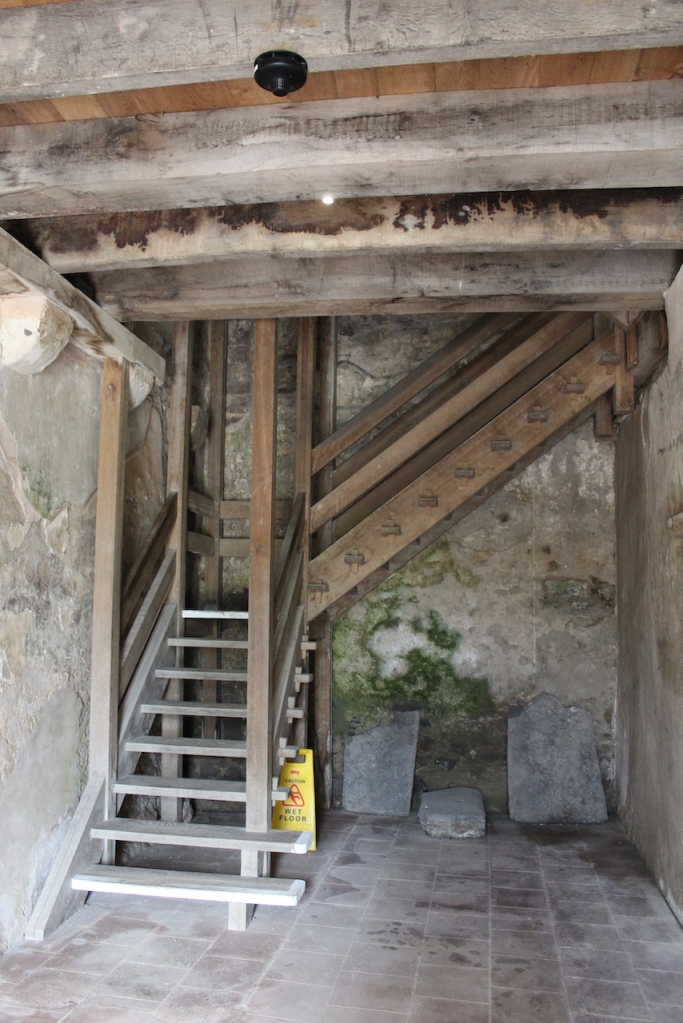
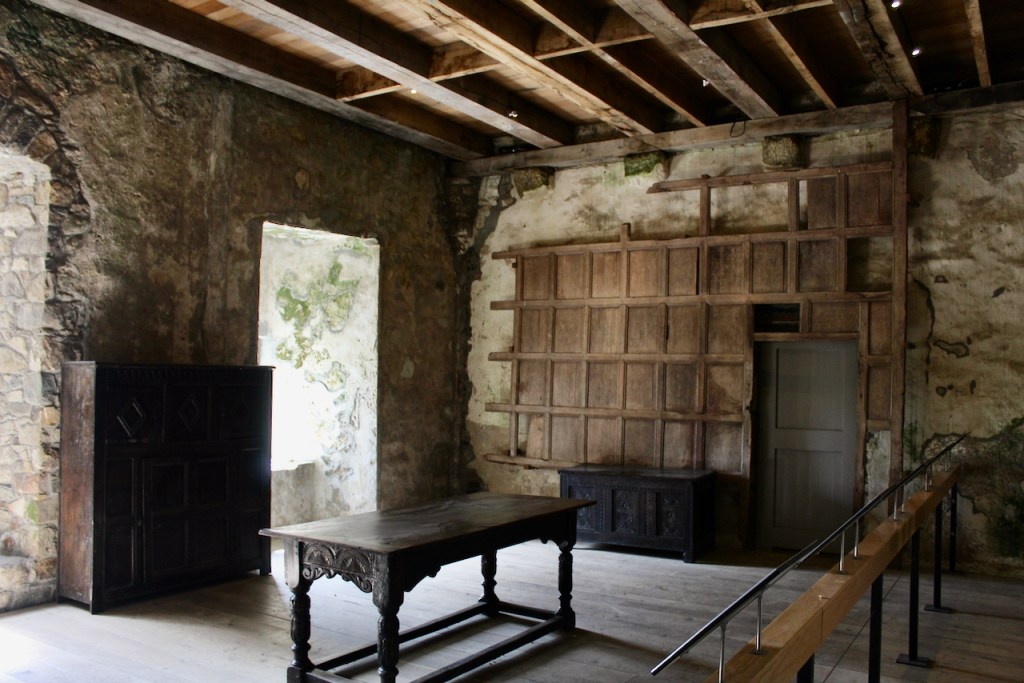
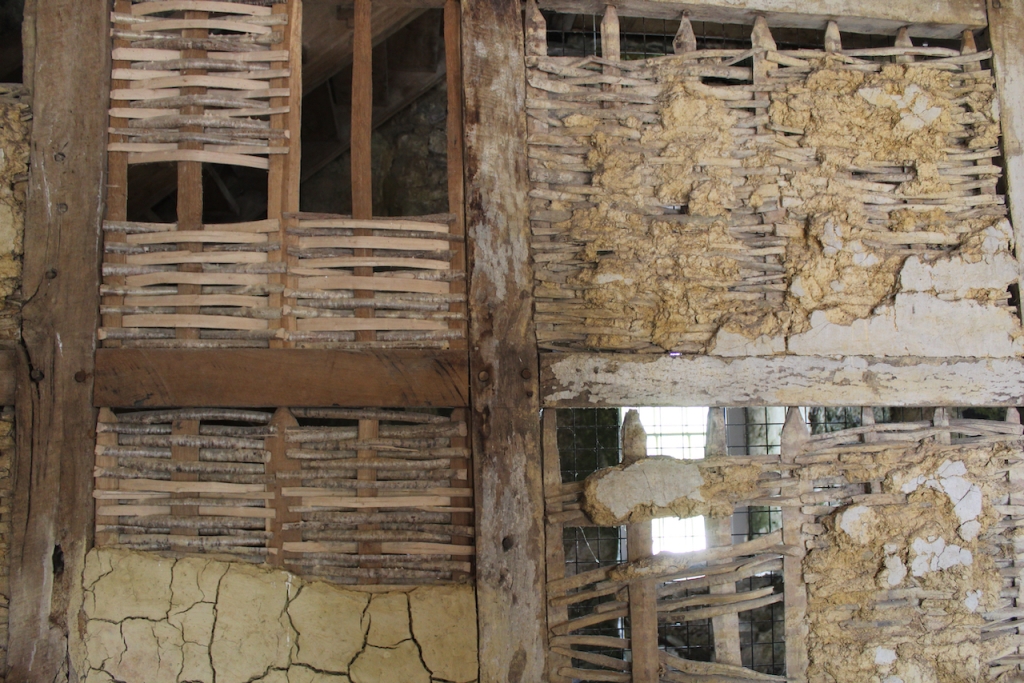
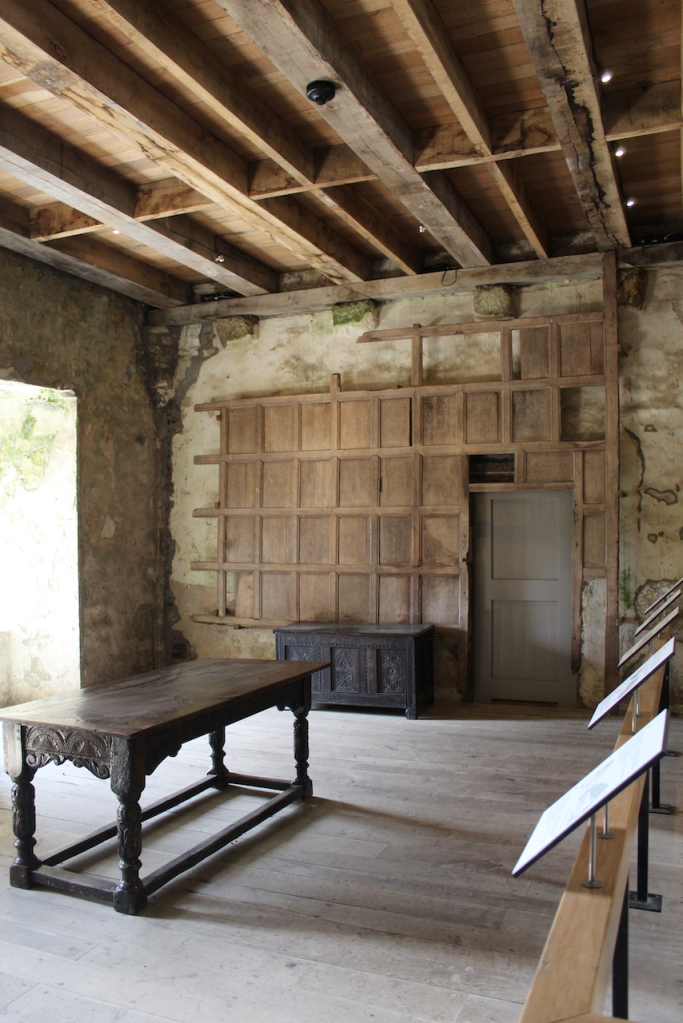
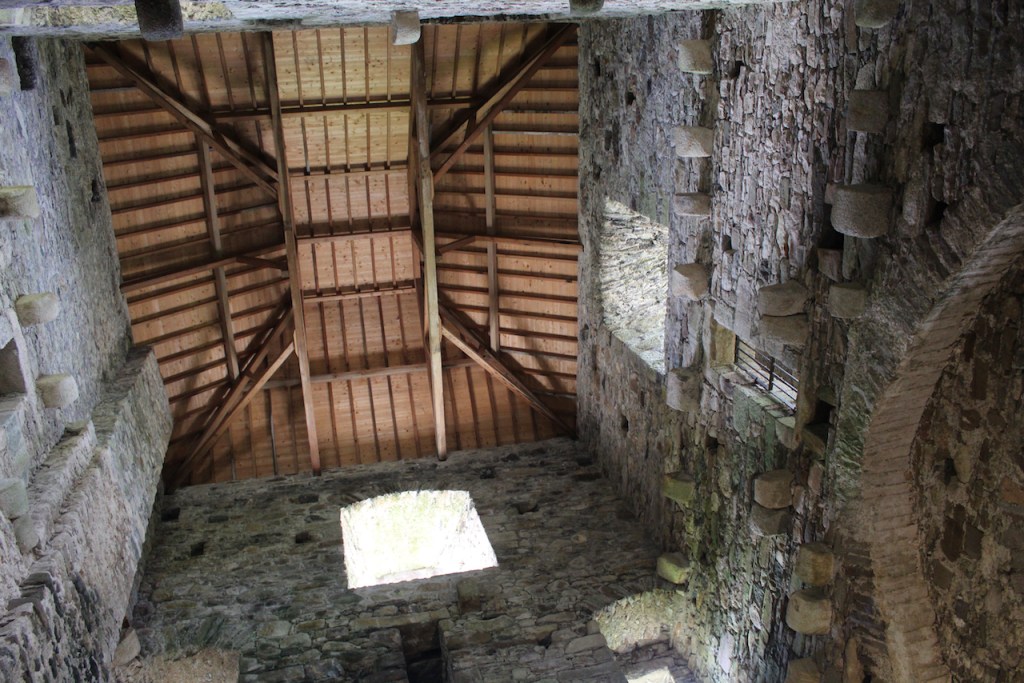
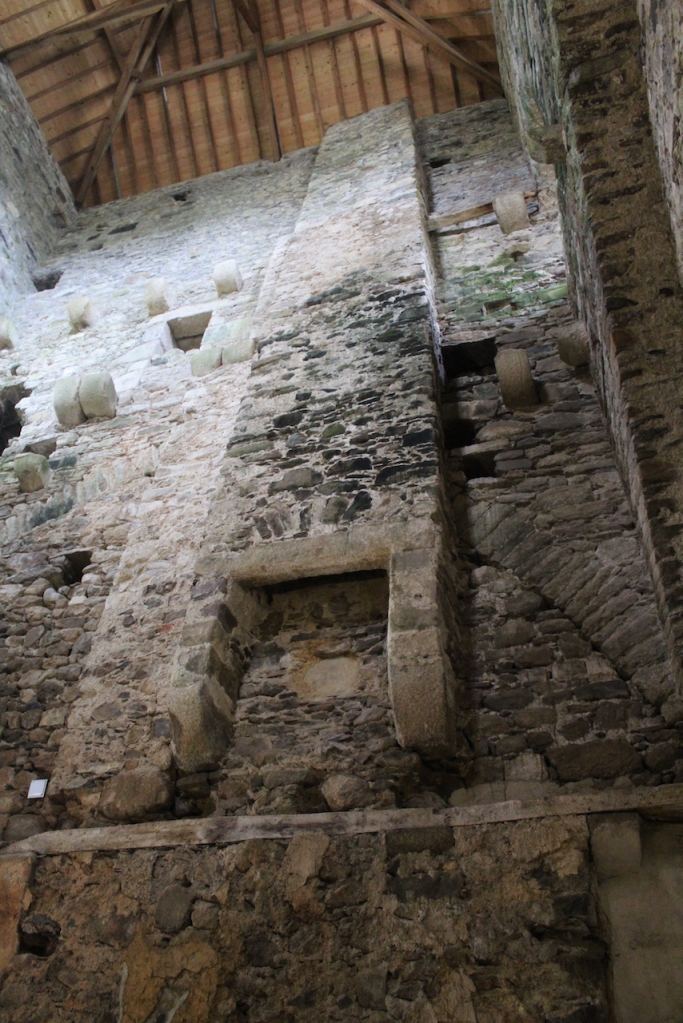
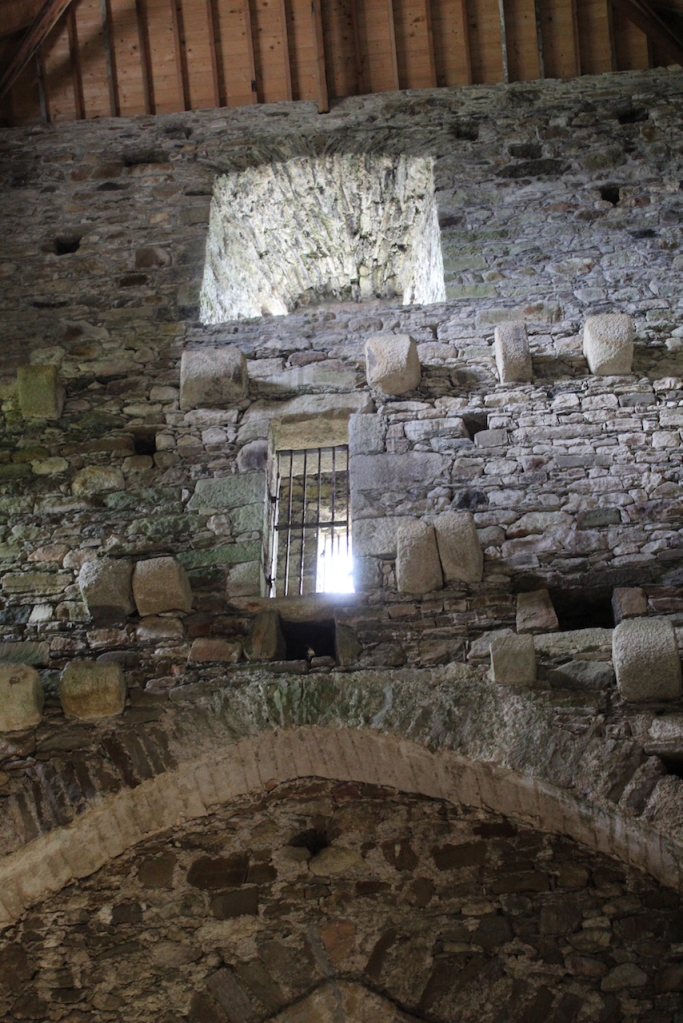
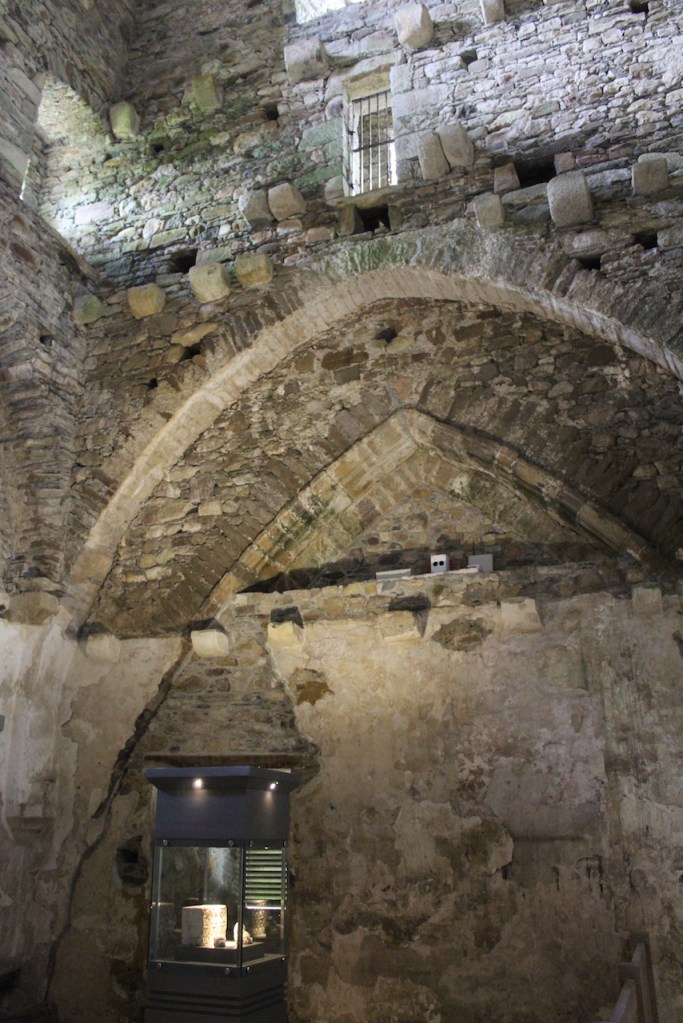
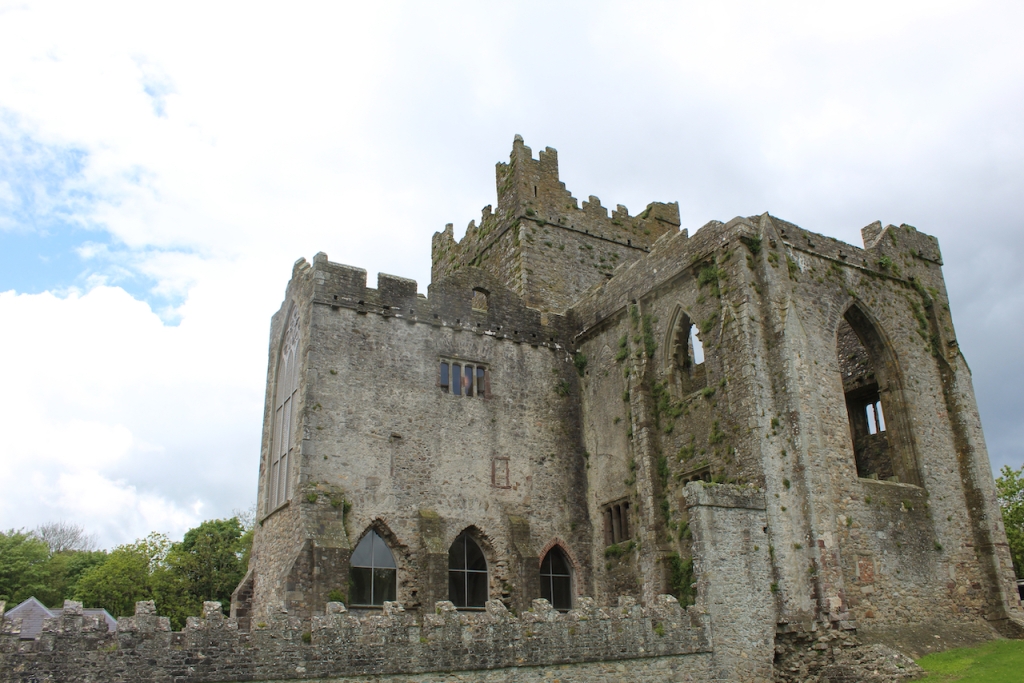



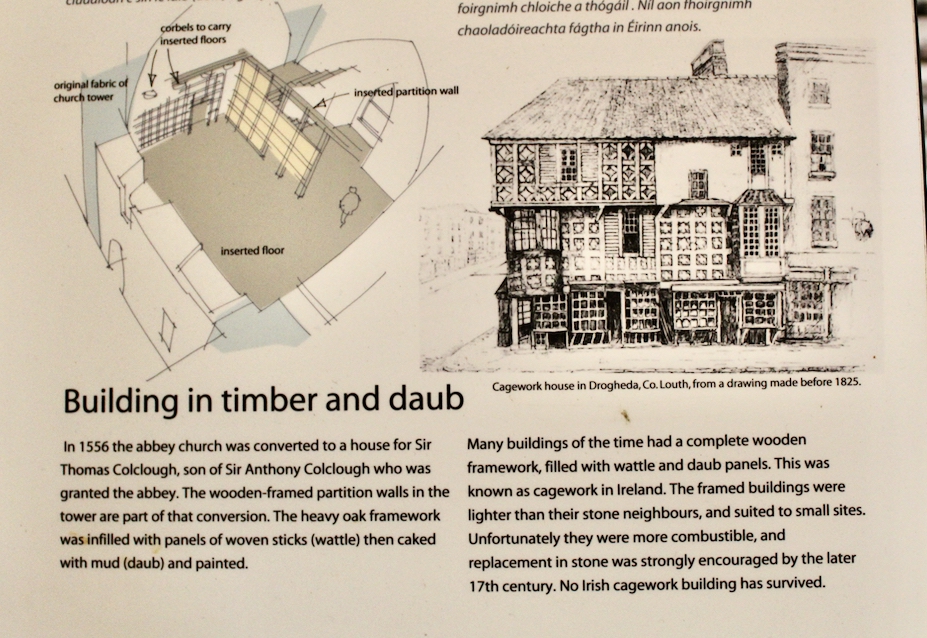














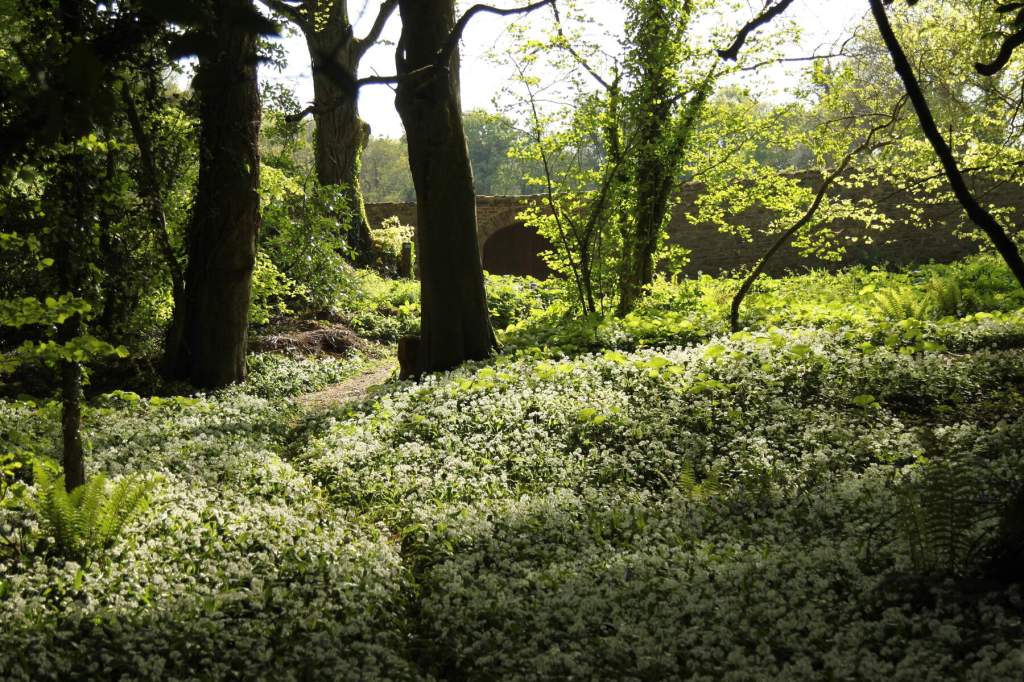
The website continues: “Conservation works have included special measures to protect the local bat colonies. The abbey is set in a special area of conservation and is surrounded by woodland within which are walking trails. Not to be missed is the restored Colclough Walled Garden situated within the old estate.“
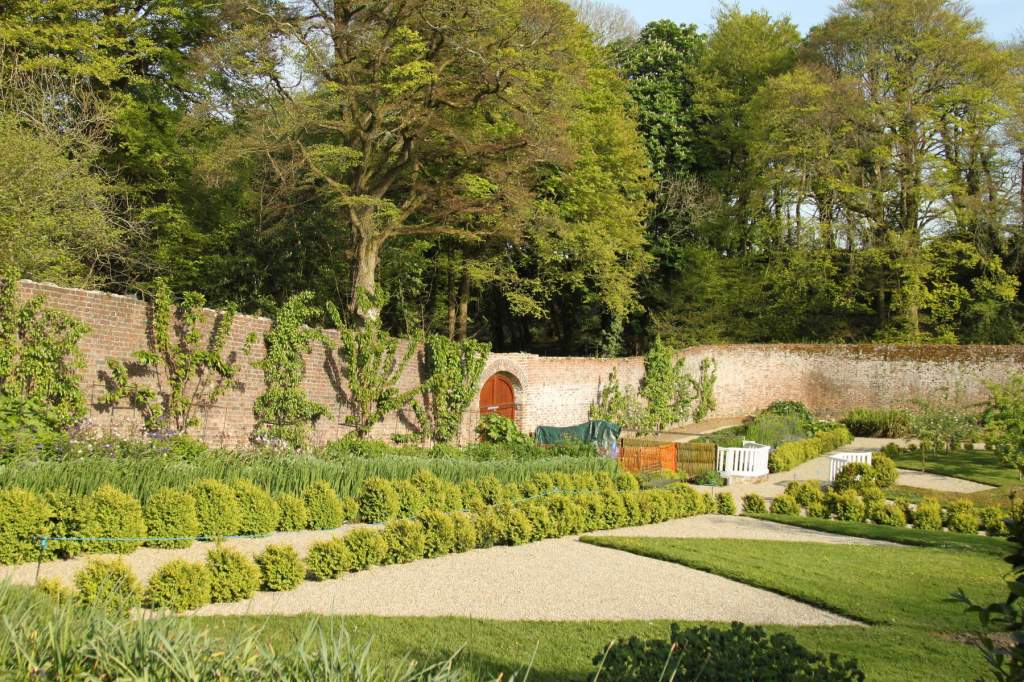



Following the donation of Tintern Abbey to the Irish State in 1959 the walled garden was abandoned to nature and became overgrown. The gradual restoration of the walled garden by a team of volunteers began in 2010 and the 1830s layout shown on the Ordnance Survey was reinstated. The restored garden, which opened to the public in 2012, is divided into two sections: the Ornamental Garden and the Kitchen Garden.



[1] https://www.irelandscontentpool.com/en/media-assets/media/81101
[2] notes from Tintern website, by Breda Lynch.
[3] https://genealogy-and-you.com/onewebmedia/Colclough.pdf
See the sale of Loftus Hall, courtesy of Colliers.
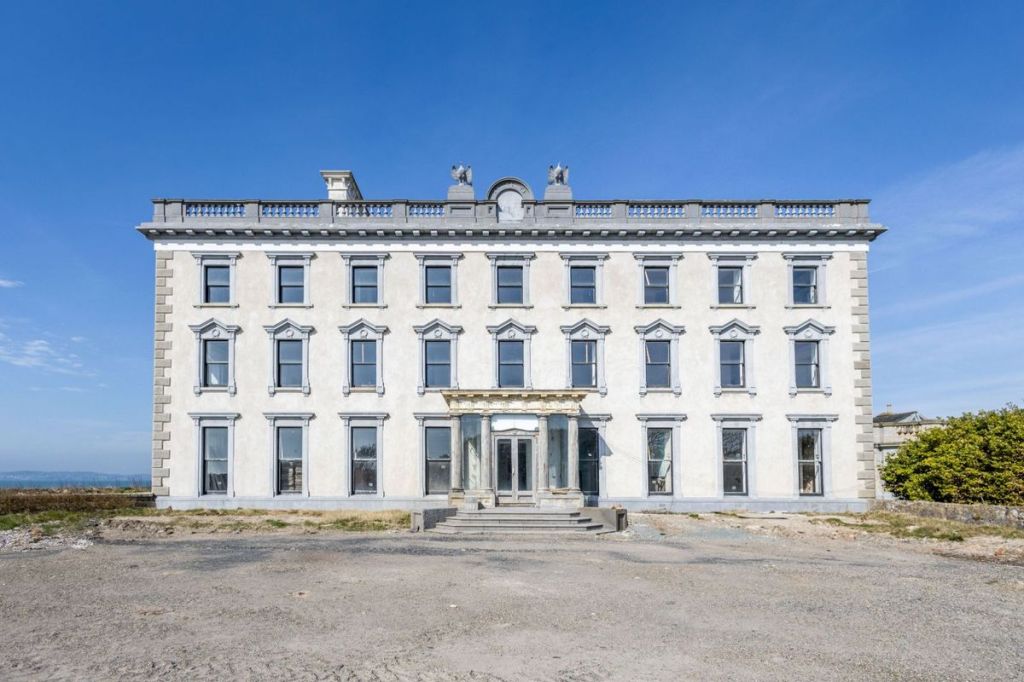

Loftus Hall is a large, partly re-furbished country house which was built on the site of the original Redmond Hall. The property boasts one of the most scenic locations in the southeast with views over Hook Peninsula and the world famous Hook Lighthouse, providing the most stunning landscape which is steeped in history and reputed by locals to have been haunted the property. The property was purchased by the Quigley family in 2011 and run as a tourist attraction with guided tours of the property and seasonal events. In 2021 the property was bought by its current owners who had a masterplan to refurbish the original building over two phases. The estate has already undergone extensive renovations, with Phase 1 nearing completion, set to transform the property into an exclusive 22-bedroom luxury hotel with high-end amenities, extensive food and beverage facilities, and beautifully landscaped gardens. The vision for Phase 2, included an additional 56 bedroom hotel block, a gym and spa, dedicated wedding facilities, 33 standalone garden cottages and 10 eco pods strategically placed along the perimeter of the property.
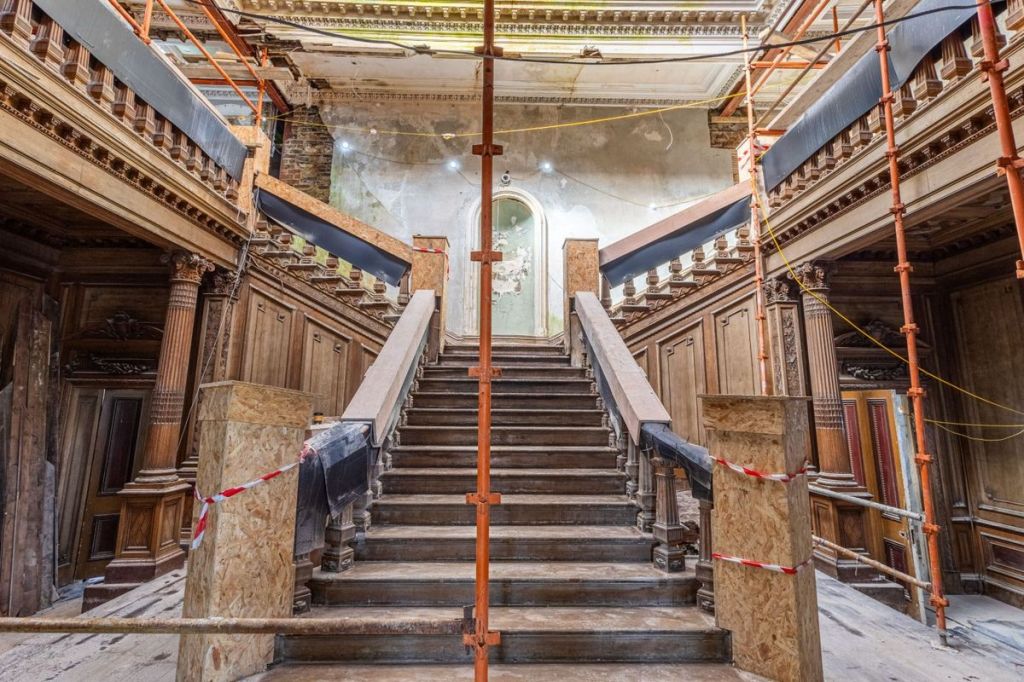

Location Loftus Hall is located on the southern tip of Hook Peninsula, close to the famous Hook Lighthouse, one of the oldest operational lighthouses in the world. Loftus Hall offers an unparalleled location for exploring the beauty and history of County Wexford. Just 4km from the iconic Hook Lighthouse, 33km from the vibrant town of New Ross, 45km from Wexford and 51km from Waterford. The property is also in close proximity to several popular tourist destinations, including Passage East (17km) and Dunmore East (30km) and the charming nearby villages such as Hookless Village, Slade, and Fethard-On-Sea, all within easy access. The location is quite picturesque, making it a popular spot for visitors interested in history, architecture, and the paranormal. Main House Built originally between 1870 and 1871 on the site of Redmond Hall, which traces its history to 1350, Loftus Hall comprises a detached nine-bay, three storey house. The estate is situated on approximately 27.68 hectares (68 acres) with the house extending to a total gross internal area (GIA) of 2,460 sq.m (26,480 sq. ft). Loftus Hall is a protected structure under RPS Ref WCC0692 and under the NIAH Ref 15705401. The estate has already undergone extensive renovations, with Phase 1 nearing completion. The ground floor of the original building has been transformed to contain a large dining room, a cigar room and a number of guest lounge areas. When completed the restaurant will seat over 100 covers which will feature visibility of the chefs working with an open pass, an outside BBQ area and fire pit adjacent to the new restaurant area with the existing bar fully refurbished. The hotel bedrooms are finished to second fix over the first and second floors and are appointed with large ensuite bathrooms and with commanding and sweeping views out to sea. The vision for Phase 2 consists of the development of a permanent marquee erected on the grounds which will cater for up to 300 seated wedding guests, a gym & spa, a new hotel bedroom block which will contain up to 56 additional bedrooms, 33 standalone garden cottages, 10 eco pods wrapped around the perimeter of the property, a children’s playground, a herb and vegetable garden, over two hundred car park spaces in total between the front and rear of the development and a walkway that will allow guests to access the beach directly from the development. The Grounds The grounds are a feature of Loftus Hall and have been maintained to the highest standards throughout the refurbishment. The gardens at Loftus Hall, particularly the walled garden, were designed to thrive in the unique climate of the Hook Peninsula. The garden’s high walls provided a sheltered environment, allowing a variety of plants to flourish. Fruit trees were a significant feature, with mulberry trees being particularly successful. The sheltered environment also supported other fruit trees like apple and pear. Additionally, the garden likely included a variety of herbs and vegetables, which were essential for the estate’s kitchen. The garden’s design and plant selection reflect the practical needs and aesthetic preferences of the time, creating a space that was both beautiful and functional.