I had initially published the County Tipperary OPW sites along with Munster counties of Clare and Limerick but the entry is too long so I am dividing it.
OPW sites in County Tipperary:
1. Cahir Castle, County Tipperary
2. Damer House and Roscrea Castle, County Tipperary
3. Famine Warhouse 1848, County Tipperary
4. Holycross Abbey, County Tipperary – must prebook for tour
5. The Main Guard, County Tipperary – closed at present
6. Nenagh Castle, County Tipperary
7. Ormond Castle, Carrick-on-Suir, County Tipperary
8. Rock of Cashel, County Tipperary
see 2. Roscrea Castle and Damer House, County Tipperary
9. Swiss Cottage, County Tipperary

donation
Help me to pay the entrance fee to one of the houses on this website. This site is created purely out of love for the subject and I receive no payment so any donation is appreciated!
€15.00

1. Cahir Castle, County Tipperary:
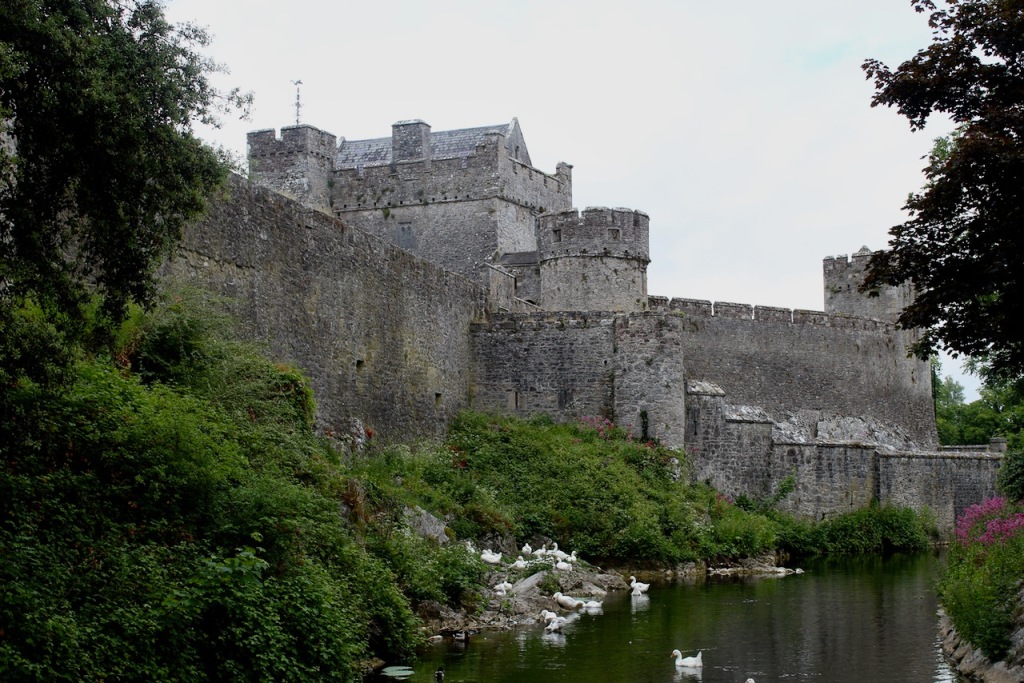


General information: 052 744 1011, cahircastle@opw.ie
Stephen and I visited Cahir Castle in June 2022, and I was very impressed. I had no idea that we have such an old castle in Ireland with so much intact. See my entry https://irishhistorichouses.com/2024/03/29/cahir-castle-county-tipperary-an-office-of-public-works-property/
From the OPW website https://heritageireland.ie/visit/places-to-visit/cahir-castle/:
“Cahir Castle is one of Ireland’s largest and best-preserved castles. It stands proudly on a rocky island on the River Suir.
“The castle was was built in the thirteenth century and served as the stronghold of the powerful Butler family. [The Archiseek website tells us it was built in 1142 by Conor O’Brien, Prince of Thomond] So effective was its design that it was believed to be impregnable, but it finally fell to the earl of Essex in 1599 when heavy artillery was used against it for the first time. During the Irish Confederate Wars it was besieged twice more.
“At the time of building, Cahir Castle was at the cutting edge of defensive castle design and much of the original structure remains.“
Our tour guide took us through the outside of the castle, showing us its defenses. Our tour ended inside the Great Hall, or dining hall.
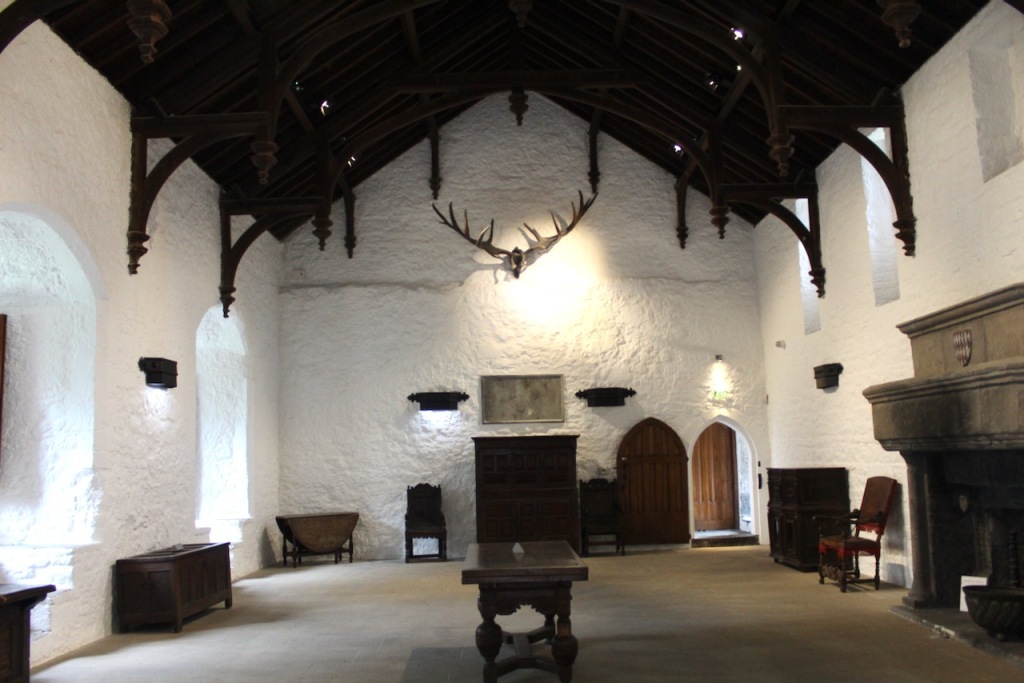

2. Damer House and Roscrea Castle, County Tipperary
https://heritageireland.ie/places-to-visit/roscrea-castle-gardens-damer-house-black-mills/
“In the heart of Roscrea in County Tipperary, one of the oldest towns in Ireland, you will find a magnificent stone motte castle dating from the 1280s. It was used as a barracks from 1798, housing 350 soldiers, and later served as a school, a library and even a sanatorium.
“Sharing the castle grounds is Damer House, named for local merchant John Damer, who came into possession of the castle in the eighteenth century. The house is a handsome example of pre-Palladian architecture. It has nine beautiful bay windows. One of the rooms has been furnished in period style.
“The grounds also include an impressive garden with a fountain, which makes Roscrea Castle a very pleasant destination for a day out. There is also a restored mill displaying St Crónán’s high cross and pillar stone.” See my entry https://irishhistorichouses.com/2024/10/03/damer-house-and-roscrea-castle-county-tipperary-office-of-public-works-properties/
3. Famine Warhouse 1848, Ballingarry, County Tipperary:
General information: 087 908 9972, info@heritageireland.ie
From the OPW website https://heritageireland.ie/visit/places-to-visit/famine-warhouse-1848/:
“How did an ordinary farmhouse near Ballingarry, County Tipperary, become the site of a bloody siege and a monument of the Young Irelander Rebellion of 1848?
“It was here that rebels, under the leadership of Protestant aristocrat William Smith O’Brien, besieged 47 police officers who had barricaded themselves into the McCormack homestead, taking 5 children hostage. After two of their number were killed, the rebels finally gave in. They were later transported to penal colonies abroad.
“The Warhouse, as it became known, is now a museum. Its contents illuminate the history of the Young Irelander Rebellion, the trials of its leaders, their exile in Australia and escape to the USA. The exhibition places the rebellion in the context of the Great Famine and the upheaval that rocked Europe during that turbulent year.“
Traditionally it was known as Ballingarry Warhouse or The Widow McCormack’s House.
4. Holycross Abbey, County Tipperary:
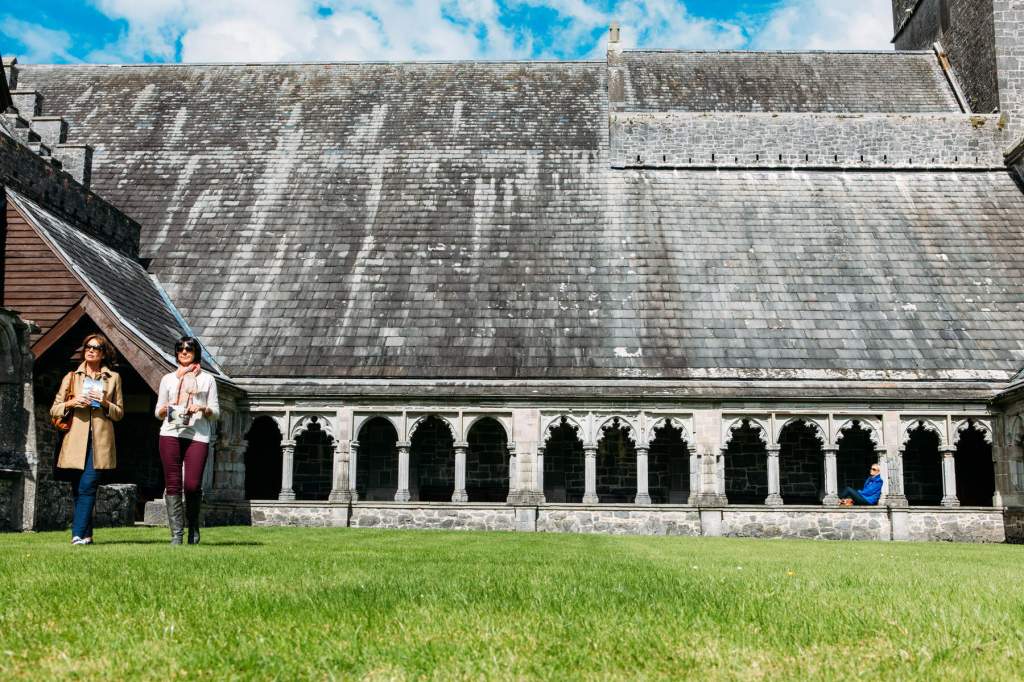

From the OPW website https://heritageireland.ie/visit/places-to-visit/holycross-abbey/:
“As destination for pilgrims, Holy Cross Abbey, near Thurles, County Tipperary, has a rich history. Pilgrims travelled here for eight centuries to venerate the relic after which the abbey and surrounding villages are named – a piece of the True Cross of Christ’s crucifixion.
“Today this working parish church is a peaceful landmark and a place for quiet contemplation and historical discovery. As well as inspecting the relic of the cross, you can marvel at the building’s ornate stonework. The chancel is possibly the finest piece of fifteenth-century architecture in the country. The abbey also houses one of the only surviving medieval wall paintings in Ireland.“
5. The Main Guard, Sarsfield Street, Clonmel, County Tipperary:

General Information: 052 612 7484, mainguard@opw.ie
From the OPW website https://heritageireland.ie/visit/places-to-visit/the-main-guard/:
“In the seventeenth century County Tipperary was a palatinate, ruled by James Butler, duke of Ormond. When the duke decided he needed a new courthouse, he built one in the heart of Clonmel [built in 1673]. Later, when it was used as a barracks, it became known as the Main Guard.
“A fine two-storey symmetrical building, some elements of its design were based on works by the famous Sir Christopher Wren.
“In the eighteenth century it was the venue for the Clonmel Assizes. The most notable trial it witnessed was that of Father Nicholas Sheehy, the anti-Penal Laws agitator. Sheehy was hanged, drawn and quartered.
“In about 1810, the ground floor was converted into shops, but the building has recently undergone an award-winning restoration. The open arcade of sandstone columns is once again an attractive feature of the streetscape, while inside you will find a fantastic exhibition and event space.“

6. Nenagh Castle, County Tipperary
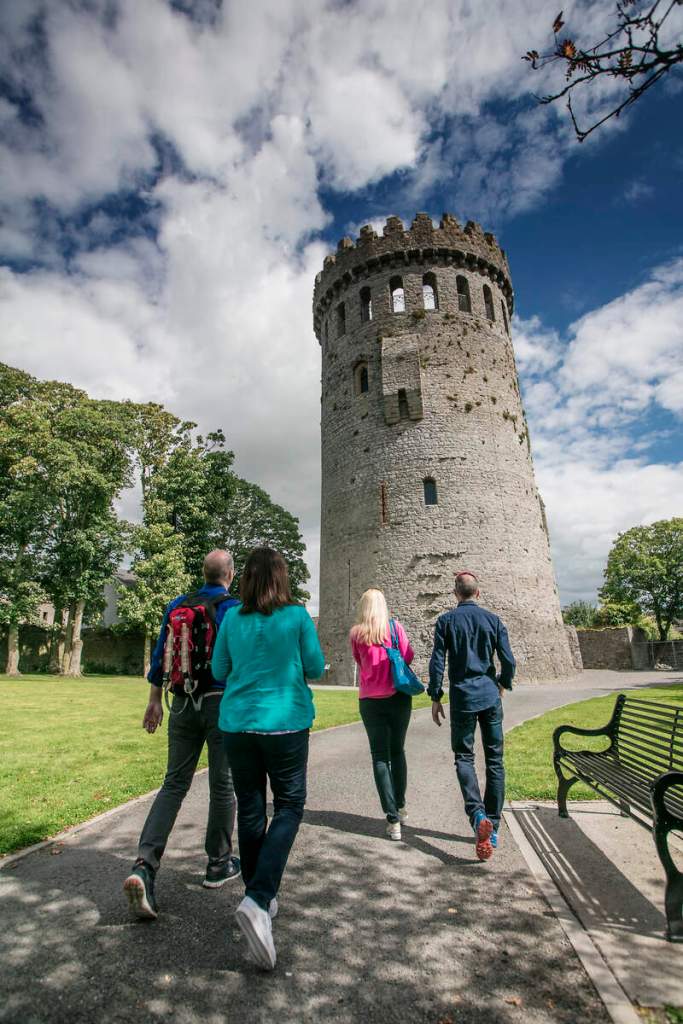

General information: 067 33850, castlenenagh@gmail.com
The OPW doesn’t seem to have a site for this currently, but there is information at a site about Nenagh:
“Nenagh Castle was built by Theobald Walter (the first of the Butlers of Ormond) around 1200. To this day the cylindrical keep adorns the town and like most keeps it formed part of the perimeter of the fortress. The walls have now almost disappeared, but fragments remain.
“Built from limestone Nenagh Castle measures fifty-five feet in external diameter at the base and rises to a height of one hundred feet. The Castle features four storeys and thanks to a recent renovation this wonderful landmark now represents the town’s premier tourist attraction.
“The building and has stone spiral stairs to the top. There are 101 steps in all to the top. Access to the tower is through a passageway within the base of the wall. This has low head room and visitors will need to stoop to avoid hitting the stone above. All children under the age of 18 must be accompanied by an adult. [3]

7. Ormond Castle, Carrick-on-Suir, County Tipperary:

See my entry https://irishhistorichouses.com/2024/09/05/ormond-castle-carrick-on-suir-county-tipperary-an-opw-property/
General Information: 051 640787, ormondcastle@opw.ie
From the OPW website https://heritageireland.ie/visit/places-to-visit/ormond-castle/:
“Joined on to an earlier medieval riverside castle, Ormond Castle Carrick-on-Suir is the finest example of an Elizabethan manor house in Ireland. Thomas, 10th Earl of Ormond [“Black Tom” (1531-1614)], built it in 1565 in honour of his distant cousin Queen Elizabeth.
“The magnificent great hall, which stretches almost the whole length of the building is decorated with some of the finest stucco plasterwork in the country. The plasterwork features portraits of Queen Elizabeth and her brother Edward VI and many motifs and emblems associated with the Tudor monarchy.“

James Butler the 12th Earl of Ormond and 1st Duke of Ormond (1610-1688) spent much of his time here and was the last of the family to reside at the castle. On his death in 1688 the family abandoned the property and it was only handed over to the government in 1947, who then became responsible for its restoration.
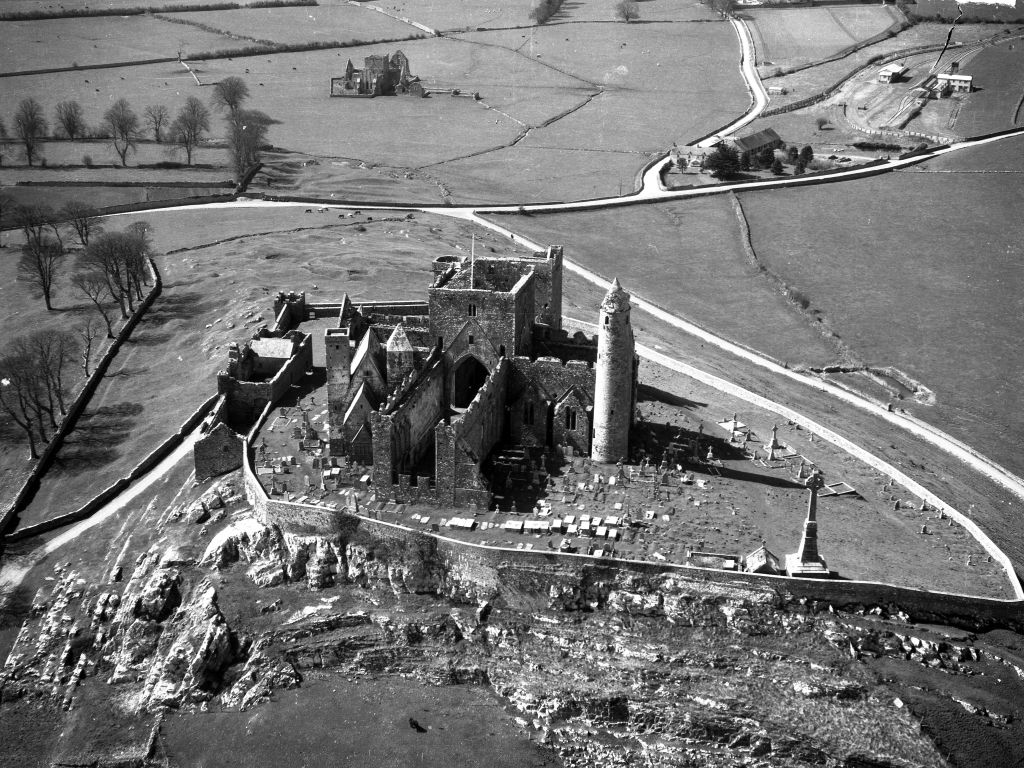
7. Rock of Cashel, County Tipperary:

General Information: 062 61437, rockofcashel@opw.ie
From the OPW website https://heritageireland.ie/visit/places-to-visit/rock-of-cashel/:
“Set on a dramatic outcrop of limestone in the Golden Vale, the Rock of Cashel, iconic in its historic significance, possesses the most impressive cluster of medieval buildings in Ireland. Among the monuments to be found there is a round tower, a high cross, a Romanesque chapel, a Gothic cathedral, an abbey, the Hall of the Vicars Choral and a fifteenth-century Tower House.
“Originally the seat of the kings of Munster, according to legend St. Patrick himself came here to convert King Aenghus to Christianity. Brian Boru was crowned High King at Cashel in 978 and made it his capital.
“In 1101 the site was granted to the church and Cashel swiftly rose to prominence as one of the most significant centres of ecclesiastical power in the country.
“The surviving buildings are remarkable. Cormac’s Chapel, for example, contains the only surviving Romanesque frescoes in Ireland.“


8. Roscrea Castle and Damer House, County Tipperary:

General information: 0505 21850, roscreaheritage@opw.ie
From the OPW website https://heritageireland.ie/visit/places-to-visit/roscrea-heritage-centre-roscrea-castle-and-damer-house/:
“In the heart of Roscrea in County Tipperary, one of the oldest towns in Ireland, you will find a magnificent stone motte castle dating from the 1280s. It was used as a barracks from 1798, housing 350 soldiers, and later served as a school, a library and even a sanatorium.
“Sharing the castle grounds is Damer House, named for local merchant John Damer, who came into possession of the castle in the eighteenth century. The house is a handsome example of pre-Palladian architecture. It has nine beautiful bay windows. One of the rooms has been furnished in period style.
“The grounds also include an impressive garden with a fountain, which makes Roscrea Castle a very pleasant destination for a day out. There is also a restored mill displaying St Crónán’s high cross and pillar stone.“
This was originally the site of a motte and bailey fortification known as King John’s Castle. The original wooden castle was destroyed in the late 13th century and was replaced with a stone structure built in 1274-1295 by John de Lydyard. The castle was originally surrounded by a river to the east and a moat on the other sides. [4] It was granted to the Butlers of Ormond in 1315 who held it until the early 18th Century. The castle as we see it today was built from 1332.
The castle was used as a barracks from 1798, housing 350 soldiers. It was used later as a school, a library, and a tuberculosis sanatorium. Roscrea Castle fell into disrepair in the 19th century, and when the roof collapsed extensive repairs were needed in the 1850s. It was named a national monument in 1892, and is now under the care of the OPW.
Damer House is of three storeys and nine bays and has a scroll pediment doorway and inside, a magnificent carved staircase. The Irish Georgian Society was involved in saving it from demolition in the 1960s.
9. Swiss Cottage, Ardfinnan Road, Cahir, County Tipperary:
General Information: 052 744 1144, swisscottage@opw.ie
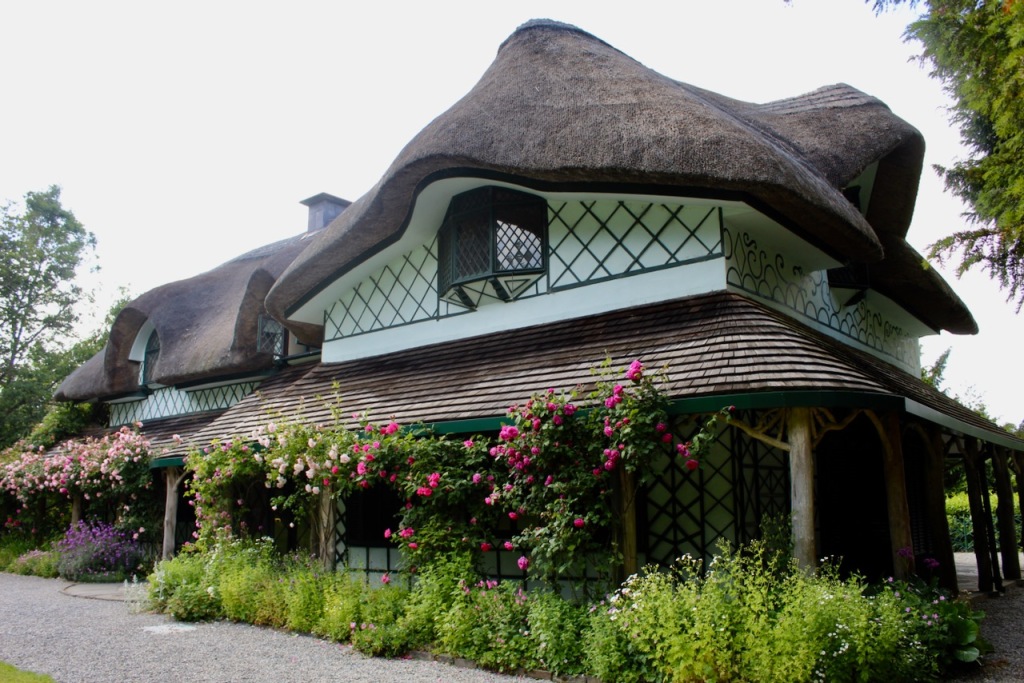

From the OPW website https://heritageireland.ie/visit/places-to-visit/swiss-cottage/:
“The Swiss Cottage, just outside the heritage town of Cahir, is a cottage orné – a fanciful realisation of an idealised countryside cottage used for picnics, small soirees and fishing and hunting parties and was also a peaceful retreat for those who lived in the nearby big house.
Built in the early 1800s [around 1810] by Richard Butler, 1st Earl of Glengall, who, we believe, managed to persuade world-famous Regency architect John Nash to design it [he also designed Buckingham Palace for the Crown]. Originally, simply known as “The Cottage” it appears to have acquired its present name because it was thought to resemble an Alpine cottage.”
See my write-up https://irishhistorichouses.com/2025/03/20/swiss-cottage-ardfinnan-road-cahir-county-tipperary-office-of-public-works/


[1] https://www.irelandscontentpool.com/en
[2] https://repository.dri.ie/
[3] https://www.nenagh.ie/places-of-interest/details/nenagh-castle
[4] See the blog of Patrick Comerford, http://www.patrickcomerford.com/search/label/castles?updated-max=2019-03-03T14:30:00Z&max-results=20&start=27&by-date=false