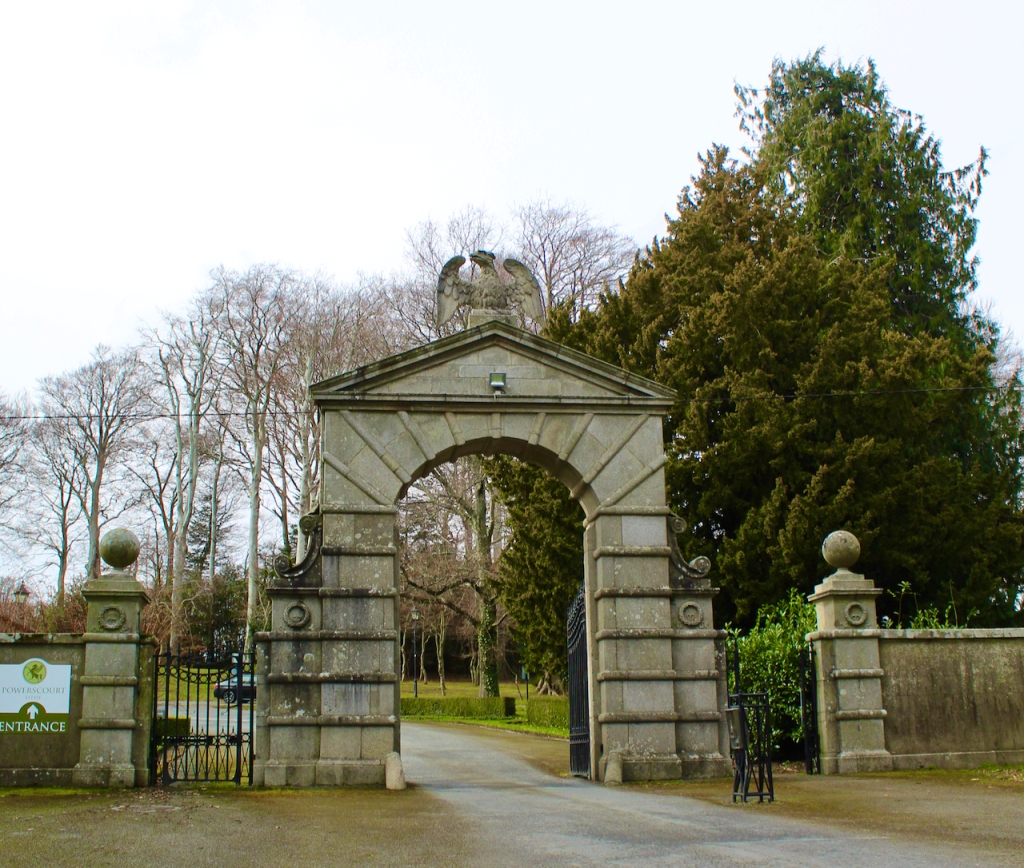
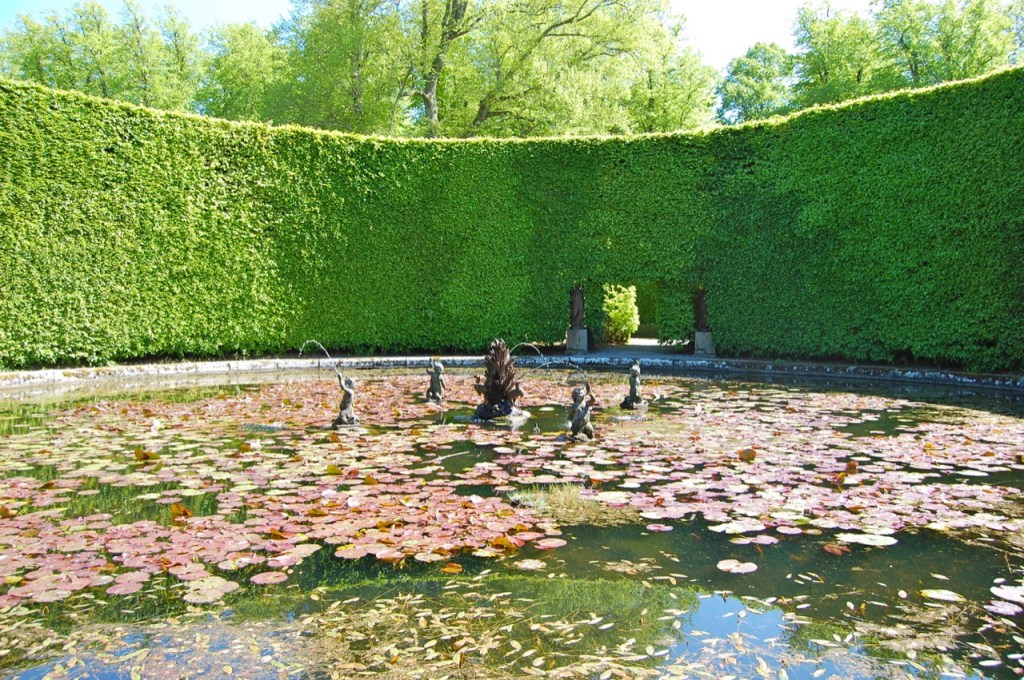
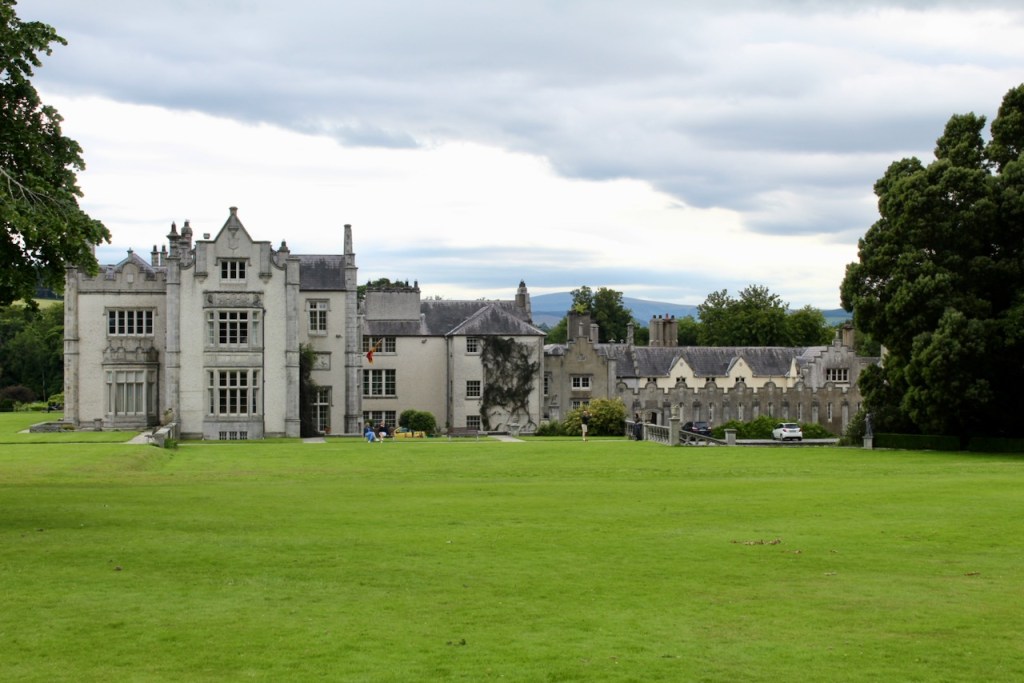
Open dates in 2026: Mar 9-30, May 4-31, June 1-7, 1pm-5pm, Aug 15-23, 2pm-6pm
Fee: adult €10, OAP/child/student €8
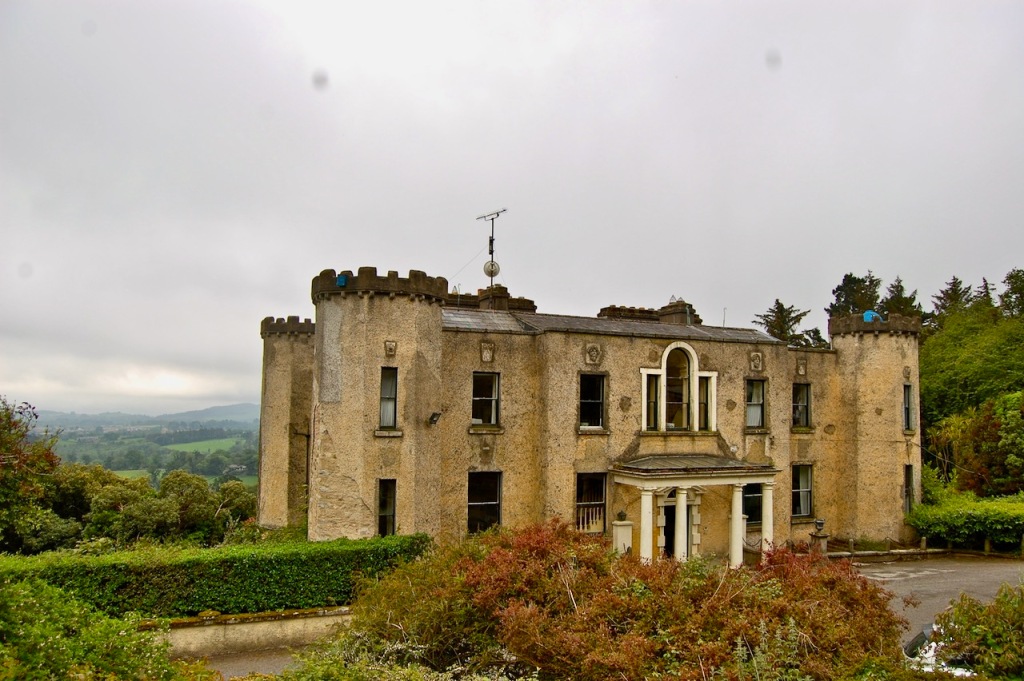


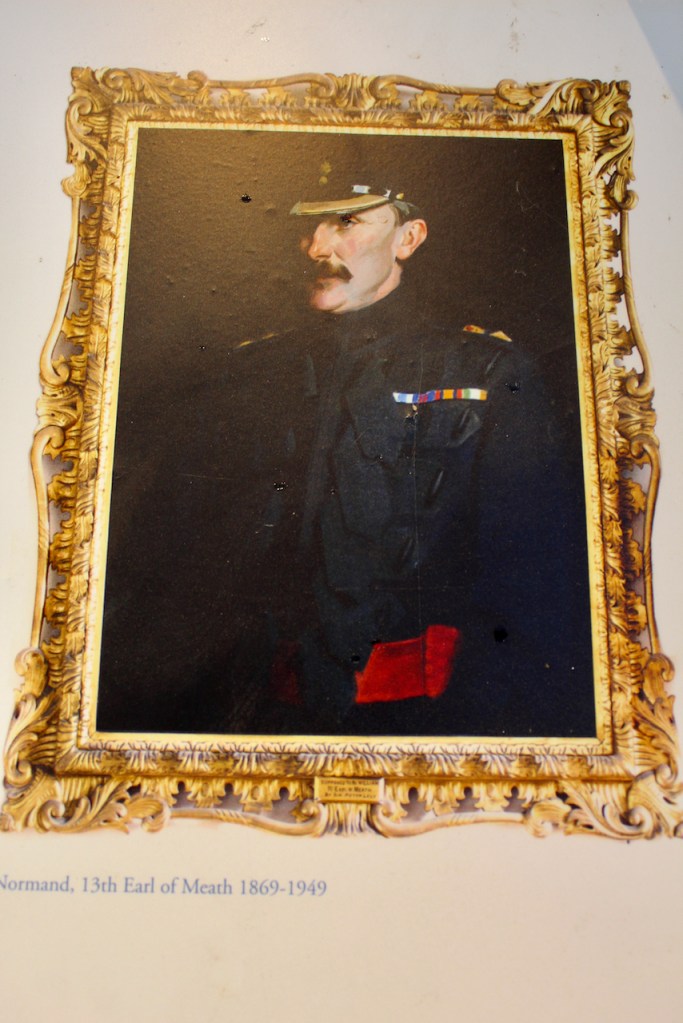
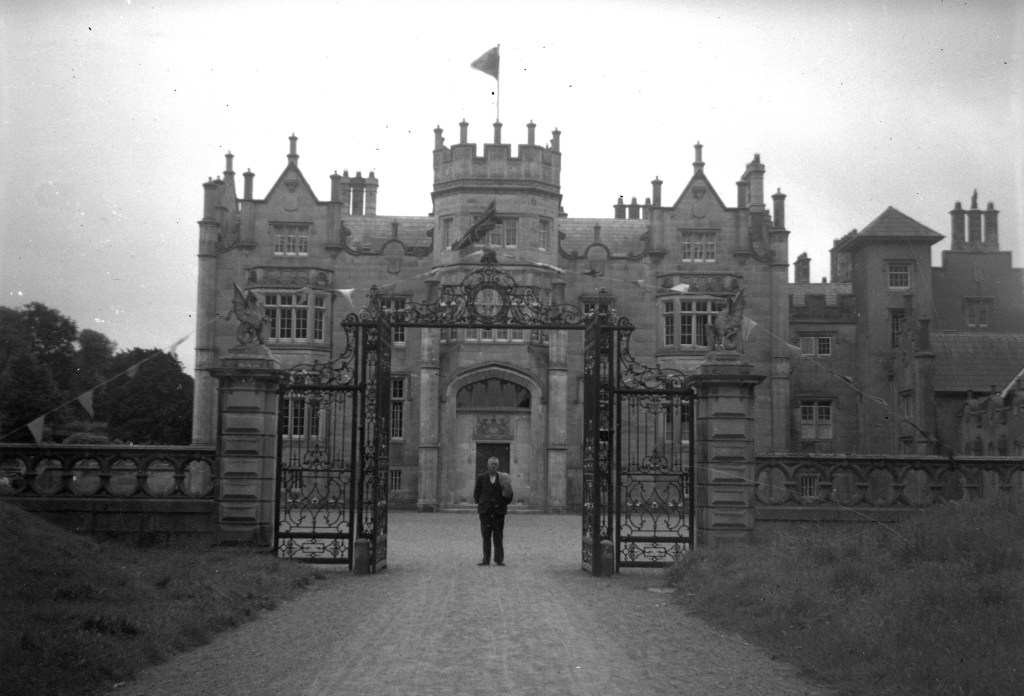
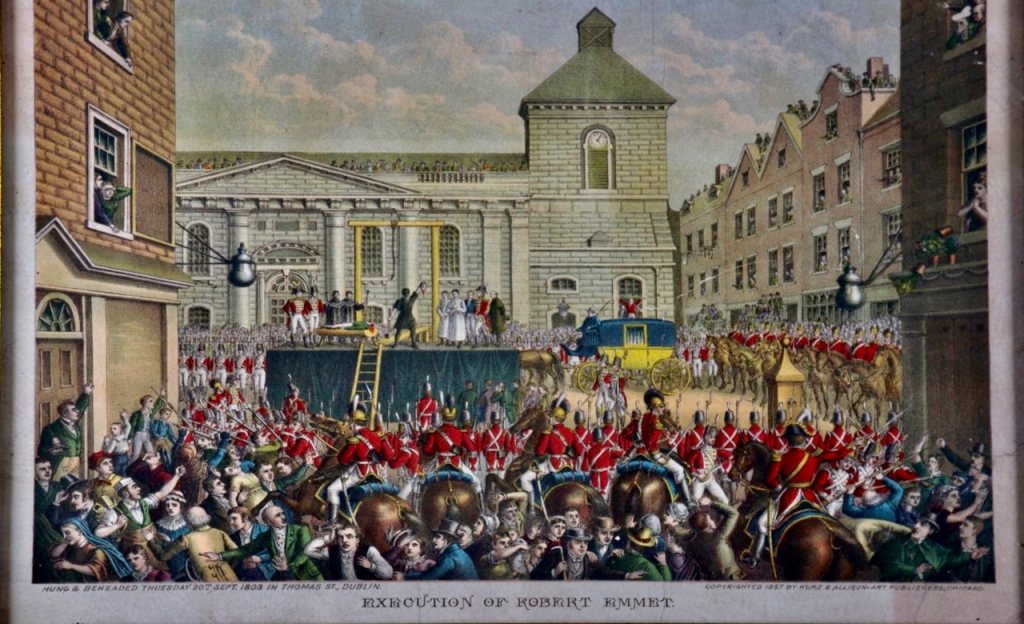
Stephen and I visited Altidore Castle on a grey Saturday, June 1st 2019. I contacted Philip Emmet beforehand and he suggested we come at 3pm for a tour of the house. Philip Emmet is a descendant of the family of the Irish rebel Robert Emmet, who was hung for treason in 1803.

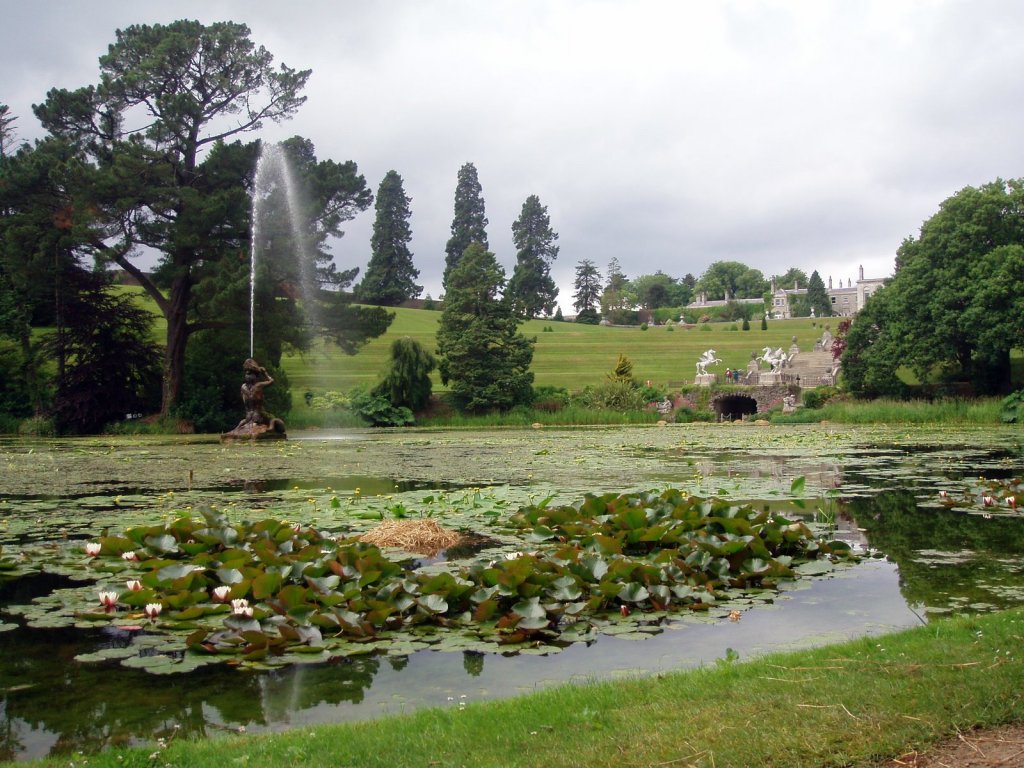
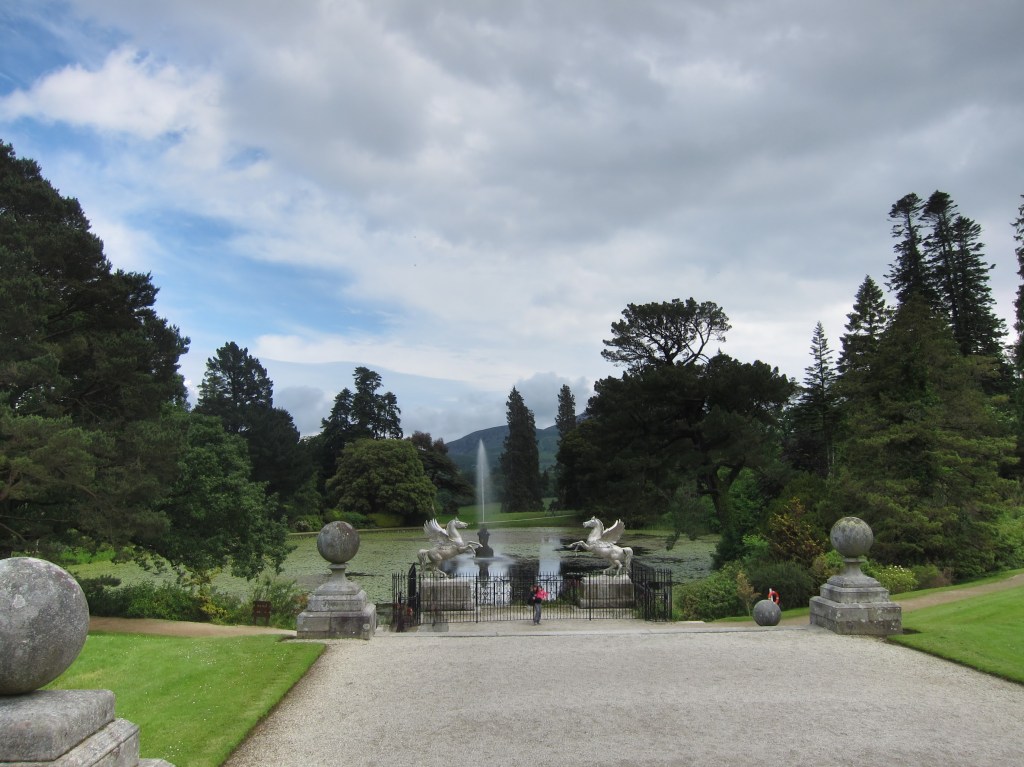
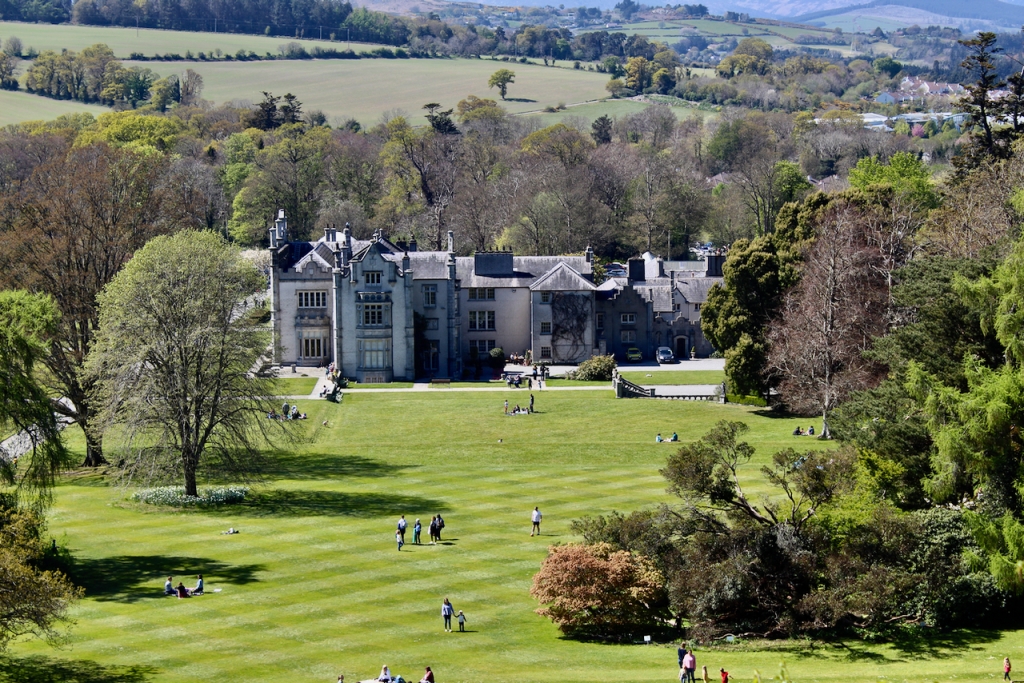
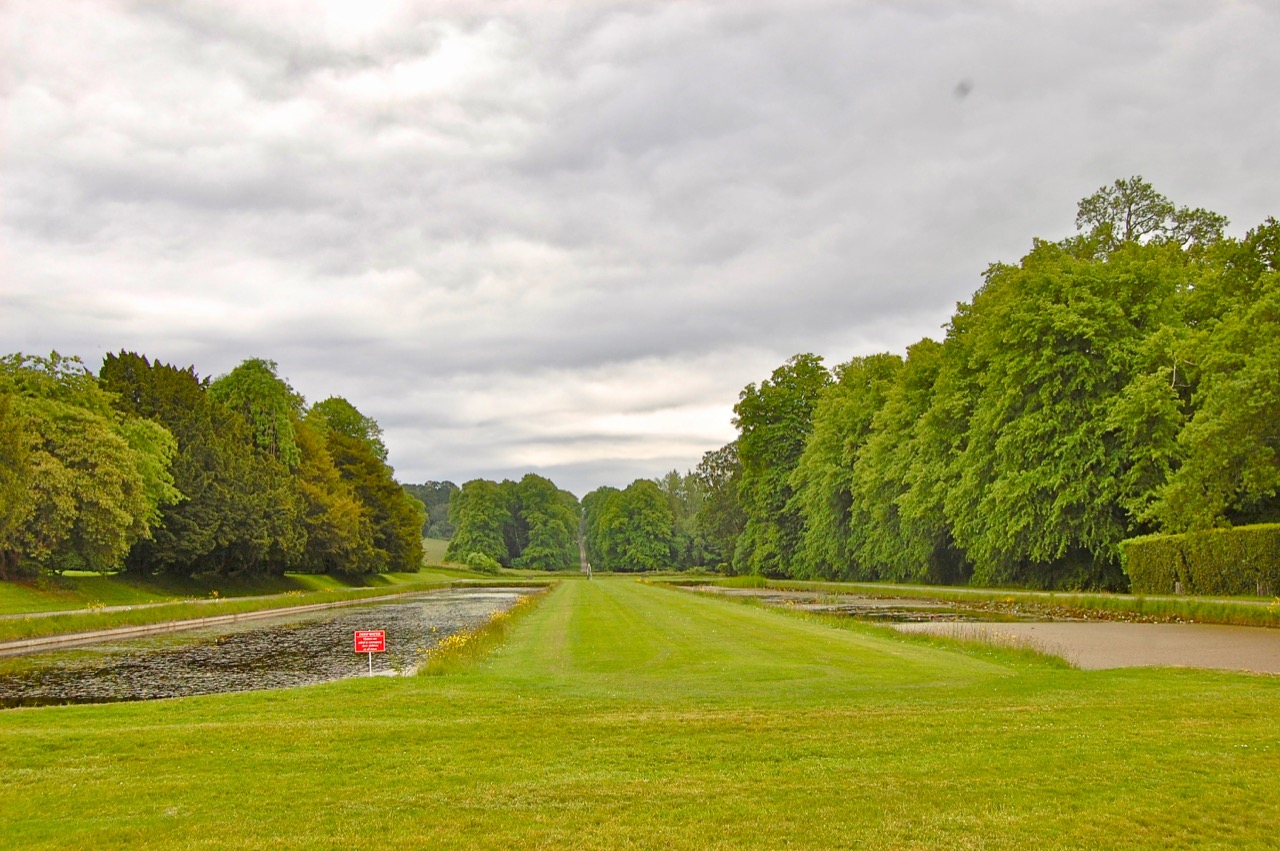
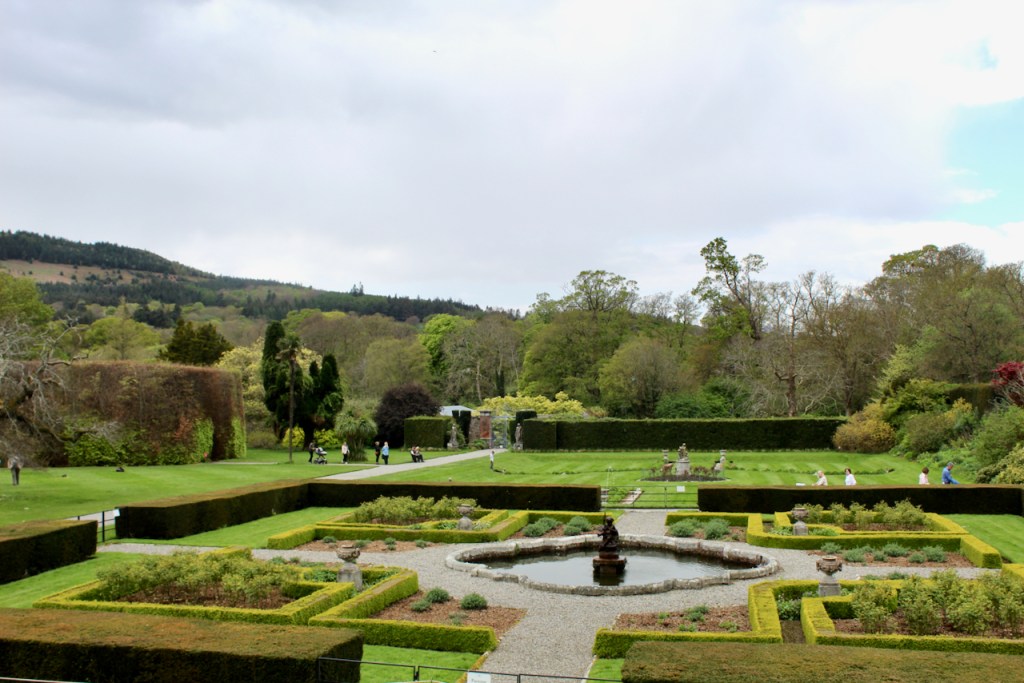
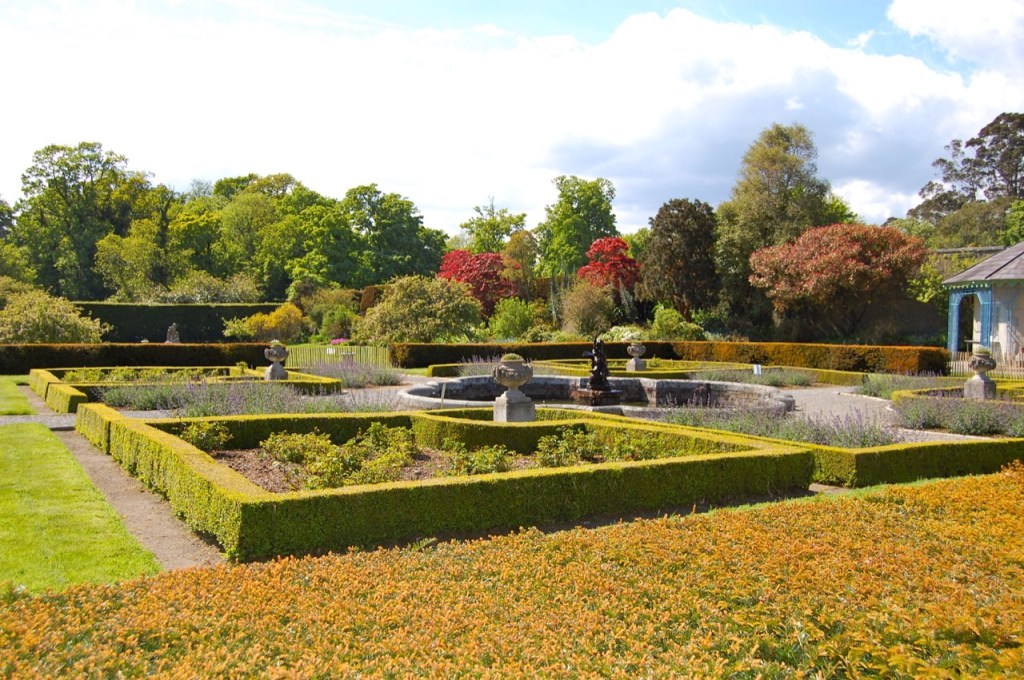
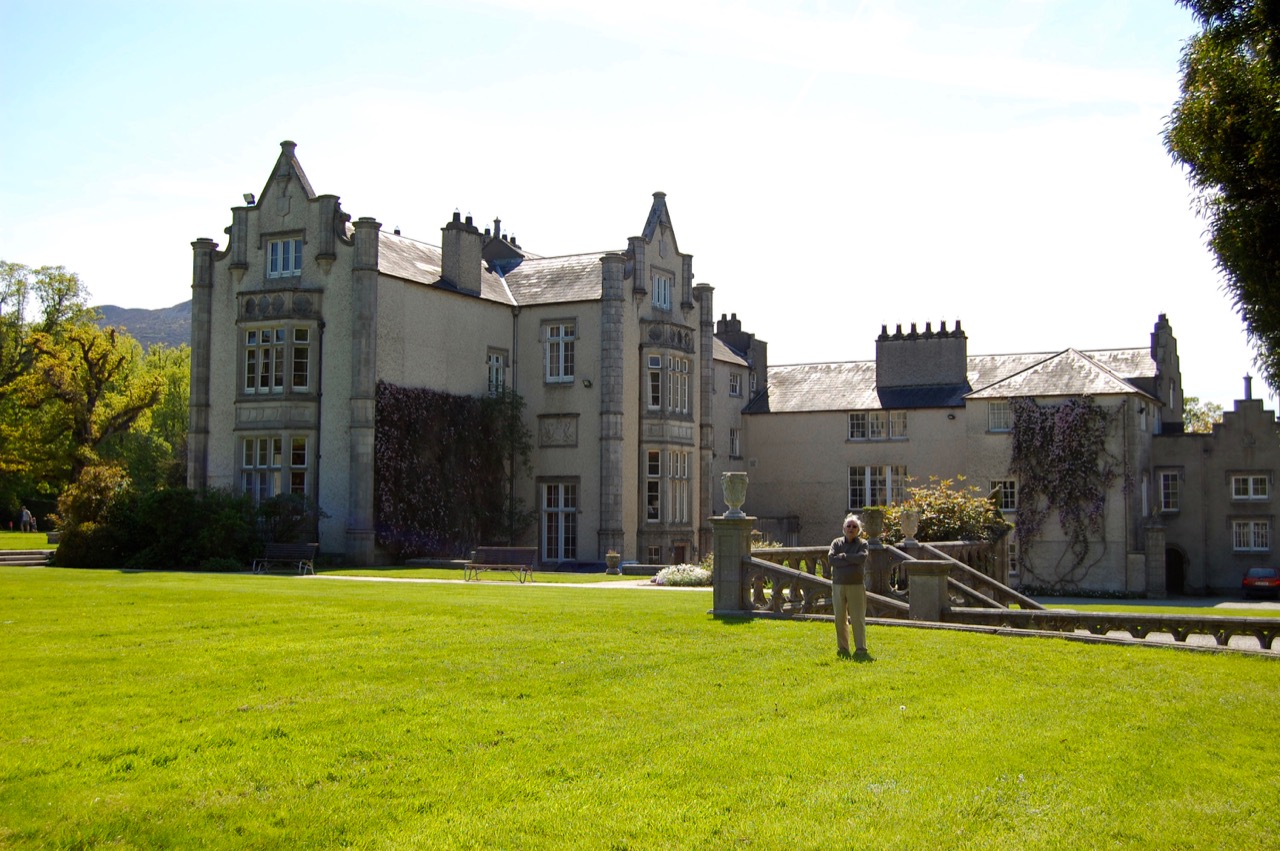
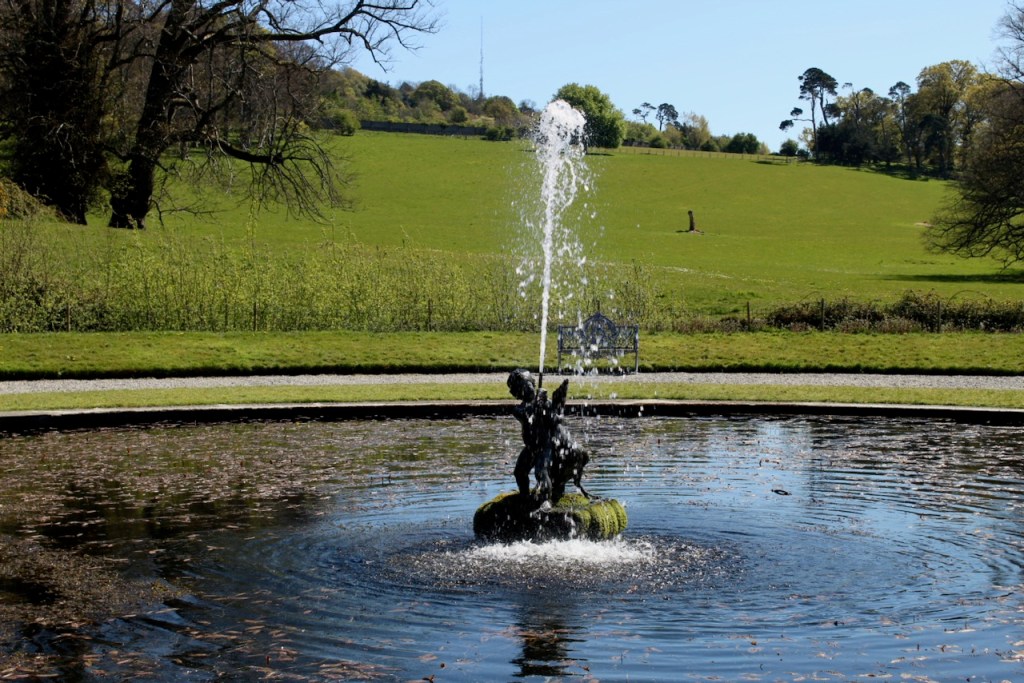
We arrived early and Philip’s wife Vicky suggested we look around the gardens until the other couple who were coming for the tour arrived. We had spied a pond to our left on our way up the long driveway, and there were stone steps up from the driveway across from the front of the house to a large rectangle of a lawn, edged by huge rhododendrons, so we headed off to explore.

We only had about fifteen minutes, so after looking at the lawn above, we went down toward the pond and the gardens directly outside the house. We found a lovely sunken garden with two lions guarding it, containing a “wishing well.”
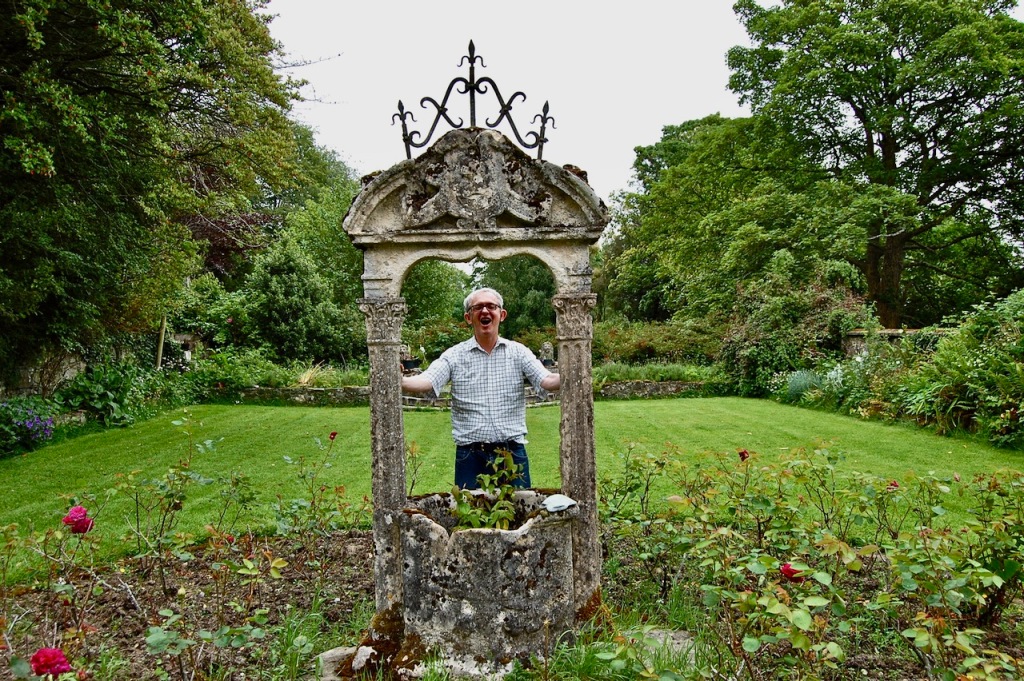
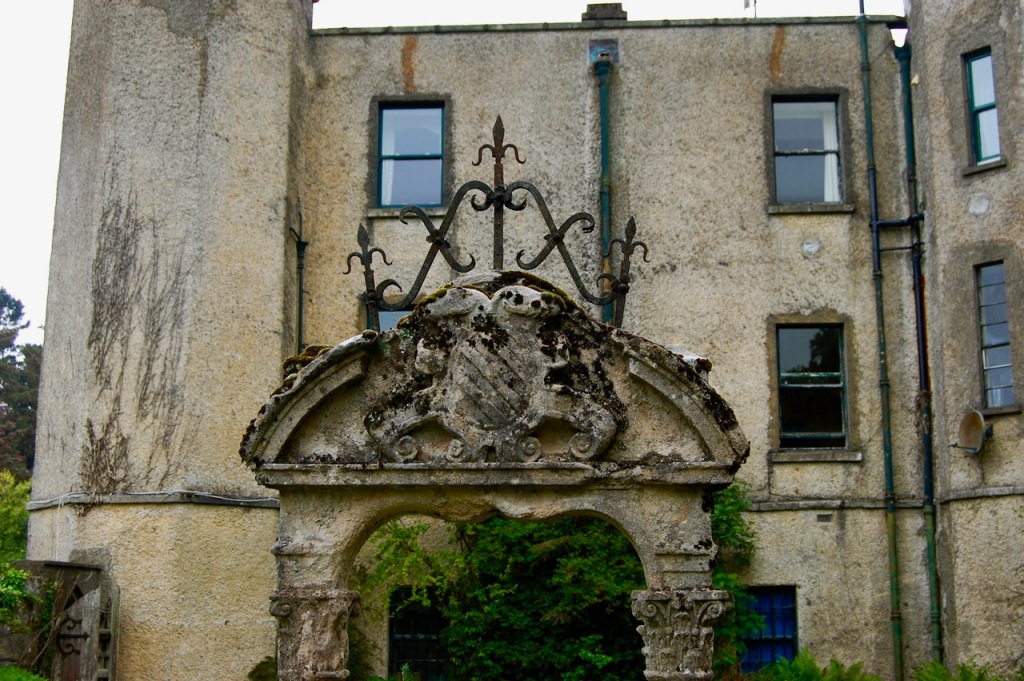





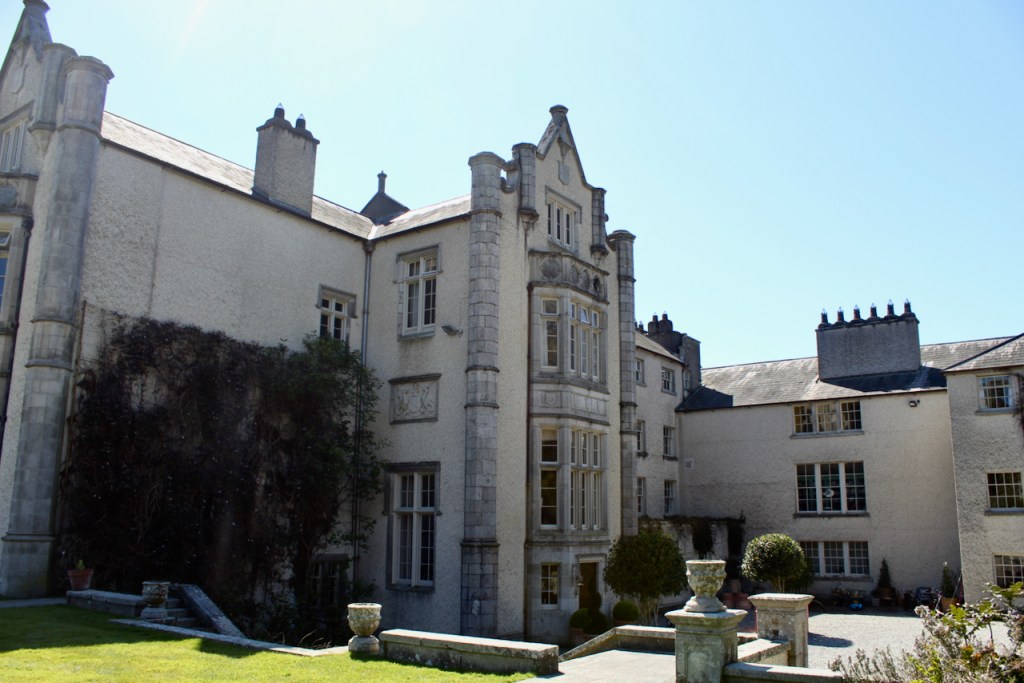
We walked around the back, I was conscious that we could look in the windows and not wanting to disturb or pry, I carefully kept my back to the windows and gazed at the impressive view of the wide valley below. What a view!

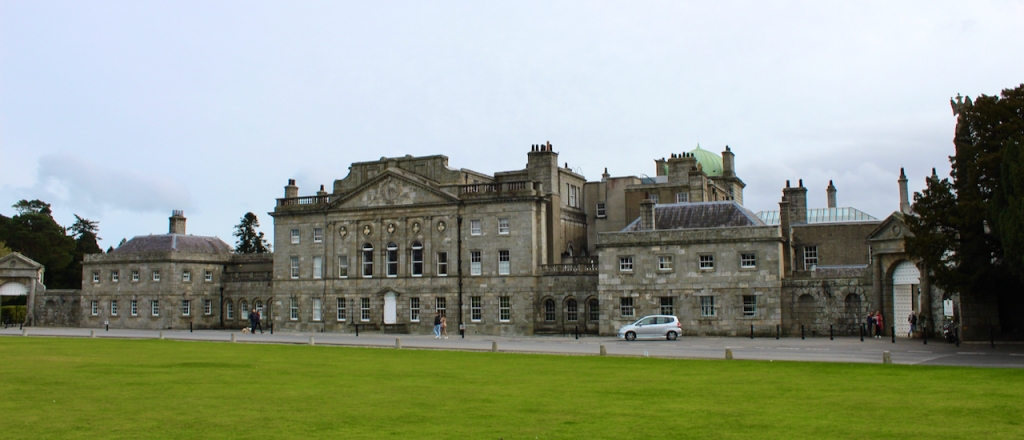
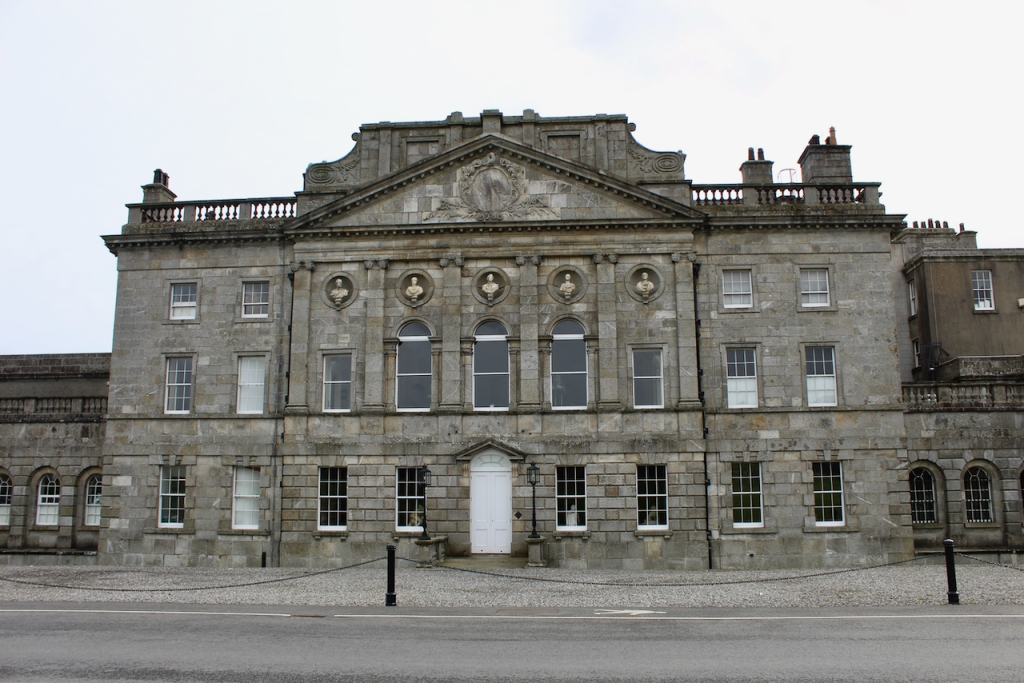
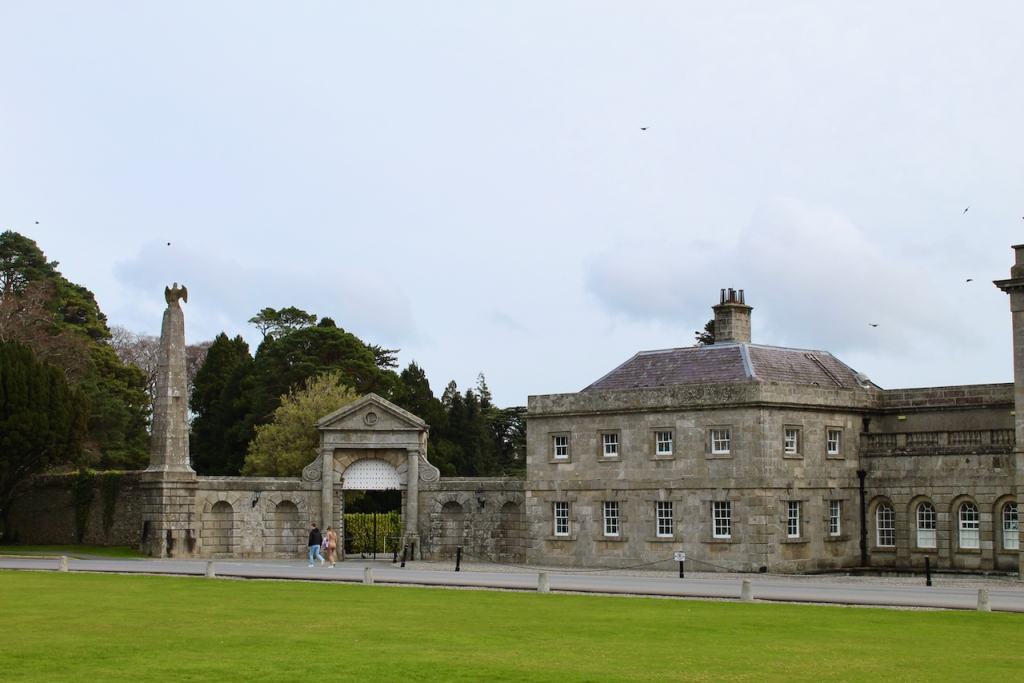
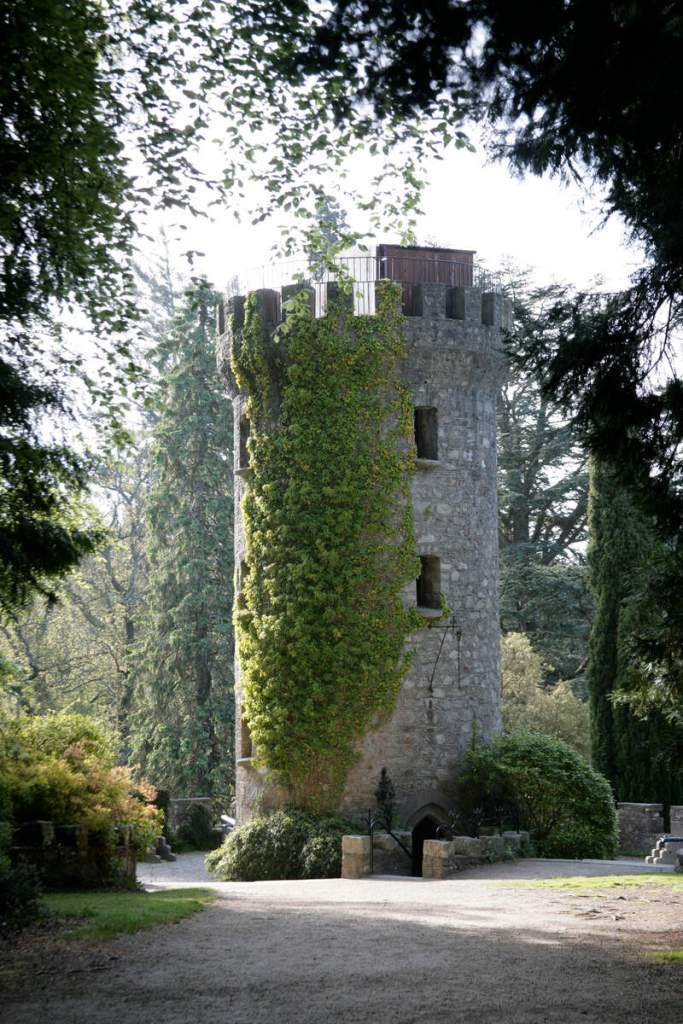
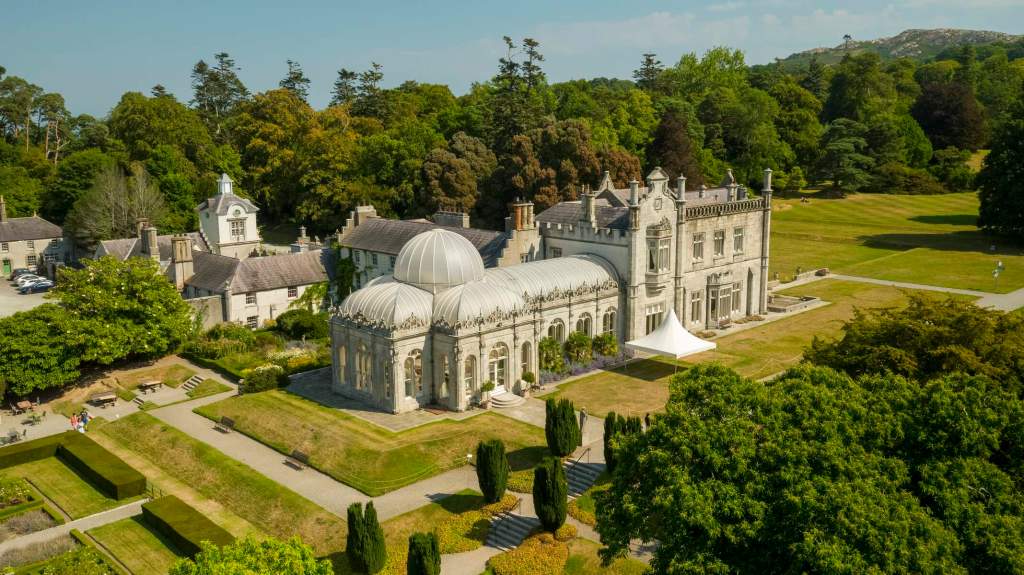
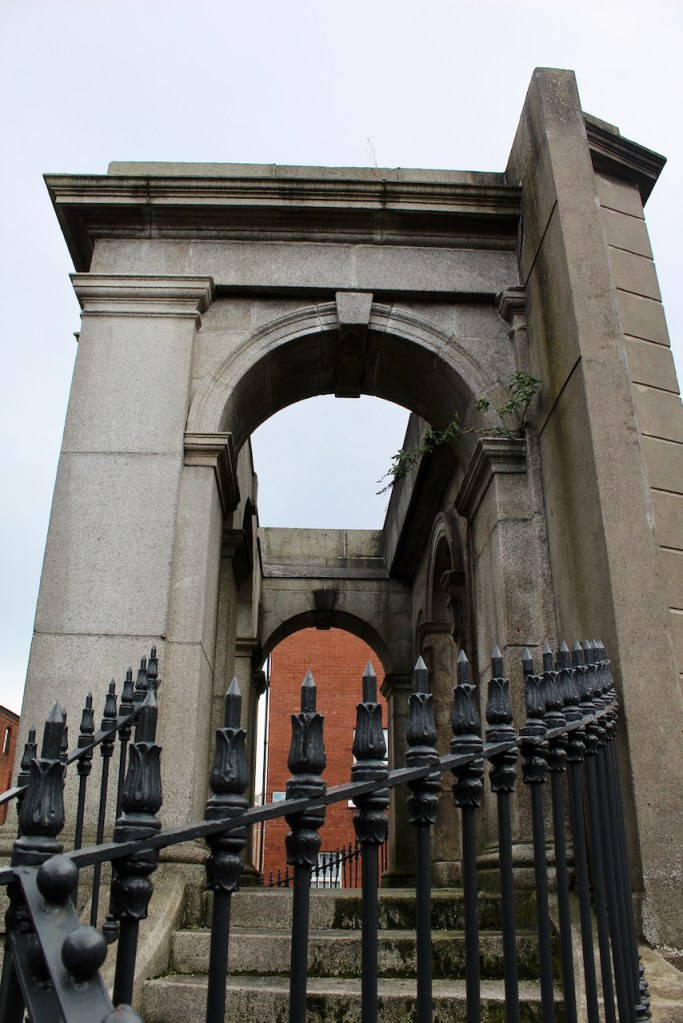
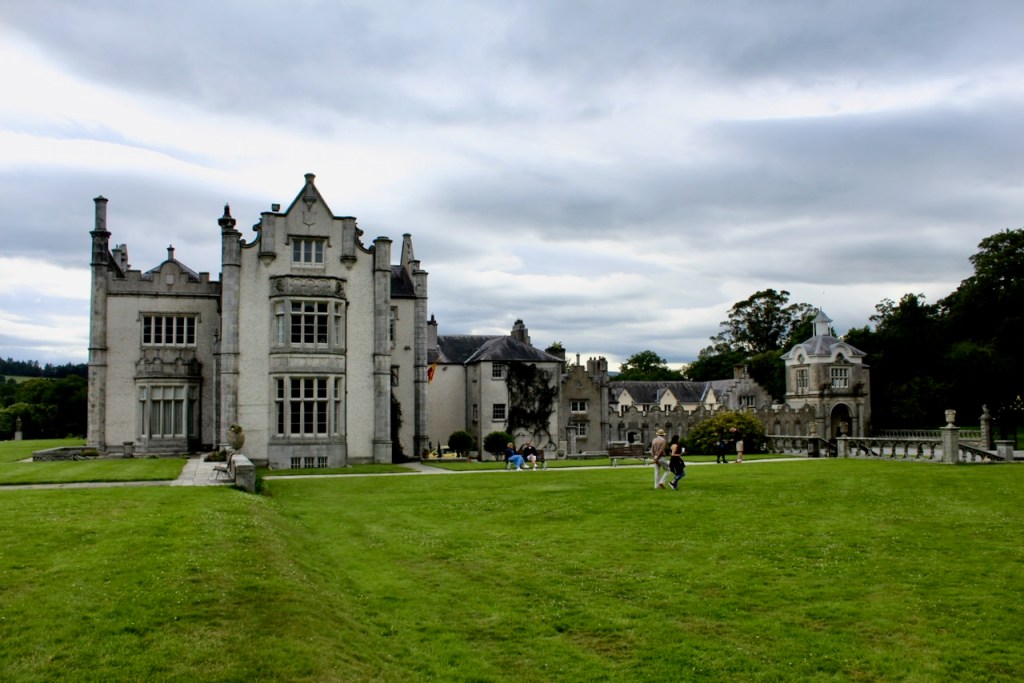
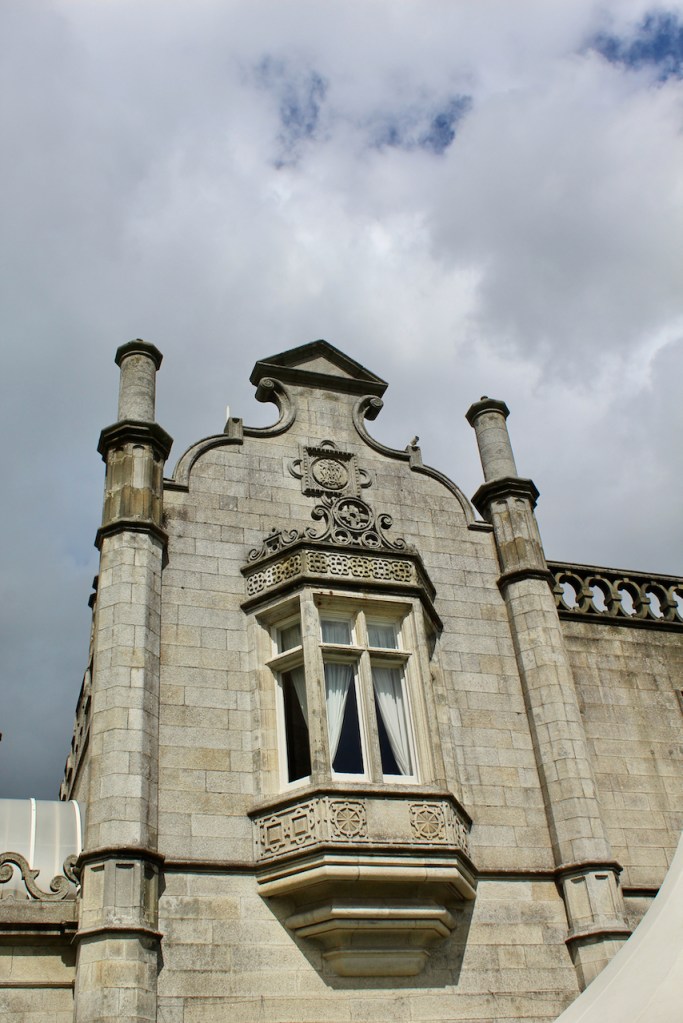
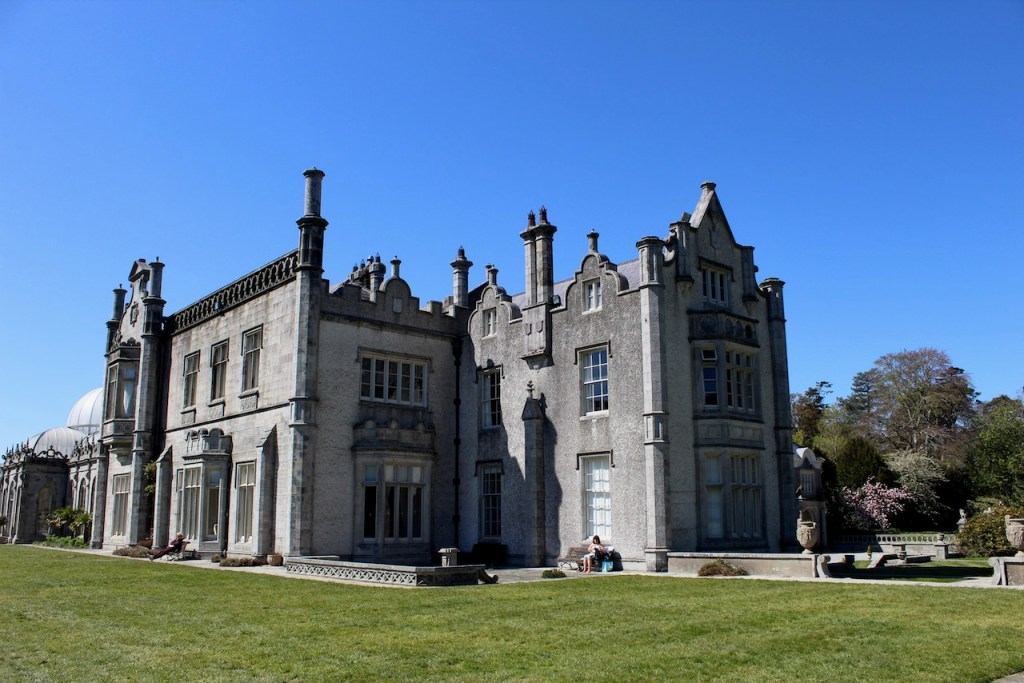
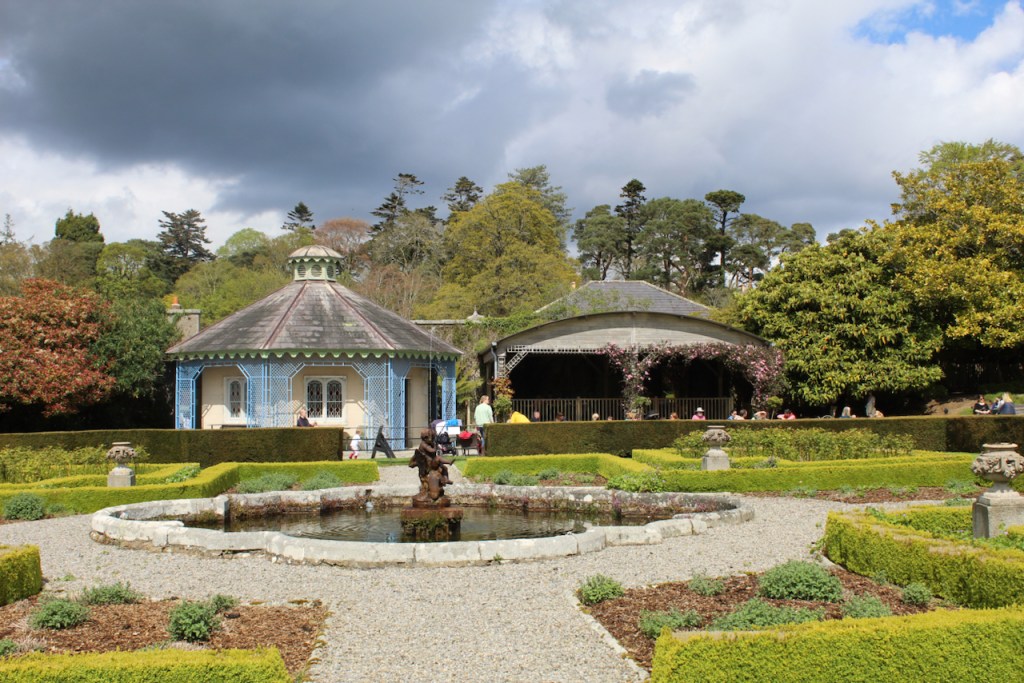
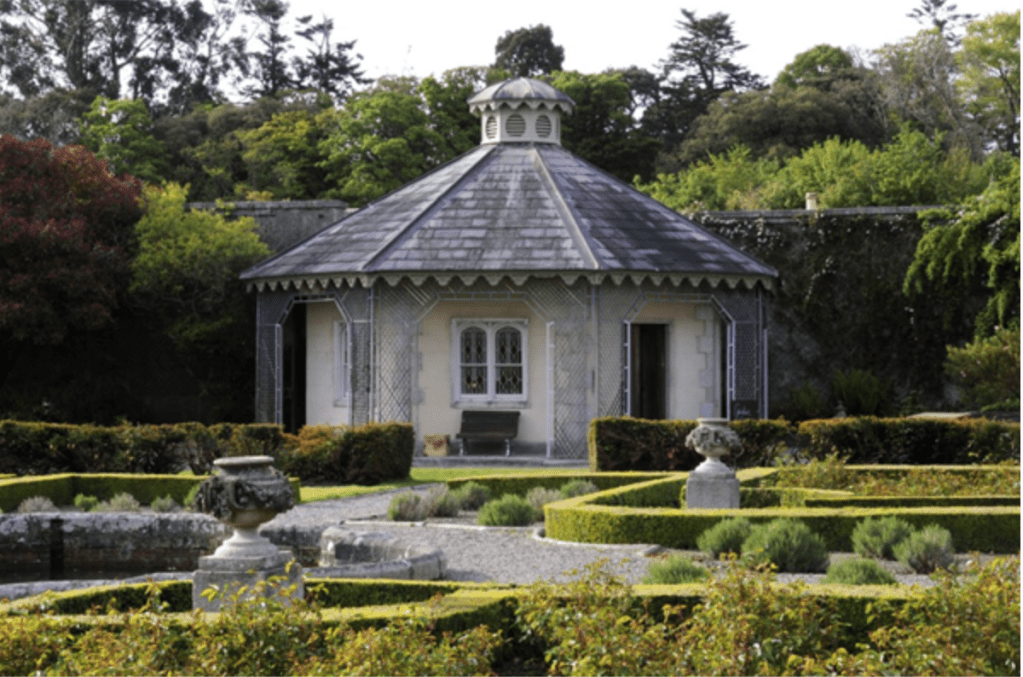
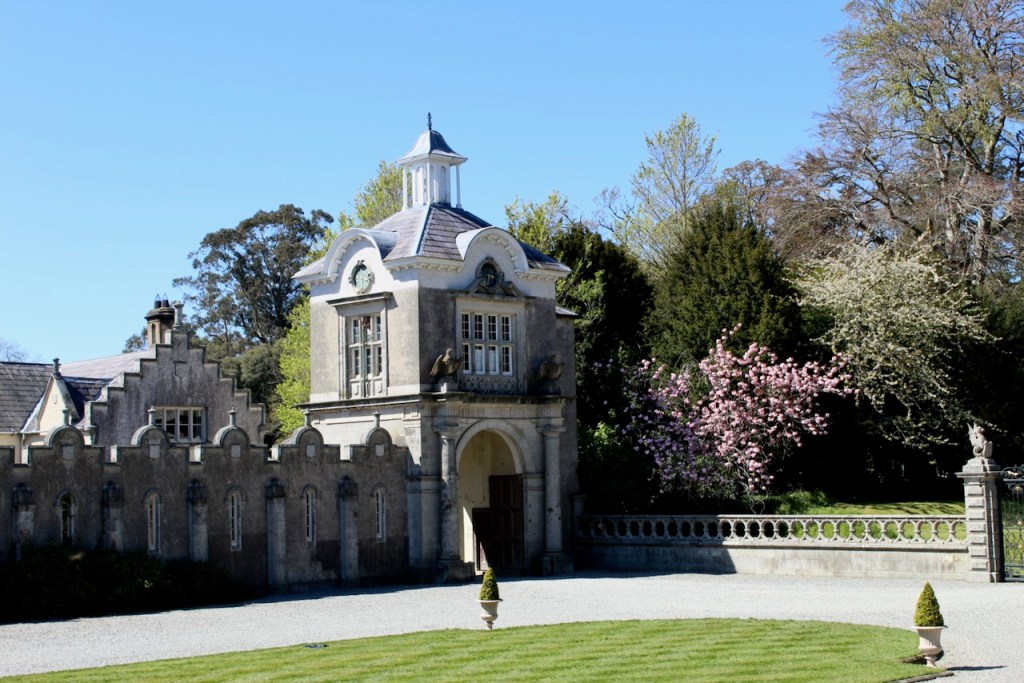
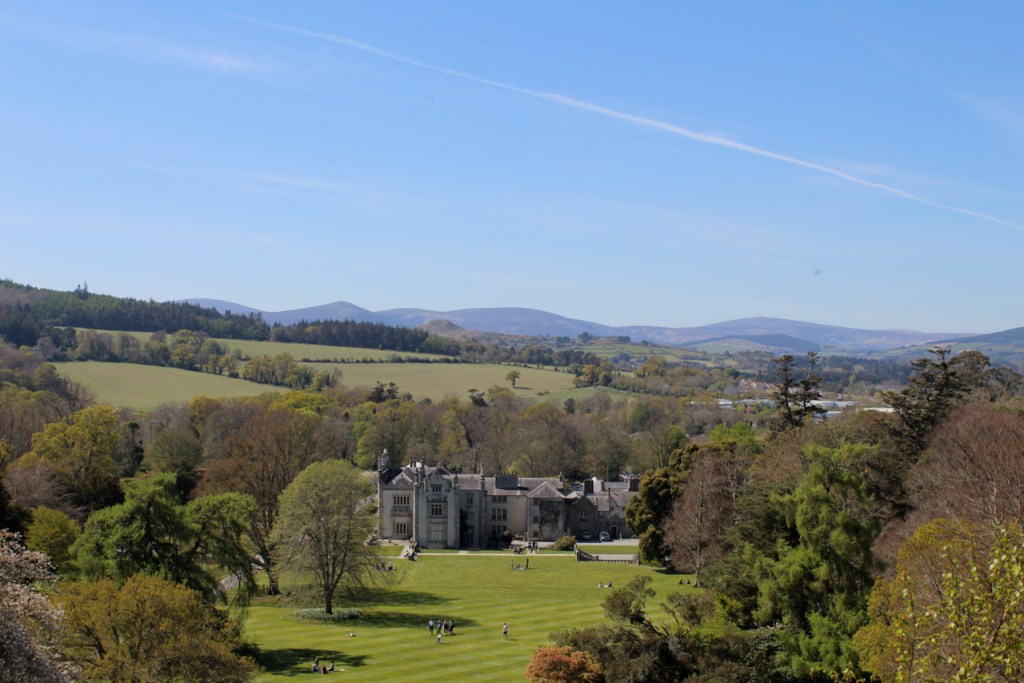
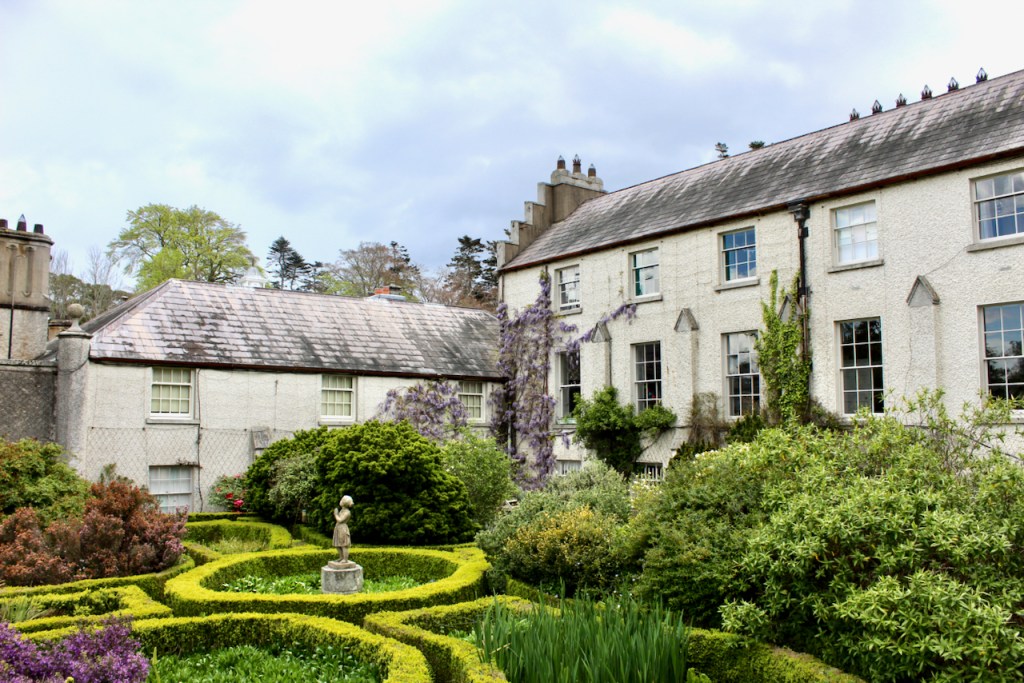
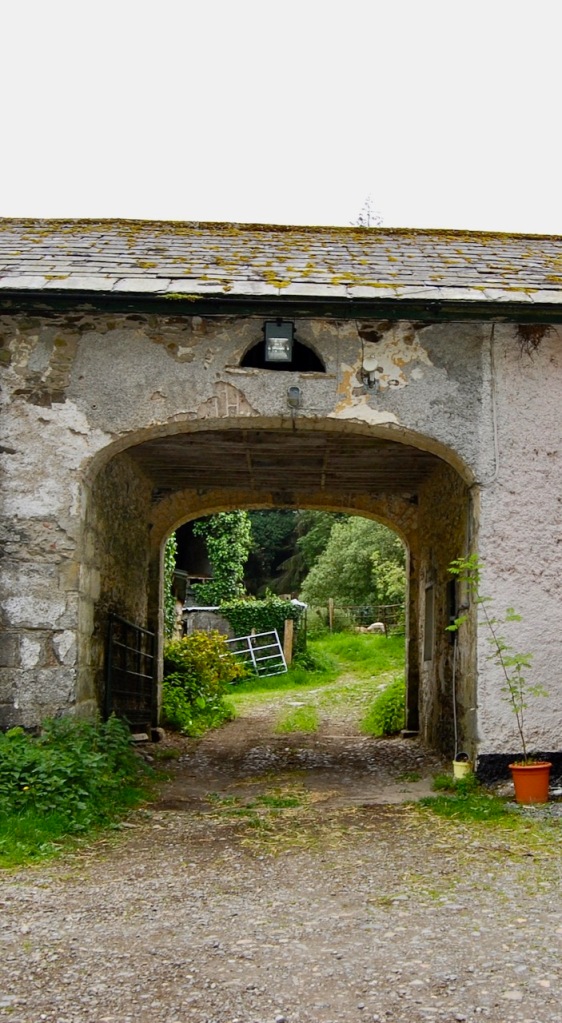
We headed back to the front of the house then. It is a most odd-looking home. It’s quite small but has imposing castellations. This must be why it is called a “toy fort” (by Mark Bence-Jones) or a “toy castle” (National Inventory of Historic Architecture).
Mark Bence-Jones describes it in his A Guide to Irish Country Houses:
A charming late-Georgian “toy fort,” with four octagonal corner turrets; of two storeys on the entrance side and three on the other sides, where the ground falls away. Despite the battlements on the turrets, the house is more Classical than Gothic; it is symmetrical and has a central Venetian window over a pillared porch. [1]
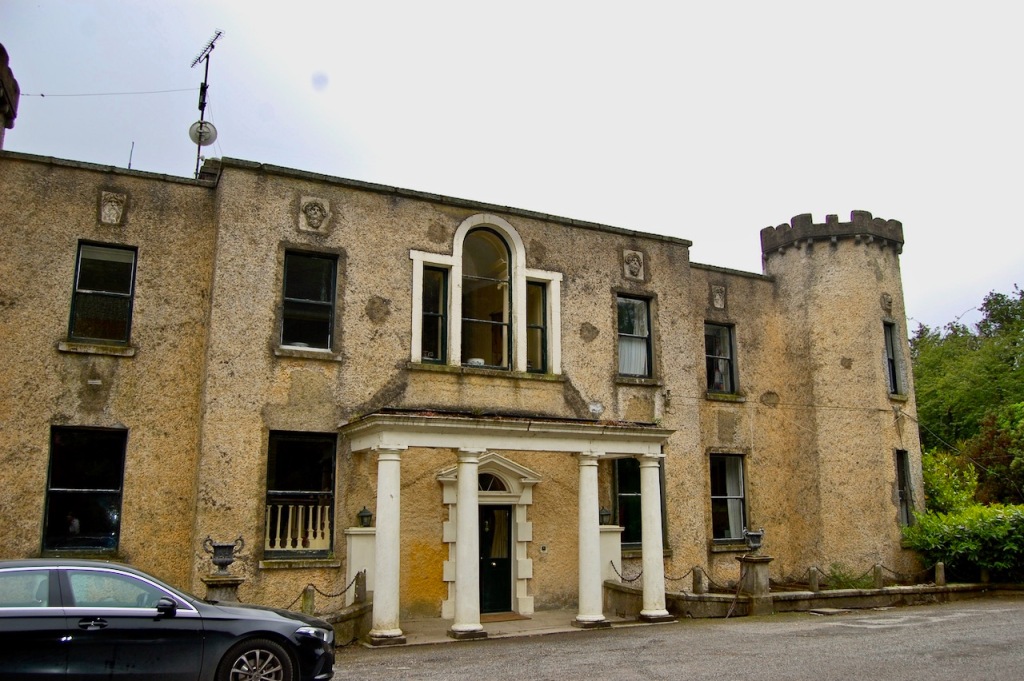
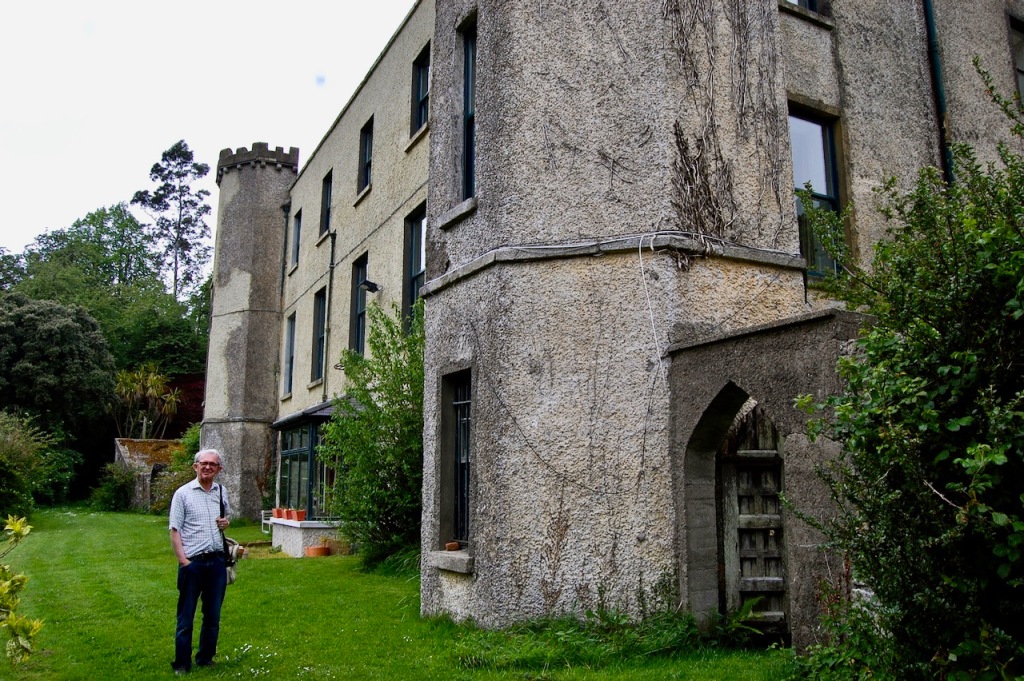


The house was built for General Thomas Pearce around 1730. It may have been designed by his nephew, Edward Lovett Pearce. General Thomas Pearce (ca. 1670-1739) was a British Army officer, a privy councillor and member of Parliament. He was appointed to Ireland in 1715, ultimately becoming General of His Majesty’s Forces in Ireland. He represented Limerick in Parliament from 1727 until his death. He married Mary daughter of William Hewes of Wrexham, and they had three sons and two daughters. His daughter Anne married her first cousin, Edward Lovett Pearce. [2]
Edward Lovett Pearce was a young Irish architect, born in 1699. He favoured the Palladian style of architecture and studied initially under his cousin the English Baroque architect John Vanbrugh. Lovett Pearce is best known for his work on Castletown House and the Irish Houses of Parliament, which later became the Bank of Ireland on College Green in Dublin. In Italy he met the Florentine architect Alessandro Galilei who was making plans for Castletown. Pearce seems to have taken over the work on Castletown based on Galilei’s plans.
Pearce was also commissioned by his uncle-in-law Thomas Coote (Coote married Edward Lovett Pearce’s aunt Anne Lovett – she was Thomas Coote’s third wife) to build Bellamont House in Cootehill, County Cavan (around 1730). He also designed two houses on Henrietta Street in Dublin, including number 9, for his cousin Mrs. Thomas Carter, and he designed Summerhill, County Meath. He died of an abscess at the young age of 34 in his home The Grove in Stillorgan, Dublin, and is buried in St. Mary’s Graveyard, now a closed graveyard in Donnybrook, which I was lucky enough to see in a tour a couple of years ago.

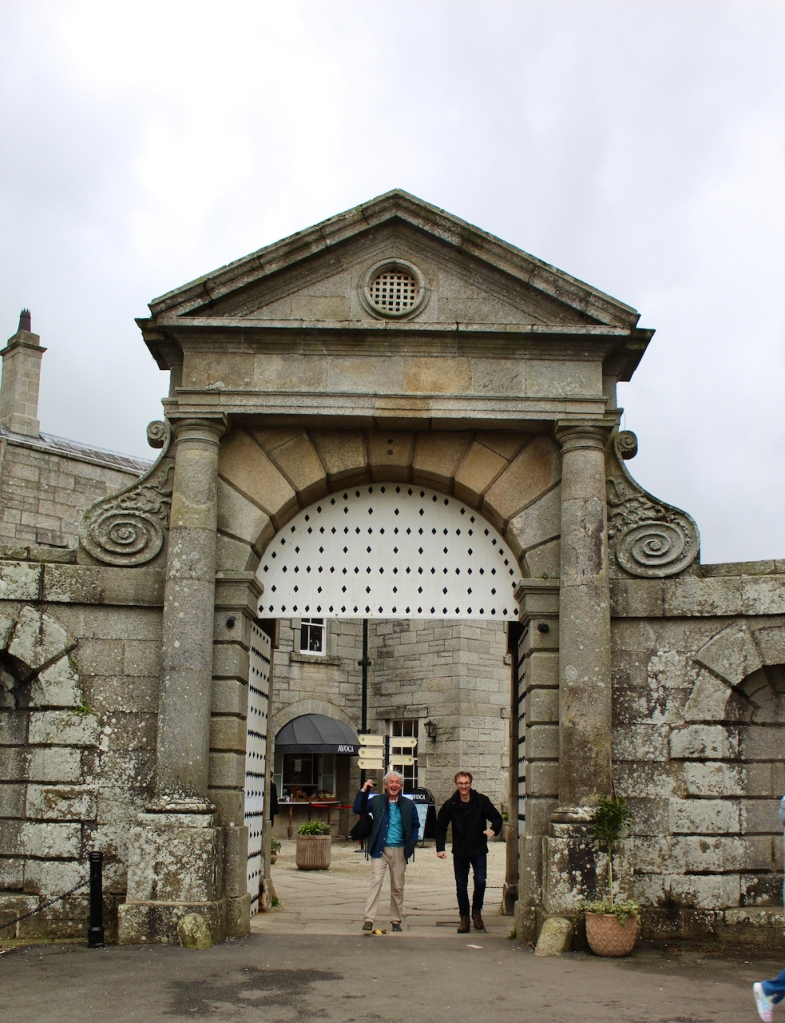
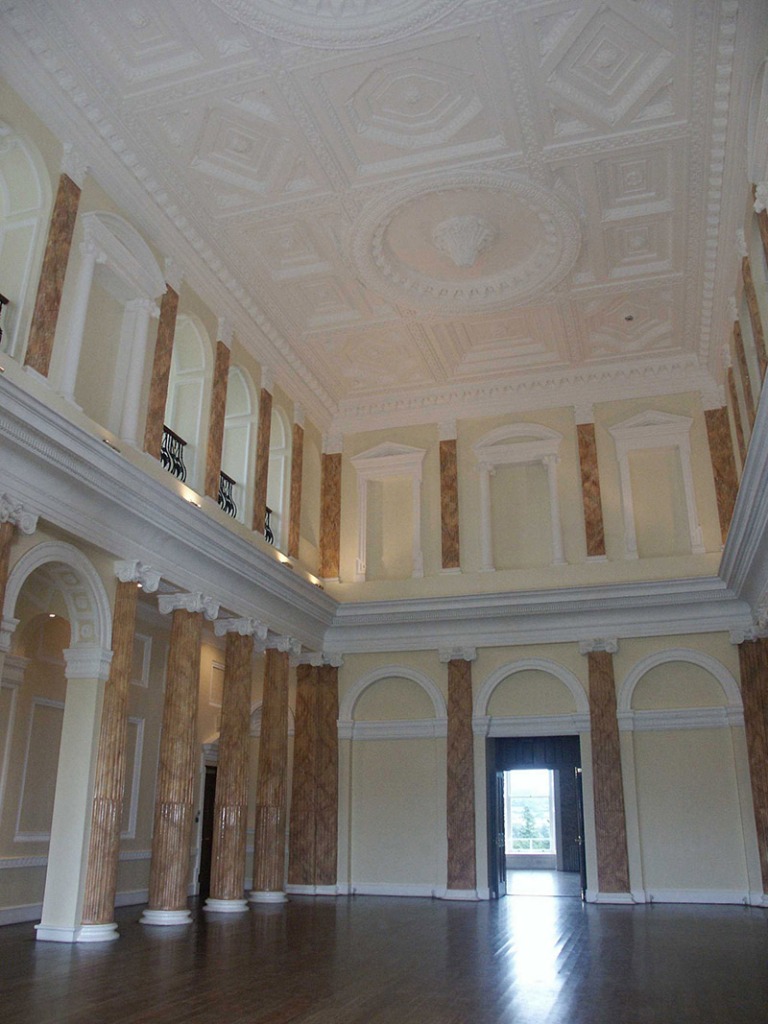
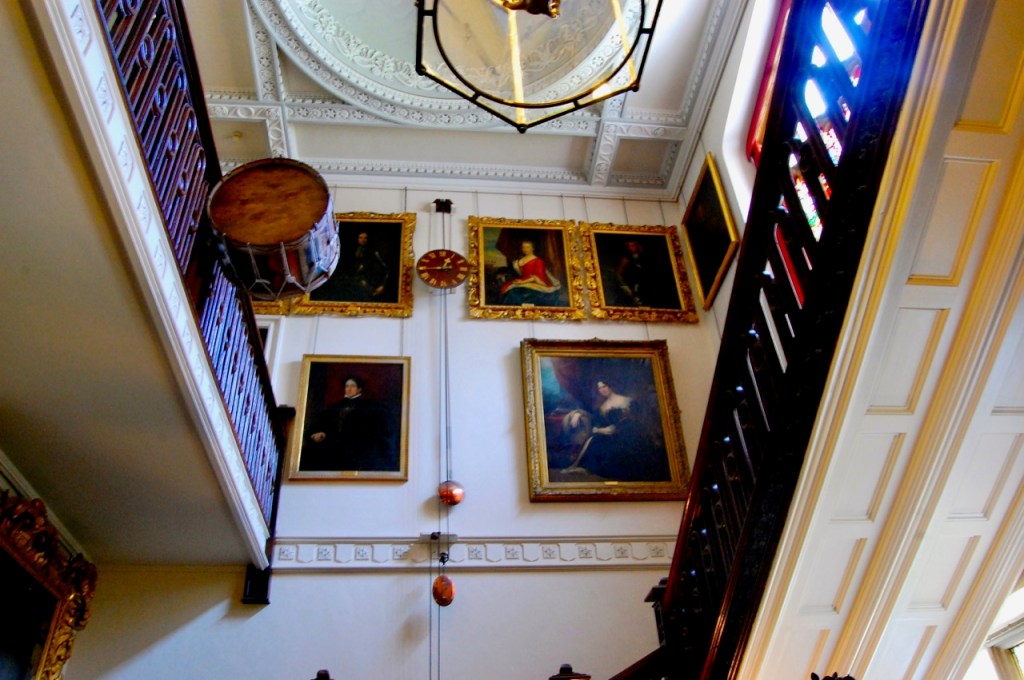
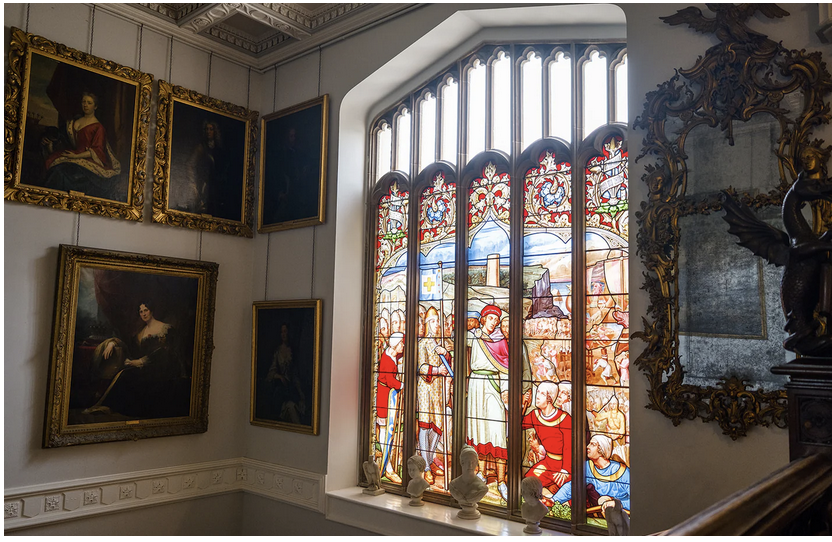
We followed the other couple in through the porch to meet Philip Emmet, who welcomed us. We stepped into a large high-ceilinged hall.
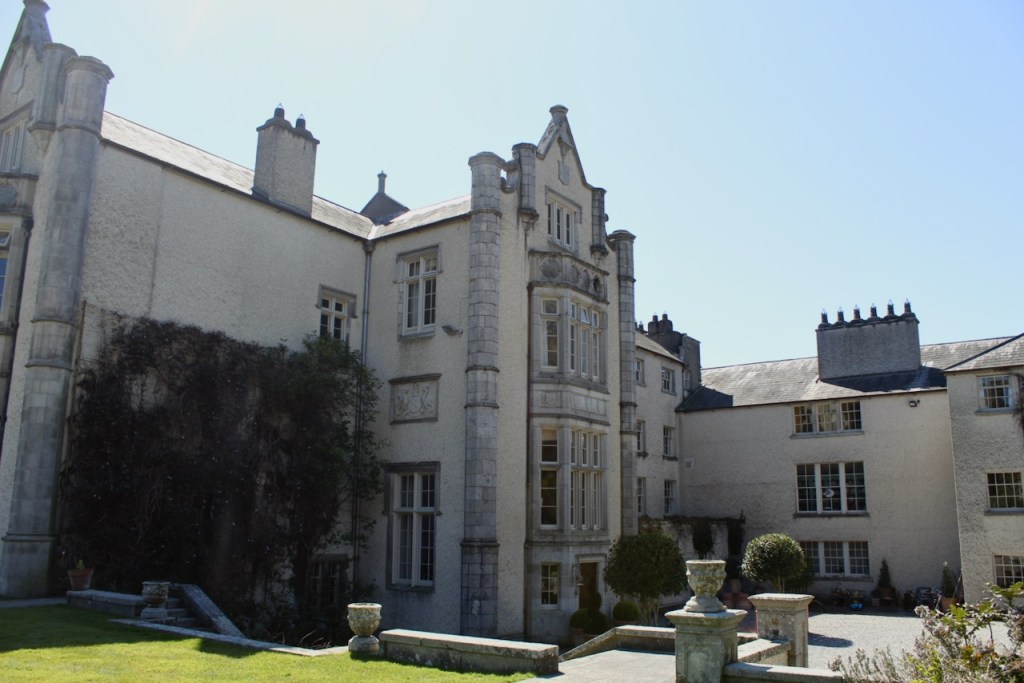
The inside of the front hall and staircase is odd as the windows don’t look as if they fit the plans, or else the staircase has been moved. Philip does not know a lot about the background of the house. The Irish Historic Houses website states that Altidore was enlarged and modified for a subsequent owner, Major Henry Brownrigg. [3] We did not go upstairs, but Mark Bence-Jones tells us that the staircase is “of stout but elegant joinery with a scrolled end to its balusters.”
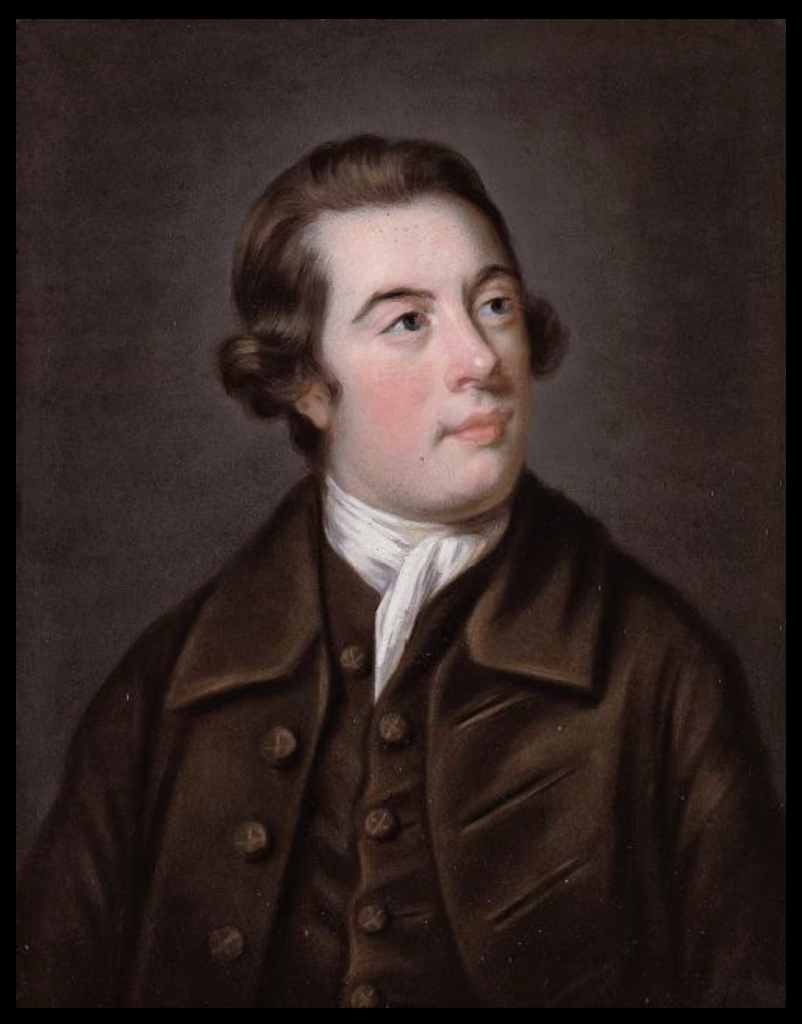
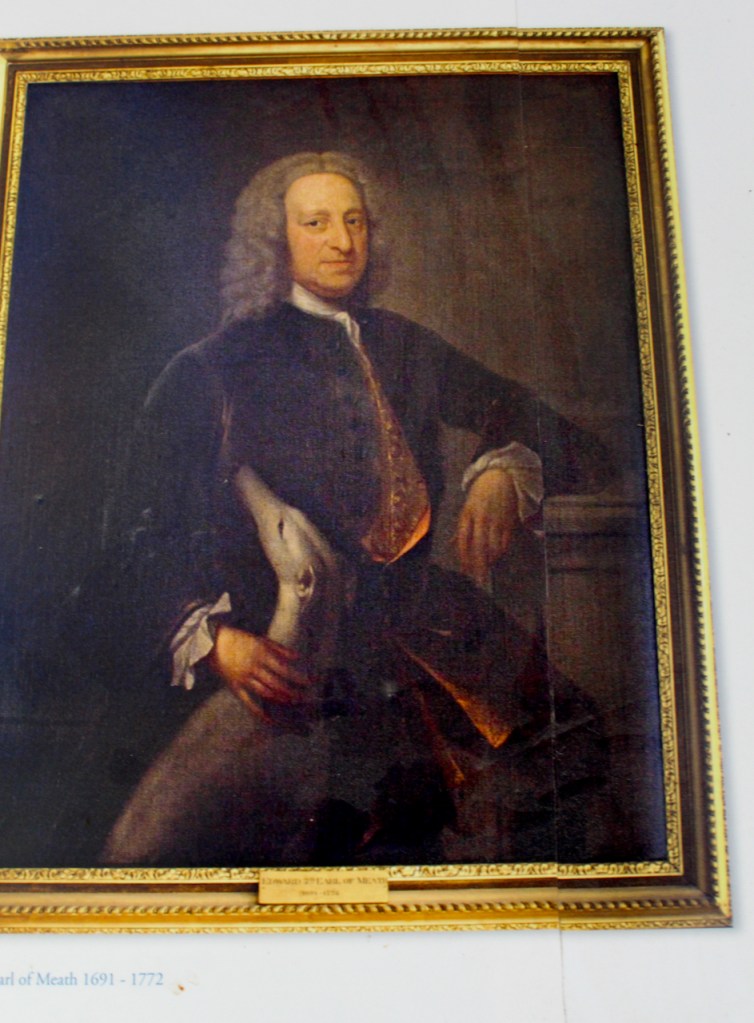
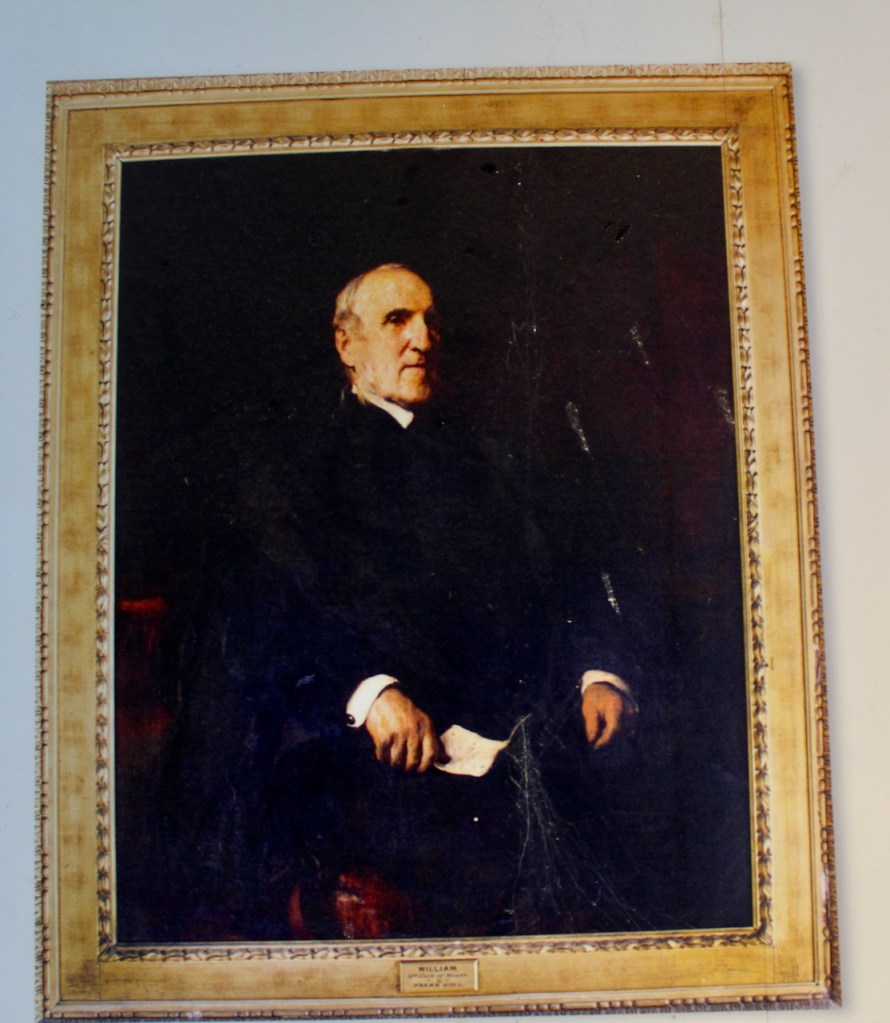
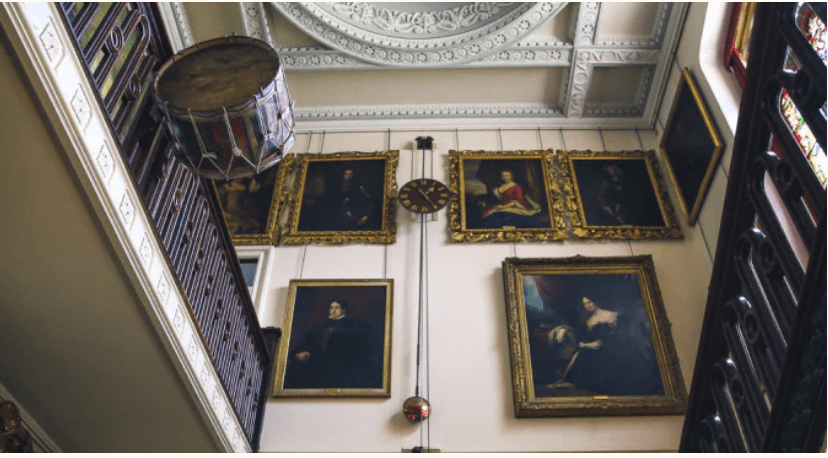
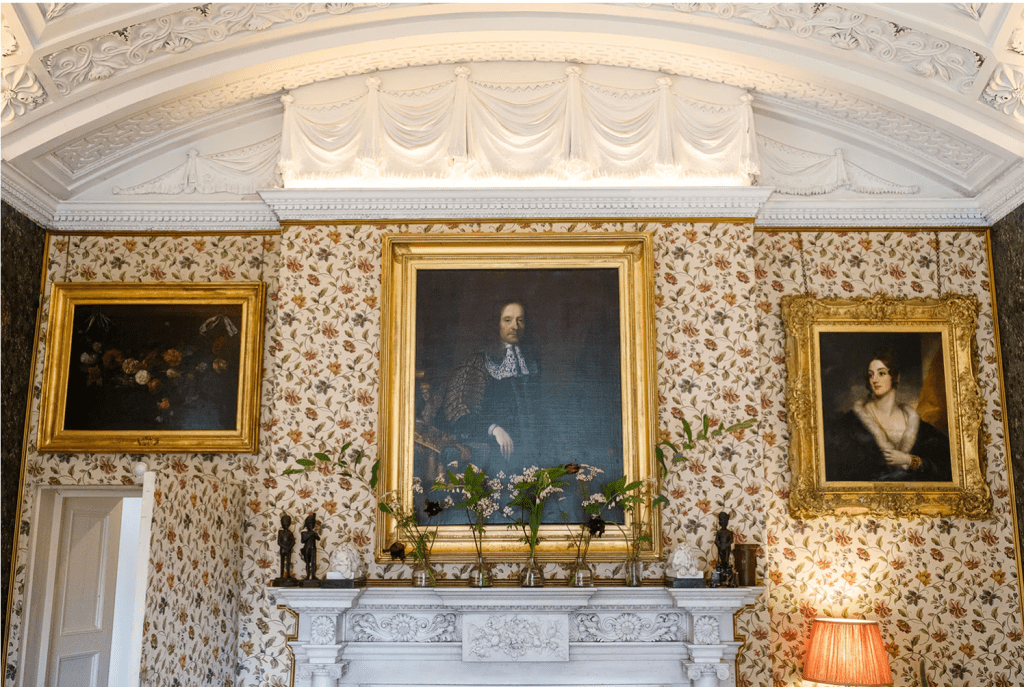
By 1773 the house was owned by Reverend William Blachford, Librarian of Marsh’s Library in Dublin. Philip has a portrait of Reverend Blachford’s daughter Mary Tighe, a poet who was famous in her time and was grouped with the Romantic writers Byron and the revolutionary Mary Wollestonecraft. The poet John Keats admired her work. I must borrow her book, Psyche or the Legend of Love from the library!

Mary, nee Blachford, had a severely religious upbringing. William Blachford died in 1773 leaving his wife Theodosia (daughter of William Tighe of Rossana, County Wicklow), a son John and daughter Mary. Theodosia converted to Methodism, founded by John Wesley, and was involved in many charitable works including supporting the Leeson Street Magdalen Asylum for unmarried mothers, and the Female Orphan House on Prussia Street in Dublin. [4]


At the young age of 21, Mary married her cousin Henry Tighe (1771-1836), son of William Tighe of Woodstock, County Kilkenny. Henry served as an MP in the Irish Parliament representing Inistioge, County Kilkenny.
Mary contracted tuberculosis and lived her final months as an invalid in her brother-in-law William Tighe’s estate of Woodstock, where she died at the age of 37.
A marble statue of Mary, commissioned by her son after her death and carved by Lorenzo Bartolini of Tuscany, stood in the hall of Woodstock before the house was burnt in 1922. Although the original statue was destroyed in the fire at Woodstock, the plaster original of Bartolini’s statue is in the Accademia in Florence. There is also another life-size sculpture of her by English sculptor John Flaxman in her mausoleum in the graveyard attached to the former Augustinian priory in Inistioge, County Kilkenny. [5]

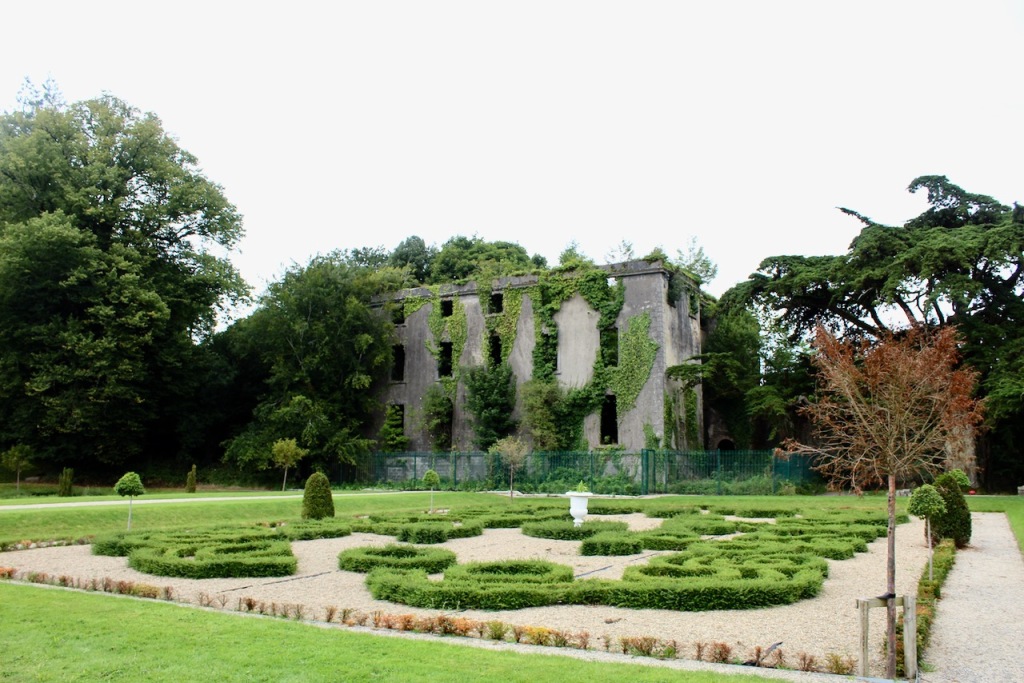
Woodstock was not rebuilt after it was burned in 1922 and it remains a ruin but the gardens are open to the public.

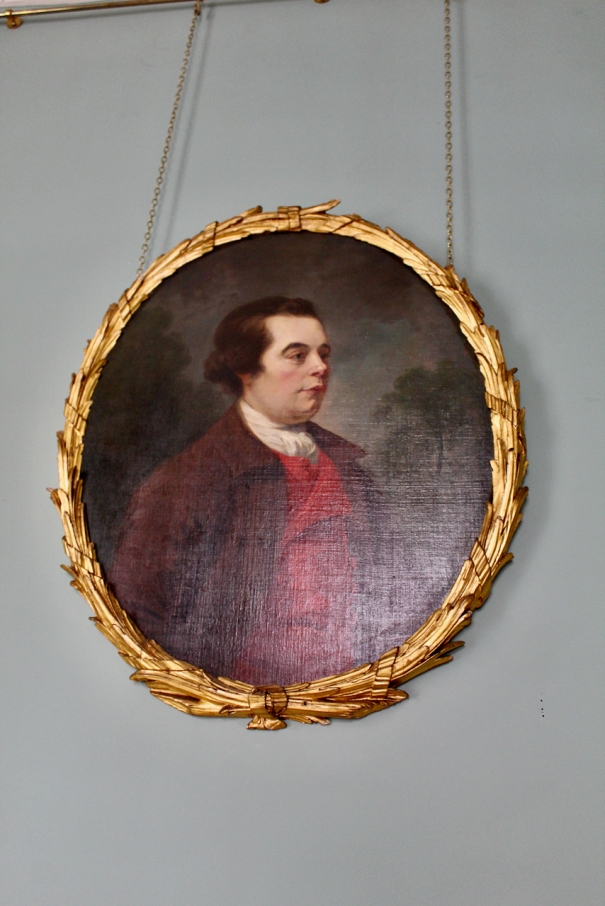
Reverend Blachford’s son John inherited Altidore and lived there with his wife Mary Anne, daughter of Henry Grattan MP (1746-1820) from nearby Tinnehinch [6]. I don’t think they had any children.
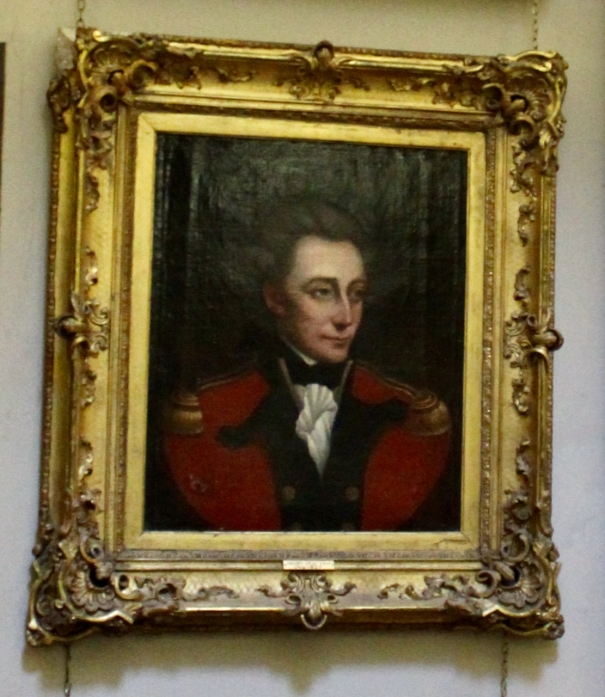

There was another fascinating portrait in one of the beautifully decorated rooms, this time of an Indian military man, who was a servant of an ancestor of Philip’s wife. This ancestor, named Dennehy, worked in India under Queen Victoria, and introduced Victoria to Indian servants – and through him she met her beloved Indian servant, about whom, and their relationship, there was a movie a few years ago, “Victoria and Abdul”! Philip’s wife was in Osbourne, Victoria’s home on the Isle of Wight, and noticed that there is a series of these pictures, matching her own, of Queen Victoria’s other Indian servants. Stephen and I also loved the tv series about young Victoria.
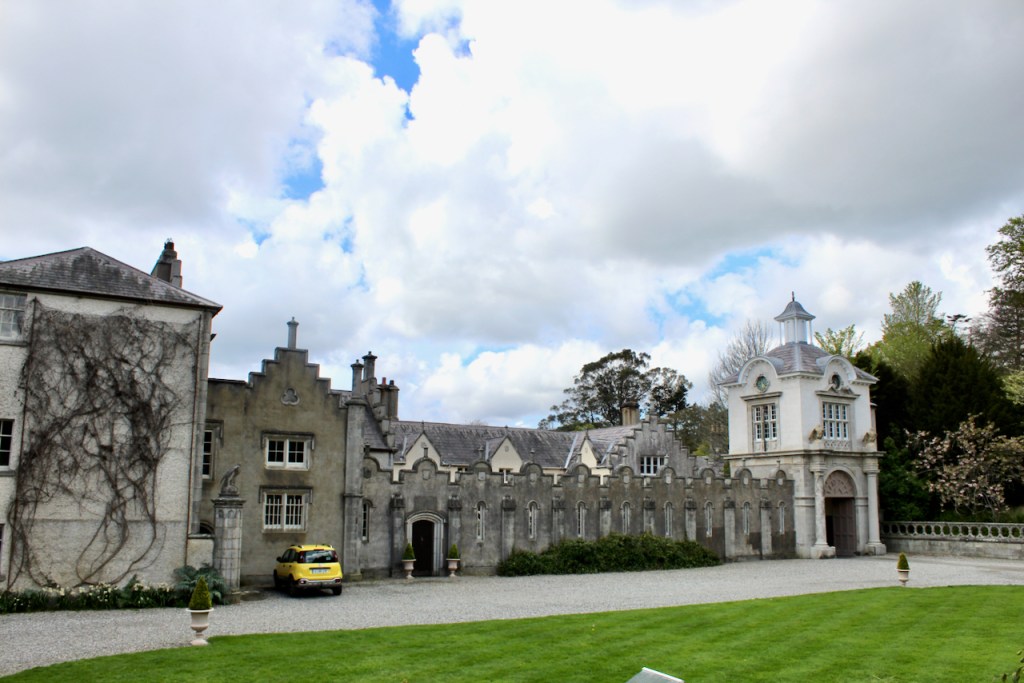
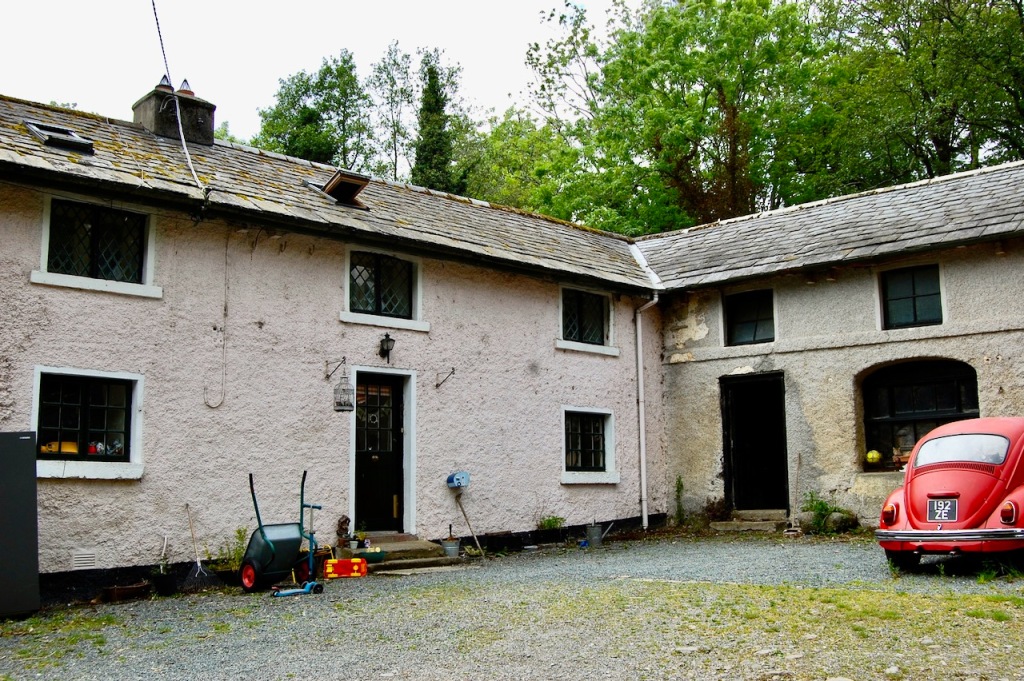
Before the Emmets purchased the house in 1944, the Dopping-Hempenstals owned the house, from 1834-1918. They owned extensive lands in County Wicklow. They rarely lived in Altidore and instead leased it out. At one stage it housed a tuberculosis sanatorium. According to the Irish Historic Houses website, Altidore changed hands many times over the next decades and was owned by two different banks on separate occasions.
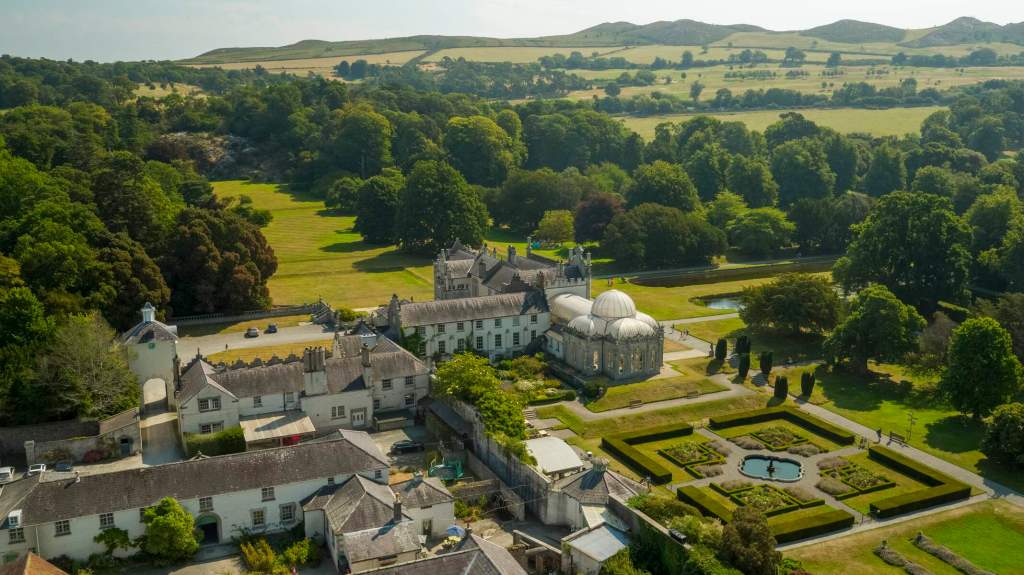
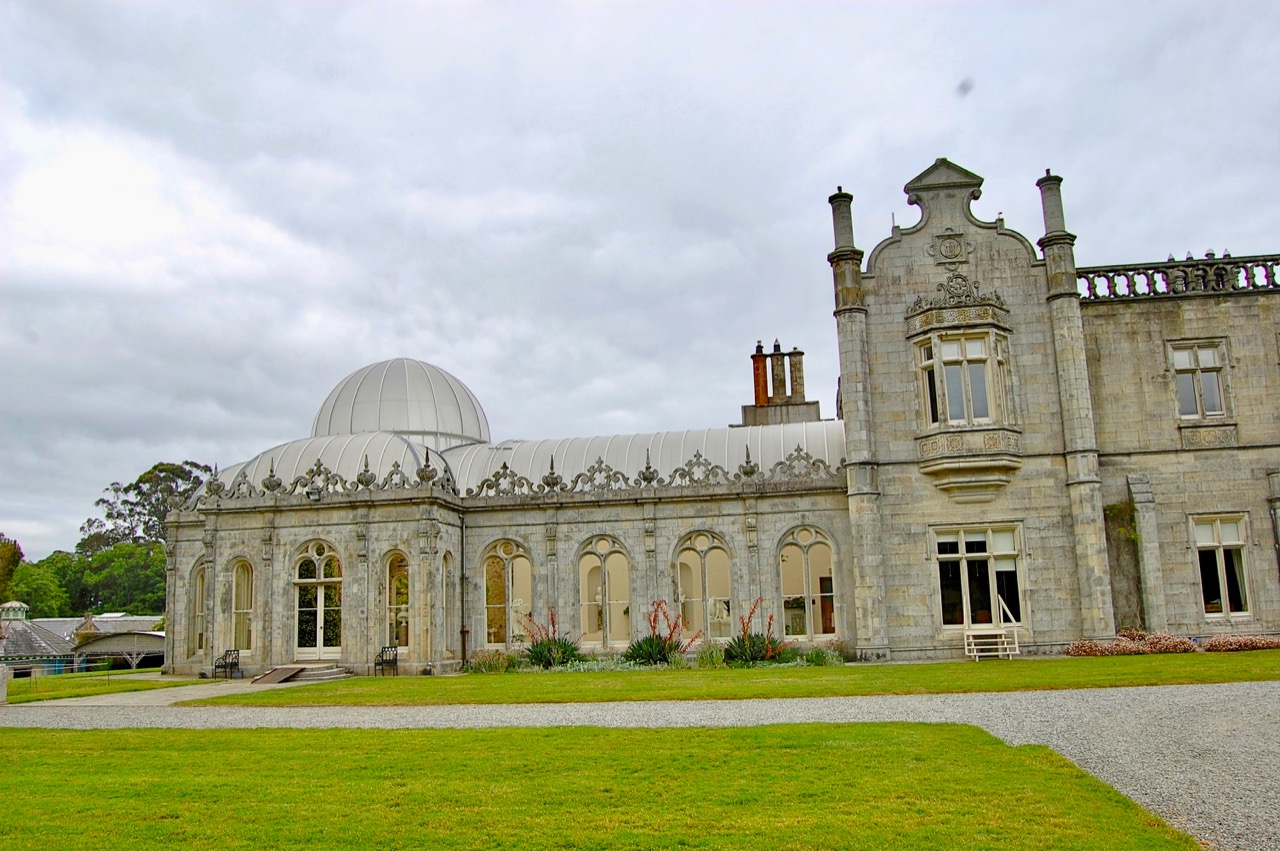
Finally, in 1945, James Albert Garland Emmet (who went by “Garland”) purchased the house on three hundred acres from Percy Burton, a bachelor. The Emmets carried out extensive restoration and created a large new garden, centred on a pair of canals from the early 18th century garden layout. These are the bodies of water we saw on the way in. The present owners, Philip (grandson of Garland Emmet) and his wife Vicky, have farmed the estate organically for nearly 20 years.


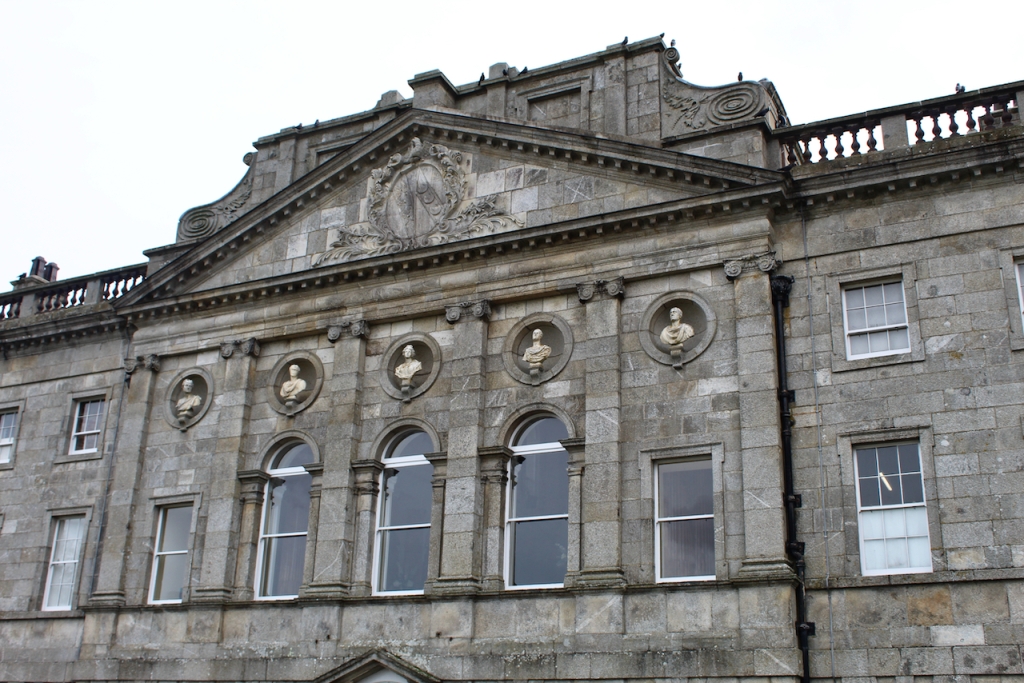
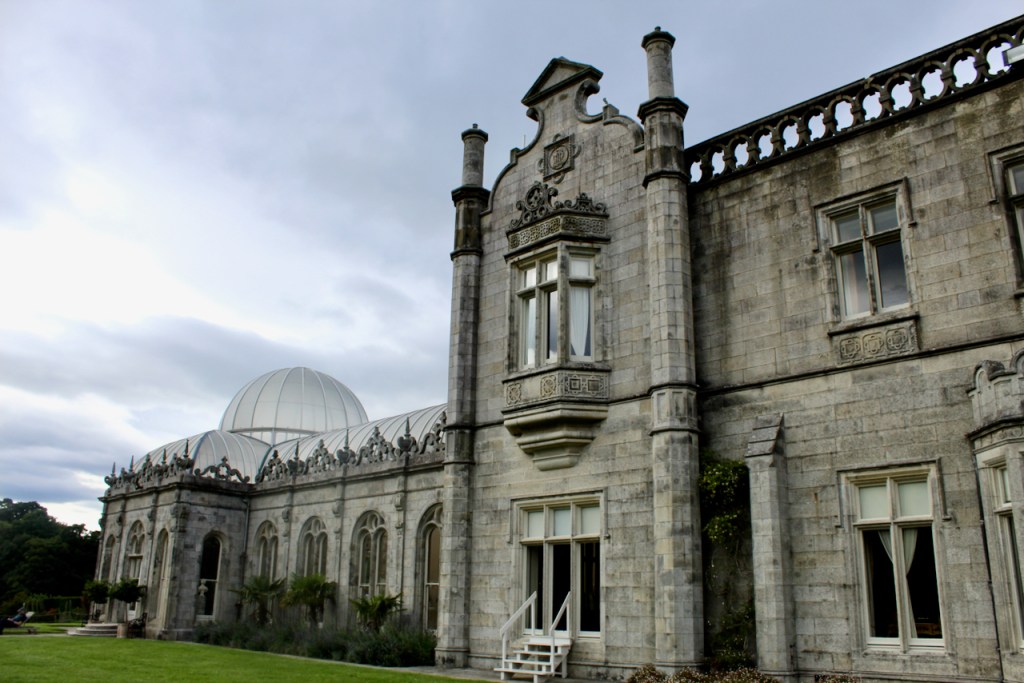
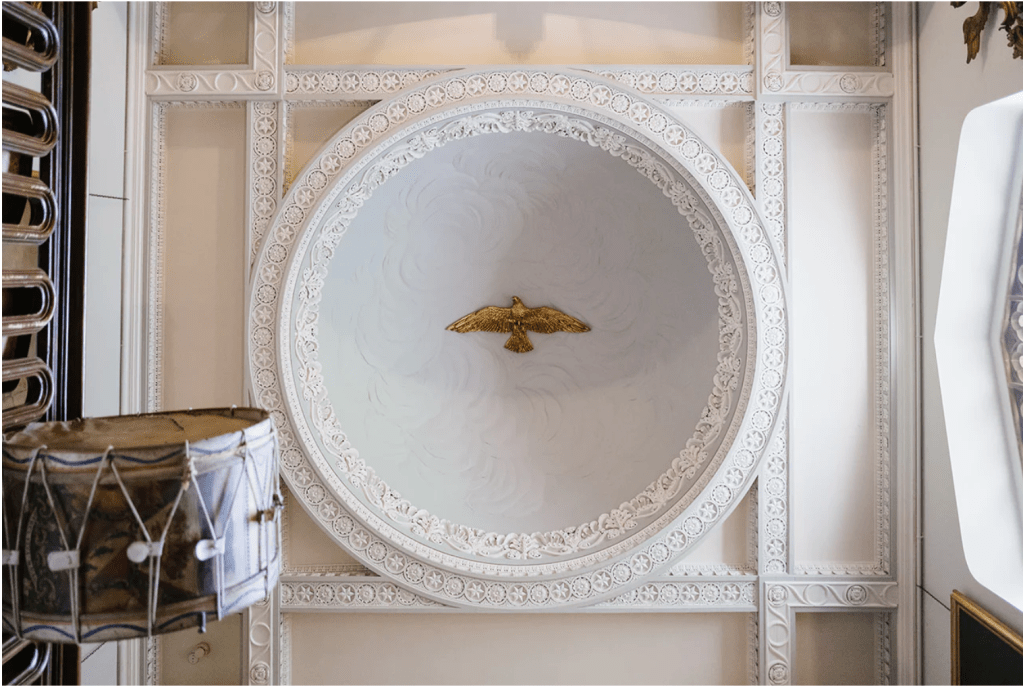
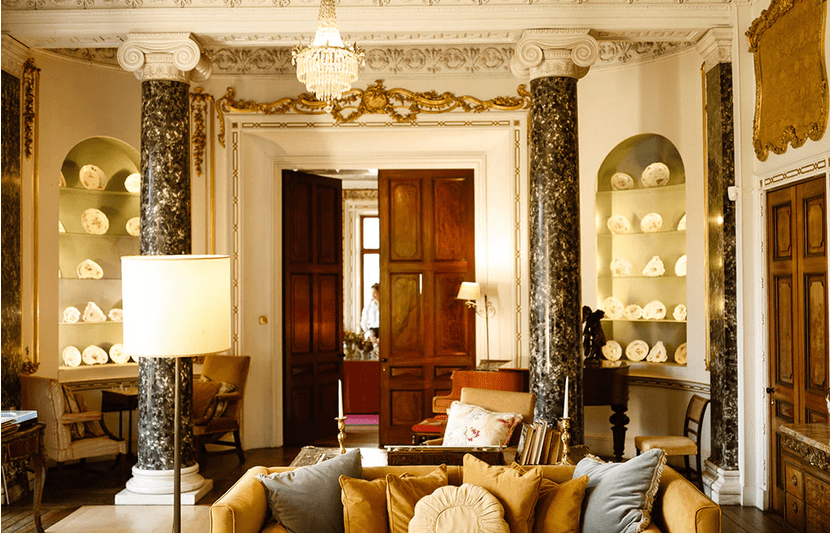
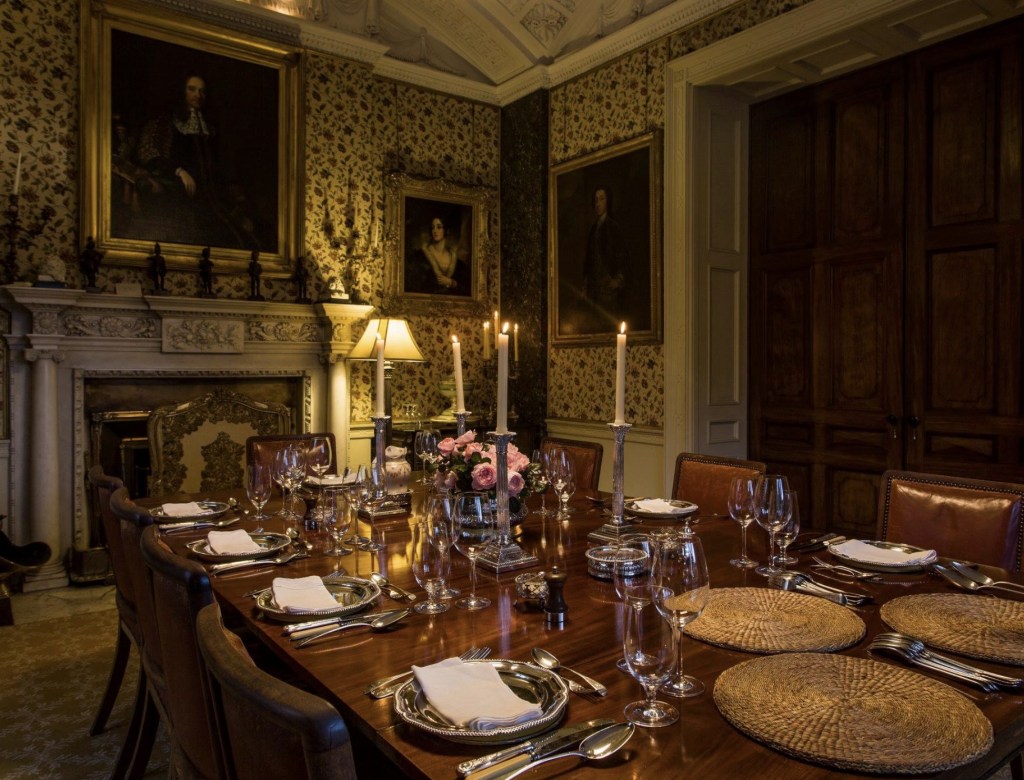
We moved from the drawing rooms to the dining room. The walls are adorned with fine medallions of Classical figures in stucco relief. They were uncovered when the walls were being redone, under layers of paint and wallpaper! The Irish Aesthete writes about them, and has beautiful photographs on his website:
“One of the past year’s most fascinating personal discoveries was the dining room at Altidore Castle, County Wicklow …. Much of the interior decoration dates from that period [ca. 1730], including the dining room’s panelling. In the last quarter of the 18th century, however, additional ornamentation was added with the introduction of oval and circular plaster medallions featuring female classical deities and graces: this would have been around the period that Altidore was owned by Rev William Blachford … During the same period the interiors of nearby Mount Kennedy – designed by James Wyatt in 1772 but only built under the supervision of Thomas Cooley the following decade – was being decorated by the celebrated stuccadore Michael Stapleton. The medallions are not unlike those seen in Lucan House, County Dublin where Stapleton also worked: might he have had a hand in the plasterwork at Altidore?” [7]
Michael Stapleton (1747-1801) was a famous Irish stuccodore, known as the “Dublin Adam,” referring to the Scottish architect and interior designer Robert Adam (1728-1792), who worked in the neo-Classical style of plasterwork. [8]

Philip told us that his ancestors, the Emmets, had to leave Ireland after Robert (1778-1803) and his brother Thomas Addis Emmet rebelled. Thomas Addis Emmet moved to the United States.
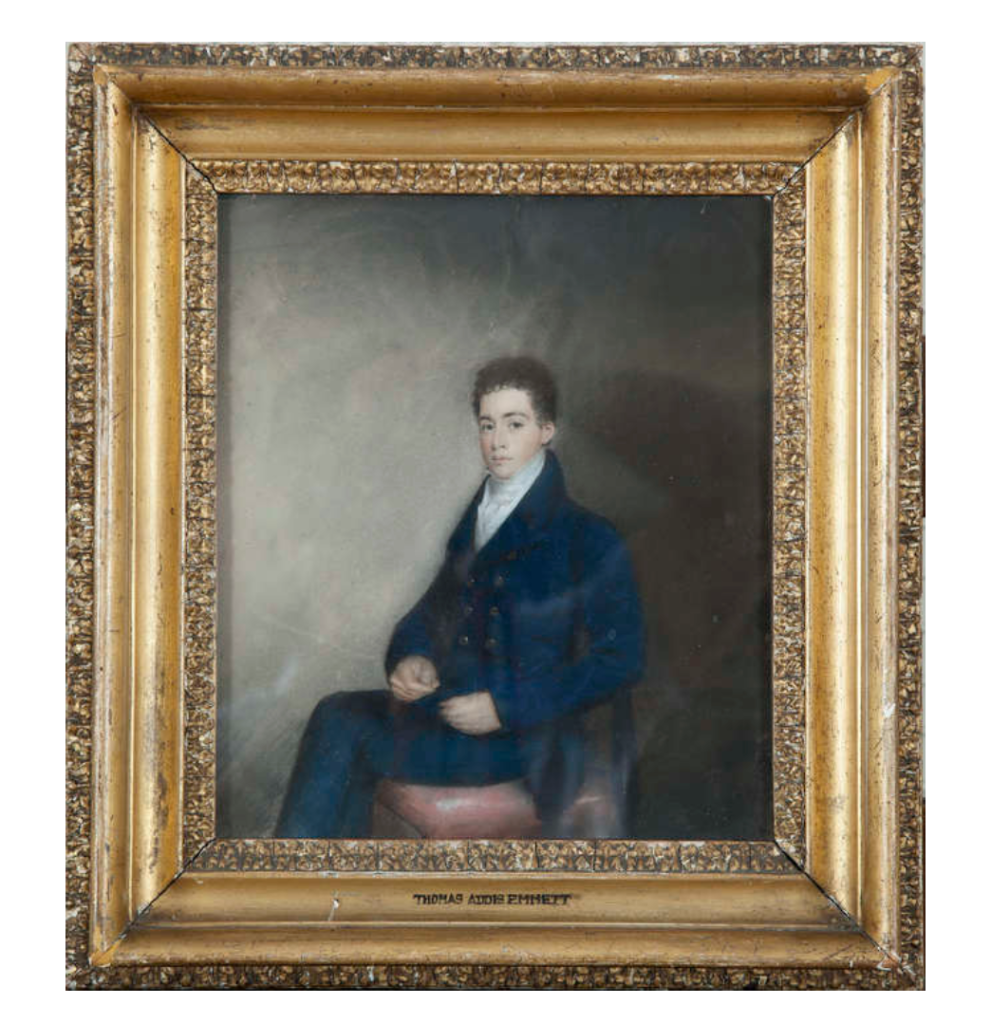


Thomas Addis Emmet (1764-1827) was a lawyer and politician from a wealthy Anglo-Irish Protestant family. He sought to end discrimination against Catholics and Protestant Dissenters such as Presbyterians. He tried to find a peaceful way of introducing a non-sectarian democracy to Ireland.
He acted as a legal advisor for the Society of United Irishmen. However, the United Irishmen were declared illegal, so efforts for a peaceful Catholic emancipation were abandoned. Instead, the United Irishmen sought independence from Britain by armed rebellion. Thomas Addis Emmet advocated waiting until the French had arrived for the rebellion, but Edward Fitzgerald (1763-1798) was more impatient and decided to go ahead with the rebellion in 1798. British intelligence infiltrated the United Irishmen and arrested most of the leaders, including Thomas Addis Emmet, on the eve of their rebellion on March 12, 1798. On his release in 1802 he went to Brussels, where he was visited by his brother Robert in October that year, who informed of the preparations for a fresh rising in Ireland in conjunction with French aid. However, at that stage France and Britain were briefly at peace, and the Emmets’ pleas for help were turned down by Napoleon.

Thomas received news of the failure of Robert Emmet’s rising in July 1803 in Paris. Robert was hung for treason in front of St. Catherine’s Church in Thomas Street in Dublin on September 20th 1803. Thomas Addis then emigrated to the United States and joined the New York bar where he had lucrative practice.


Thomas Addis Emmet became a member of the “New York Society for Promoting the Manumission of Slaves, and Protecting Such of Them as Have Been, or May Be Liberated,” commonly known as the New-York Manumission Society (N-YMS). Emmet denounced slavery for destroying the character, dignity and natural rights of man. [9]
Thomas Addis’s son John Patten Emmet (1796–1842) studied medicine and developed an interest in Chemistry. He was a chemistry professor at the University of Virginia from 1825 until his death in 1842.
Thomas Addis Emmet’s grandson, son of John Patten Emmet, also named Thomas Addis Emmet (1828-1919), visited Ireland in 1880. He hoped to move to Ireland but unfortunately he was not allowed by the government to live in Ireland, although he was a gynaecologist by profession, because it was thought that, like his ancestors, he may harbour rebellious tendencies. He requested that he be buried in Ireland so he could “rest in the land from which my family came.” Dr Emmet was interred according to his wishes in Glasnevin Cemetery in Dublin in 1922. His grave marker was designed by the father and brother of the revolutionary Padraig Pearse (they also sculpted the statues adorning St. Augustine and St. John church on Thomas Street).
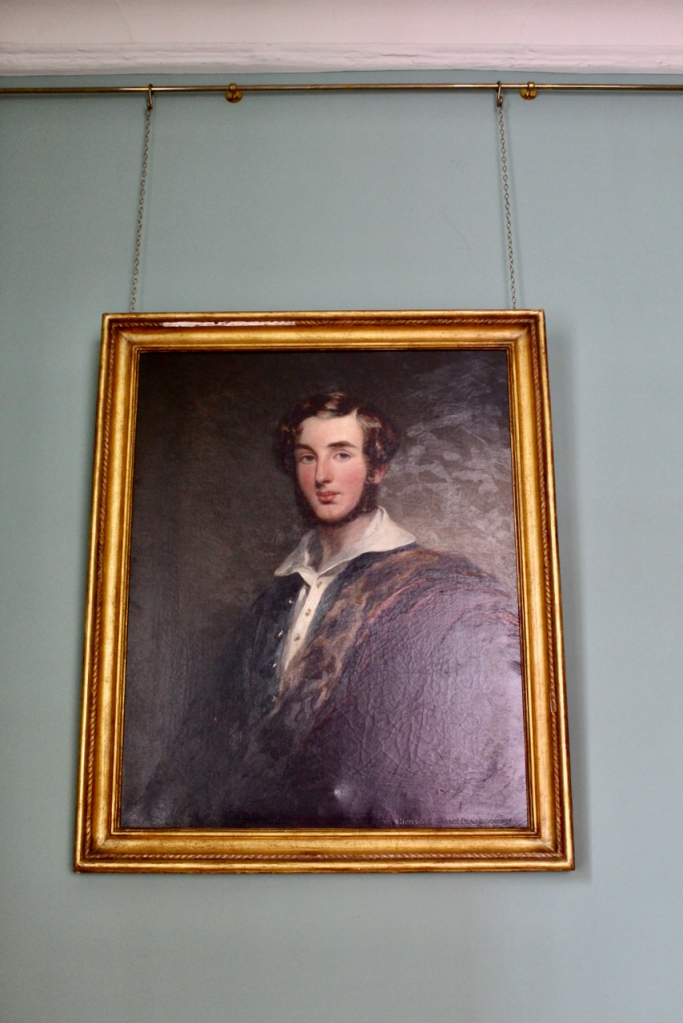
It was Dr. Thomas Addis Emmet’s grandson, James Garland Emmet, who returned to Ireland and purchased Altidore Castle in 1944. He married Jocelyn Portman, daughter of Claud Berkeley Portman, 4th Viscount Portman of Bryanston, County Dorset in England.
He set up his home as the base the Irish branch of the Emmet family and gathered objects for a collection of Emmet memorabilia. Altidore still hosts an Emmet Museum. Fascinated, Stephen lingered in the museum room and traded stories with Philip. There are lovely miniatures of the Emmet family, and a sketch of Emmet done from his time in court, by – oh, who was it? Someone famous! [10] They also have Robert Emmet’s college books, with his sketches of uniforms – he was a good artist! He was thrown out of Trinity for being a revolutionary. The house also has some artifacts from Thomas Addis Emmet, and also Robert Emmet’s final letter from prison – written not to his fiance, Sarah Curran, as Stephen and I had believed, but to a politician, to urge him to excuse himself for not anticipating the rebellion. Robert Emmet was reknown for his secrecy.

We wandered back out to the ponds, which are divided into three, and are part of a canal running down the mountain. We found the old walled garden – not in use currently – and looked around the farm and the beautiful old farm buildings.
© Jennifer Winder-Baggot, www.irishhistorichouses.com






Donation
Help me to fund my creation and update of this website. It is created purely out of love for the subject and I receive no payment so any donation is appreciated! For this entry I paid for petrol to drive from Dublin and for the entrance fee for myself and Stephen.
€15.00
[1] Bence-Jones, Mark. A Guide to Irish Country Houses published by Constable and Company Limited, London, 1988, previously published by Burke’s Peerage Ltd as Burke’s Guide to Country Houses, vol. 1 Ireland, 1978.
[2] https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Thomas_Pearce_(British_Army_officer)
[3] https://www.ihh.ie/index.cfm/houses/house/name/Altidore%20Castle
[4] Mary Delany (1700-1788) whose letters are published, was Godmother to a musician in the Wesley family, and explains how the Methodist Wesleys were cousins of Arthur Wellesley, the Duke of Wellington – who is honoured in the Wellington obelisk in the Phoenix Park.
[5] https://theirishaesthete.com/2013/05/13/of-wonderous-beauty-did-the-vision-seem/
The Irish Aesthete also notes: A new biography of Mary Tighe by Miranda O’Connell has been published by the Somerville Press.
[6] Tinnehinch was presented to Grattan, according to Mark Bence-Jones, in gratitude for the part he played in obtaining freedom from British control in 1782. The house has been destroyed by fire but one storey of the ruin still stands and has been made into a feature of the garden of the present house, which is in the former stables.
[7] https://theirishaesthete.com/2016/01/02/getting-thoroughly-plastered/
[8] Other work by Michael Stapleton can be seen in Marlay House in Dublin, several houses in North Great George’s Street including Belvedere House, Powerscourt Townhouse, 59 South William Street, Dublin 2 and in Trinity College Dublin, especially in the Exam Hall and the Chapel. Note that Stapleton was the executor of Robert West’s will, and may have trained with Robert West. We came across Robert West’s characteristic stucco work in Colganstown.

[9] Landy, Craig A. “Society of United Irishmen Revolutionary and New-York Manumission Society Lawyer: Thomas Addis Emmet and the Irish Contributions to the Antislavery Movement in New York” New York History, Vol. 95, No. 2 (Spring 2014), pp. 193-222 (30 pages).
[10] Perhaps the artist was John Comerford, who sketched Robert Emmet during his trial, and a miniature has been made from the sketch. The miniature is now in the National Gallery.