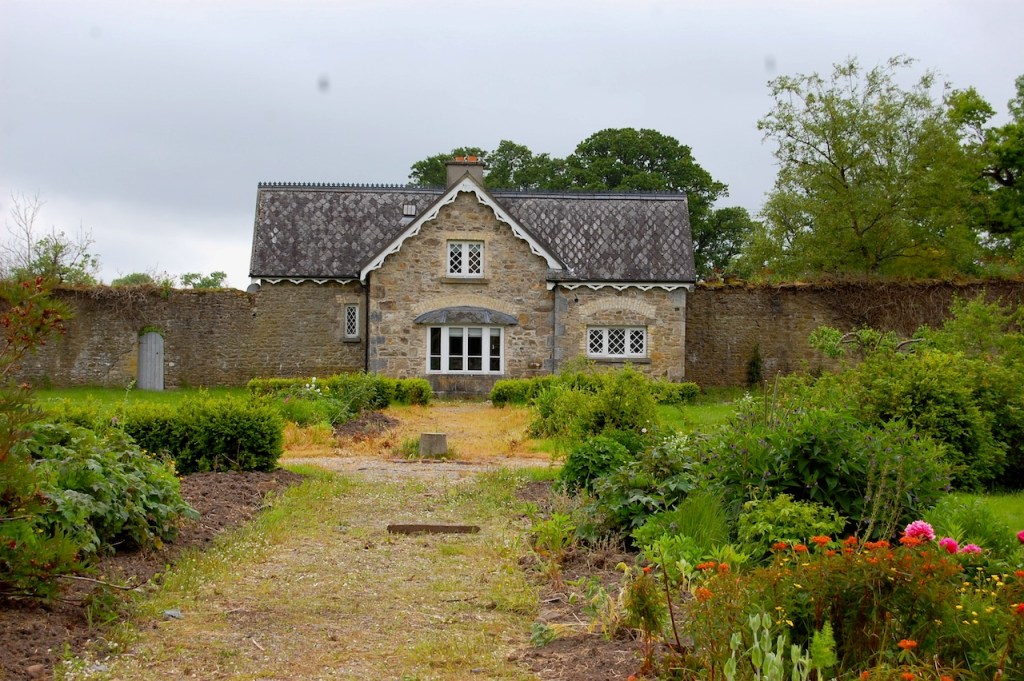
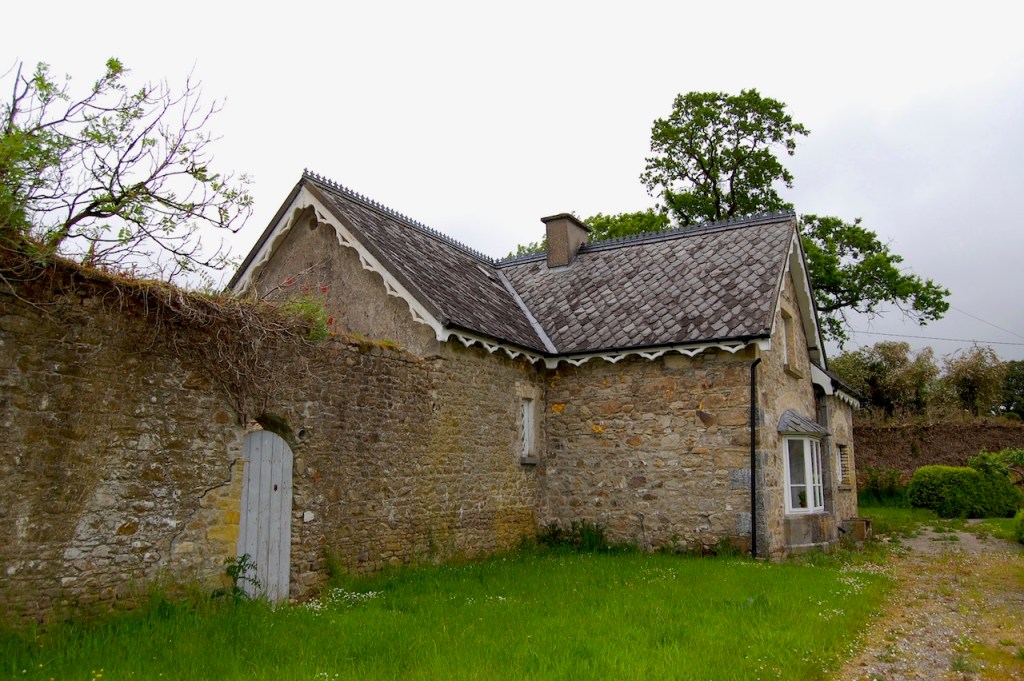
Tourist Accommodation Facility – not open to visitors, overnight guests only
www.wiltoncastleireland.com
Open for accommodation: all year
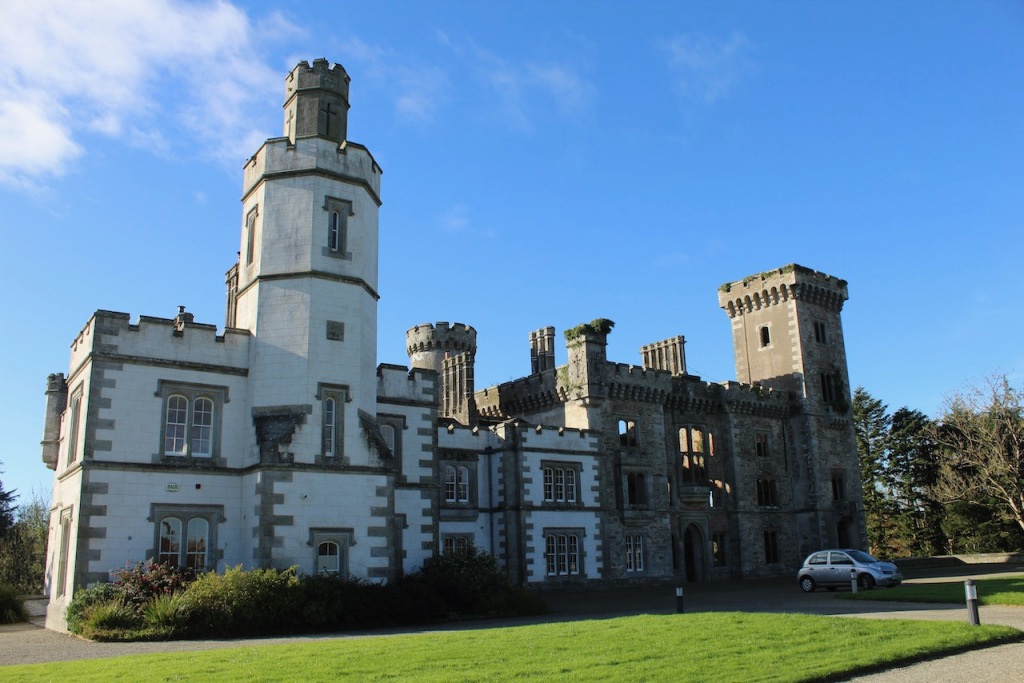


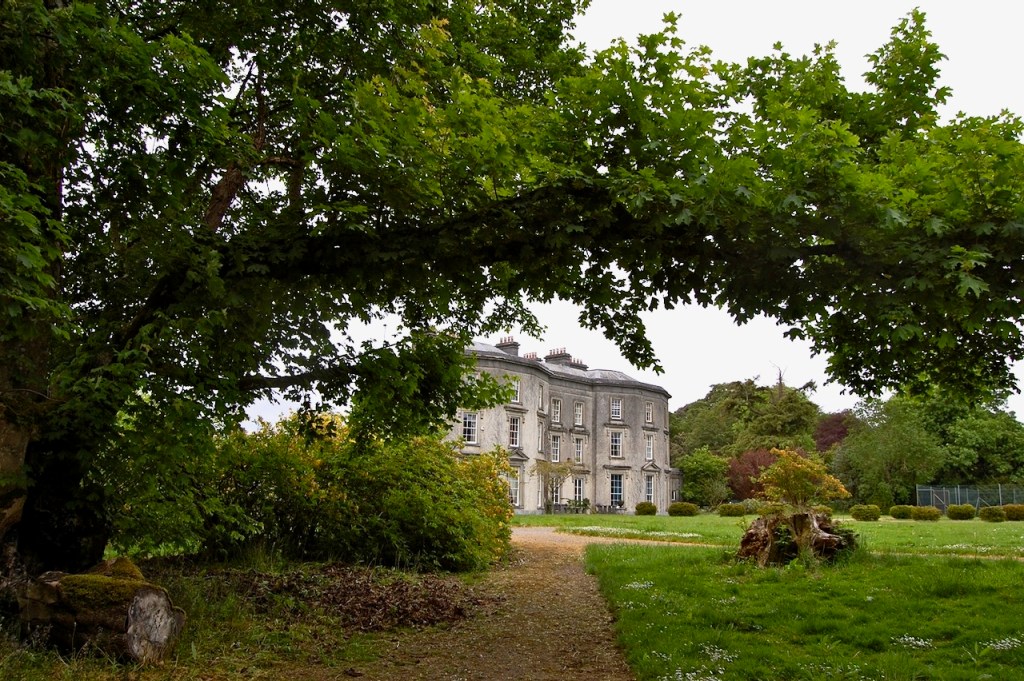
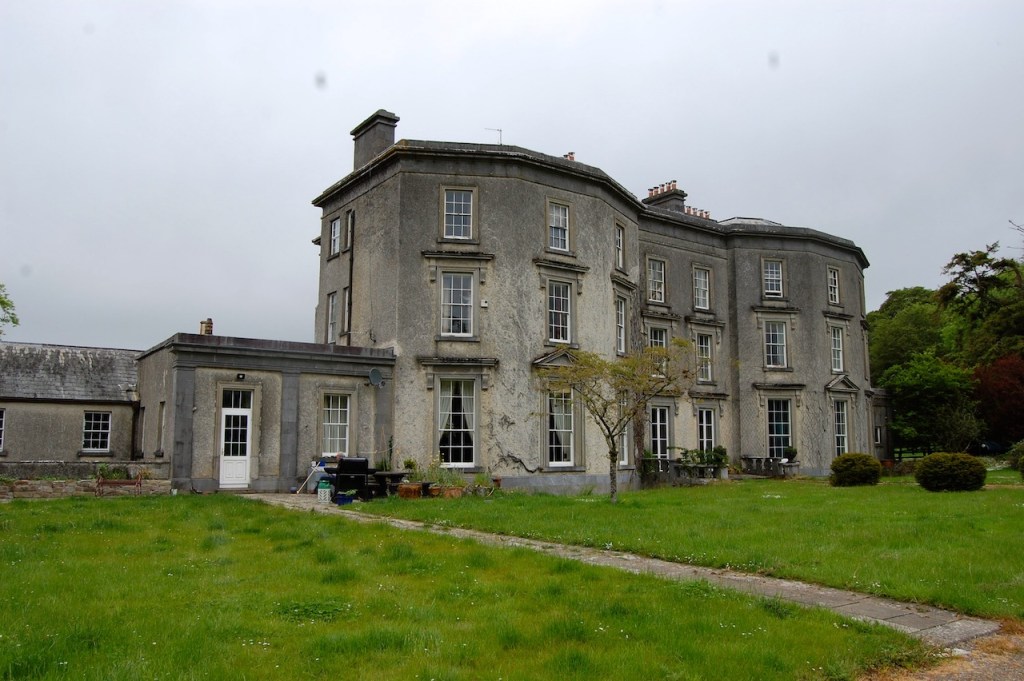
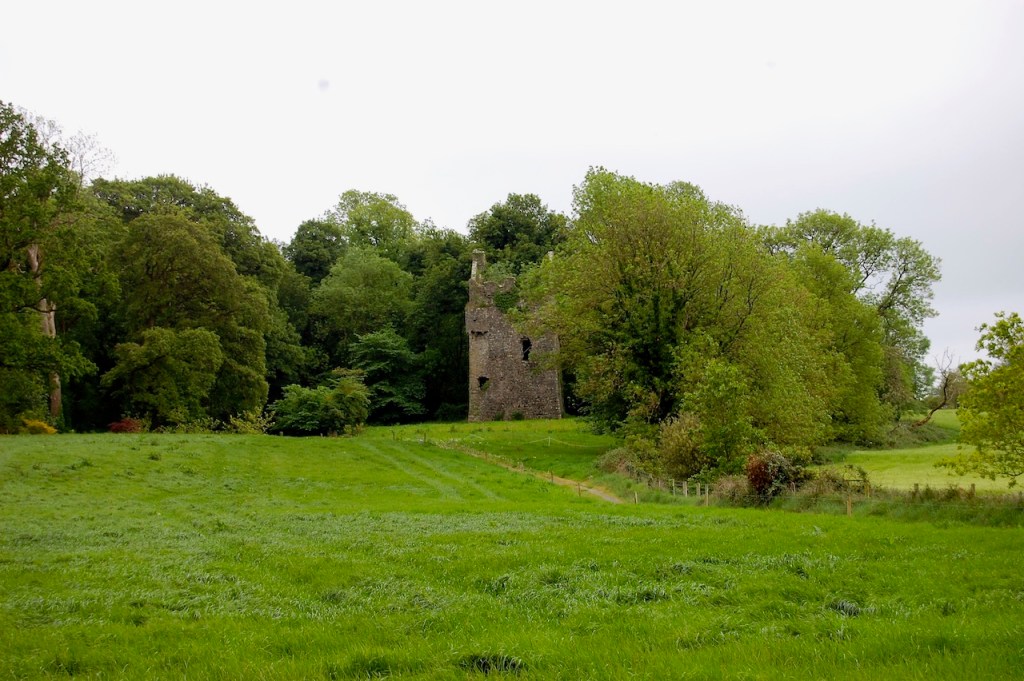
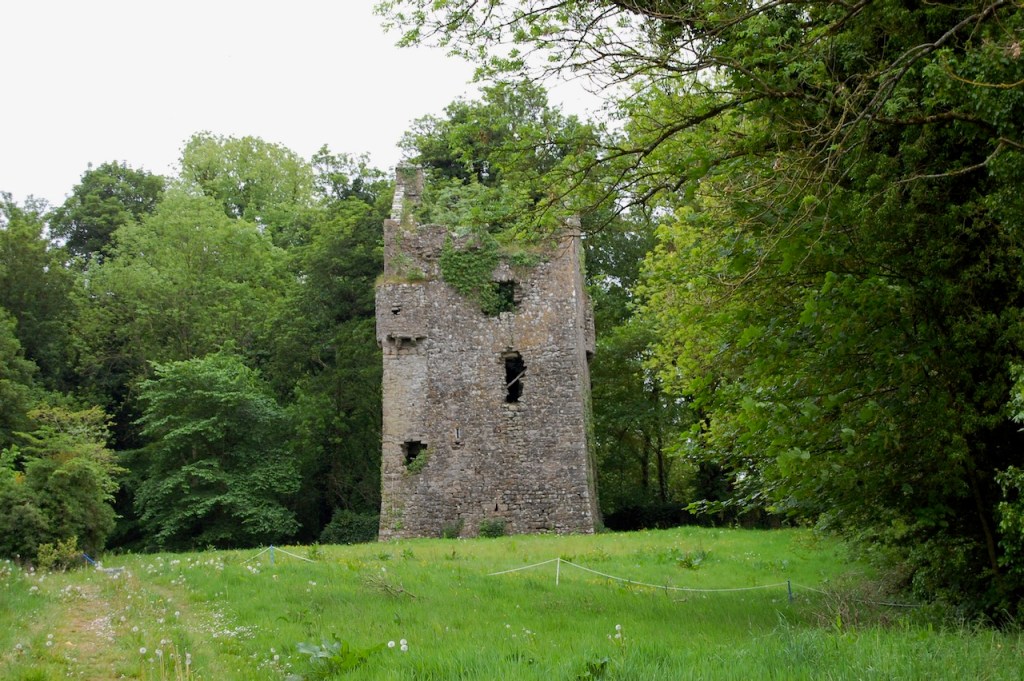
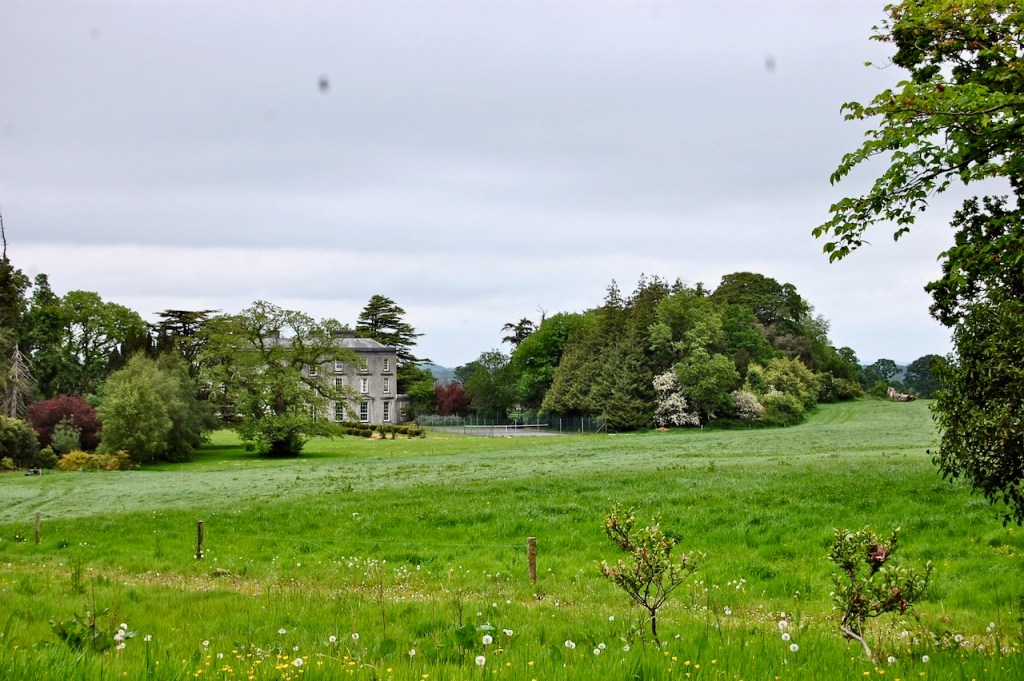
We treated ourselves to a stay in Wilton Castle in November in 2021. Having been gutted in a fire in 1923, it stood as a dramatic ruin until the Windsors purchased and began to refurbish it into luxurious accommodation. The current restoration was completed in 2014. So far just half of it has been rebuilt, the rest has been stabilised but remains empty and without a roof. The work which has been done by the Windsors is incredible – it seems to have been rebuilt to a very high standard. I’m not sure if they intend to continue to rebuild the rest of the castle.
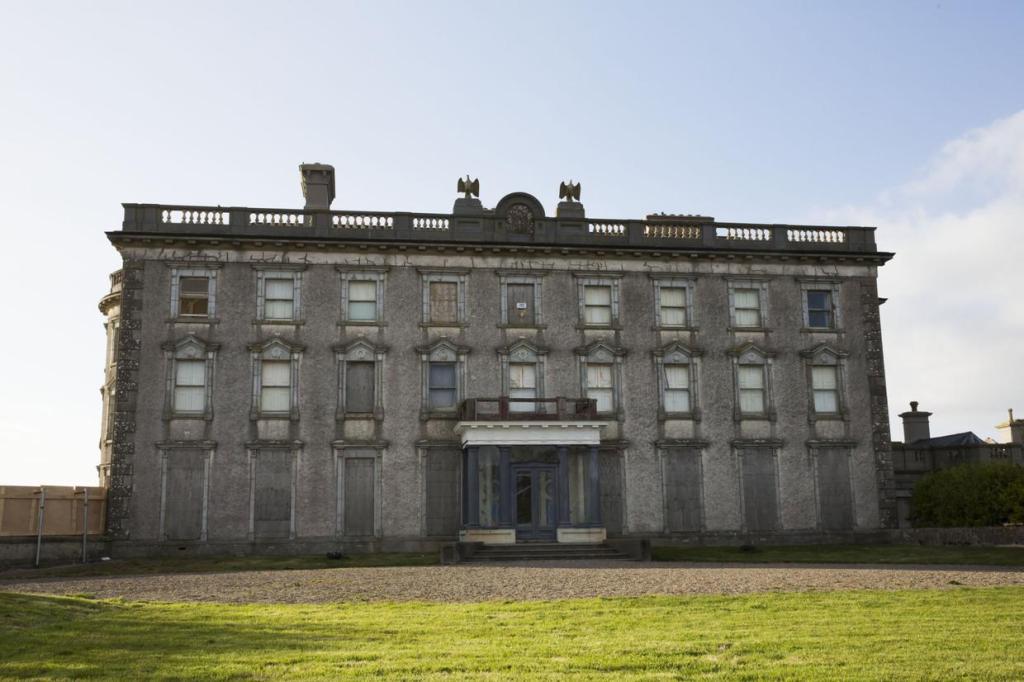
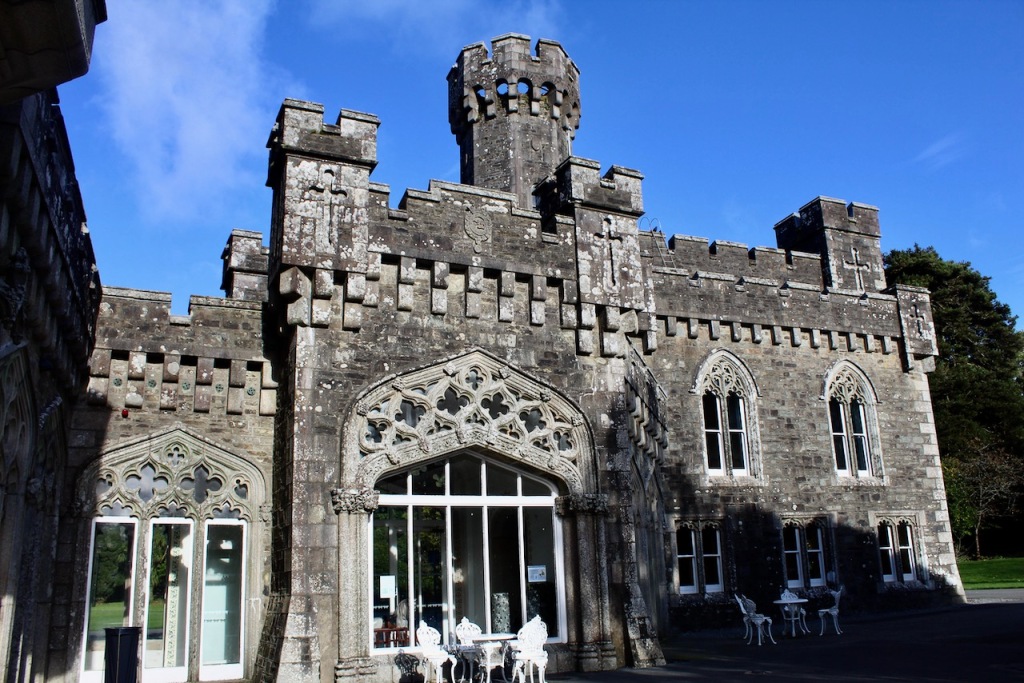
Wilton Castle was designed for Harry Alcock (1792-1840) by Daniel Robertson (d. 1849) in 1836-38, subsuming parts of an earlier castle and house.
The area was previously known as Clogh na Kayer (The Castle of the Sheep). Herbert Hore writes in History of the Town and County of Wexford that an ancient Castle of Cloghnakayer was built in the fourteenth century. The De Dene family owned the land until 1354, when an only daughter married Philip Furlong whose descendant, Sir Fulke Furlong, knight, of Horetown, built a castle around 1410.
The land then passed to the Butlers of Mountgarret. Edward Butler, Baron of Kayer (eldest son of Pierce, second son of Richard 1st Viscount Mountgarret) rebuilt and restored the ancient Castle, and added a mansion house to it in 1599. [1]

Edward Butler’s son, Pierce, inherited. Pierce Butler was a Catholic and a supporter of the monarchy and his land was confiscated by the Cromwellian parliament in 1655 and granted to a Cromwellian soldier, Captain Robert Thornhill. Captain Robert’s son sold the estate in 1695 to William Alcock (d. 1705) of Downpatrick, County Down. [2]
Herbert Hore tells us that William Alcock rebuilt the castle, and called it Wilton. It was this castle that was subsumed in Daniel Robertson’s design for Harry Alcock. Herbert Hore writes that “the late Colonel Alcock [Harry, (1821-93)] told me that some of the walls of the ancient Castle of the Butlers are incorporated in the present building.”
Robert O’Byrne writes: “William Alcock built a new residence for himself on the site of an old castle, and this was occupied by his descendants for several generations. A handsome classical doorcase of granite with segmental pediment above fluted pilasters survives on the façade of the former steward’s house at Wilton to indicate the appearance of the original Alcock house, dismissed by Martin Doyle in his 1868 book on the county as being ‘in the dull style of William and Mary.’ ” [3]


A daughter of William and his wife Jane nee Bamber of Bamber Hall of Lancaster, England, married Patrick Lattin and was the mother of the famous Jack Lattin of Morristown Lattin, County Kildare, who danced himself to death!
The estate passed to William Alcock’s son, another William Alcock (1681-1739), then to his son, Col. William Alcock (d. 1779) (Colonel in the Waterford Militia). He married Mary Loftus of Loftus Hall, County Wexford, daughter of Nicholas Loftus, 1st Viscount Loftus of Ely and his wife Anne Ponsonby, daughter of William Ponsonby, 1st Viscount Duncannon.

Wilton then passed to his son, Henry Alcock (d. 1811). Henry Alcock married Elizabeth Katherine Ussher, daughter of Beverly Ussher of Kilmeadon, County Waterford, who was a long term MP for County Waterford. Henry Alcock also served as an MP for Waterford. Elizabeth Katherine’s sister Mary also married an MP, John Congreve of Mount Congreve in Waterford (which has beautiful gardens open to the public, although temporarily closed – I wonder if the house is to be opened also?).
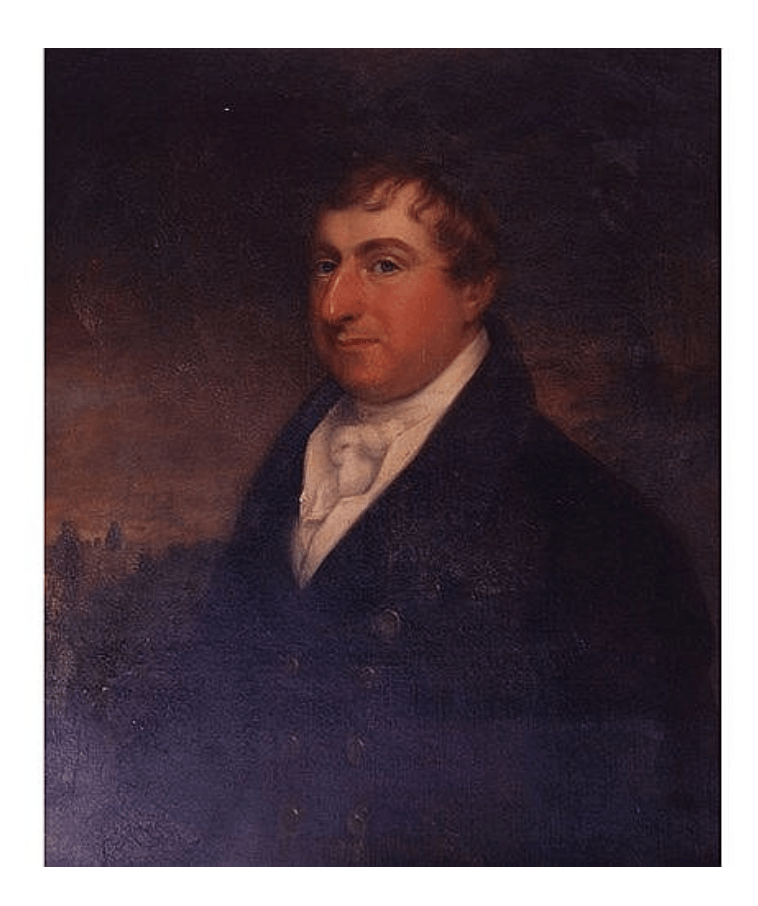
The estate then passed to his son, William Congreve Alcock (1771-1812). William competed in the general election of 1807 against John Colclough of Tintern Abbey (son of Vesey Colclough, MP for County Wexford). Unfortunately they decided to settle a dispute by a duel, and William shot and killed John. John had been engaged to a sister of William’s. William was tried for murder but acquitted. He never got over the incident however and it affected his mental health and he died five years later. [4] Thus Wilton Castle passed to his brother, Harry Alcock (1792-1840).
In 1818 Harry Alcock married Margaret Elinor Savage, daughter of James Savage of Kilgibbon, County Wexford (this house is now a ruin). He then engaged Daniel Robertson in 1837 to renovate Wilton House, which became Wilton Castle. The newer house was built in front of the older Wilton House.

The details of Daniel Robertson’s training are not known. He struggled with bankruptcy for a large part of his life and moved from working in Oxford in England to Ireland, at the urging of his father-in-law. The Dictionary of Irish Architects tells us:
“From the early 1830s he did no further work in Britain but received a series of commissions in Ireland, mainly for country house work in the south eastern counties. Most of these houses or additions were in the Tudor style, which, he asserted in a letter to a client, Henry Faulkner, of Castletown, Co. Carlow, was ‘still so new and so little understood in Ireland’. For some of them he used Martin Day as his executant architect. In spite of his success in attracting commissions, when he was working at Powerscourt in the early 1840s he was, in the words of Lord Powerscourt, ‘always in debt and…used to hide in the domes of the roof of the house’ to escape the Sheriff’s officers who pursued him. By then he was crippled with gout and in an advanced state of alcoholism; at Powerscourt he ‘used to be wheeled out on the terrace in a wheelbarrow with a bottle of sherry, and as long as that lasted he was able to design and direct the workmen, but when the sherry was finished he collapsed and was incapable of working till the drunken fit had evaporated.’ In at least two instances – at Powerscourt and at Lisnavagh – he lived on the premises while work was in progress, and it seems that from the 1830s until the year of his death his wife and family never settled for any time in Ireland… Robertson was overseeing the completion of Lisnavagh, Co. Carlow, where he had been living intermittently since the start of building in 1846, when he fell seriously ill in the spring of 1849” and died in September of that year. [5]


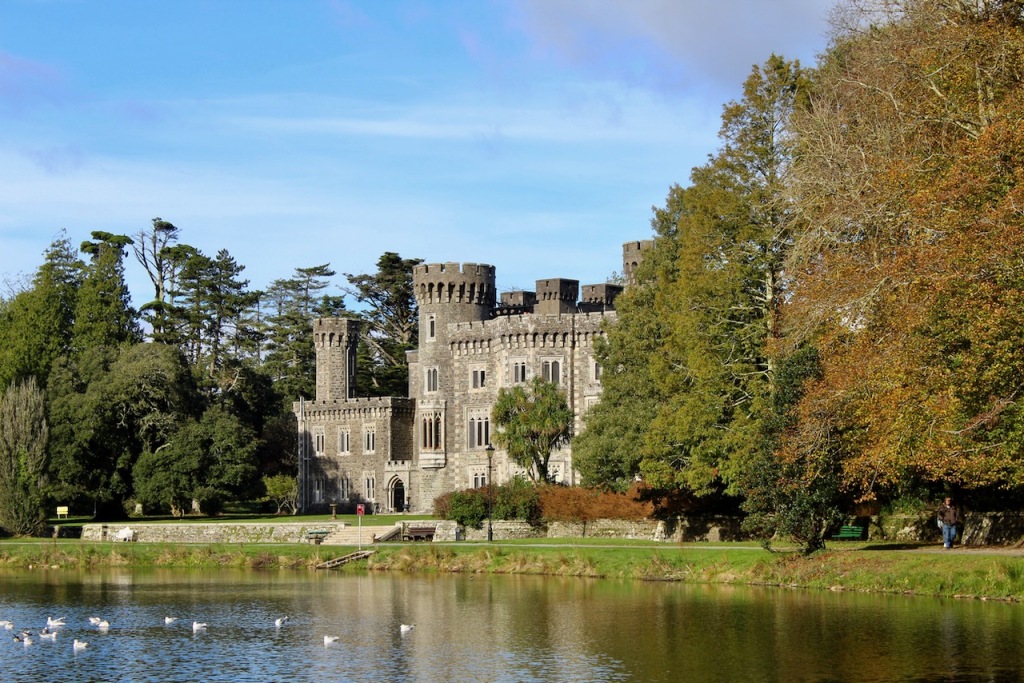
Daniel Robertson also designed the nearby Johnstown Castle in County Wexford. We visited Johnstown Castle also but unfortunately it was closed the only day we were in Wexford, as they were taking down Hallowe’en decorations from a special event! Such a pity we weren’t able to see the inside of the castle yet, but we shall certainly visit again.
Johnstown Castle is described in the National Inventory of Architectural Heritage: “the construction in a blue-green rubble stone offset by glimmering Mount Leinster granite dressings not only demonstrating good quality workmanship, but also producing a sober two-tone palette.” [6] Wilton Castle also has Mount Leinster granite dressings. It was covered however in white lime plaster – which has been reinstated on the renovated part of the castle.


Harry’s daughter Henrietta married William Russell Farmar who also had a house built by Daniel Robertson: Bloomfield in County Wexford.

Another daughter, Sarah, married Thomas John Fetherston, 5th Baronet, of Ardagh, County Longford (the house is now in use as training college, St. Brigid’s Training College, by the Sisters of Mercy).
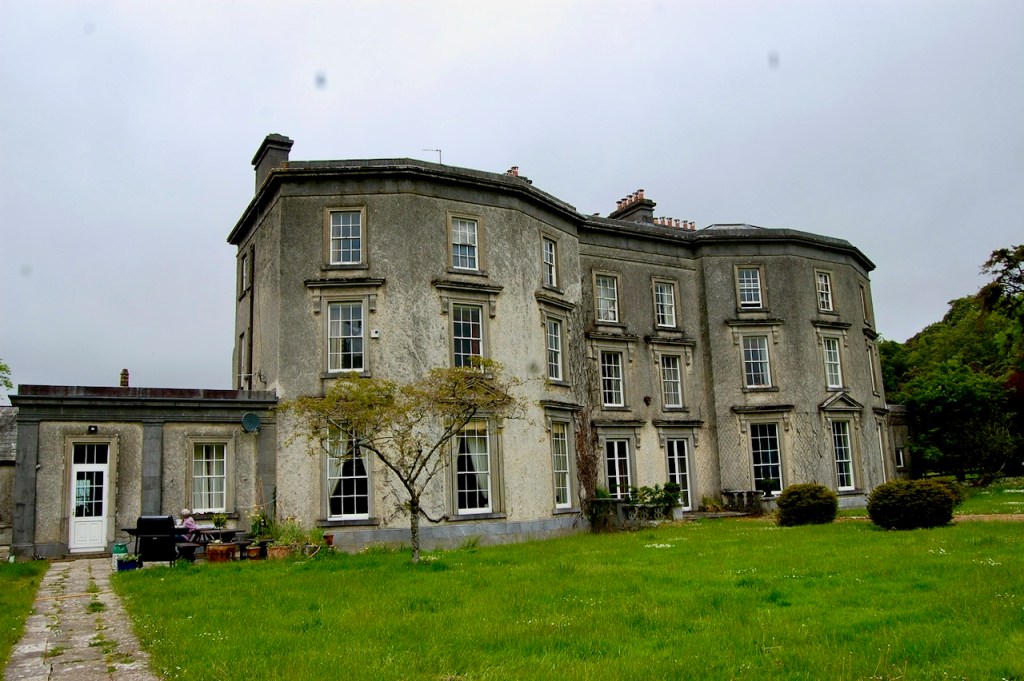
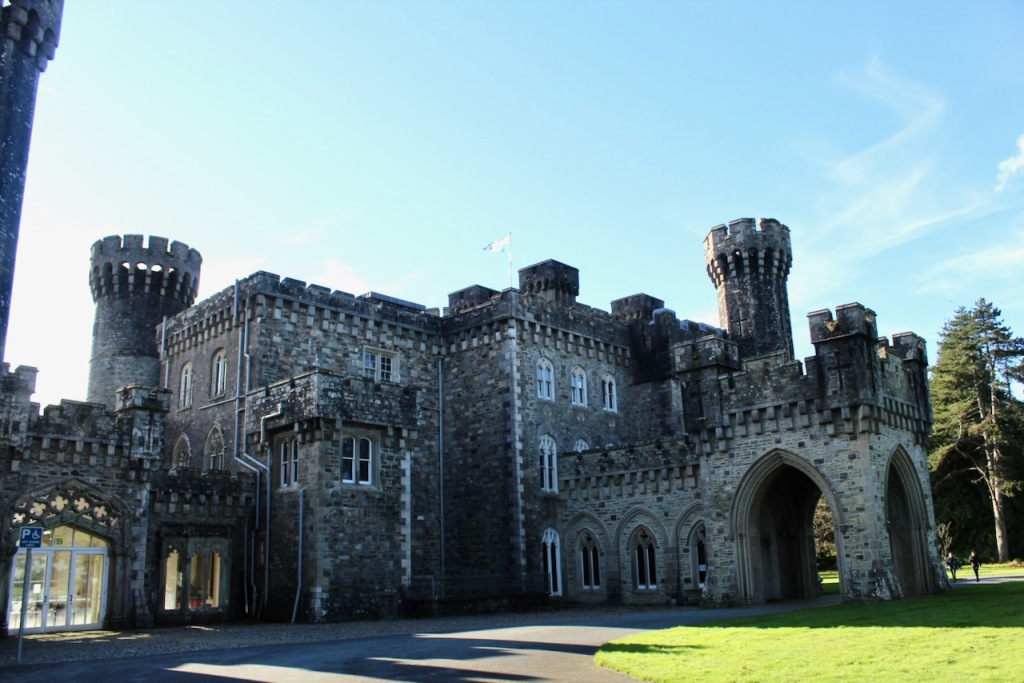
Harry’s son, another Harry Alcock (1821-93), inherited Wilton Castle and the estate. He served as High Sheriff of Wexford in 1846 and was Lt-Col. of the Wexford Militia. He continued the building work, which finished in 1844, adding the large square four storey tower with its elaborate balconies. He also improved the surrounding estate. He increased the plantation of trees and implemented a programme of road construction, fence building and draining of land which was carried out as Famine relief work. [8]

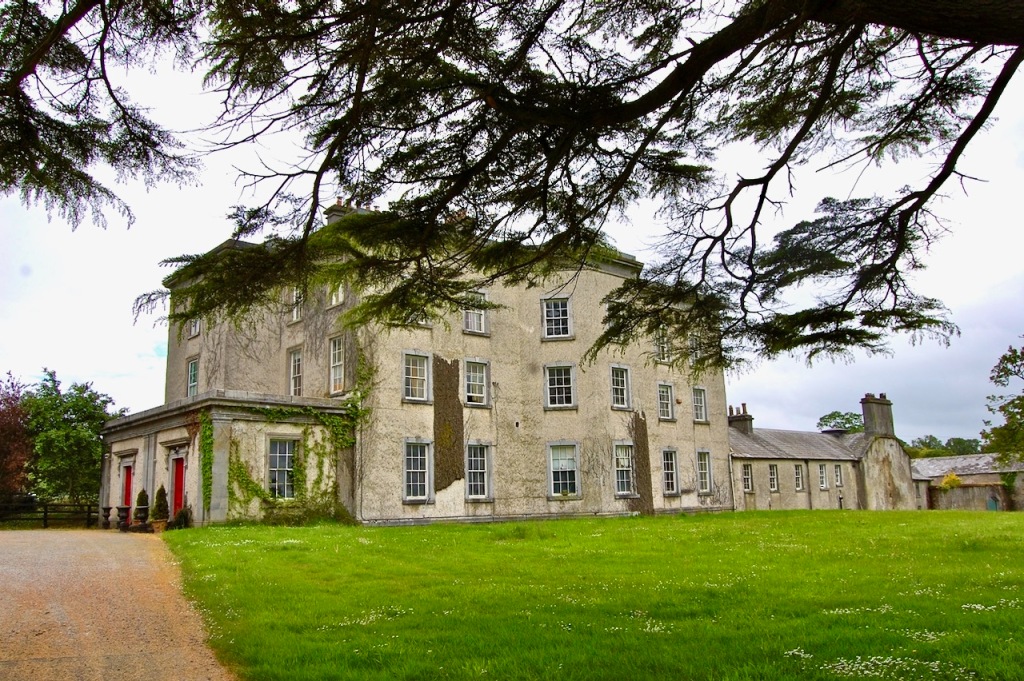
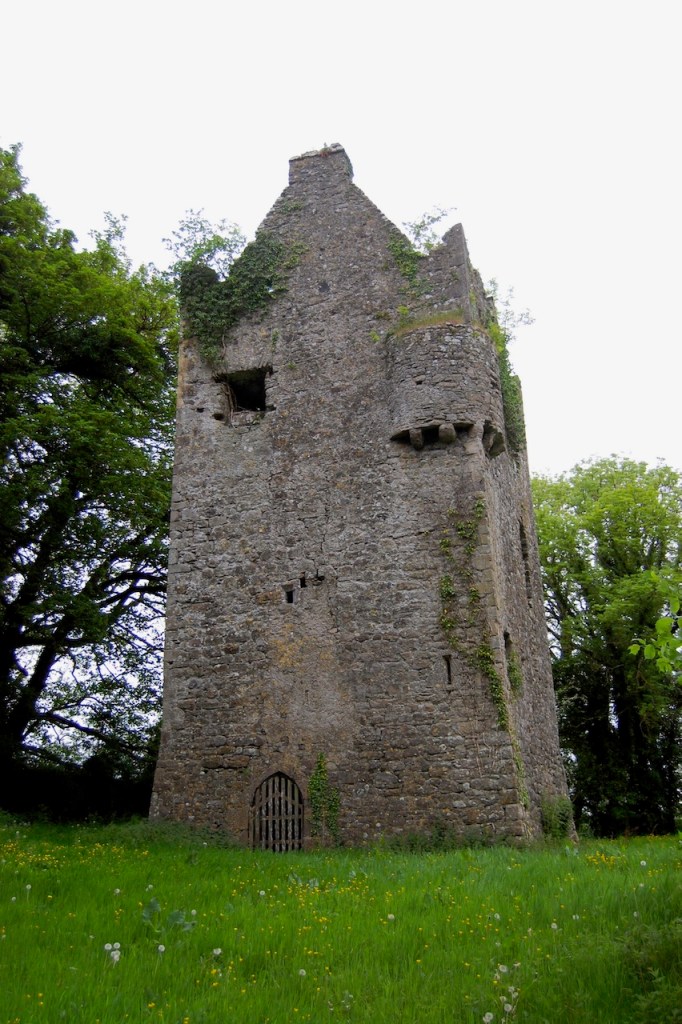
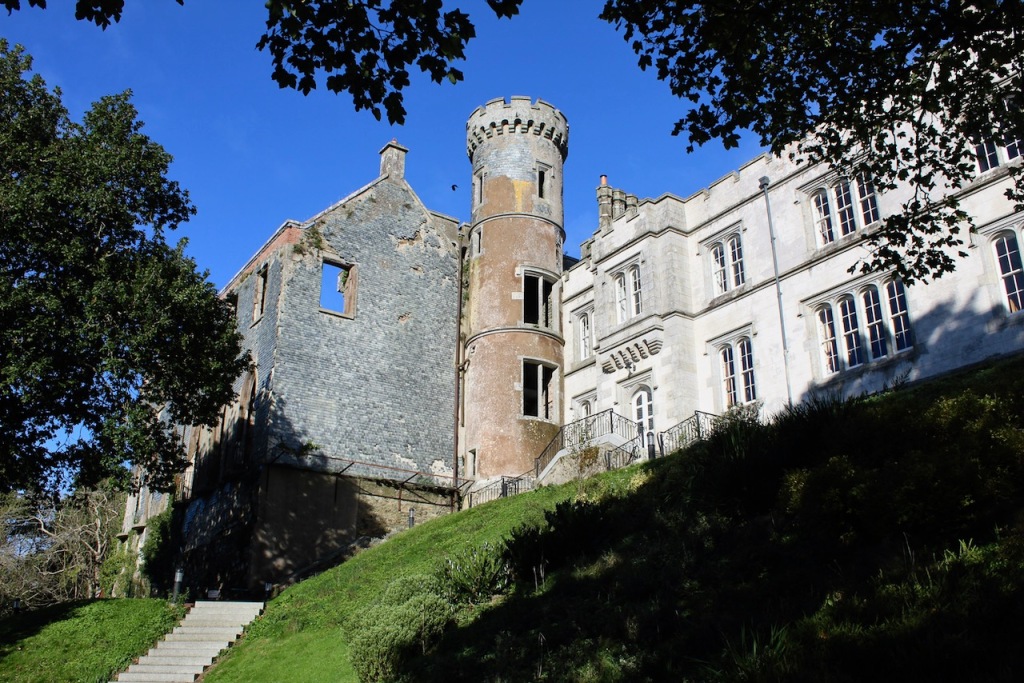
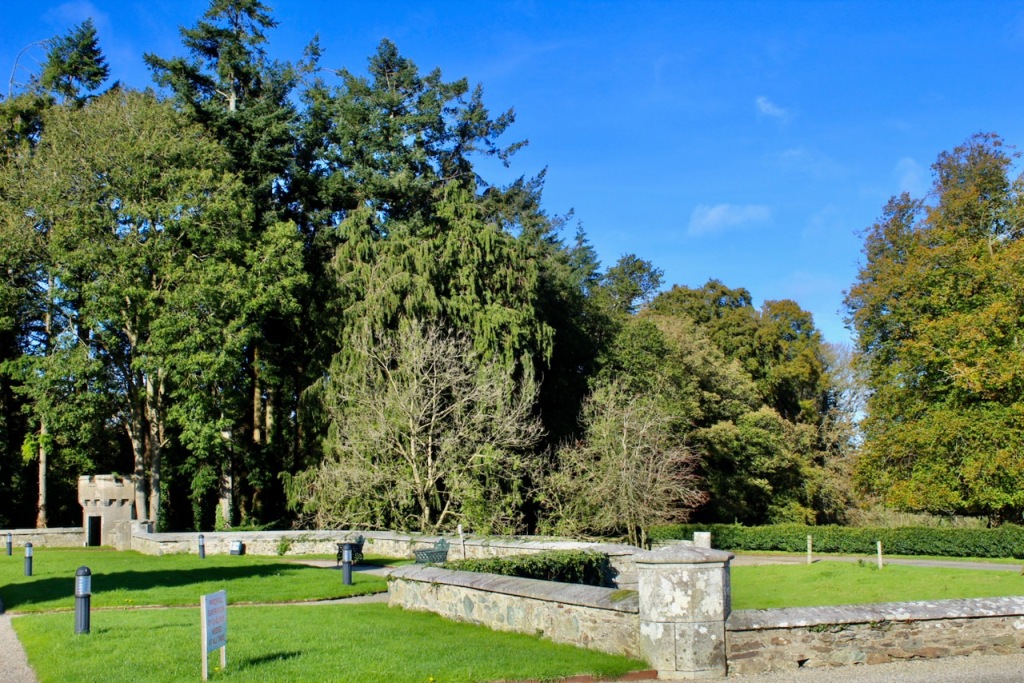
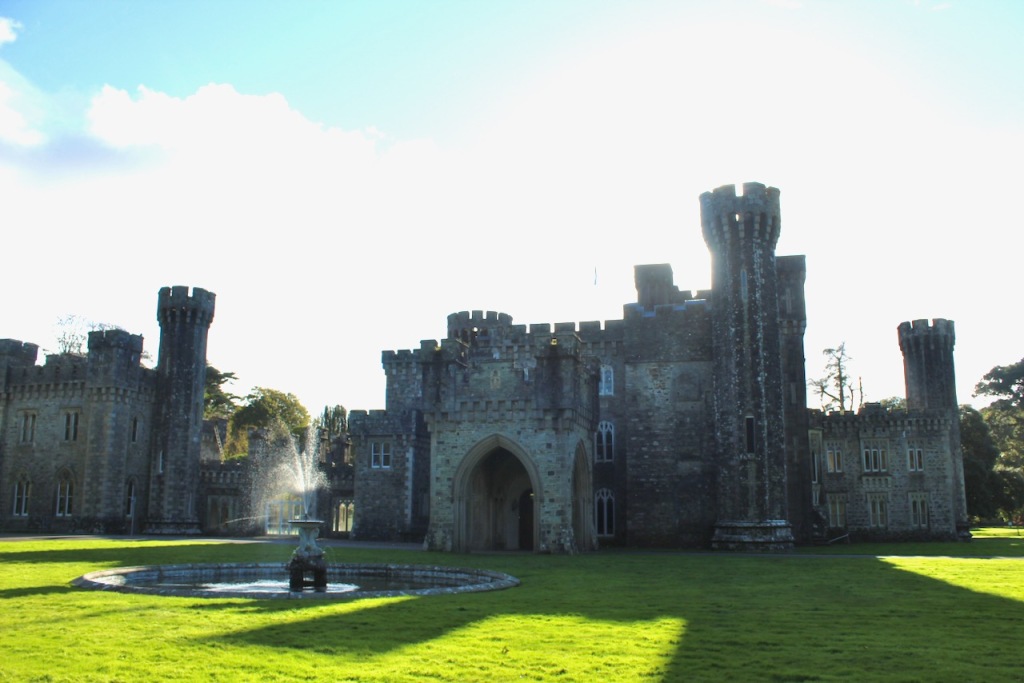
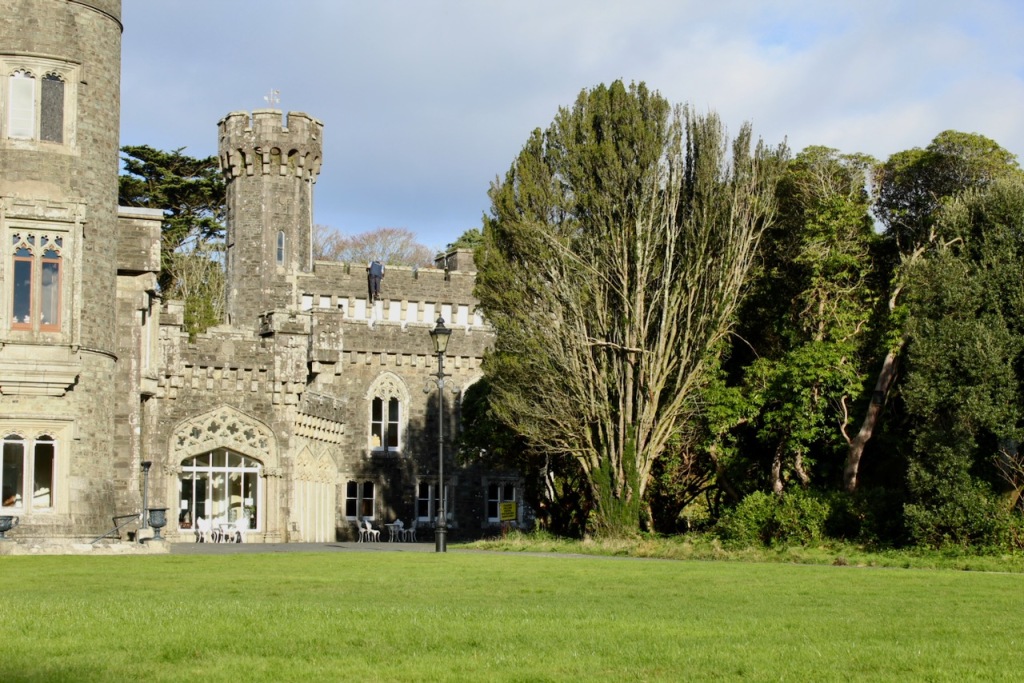
Wilton Castle, when designed by Daniel Robertson, consisted of a three-storey main block and two-storey wing, all dominated by a tall square tower at one end and a tall polygonal tower and turret at the other, and it is heavily machicolated and battlemented. It is the two storey wing which has been renovated for accommodation.

Harry Alcock died unmarried in 1893 and the estate (some 7,000 acres in the 1870s) passed to his nephew, Philip Clayton Alcock (1861-1949), son of Harry’s brother Philip Savage Alcock (1828-86) of Park House on the Wilton estate and his wife Katherine Annette Browne-Clayton of Carrickbyrne Lodge in County Wexford. Philip Clayton Alcock was a Captain in the Gloucestershire Regiment, and in 1900 High Sheriff of Wexford, but by 1922 he felt it was too dangerous to remain at Wilton and moved to England. In 1923 his fears about his Irish property were justified when Wilton Castle was burned by arsonists. [9]
A contemporary account in the Irish Times, 7 March 1923 tells us about the burning: “Wilton Castle, the residence of Captain P.C. Alcock, about three miles from Enniscorthy, was burned by armed men on Monday night. Nothing remains of the beautiful building but smoke-begrimed, roofless walls, broken windows, and a heap of smouldering debris. The Castle was occupied by a caretaker – Mr. James Stynes – the owner, with his wife and family, having gone to England about a year ago. Shortly after 9 o’clock on Monday night the caretaker was at the Steward’s residence…when he was approached by armed men, who demanded the keys to the Castle. When he asked why they wanted the keys, one of the armed men said: “We have come to burn the place. We are sorry”. The raiders told the caretaker that he could remove his personal belongings from the part of the Castle that he occupied, but they would not allow him to remove the furniture. Fearing that the Castle might be burned, however, Captain Alcock had removed the most valuable portion of his furniture some weeks ago, but a good many rooms were left furnished. When the caretaker had removed his property he was ordered back to the Steward’s house. Soon the noise of breaking glass was heard. It appears that the armed men broke all the windows on the ground floor, and having sprinkled the floors with petrol, set them alight. They did not hurry over their work of destruction, and they did not leave the Castle until near 12 o’clock, when the building was enveloped in flames. About thirty men took part in the raid. After the raiders left, the caretaker and Steward, with what help they could procure, tried to extinguish the flames, but their effort was hopeless”. [10]


Wilton Castle was built on a moated platform surrounded by parapet walls and sham fortifications.
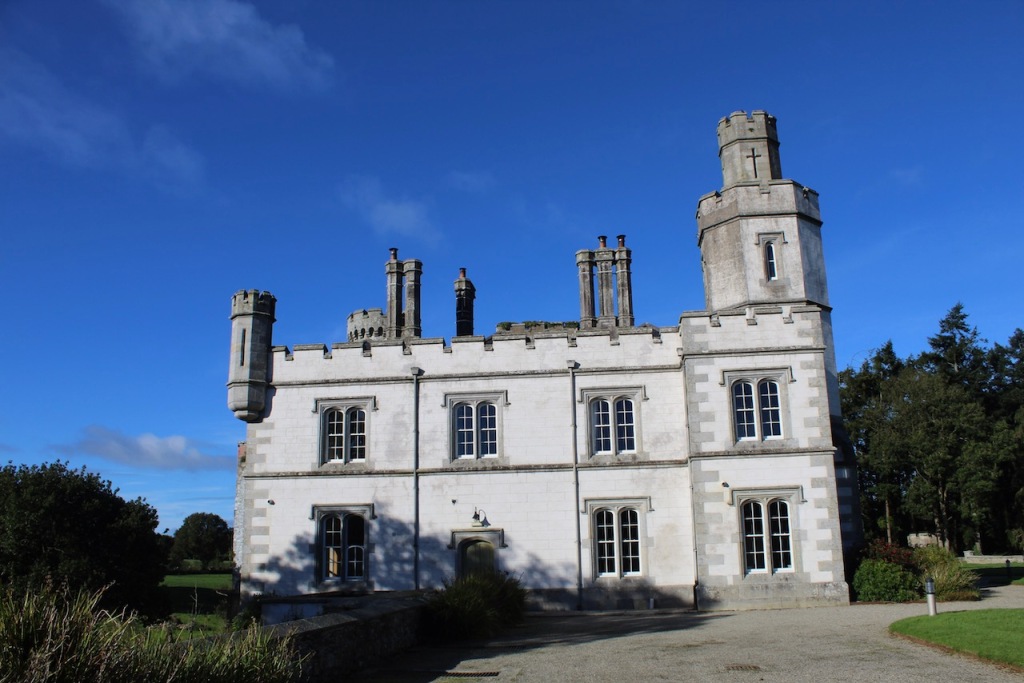
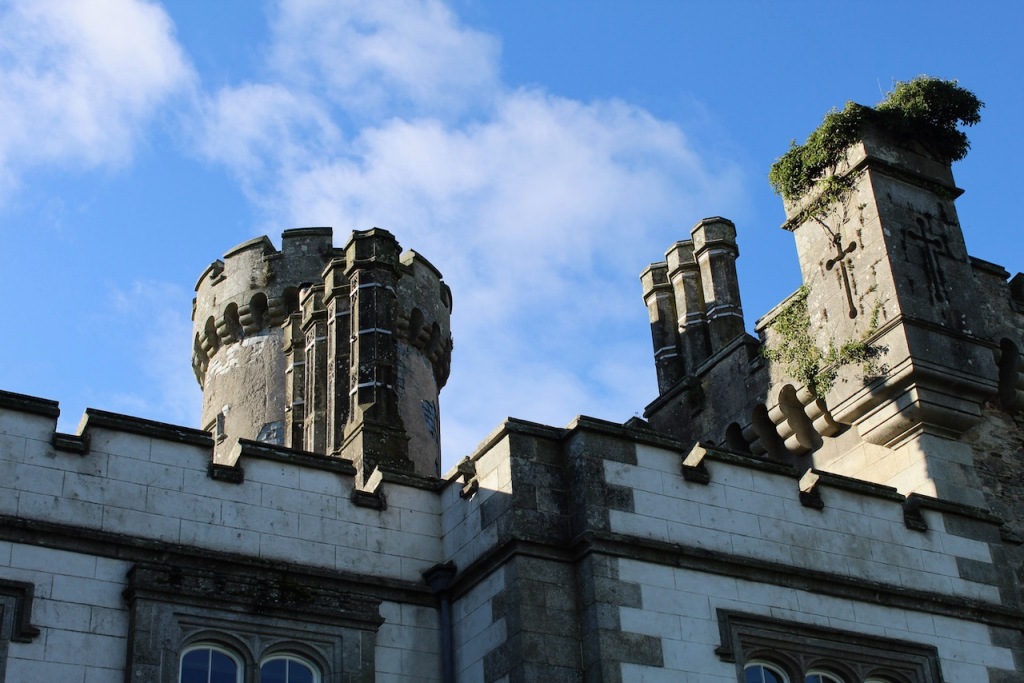






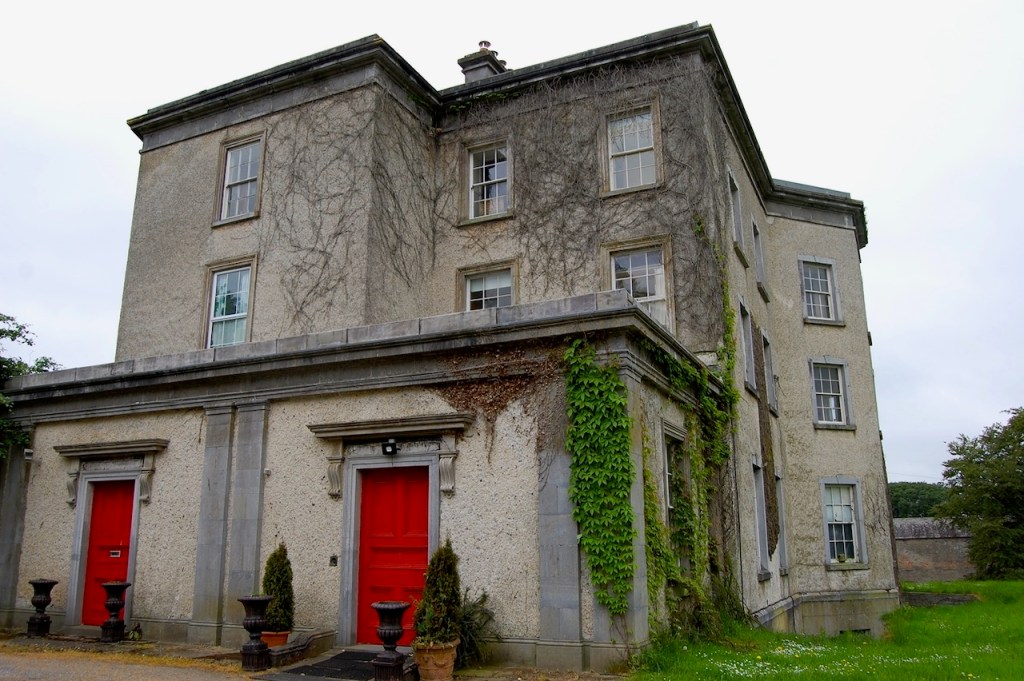
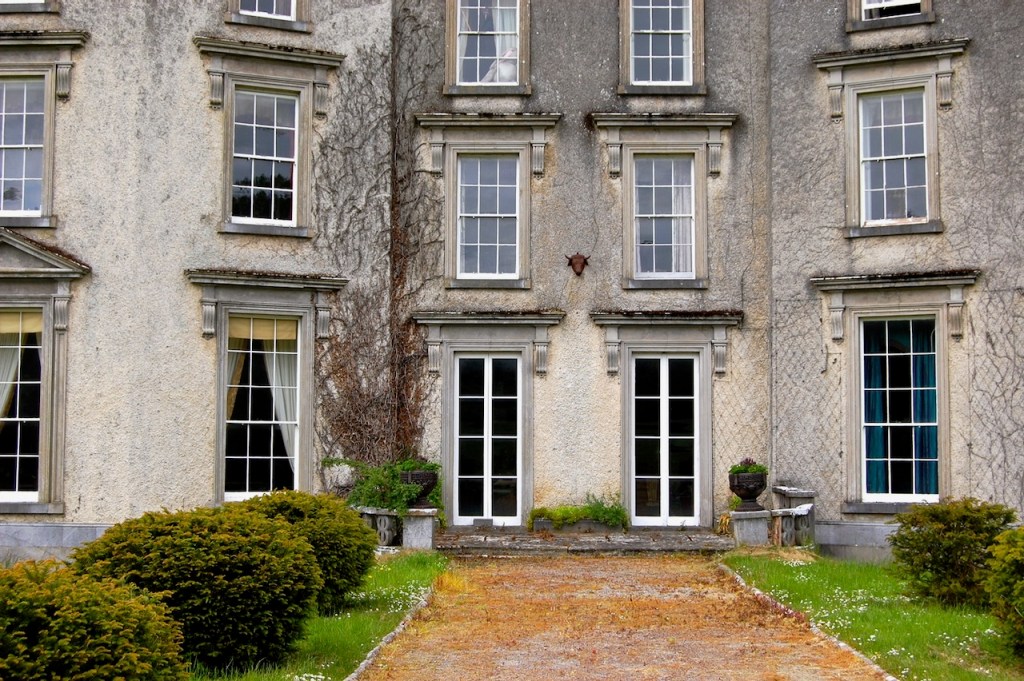
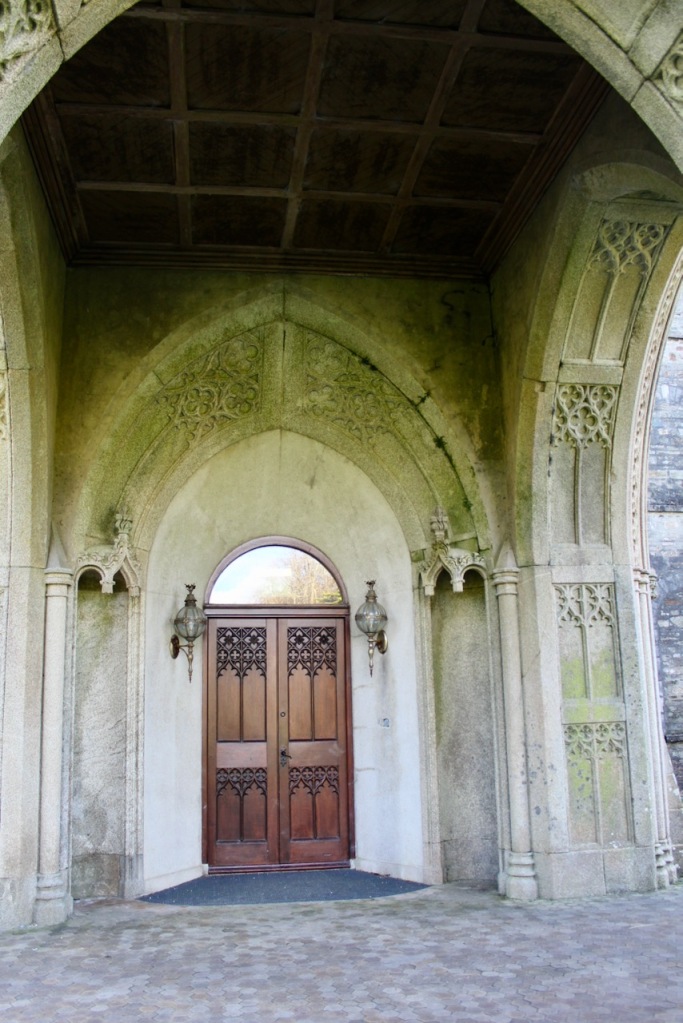
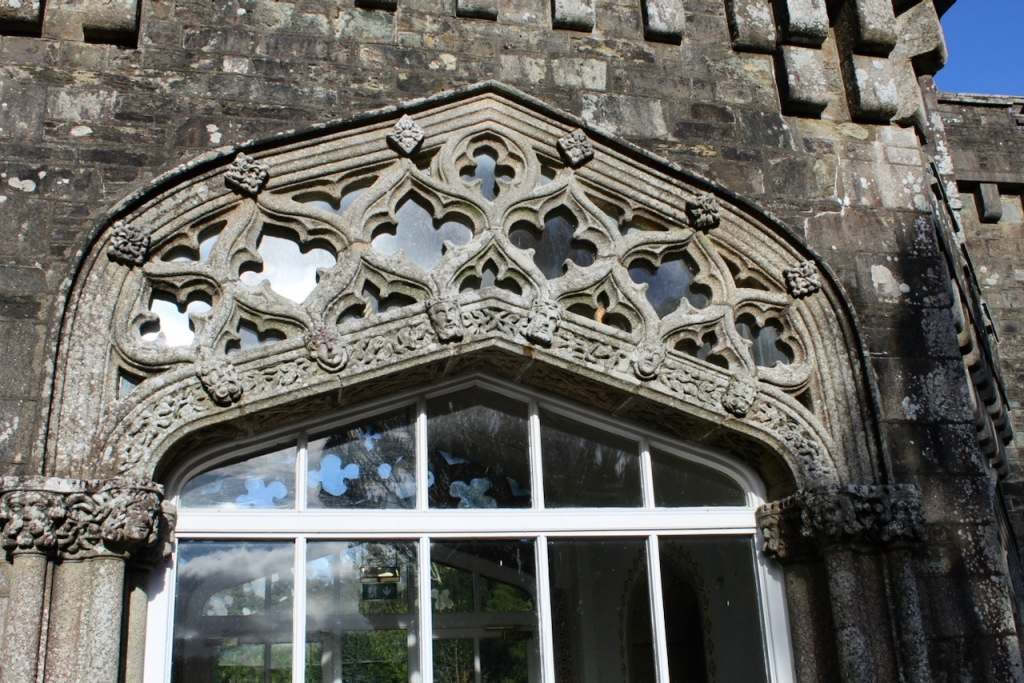
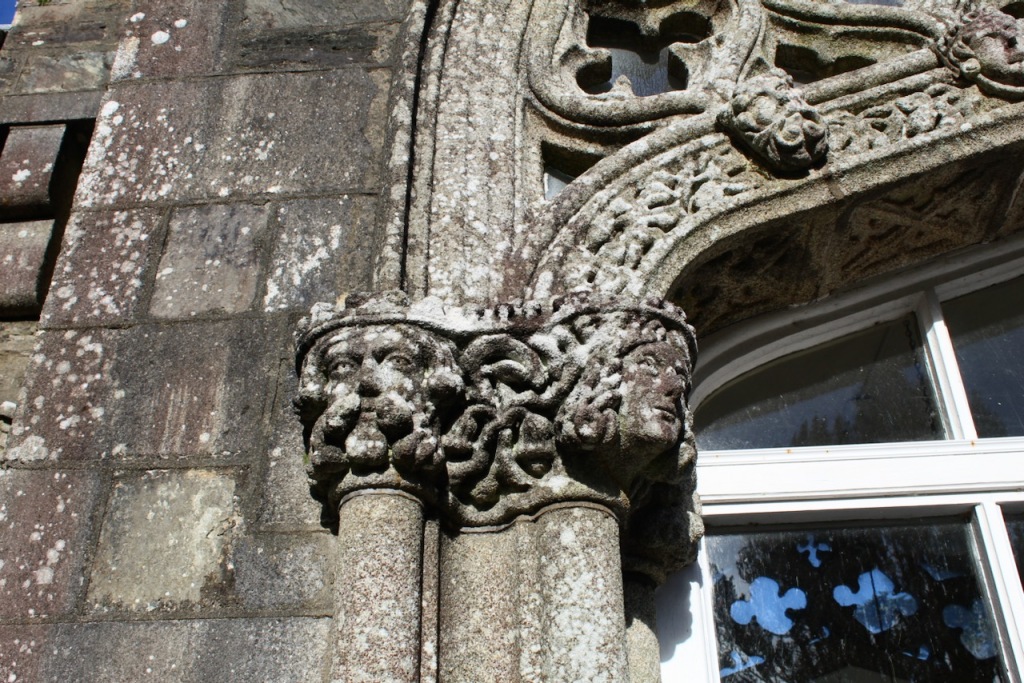
In the three storey section of the castle, there is a beautiful carved doorcase, and an oriel window over it with delicate stone tracery and crenellations on top of the windowframe. Mark Bence-Jones defines an oriel window as “a large projecting window in Gothic, Tudor, Gothic-Revival and Tudor-Revival architecture; sometimes rising through two or more storeys, sometimes in an upper storey only and carried on corbelling.” [12] There is a similar oriel window at Johnstown Castle, which is only one storey high.


At Wilton Castle there are double sets of sidelight windows either side of the doorcase, with arched carved window frames.

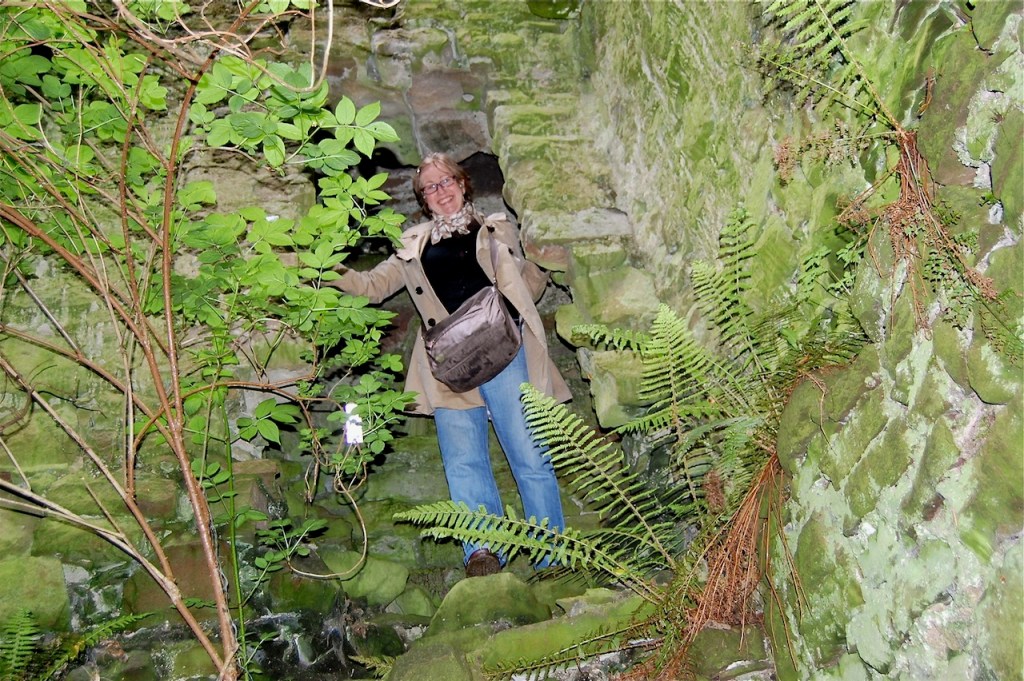
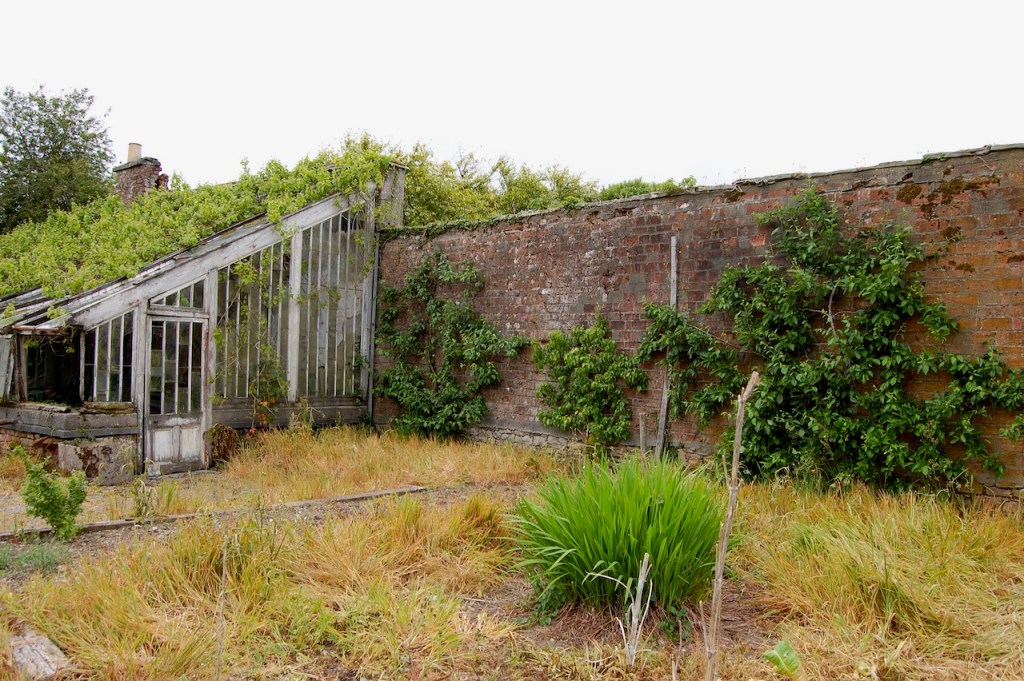
I was most excited to discover that we could explore the ruined part of the castle as it has been stabilised securely. It was wonderful to explore the detail.
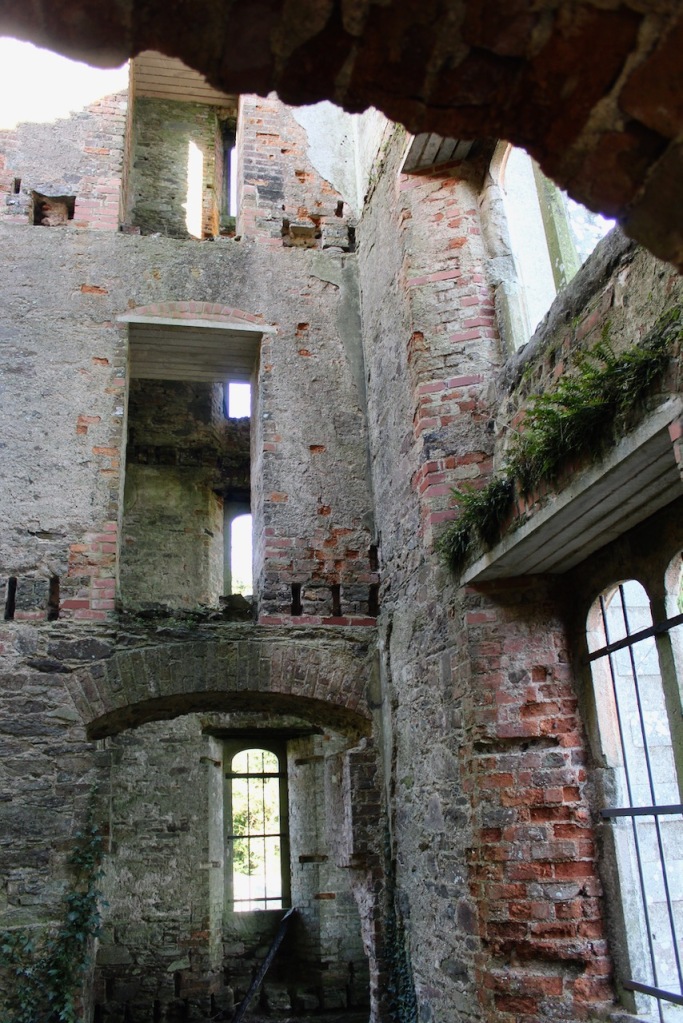
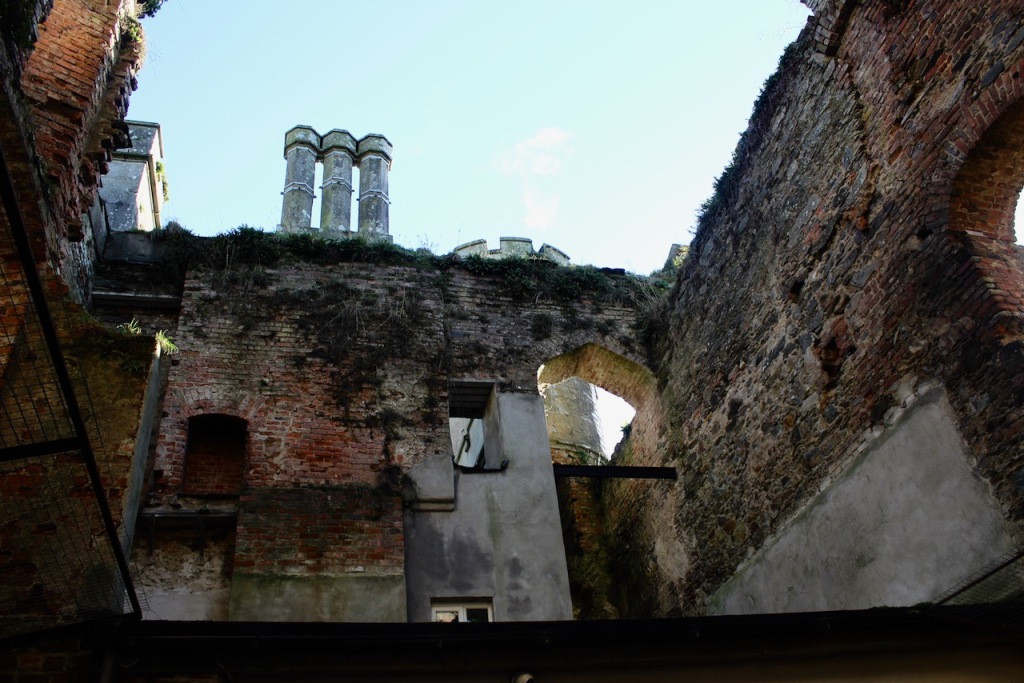
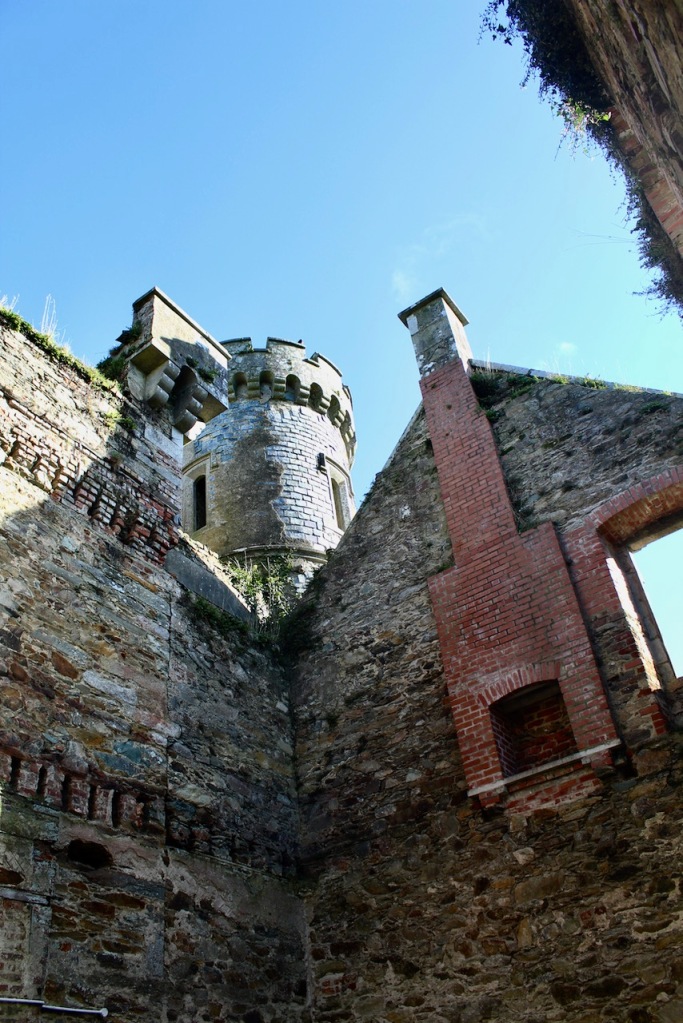





We kept discovering more. Pictures from the front of the castle do not do it justice. The land drops down behind the castle to the River Boro, to reveal beautiful pastoral views from the back windows of the castle.
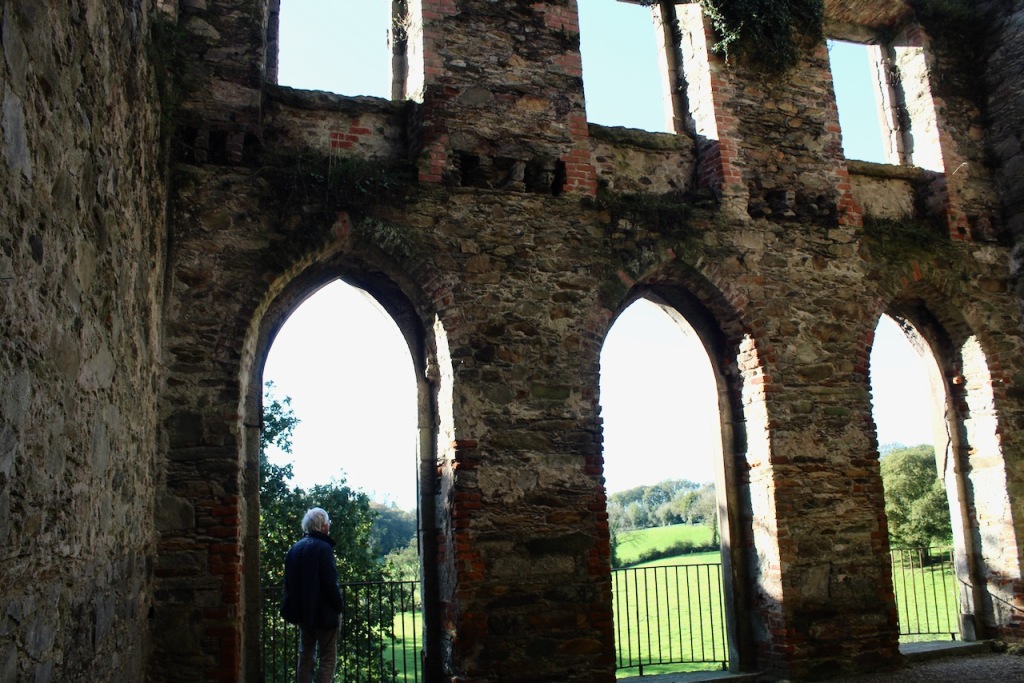
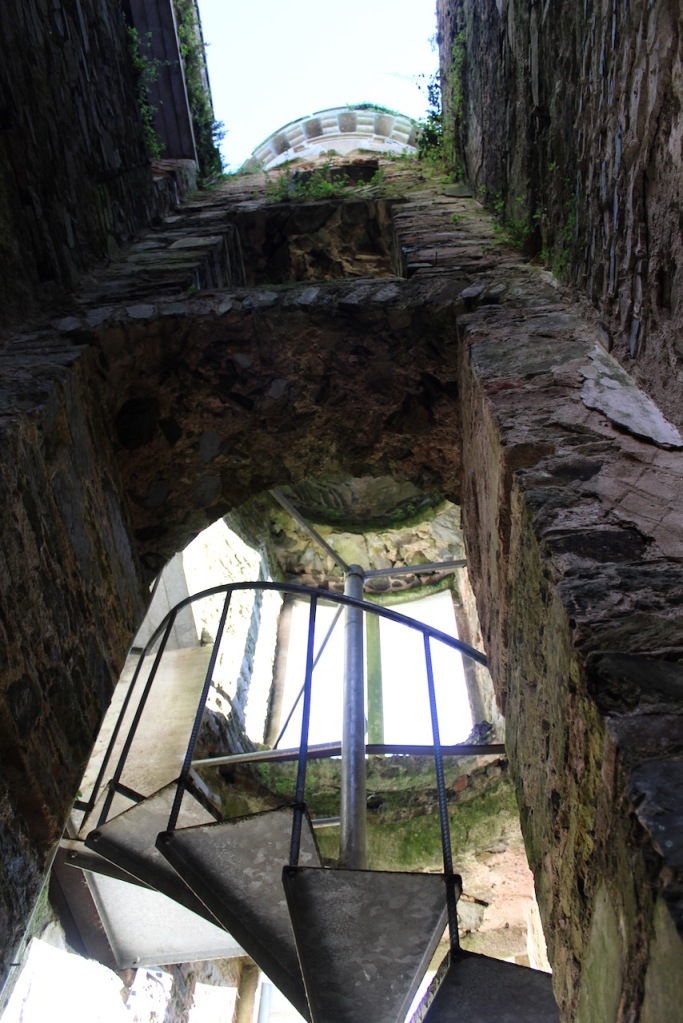
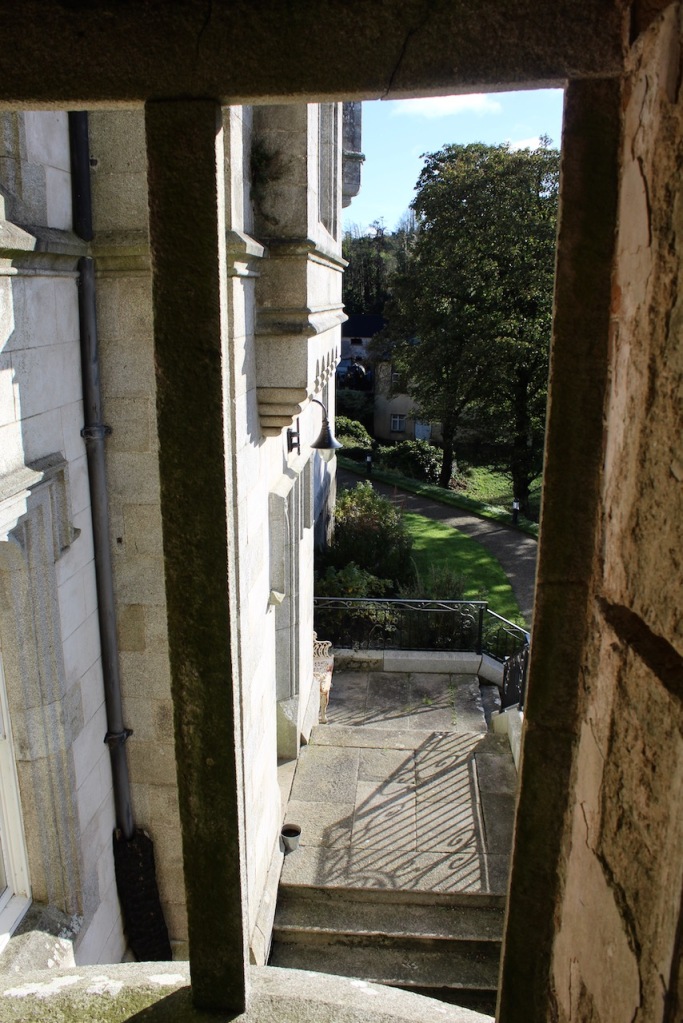






One can walk down to the river and more of the detail of the castle is revealed from behind. We found a warren of tunnels to one side on a level below the castle.
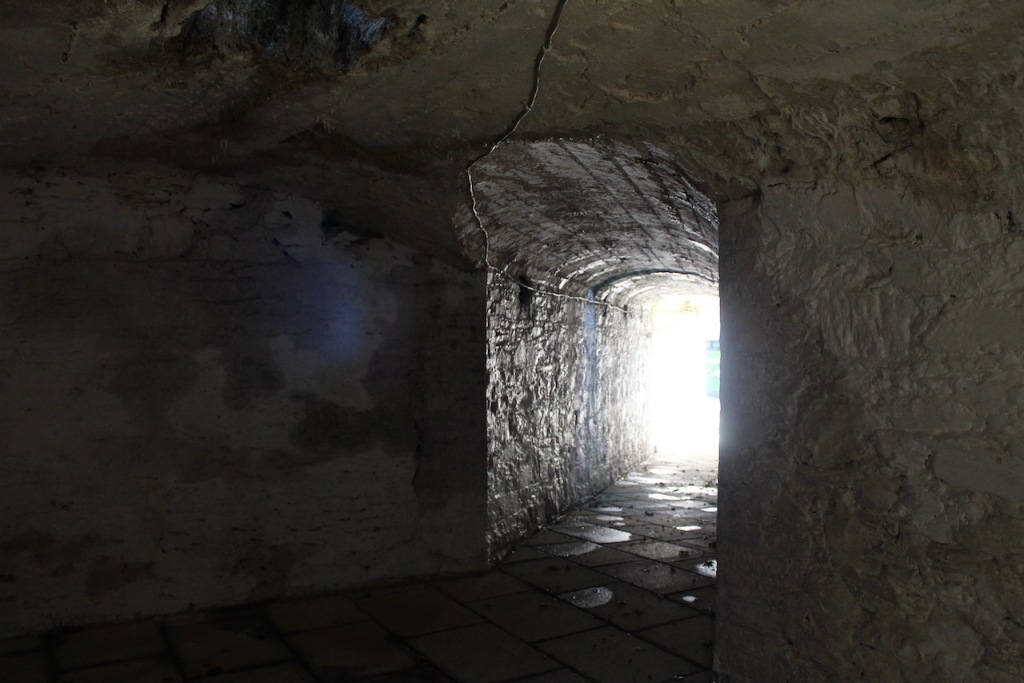



The tunnels provided quick access for servants to different parts of the castle, stable yard and grounds. There were cellars for wine and storage areas for food. Cast iron grilles let natural light and air into the tunnels. [13]
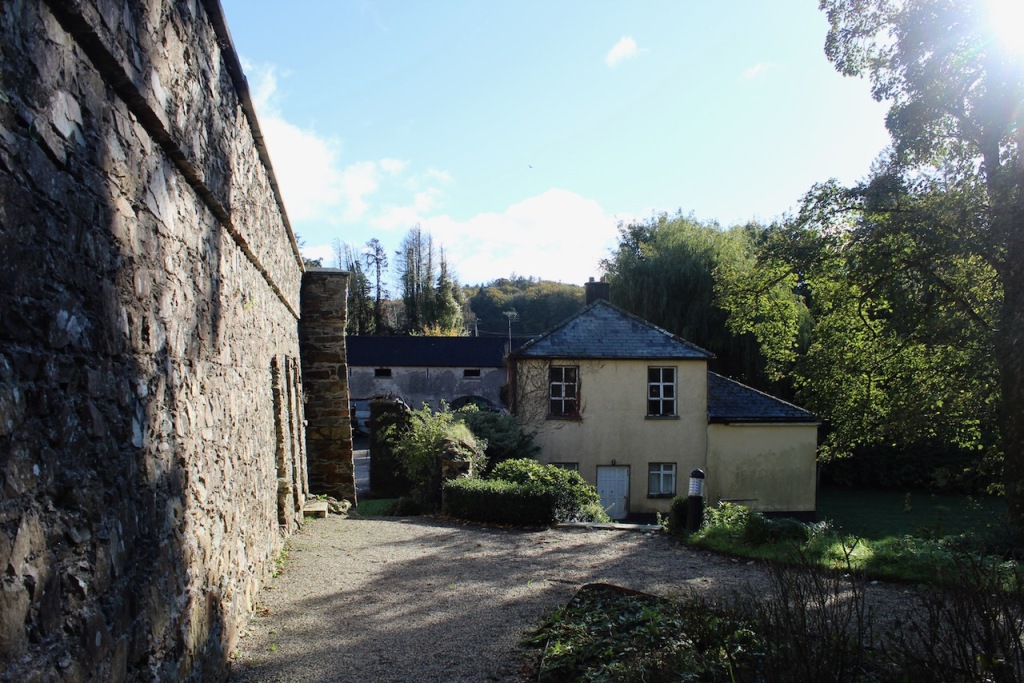
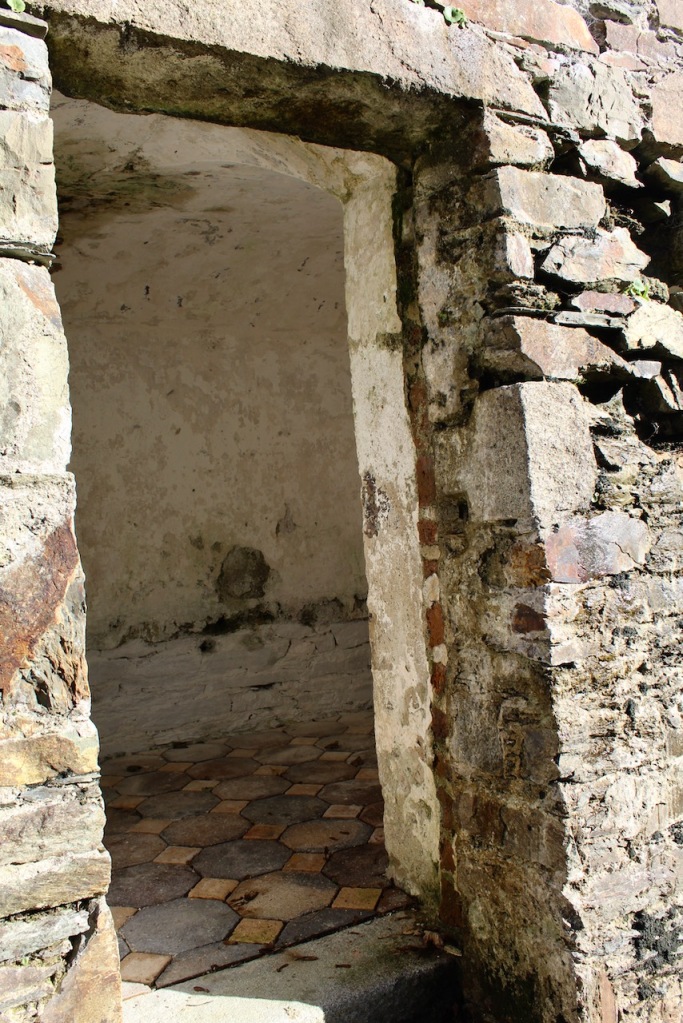
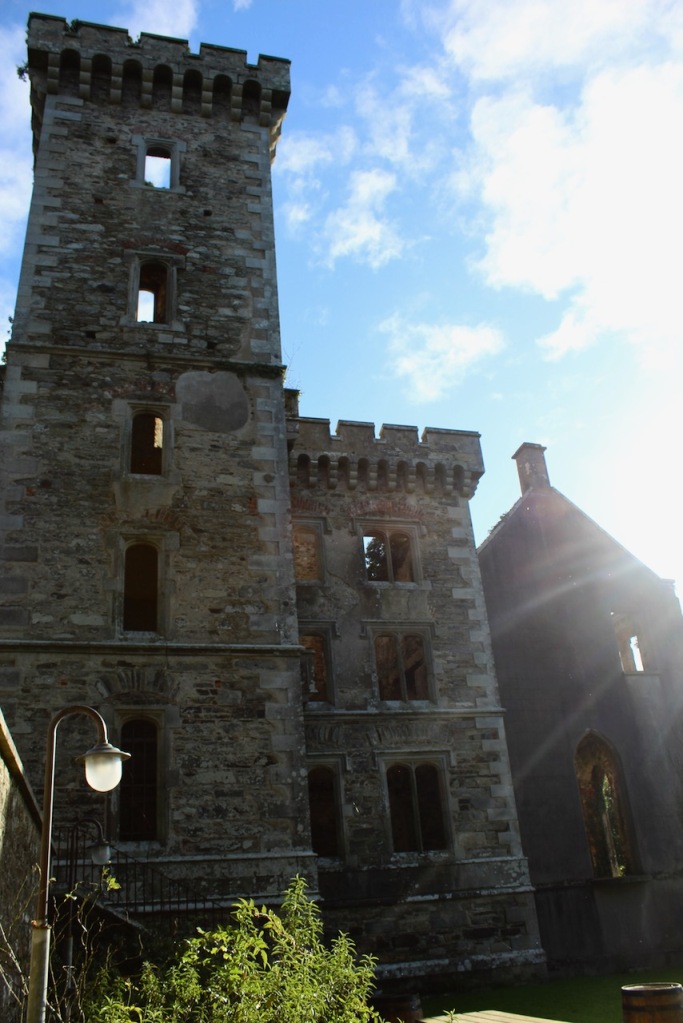












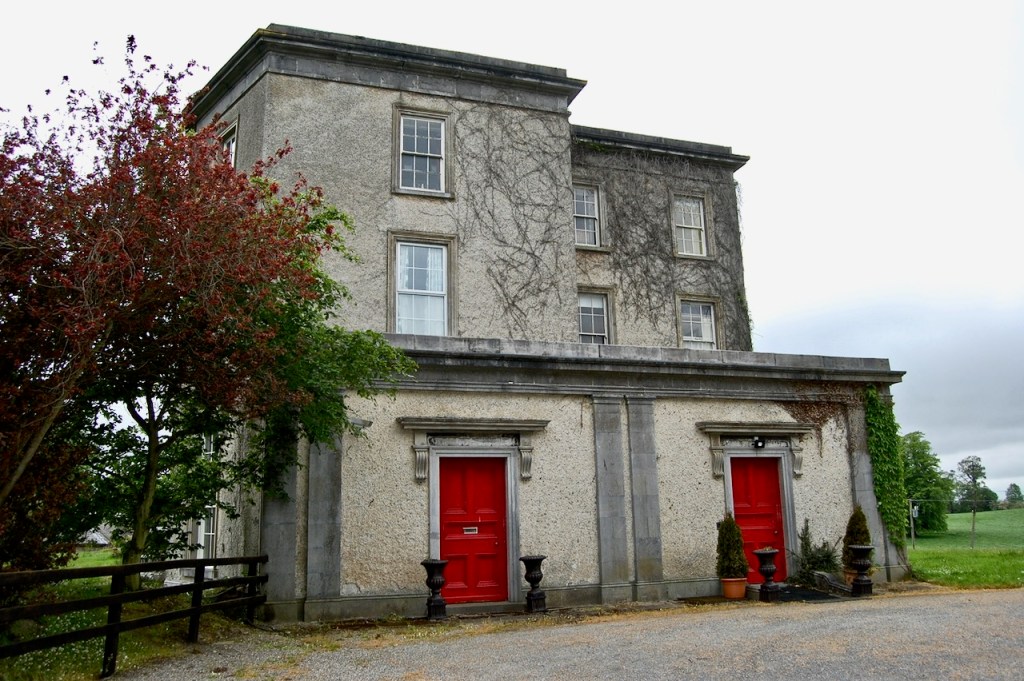
After the fire, the Alcocks were unable to rebuild as the house had not been insured. The lands were redistributed by the Irish Lands Commission, and the castle and land was purchased by local farmer, Sean Windsor.
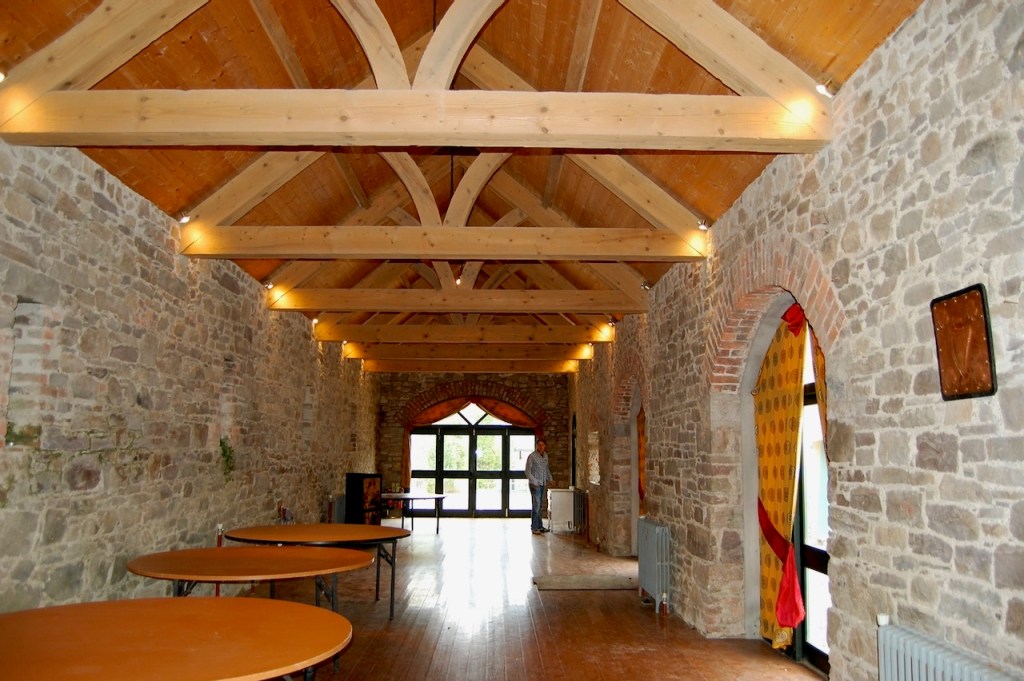
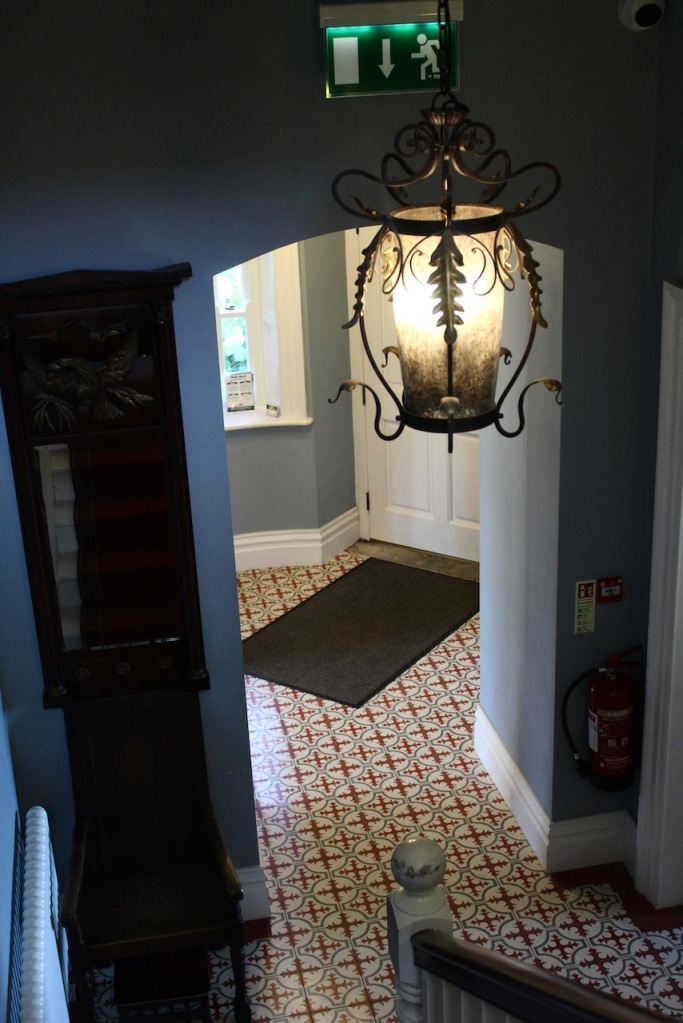
When we arrived we were welcomed and brought inside the renovated section of the castle. It opens into a nicely tiled hallway.

The accommodation consists of four suites, one of which has a large entertaining space. Two suites are upstairs and two downstairs, with the large one being downstairs. Our accommodation was upstairs.


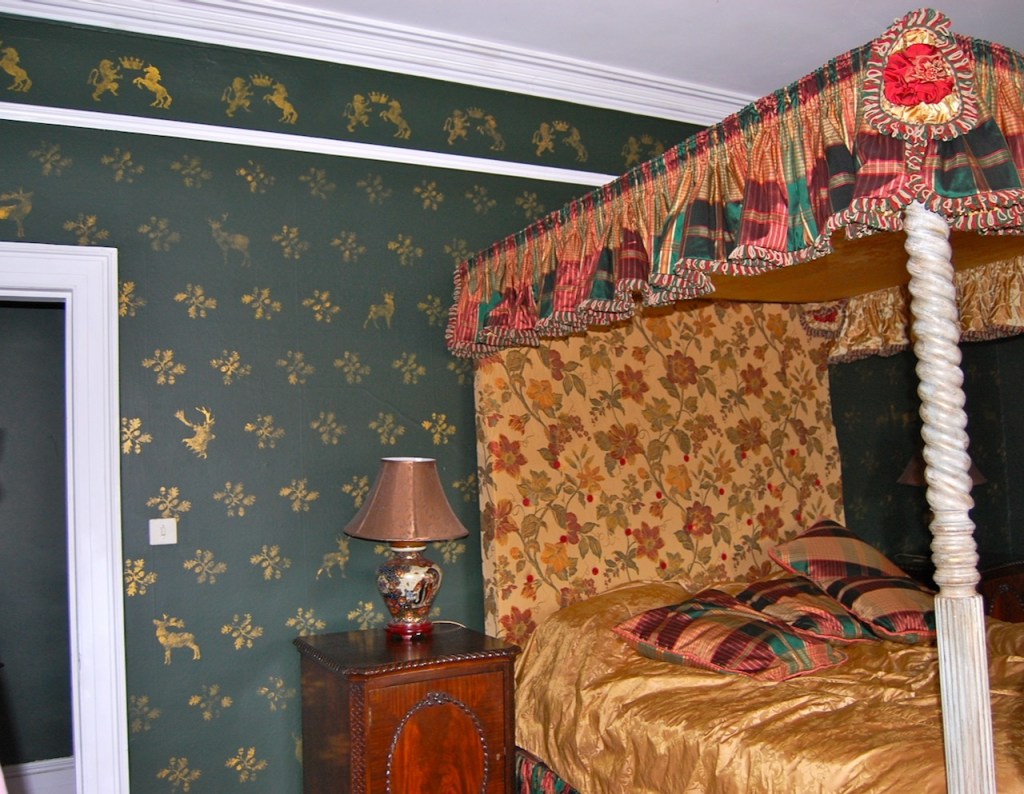
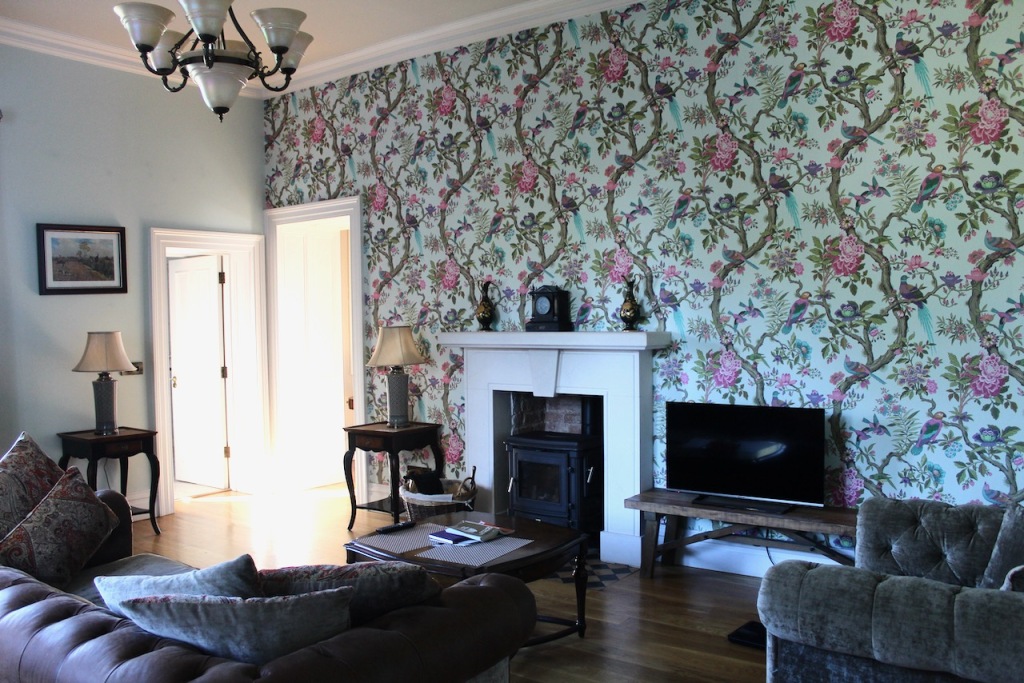
Our accommodation was a suite, with sitting room, fully stocked kitchen, bathroom with walk-in shower, and bedroom. The sitting room and bedroom have beautiful wallpaper.
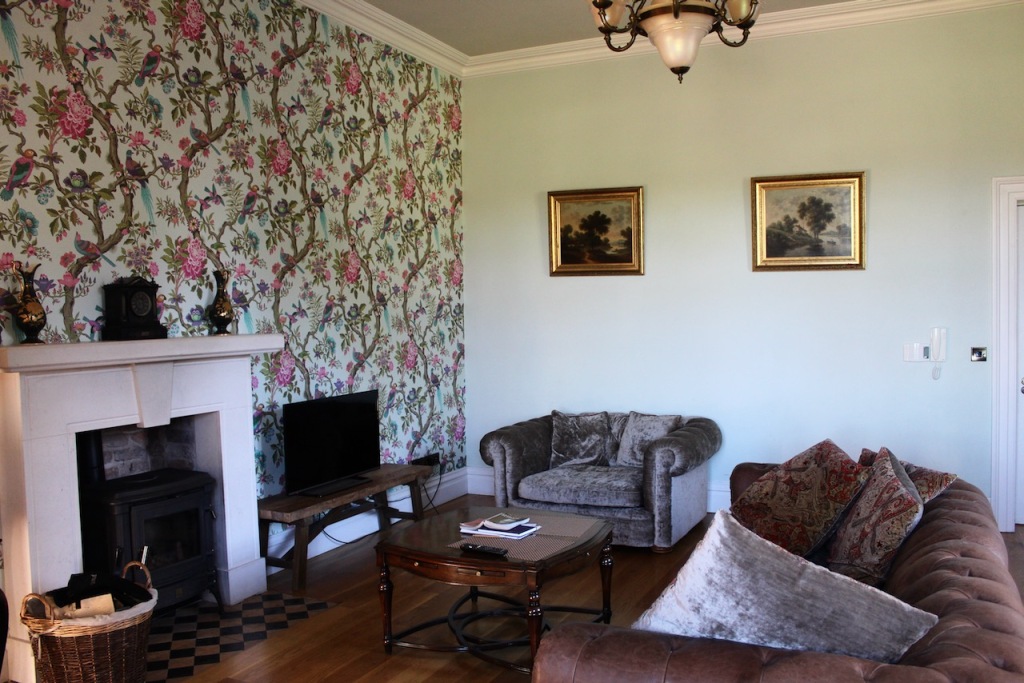
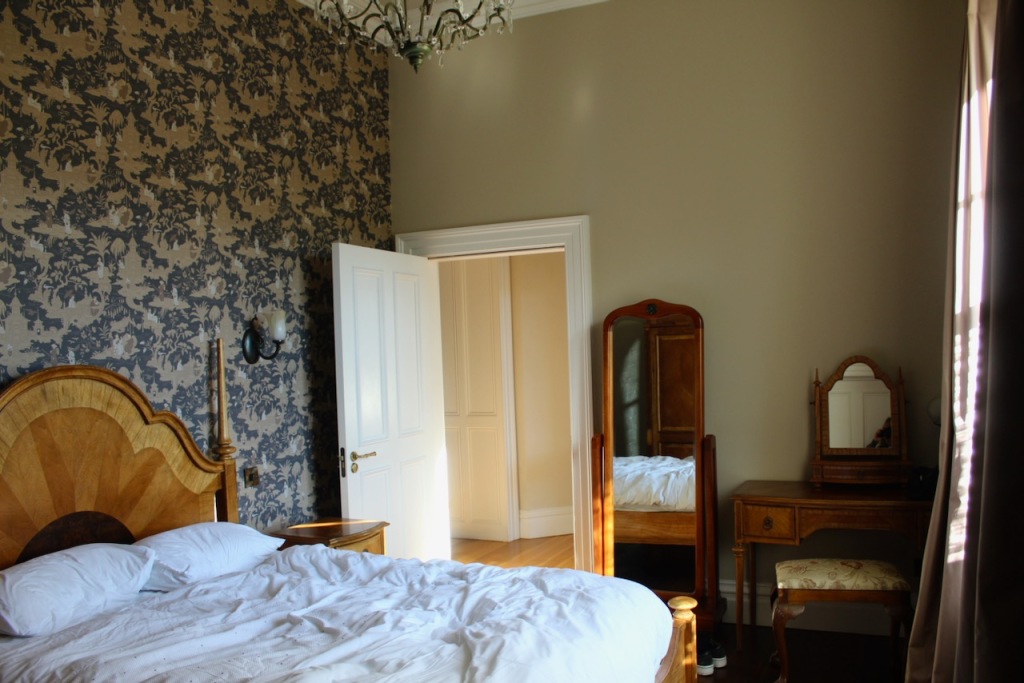
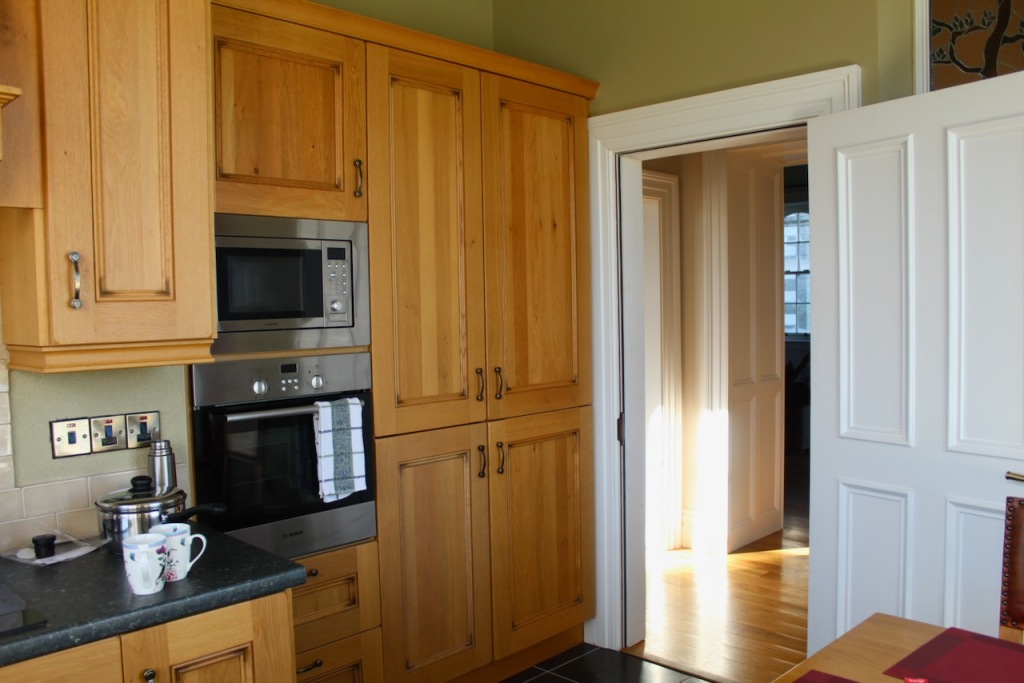






Our bathroom was in the round tower of the castle!


Our host showed us the larger suite downstairs that has room for a party. The double doors in the room open up to the view of the river below, onto a fine sweep of steps.
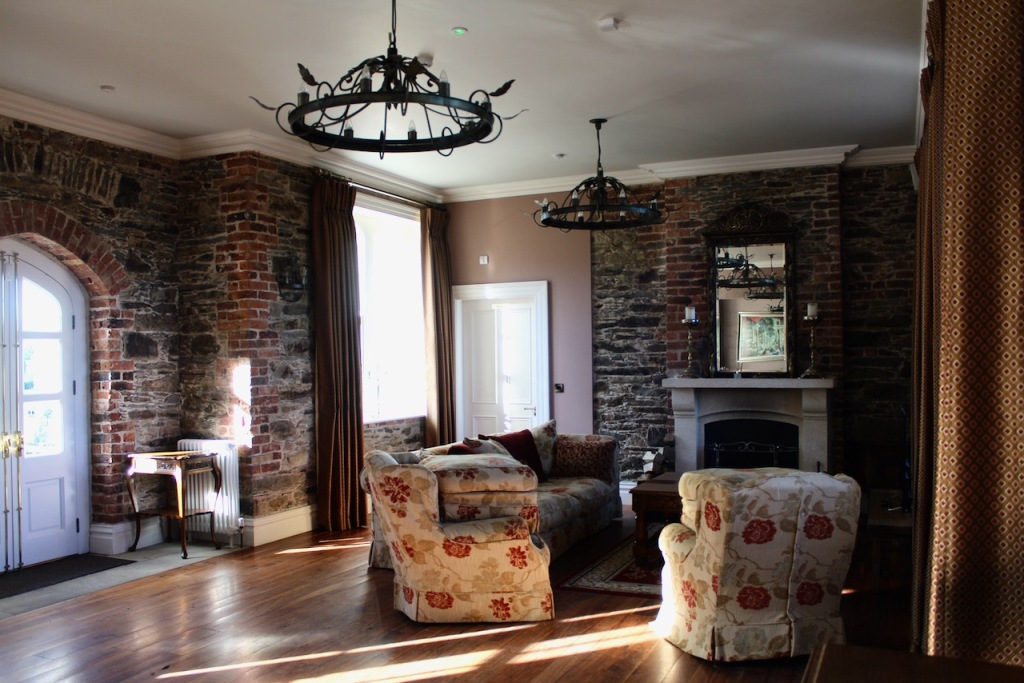
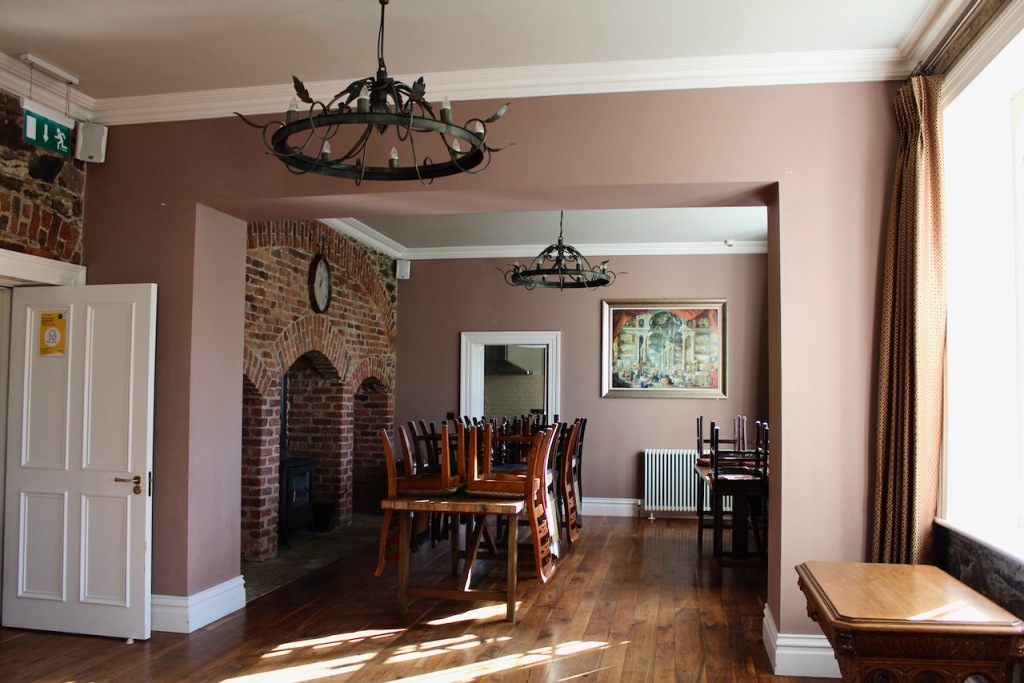




The accommodation is more pricey than we can usually afford but for a romantic getaway it is hard to beat! It’s very quiet. There seemed to be one other suite occupied when we were there, but we never saw or heard the inhabitants. The Windsors live in a house next door. We chose to have breakfast provided, which was brought to us on a tray in the morning. We used the kitchen facilities one evening to make our dinner, and the next night, ordered a delivery from nearby Enniscorthy, which was delivered to the castle!

donation
Help me to pay the entrance fee to one of the houses on this website. This site is created purely out of love for the subject and I receive no payment so any donation is appreciated!
€15.00
[1] p.560-561, Hore, Herbert. History of the Town and County of Wexford, Volume 6, ed. Philip Hore, pub. 1901-1911. Reference from http://butlerancestryireland.blogspot.com/2012/11/butlers-co-wexford-ch1-richard-1stviscount-mountgarrett.html
There is also an excellent history of the early days of the area on the Bree Heritage website, https://breeheritage.com/2015/02/27/the-early-history-of-wilton-castle-bree-co-wexford/
[2] https://landedfamilies.blogspot.com/search/label/Wexford
[3] https://theirishaesthete.com/2018/05/21/wilton-castle/
[4] For more on this, see the chapter in The Wexford Gentry by Art Kavanagh and Rory Murphy. Published by Irish Family Names, Bunclody, Co Wexford, Ireland, 1994.
[5] https://www.dia.ie/architects/view/4570/ROBERTSON%2C+DANIEL#tab_biography
[7] https://www.archiseek.com/2014/johnstown-castle-county-wexford/
[8] p. 130, Hicks, David. Irish Country Houses: A Chronicle of Change. The Collins Press, Cork, 2012.
[9] https://landedfamilies.blogspot.com/search/label/Wexford
[10] https://www.archiseek.com/2015/1838-wilton-castle-co-wexford/
[11] Note taken from the Wilton Castle facebook page, where you can see the progress of restoration that took place. https://www.facebook.com/WiltonCastleIreland
[12] Bence-Jones, Mark. A Guide to Irish Country Houses (originally published as Burke’s Guide to Country Houses volume 1 Ireland by Burke’s Peerage Ltd. 1978); Revised edition 1988, Constable and Company Ltd, London.
[13] p. 130, Hicks, David. Irish Country Houses: A Chronicle of Change. The Collins Press, Cork, 2012.
Here are more photographs from our visit to Johnstown Castle, also designed by Daniel Robertson.









Text © Jennifer Winder-Baggot, www.irishhistorichouses.com