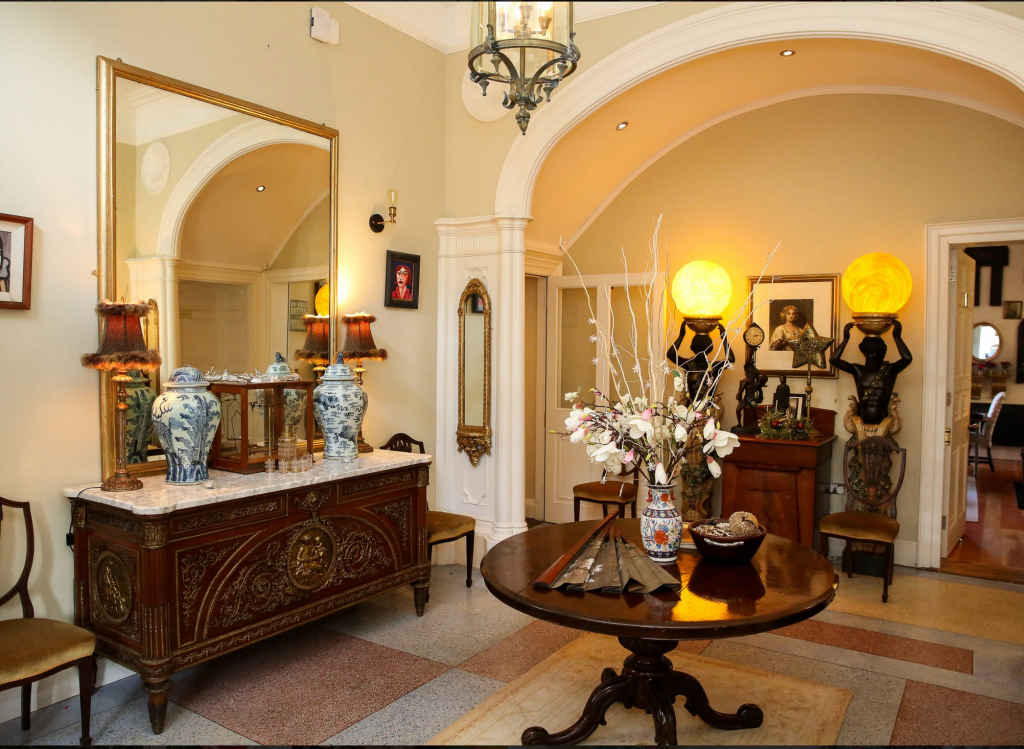
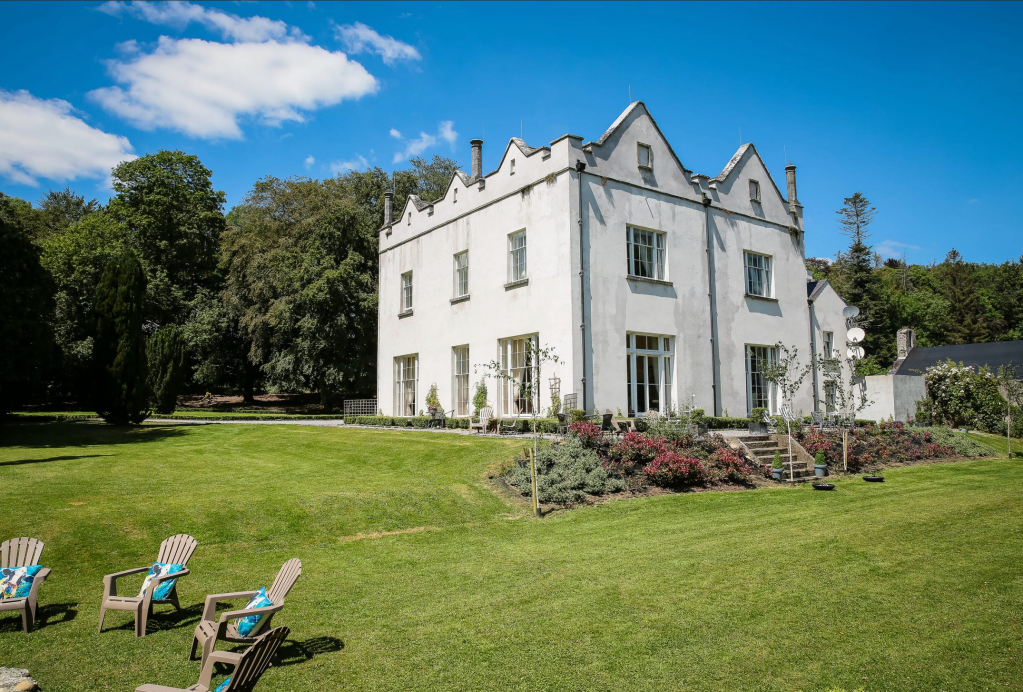
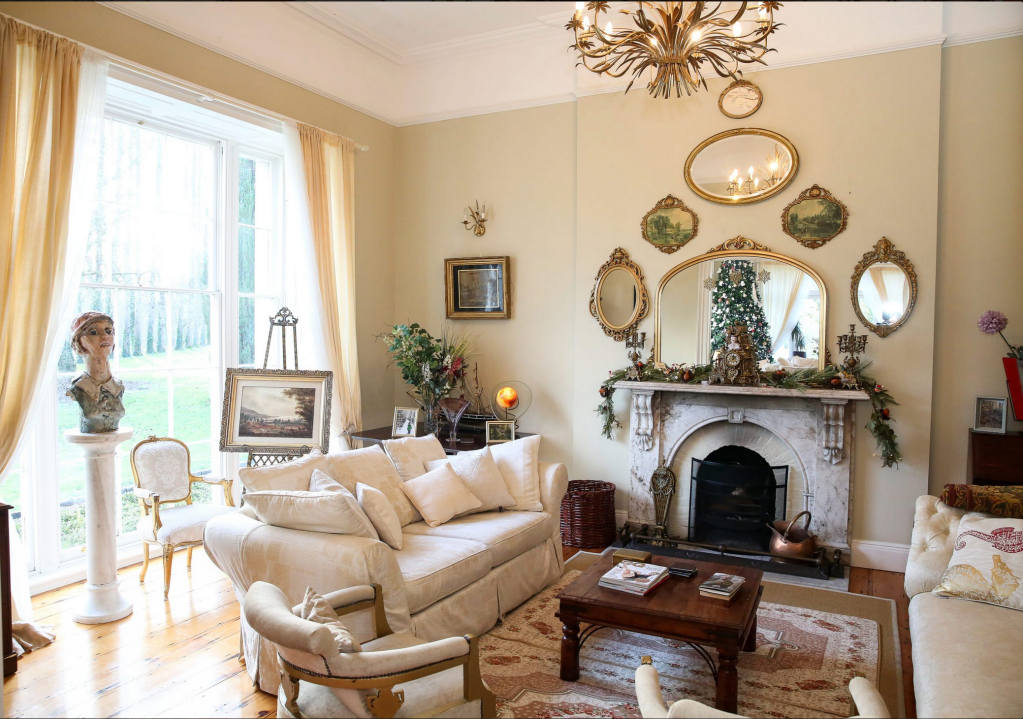
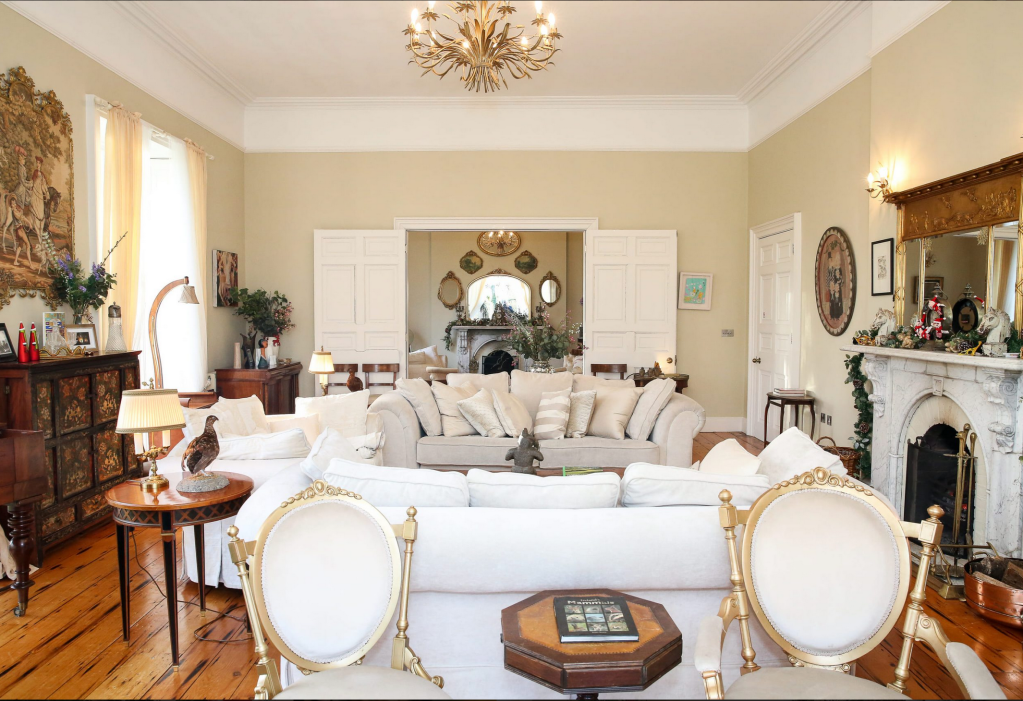
I am going to start collating a portrait gallery, as I love to put a name to the faces. I will add to these pages as I go.
I’ll be collecting them from my house entries and put them in alphabetical order by surname. I’ve also been going through the National Gallery collection and will also look at the National Portrait Gallery in London’s collection! It will be an ongoing project and a resource. I do think Ireland should have a National Portrait gallery! It would be a place where home owners could loan portraits for safekeeping also.
I have an editorial decision to make regarding women. Do I put them under their married name or under their maiden name? I think for now I’ll put them under both, as it’s nice to see them in relation to their fathers as well as in relation to their husband!
B
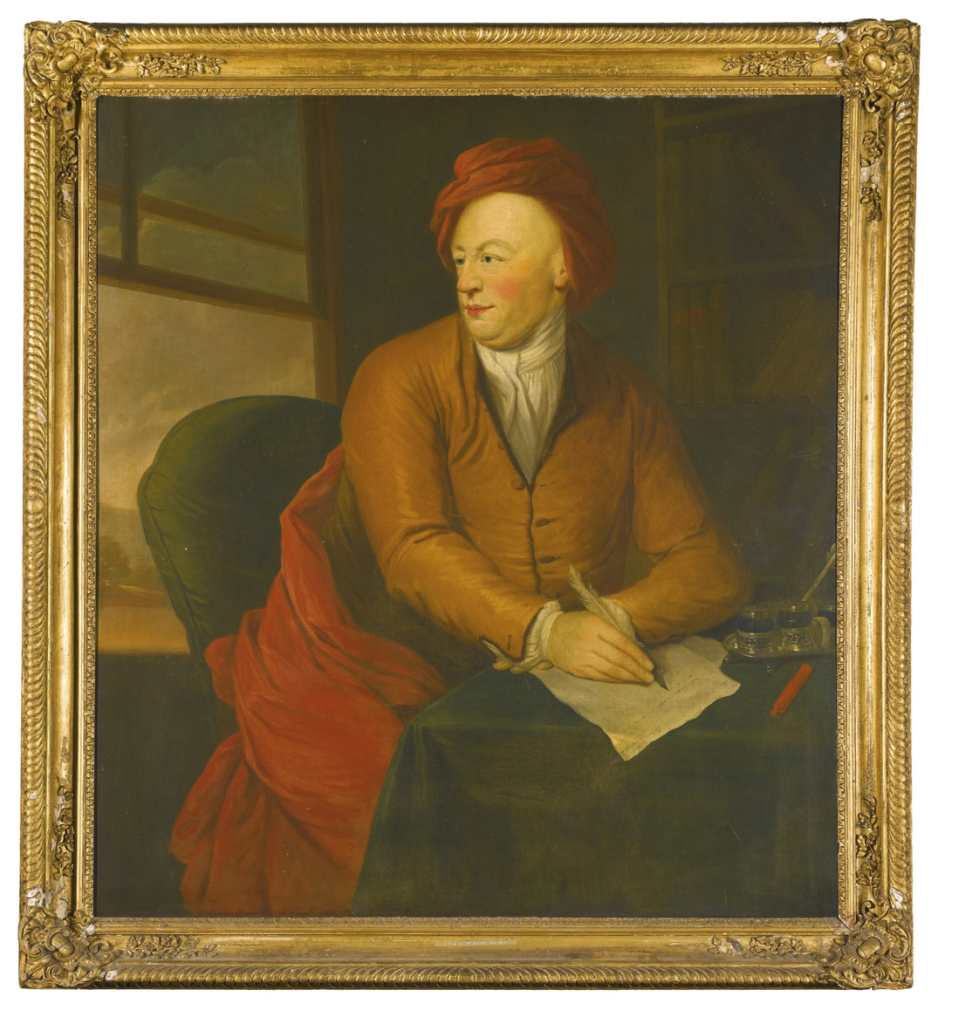
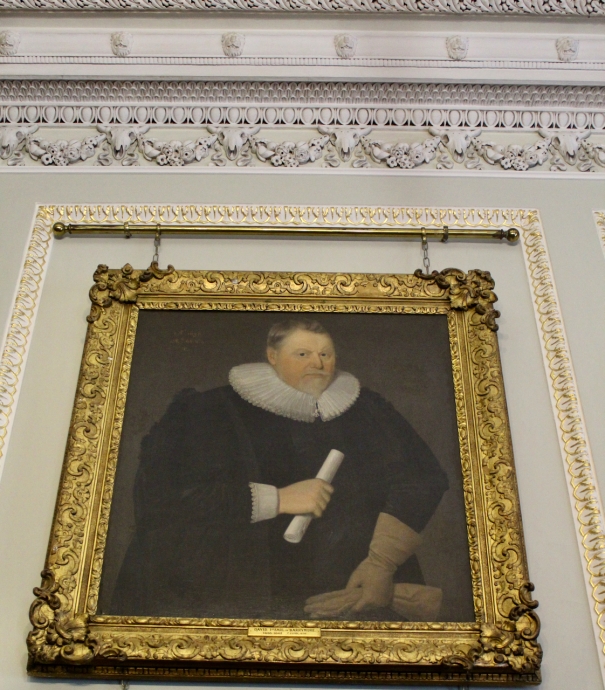






Barons Barry (c. 1261)
- David de Barry, 1st Baron Barry (died 1278). In 1267, King Henry III of England appointed Lord David de Barry as Chief Justice of Ireland.
- John Barry, 2nd Baron Barry (died 1285)
- David FitzDavid Barry, 3rd Baron Barry (died 1290)
- John Barry, 4th Baron Barry (died 1330)
- David Barry, 5th Baron Barry (died 1347)
- David Barry, 6th Baron Barry (died 1392)
- John Barry, 7th Baron Barry (died 1420)
- William Barry, 8th Baron Barry (died 1480)
- John Barry, 9th Baron Barry (died 1486)
- Thomas de Barry, 10th Baron Barry (died 1488)
- William Barry, 11th Baron Barry (died 1500)
- John Barry, 12th Baron Barry (died 1530)
- John Barry, 13th Baron Barry (died 1534)
- John FitzJohn Barry, 14th Baron Barry (1517–1553) (created Viscount Buttevant in 1541)
Viscounts Buttevant (1541)
- John FitzJohn Barry, 1st Viscount Buttevant (1517–1553)
- Edmund FitzJohn Barry, 2nd Viscount Buttevant (died 1556)
- James FitzJohn Barry, 3rd Viscount Buttevant (died 1557)
- James de Barry, 4th Viscount Buttevant (c. 1520–1581) 1st wife: Elizabeth Boyle, daughter of Charles Boyle, 3rd Viscount Dungarvan; 2nd wife: Elizabeth née Savage (d. 1714), daughter and heir of Richard Savage 4th Earl Rivers; 3rd wife: Anne Chichester, daughter of Major-General Arthur Chichester, 3rd Earl of Donegall (1666-1706), she was the mother of James Smith-Barry of Fota, County Cork.
- David de Barry, 5th Viscount Buttevant (died 1617)
- David Barry, 6th Viscount Buttevant (1604–1642) (created Earl of Barrymore in 1627/28)
Earls of Barrymore (1627/28)
- David Barry, 1st Earl of Barrymore (1604–1642)
- Richard Barry, 2nd Earl of Barrymore (1630–1694)
- Laurence Barry, 3rd Earl of Barrymore (1664–1699)
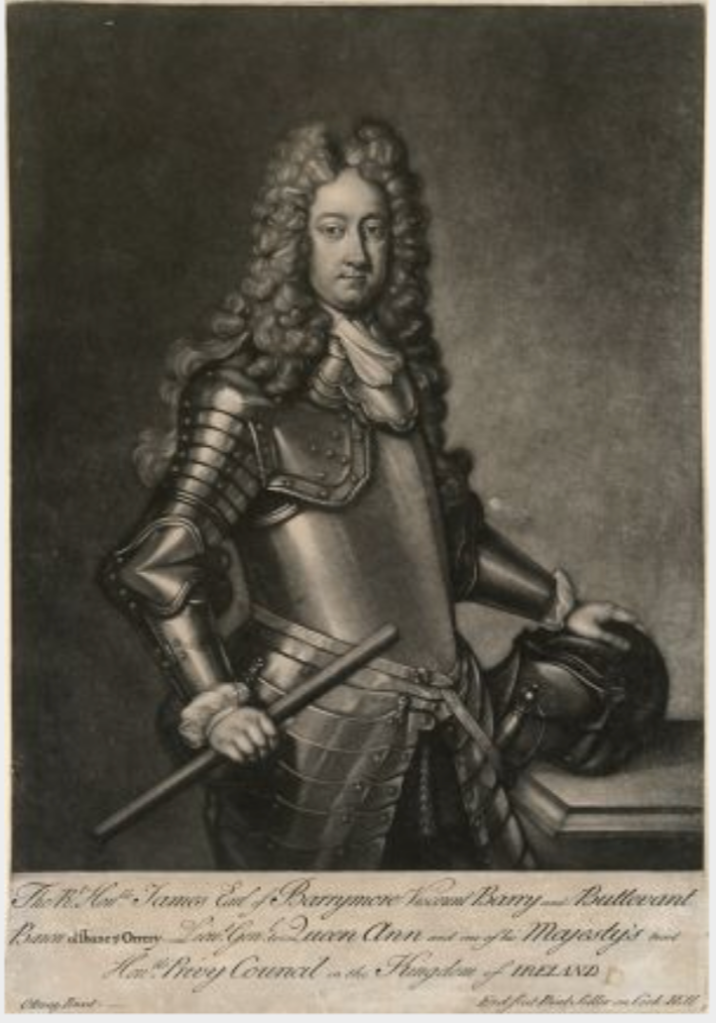
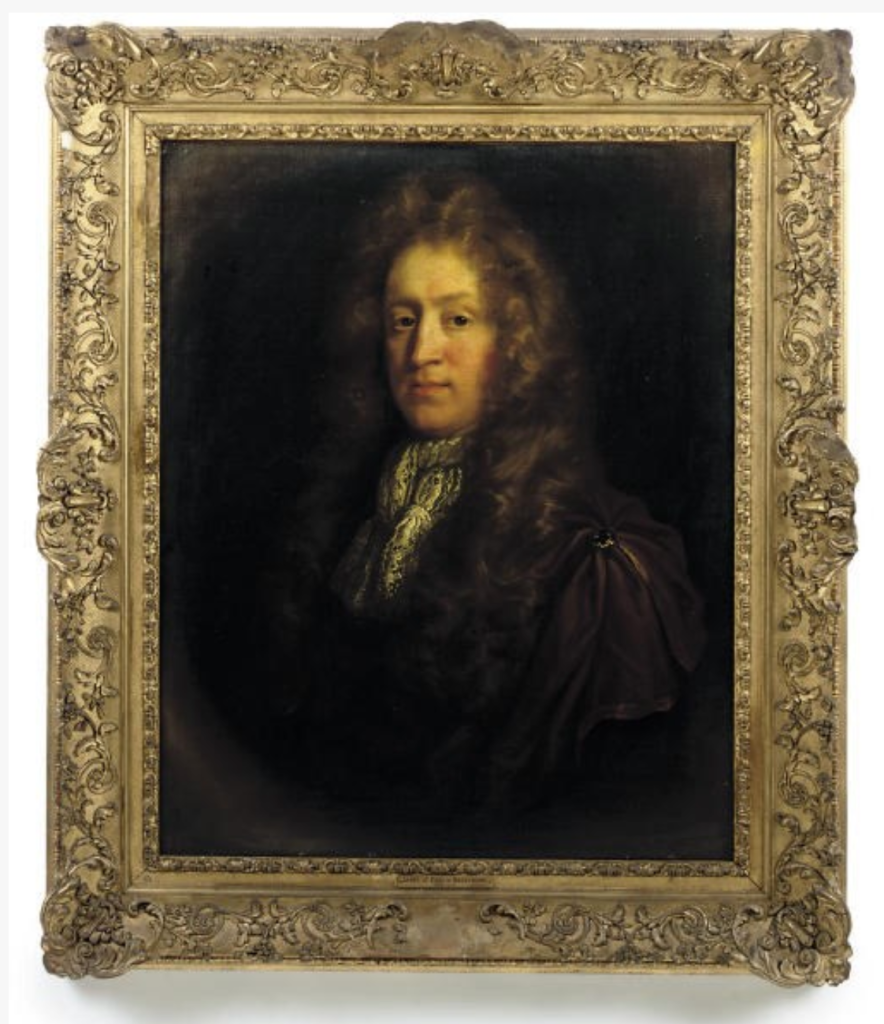
- James Barry, 4th Earl of Barrymore (1667–1747)
- James Barry, 5th Earl of Barrymore (1717–1751)
- Richard Barry, 6th Earl of Barrymore (1745–1773)
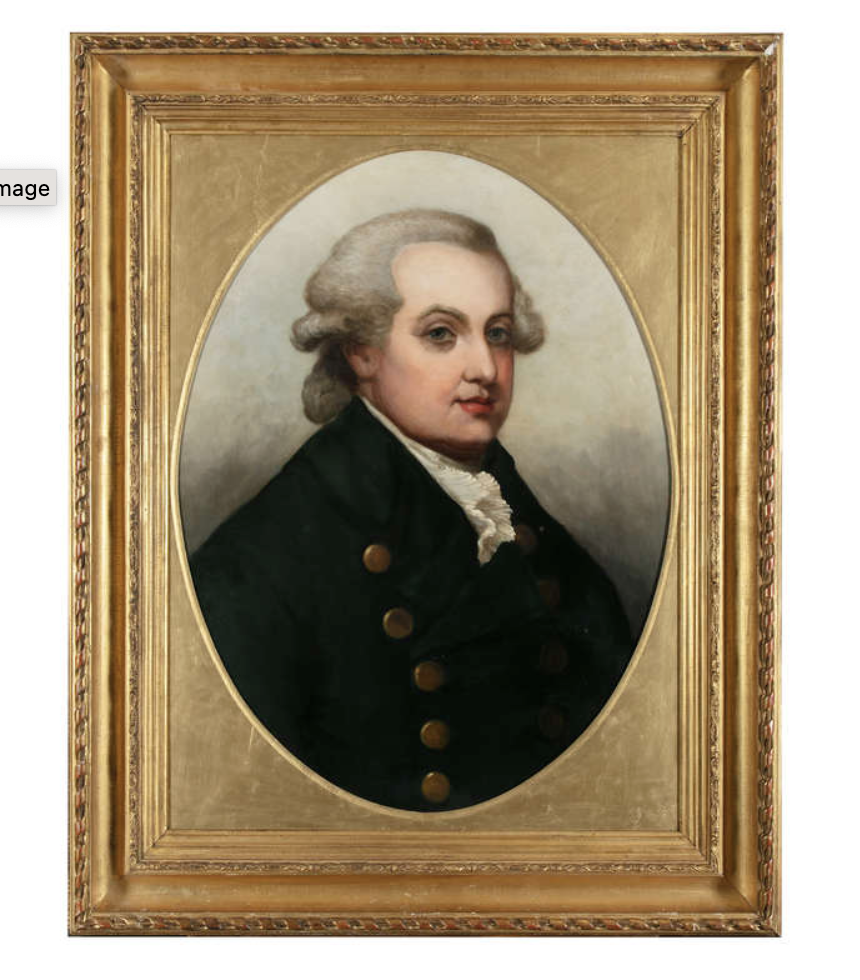
- Richard Barry, 7th Earl of Barrymore (1769–1793)
- Henry Barry, 8th Earl of Barrymore (1770–1823) [1]
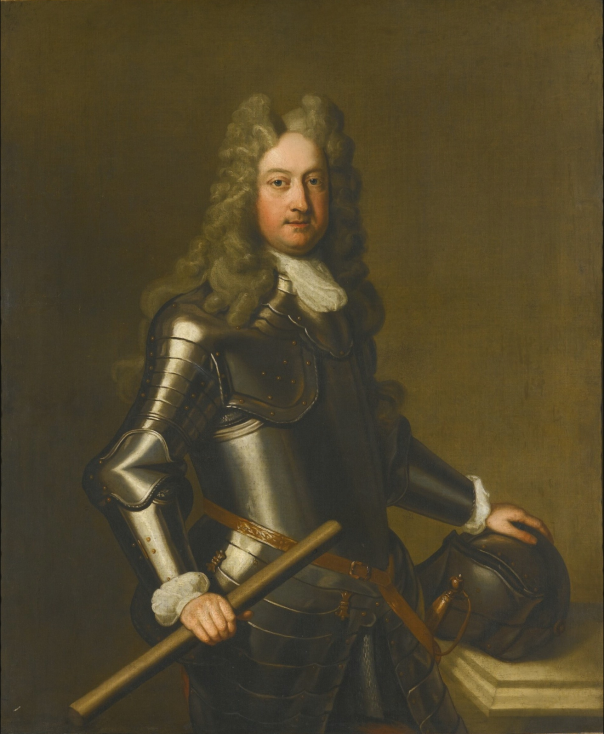
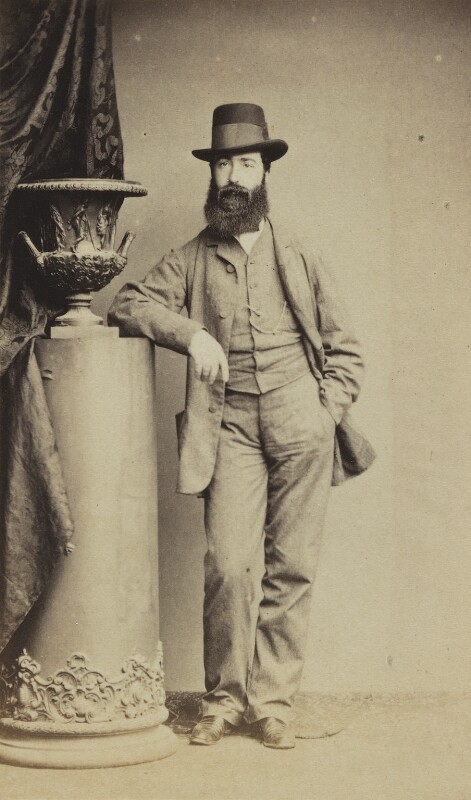



















Timothy William Ferres tells us of the Beresfords of Curraghmore: http://lordbelmontinnorthernireland.blogspot.com/search/label/County%20Waterford%20Landowners
SIR TRISTRAM BERESFORD (1595-1673), who was created a baronet in 1665, designated of Coleraine, County Londonderry. He married firstly, Anne, eldest daughter of John Rowley, of Castleroe, County Londonderry, by whom he had one son, RANDAL, his heir, and two daughters; and secondly, Sarah Sackville, and had three sons and three daughters: Tristram; Michael; Sackville; Susanna; Sarah; Anne.

Sir Tristram was succeeded by his eldest son, SIR RANDAL BERESFORD, 2nd Baronet (c. 1636-81), MP for Coleraine, 1661-68, who married Catherine Annesley, younger daughter of Francis, 1st Viscount Valentia, and dying in 1681, left issue, TRISTRAM, his heir; Jane; Catherine.
Sir Randal was succeeded by his eldest surviving son, SIR TRISTRAM BERESFORD, 3rd Baronet (1669-1701), MP for Londonderry County, 1692-99, who commanded a foot regiment against JAMES II, and was attainted by the parliament of that monarch. Sir Tristram wedded, in 1687, Nichola Sophia, youngest daughter and co-heiress of Hugh Hamilton, 1st Viscount Glenawly.
He was succeeded by his son, SIR MARCUS BERESFORD, 4th Baronet (1694-1763), MP for Coleraine, 1715-20, who espoused, in 1717, Catherine, BARONESS LE POER, daughter and heiress of James, 3rd Earl of Tyrone, and in consequence of that alliance, was elevated to the peerage, in 1720, in the dignity of Baron Beresford and Viscount Tyrone. His lordship was further advanced to an earldom, in 1746, as EARL OF TYRONE.

Marcus Beresford (1694-1763) 1st Earl of Tyrone had surviving issue: GEORGE DE LA POER (1735-1800) his successor who became 2nd Earl of Tyrone;
John (1737/38-1805);
William (1743-1819) (Most Rev), created BARON DECIES;
Anne; Jane; Catherine; Aramintha; Frances Maria; Elizabeth.
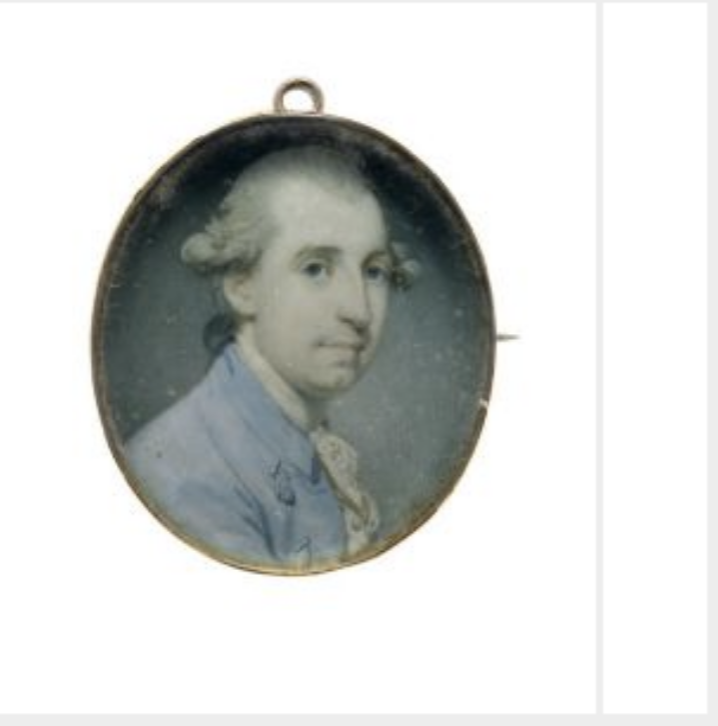
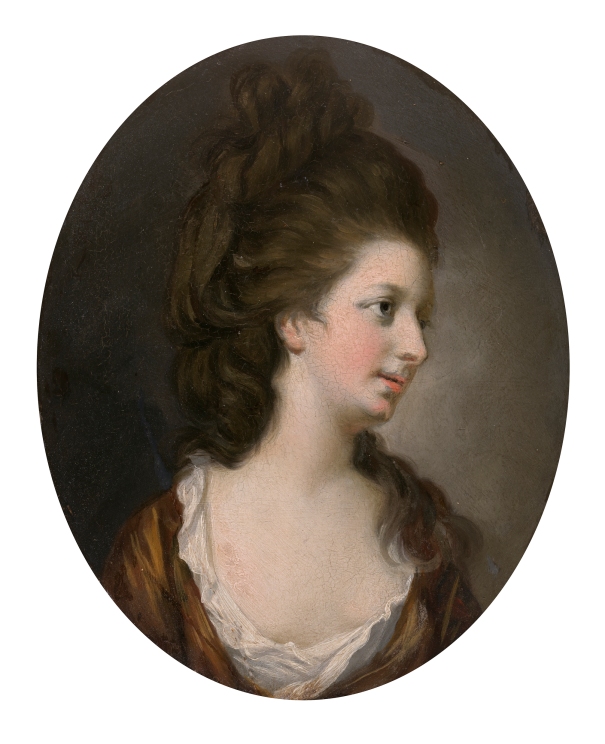
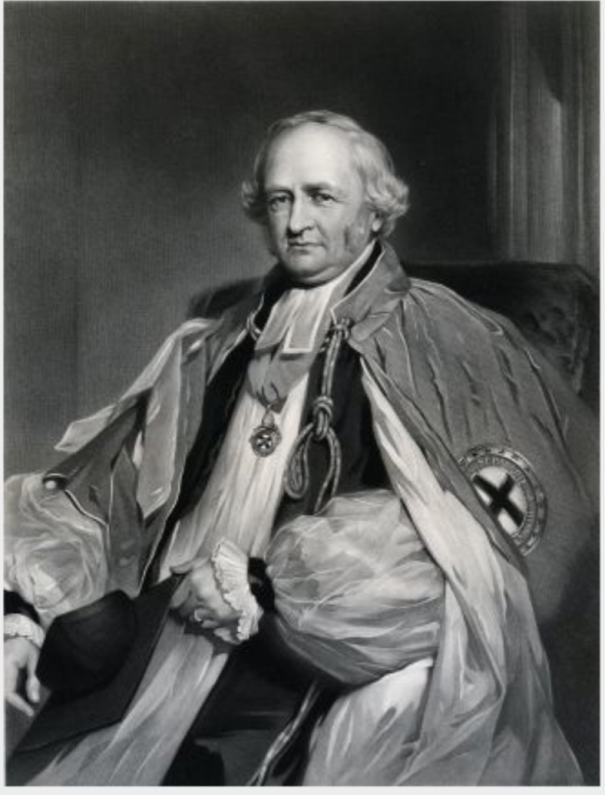
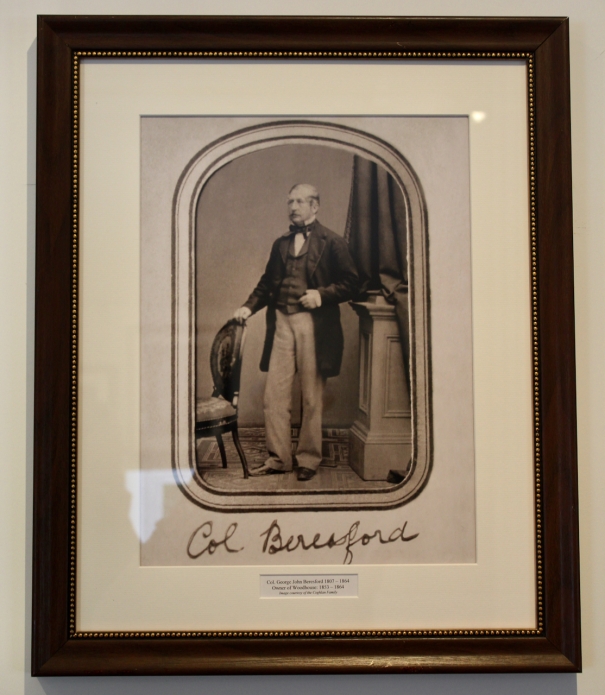




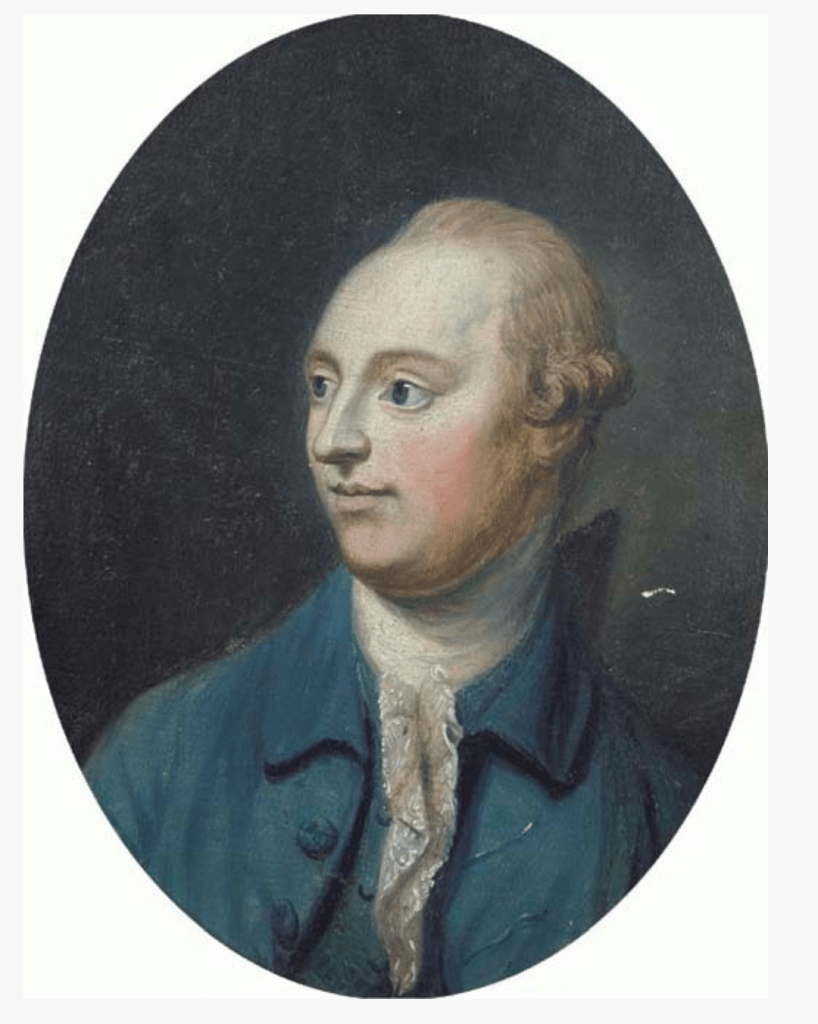





George de la Poer Beresford, 2nd Earl of Tyrone (1735-1800) inherited the ancient Barony of de la Poer at the decease of his mother in 1769. His lordship was enrolled amongst the peers of Great Britain, in 1786, as Baron Tyrone; and created, in 1789, MARQUESS OF WATERFORD.
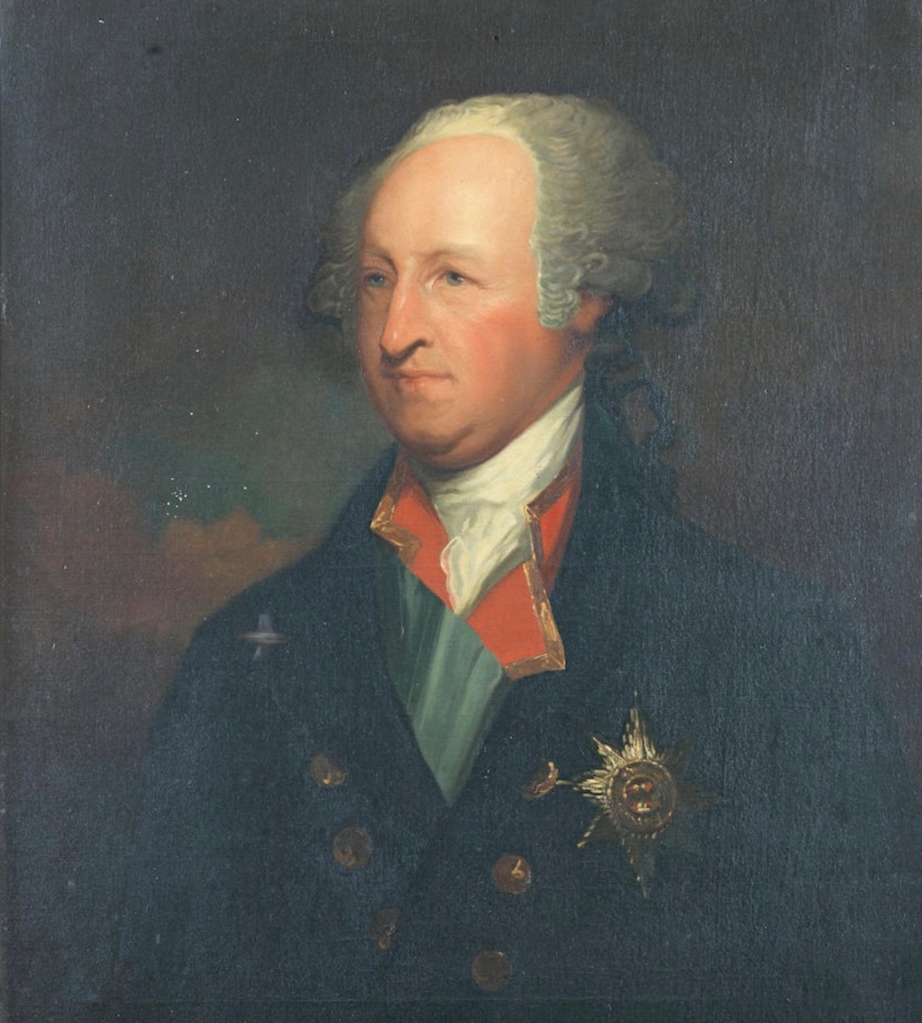

He married, in 1769, Elizabeth, only daughter and heiress of Henry Monck, of Charleville. They had issue:
Marcus, died at 8 years old; Henry de la Poer Beresford (1772-1826) his successor who became 2nd Marquess of Waterford; John George (1773-1862) (Most Rev), Lord Archbishop of Armagh;
George Thomas (1781-1839) (Rt Hon), Lt-Gen, GCH; Isabella Anne; Catherine; Anne; Elizabeth Louisa (1783-1856).
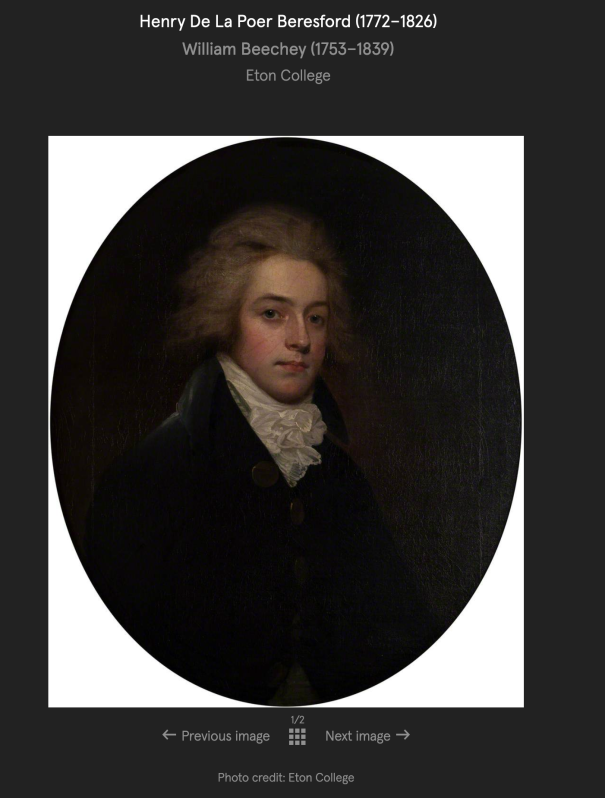
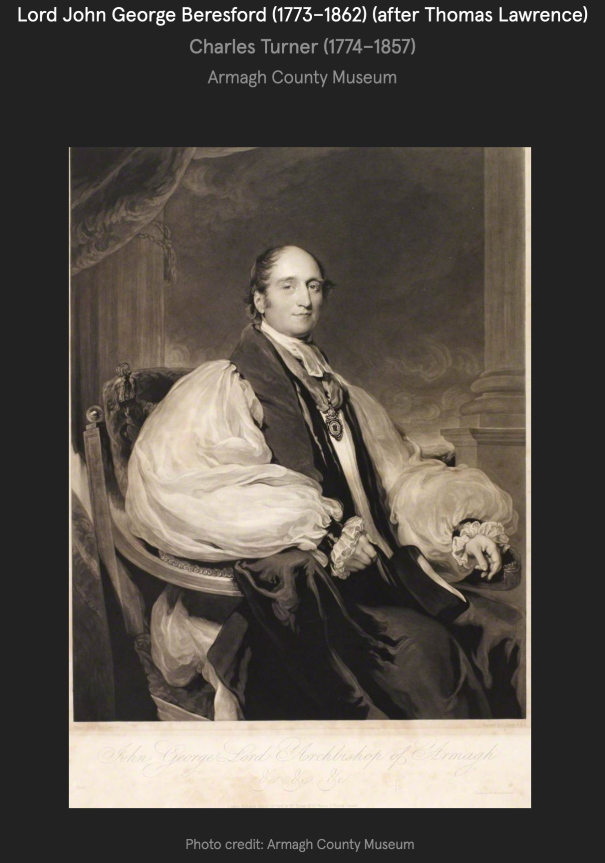



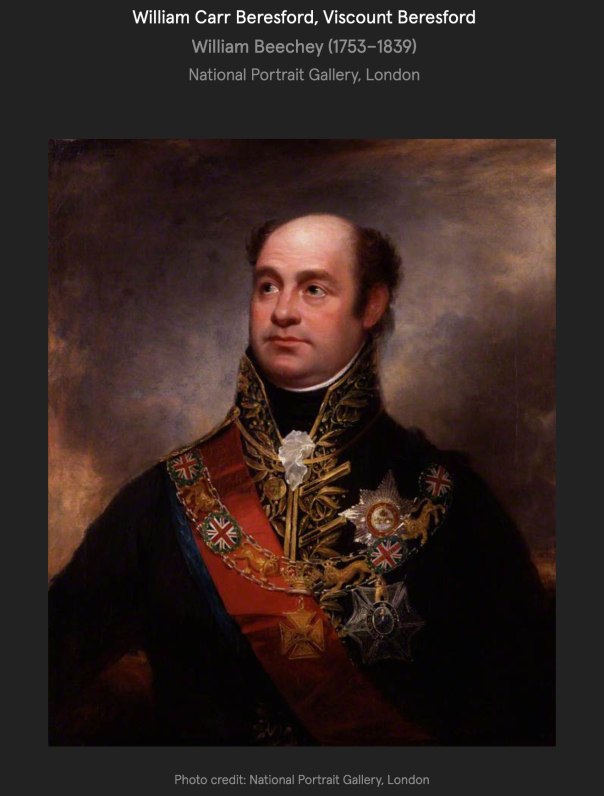
He had an illegitimate son Admiral Sir John de la Poer Beresford (1766-1844) 1st Bt Beresford, of Bagnall, Co. Waterford, and also Lt.-Gen. William Carr Beresford (1768-1854) 1st and last Viscount Beresford of Beresford.


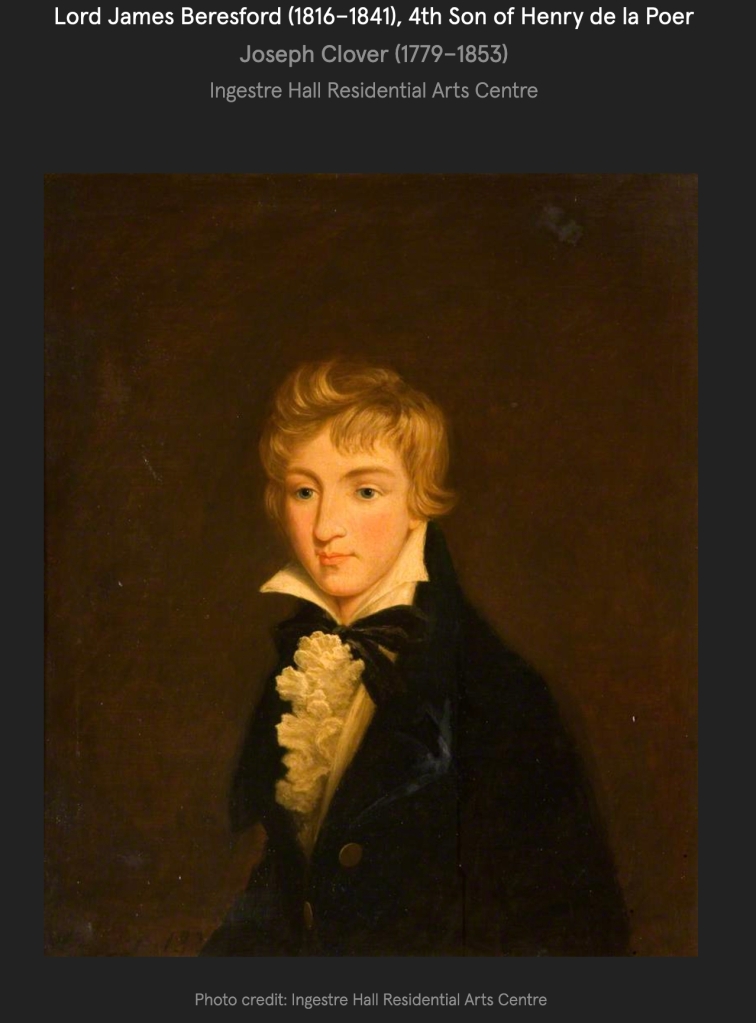
Henry de la Poer Beresford 2nd Marquess (1772-1826) wedded, in 1805, Susanna Carpenter, only daughter and heiress of George Carpenter 2nd Earl of Tyrconnell, and had issue,
HENRY de la Poer Beresford (1811-1859) his successor who became 3rd Marquess of Waterford;
William;
John (1814-1866) who became 4th Marquess of Waterford;
James;
Sarah Elizabeth (1807-1854) who married Henry John Chetwynd-Talbot, 18th Earl of Shrewsbury.

Henry de la Poer Beresford 3rd Marquess married Louisa Anne Stuart (1818-1891), daughter of Charles Stuart, 1st and last Baron Stuart de Rothesay. They did not have children.


When the 3rd Marquess died, his brother John became the 4th Marquess. The 4th Marquess married Christiana, daughter of Charles Powell Leslie of Castle Leslie in County Monaghan.
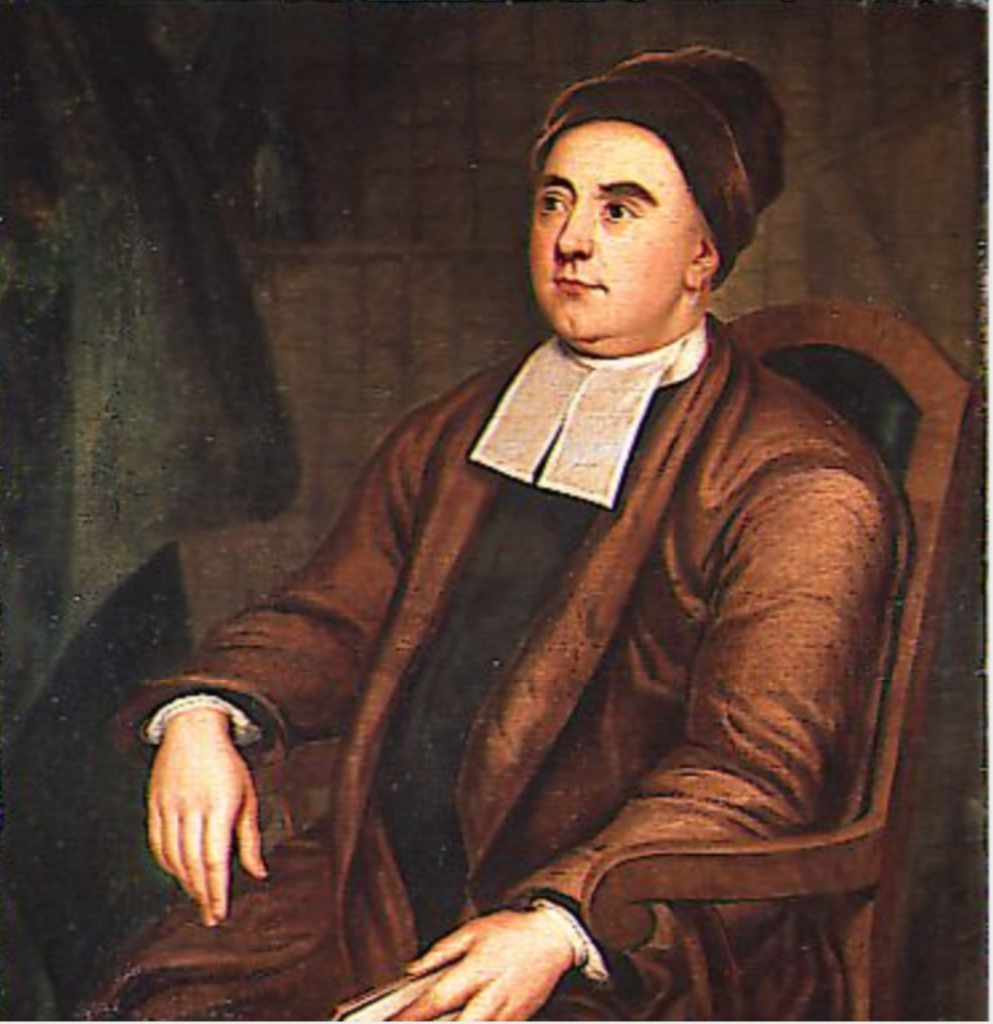
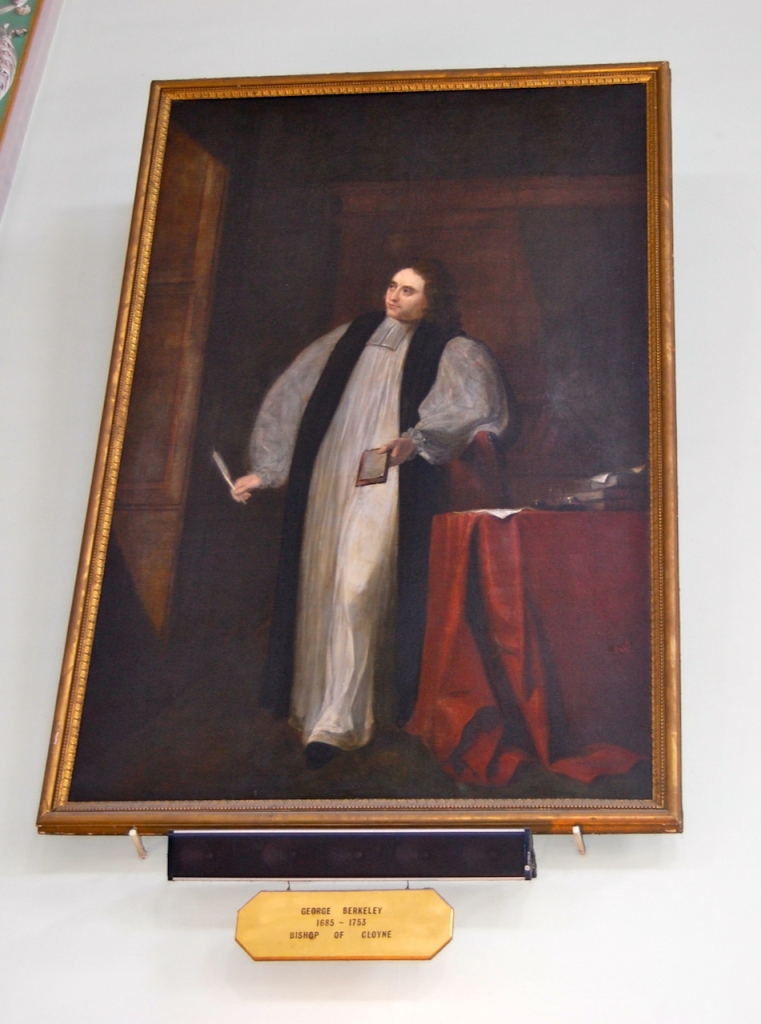
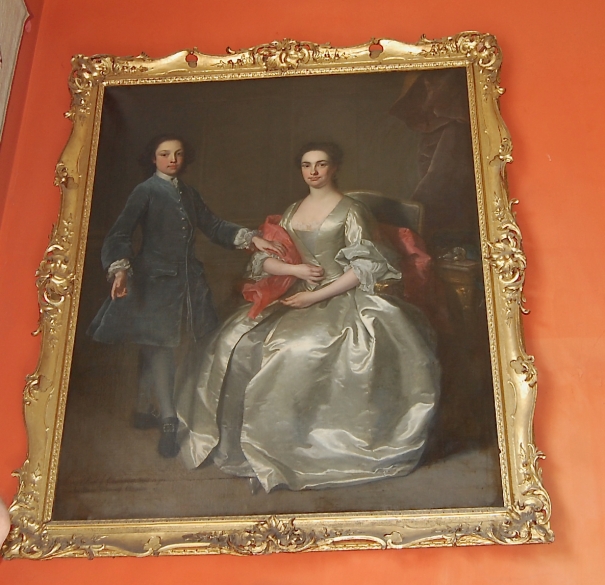
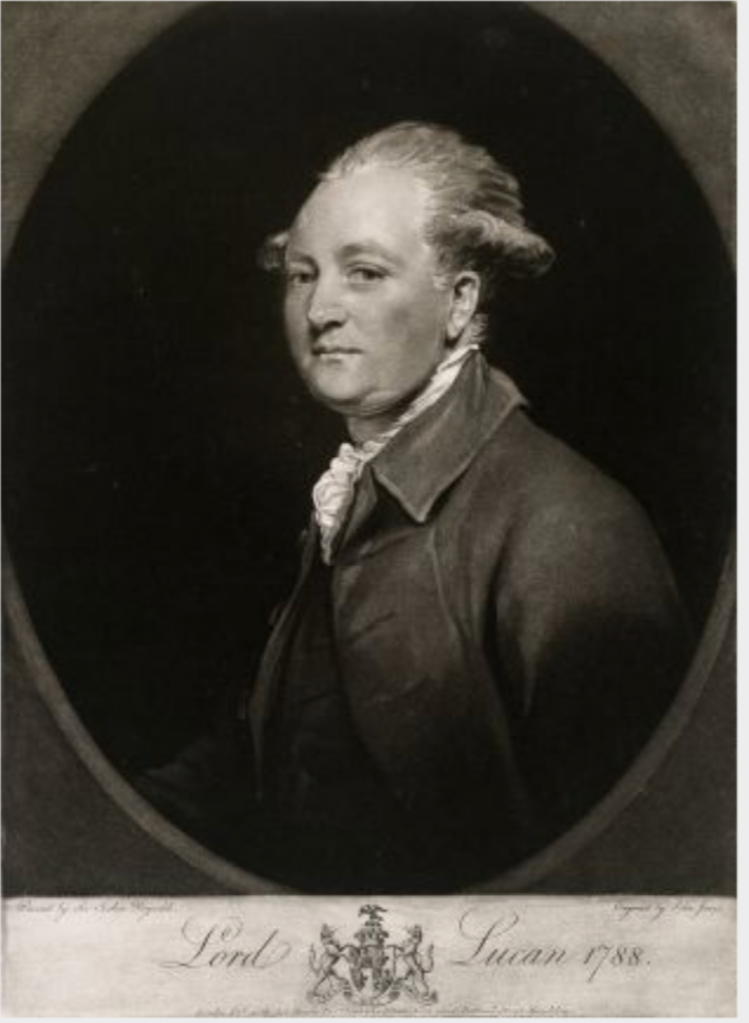
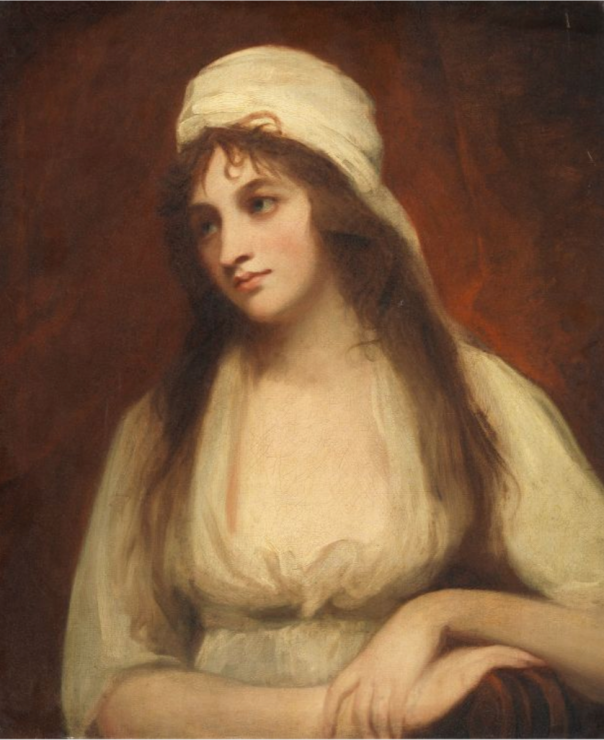
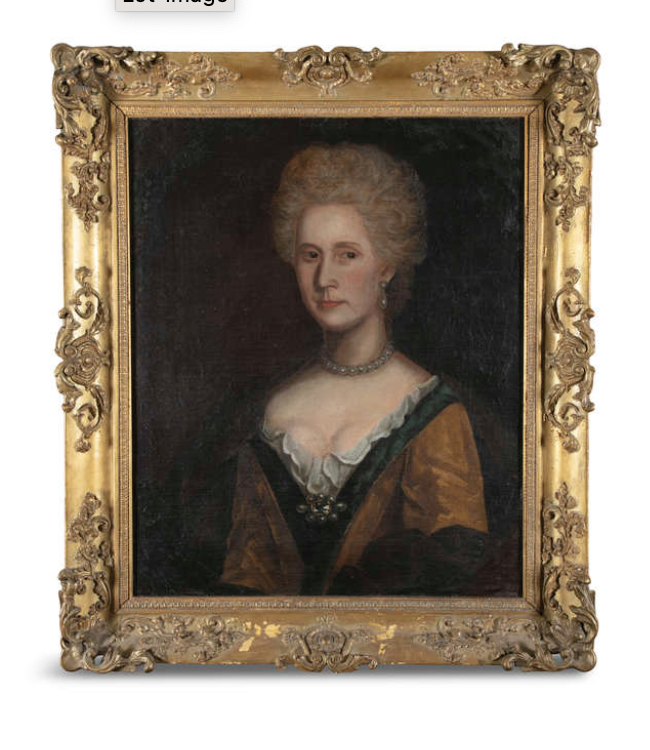
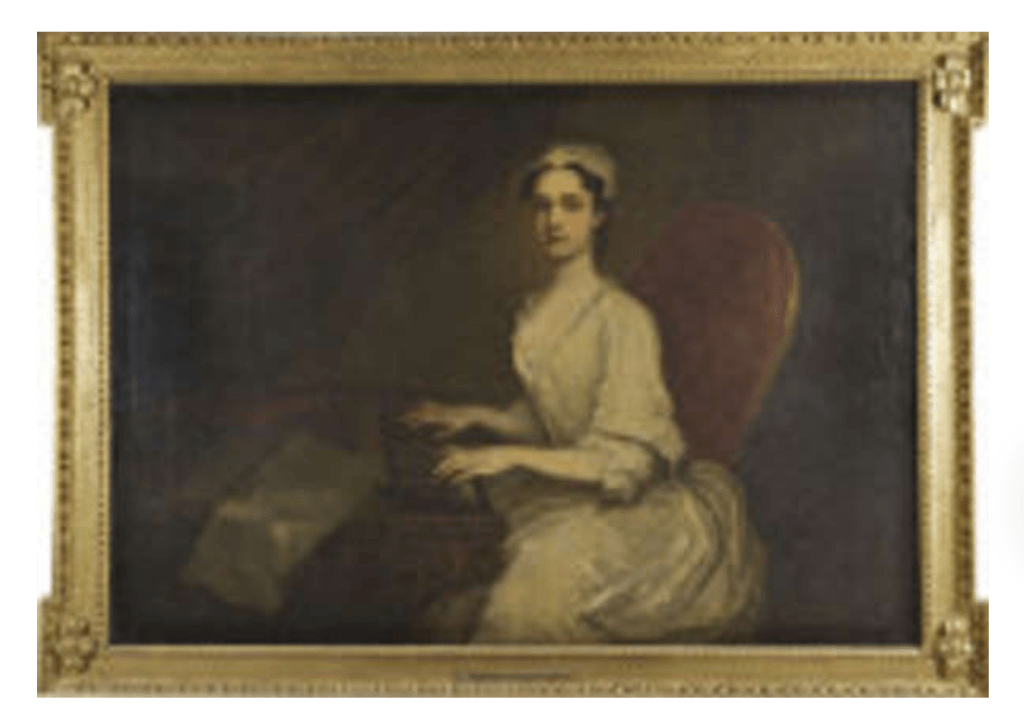
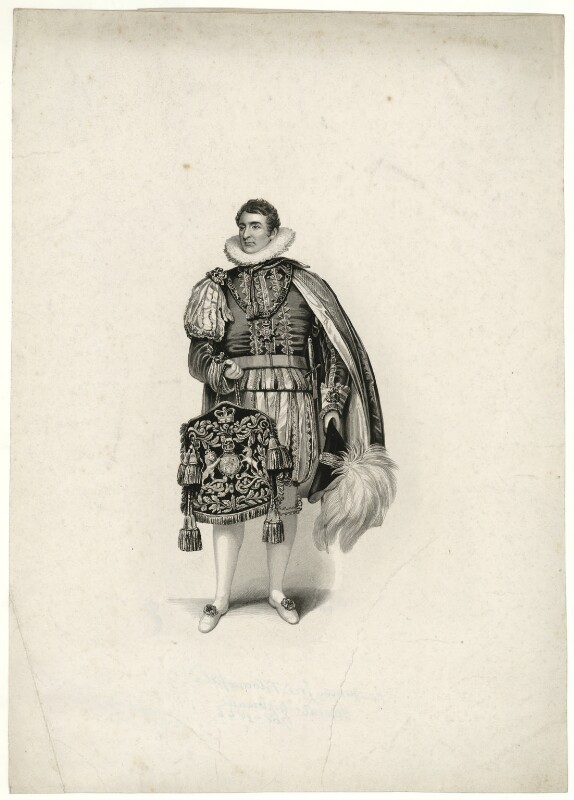
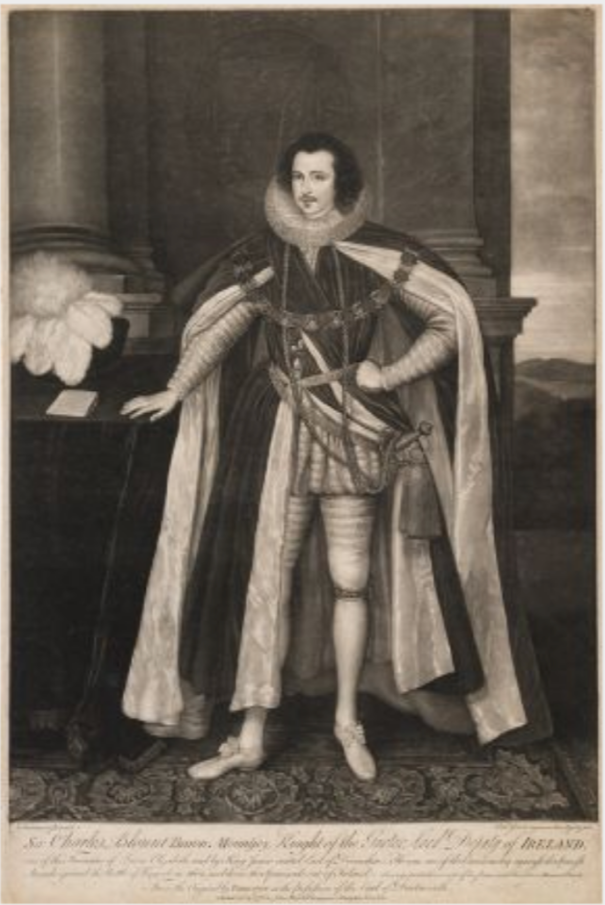
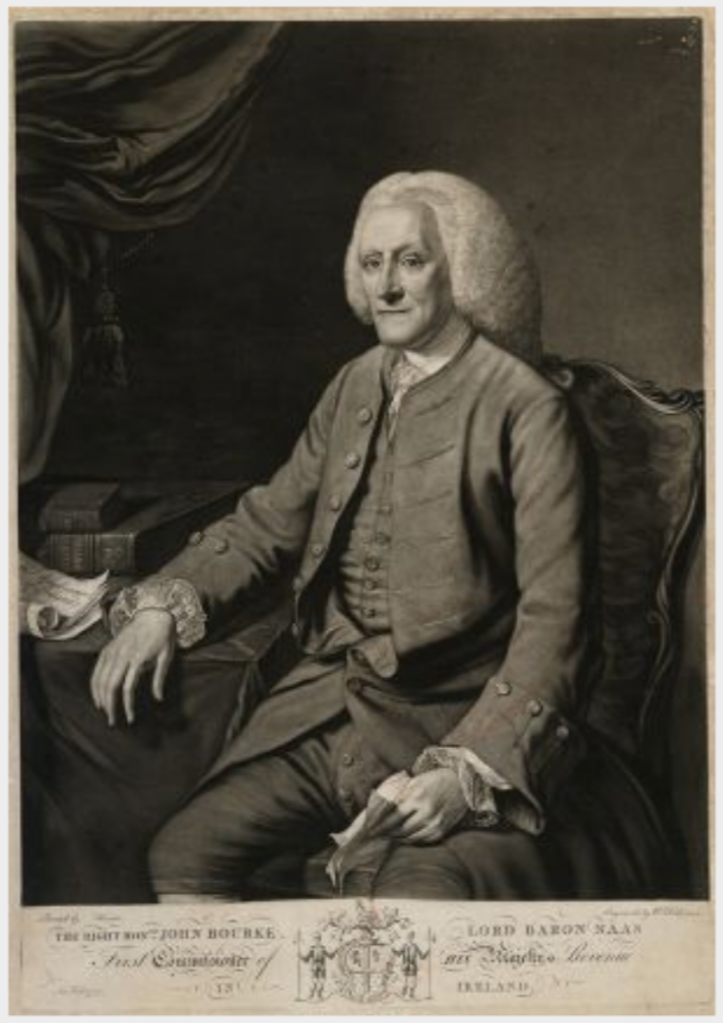

































Timothy William Ferres tells us of the family of the Boyles, Earls of Cork:
Richard Boyle (1566-1643) 1st Earl of Cork married firstly, in 1595, Joan, daughter and co-heiress of William Apsley, of Limerick, without surviving issue; and secondly, Catherine, daughter of Sir Geoffrey Fenton, Knight, principal secretary of state for Ireland, and had issue (with eight daughters):
Roger (1606-15);
RICHARD (1612-98) his successor; Geoffrey d. 1 year old; Lewis (1619-1642) created Viscount Boyle of Kinalmeaky;
ROGER (1621-1679) created 1st Earl of Orrery; ancestor of John, 5th Earl of Cork;
Francis (1623-1699) created Viscount Shannon;
Robert (1626/1627-1691), the philosopher.
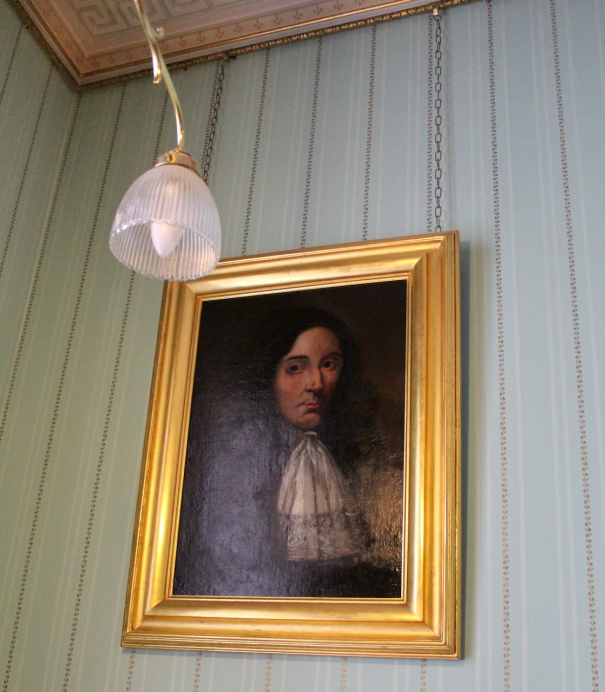
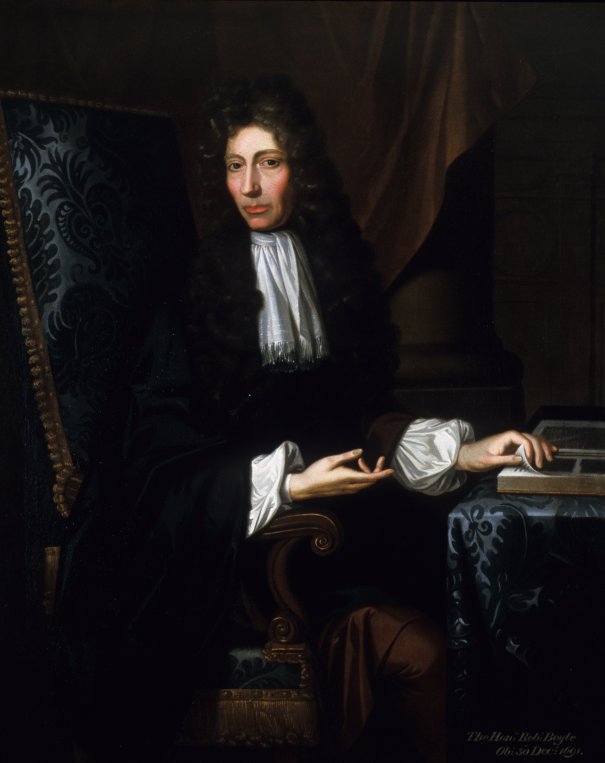


The 1st Earl of Cork’s daughter Alice (1607-1666) married David Barry 1st Earl of Barrymore. His other daughters were Sarah (1609-1633) who married first Thomas Moore son of Garret Moore 1st Viscount of Drogheda, and then second, Rober Digby 1st Baron Digby; Lettice who married Lord Goring; Joan who married George Fitzgerald 16th Earl of Kildare; Catherine (1615-1691) who married Arthur Jones 2nd Viscount Ranelagh; Dorothy (1617-1668) who married Arthur Loftus and second, Gilbert Talbot son of William Talbot 1st Baronet; Mary (1625-1678) who married Charles Rich 4th Earl of Warwick;
The 1st Earl of Cork was succeeded by his eldest son, RICHARD, 2nd Earl (1612-98); who, having wedded, in 1635, the Lady Elizabeth Clifford, daughter and heiress of Henry, 5th Earl of Cumberland, was created a Peer of England, 1644, in the dignity of Baron Clifford of Londesborough, Yorkshire; and, in 1664, EARL OF BURLINGTON.
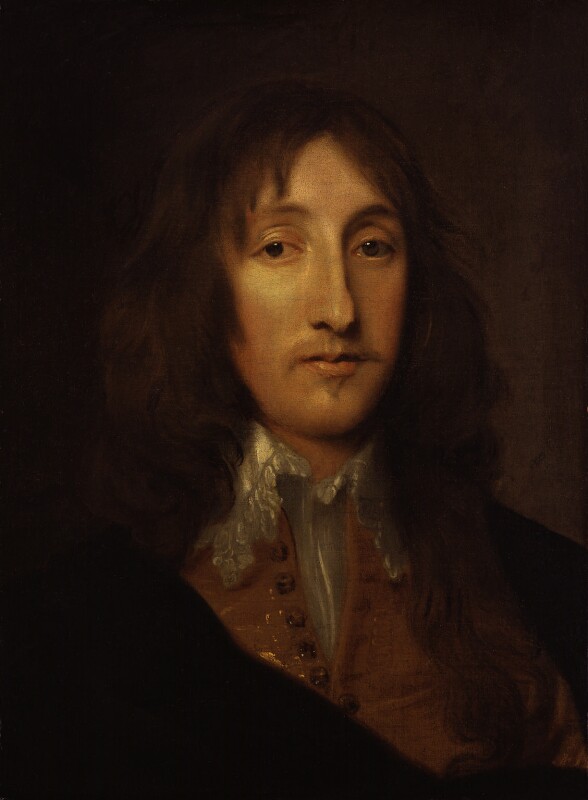


The 2nd Earl of Cork had issue:
Charles, 3rd Viscount Dungarvan (1639-94); father of the 3rd Earl of Cork; Richard, who died in 1665 at the battle of Lowestoft; and daughters Frances who married Colonel Francis Courtenay, 3rd Bt. then second, Wentworth Dillon, 4th Earl of Roscommon; Anne who married Edward Montagu, 2nd Earl of Sandwich; Elizabeth who married Nicholas Tufton, 3rd Earl of Thanet; Mary; Henrietta who married Laurence Hyde, 1st Earl of Rochester.
His lordship’s eldest son Charles, 3rd Viscount Dungarvan (1639-94) having predeceased him, was succeeded by his grandson, CHARLES (c. 1662-1704), 3rd Earl of Cork and 2nd Earl of Burlington.

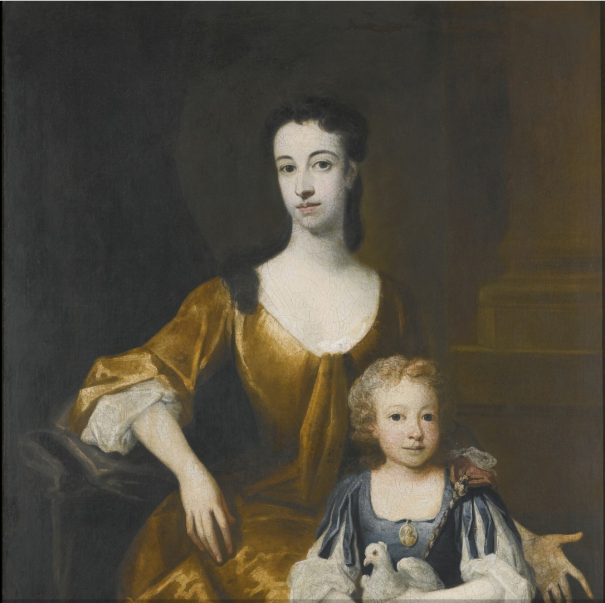
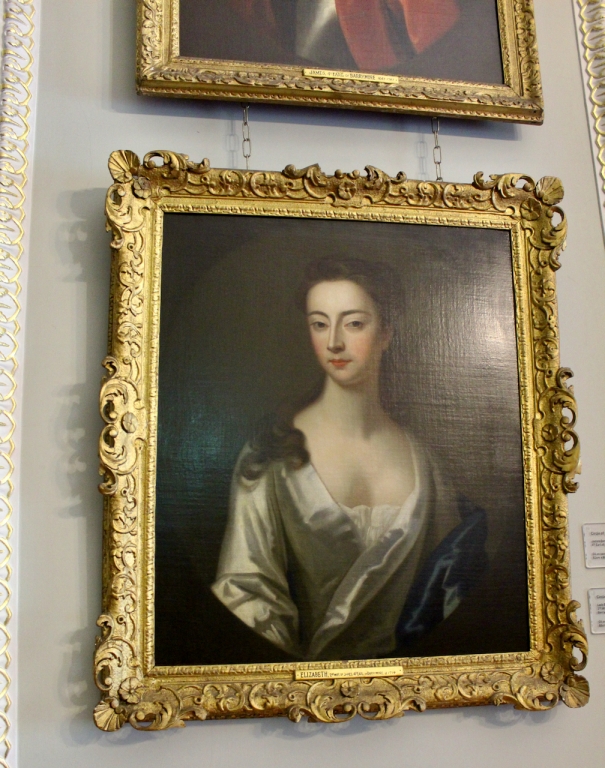
Charles, 3rd Viscount Dungarvan (1639-94) had a daughter Elizabeth (1662-1703) who married Lt.-Gen. James Barry, 4th Earl of Barrymore.
The 3rd Earl of Cork, 2nd Earl of Burlington espoused Juliana, daughter and heiress of the Hon Henry Noel, of Luffenham, Rutland, by whom he had surviving issue, RICHARD (1694-1753) his successor, 3rd Earl of Burlington.
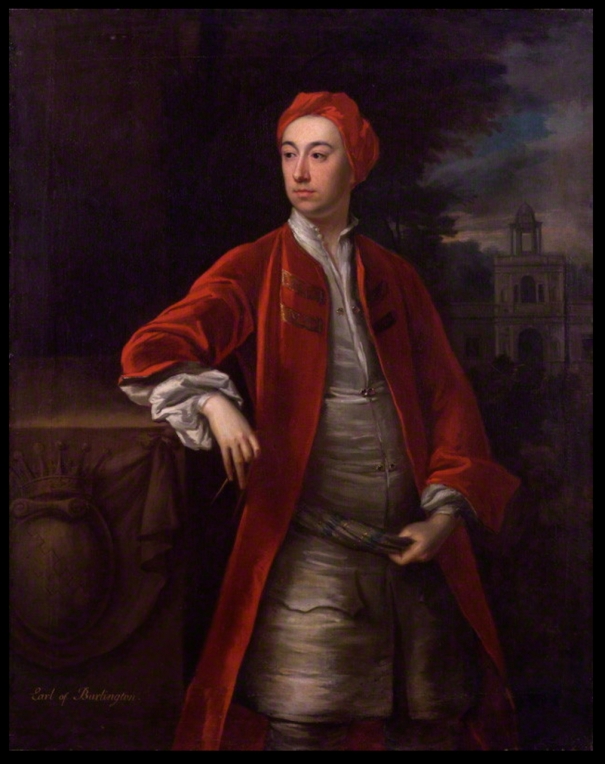

The 3rd Earl of Cork, 2nd Earl of Burlington had daughters Elizabeth; Juliana; Jane; Henrietta (1700-1746) who married Henry Boyle, 1st Earl of Shannon.
The 3rd Earl of Cork, 2nd Earl of Burlington was succeeded by his only son, RICHARD (1694-1753), 4th Earl of Cork and 3rd Earl of Burlington, KG, who married, in 1720, the Lady Dorothy Savile, elder daughter and co-heiress of William, 2nd Marquess of Halifax, by which lady he had three daughters, Dorothy; Juliana; Charlotte Elizabeth, m William Cavendish, Marquess of Hartington.
His lordship claimed, in 1727, the barony of Clifford, as great-grandson of the Lady Elizabeth Clifford, daughter and heiress of Henry, Lord Clifford, and the house of peers acknowledged and confirmed his lordship’s right thereto.
This nobleman was eminent as a munificent encourager of literature and the fine arts, and as a friend of Alexander Pope he will always be remembered.
His lordship died in 1753, and leaving an only surviving daughter, Lady Charlotte, who had wedded William, 4th Duke of Devonshire, and inherited the barony of Clifford; all his lordship’s other English honours ceased, while those of Ireland devolved upon his kinsman, JOHN BOYLE (1707-62), 5th Earl of Orrery, in Ireland; Baron Boyle of Marston, in Great Britain; succeeded as 5th EARL OF CORK (refer to Roger, third son of the first Earl of Cork).




The 1st Earl of Cork’s son ROGER (1621-1679) was created 1st Earl of Orrery.
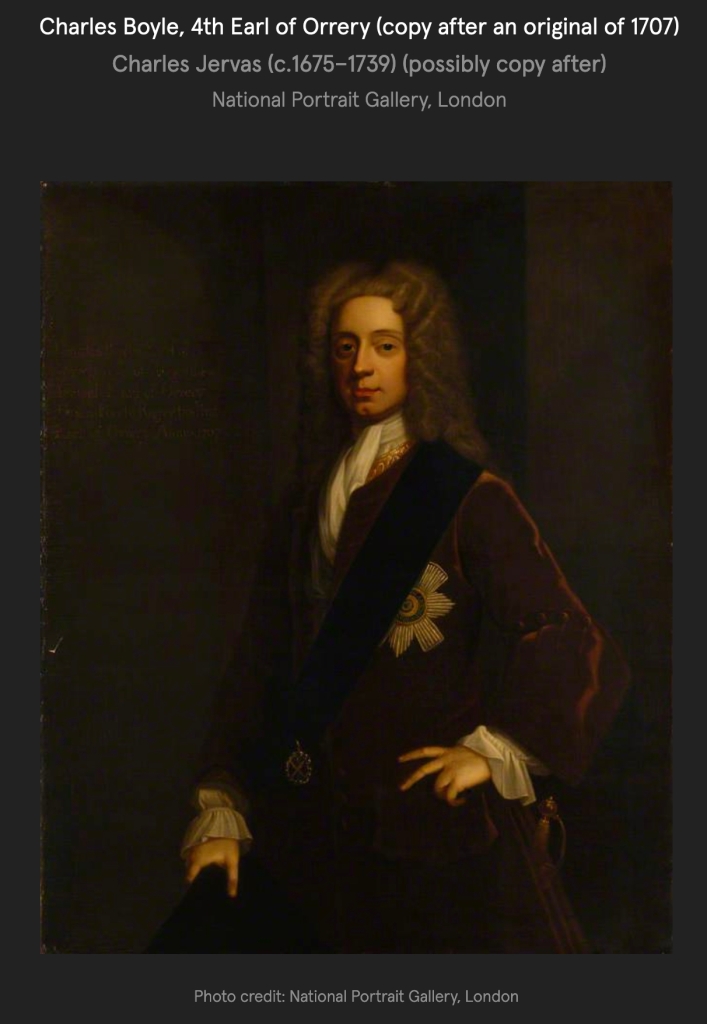


JOHN BOYLE (1707-62), 5th Earl of Orrery, in Ireland; Baron Boyle of Marston, in Great Britain; succeeded as 5th EARL OF CORK (refer to Roger, third son of the first Earl of Cork).
His lordship wedded firstly, in 1728, the Lady Henrietta Hamilton, youngest daughter of George, 1st Earl of Orkney KT, and had issue: Charles, Viscount Dungarvan (1729-1759); HAMILTON, his successor; Elizabeth.

He espoused secondly, Margaret, daughter and sole heiress of John Hamilton, by whom he had further issue: EDMUND, 7th Earl of Cork; Catherine Agnes; Lucy. He was a writer.
He was succeeded by his eldest surviving son, HAMILTON (1729-64), 6th Earl of Cork and Orrery, who died unmarried, in little more than a year after his father, when the honours devolved upon his brother, EDMUND (1742-98), 7th Earl of Cork and Orrery, who married firstly, in 1764, Anne, daughter of Kelland Courtenay, and had issue: John Richard, Viscount Dungarvan (1765-8); EDMUND, of whom hereafter; Courtenay (the Hon Sir), Vice-Admiral in the Royal Navy; Lucy Isabella.

His lordship espoused secondly, in 1786, Mary, youngest daughter of John, 1st Viscount Galway, without further issue.
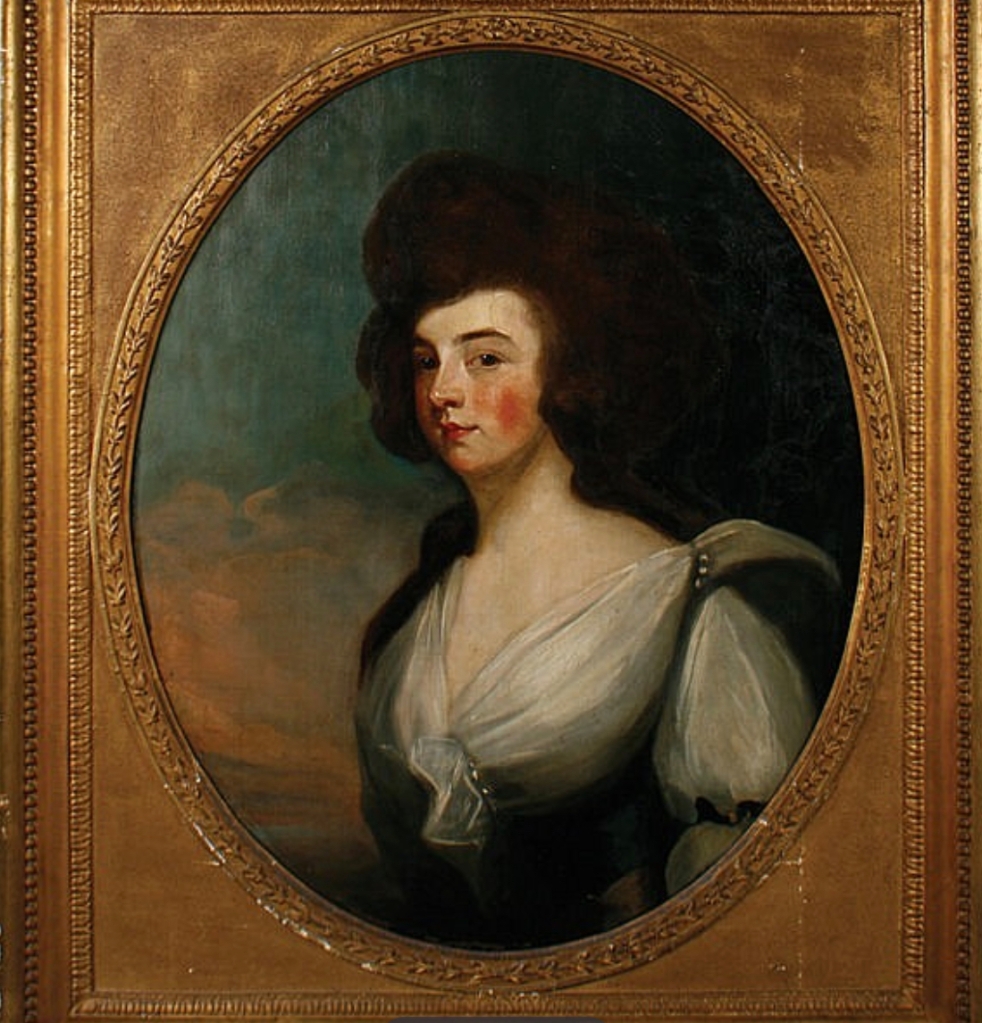
He was succeeded by his eldest surviving son, EDMUND (1767-1856), 8th Earl of Cork and Orrery, KP, a General in the Army, who married, in 1795, Isabella Henrietta, third daughter of William Poyntz, of Midgam house, Berkshire, and had issue: Edmund William, Viscount Dungarvan (1798-1826); George Richard (1799-1810); CHARLES, of whom presently; John, ancestor of the 12th and 13th Earls; Robert Edward; Richard Cavendish; Isabella Elizabeth; Lucy Georgina; Louisa.
His lordship’s eldest surviving son CHARLES (1800-34), styled Viscount Dungarvan, wedded, in 1828, the Lady Catherine St Lawrence, daughter of William, 2nd Earl of Howth, and had issue:
RICHARD EDMUND ST LAWRENCE, his successor;
William George;
Edmund John;
Louisa Caroline Elizabeth; Mary Emily.
His lordship predeceased his father, and the family honours devolved upon his eldest son,
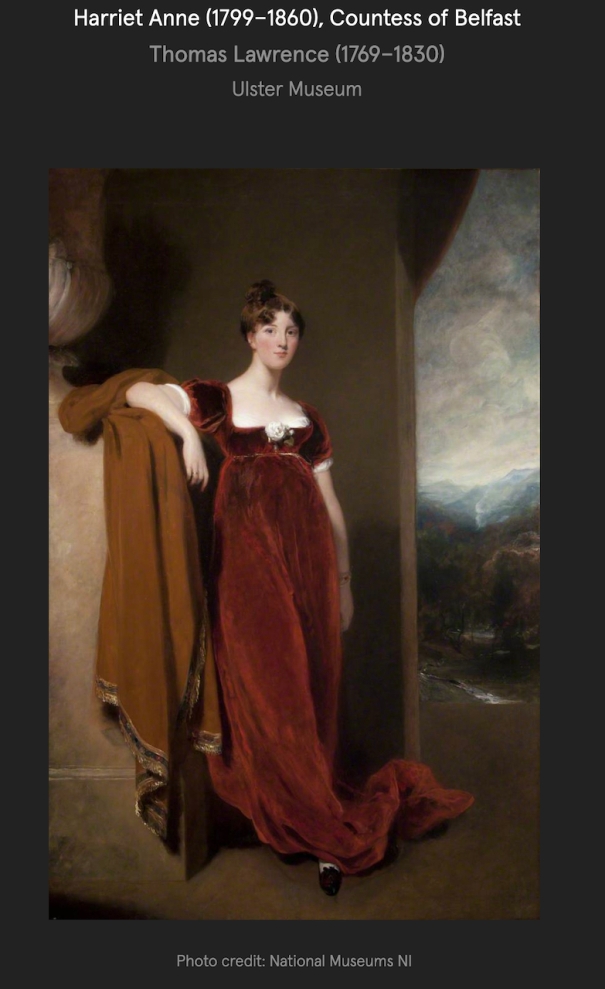
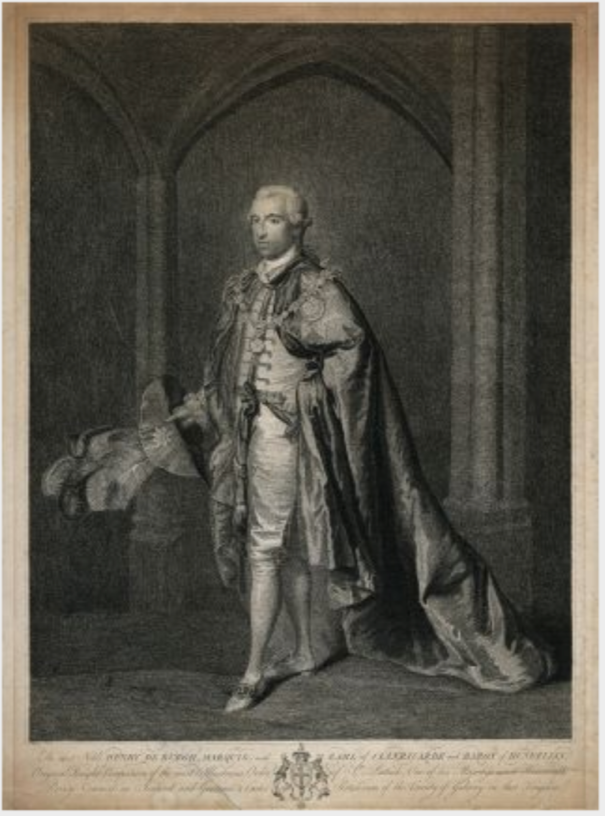
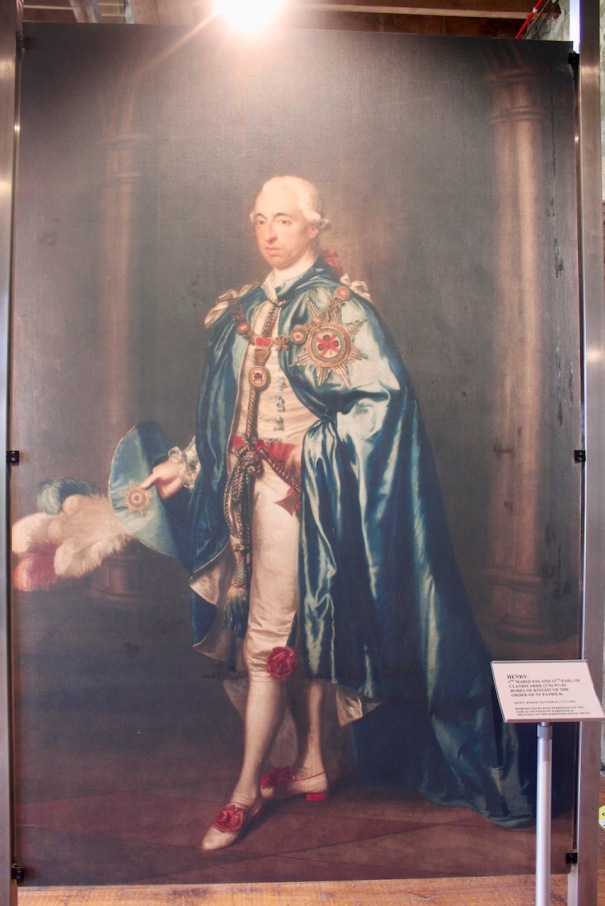
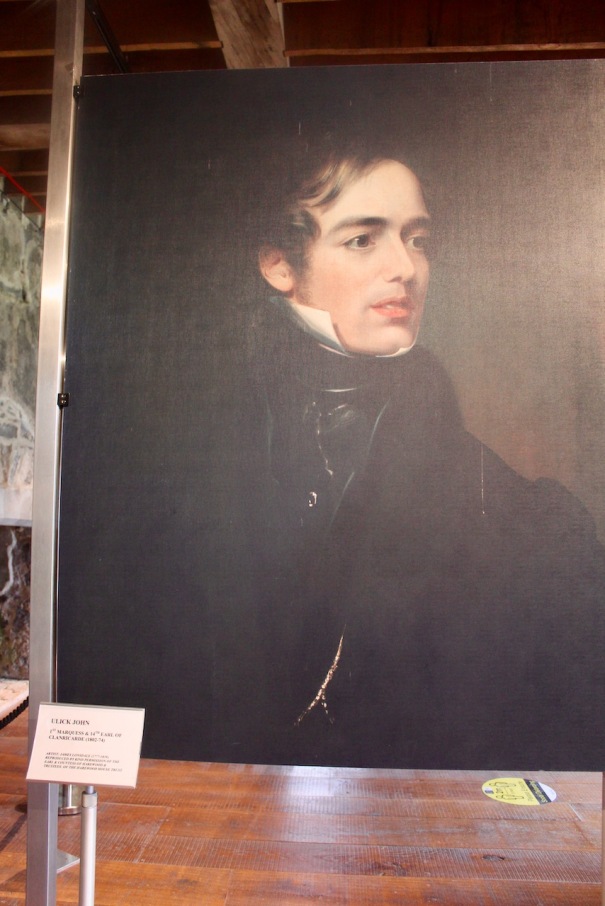
RICHARD EDMUND ST LAWRENCE (1829-1904), as 9th Earl of Cork and Orrery, KP, who married, in 1853, the Lady Elizabeth Charlotte de Burgh, daughter of Ulick John, 1st Marquess of Clanricarde, and had issue: CHARLES SPENCER CANNING, his successor; ROBERT JOHN LASCELLES, 11th Earl; Emily Harriet Catherine; Grace Elizabeth; Isabel Lettice Theodosia; Honora Janet; Dorothy Blanche.
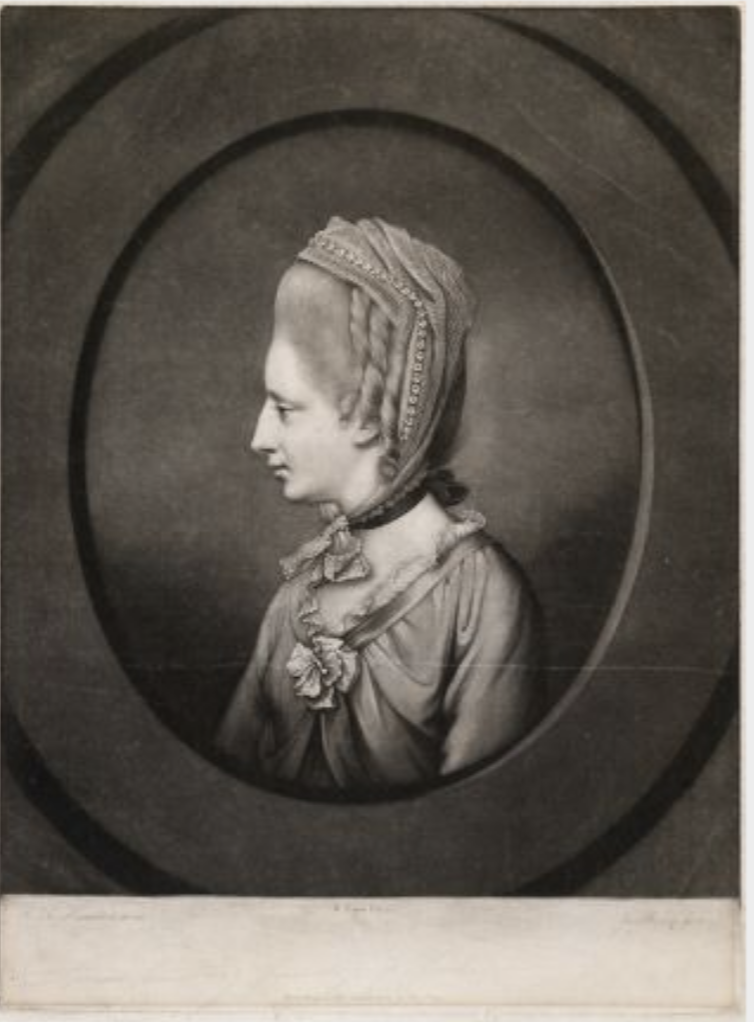

The 1st Earl of Cork’s son Francis (1623-1699) was created 1st Viscount Shannon.
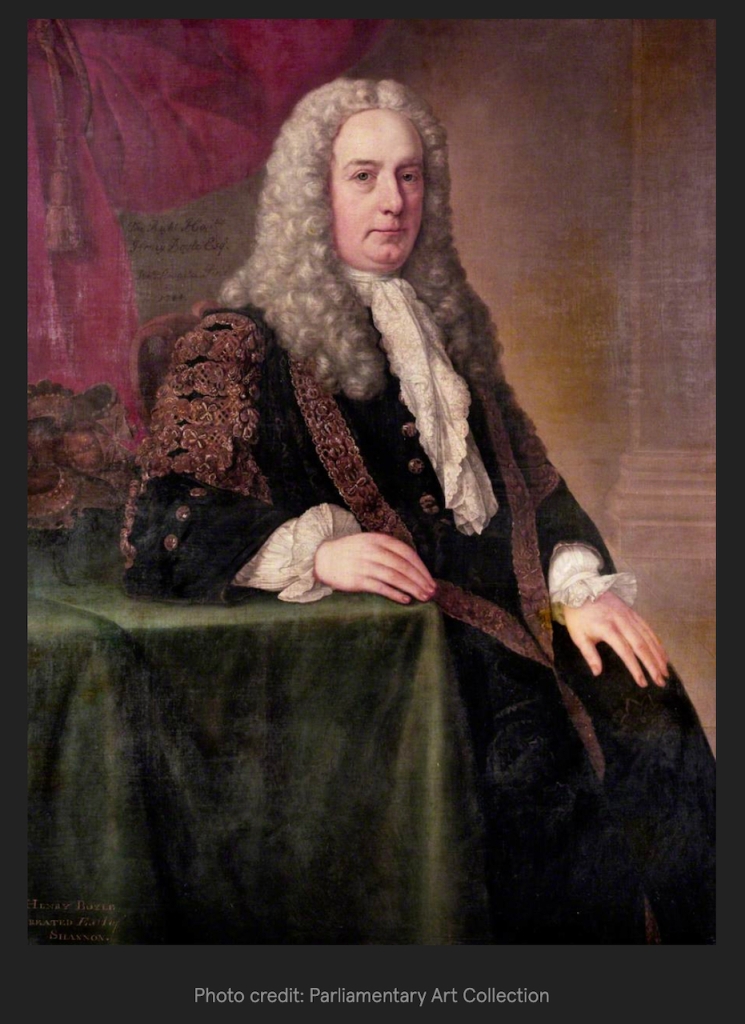
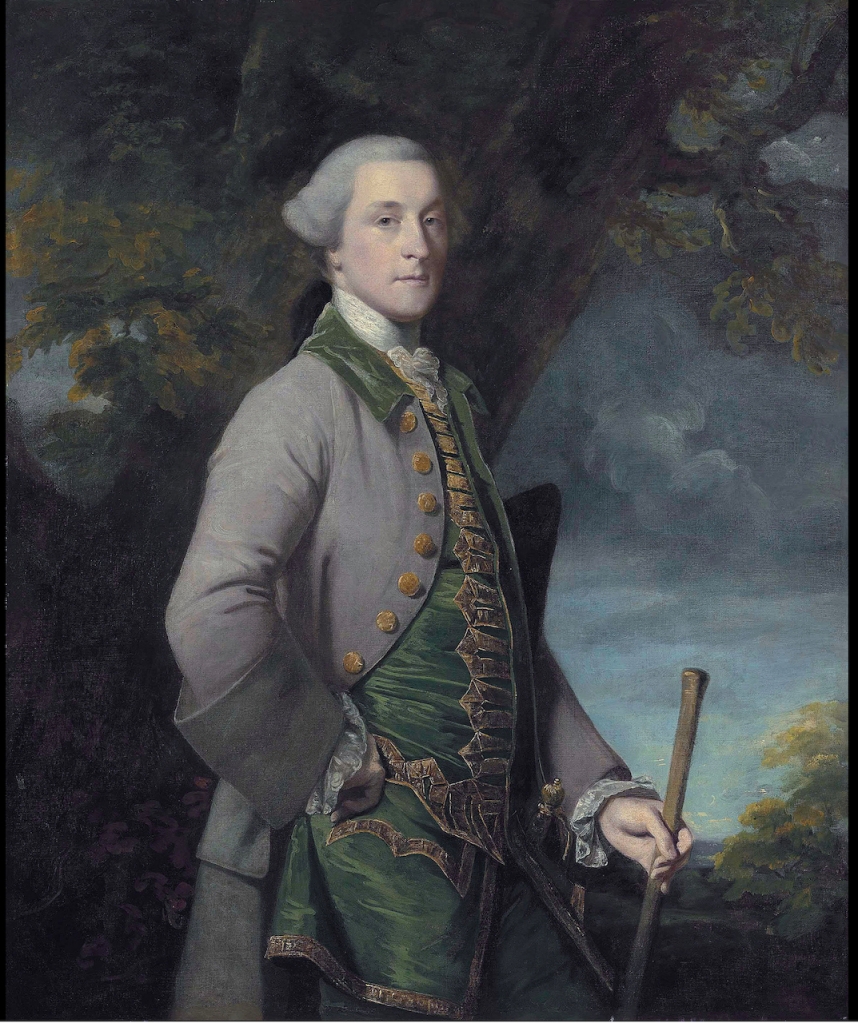
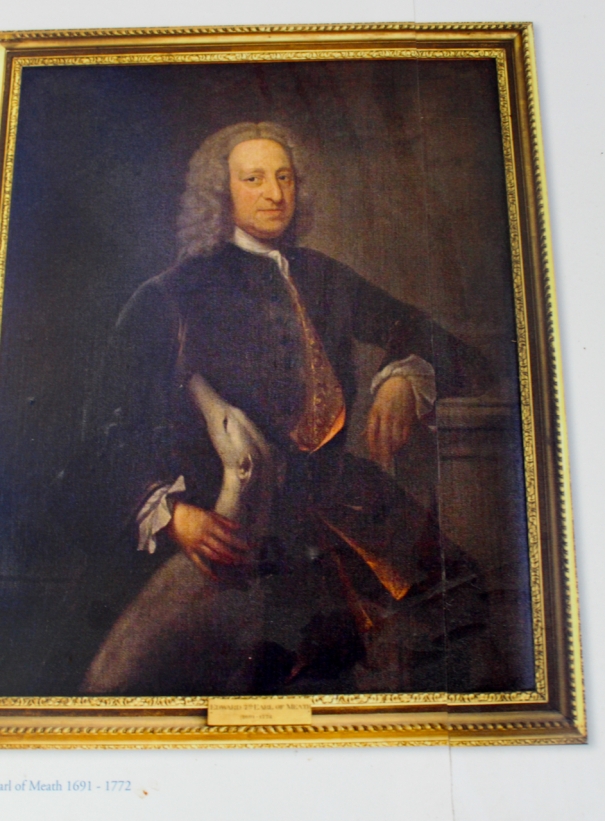
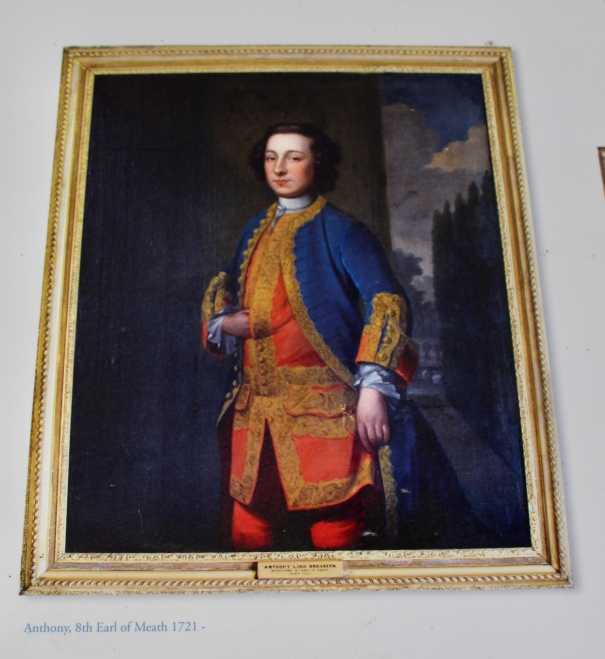
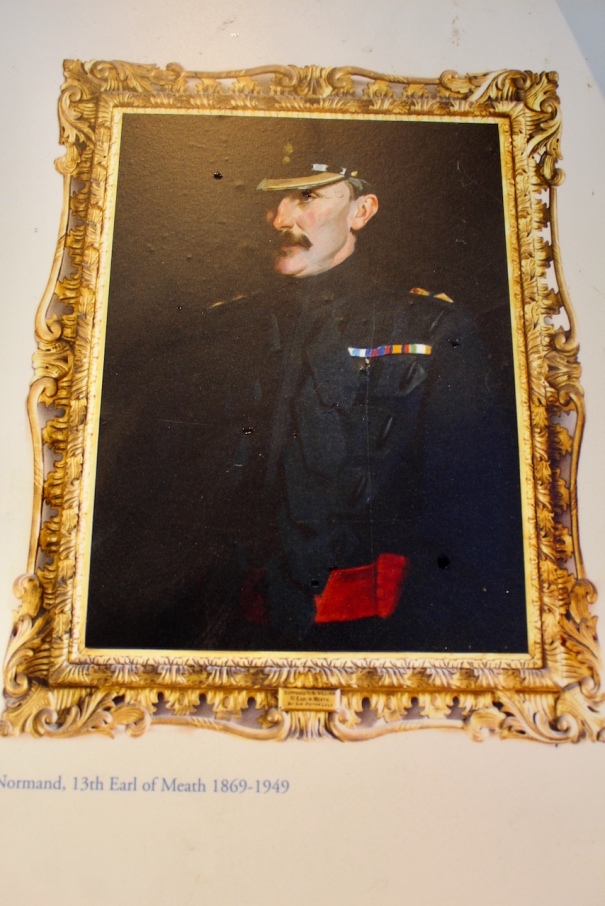
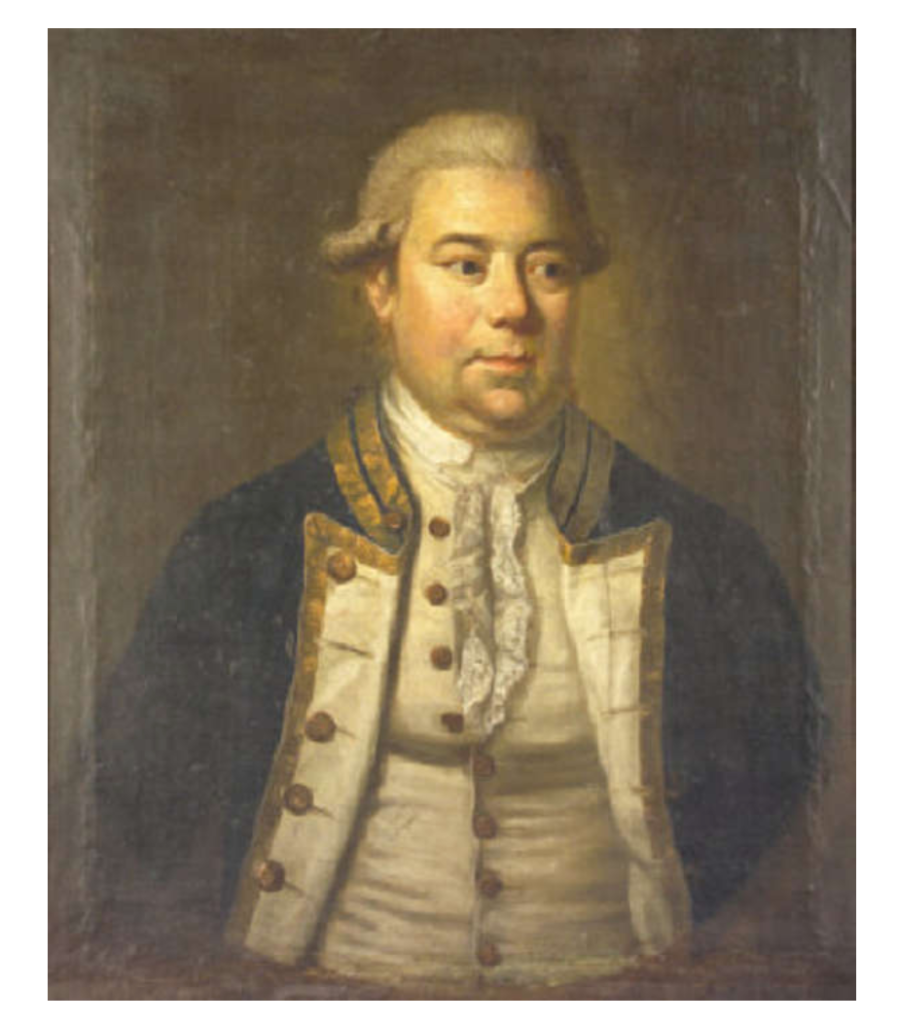
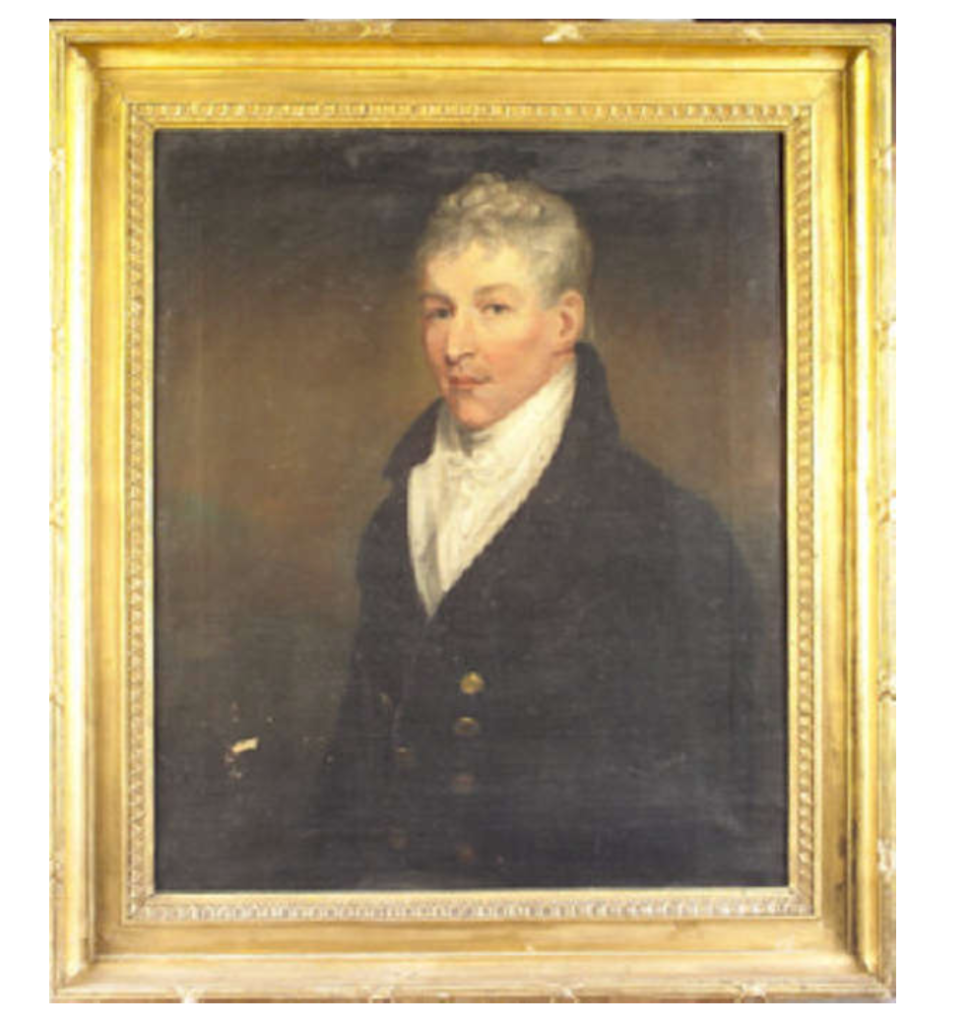
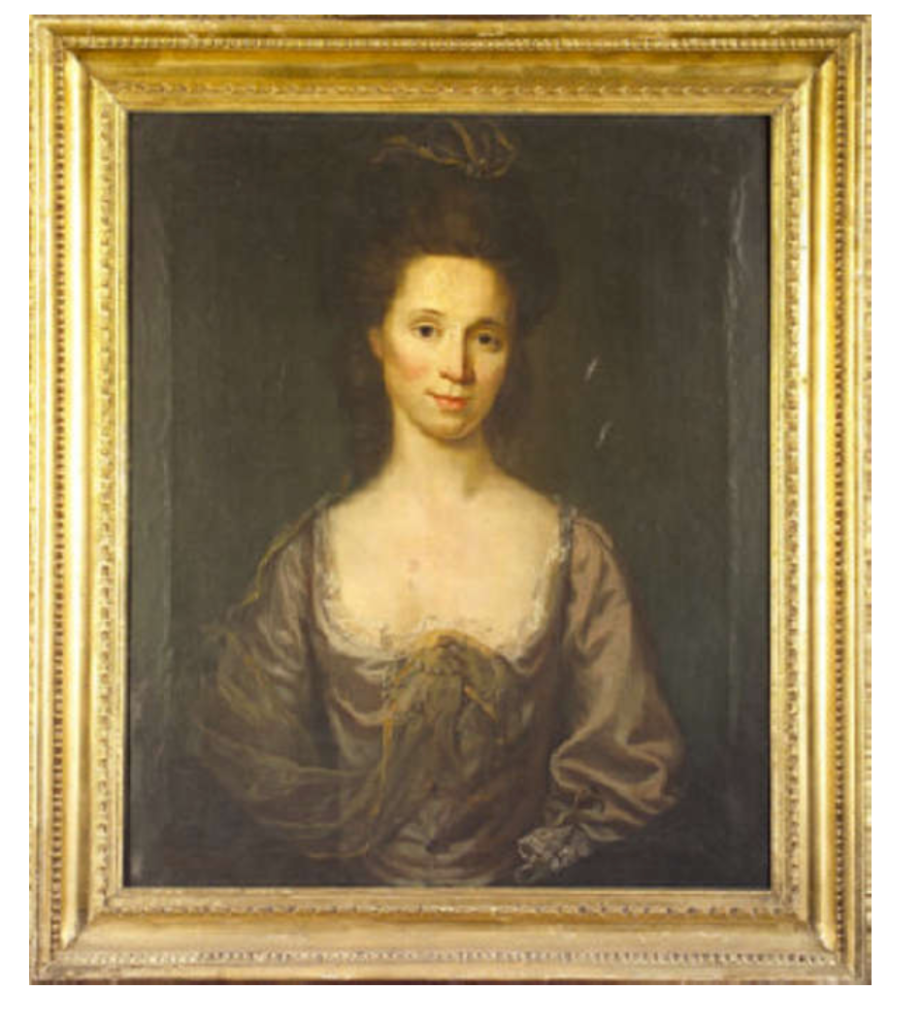
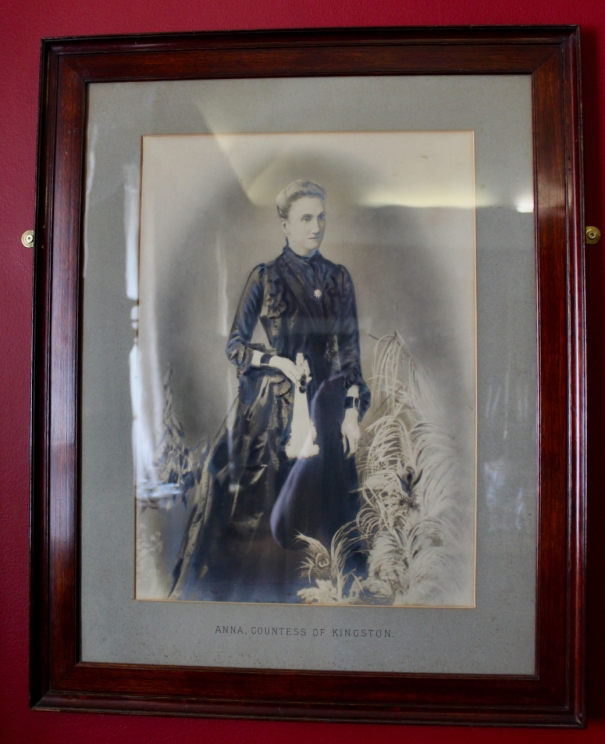
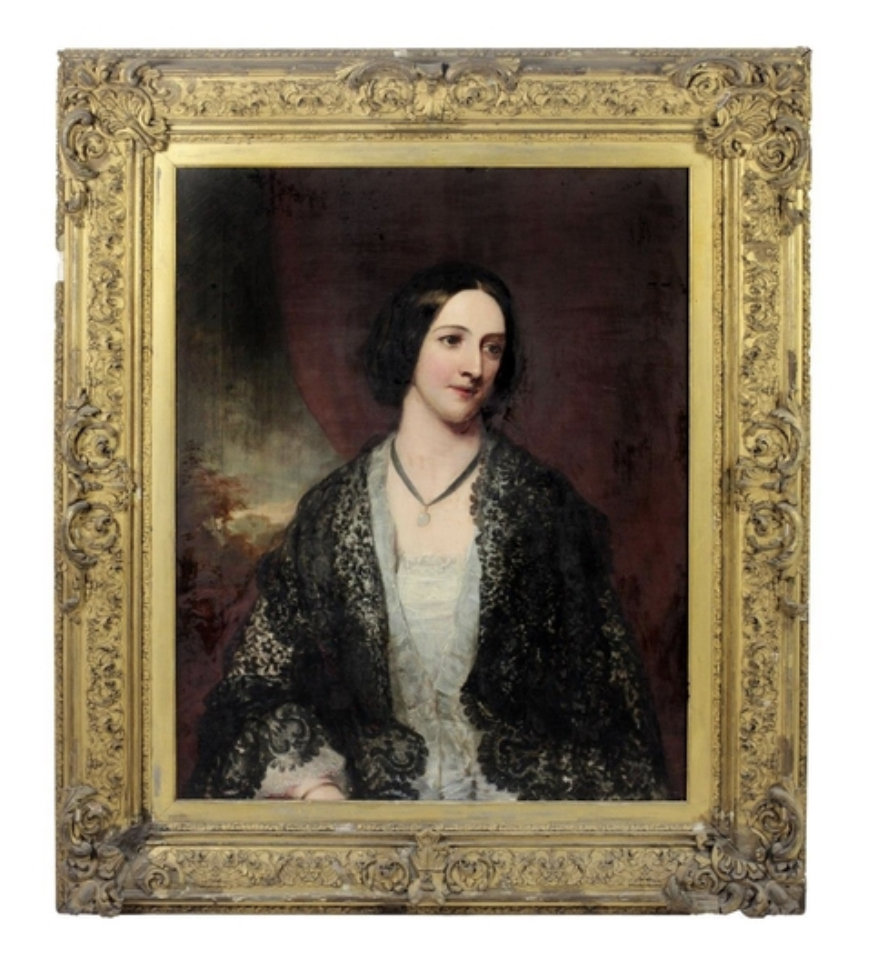
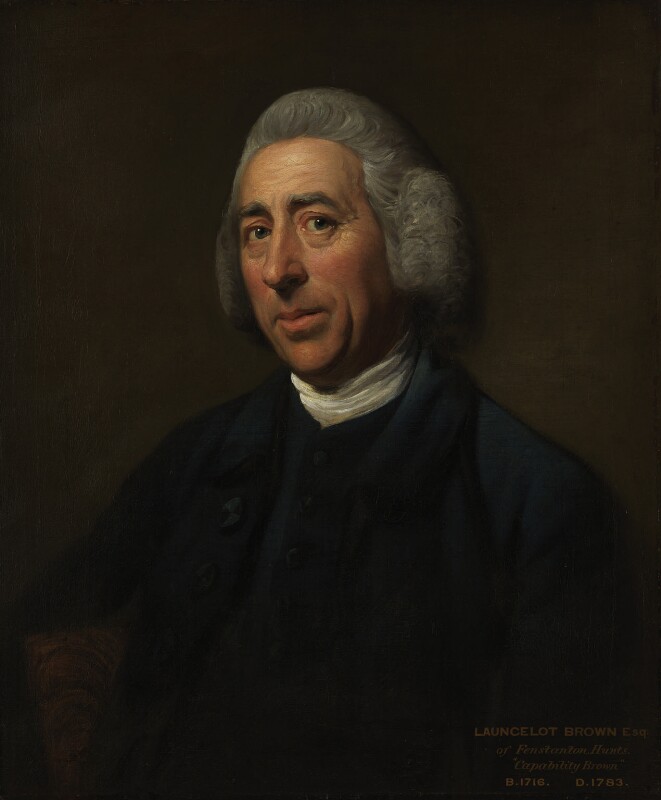
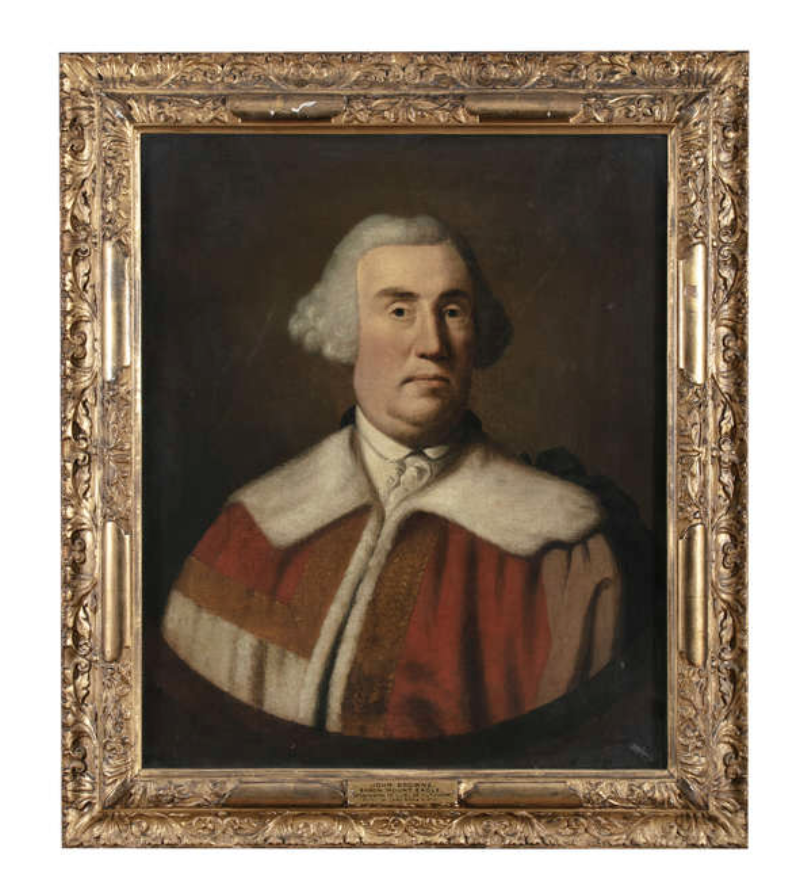

























Timothy William Ferres tells us of the Earls of Kenmare, County Kerry: http://lordbelmontinnorthernireland.blogspot.com/2013/08/kenmare-house.html
“THE RT HON SIR VALENTINE BROWNE (d 1589) in 1583, received instruction, jointly with Sir Henry Wallop, for the survey of several escheated lands in Ireland. He was subsequently sworn of the Privy Council, and represented County Sligo in parliament in 1585. In the same year, Sir Valentine purchased from Donald, Earl of Clancare, all the lands, manors, etc in counties Kerry and Cork, which had been in the possession of Teige Dermot MacCormac and Rorie Donoghoemore.
“Sir Valentine married firstly, Alice or Elizabeth, daughter of Robert Alexander, of London, and had issue, a son. He wedded secondly, Thomasine, sister of the Lord Keeper of the Great Seal, Sir Nicholas Bacon, and had further issue (with a daughter), two sons.
“Sir Valentine’s eldest surviving son, SIR NICHOLAS BROWNE, Knight, of Ross, County Kerry, who wedded Sicheley Sheela, daughter of O’Sullivan Beare, and had issue: VALENTINE, his heir;
Anne.
“Sir Nicholas died in 1616, and was succeeded by his son, VALENTINE BROWNE, High Sheriff of County Kerry, 1623, who was created a baronet in 1622, designated of Molahiffe, County Kerry.
“Sir Valentine, after his father’s decease, presented a petition to JAMES I, praying an abatement of the yearly rent reserved on the estate which he held from the Crown, as an undertaker, at the annual sum of £113 6s 8d, in regard of the small profit he made of it, being set out in the most barren and remote part of County Kerry; which request was complied with, and he received a confirmation, by patent, of all his lands at a reduced rent.
“He married Elizabeth, fifth daughter of Gerald, Earl of Kildare [I’m not sure if this – JWB], and was succeeded by his grandson, THE RT HON SIR VALENTINE BROWNE, 3rd Baronet (1638-94); who was sworn of the Privy Council of JAMES II, and created by that monarch, subsequently to his abdication, in 1689, Baron Castlerosse and Viscount Kenmare.
“His lordship, who was Colonel of Infantry in the army of JAMES II, forfeited his estates by his inviolable fidelity to that unfortunate monarch. He wedded Jane, only daughter and heir of Sir Nicholas Plunket [of Balrath], and niece of Lucas, Earl of Fingall, and had five sons and four daughters.
“The 1st Viscount was succeeded by his eldest son, SIR NICHOLAS BROWNE, 4th Baronet (called 2nd Viscount); an officer of rank in the service of JAMES II, and attainted in consequence, who espoused, in 1664, Helen, eldest daughter and co-heir of Thomas Brown, by whom he obtained a very considerable fortune, but which, with his own estates, became forfeited for his life. The crown, however, allowed his lady a rent-charge of £400 per year for the maintenance of herself and her children. Sir Nicholas died in 1720, leaving four daughters and his son and successor,
“SIR VALENTINE BROWNE, 5th Baronet (called 3rd Viscount) (1695-1736), who continued outlawed by the attainder of his father and grandfather. [The 4th Baronet’s daughter Frances married Edward Herbert (1693-1770 of Muckross, County Kerry]
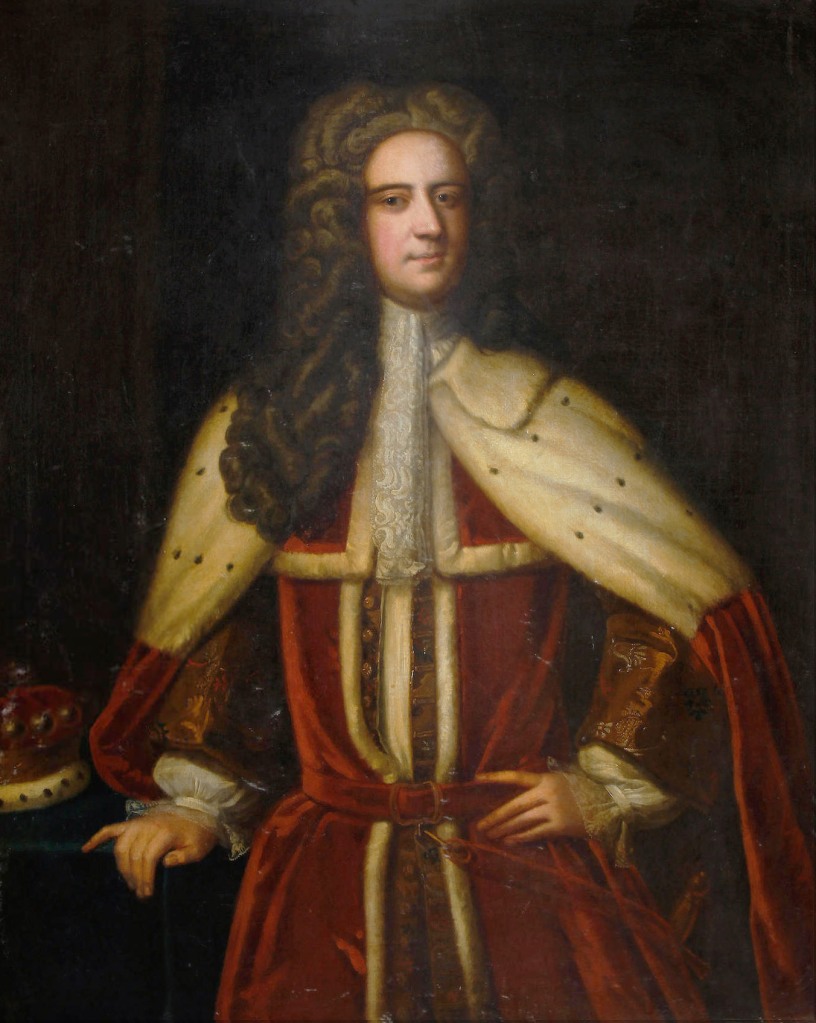

“He married, in 1720, Honora, second daughter of Colonel Thomas Butler [of Kilcash (1671-1738)], and great-grandniece of James, Duke of Ormonde, by whom he had issue, Thomas, his successor, and two daughters.
“Sir Valentine espoused secondly, in 1735, Mary, Dowager Countess of Fingall, by whom he left a posthumous daughter, Mary Frances. [Mary née Fitzgerald (1716-1741/2) was the daughter of Maurice Fitzgerald, 5th Baronet of Castle Ishen, County Cork; Mary was first married to Justin Plunkett, 5th Earl of Fingall. She married thirdly John Bellew, 4th Baron Bellew of Duleek]
“He was succeeded by his only son, SIR THOMAS BROWNE, 6th Baronet (called 4th Viscount) (1726-95), who wedded, in 1750, Anne, only daughter of Thomas Cooke, of Painstown, County Carlow, by whom he had a son and a daughter, Catherine, married to Count de Durfort-Civrac.
“He was succeeded by his son, SIR VALENTINE BROWNE, 7th Baronet (called 5th Viscount) (1754-1812), who was created (the viscountcy of JAMES II never having been acknowledged in law), in 1798, Baron Castlerosse and Viscount Kenmare.
“His lordship was further advanced to the dignity of an earldom, in 1800, as EARL OF KENMARE.”
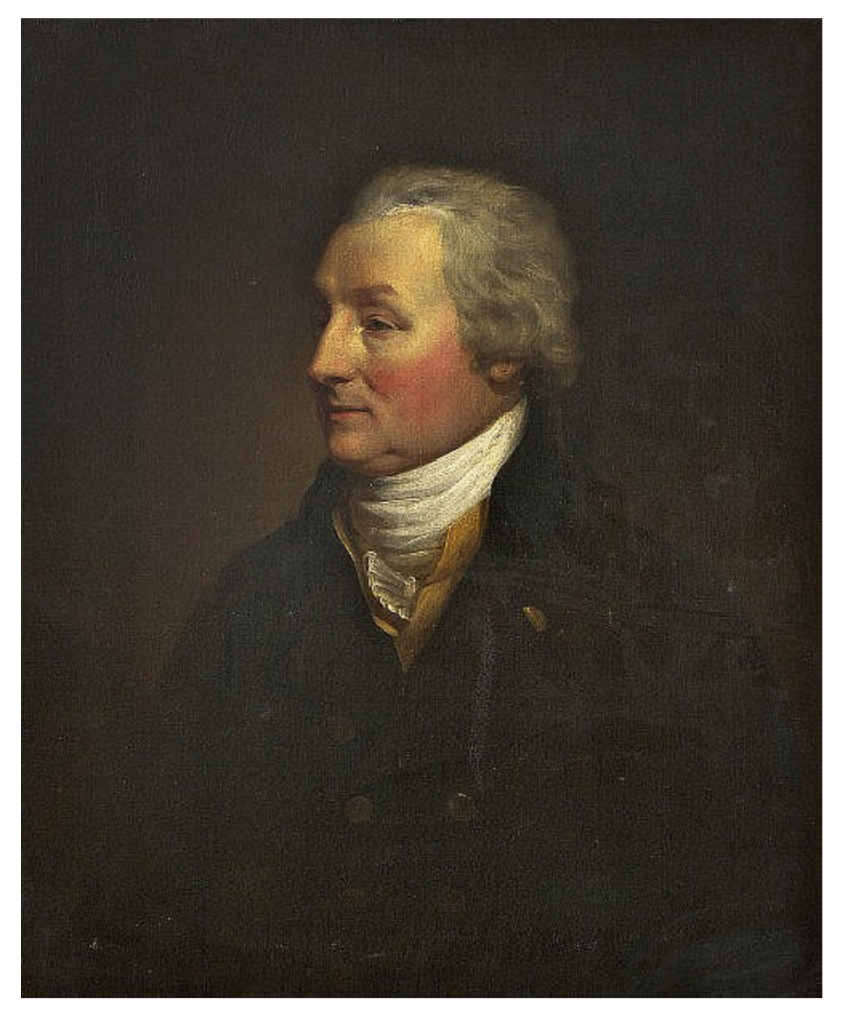

“He married firstly, in 1777, Charlotte, daughter of Henry, 11th Viscount Dillon [of Costello-Gallin], and had an only daughter, Charlotte. [She married George Goold, 2nd Bt of Old Court, Co. Cork.]
“His lordship wedded secondly, in 1785, Mary, eldest daughter of Michael Aylmer, of Lyons, County Kildare, and had issue,
VALENTINE (1788-1853) his successor as 2nd Earl;
Thomas (1789-1871) who became 3rd Earl;
William;
Michael;
Marianne; Frances.
“His lordship was succeeded by his eldest son, VALENTINE, 2nd Earl (1788-1853), PC, who espoused, in 1816, Augusta, daughter of Sir Robert Wilmot, 2nd Baronet, though the marriage was without issue, when the family honours devolved upon his brother,
“THOMAS, 3rd Earl (1789-1871), who married, in 1822, Catherine, daughter of Edmond O’Callaghan [d. 1791. Another daughter of Edmond O’Callaghan, Ellen, married James John Bagot of Castle Bagot, Rathcoole. His daughter Elizabeth married Gerald Dease of Turbotstown, a Section 482 property].
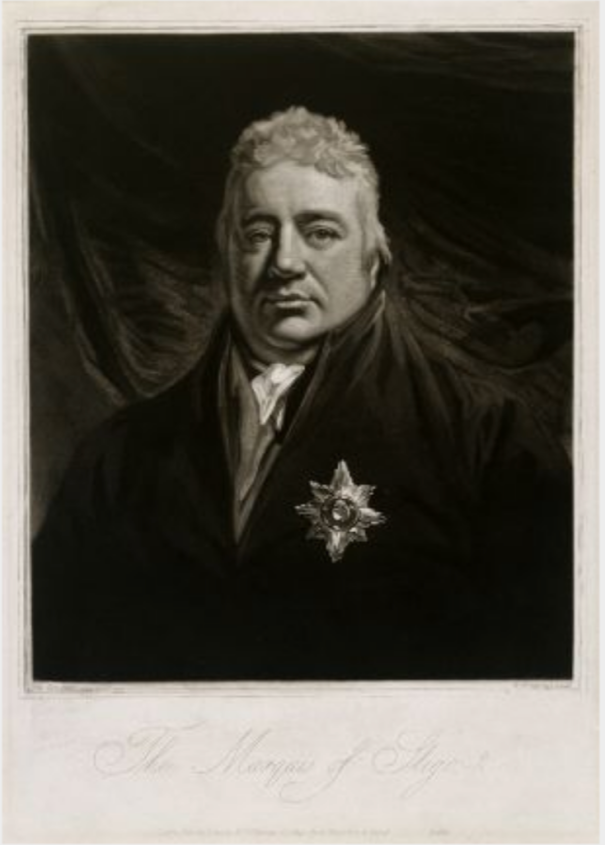
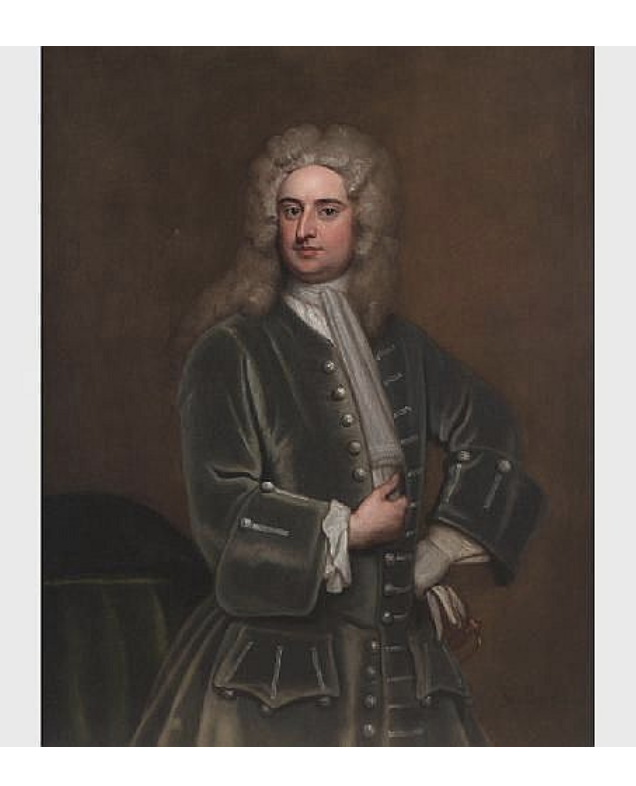
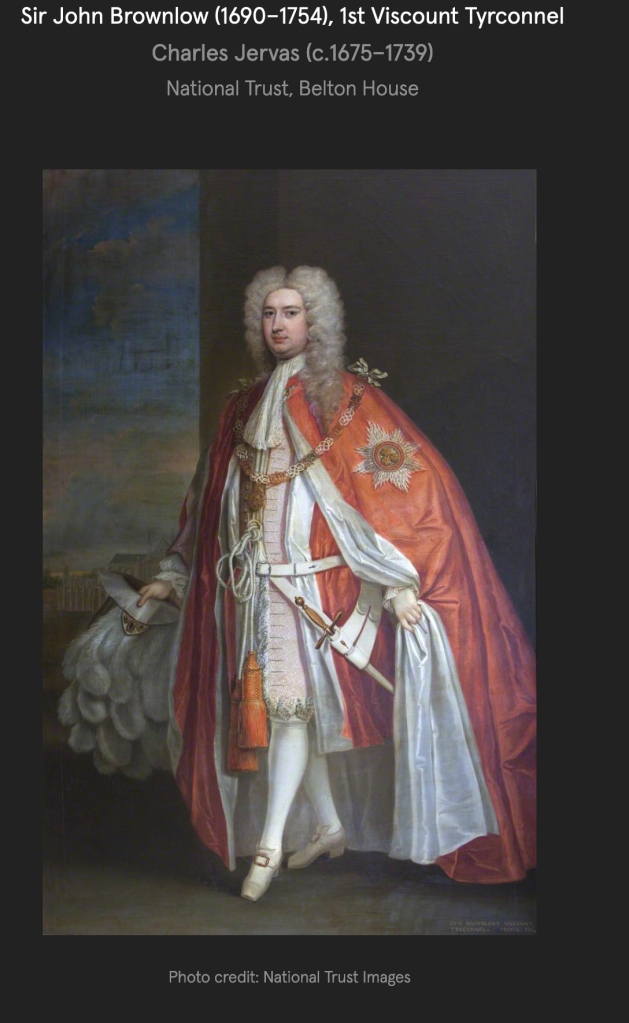
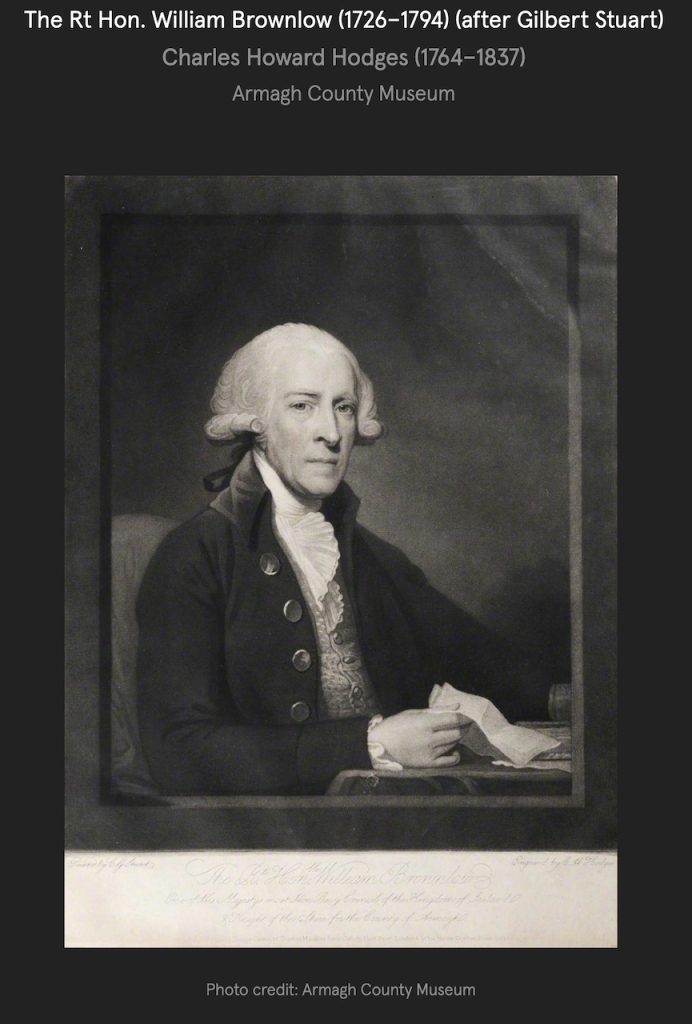
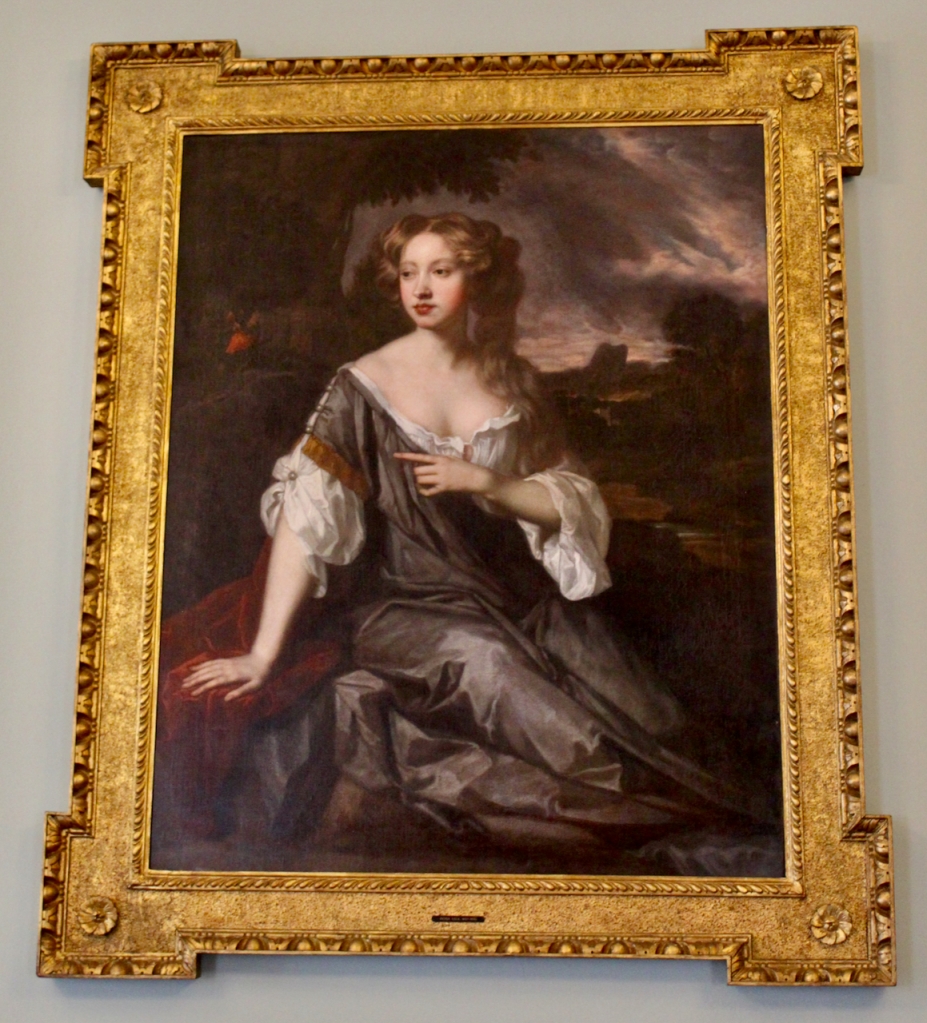
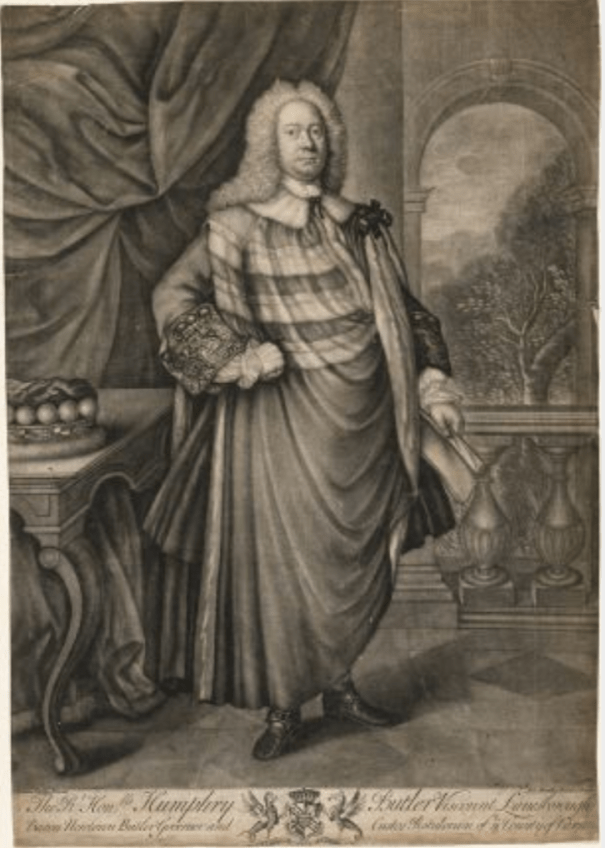























The Butlers of Ormonde
Piers Butler (d. 1539) 8th Earl of Ormonde married Margaret Fitzgerald, daughter of Gerald Fitzgerald 8th Earl of Kildare.
They had daughters Ellen (d. 1597) who married Donough O’Brien (d. 1553) 1st Earl of Thomond; Margaret married Barnaby FitzPatrick, 1st Baron of Upper Ossory; Joan married James Butler, 10th Baron Dunboyne; Eleanor married Thomas Butler 1st Baron Caher; Katherine married Richard Power, 1st Baron le Power and Coroghmore first and secondly, James FitzJohn FitzGerald, 13th Earl of Desmond; Ellice married Gerald FitzJohn FitzGerald (d. 1553, father of 1st Viscount Decies).
They had sons John Butler (d. 1570) who lived in Kilcash, County Tipperary and was father of Walter (1569-1632) 11th Earl of Ormond; Richard Butler (d. 1571) 1st Viscount Mountgarret; Thomas who died in 1532; and James Butler (d. 1546) 9th Earl of Ormonde.
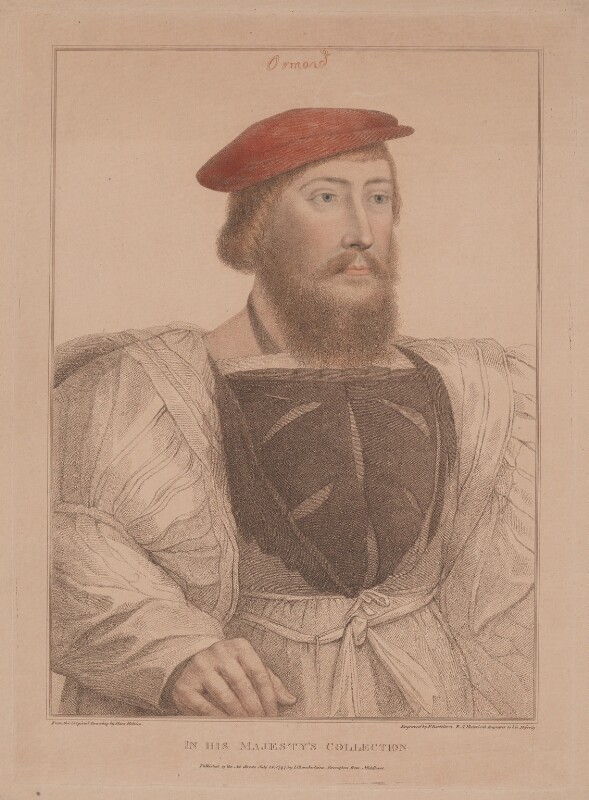

James Butler (d. 1546) 9th Earl of Ormonde married Joan Fitzgerald, daughter of James FitzMaurice FitzGerald, 10th Earl of Desmond. She gave birth to Thomas Butler (1531-1614) who became 10th Earl of Ormond.
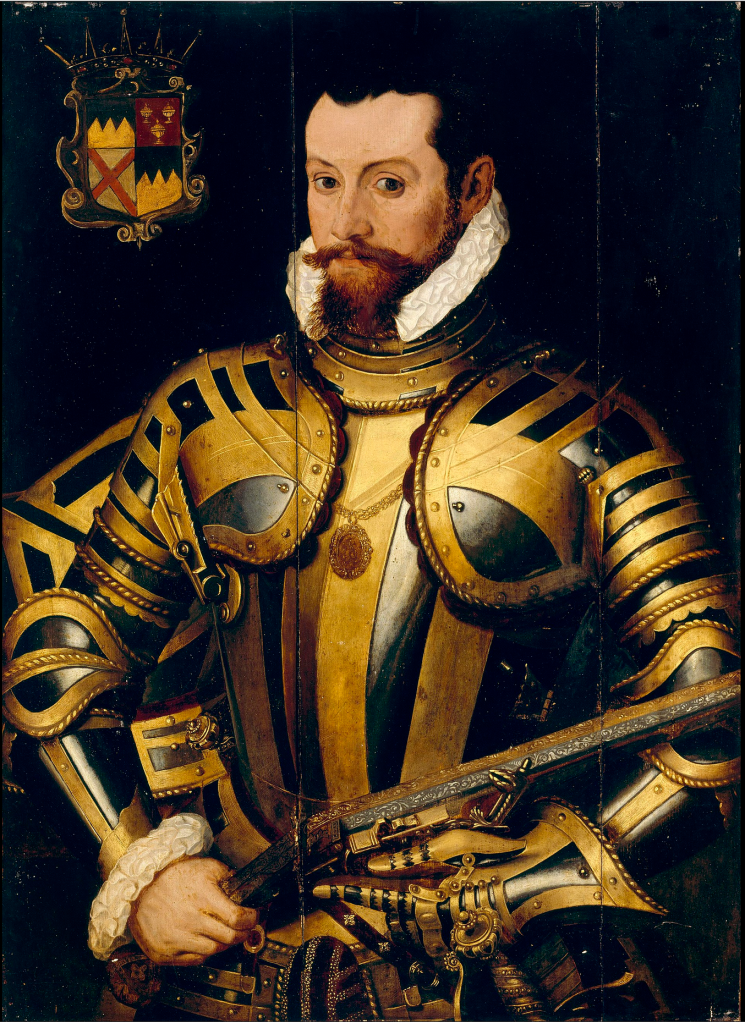

The 9th Earl also had a son Edmond (d. 1602) who lived in Cloughgrenan, County Carlow, who gave rise to the Baronets of Cloughgrenan.
The 10th Earl of Ormond, “Black Tom,” had no direct heir so the Earldom passed to his nephew, Walter, a son of Sir John Butler (d. 1570) of Kilcash. Unlike his uncle, who had been raised at Court and thus reared a Protestant, Walter the 11th Earl of Ormond was a Catholic. See my entry about the Ormond Castle at Carrick-on-Suir for more on “Black Tom.” https://irishhistorichouses.com/2022/06/26/opw-sites-in-munster-clare-limerick-and-tipperary/
Walter Butler’s claim to the family estates was blocked by James I. The latter orchestrated the marriage of Black Tom’s daughter and heiress Elizabeth to a Scottish favourite Richard Preston, Baron Dingwall. The King gave Preston the title Earl of Desmond (after the Fitzgeralds lost the title, due to their Desmond Rebellion), and awarded his wife most of the Ormond estate, thus depriving Walter of his inheritance. Walter refused to submit and was imprisoned for eight years in the Fleet, London. He was released 1625. Walter’s nine-year-old grandson, James, became the heir to the titles but not the estates.
James (1610-1688) 12th Earl of Ormond (later 1st Duke of Ormond) was the son of Thomas Butler (d. 1619) Viscount Thurles, and Elizabeth Poyntz. Following his father’s death in 1619, 9-year-old James became direct heir to the Ormond titles. He was made a royal ward and was educated at Lambeth Palace under the tutelage of George Abbot, Archbishop of Canterbury.
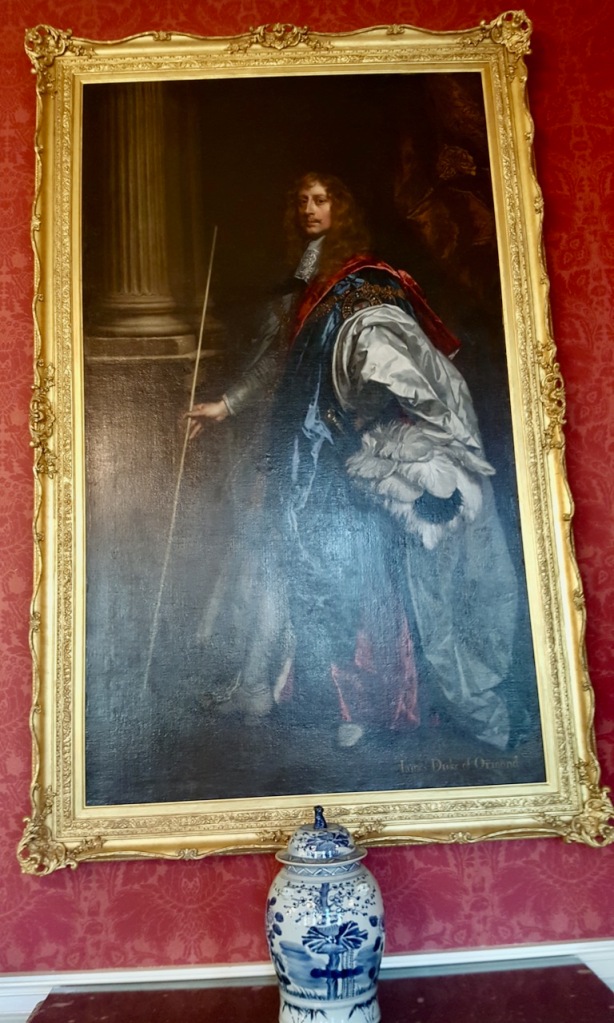
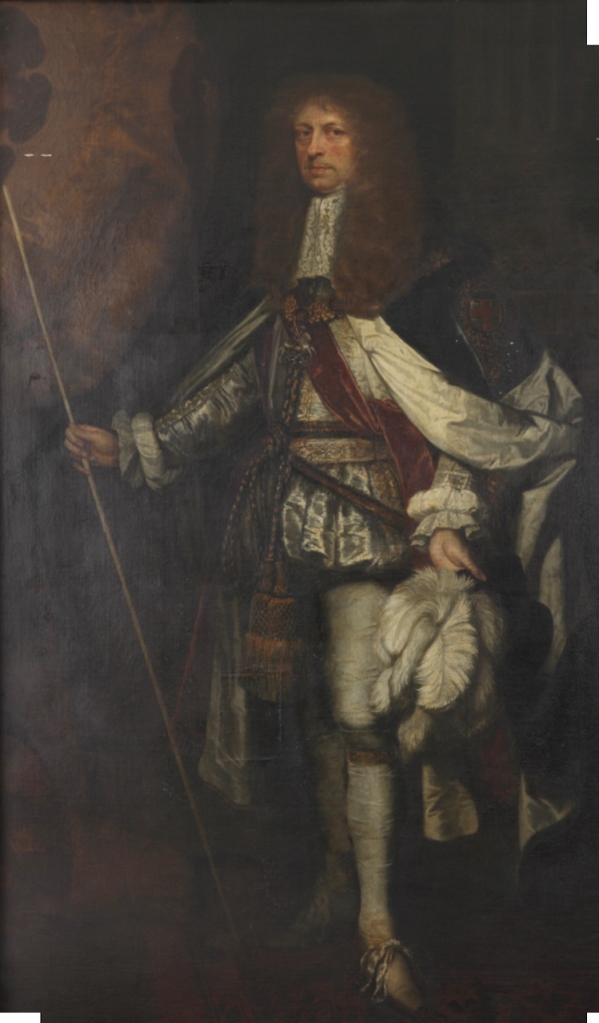


Another son of Thomas Butler (d. 1619) Viscount Thurles, and Elizabeth Poyntz was Richard Butler (d. 1701) of Kilcash, County Tipperary.
In order to reunite the Ormond title with the estates, plans were made for a marriage between James and the daughter of the Prestons, Elizabeth, to resolve the inheritance issue. In 1629 James married his cousin Elizabeth Preston and reunited the Ormond estates.
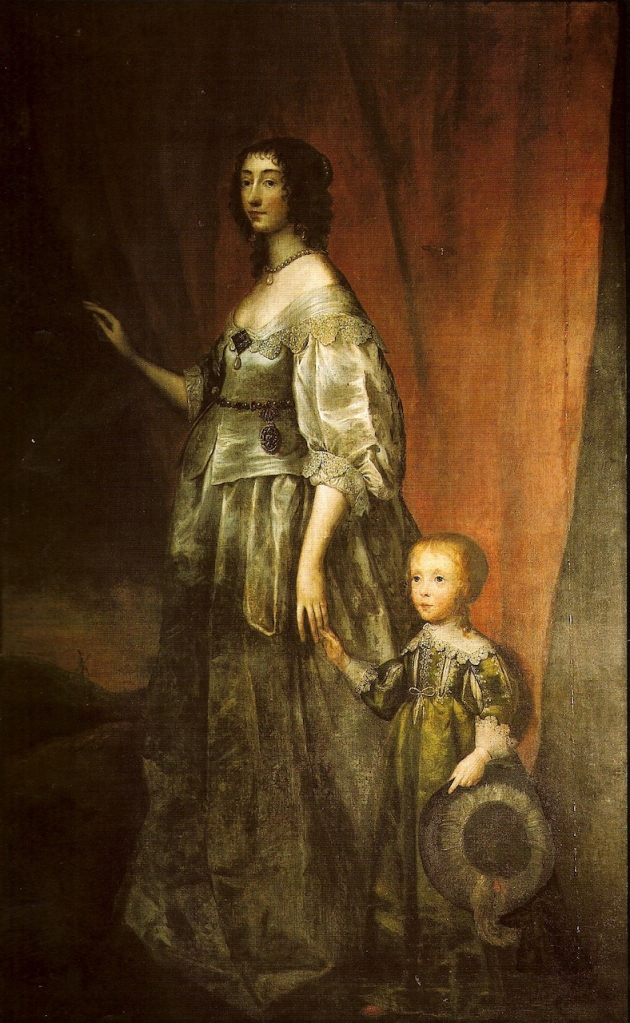
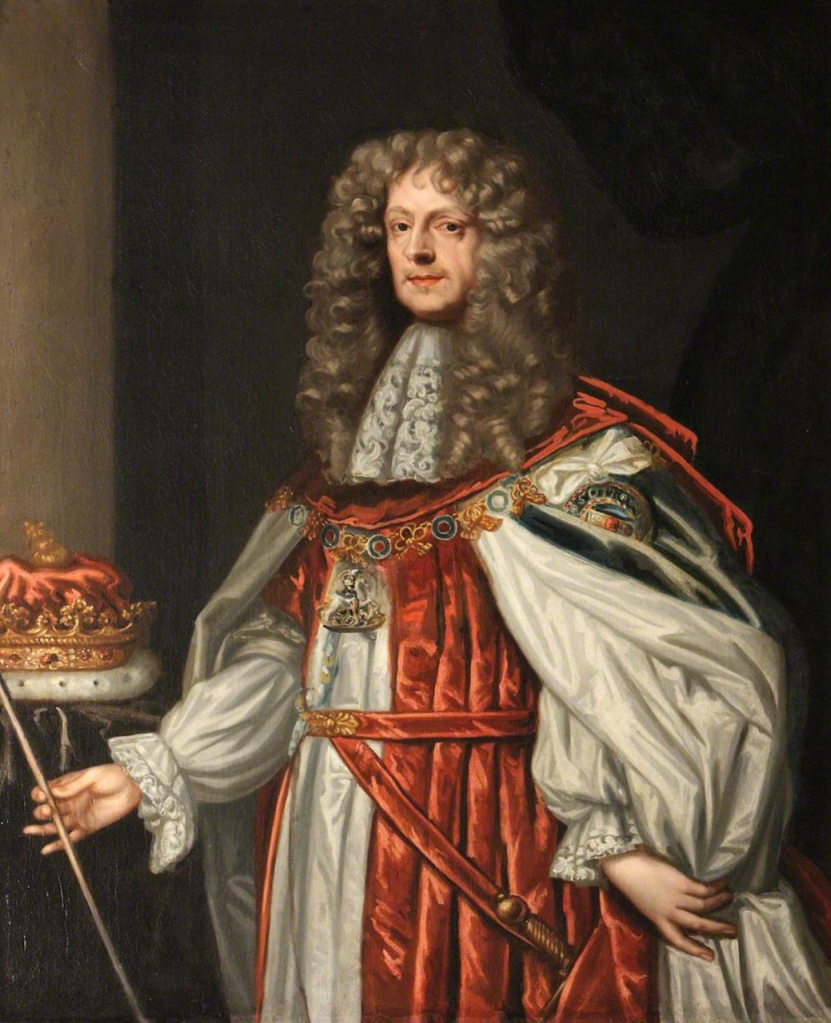




The 1st Duke of Ormond had three sons: Thomas (1634-1680), 6th Earl of Ossory; Richard (1639-1686), 1st and last Earl of Arran; and John (1634-1677), 1st and last Earl of Gowran. He had two daughters, Elizabeth (1640-1665) and Mary (1646-1710). Mary married William Cavendish, 1st Duke of Devonshire and Elizabeth, the 2nd Earl of Chesterfield.

Thomas Butler, 6th Earl of Ossory, (1634-1680) was born at Kilkenny Castle, the eldest son of James Butler, 1st Duke of Ormonde and Lady Elizabeth Preston.
His early years were spent in Ireland and France. He was an accomplished athlete and a good scholar. In 1661 Butler became a member of both the English and Irish houses of Commons, representing Bristol in the former and Dublin University in the latter House. In 1665 he was appointed lieutenant-general of the army in Ireland and in 1666 was created an English peer as Lord Butler.
Having proven himself as an expert military strategist, and whilst visiting France in 1672, he rejected the liberal offers made by Louis XIV to induce him to enter the service of France, and returning to England he added to his high reputation by his conduct during the Battle of Texel in August 1673. From 1677 until 1679, he served alongside his father as a Lord of the Admiralty.
The earl was chosen to William, Prince of Orange, and in 1677 he joined the allied army in the Netherlands, commanding the British section and winning great fame at the siege of Mons in 1678. He acted as deputy for his father, who was lord-lieutenant of Ireland, and in parliament he defended Ormonde’s Irish administration with great vigour. In 1680 he was appointed governor of English Tangier, but his death prevented him from taking up his new duties.
Ossory had eleven children, including James Butler who became the 2nd Duke of Ormonde in 1688. A Portrait of Thomas Butler by Lely, painted in 1678 is in the National Portrait Gallery, London and a portrait by the same hand as his father, the 1st Duke is in the ownership of the National Trust at Kedleston Hall.
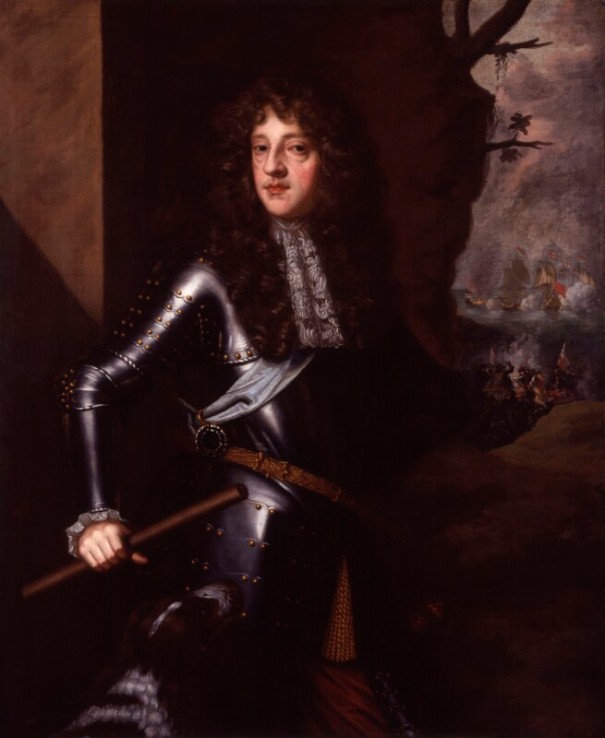
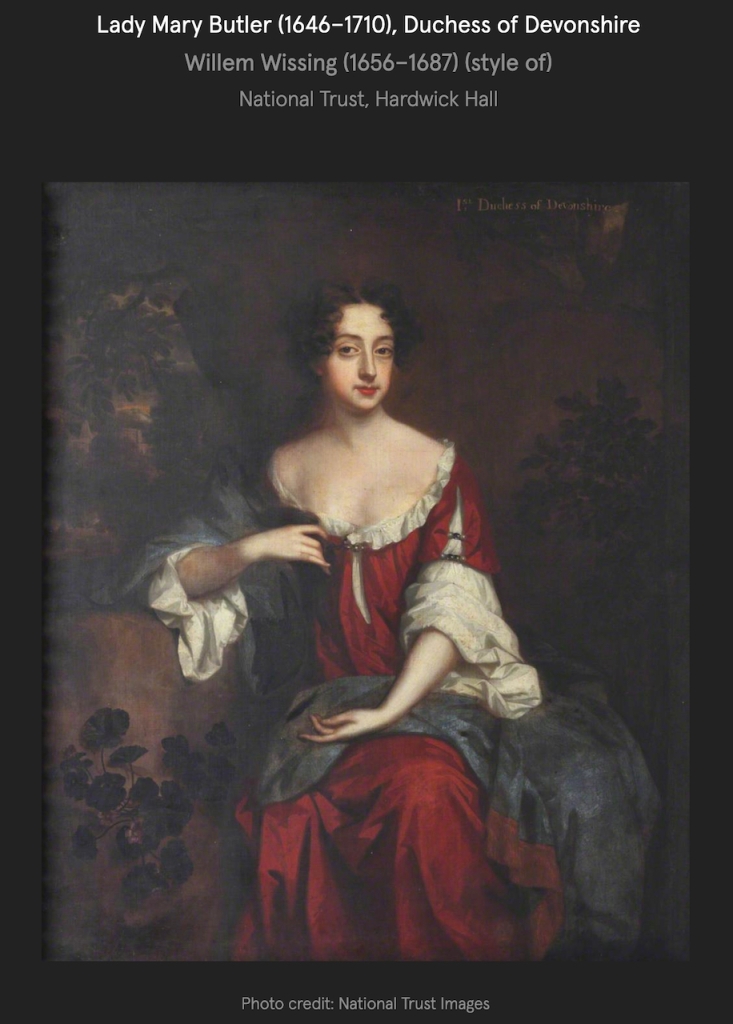





Thomas Butler (1634-1680) 6th Earl of Ossory and his wife Amelia of Nassau were the parents of James Butler (1665-1745) 2nd Duke of Ormonde. Another son was Lt.-Gen. Charles Butler, 1st Earl of Arran (1671-1758).
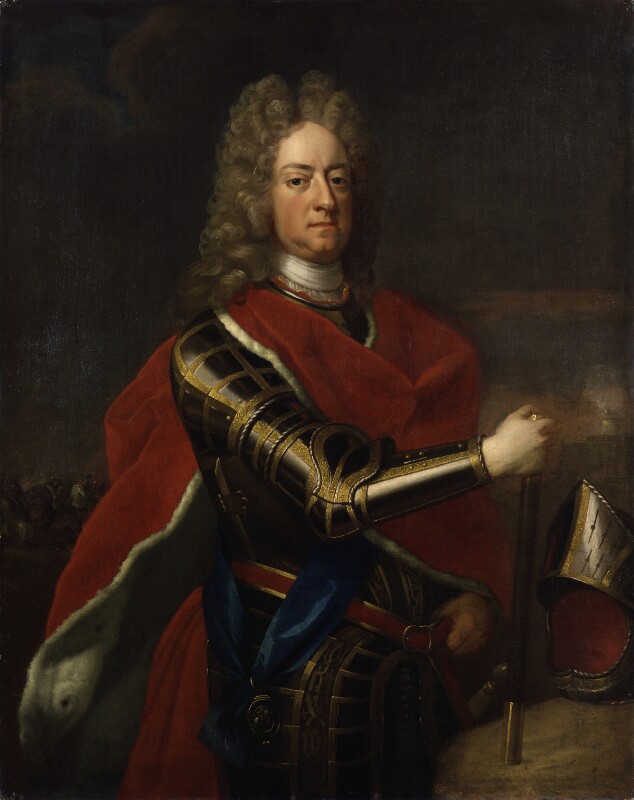
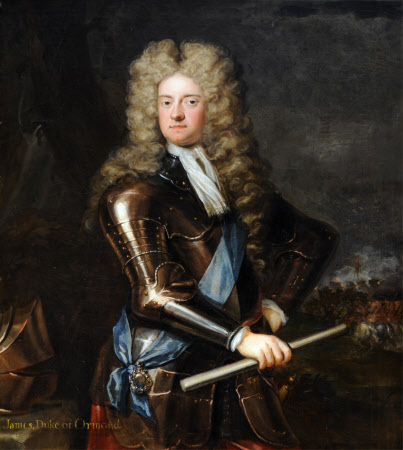



James Butler (1665-1745) 2nd Duke of Ormond married, first, Anne Hyde, and second, Mary Somerset.


James the 2nd Duke had no son, so the title passed to his brother Charles Butler (1671-1758) 1st Earl of Arran. He was enabled by an Act of Parliament in 1721 to recover his brother’s forfeited estates, but the dukedom ended with him. He was, however, also the 14th Earl of Ormonde and this title continued. He had no children, however, so the title passed to a cousin.
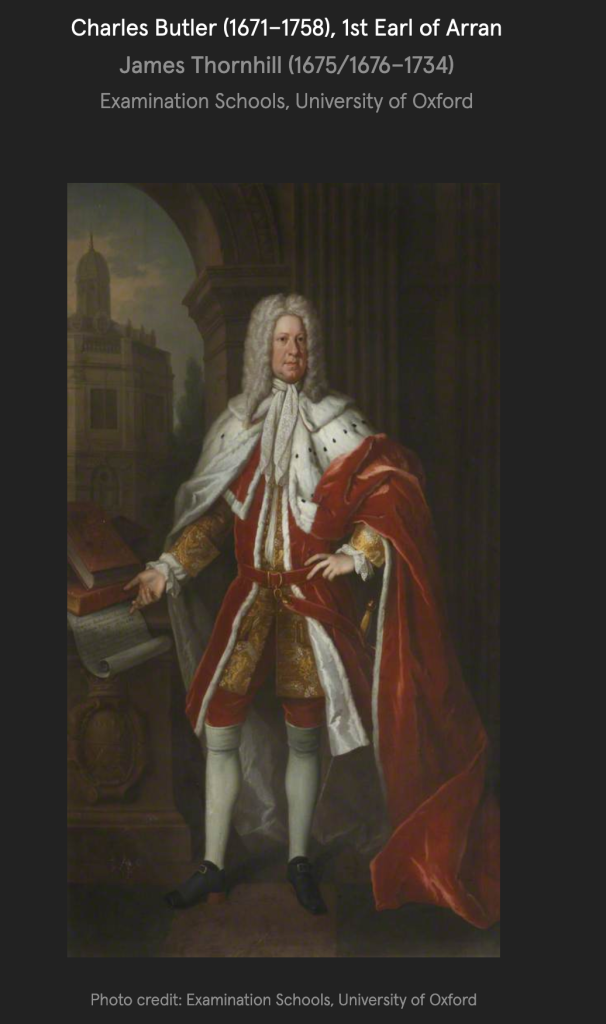

John Butler (d. 1766) of Kilcash and Garryricken became 15th Earl of Ormonde. He was a descendant of Walter Butler the 11th Earl.
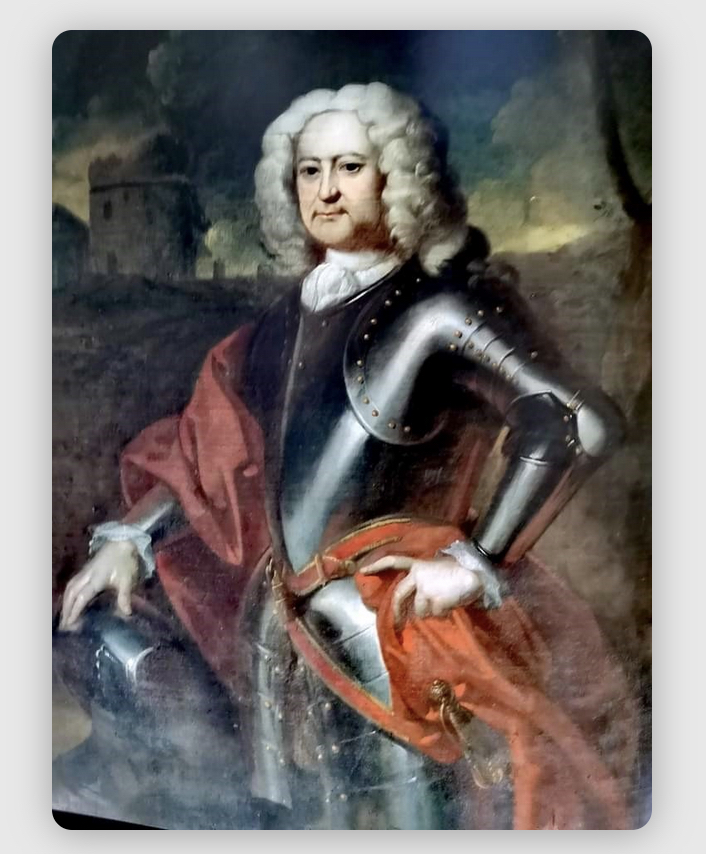

Richard Butler (d. 1701) of Kilcash, County Tipperary was a younger brother of James the 1st Duke of Ormond. There is a castle ruin still in Kilcash, under the protection of the Office of Public Works but not open to the public. His son was Walter Butler of Garryricken (1633-1700). Walter had sons Christopher (the Catholic Archbishop) and Thomas (d. 1738).

The 15th Earl had no children so the title then passed to a cousin, Walter Butler (1703-1783), 16th Earl, another of the Garryricken branch, who also became the 9th Earl of Ossory. He took up residence at Kilkenny Castle. Walter, a Catholic, was unable to exercise a political role.
John Butler 17th Earl of Ormonde, nicknamed “Jack of the Castle,” was son of the 16th Earl. He in turn was father of Walter Butler (1770-1820) 18th Earl of Ormonde, 1st And Last Marquess of Ormonde (of the 2nd creation).


His younger brother James Wandesford Butler (1777-1838) was later created 1st Marquess of Ormonde of the third creation, 19th Earl of Ormonde. He was the father of John Butler (1808-1854) 2nd Marquess (3rd creation) and 20th Earl of Ormonde, who was the father of James Edward William Theobald Butler (1844-1919) 3rd Marquess of Ormonde and also James Arthur Wellington Foley Butler (d. 1943) 4th Marquess of Ormonde, who was father of 5th and 6th Marquesses.








































































