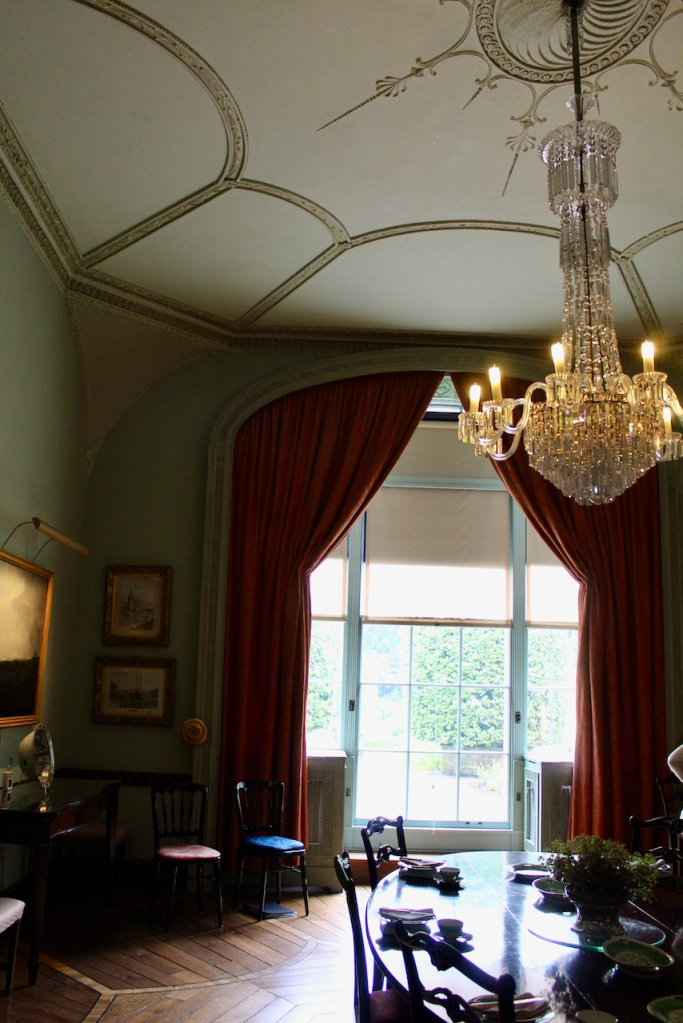
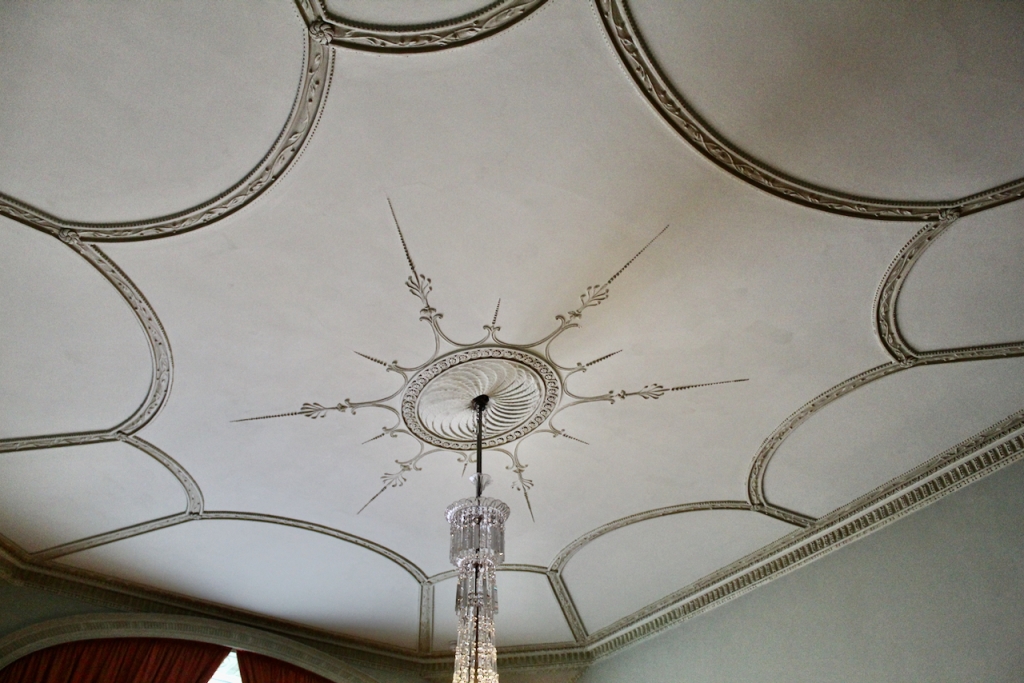
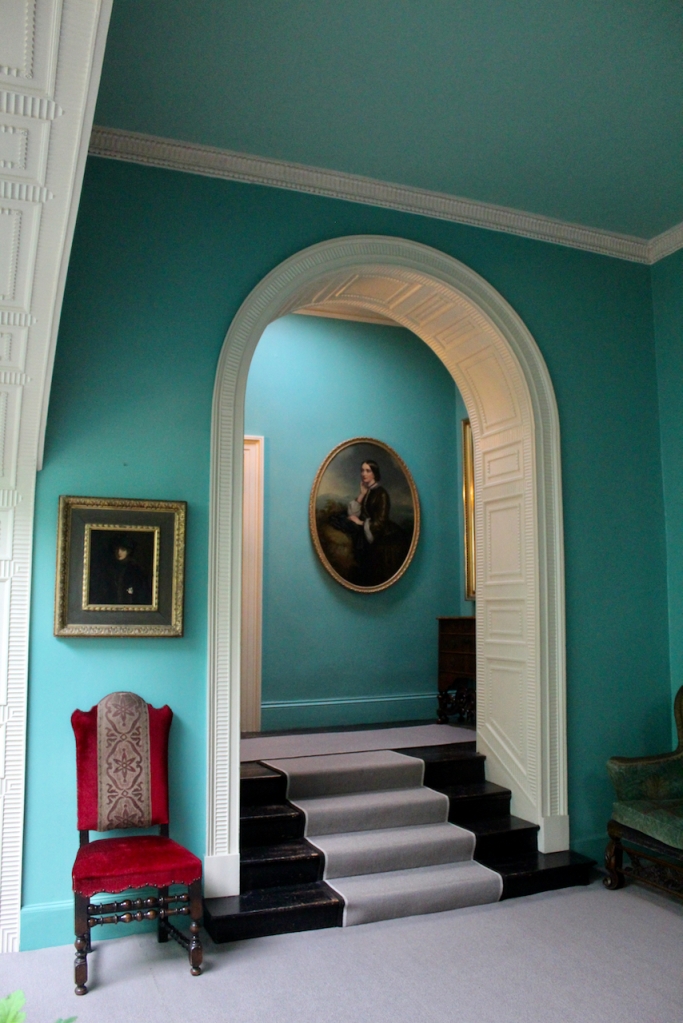
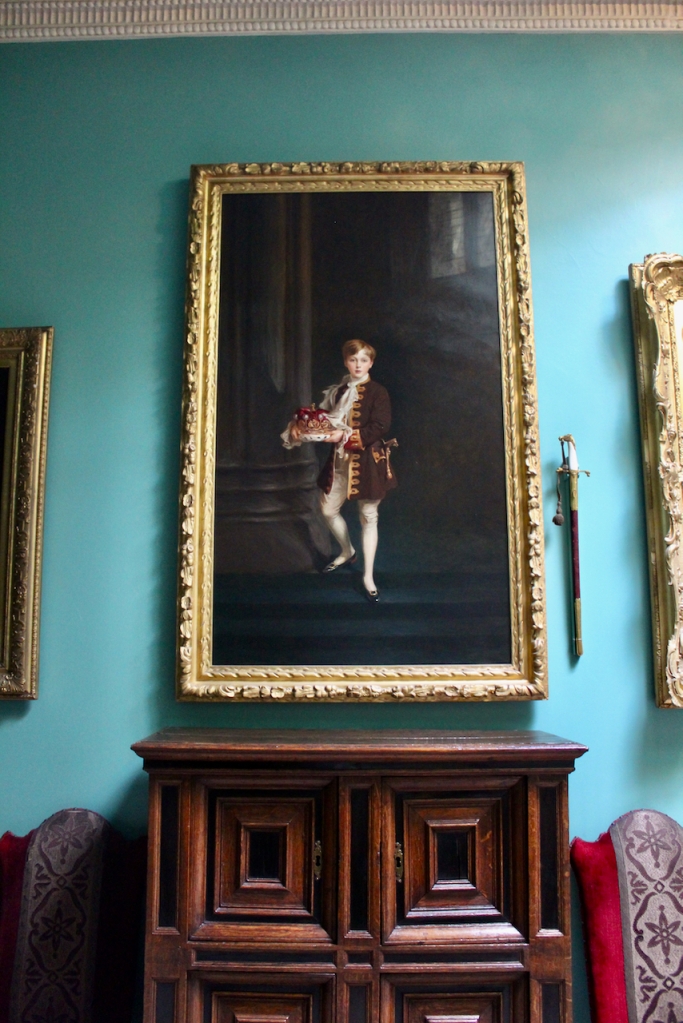
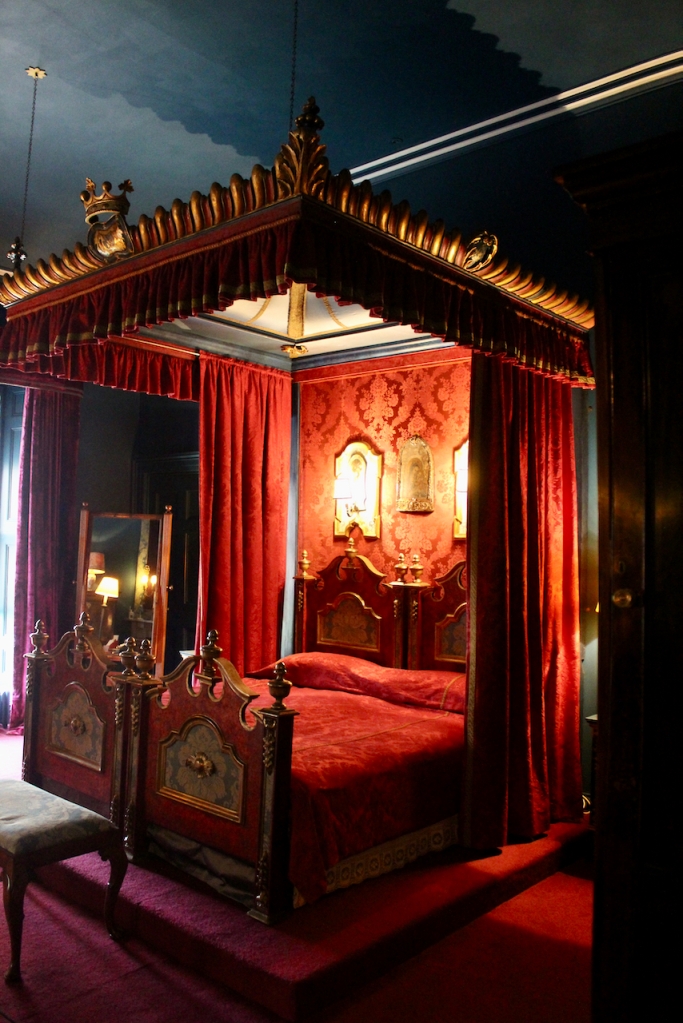
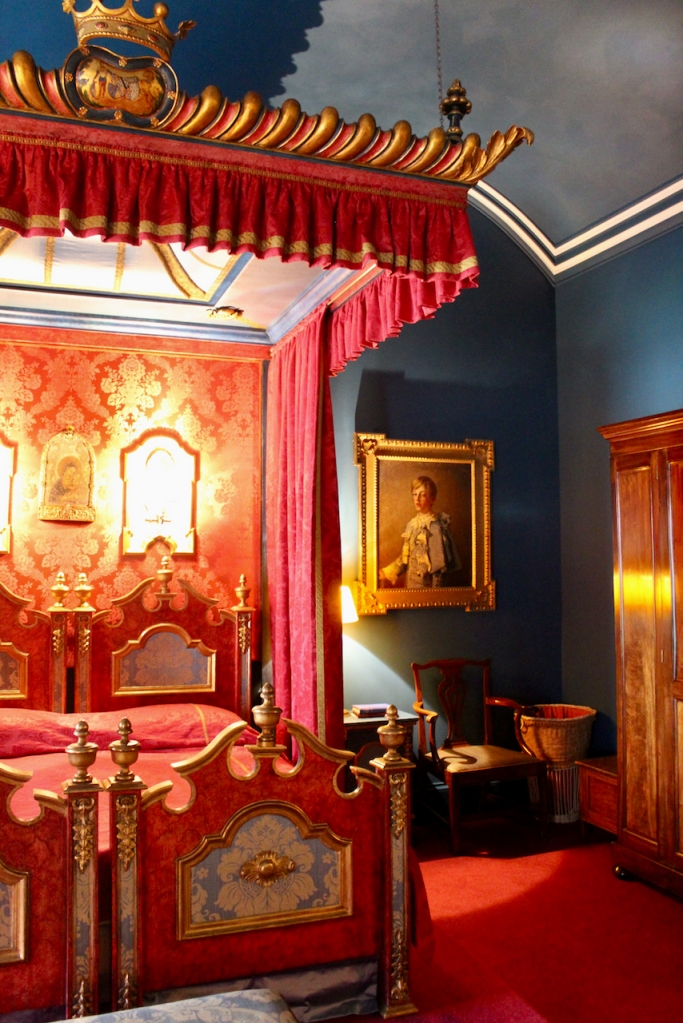
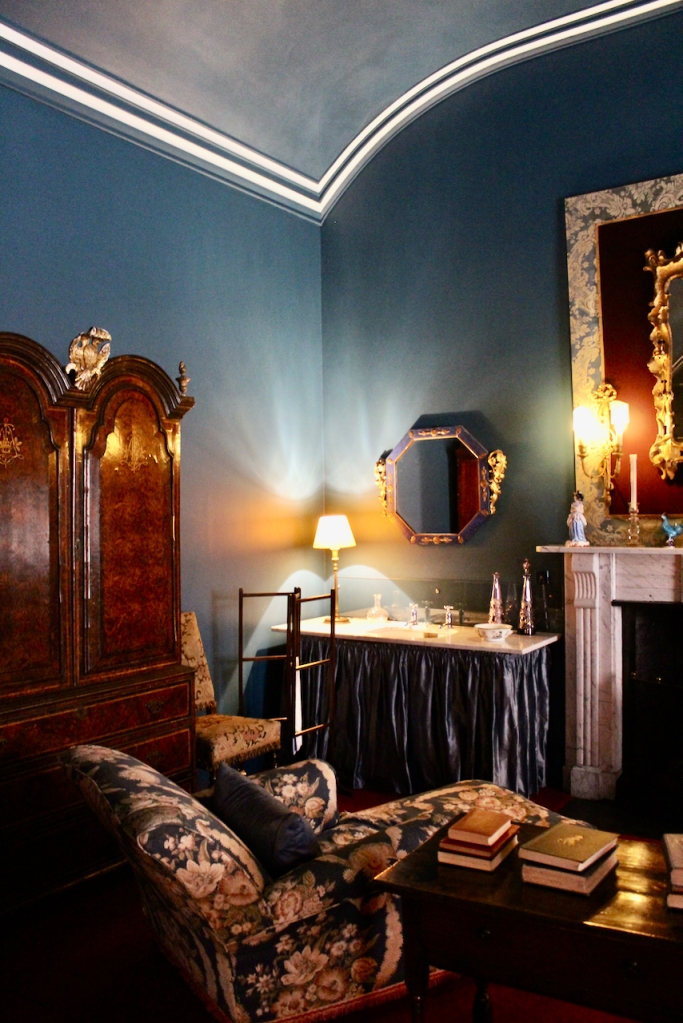
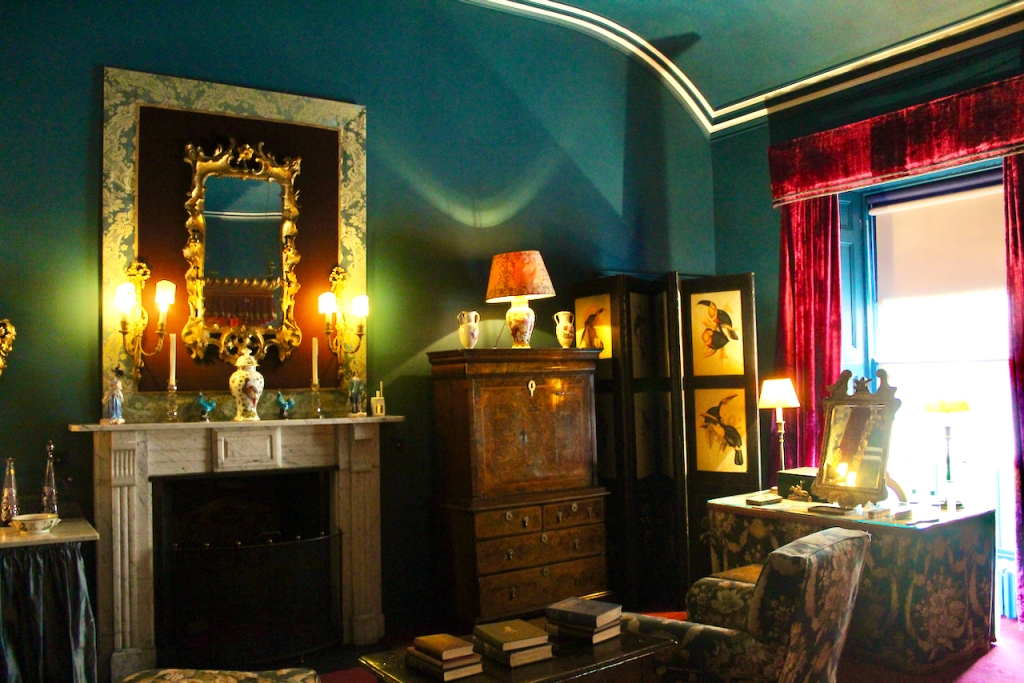
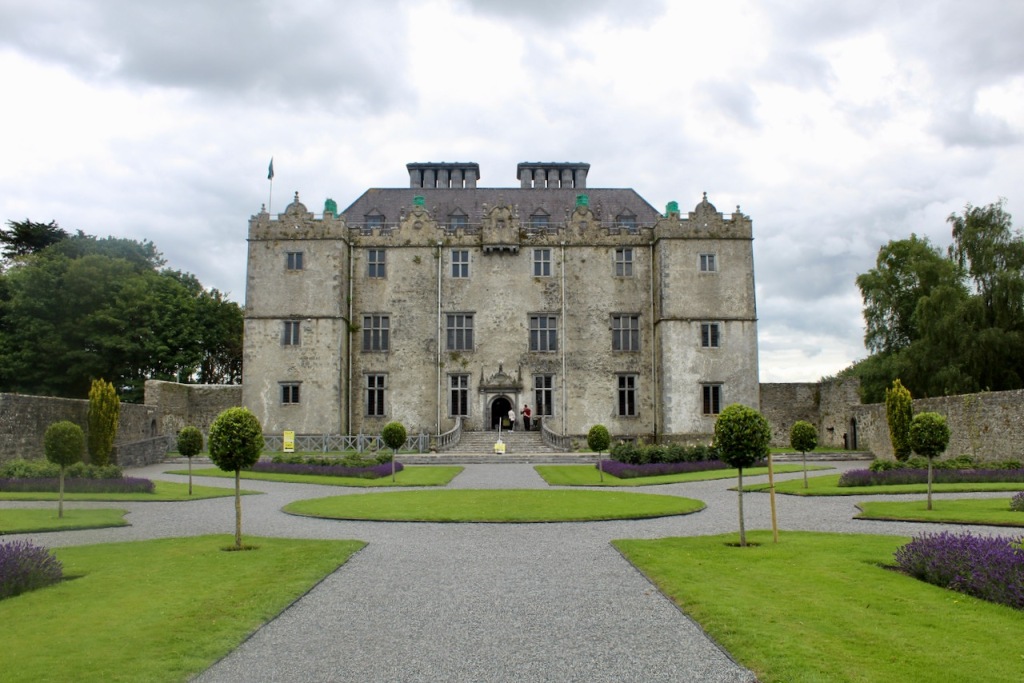
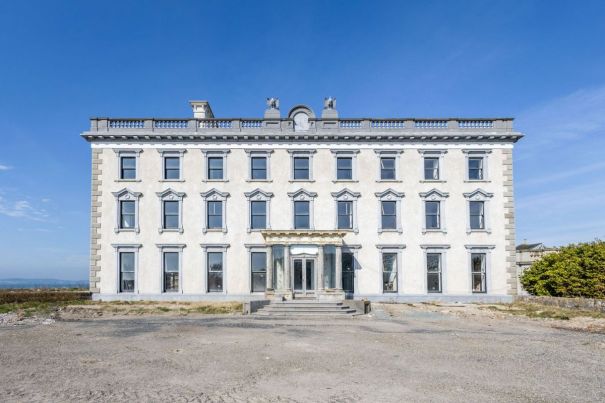
Rathfarnham Castle, Dublin
https://heritageireland.ie/places-to-visit/rathfarnham-castle/

General Enquiries: 01 493 9462, rathfarnhamcastle@opw.ie
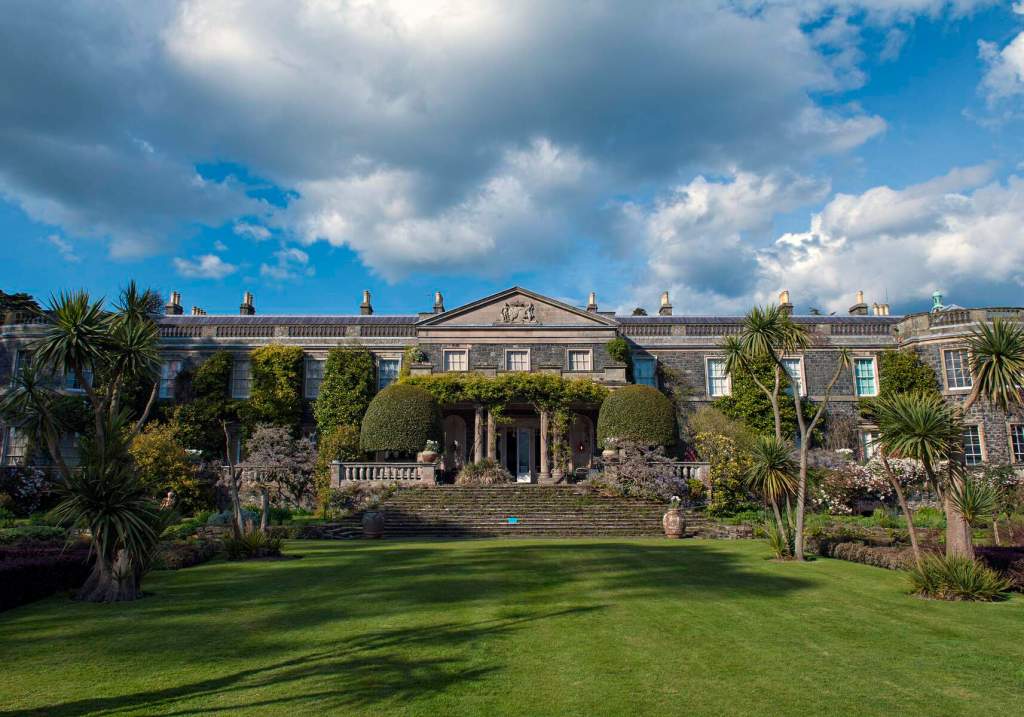
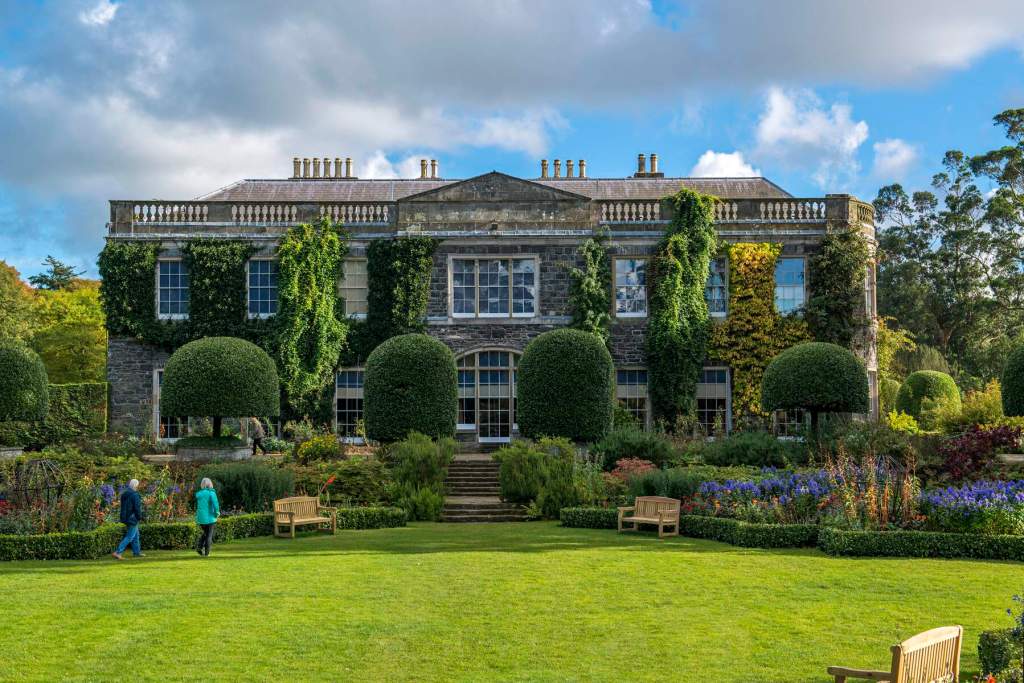
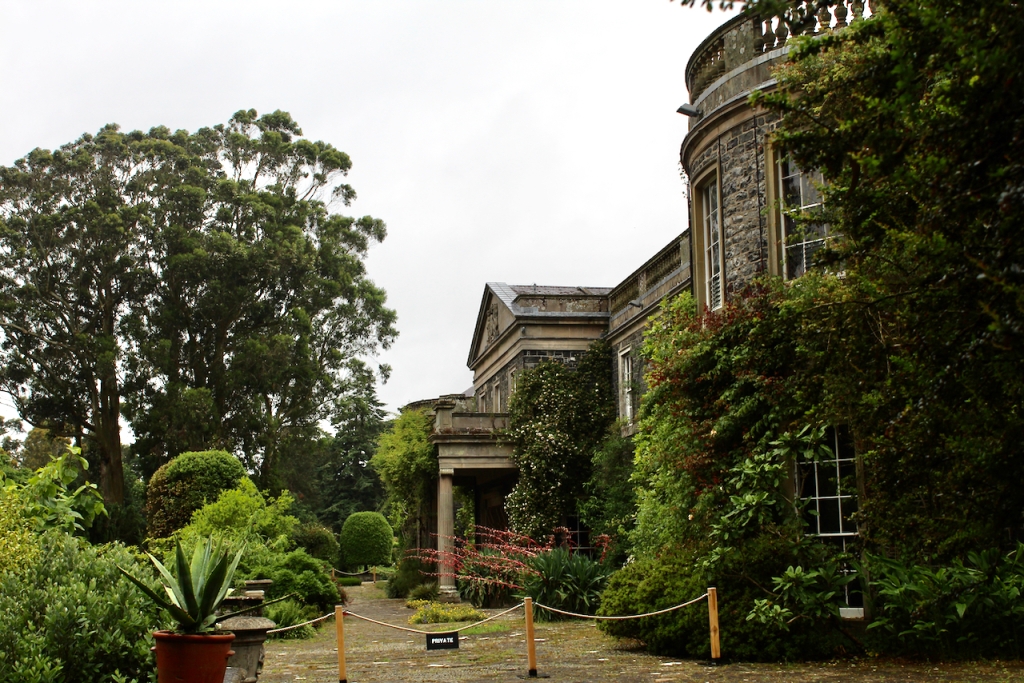
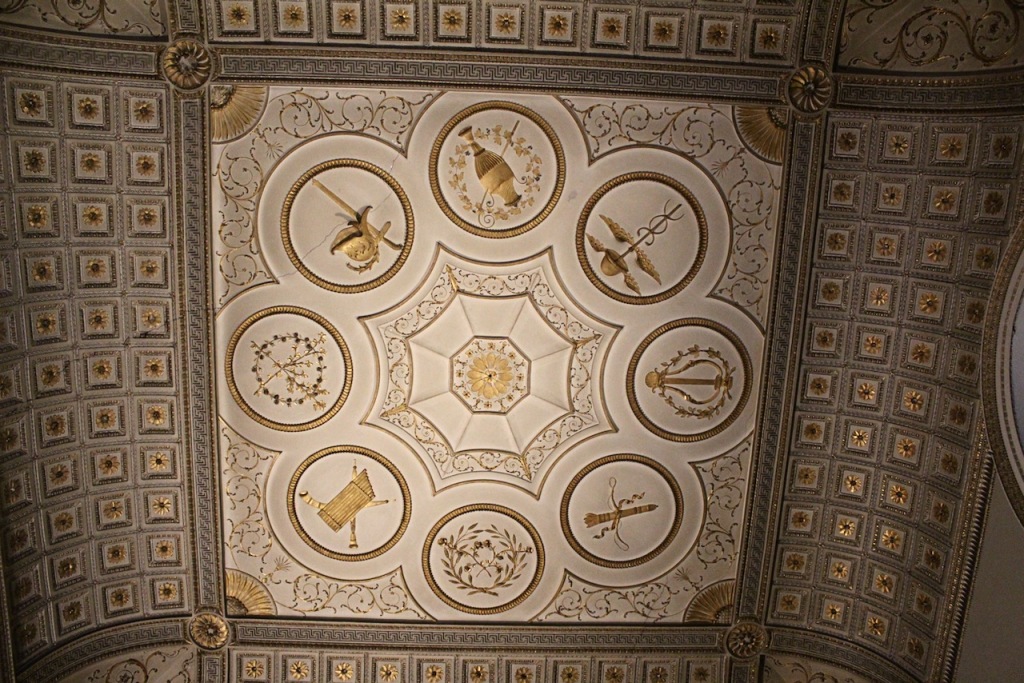
Rathfarnham Castle is a wonderful property to visit and I suspect, much underappreciated! It is one of the oldest surviving residences in Ireland, and has a variety of impressive ceilings. It is also another property which was inhabited by the Jesuits at one time, as was Emo Court in County Laois. Although they no longer own either of these properties, they still run schools in the former Castle Browne in County Kildare (now Clongowes Wood College) and Belvedere House in Dublin. They certainly knew how to pick impressive properties! [1]
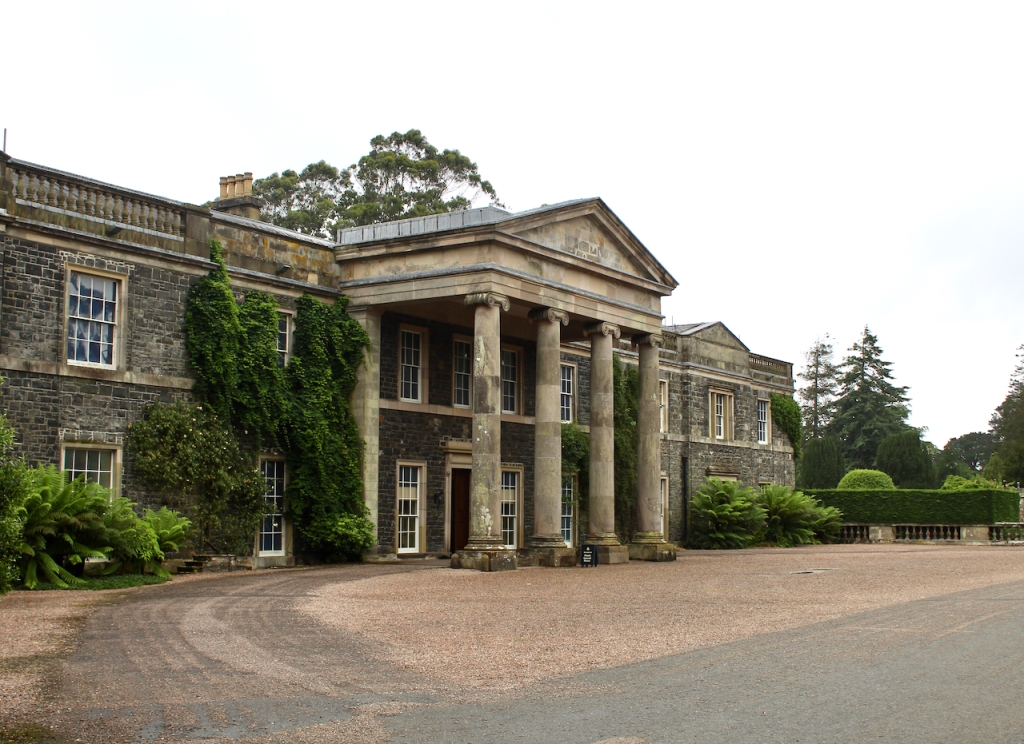
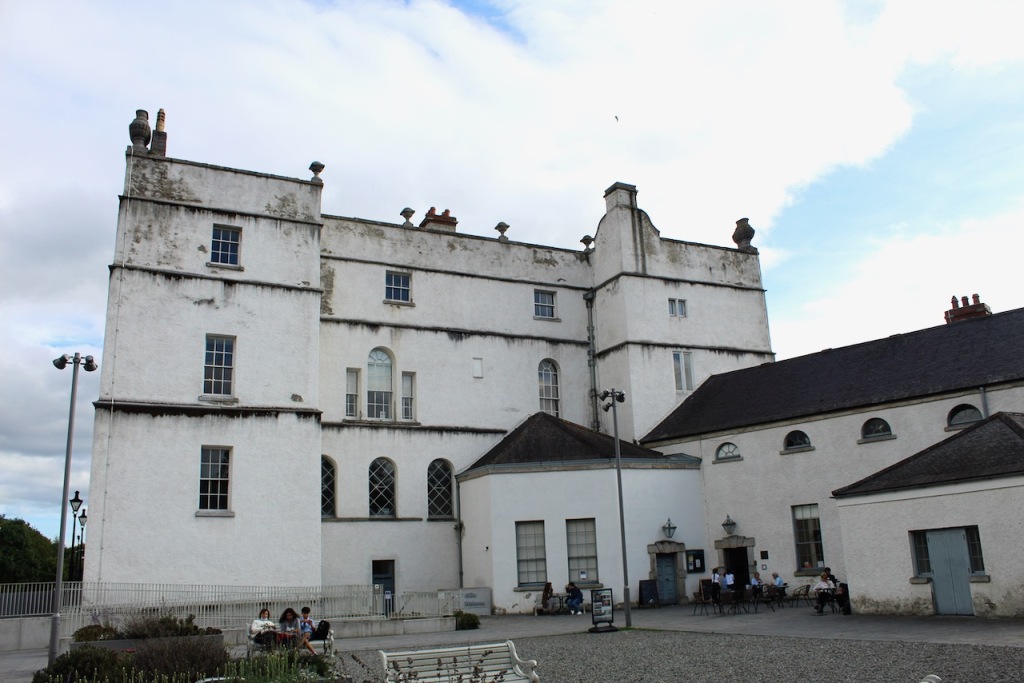
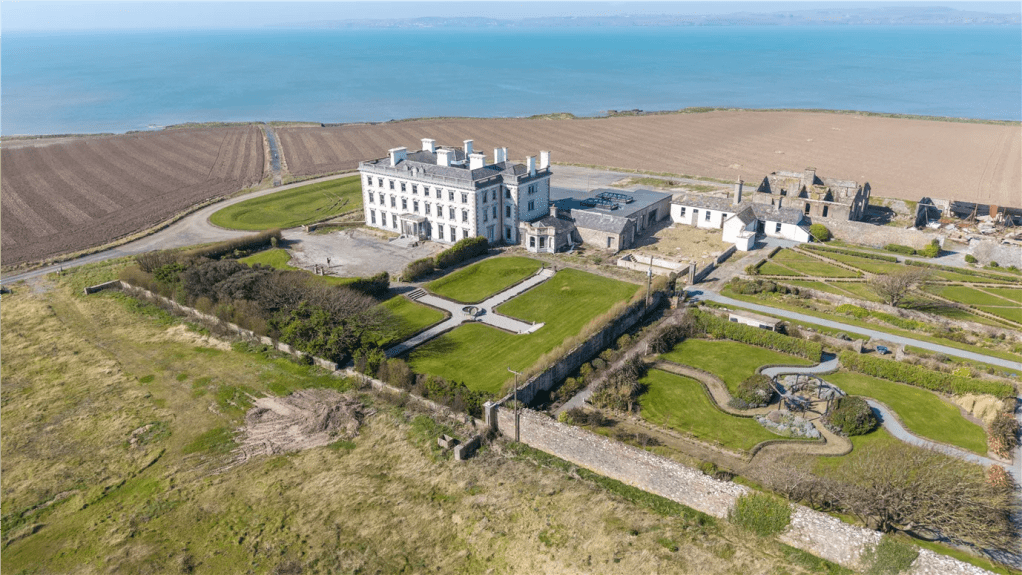
Rathfarnham Castle was built around 1583 for Adam Loftus (1533-1605), a clergyman originally from Yorkshire, who rose to the position of Archbishop of Dublin and Lord Chancellor of Ireland. Its position outside the city of Dublin made it vulnerable to attack, so it was built as a fortified house, with four flanker towers shaped to give maximum visibility of the surrounding landscape. The OPW website tells us:
“Loftus wanted the Castle to be a grand and impressive home which would reflect his high status in Irish society. He also needed it to be easily defended against attack from hostile Irish families such as the O’Byrnes based in the mountains to the south. The design was radically modern for the time and based on recent continental thinking about defensive architecture. The angled bastion towers located at each corner of the building were equipped with musket loops which allowed a garrison of soldiers to defend all approaches to the castle.”



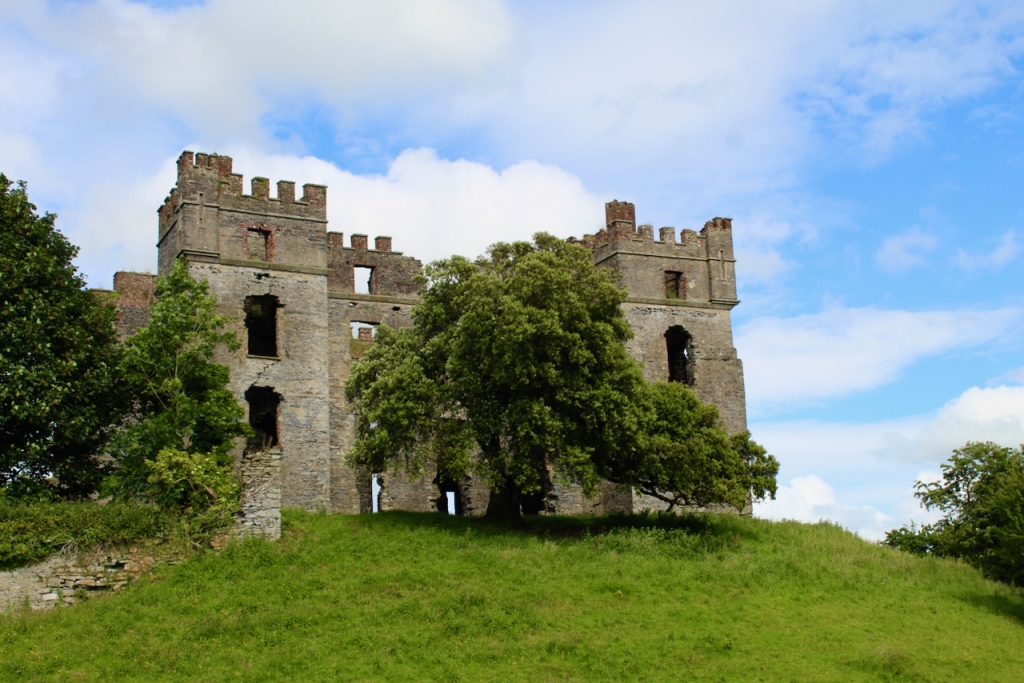
Loftus had previously lived in an archiepiscopal palace in Tallaght, and it had been sacked by the O’Byrnes and O’Tooles from the Wicklow mountains, which is why he ensured that his new house in Rathfarnham had strong defenses. The Bishop’s Palace in Raphoe, now a ruin, is similarly shaped.

Maurice Craig points out in his The Architecture of Ireland from the earliest times to 1880 that there are a group of similar buildings, built over a period of fifty years or more: Rathfarnham; Kanturk for MacDonagh MacCarthy, built before 1609; Portumna for the Earl of Clanrickarde, before 1618; Manorhamilton for Sir Frederick Hamilton, probably around 1634; Raphoe, for Bishop John Leslie (the “Fighting Bishop” – see my entry on Castle Leslie https://irishhistorichouses.com/2020/08/07/castle-leslie-glaslough-county-monaghan/) in 1636, and Burncourt for Sir Richard Everard before 1650. Manorhamilton is a section 482 ruin (see my entry https://irishhistorichouses.com/2025/02/20/manorhamilton-castle-castle-st-manorhamilton-co-leitrim/) and we visited Portumna in County Galway – see my entry https://irishhistorichouses.com/2022/02/14/office-of-public-works-properties-connacht/. The buildings resemble a fort, such as Mountjoy Fort in County Tyrone built 1600-1605. Killenure, County Tipperary, is similar but has cylindrical flankers, Craig tells us. This last was unroofed by 1793, and it is now (2025) a Section 482 property which I must visit!





Loftus attended Cambridge, where he took holy orders as a Catholic priest. Upon Queen Elizabeth’s accession to the throne in 1558, he declared himself Anglican. The Dictionary of Irish Biography tells us that a major turning point in Loftus’s life and career occurred in 1560, when he emigrated to Ireland as a chaplain to Thomas Radcliffe, 3rd Earl of Sussex, who had been granted a commission to serve as Lord Lieutenant of Ireland by Queen Elizabeth. On the recommendation of Sussex, Loftus was appointed Archbishop of Armagh, his consecration taking place on 2 March 1563. In January 1565, on account of the poverty of the archbishopric of Armagh, Queen Elizabeth granted Loftus the deanery of St Patrick’s cathedral in Dublin. In 1567 he was made Archbishop of Dublin.
It was Adam Loftus who had Reverend Dermot O’Hurley executed, whom I wrote about a couple of weeks ago in my entry about Doheny & Nesbitt.
The Dictionary of Irish Biography tells us:
He was “a strongly delineated establishment figure whose primary concerns were to serve the crown in Ireland, in whatever capacity the queen and her advisers thought fit; and to build up his own personal affinity, so that he would be in a position to execute the offices that came his way with a measure of genuine political and social authority. Thus, during the periods when the archbishop served as lord chancellor of Ireland (1581–1605), or as acting governor of the country during the periodic absences from Ireland of a serving viceroy (August 1582–June 1584, November 1597–April 1599, September 1599–February 1600), he was also careful to establish a network of connections throughout the country, particularly through the marriage of his children to leading families among the new English protestant elite. Among the families with which Loftus made these connections were the Bagenals of Co. Down, the Dukes of Castlejordan, the Hartpoles of Shrule, the Usshers of Dublin, the Colleys of Castle Carbury, the Berkeleys of Askeaton, and the Warrens of Warrenstown. The social ascent of Loftus and his family was also evident in the archbishop’s decision to proceed with the purchase of the estate of Rathfarnham, Co. Dublin (c.1589–90), on which he built a stately castle.” [2]
Adam Loftus married Jane Purdon. They had twenty children, not all of whom survived to adulthood, and those who did married very well.
- Anne Loftus married, first, Henry Colley of Castle Carbury in County Kildare, and second, Edward Blayney, 1st Lord Blayney, Baron of Monaghan.
- Martha Loftus (d. 1609) married Thomas Colclough (1564-1624) of Tintern Abbey in Wexford.
- Isabelle Loftus (d. 1597) married William Ussher (1561-1659)
- Thomas Loftus (d. 1635) married Helen Hartpole of Shrule.
- Alice Loftus (d. 1608) married Henry Warren of Warrenstown, County Offaly.
- Katherine Loftus married Francis Berkeley of Askeaton, County Limerick.
- son Adam died unmarried in 1599.
- Margaret Loftus married George Colley of Castle Carbury.
- Edward Loftus (d. 1601) married Anne Duke of Castle Jordan, County Meath.
- Dudley Loftus (1561-1616) married Anne Bagenal of Newry Castle, County Down, daughter of Nicholas Henry Bagenal, Marshal of Ireland.
- Dorothy Loftus (d. 1633) married John Moore (d. 1633)
Adam Loftus was the first Provost of Trinity College Dublin.
The Dictionary of Irish Biography continues:
“Although by the early 1590s Loftus had largely reconciled himself to the reality that the task of converting the indigenous community to protestantism, and securing its allegiance to the state church, was beyond him, the queen and her advisers still expected him to discharge his religious duties and press ahead with reforming initiatives on behalf of the state church. To this end, and in the midst of a period of mounting political crisis that culminated in the outbreak of the Nine Years War, Loftus was the prime mover behind the foundation of TCD, which received its royal charter on 3 March 1592. The archbishop also served as the college’s first provost till June 1594.“
Adam Loftus died in the old Palace of St. Sepulchre beside St. Patrick’s Cathedral, which until recently was the Garda barracks on Kevin Street, now housed in a new building. I hope they will make something of the historic old archbishop’s palace now, which could be a great museum!
Adam’s son Dudley (1561-1616) sat in the Irish parliament for Newborough in County Wexford. He married Anne Bagenal of Newry Castle, County Down, daughter of Nicholas Henry Bagenal, Marshal of Ireland. The castle passed to their son, Adam Loftus (1590-1666), who married Jane Vaughan of Golden Grove, County Offaly.
Another son of Dudley and Anne Bagenal was Nicholas Loftus (1592-1666), the ancestor of Henry Loftus, the Earl of Ely. Nicholas’s second son Henry (1636-1716) lived in Loftus Hall in County Wexford.

Adam Loftus (1590-1666) and Jane née Vaughan’s children also made good marriages. Their son Arthur Loftus (1616-1659) married Dorothy Boyle (1616-1668), daughter of Richard Boyle the 1st Earl of Cork. Arthur also served as MP for County Wexford, as well as Provost Marshall of Ulster.
The castle came under seige in 1641 and in 1642 the house was occupied by Cromwell’s Parliamentary troops. [4] In 1649 it was stormed and taken by Royalist troops under the Marquess of Ormond and all occupants were taken as prisoners. Ormond writes that nobody was killed. [5] Rathfarnham Castle was restored to Adam Loftus (1590-1666) when Charles II was crowned king.
Adam’s son Arthur predeceased him, so the castle passed to Arthur’s wife Dorothy née Boyle. In 1665 she obtained six firelock muskets from the Master of Ordinance to protect the castle.
Arthur Loftus and Dorothy née Boyle had a son Adam Loftus (1632-1691). Adam Loftus was Ranger of the Phoenix Park in Dublin and from 1685, a member of the Irish Privy Council. King James II created him Baron of Rathfarnham and Viscount Lisburne in the Peerage of Ireland. Adam married Lucy Brydges, daughter of George Brydges, 6th Baron Chandos of Sudeley, England.
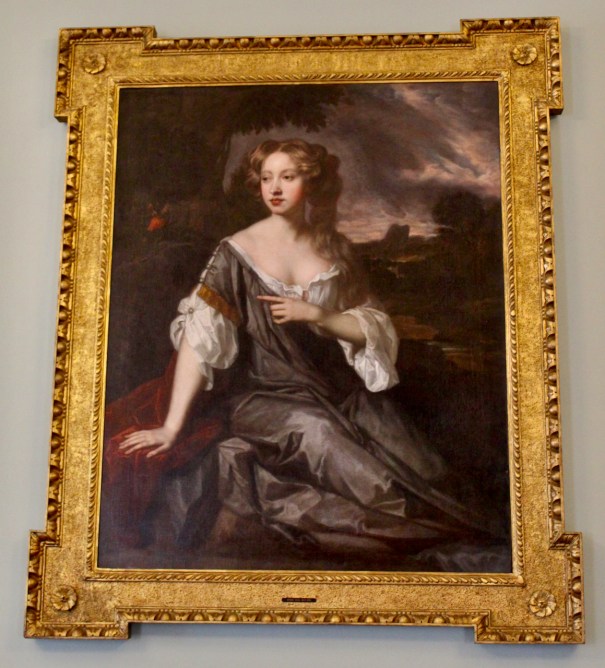

After his wife Lucy died, Adam Loftus married Dorothy, the daughter of Patrick Allen or Alen, of St. Wolstan’s of Celbridge in County Kildare. Adam was a gallant at the court of King Charles II.
Despite earning his peerage from King James II, Adam Viscount Lisburn supported the cause of William III. He died at the Siege of Limerick in 1691 and the cannon ball which reputedly killed him hangs in St Patrick’s Cathedral.
The castle passed to Adam’s daughter Lucy, who married Thomas Wharton, 1st Marquess of Wharton in 1692, who in 1715 was created 1st Earl of Rathfarnham, 1st Marquess of Carlow and 1st Baron of Trim.

Lucy and the Marquess of Wharton had a son Philip, who became the Duke of Wharton. He was a Jacobite and supporter of the titular James III, and was subsequently granted many titles. The Peerage website lists the titles. As well as those he inherited from his father, he was created 1st Viscount Winchendon, Co. Buckingham [England] and 1st Marquess of Woodburn, Co. Buckingham [England], 1st Earl of Malmesbury, Co. Wilts [England] on 22 December 1716, Jacobite.
He was appointed Privy Counsellor (P.C.) in Ireland between 1717 and 1726. He was created 1st Duke of Wharton, Co. Westmorland [Great Britain] on 28 January 1717/18, in an attempt by the authorities to wean him from his Jacobitism and make him a good Whig like his father. Darryl Lundy of The Peerage website tells us that his Dukedom did at least make him for a while speak and vote with the Tories in the House of Lords, for instance in debates on the South Sea Bubble. He lost a fortune from participation in the South Sea Bubble. In June 1725 he left the country. He was Envoy to Vienna in August 1725, for the Jacobite King James III, and then Envoy to Madrid in March 1725/26.

Out of money, he took a position in the Jacobite forces and commanded a Spanish detachment at the Siege of Gibraltar in 1727, fighting against the English. On 3 April 1729 he was outlawed and his titles and such estates as he still held in Britain forfeited.
He had no surviving male issue when he died on 31 May 1731. On his death, all his titles, most forfeited by his treason, expired, except the Barony of Wharton, which was deemed by the House of Lords in 1915 to be descendible to his heirs.
He sold Rathfarnham Castle in 1724. It was purchased by Speaker William Conolly for £62,000. Speaker Conolly never lived in the Castle since he had built Castletown in County Kildare, and he leased Rathfarnham in 1742 to Dr. Hoadley, Archbishop of Armagh.
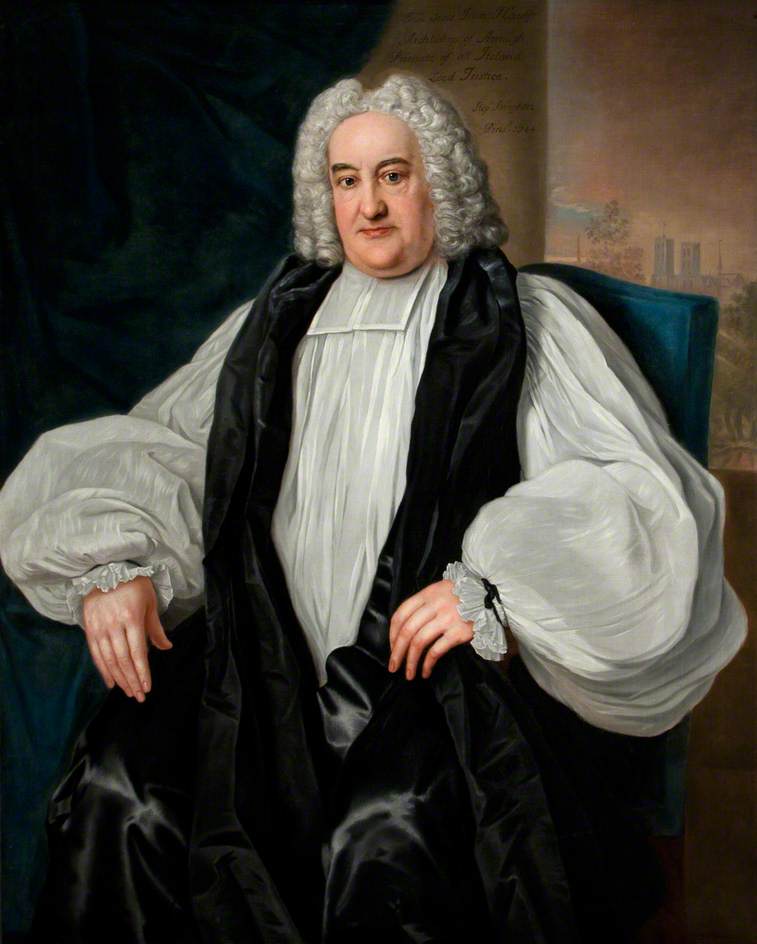

Dr. Hoadley was interested in building, and he had built an Episcopal mansion in Tallaght to replace a medieval castle. He then restored Rathfarnham Castle. It was famed for its excellent agriculture and fruit gardens. [see 5].
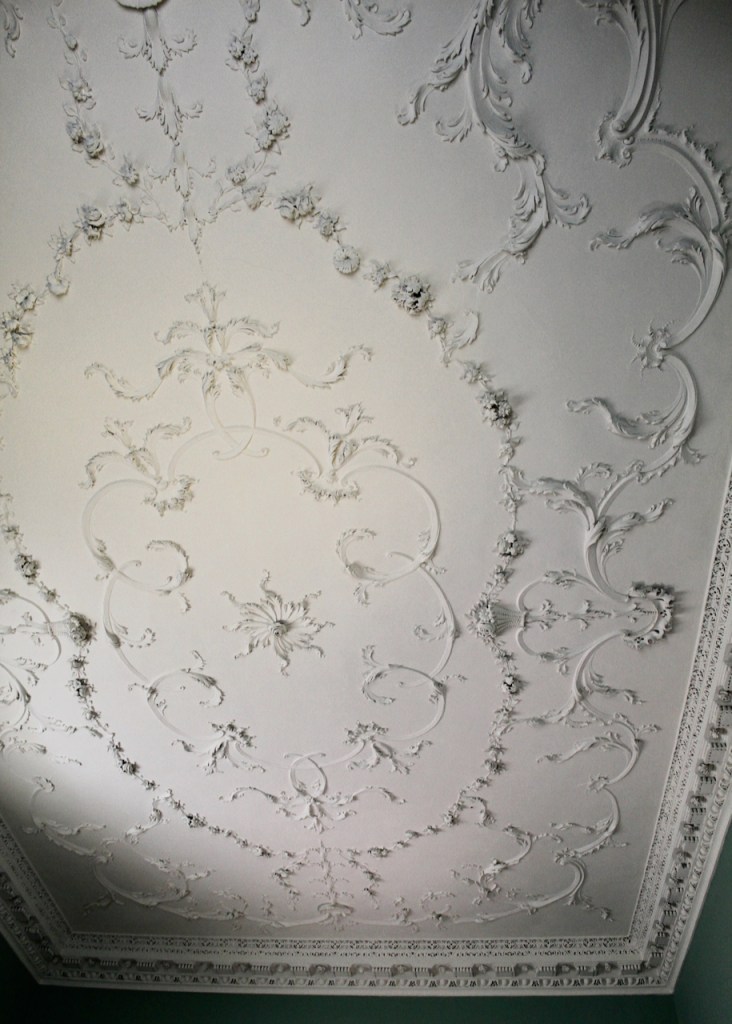
Dr. Hoadley’s daughter Sarah married Bellingham Boyle (1709-1772), and they inherited Rathfarnham Castle. Boyle also took an interest in farming and grew the first oats in Ireland. [see 5]. The Hoadley-Boyle tenancy lasted for twenty-five years, and Bellingham Boyle and his wife mixed in high society, entertaining two Lords Lieutenant in the castle: the Duke of Devonshire and the Earl of Harrington. Boyle may be be responsible for installing some of the delicate rococo ceilings in the castle.

Interestingly, in Aug 1742, Bellingham Boyle was appointed to a commission to investigate the soundness of mind of Jonathan Swift, Dean of St. Patrick’s Cathedral in Dublin. The Writ “De Lunatico Inquirendo,” in the case of Jonathan Swift, D.D. was issued to investigate and ascertain whether the ailing Dean Swift was of unsound mind and memory to safely conduct his own business. Belllingham Boyle was one of 12 commissioned to perform the investigation. Dean Swift was found to be of unsound mind and memory and was placed under the protection of the Court of Chancery. [6]
Boyle’s daughter Anne married Robert Langrishe 2nd Baronet Langrishe, of Knocktopher, Co. Kilkenny.

The castle returned to the ownership of the Loftus family in 1767, to Nicholas Hume Loftus, 2nd Earl of Ely, a descendant of the original owner Adam Loftus. Nicholas never married and on his death in 1769 the Castle passed to his uncle, Henry Loftus (created Earl of Ely in 1771). Henry continued the remodelling of the castle and the works were completed by the time of his death in 1783.
Let us backtrack now to look at the descendants of the first Adam Loftus. Adam’s grandson Nicholas lived in Fethard, County Wexford, in the precursor to Loftus Hall. His son Henry (1636-1716) of Loftus Hall was the father of Nicholas Loftus (1687-1763) who was created 1st Viscount Loftus of Ely.
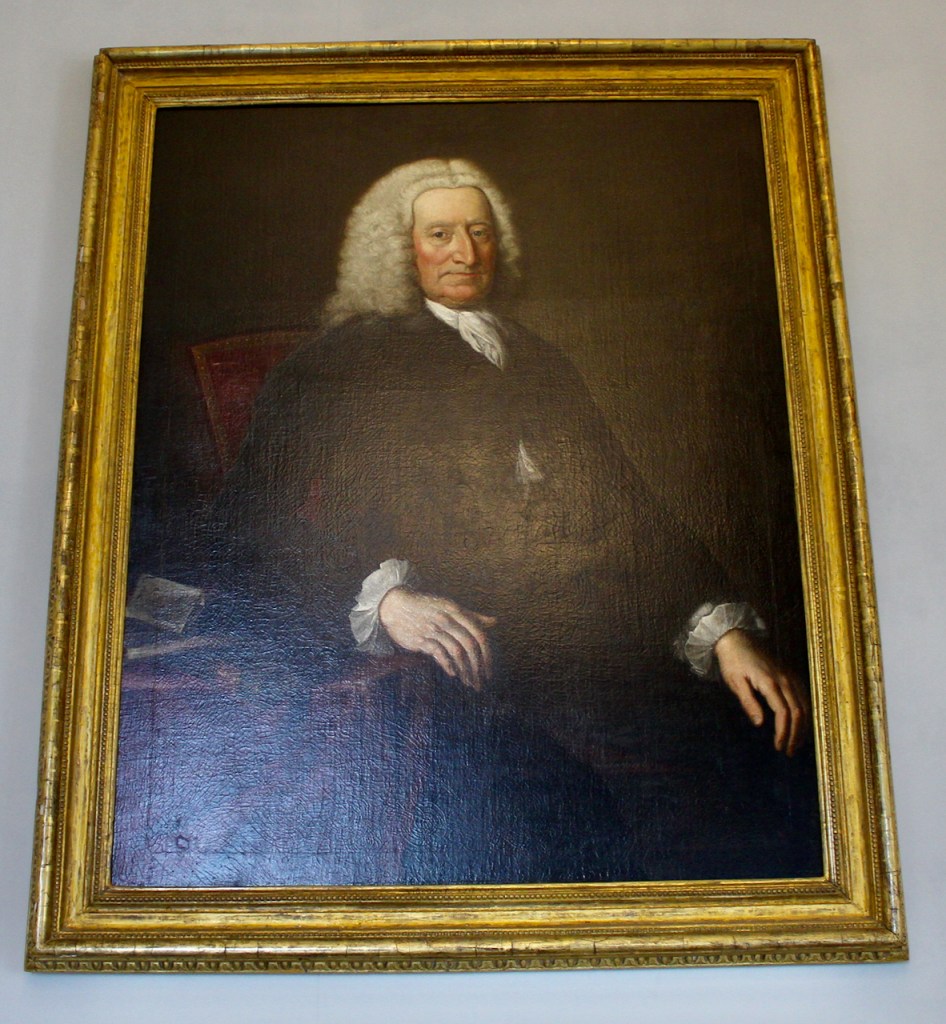

Nicholas served as MP for Wexford, and married Anne Ponsonby, daughter of William Ponsonby, 1st Viscount Duncannon. He was first created Baron Loftus of Loftus Hall in 1751, and then assumed a seat in the House of Lords, and became Privy Counsellor of Ireland in 1753. He was created Viscount Loftus of Ely in County Wicklow in 1756.
After Anne died, around 1724, Nicholas Viscount Ely married Letitia Rowley (d. 1765) of Summerhill in County Meath. To make matters more confusing, she had been previously married to Arthur Loftus (1644-1725) 3rd Viscount of Ely!

Viscount Loftus is a title that has been created three times in the Peerage of Ireland for members of the Anglo-Irish Loftus family. The first creation was for Adam Loftus (1568-1643) on 10 May 1622, who served as Lord Chancellor of Ireland in 1619. He is not to be confused the our Adam Loftus (1533-1605) of Rathfarnham Castle. This title became extinct in 1725 upon the death of the third viscount, who had no male heir, despite having married three times.
Nicholas Viscount Loftus and Anne née Ponsonby had a daughter Elizabeth Loftus (d. June 1747) who married John Tottenham 1st Baronet, MP for New Ross. Another daughter, Mary (1710-1779), married William Alcock (1702-1779) of Wilton Castle in Wexford (see my entry https://irishhistorichouses.com/2022/02/04/wilton-castle-bree-enniscorthy-co-wexford-and-a-trip-to-johnstown-castle/ )
Nicholas and Anne’s son Nicholas Loftus (1708-1766) became the 1st Earl of Ely, and added Hume to his surname after marrying Mary Hume, daughter of Gustavus Hume, 3rd Baronet of Castle Hume, County Fermanagh. As well as Loftus Hall in Wexford, they owned 13 Henrietta Street in Dublin. He became known as the “wicked earl” due to a court hearing about the supposed mental incapacity of his son, also named Nicholas. Young Nicholas’s uncle, George Rochfort (1713-1734), brother of the 1st Earl of Belvedere, sought to have young Nicholas declared incapable of succeeding to the title. George Rochfort was married to another daughter, Alice, of Gustavus Hume, 3rd Baronet of Castle Hume. Family members testified that young Nicholas was of normal intelligence, and that any eccentric behaviour should be blamed on his father’s ill-treatment. The trial lasted for nine years and was even brought to the House of Lords. Poor young Nicholas died before the trial was finished and Rochfort’s case was declared invalid.
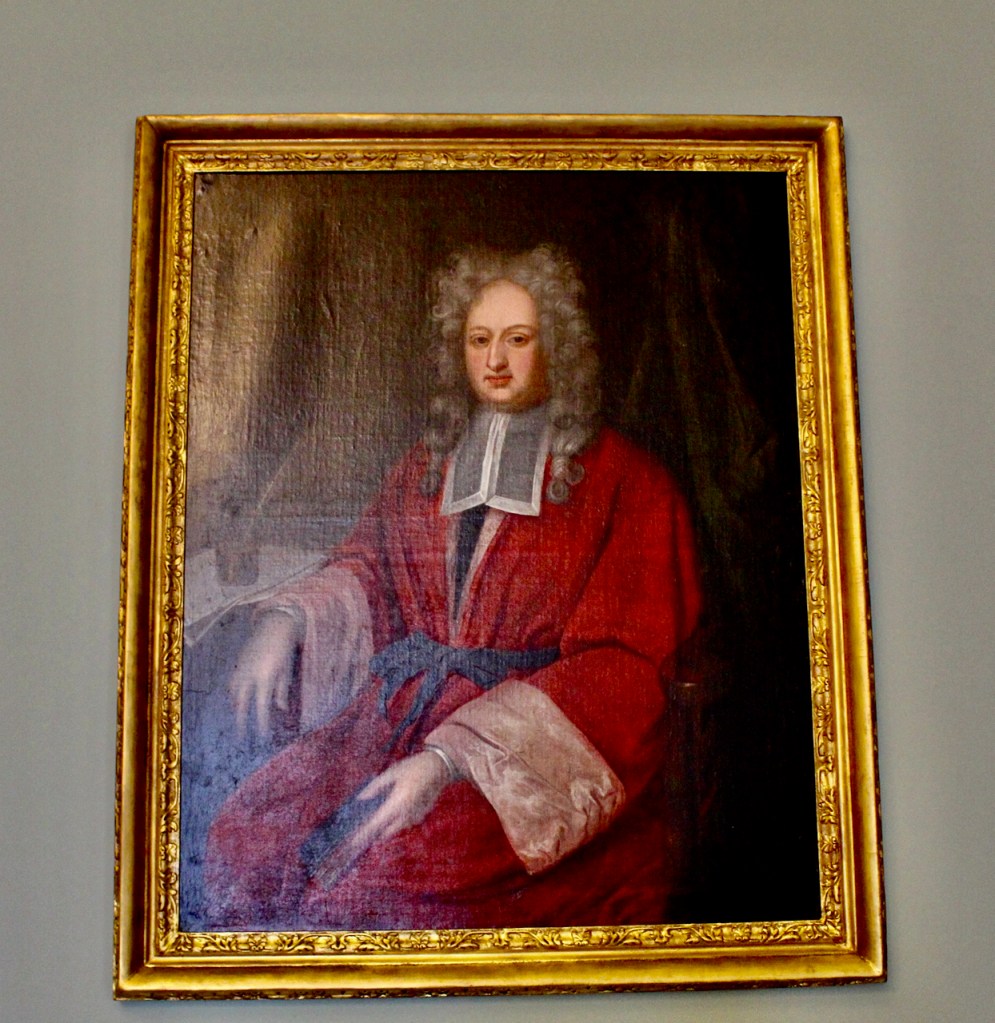


Nicholas Loftus Hume officially succeeded as 2nd Earl of Ely (1738-1769). It was through him that Rathfarnham Castle returned to Loftus ownership. Nicholas bequeathed Rathfarnham Castle and the estate to his uncle, Henry Loftus (1709-1783) who became the 1st Earl of Ely of the second creation. Henry was the younger son of Nicholas Loftus (d. 1763) 1st Viscount Loftus and Anne née Ponsonby, brother to the earlier Nicholas Hume Loftus (d. 1766) 1st Earl of Ely, the Wicked Earl.

Between 1769 and his death in 1783 Henry funded some of the most substantial 18th century changes to Rathfarnham Castle and the demesne.
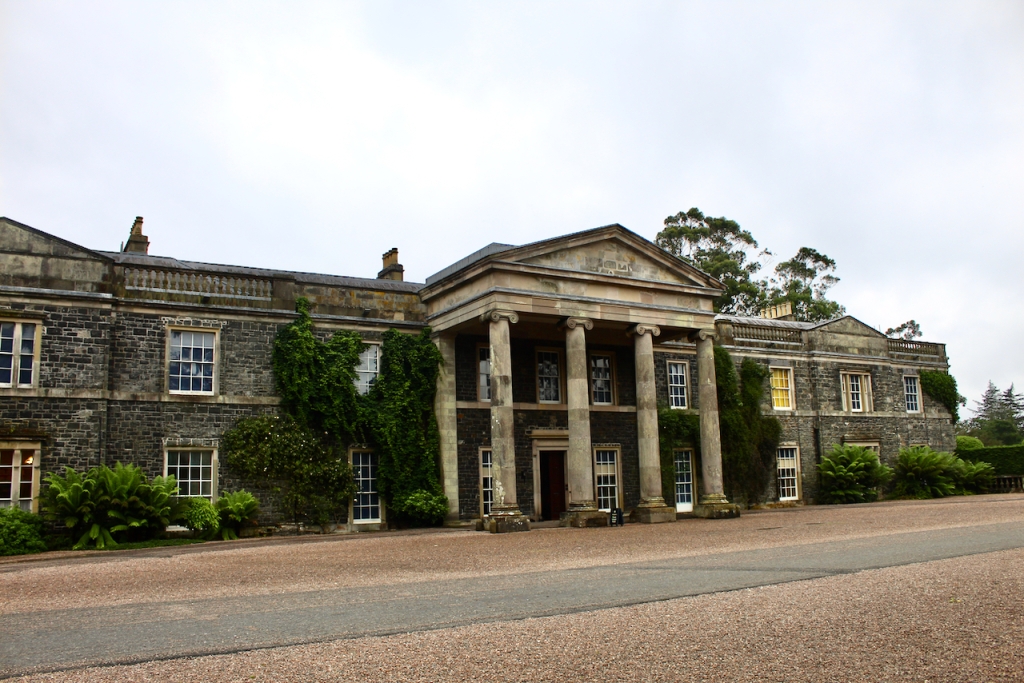
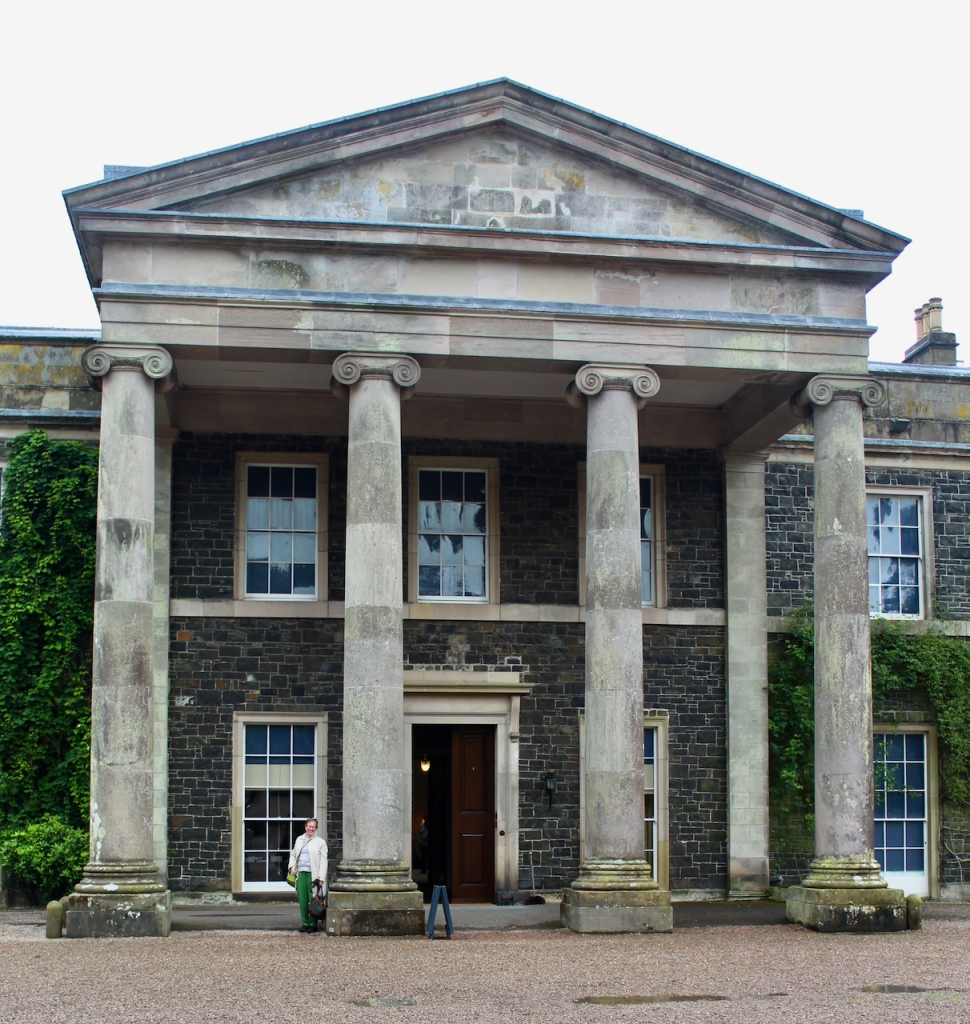
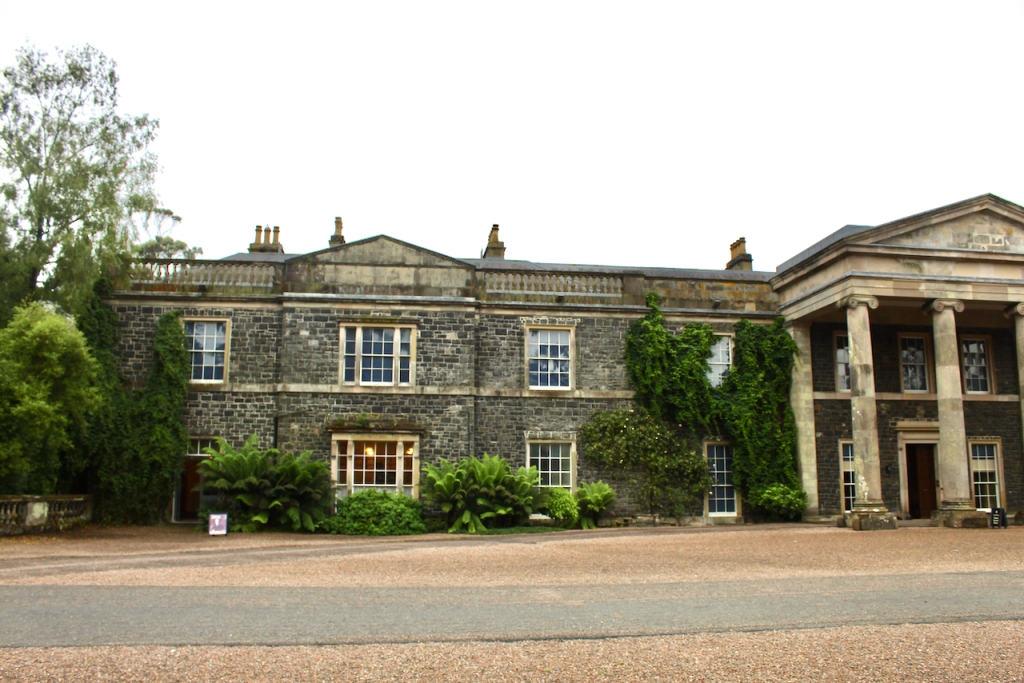
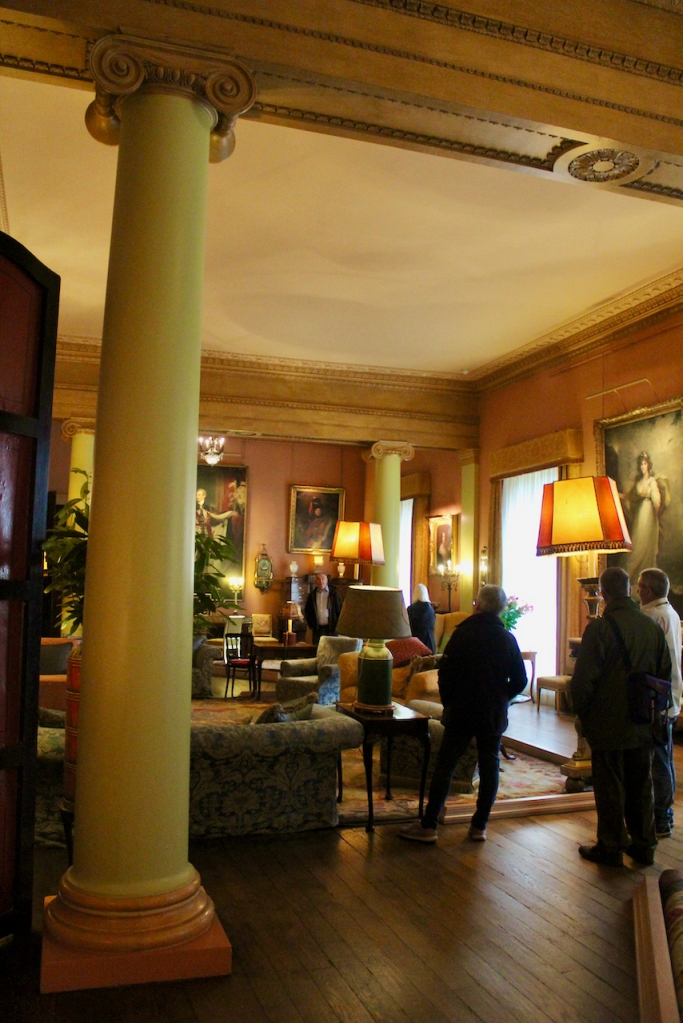
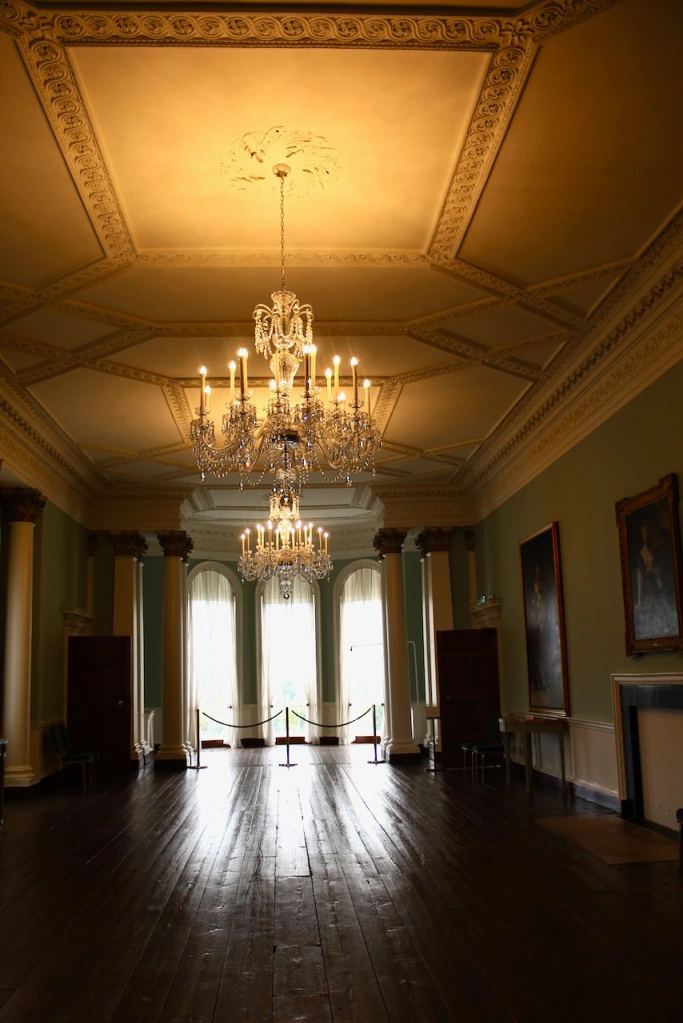
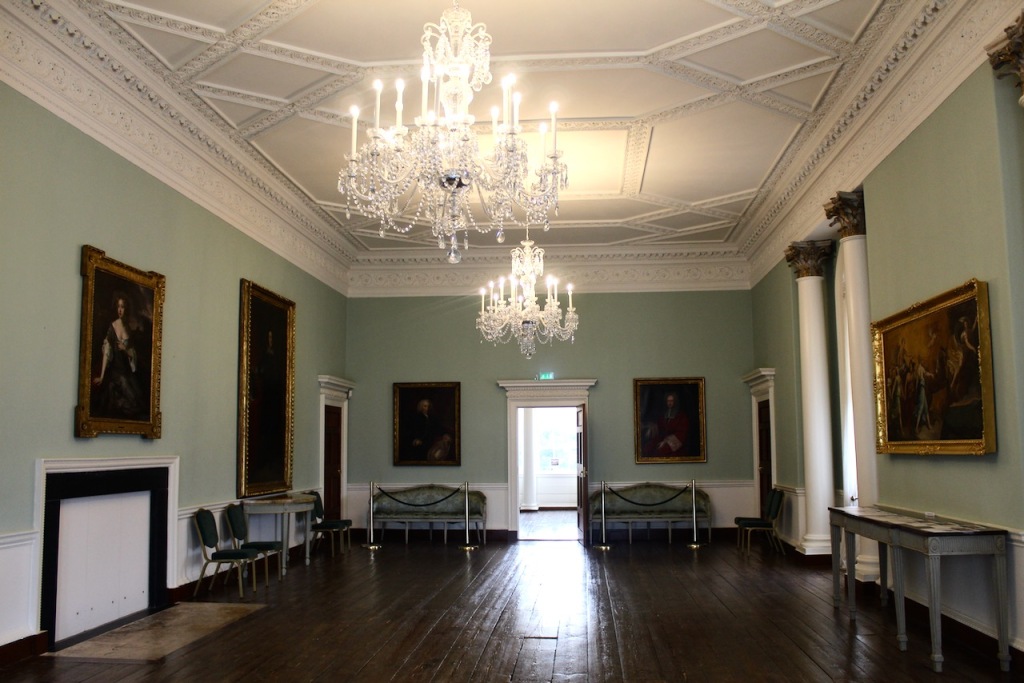
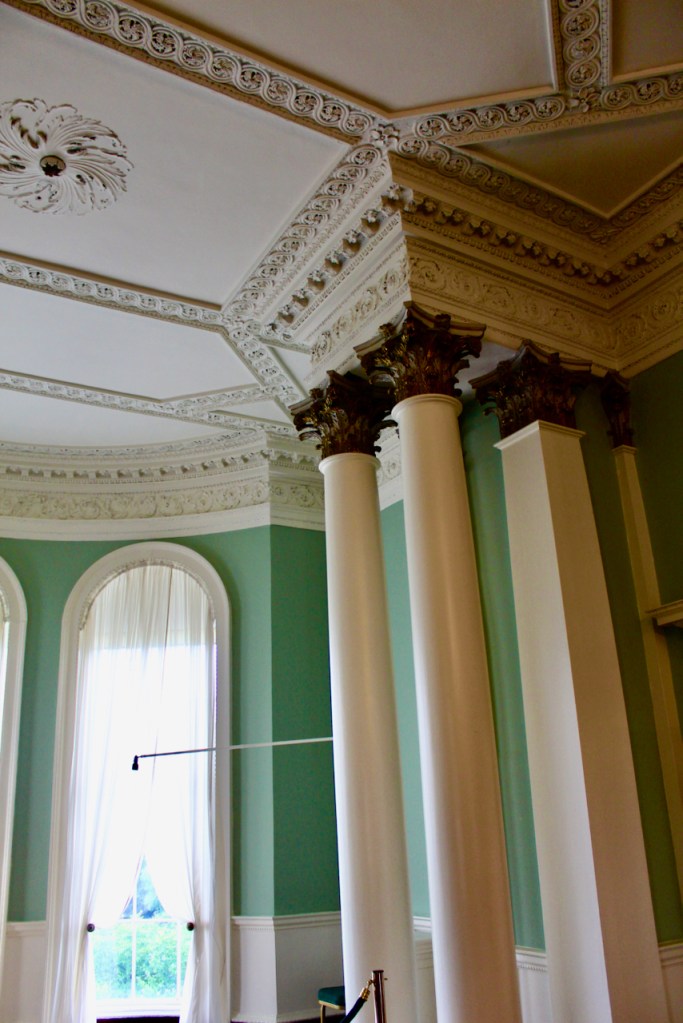
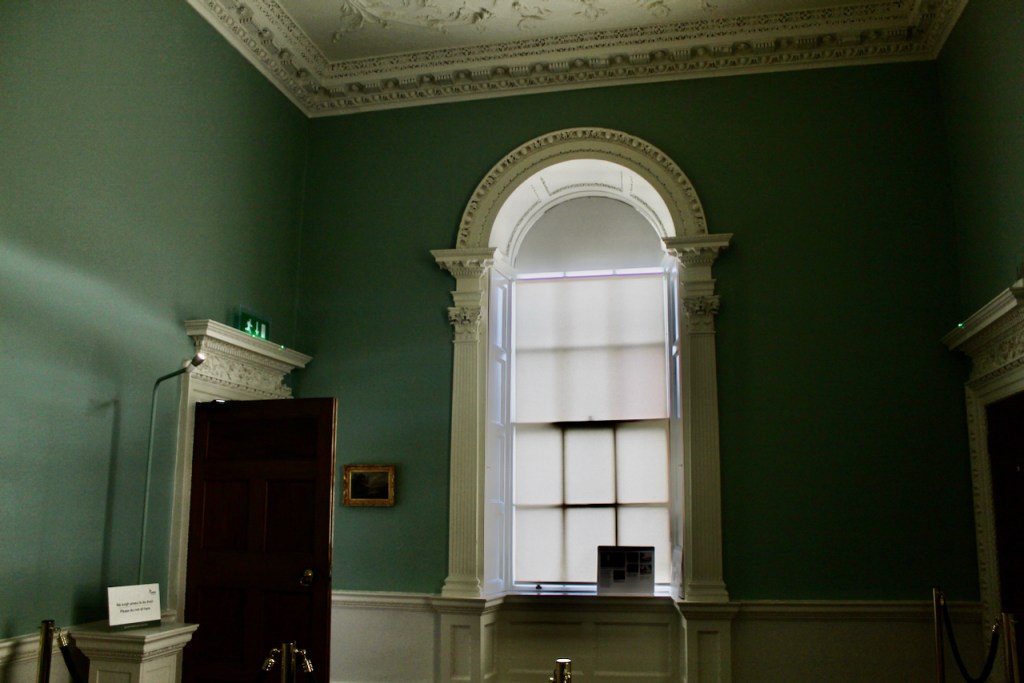
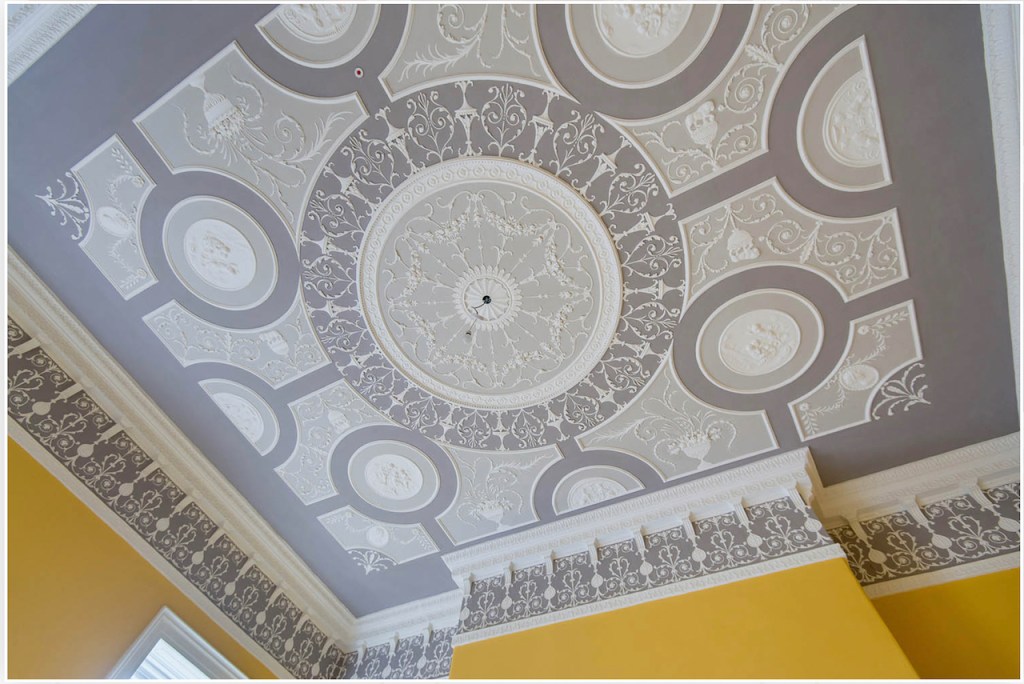
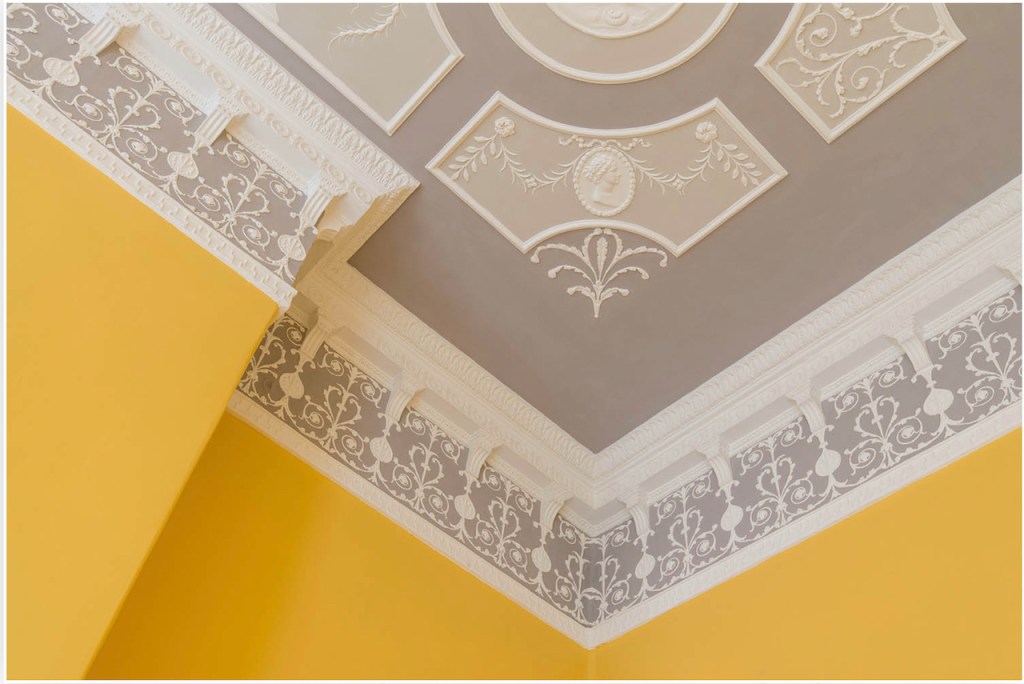
He contracted Sir William Chambers to remodel several of the rooms including the Ballroom and Anteroom. Externally, the window openings were enlarged, and a new stone Tuscan entrance portico added, probably to the designs of William Chambers. The original battlements were removed and the new parapet was embellished with ball finials and urns some of which also serve as chimneys. On the south front new garden steps were added, while on the east front a three bay bow had been added by 1774.
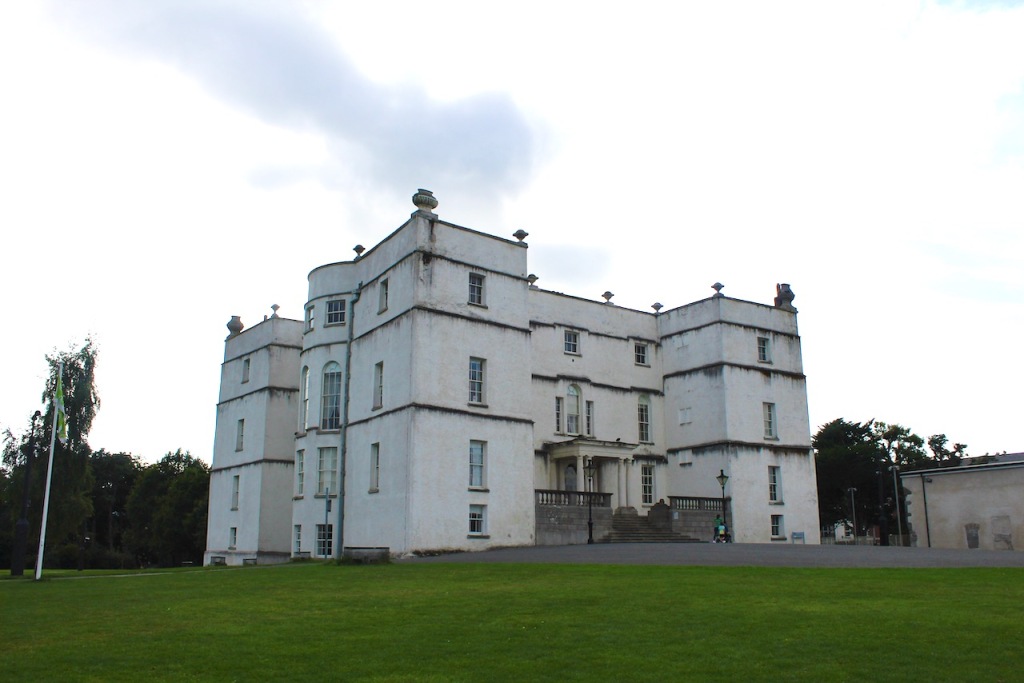


From the OPW website:
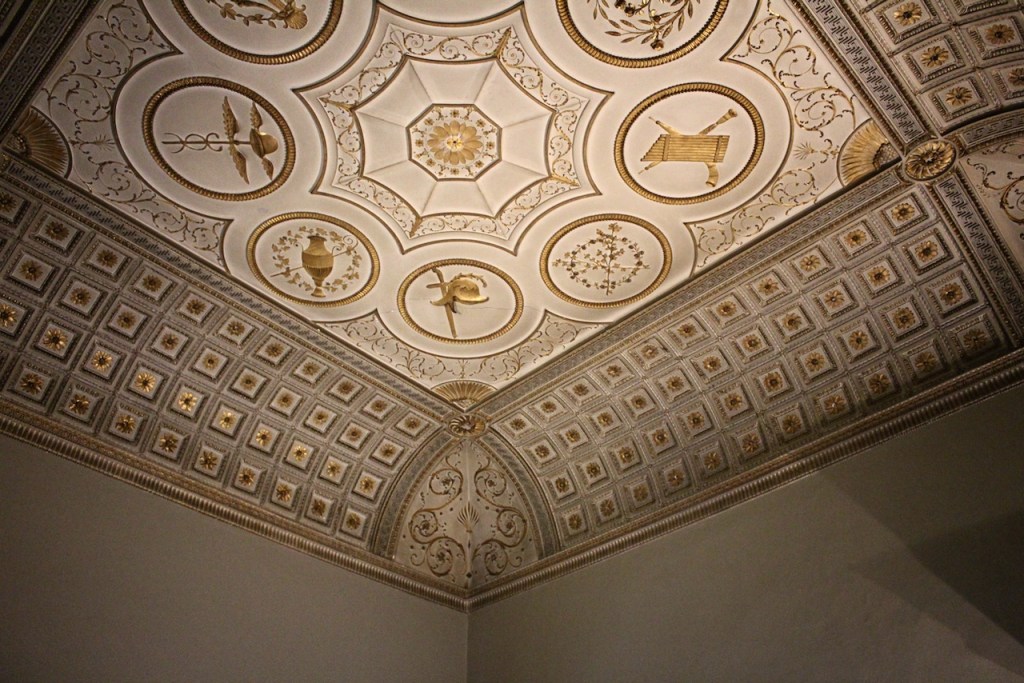
“Loftus’s castle, with its four flanker towers, is an excellent example of the Elizabethan fortified house in Ireland. In the late eighteenth century, the house was remodelled on a splendid scale employing some of the finest architects of the day including Sir William Chambers and James ‘Athenian’ Stuart. The collection includes family portraits by Angelica Kauffman, Sir Peter Lely, and Hugh Douglas Hamilton.“
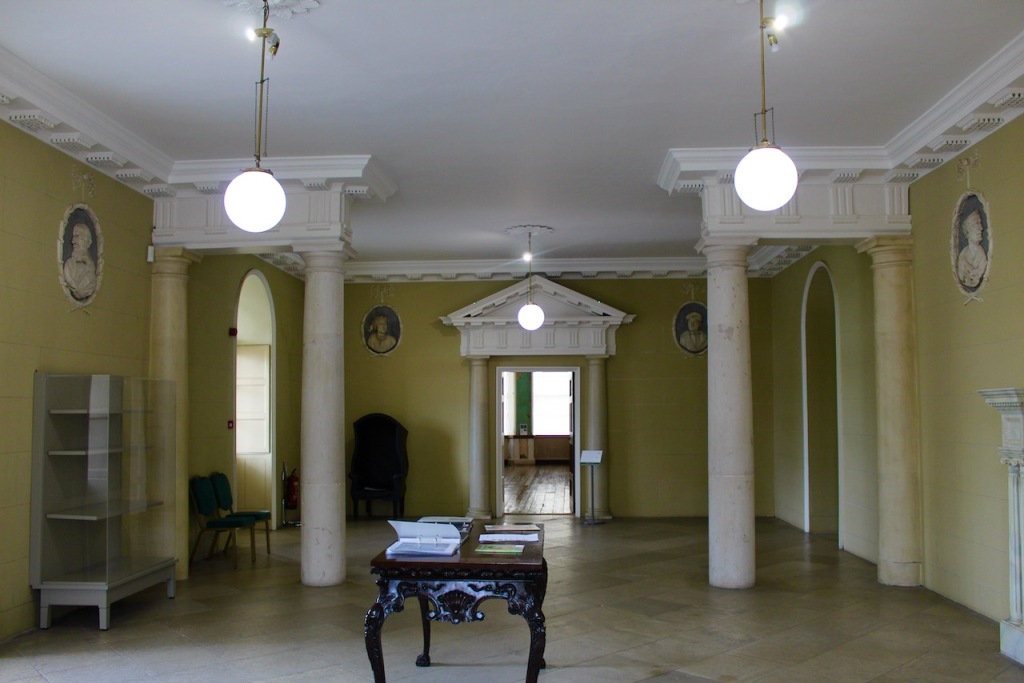

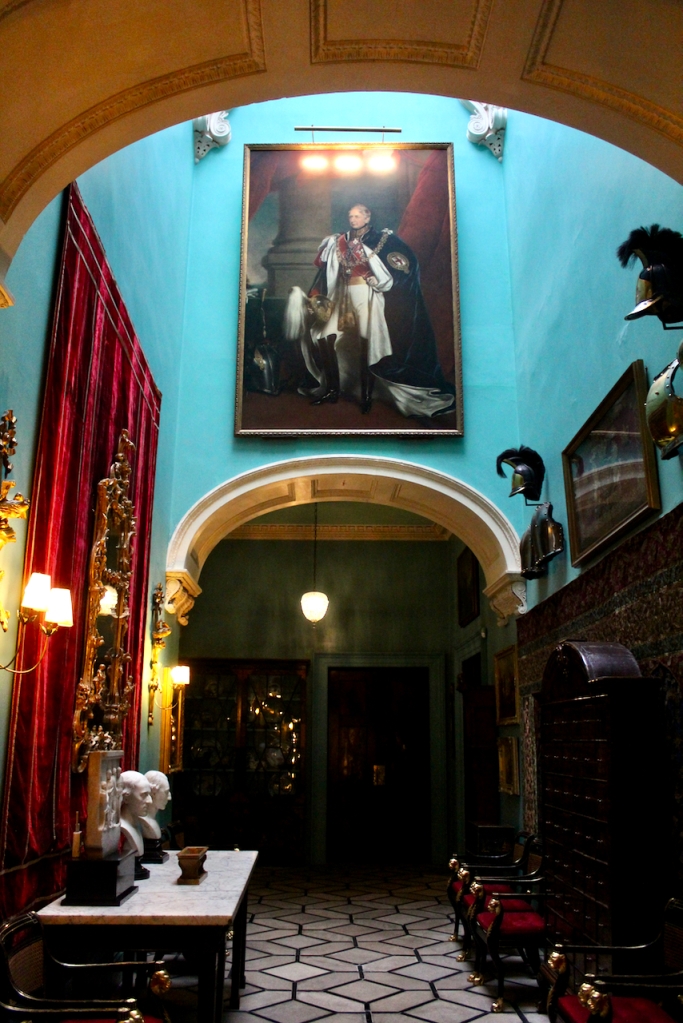
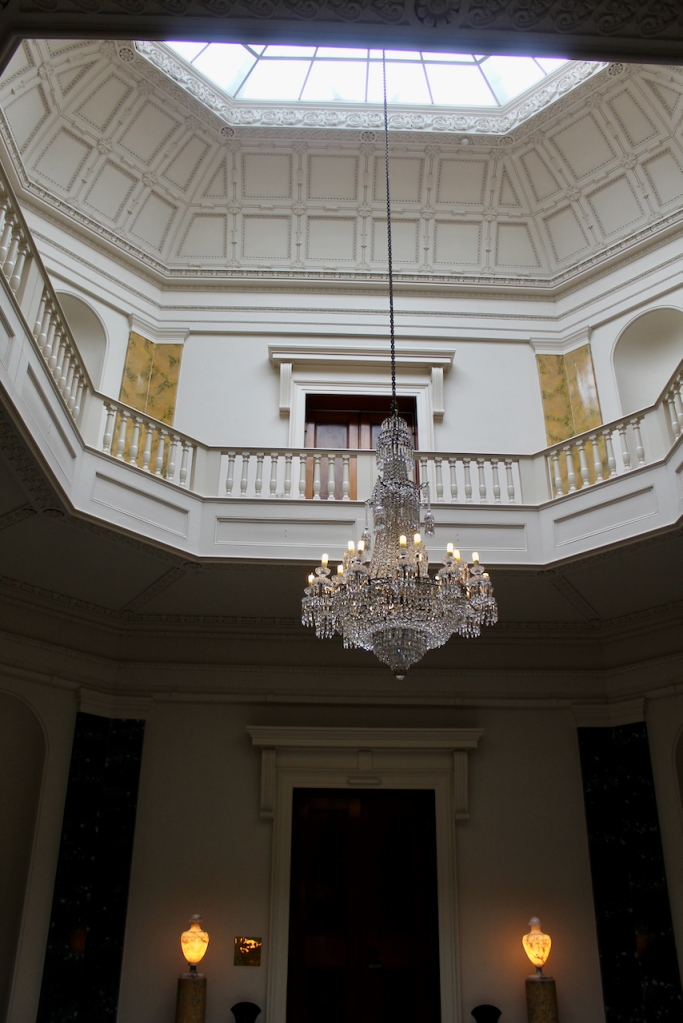
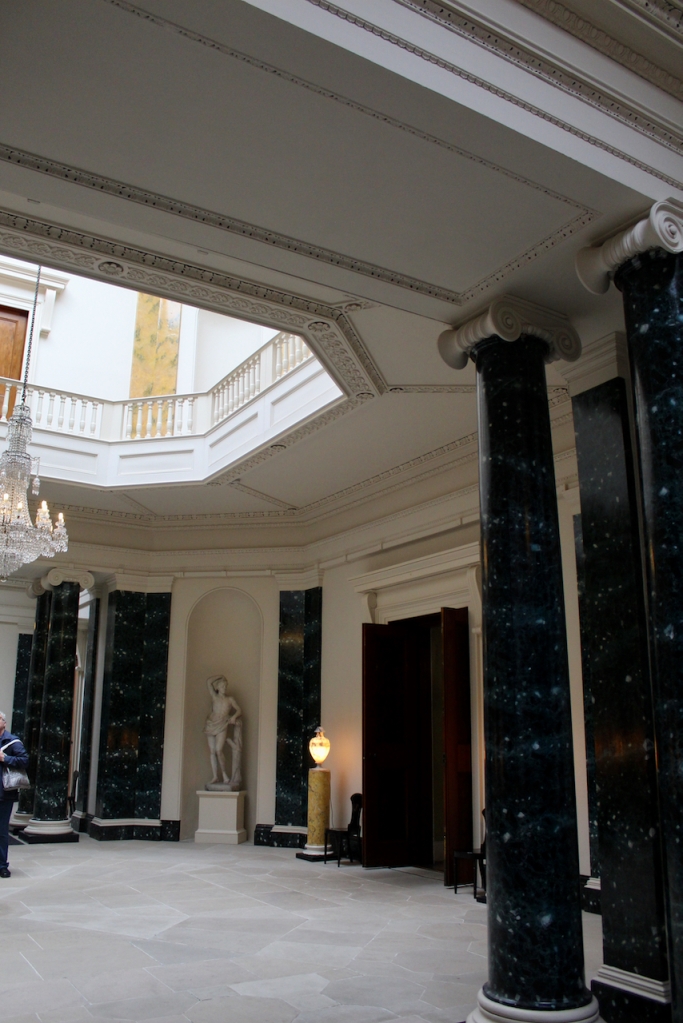
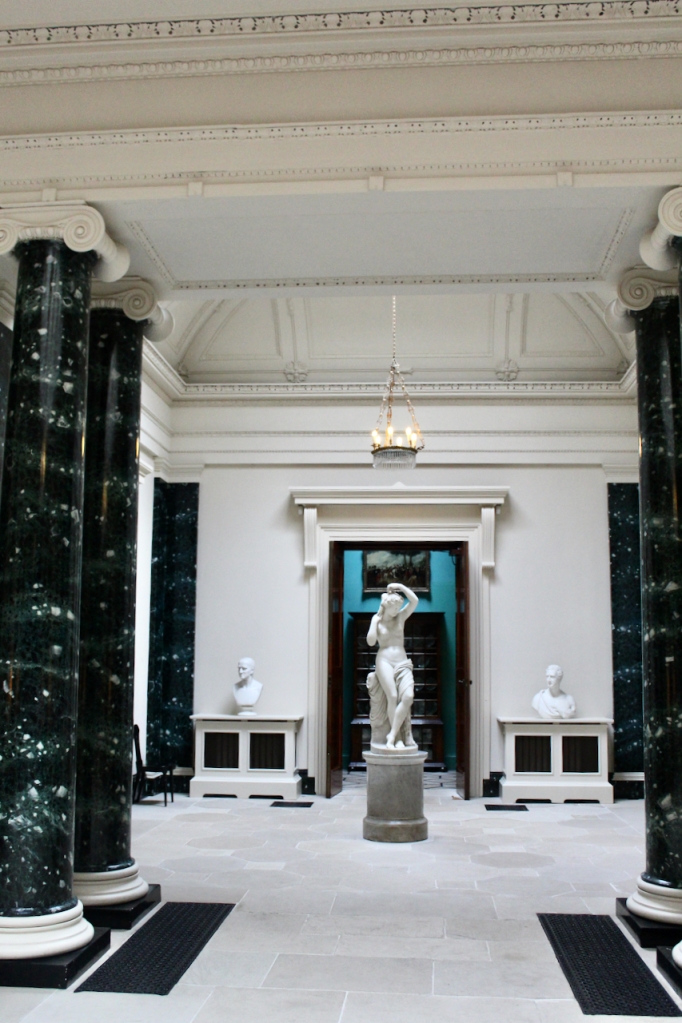
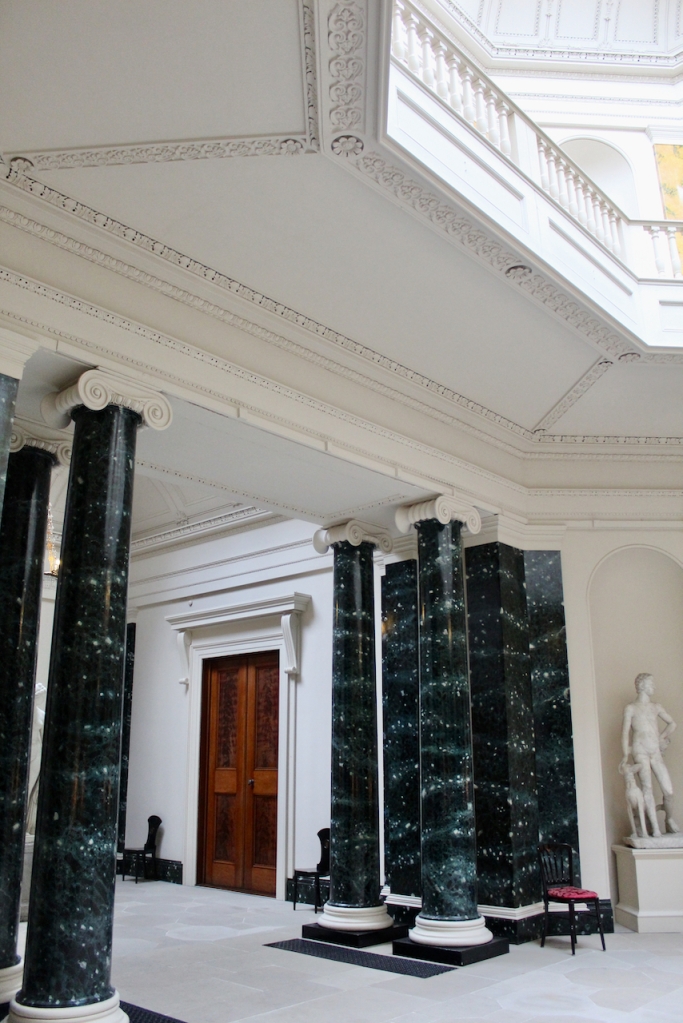
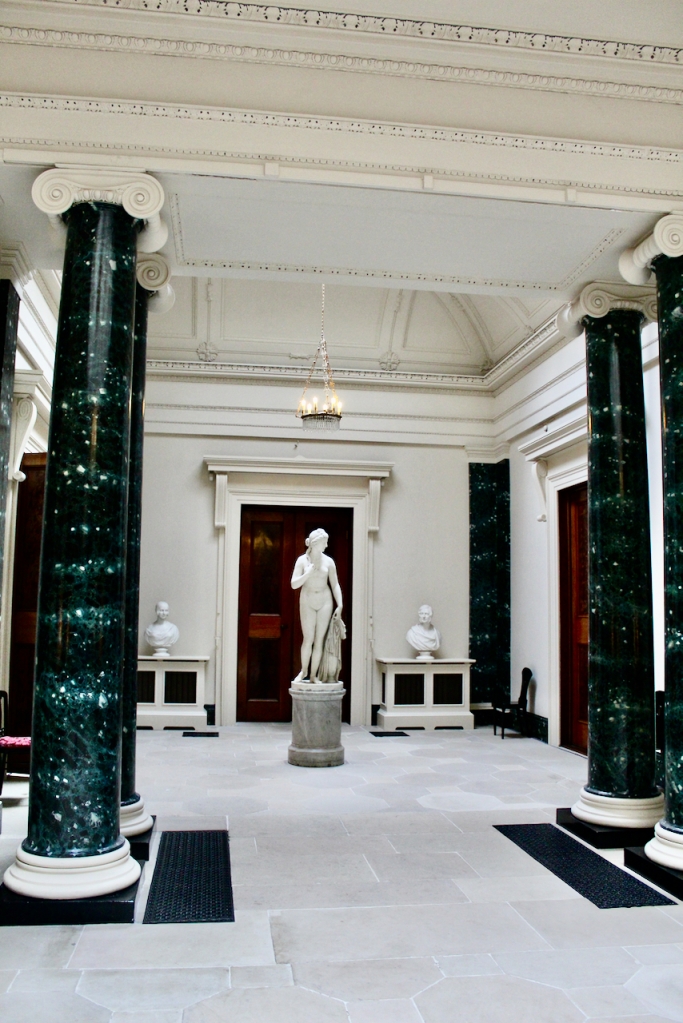
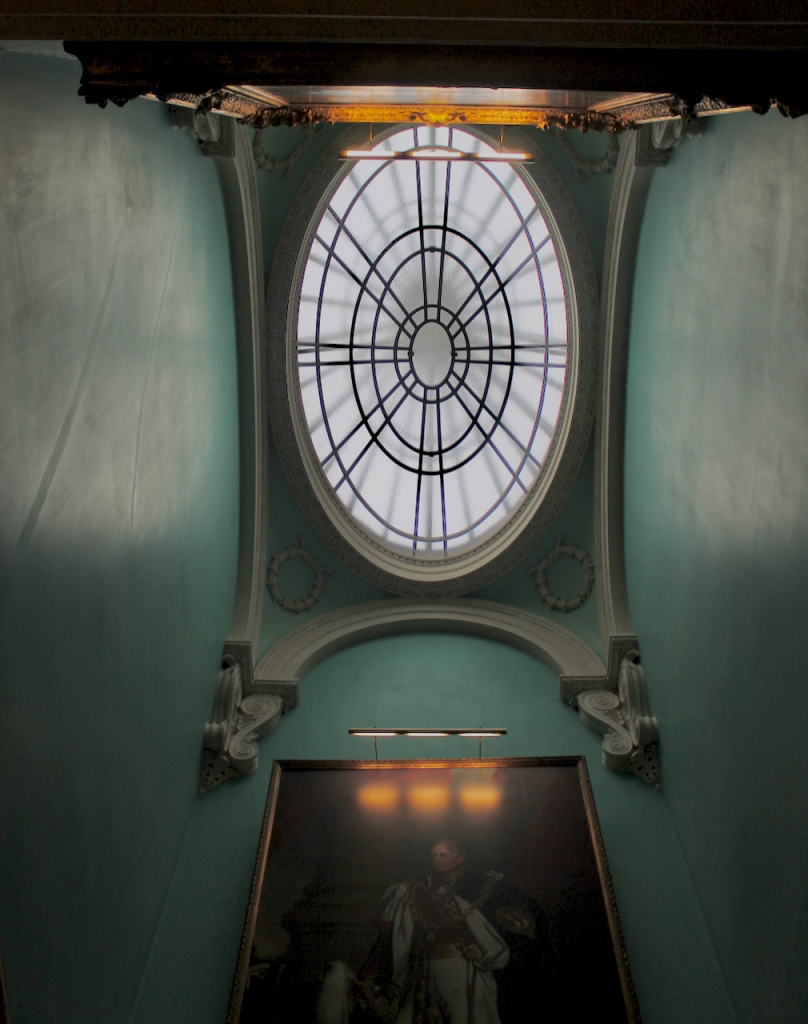
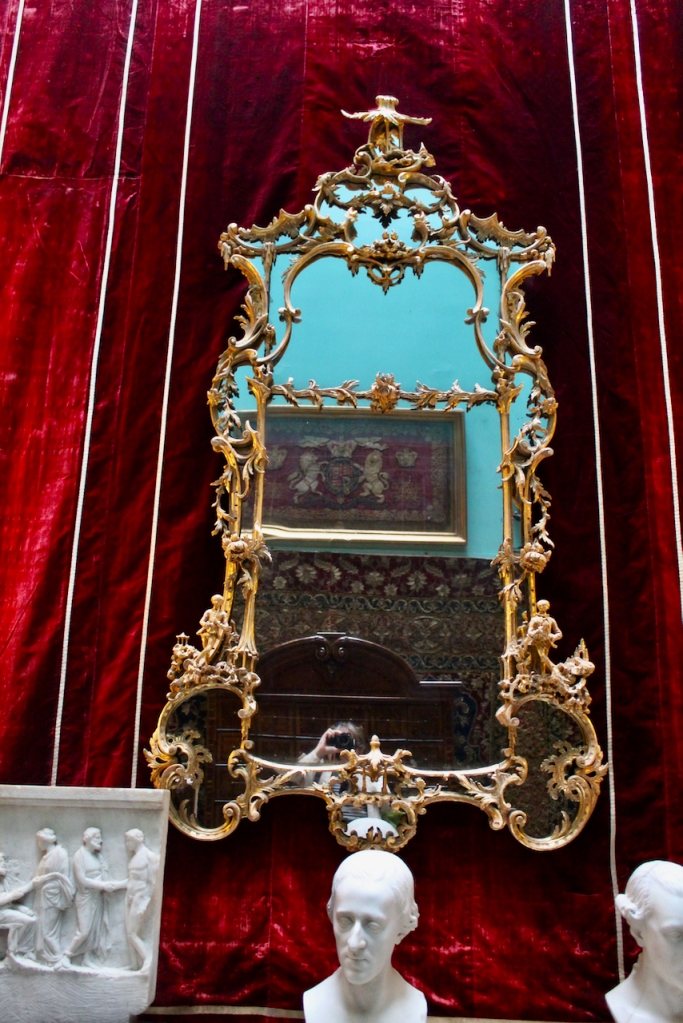
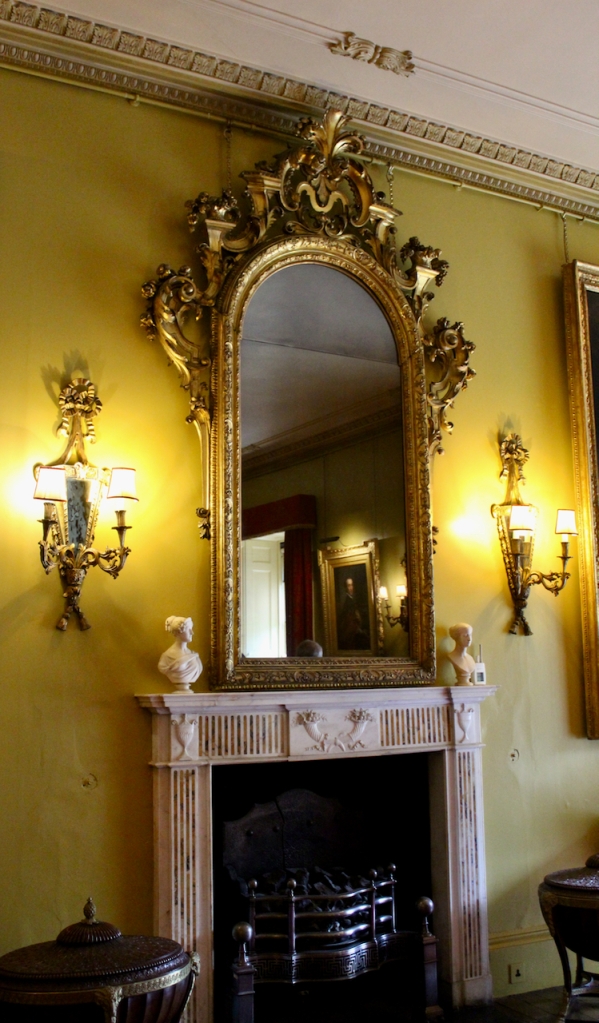
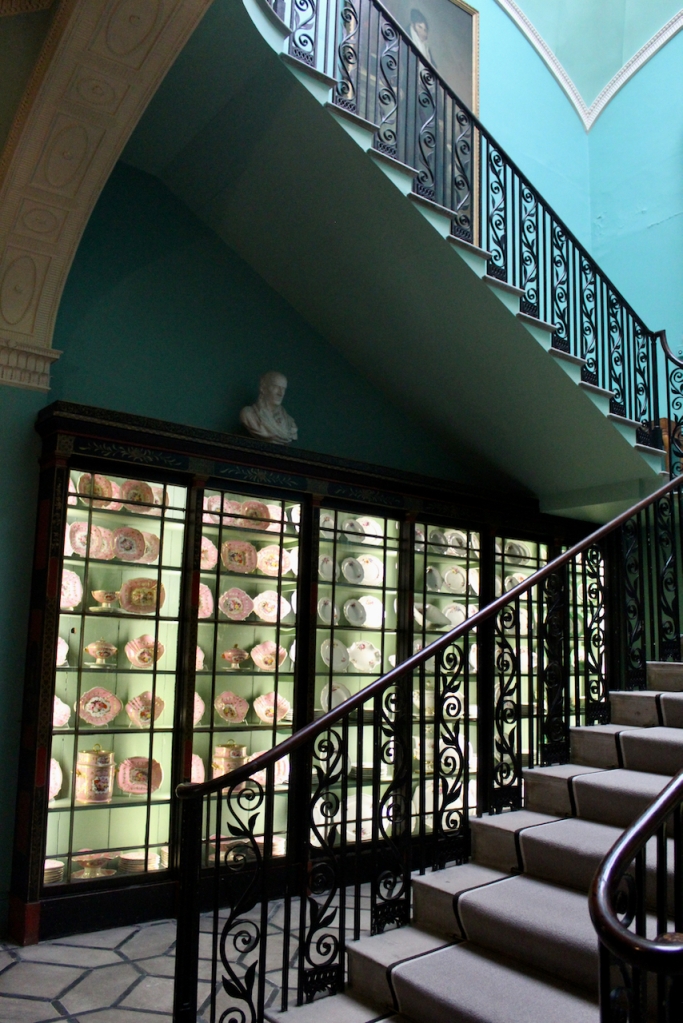
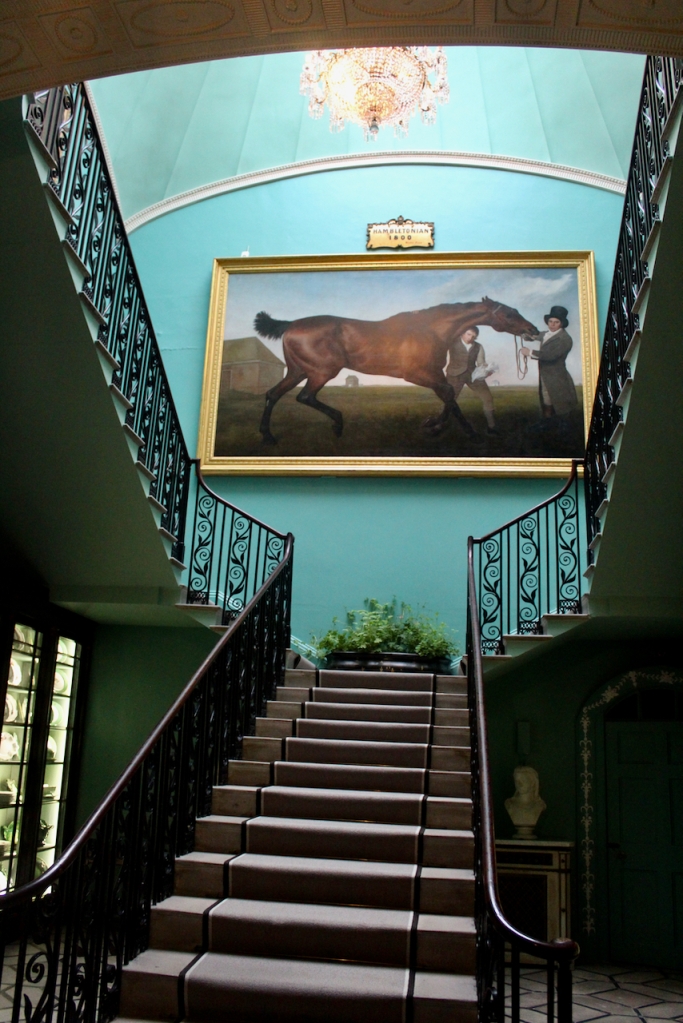
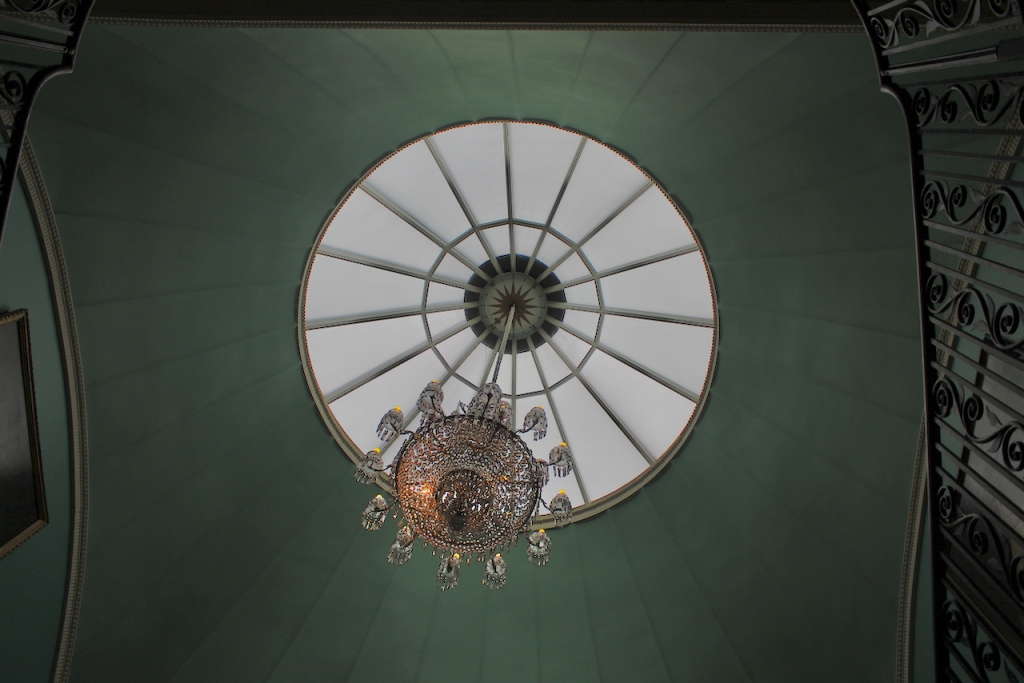
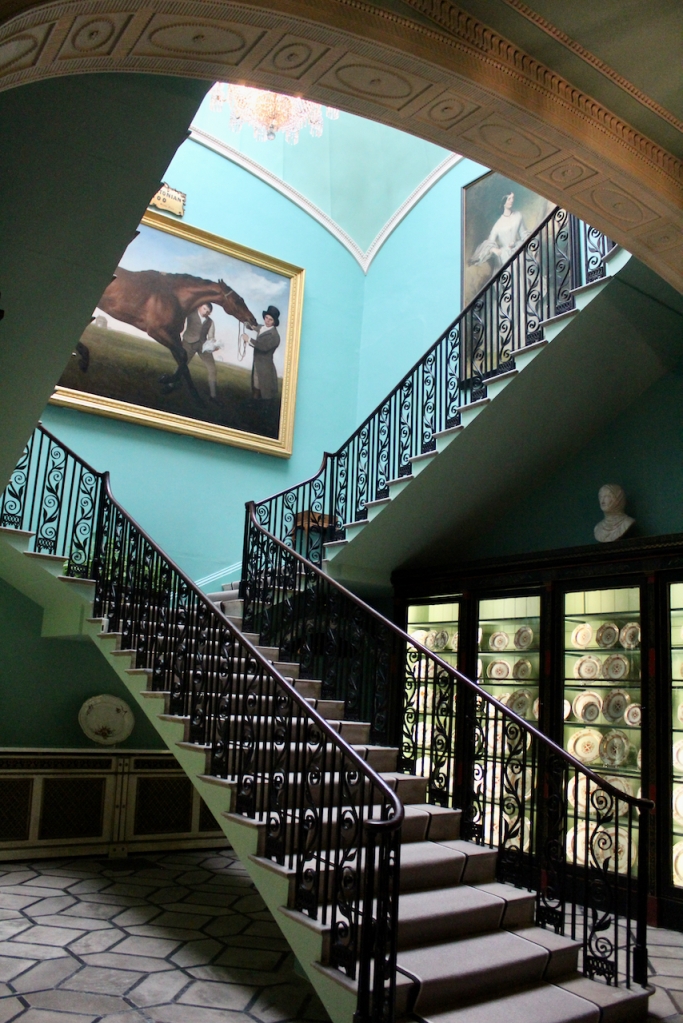
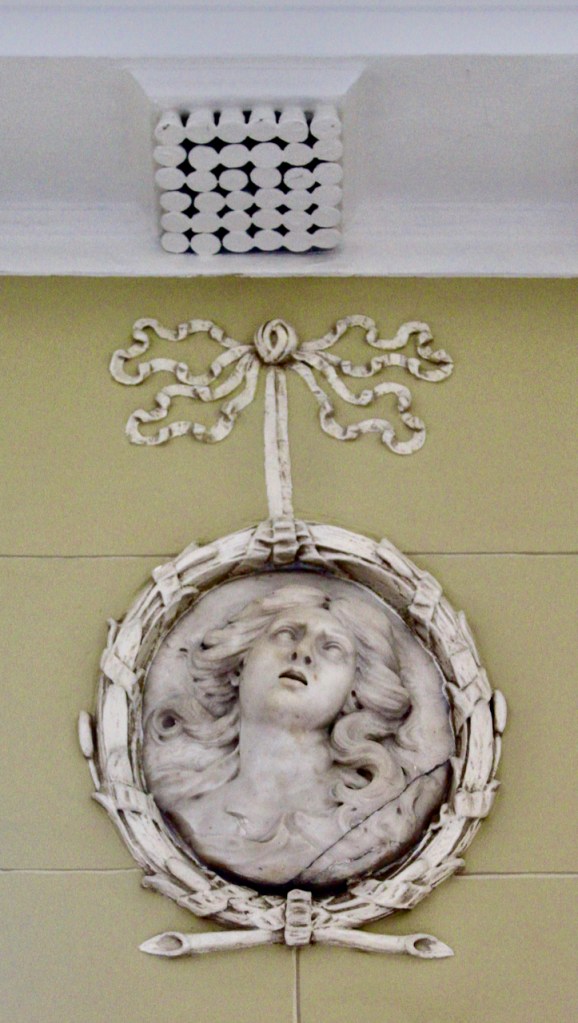
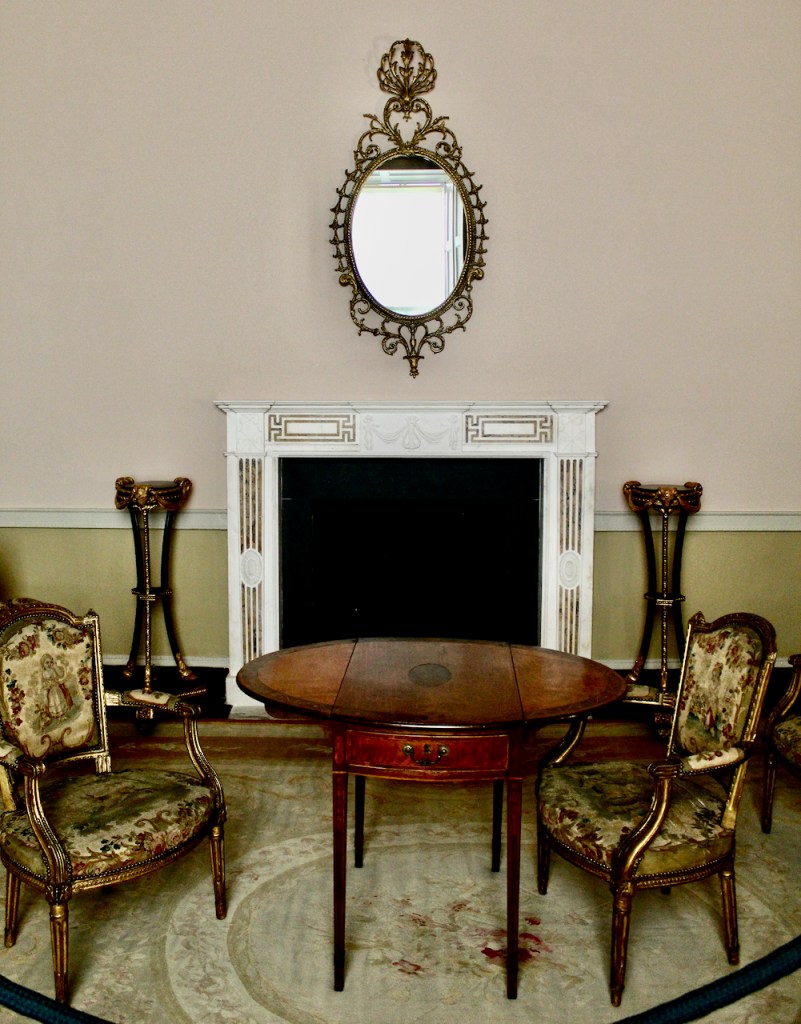
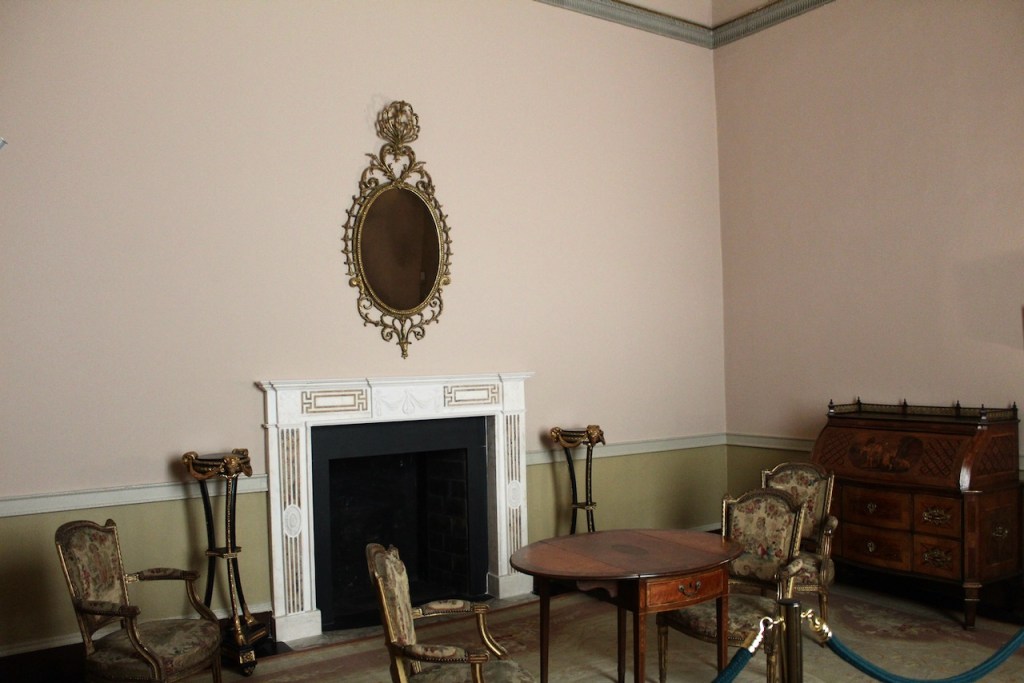
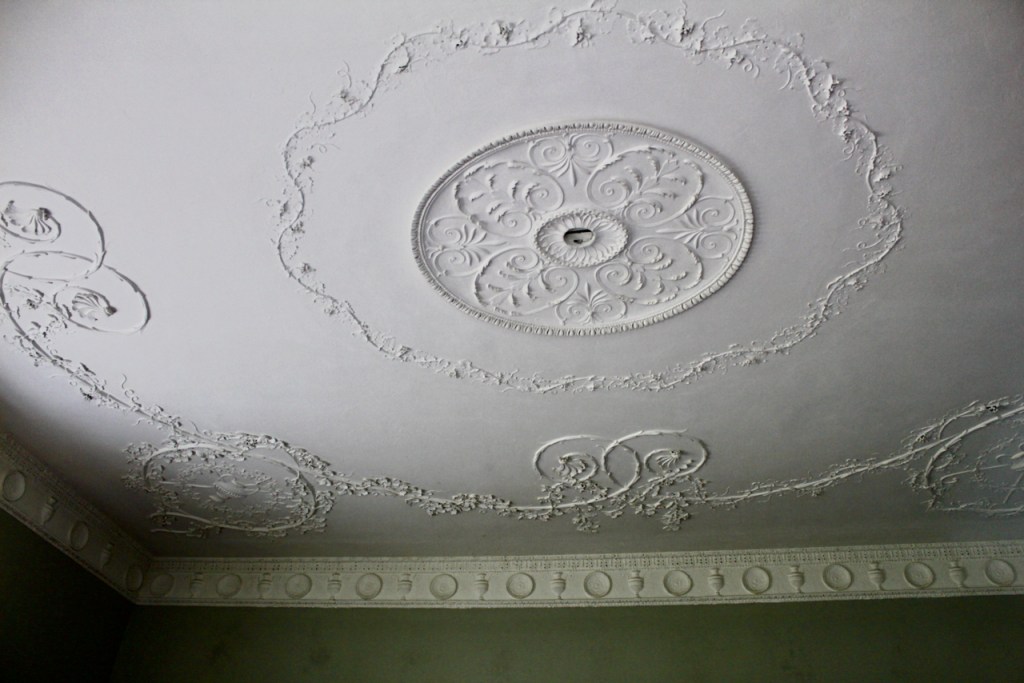
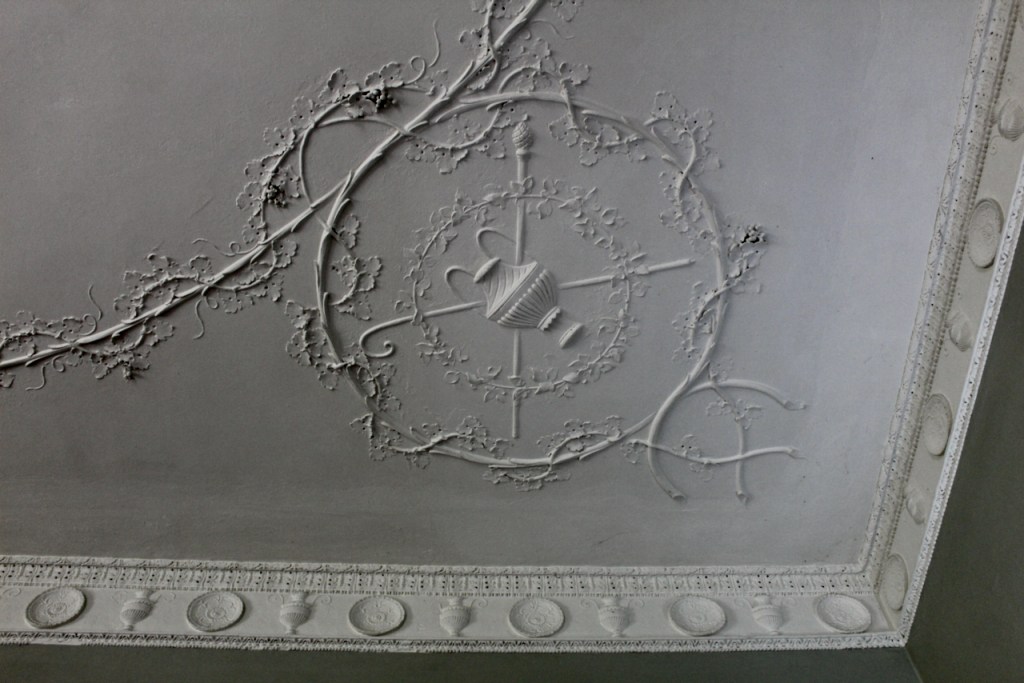
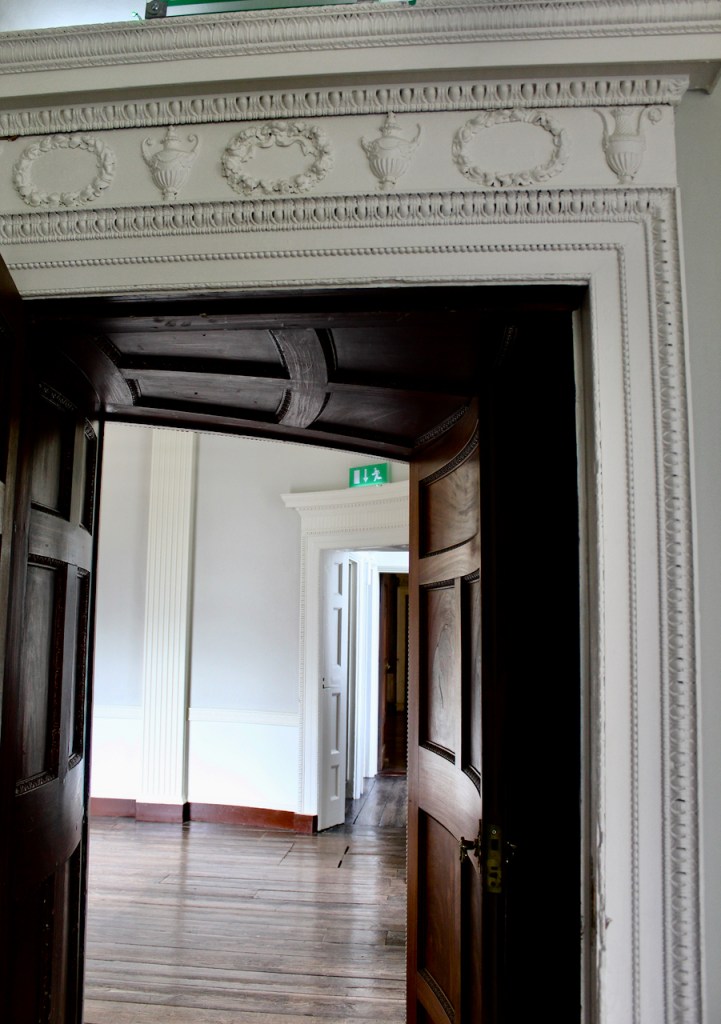
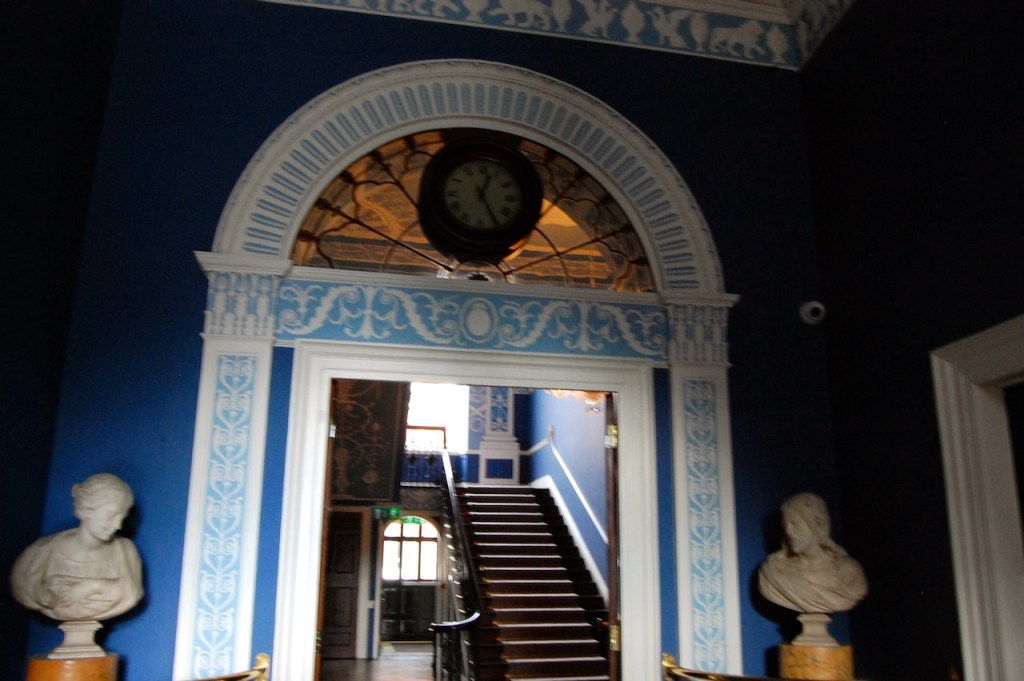
From an information panel in the entrance hall: “This room is believed to have been built to a design by the influential architect Sir William Chambers (1723-1796). Despite never visiting Ireland, Chambers left a significant mark on Dublin where he also designed the Casino at Marino, Charlemont House on Parnell Square, and much of Front Square in Trinity College. The floor and free standing Doric columns are in Portland stone. The painted glass panels featuring fruit and flowers are believed to be by the Dublin Huguenot artist Thomas Jervais (d. 1799). The marble relief busts on the walls depict well known figures from the Classical and Renaissance past, including the Egyptian queen Cleopatra and Italian poet Dante. These sculptures seem to have been acquired in Italy and would have been incorporated into the design of the Entrance Hall to signal the taste and refinement and learning of the Loftus family. The original eighteenth century marble fireplace was replaced with a painted timber one in around 1913. It was one of several of the original fireplaces which were removed and sold when the Blackburne family left the castle in 1911.“
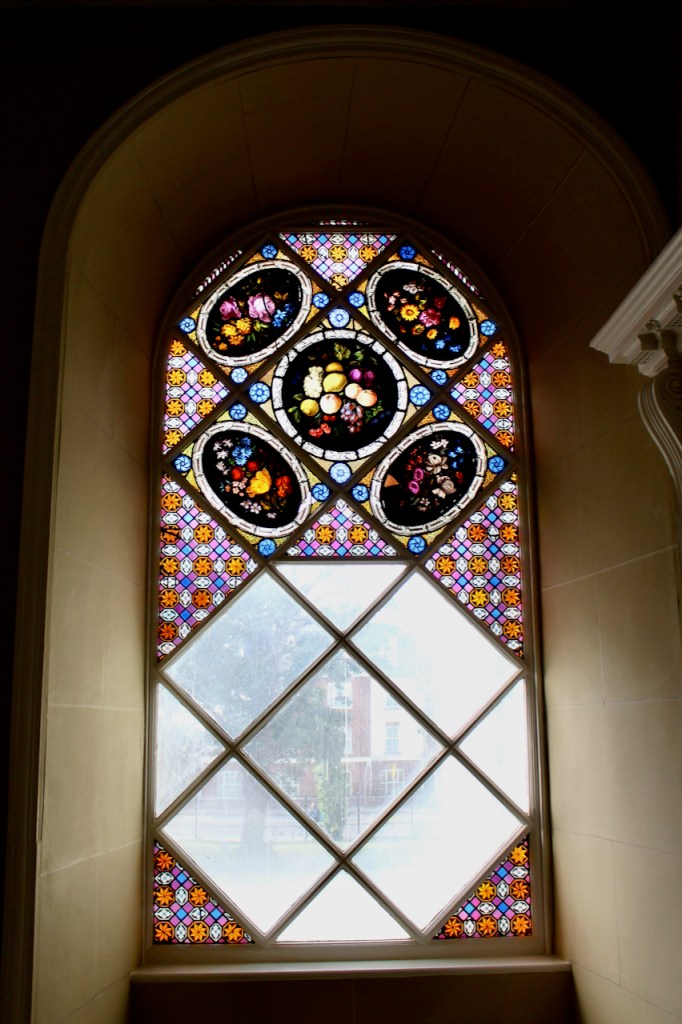
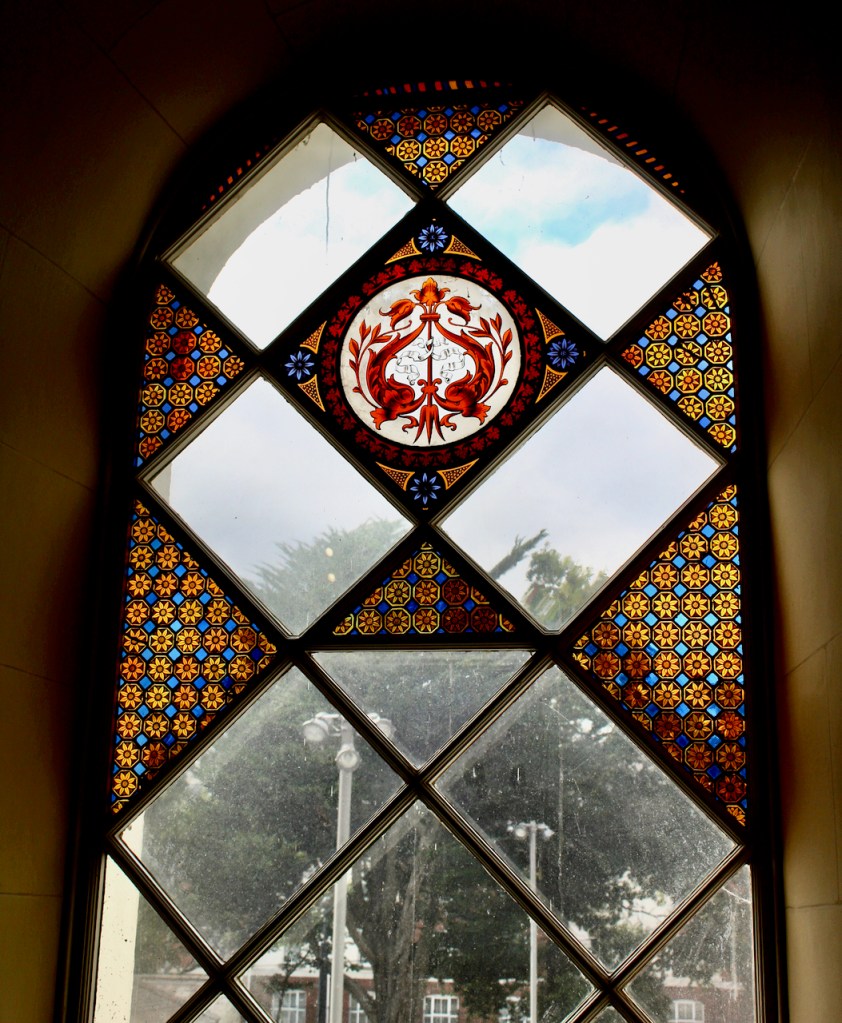
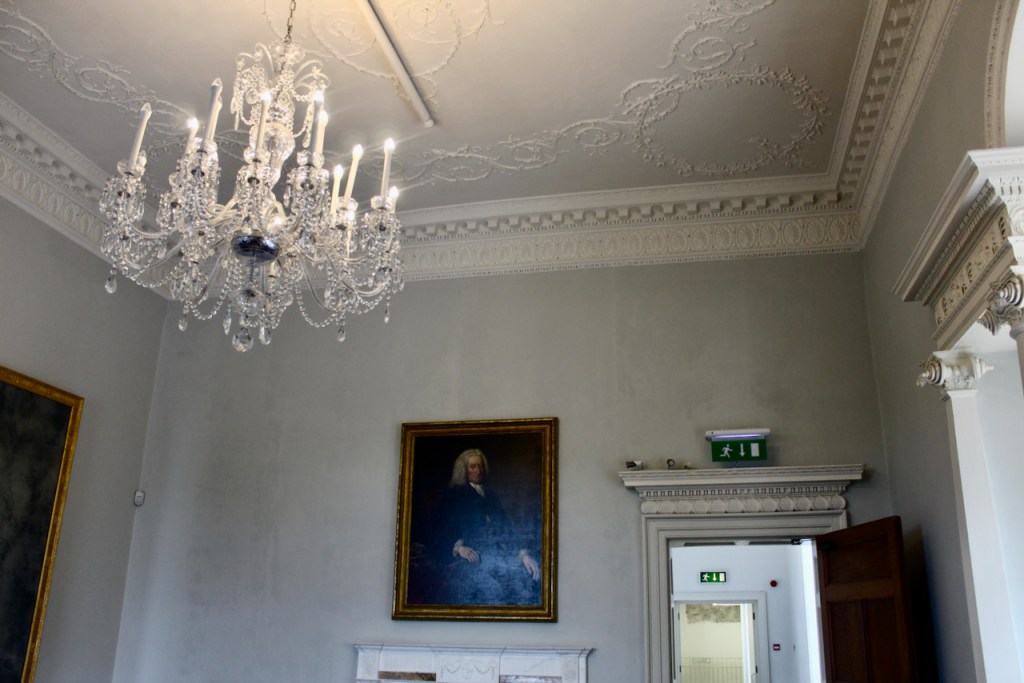
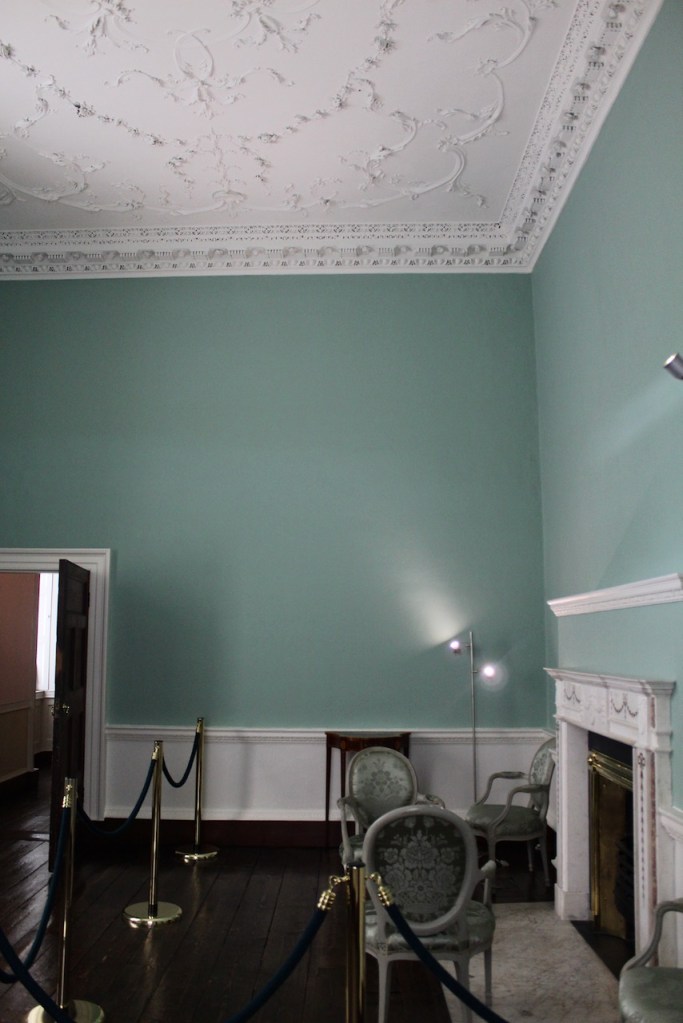














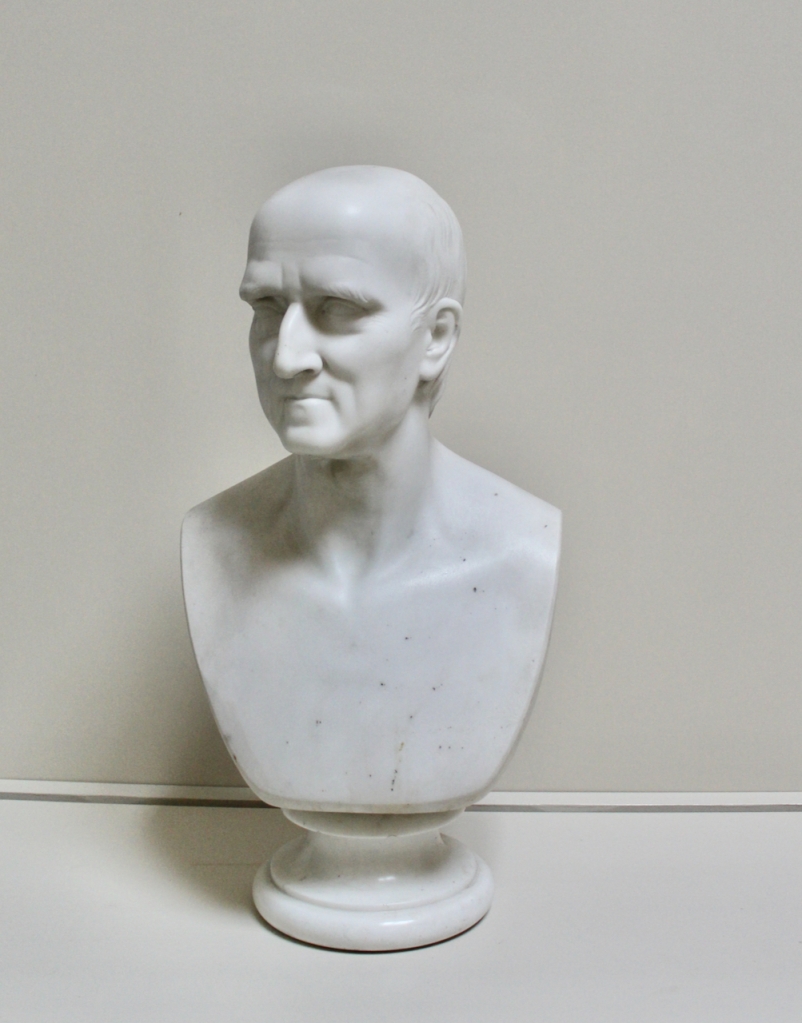
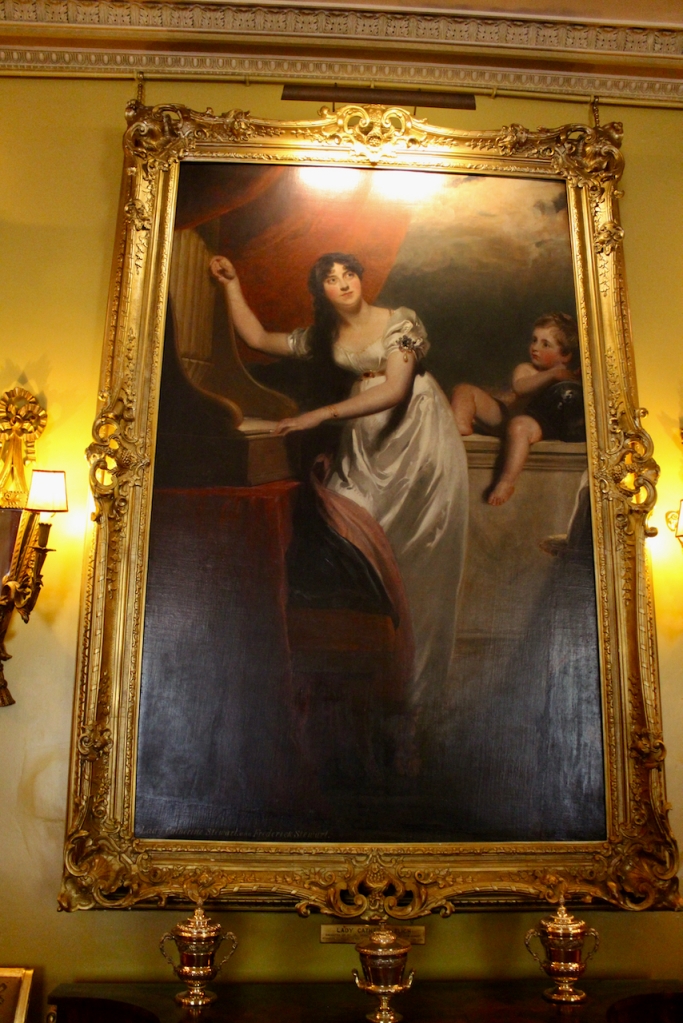
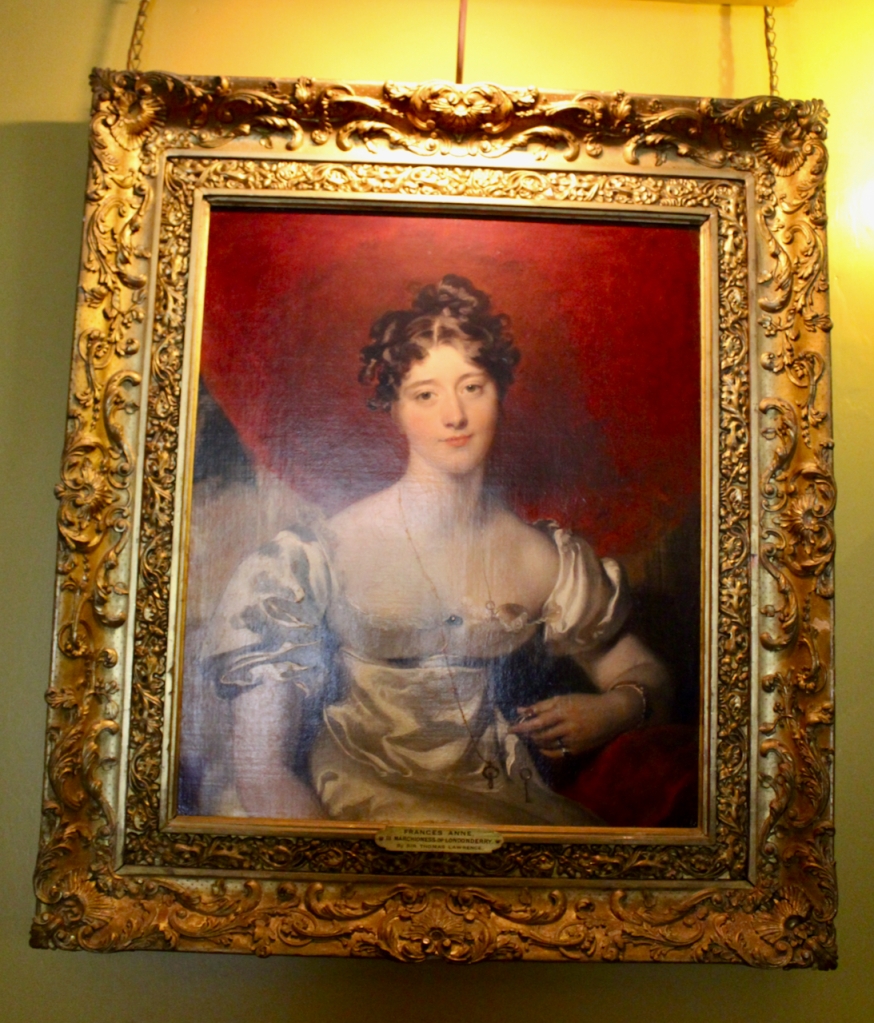
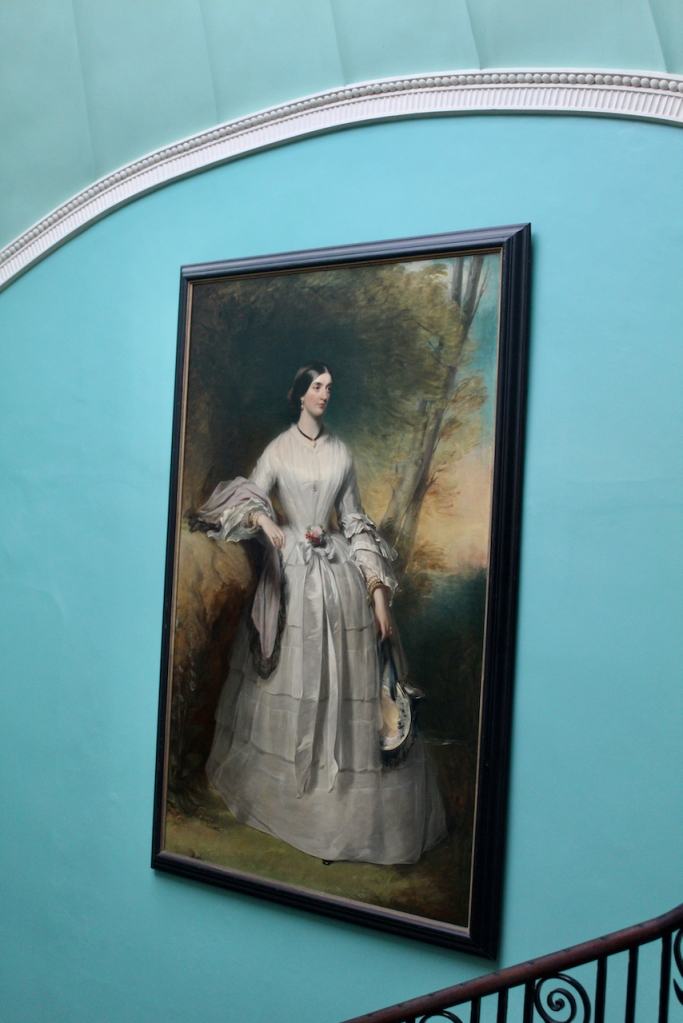
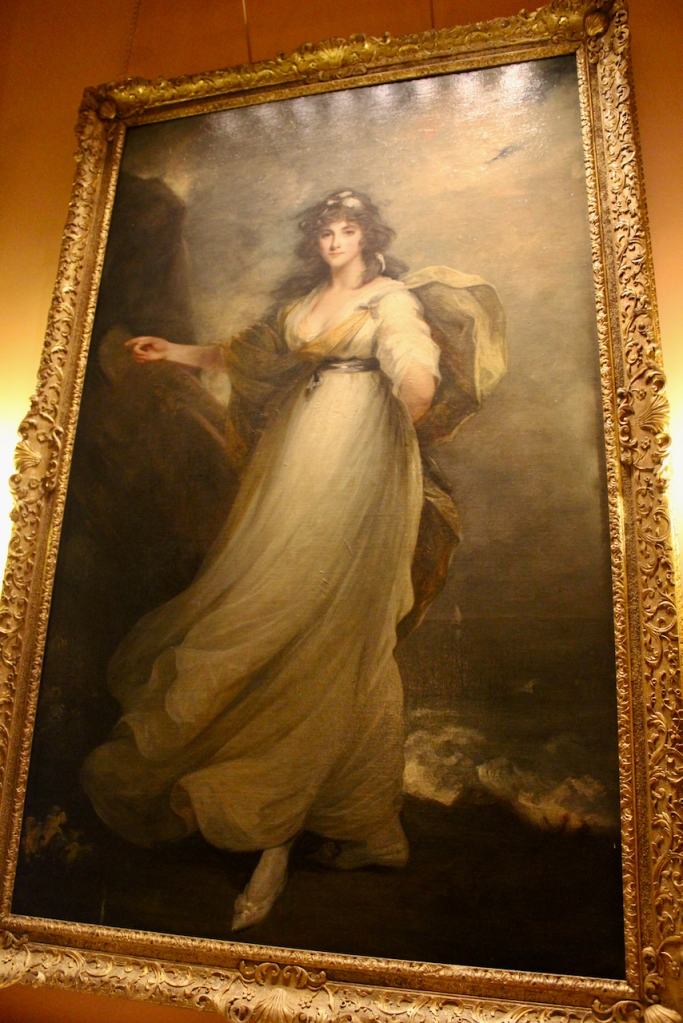
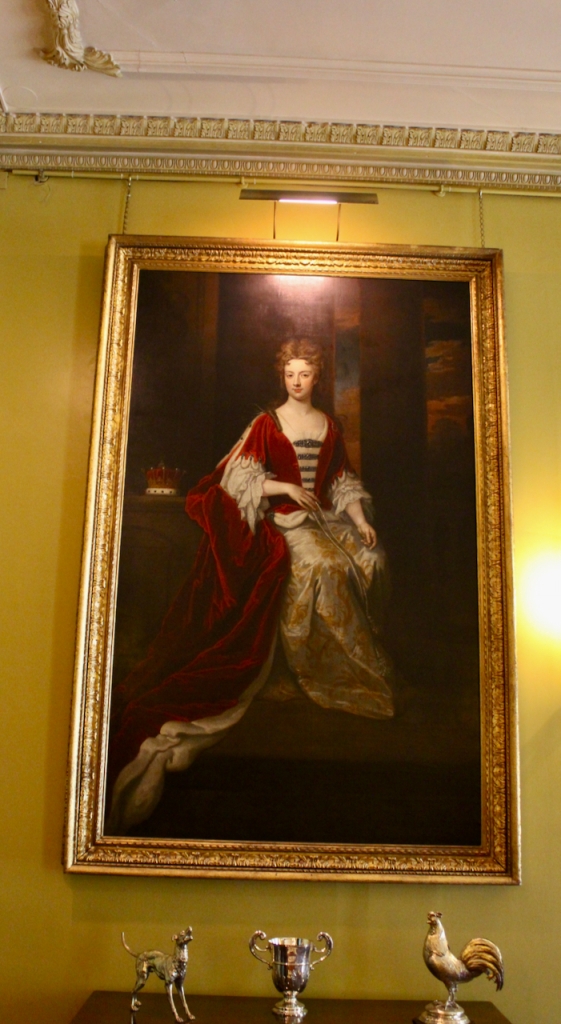
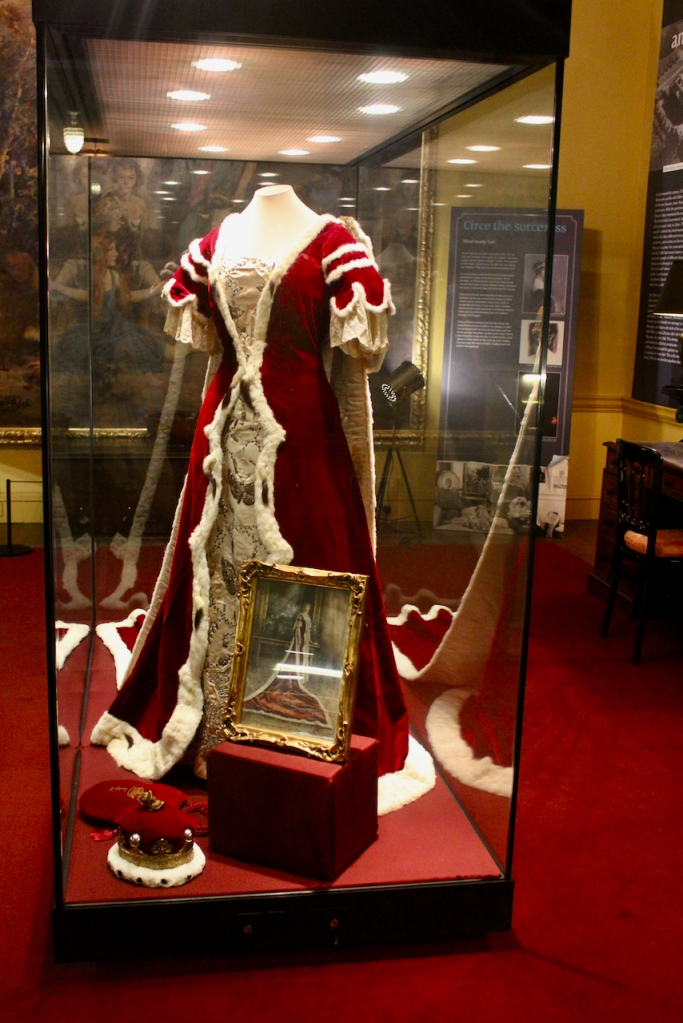
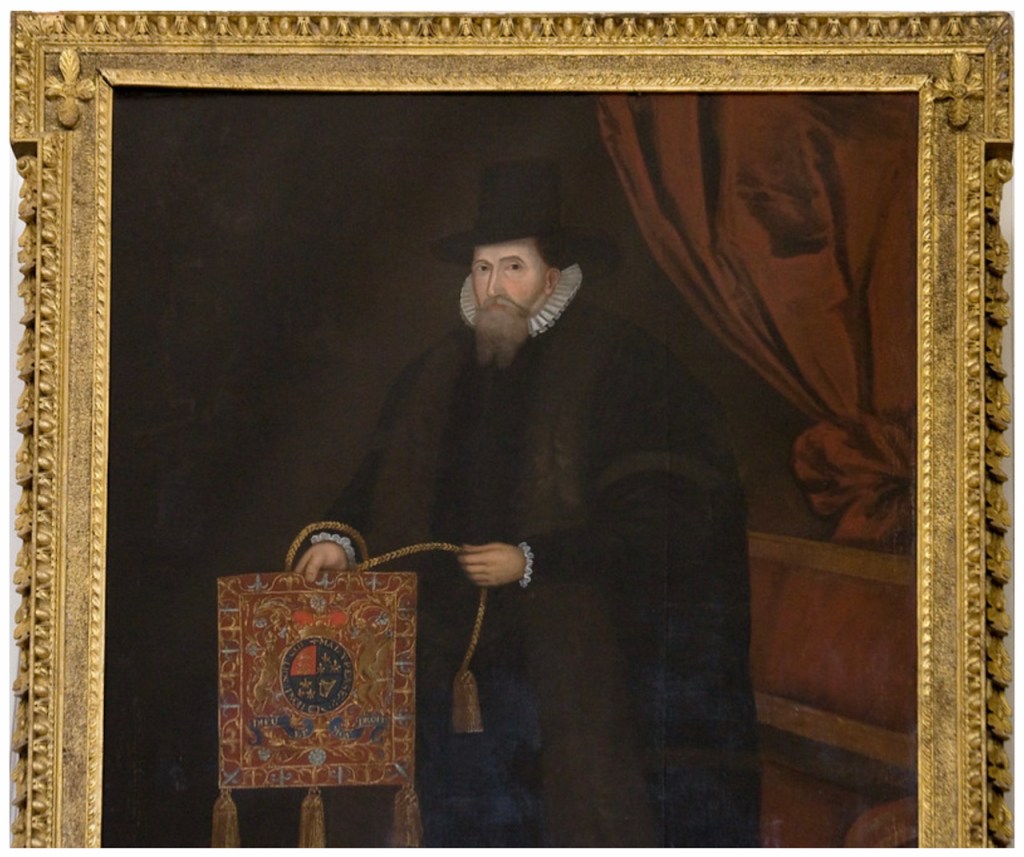
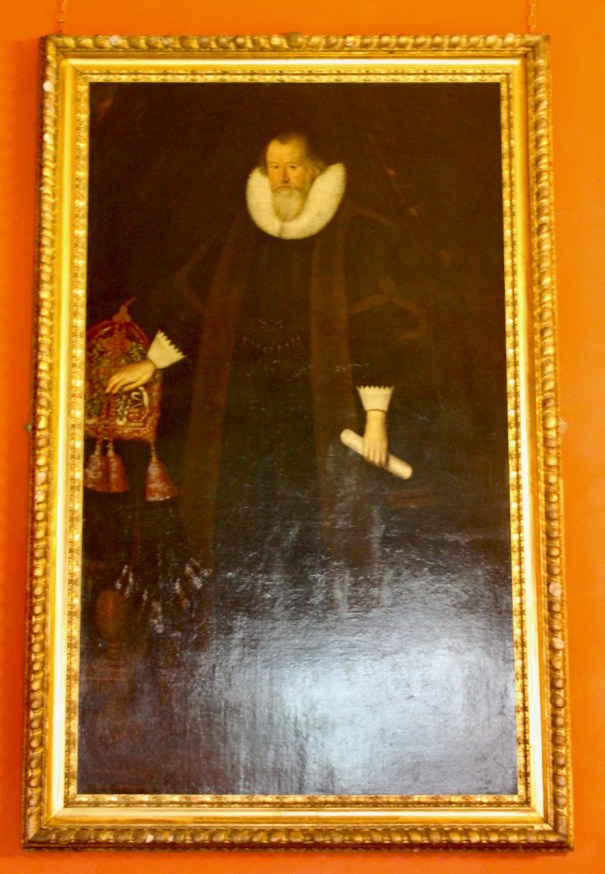
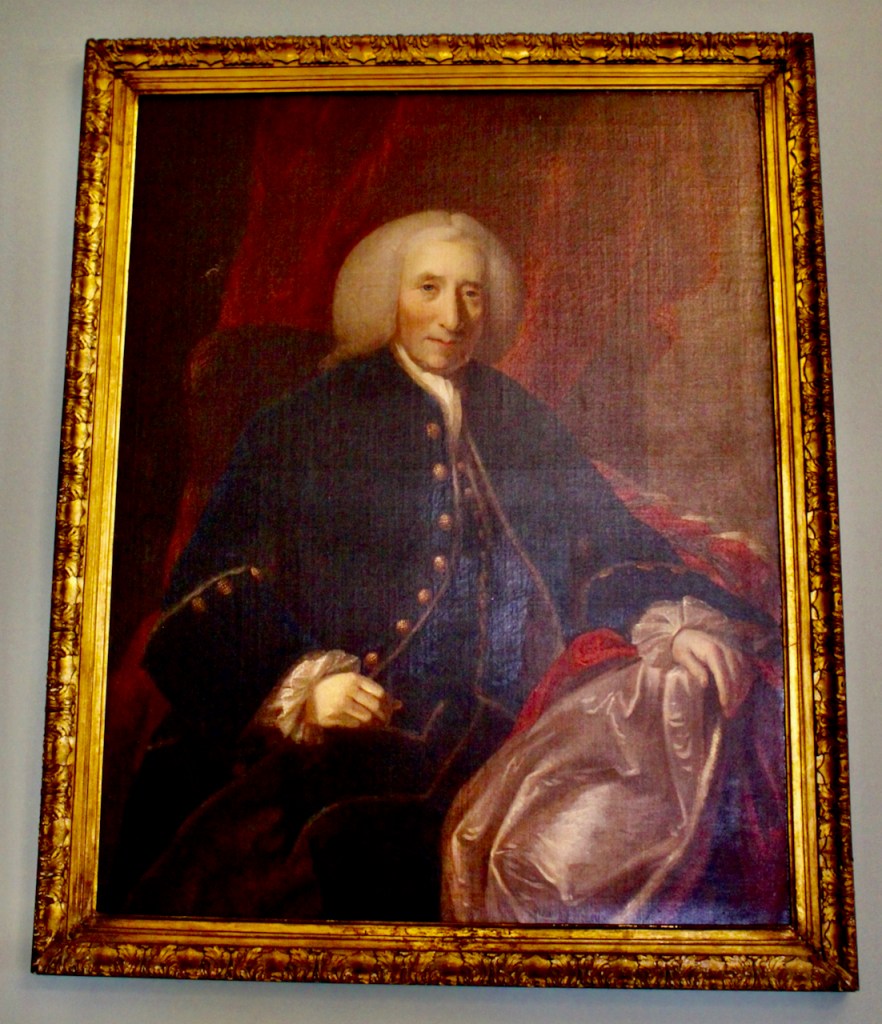
Henry Loftus (1709-1783) is pictured below. He married first, Frances Monroe of Roe’s Hall, County Down, (pictured below), who died in 1774, then married secondly Anne Bonfoy. He purchased Ely House in Dublin (built 1770) from Sir Gustavus Hume, 3rd Baronet (now owned by the Knights of Columbanus).

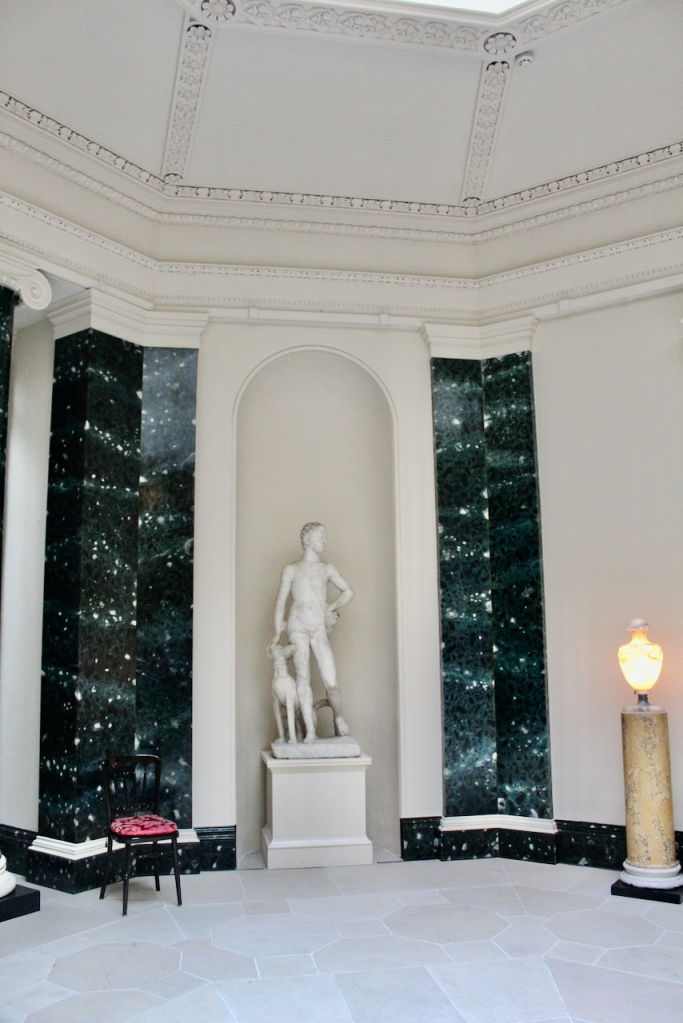
As well as the ante room and ballroom and the entrance hall on the first floor, Chambers was responsible for the small drawing room ceiling, back staircase lobby, and the octagonal room in one of the towers.
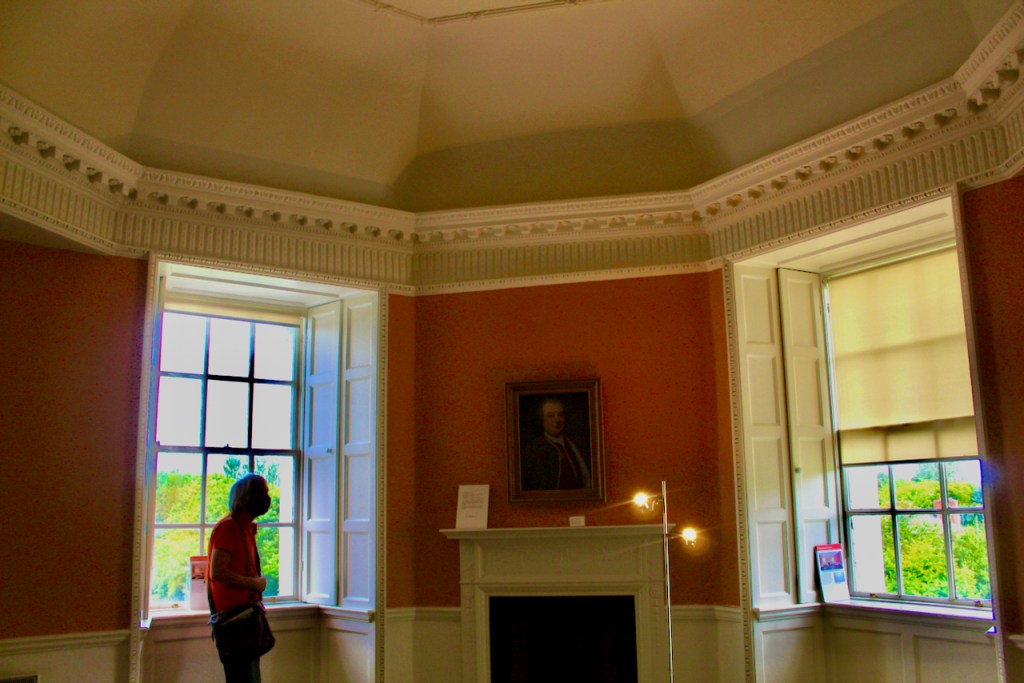
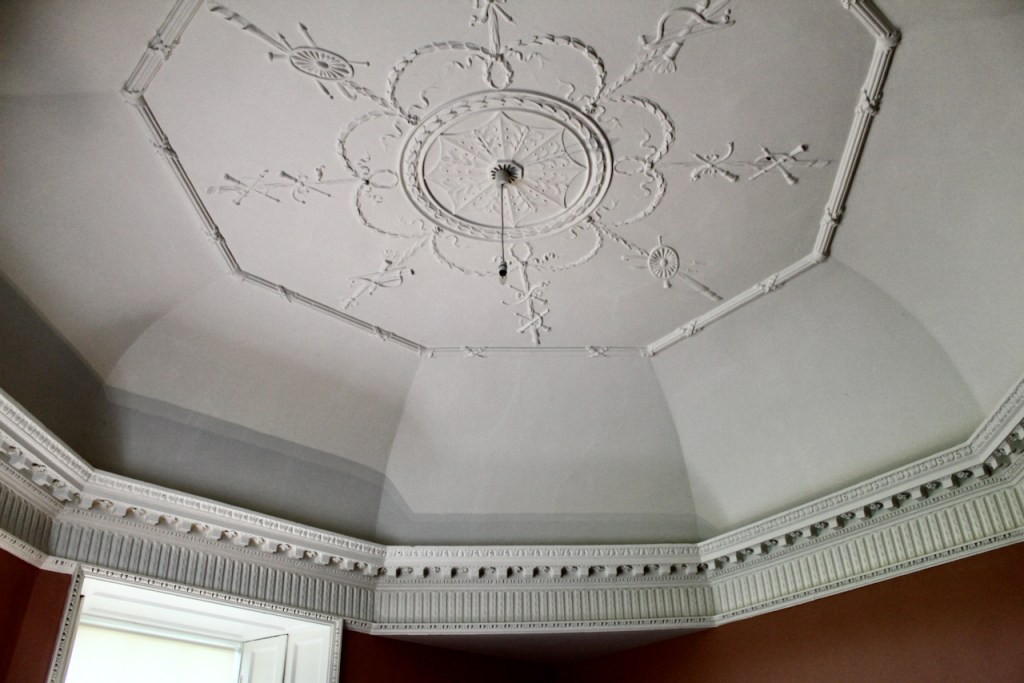
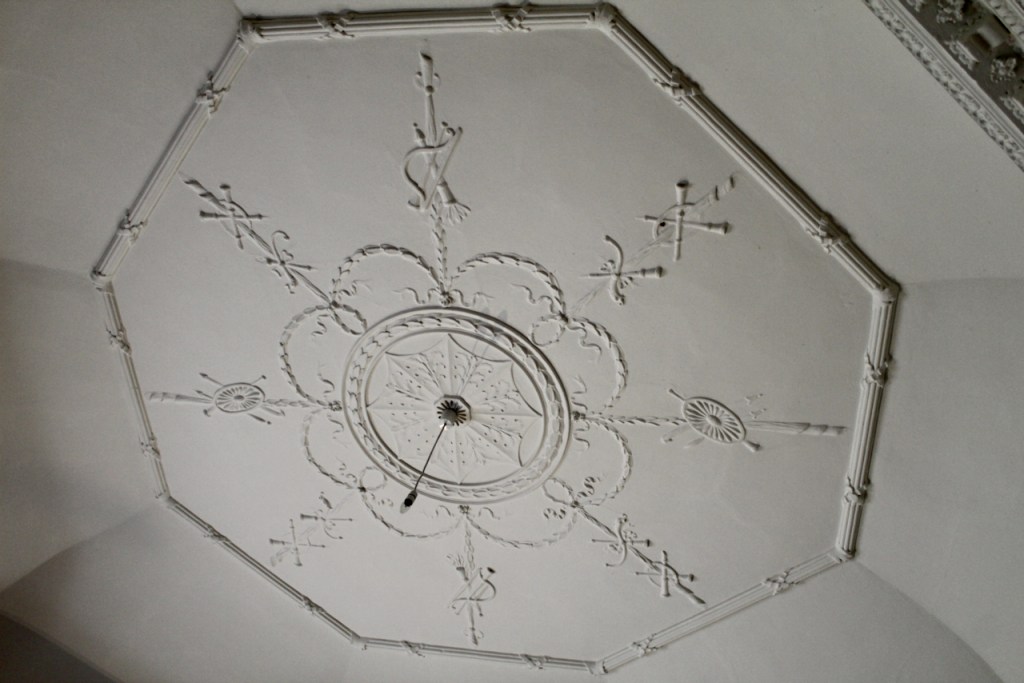
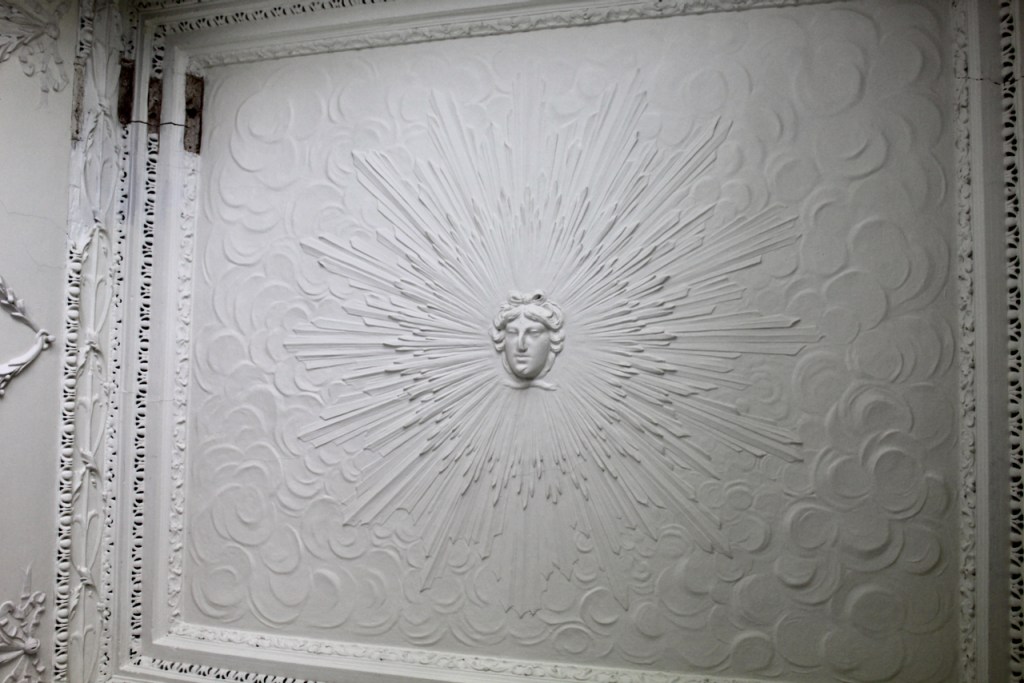
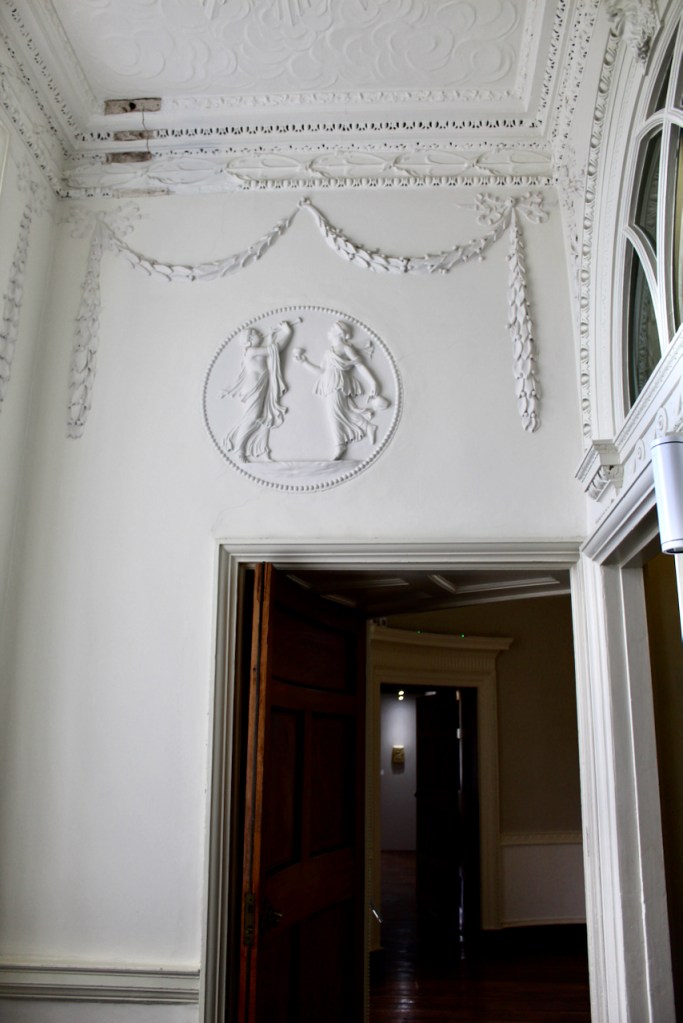





There are also several rooms which are attributed to architect and designer James “Athenian” Stuart, whose best work in Ireland is the Temple of the Winds at Mount Stewart, County Down. Stuart was employed at Rathfarnham from at least 1769 and was responsible for the design of the ground floor gallery and two rooms above it. He was also involved in the decoration of some interiors at the family townhouse, Ely House, Dublin.
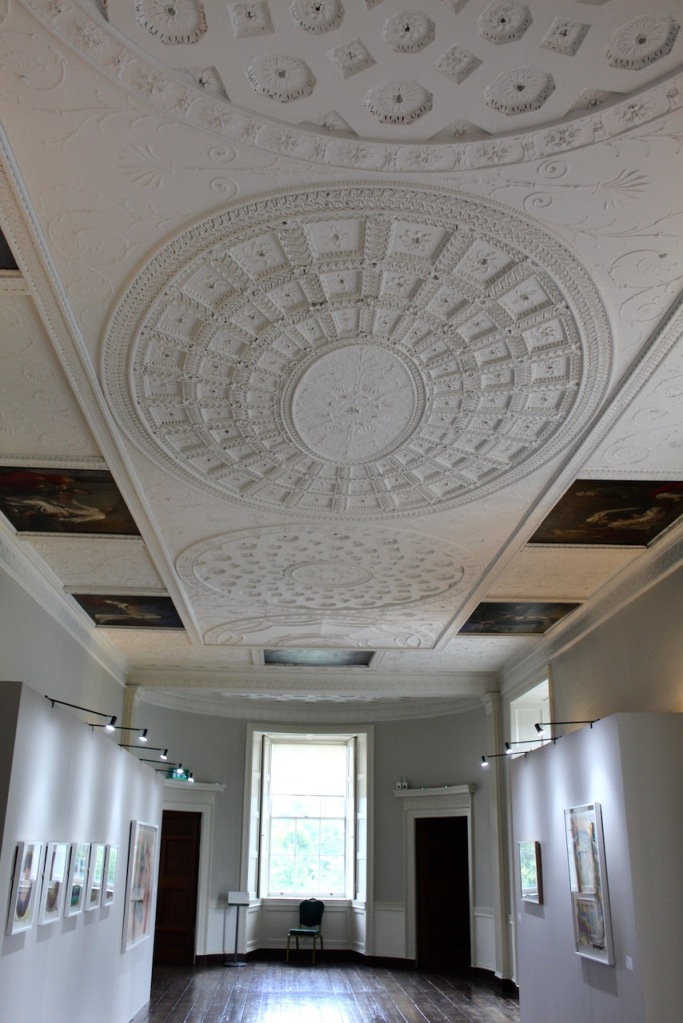
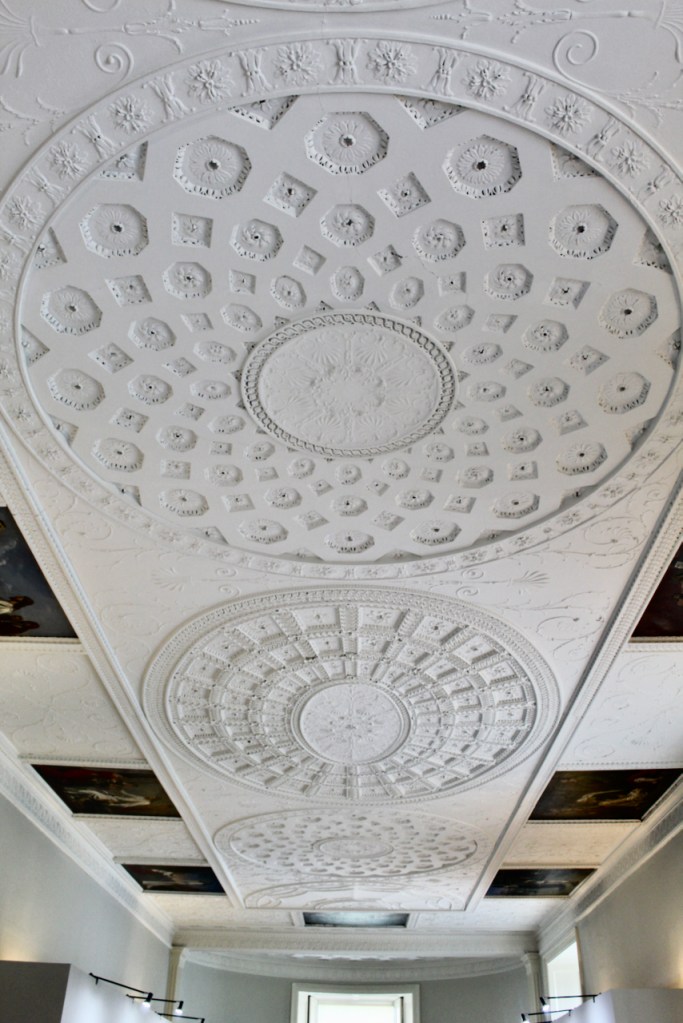
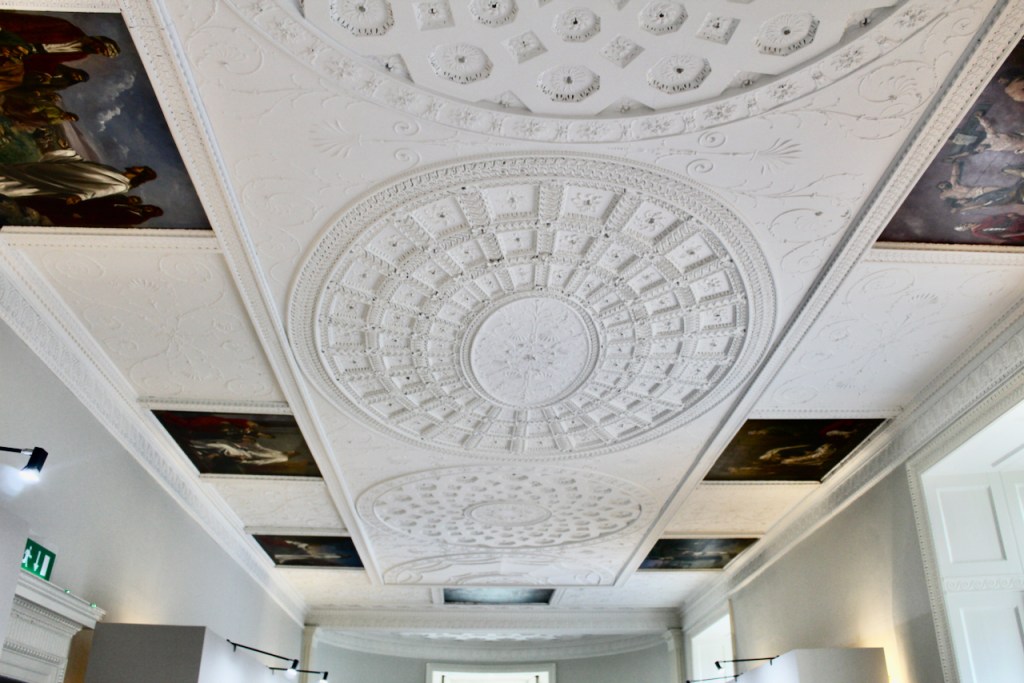
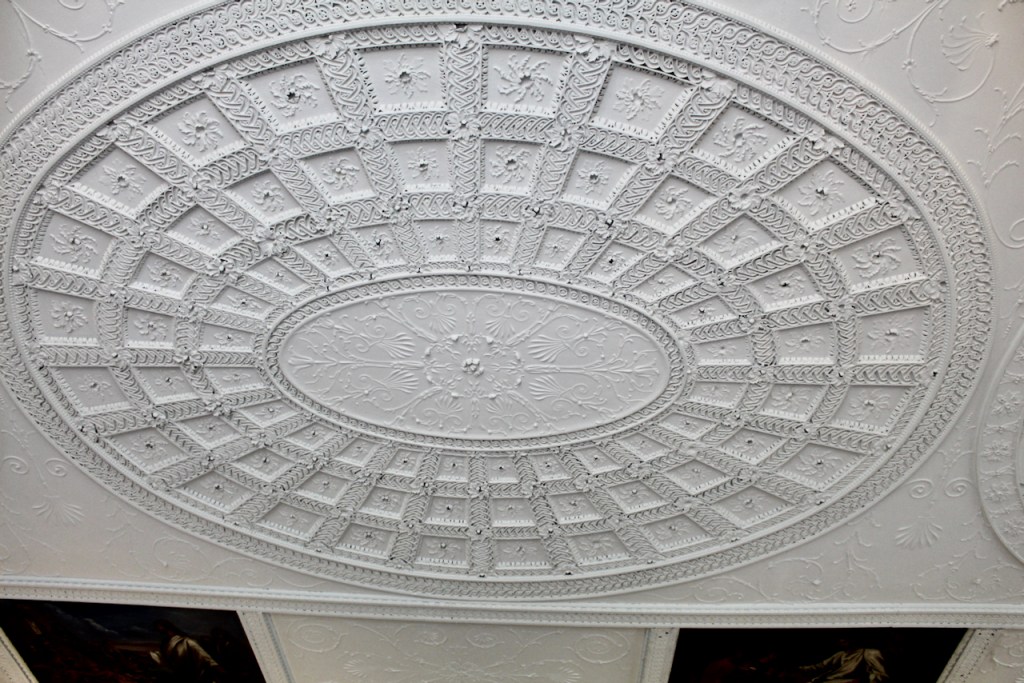
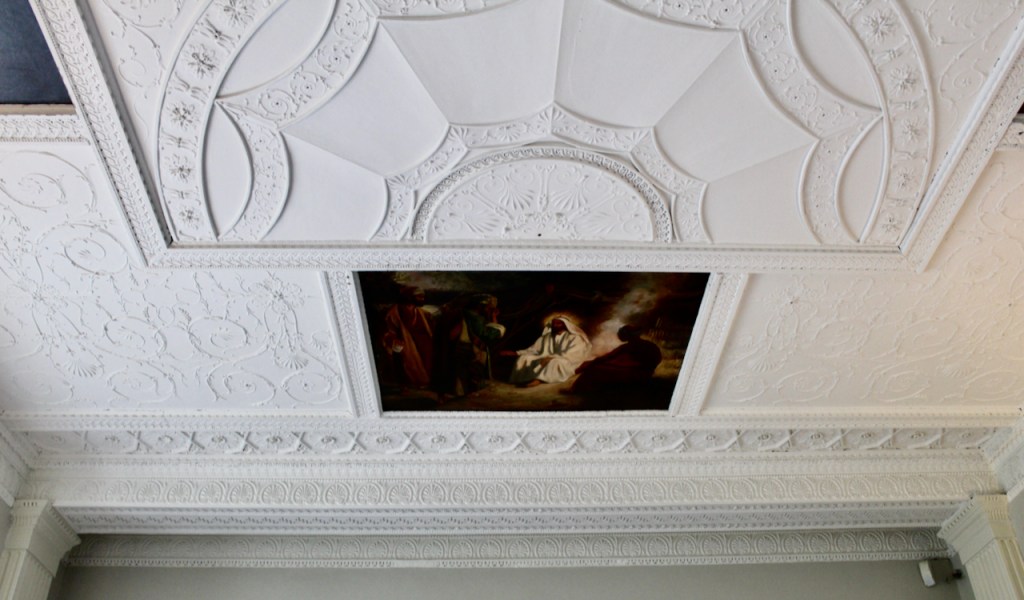
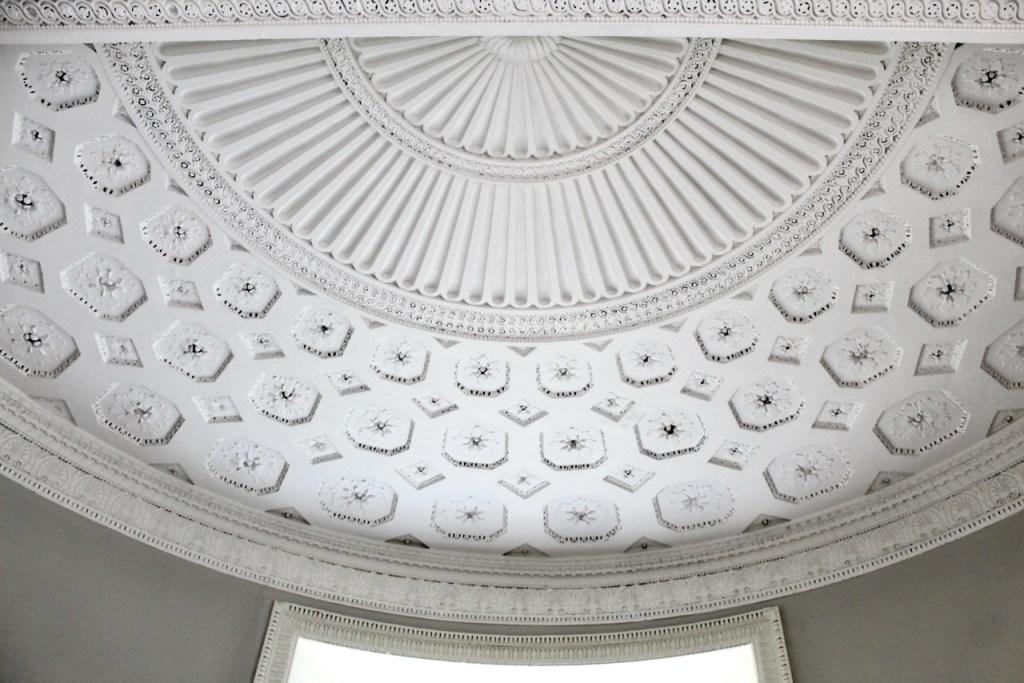
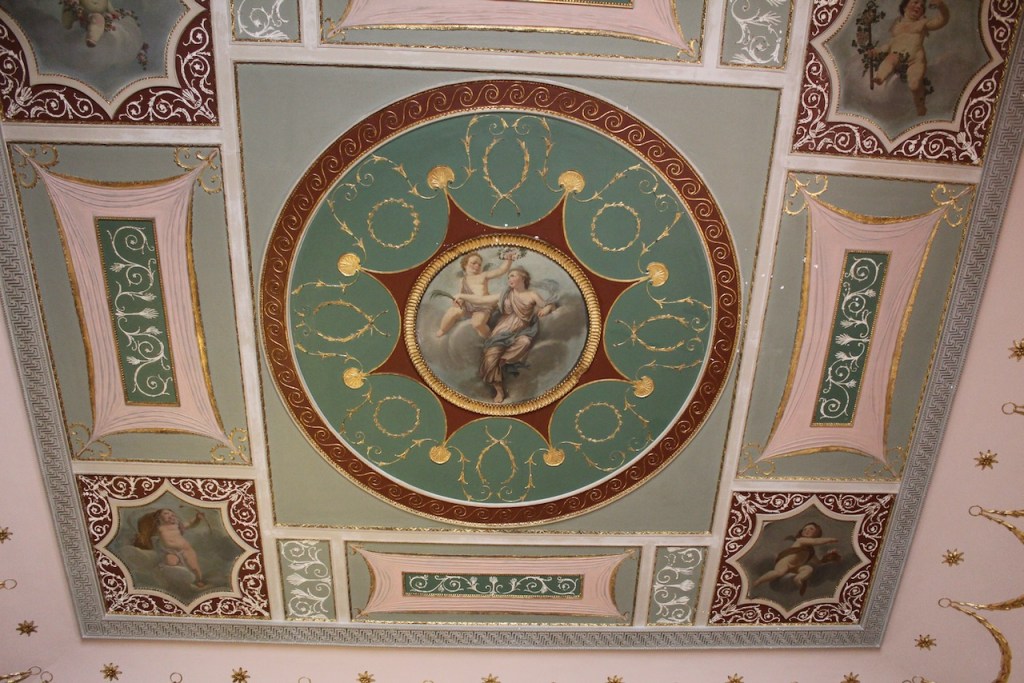















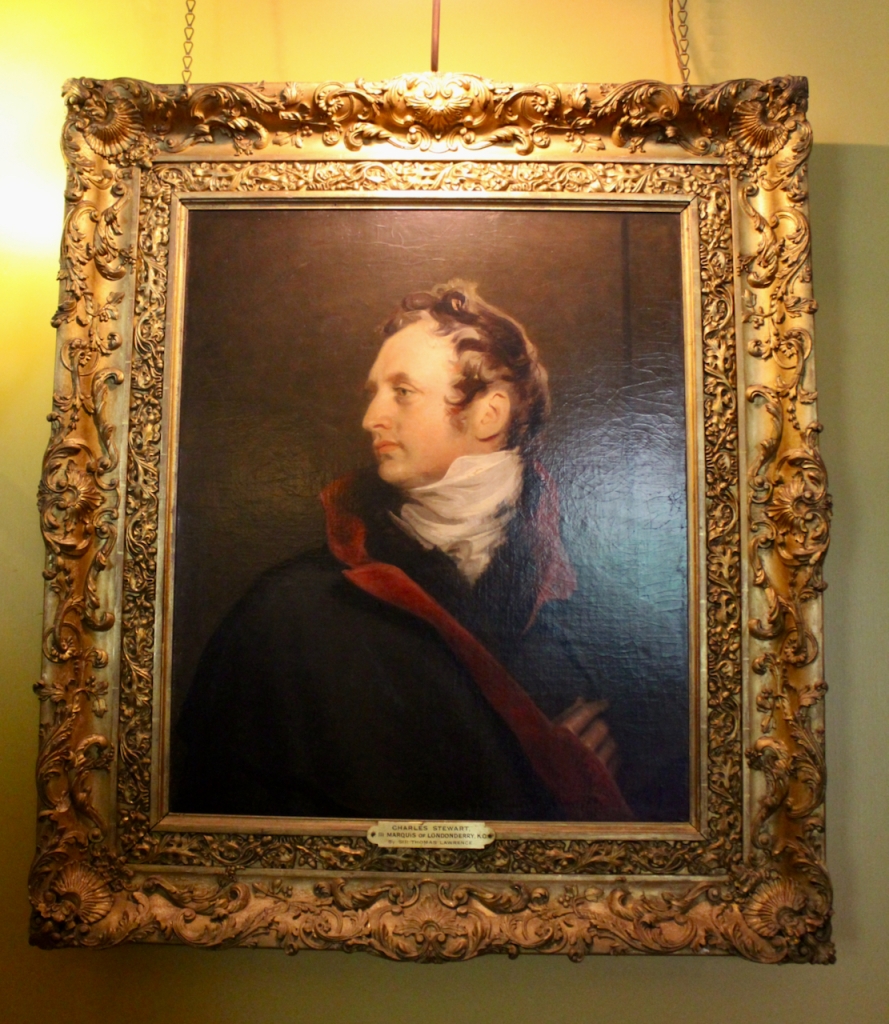
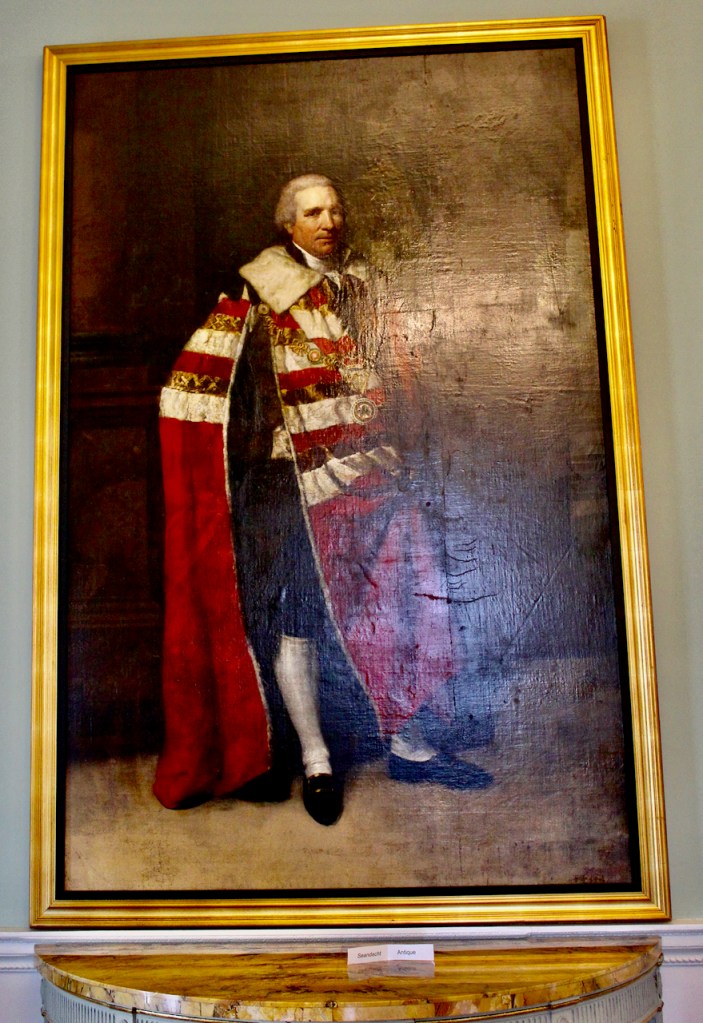
Henry Loftus was succeeded by his nephew Charles Tottenham (1738-1806), son of Henry’s sister Elizabeth (1720-1747) and her husband John Tottenham (1714-1786) 1st Baronet of Tottenham Green, County Wexford. Charles Tottenham’s name was changed to Charles Loftus in 1783 after the death of Henry Loftus 1st Earl of Ely of the 2nd Creation.
Charles held the office of Member of Parliament (M.P.) for New Ross between 1761 and 1768, M.P. for Bannow between 1768 and 1776, M.P. for New Fethard between 1776 and 1783. and M.P. for County Wexford between 1783 and 1785. He was created 1st Baron Loftus of Loftus Hall, Co. Wexford [Ireland] on 28 June 1785. He succeeded as the 2nd Baronet Tottenham [I., 1780] on 29 December 1786. He was created 1st Viscount Loftus of Ely [Ireland] on 28 December 1789 and 1st Earl of Ely [Ireland] on 2 March 1794. He was created 1st Marquess of Ely [Ireland] on 1 January 1801 and 1st Baron Loftus of Long Loftus, Co. York [U.K.] on 19 January 1801. He was also Privy Counsellor.

At Rathfarnham, Charles did little beyond the erection in 1790 of the Gothic or Back Gate, now almost competely demolished to make way for a road.
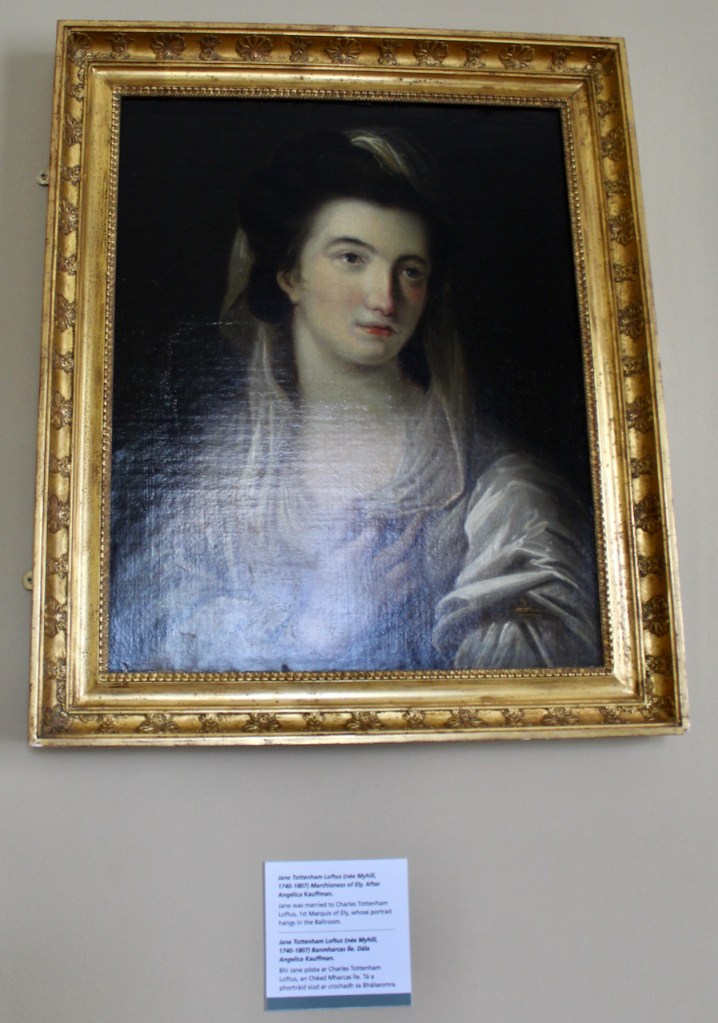
He married Jane Myhill of Killarney, County Kerry. Her sister Hannah married Hercules Langrishe, 1st Baronet of Knocktopher, County Kilkenny.
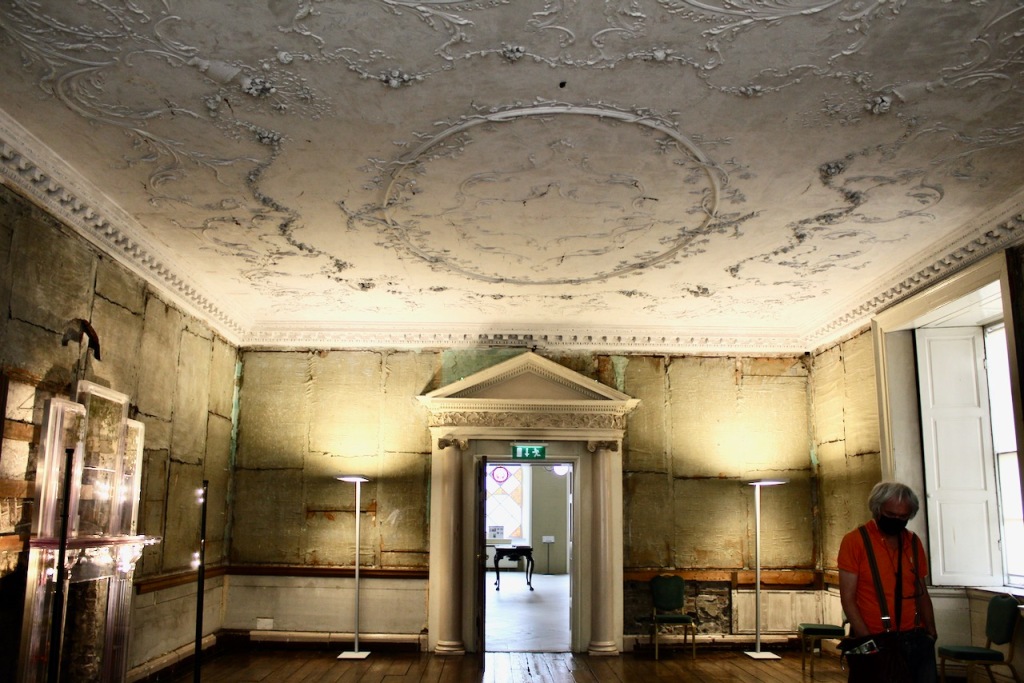


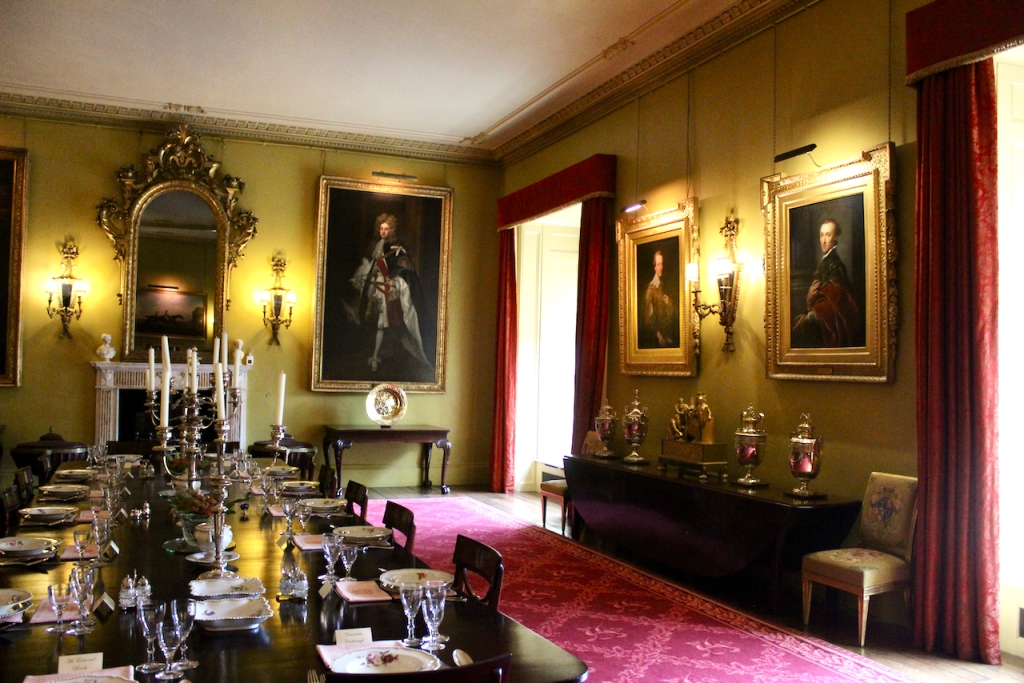
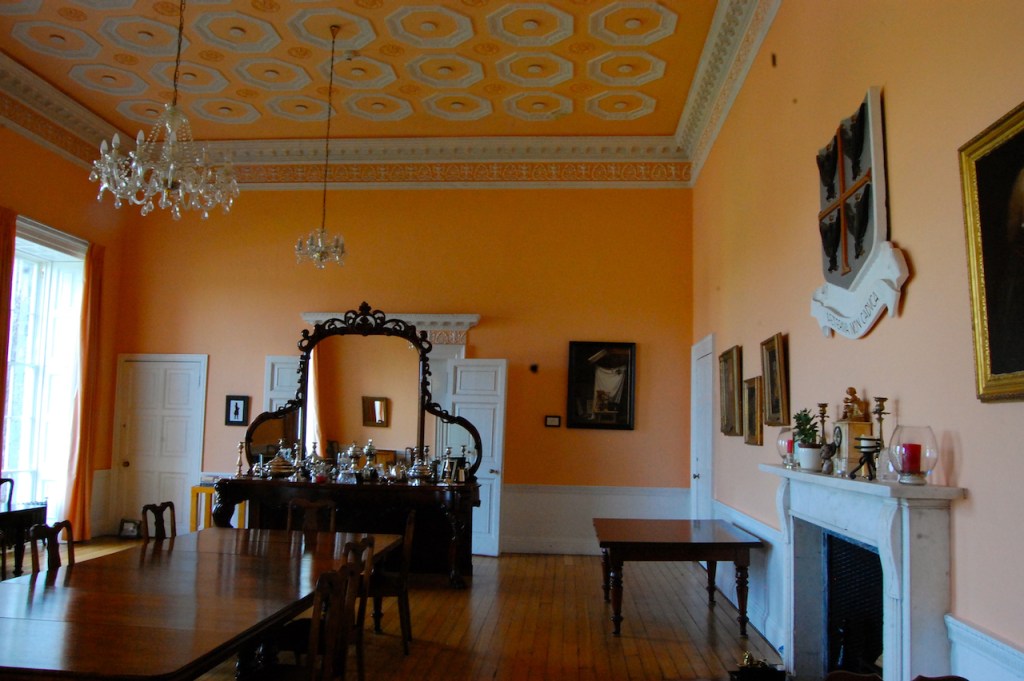
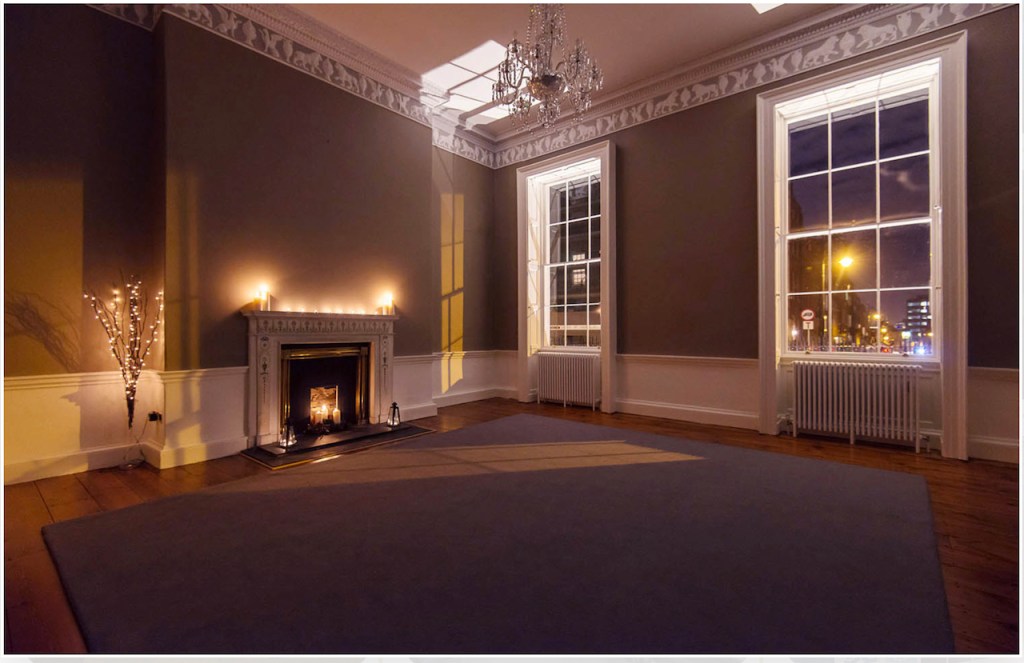
The Dining Room. “This room remains unrestored which allows us to see the changes and alternations which were made to the building over the years. The door on the left-hand (northern) wall is typically eighteenth century in style and decoration. However to the left of it a trace of the original Elizabethan doorway is visible. It was blocked up during the 18th century refurbishments. The bow extension to the eastern side of the building is another change dating to that period which added space and brought more light into these rooms. The 18th century timber wall panelling and lining paper survives in this room. It is likely that the walls were covered with silk. Although designed as a dining room, in the 20th century the Jesuits used this room as a library.“
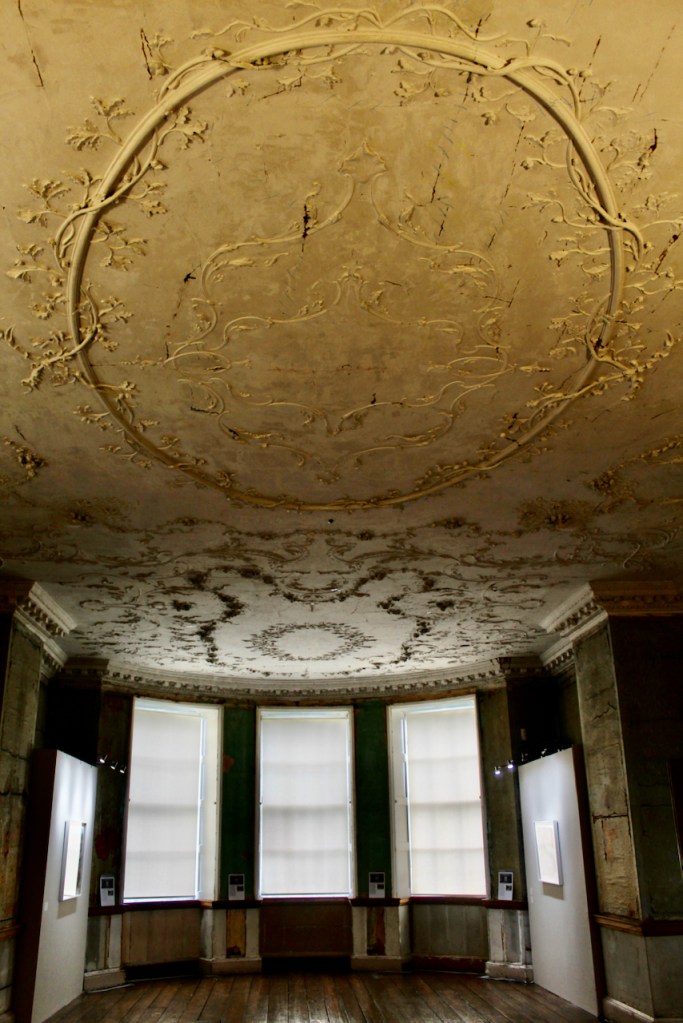
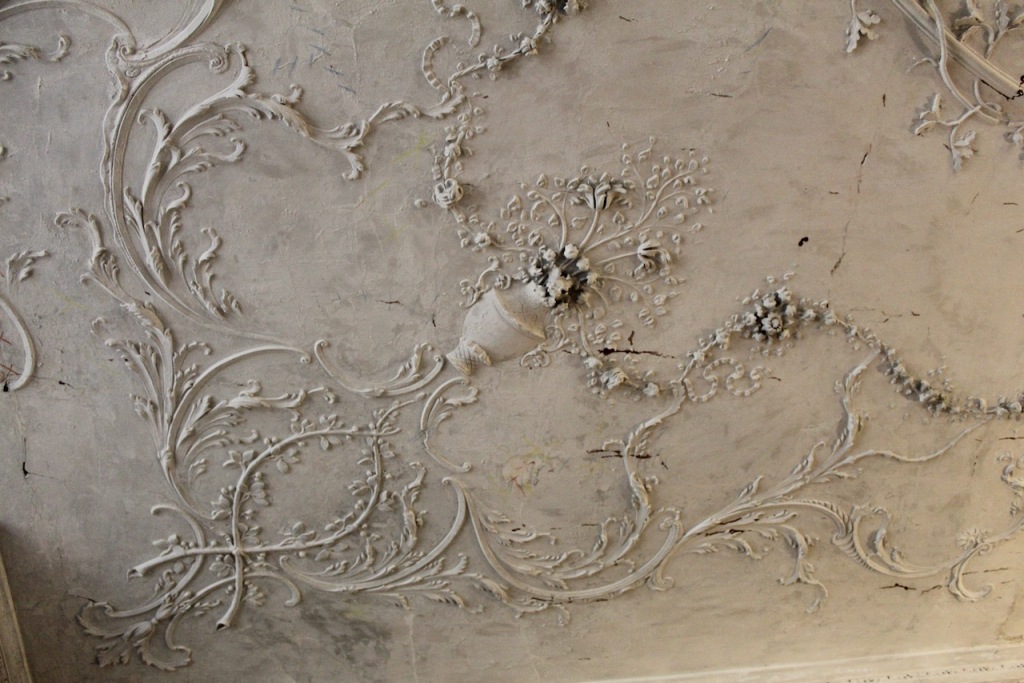
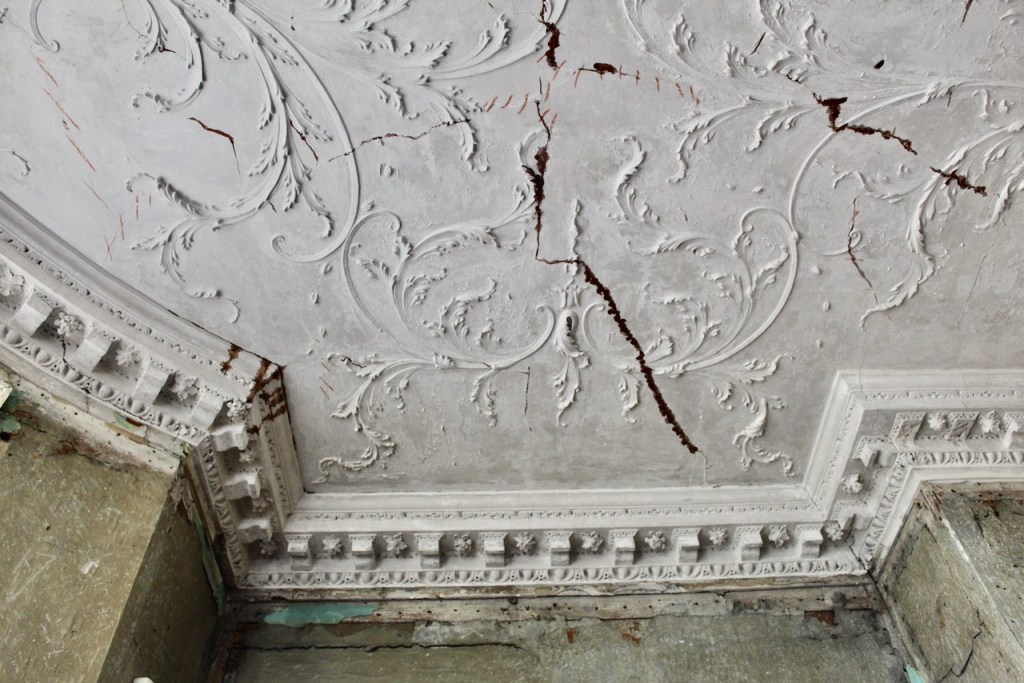
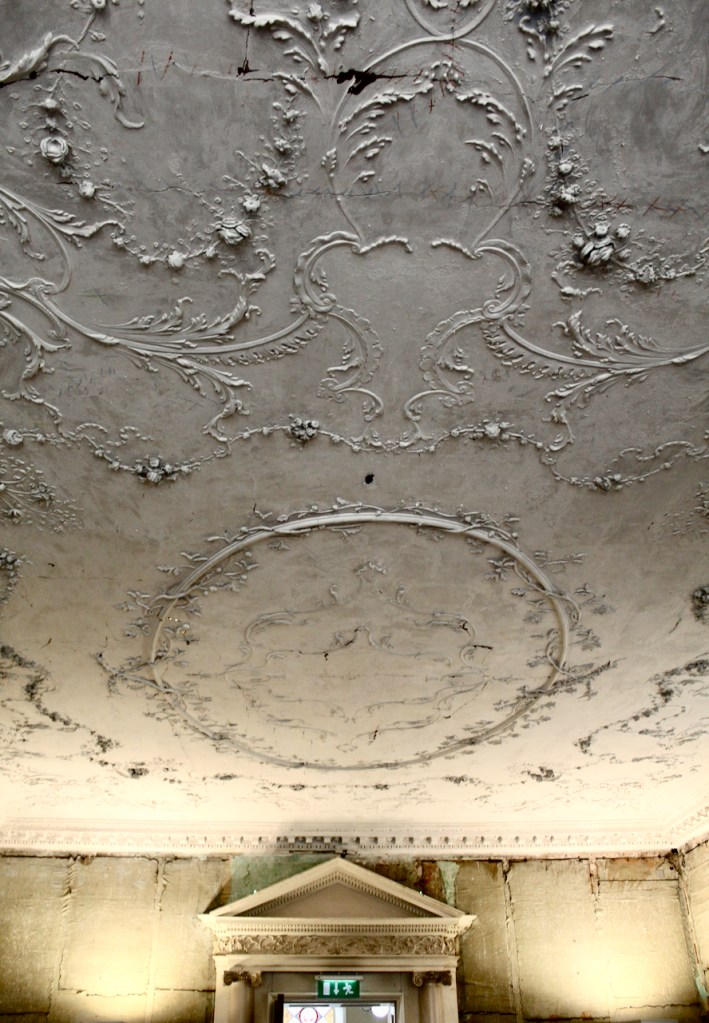
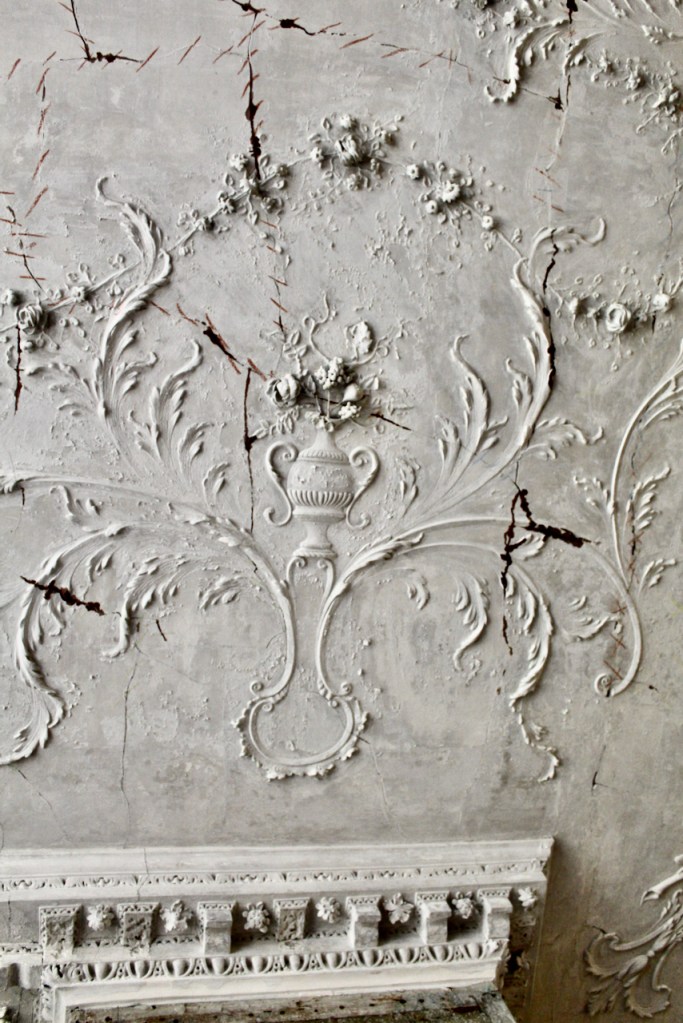
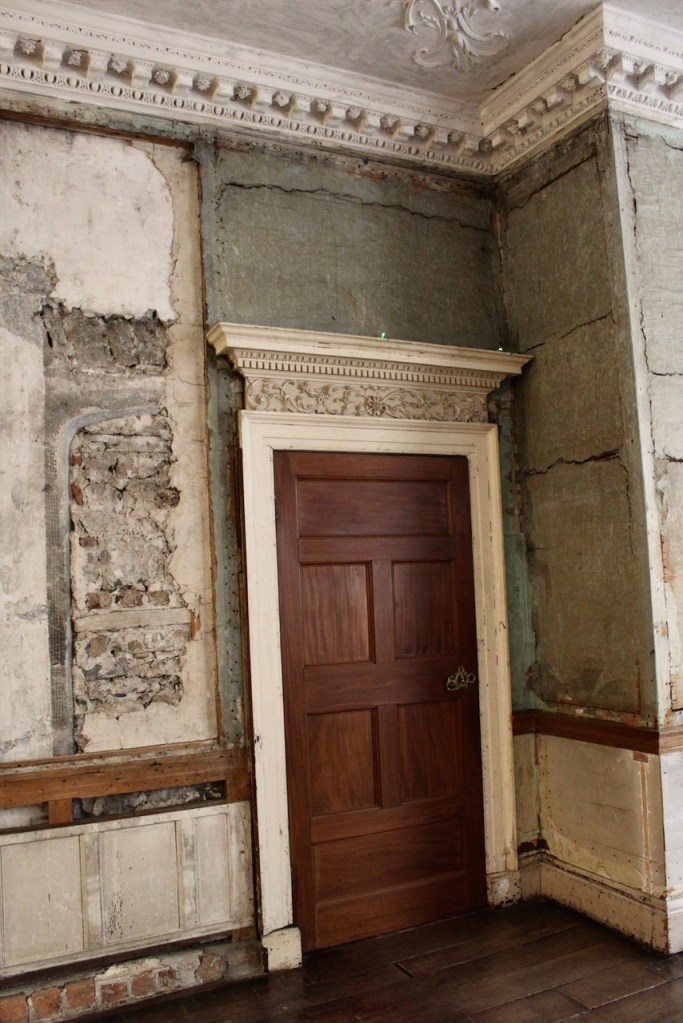






The Castle fell into disrepair. From the Parliamentary Gazetteer of Ireland 1846 (vol. iii):
‘Rathfarnham Castle, situated in a once noble demesne, at the south-east extremity of the village, was not long ago esteemed a magnificent building, and boasted a gorgeous picture-gallery, and superb series of garden and pleasure grounds, but it was allowed to fall into decay in consequence of the prolonged non-residence of its proprietor, the Marquis of Ely, and it now prosaically, though usefully, figures as a diary‘.
At this time, John Loftus (1770-1845) was 2nd Marquess of Ely, who inherited the Castle and lands from his father, Charles Tottenham Loftus. John Loftus rented out the house and surrounding lands, and between 1812 and 1852 the estate was leased to the Roper family. [from the castle’s Instagram page]

Rathfarnham Castle was sold in 1852 to Francis Blackburne (1782-1867), Lord Chancellor of Ireland.

His family lived there until 1911. Coincidentally almost in the footsteps of Adam Loftus who built Rathfarnham Castle, Francis Blackburne became Vice-Chancellor of Trinity College.
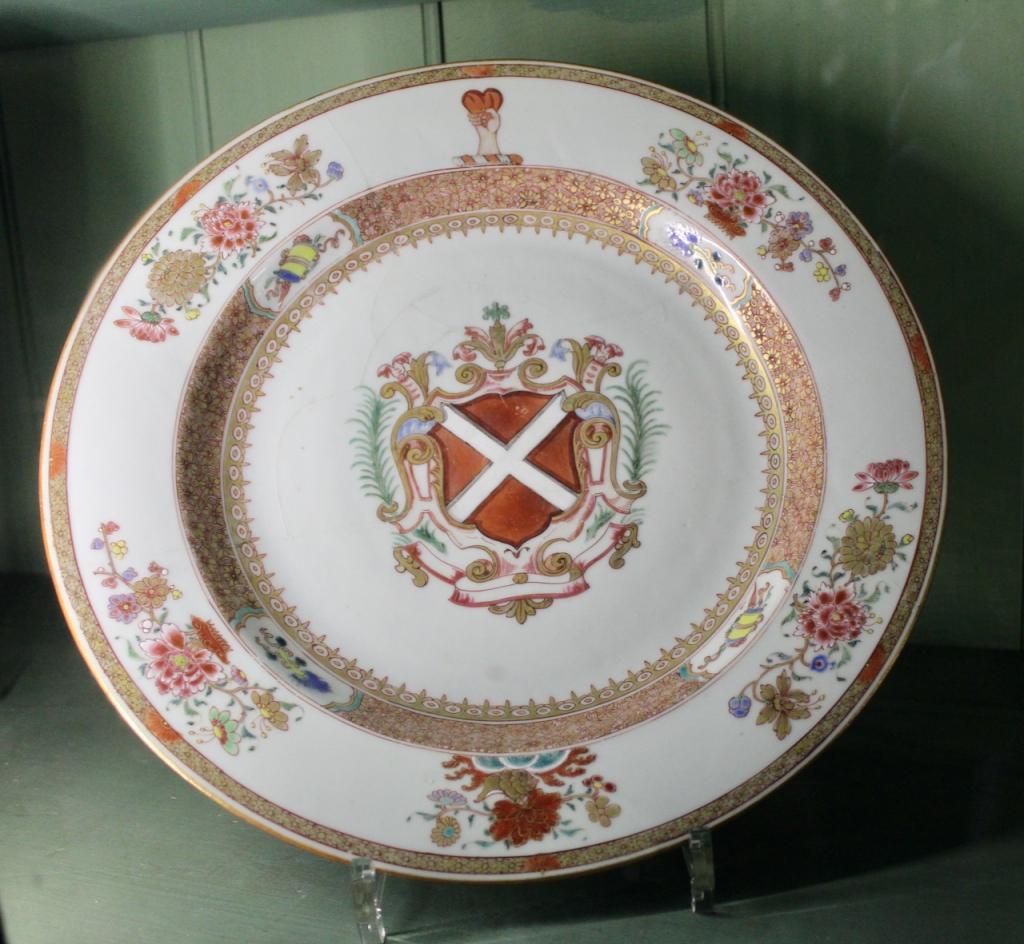
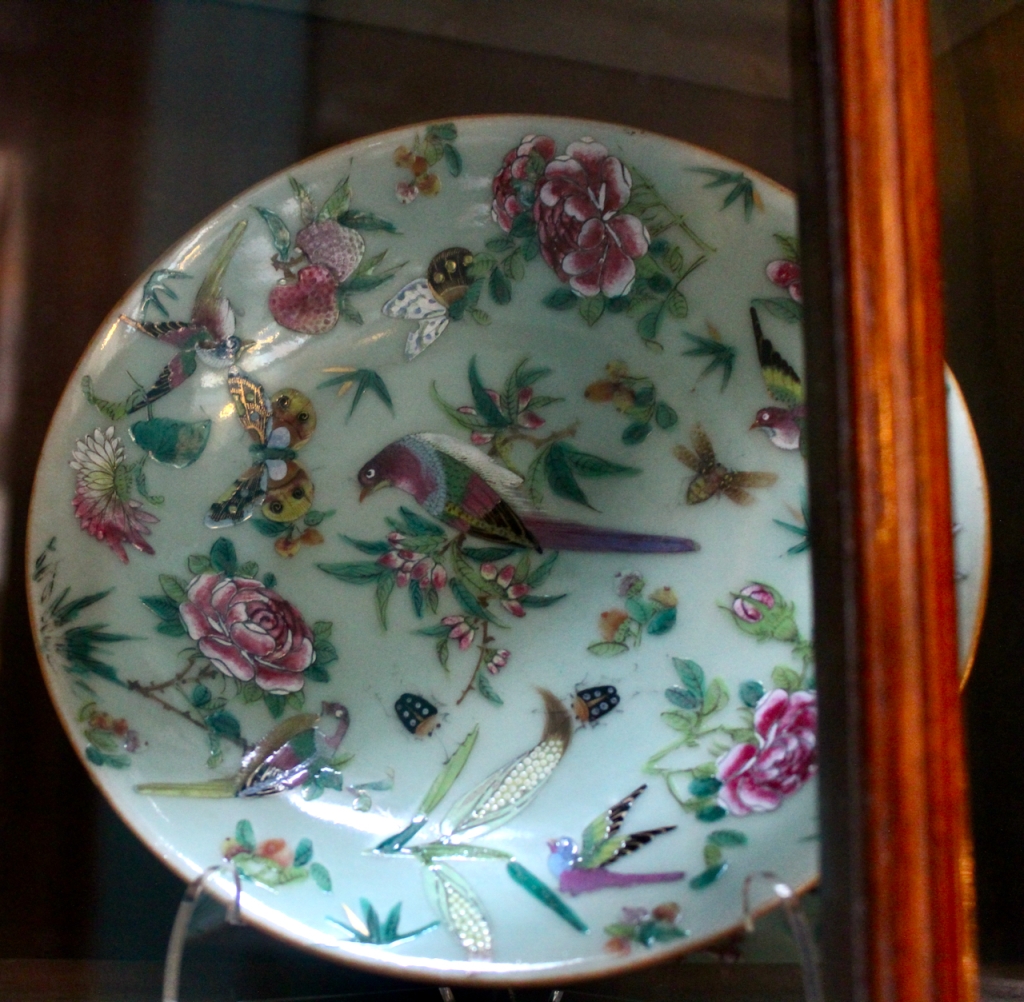
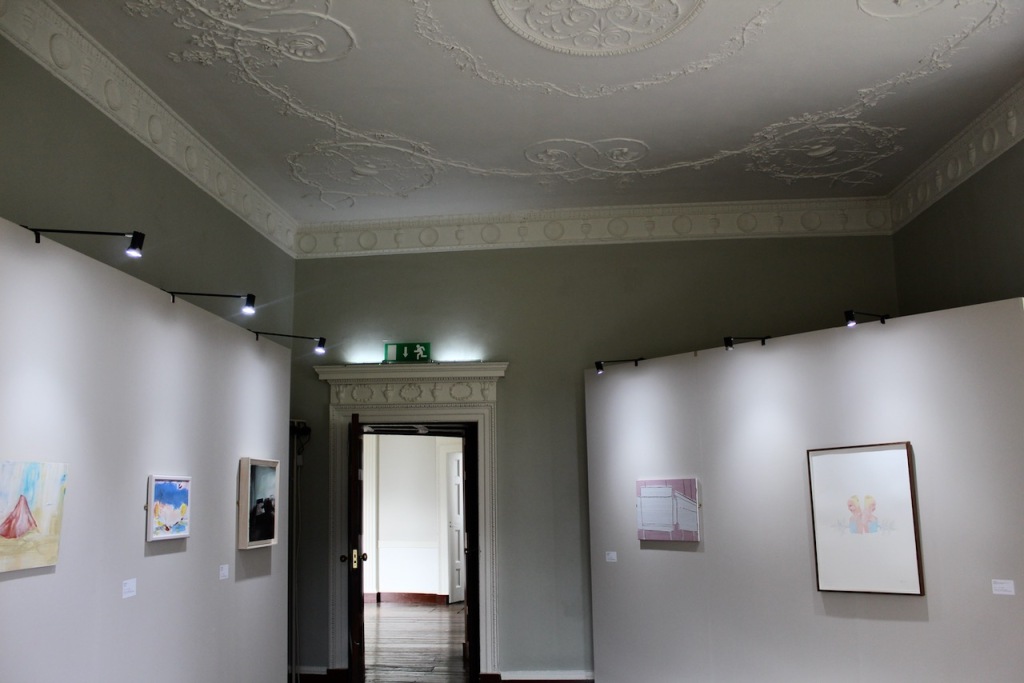
The Society of Jesus then acquired the building and for much of the remainder of the 20th century it was used as a Retreat House for lay visitors as well as accommodation for seminarians attending college in the city. Following the departure of the Jesuits in 1985, the Castle came into the care of the state and a great deal of restoration work has been carried out. Most of the rooms have been restored to their 18th century state and several are furnished with a collection of fine eighteen and nineteenth century pieces from continental Europe, Britain and Ireland.








[1] Other Jesuit properties include Emo Court, see my entry, https://irishhistorichouses.com/2024/10/22/emo-court-county-laois-office-of-public-works/
Belvedere House in Dublin, Castle Browne, now Clongowes Wood College, and Manresa House in Clontarf, formerly called Granby Hall and Baymount Castle.

Clongowes Wood College, County Kildare:
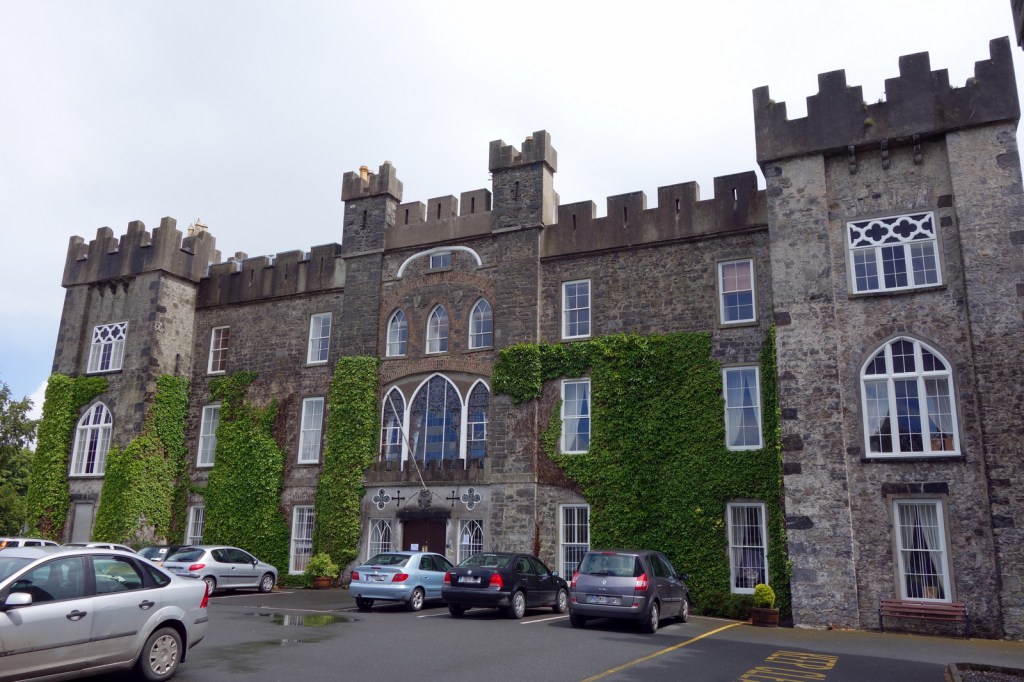

In 1718 Stephen Fitzwilliam Browne (d. 1767) rebuilt Clongowes Wood Castle, creating the western front facade as it appears today, comprising the central keep and two square towers. In 1788 Thomas Wogan Browne (d. 1812) extended and decorated the castle. The extension consists of the eastern facade and two round towers at the back of the castle. Note that this information is from the Clongowes Wood school website, with information from A Short History of Clongowes Wood College by Brendan Cullen.
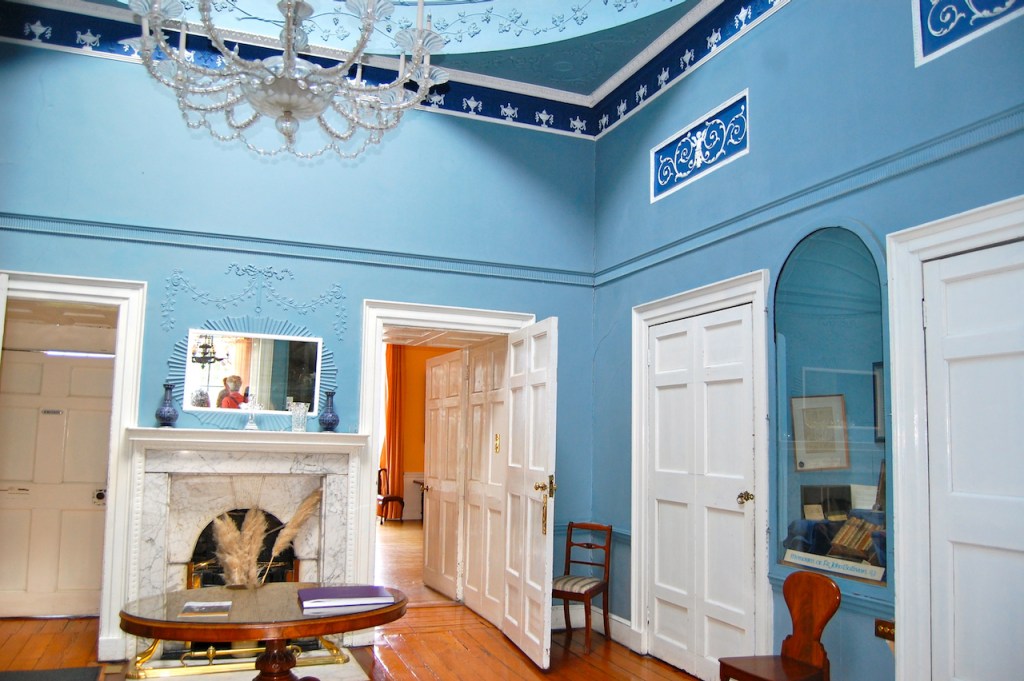



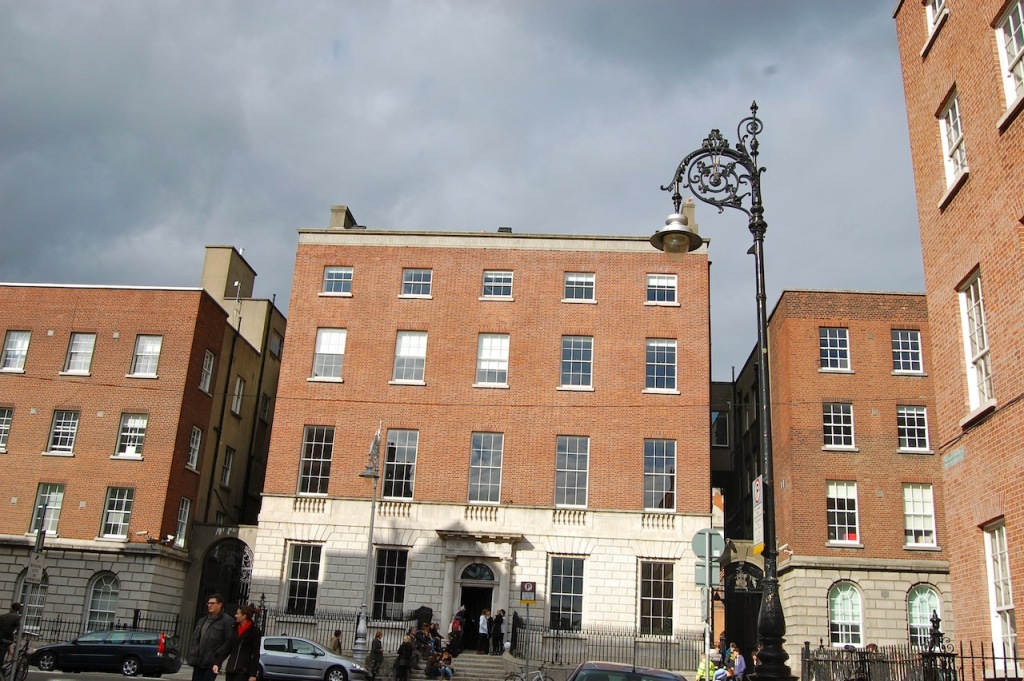
Belvedere House, 6 Great Denmark Street, Dublin (visited during Open House 2015):
https://www.oreillytheatre.com/belvedere-house.html

Stephen and I visited Belvedere House during Open House in 2015. We went into three rooms upstairs, up the beautiful staircase. We weren’t allowed photograph on the tour, unfortunately, in the Apollo Room, Venus Room and Jupiter Room.
Belvedere House is a symmetrical five-bay four-storey Georgian townhouse over exposed basement, completed 1786, designed by Robert West who, in addition to being a stuccodore was also an architect and property developer. It was built for George Augustus Rochfort, 2nd Earl of Belvedere. The house was built for £24,000 on what would have been rural green fields with a view of the Custom House, the bay and distant mountains. It is alleged that the house is haunted by Mary Molesworth, the first lady of Belvedere, mother to George Rochfort – we came across her at Belvedere in County Westmeath.
Rochfort was the son of the cruel Robert Rochfort, 1st Earl of Belvedere, who kept his wife under lock and key in the countryside after he believed she had an affair with his brother. Some believe that she was the inspiration for Charlotte Bronte’s “madwoman in the attic.” Robert Rochfort had the summer lodge, Belvedere, built in County Westmeath, now open to the public, which also has fine plasterwork. Robert O’Byrne writes that it was the 1st Earl who bought the property on Great Denmark Street. At first his son attempted to sell the property, but then he finished having the house built. Robert O’Byrne also tells us that it is similar to 86 St Stephen’s Green (Newman House, now housing the Museum of Literature of Ireland (MOLI), which was begun in 1765, and which is also attributed to Robert West.
North Great Georges Street itself was originally laid out in 1774 as a driveway leading to Belvedere House.
In 1841 the house was bought by the Society of Jesus (Jesuits) to accommodate their growing boys school which had started life ten years previously around the corner on Hardwicke Street, now known as Belvedere College.
One of the more outstanding features of the house is the stucco-work of Adamesque style popularised by Robert and James Adam. This can be seen in the ornamental surrounds, wherein pictures are framed in plaster rather than oil.
Dublin stuccodore and designer Michael Stapleton (1740-1801) was responsible for this work and further examples of his craftsmanship include the ceiling in the exam hall in Trinity College as well as some of the plasterwork in Powerscourt House in South William Street in Dublin and the Aras an Uachtarain in Phoenix Park.


It seems odd that a house designed by Robert West would have plasterwork by Michael Stapleton. Robert O’Byrne elucidates this for us:
“In 1967 C.P. Curran’s Dublin Decorative Plasterwork of the 17th and 18th centuries noted in the collection of drawings left by stuccodore Michael Stapleton several items directly relating to the design of ceilings in Belvedere House. Accordingly, this work was assigned to Stapleton. However, the fact that West was responsible for designing the house complicates matters, and the consensus now appears to be that both he and Stapleton had a hand in the plasterwork. Conor Lucey (in The Stapleton Collection, 2007) suggests that Stapleton may have been apprenticed to, or trained with, West and the fact that he was named the sole executor of the latter’s will in 1790 indicates the two men were close. The source material for the stucco work is diverse, that in the stair hall deriving in part from a plate in Robert Adam’s Works in Architecture, but the first-floor rooms feature a wider range of inspiration, much of it from France and Italy.”
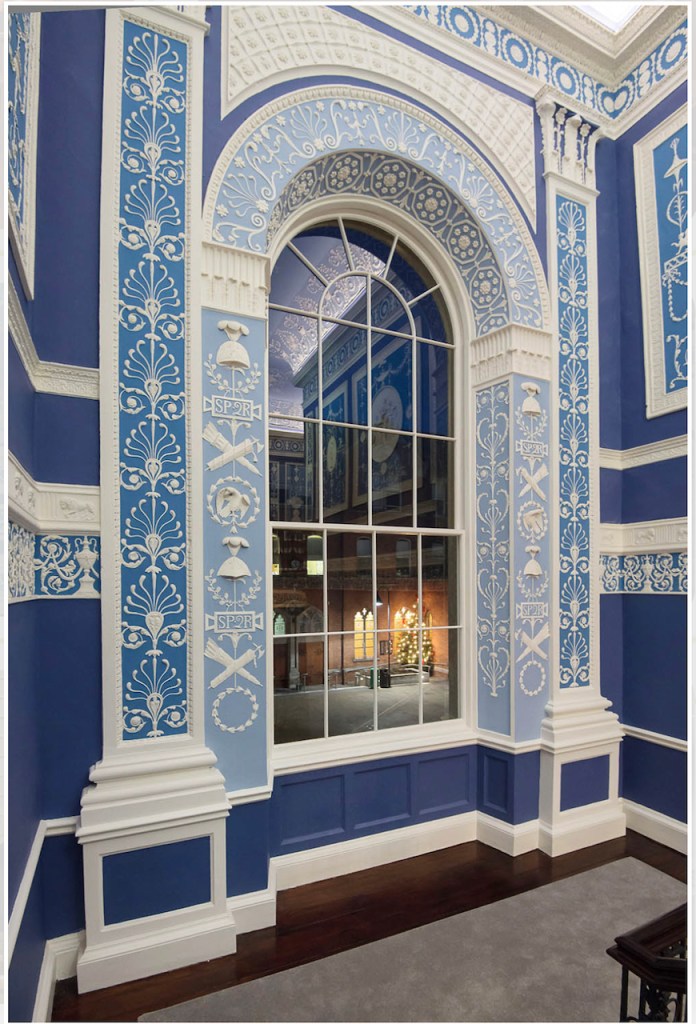


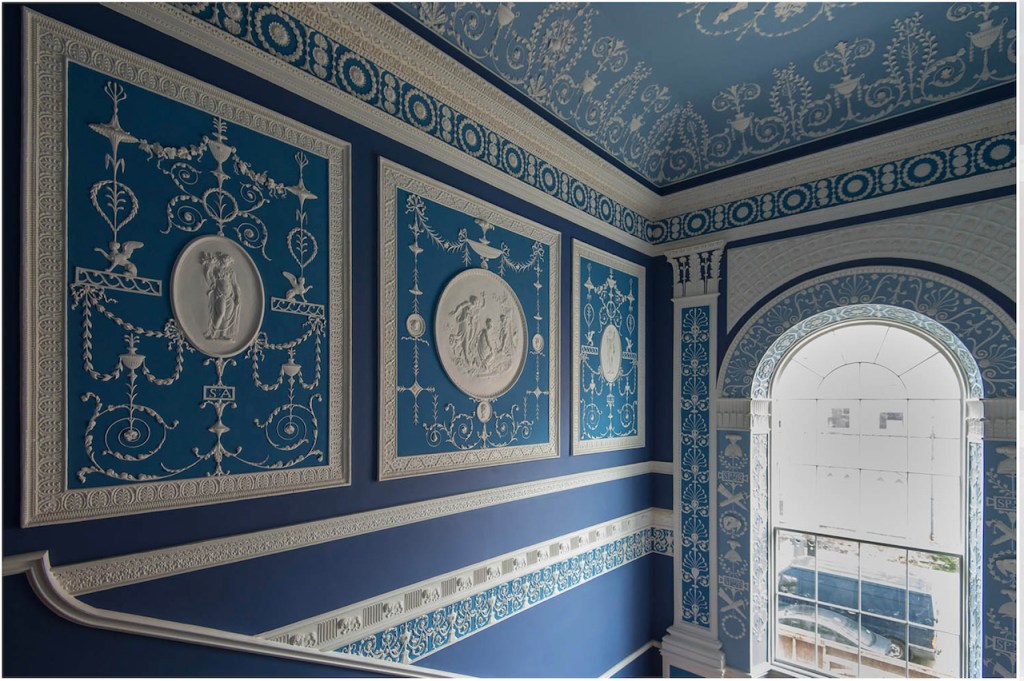
We were given a leaflet, which tells us:
“The ground floor rooms were intended for everyday and business use and therefore are minimally ornamented. However when one ascends they will encounter Stapleton’s stucco-work that depicts scenes from Greek and Roman mythology. On the half-landing the Bacchanalia is celebrated. The left panel depicts Bacchus with his thyrsis and staff, the right panel is Ceres with her cornucopia. The central oval shows Cupid being demoted by the three Graces. The arched window is ornamented with symbols of the authority of ancient Rome. The tall pilasters on each side have the Green anthemion (honeysuckle) motifs.
“At the top of the stairs the panel between the two doors on the right show Juno seated on a cloud with her peacock. The panel on the centre wall is Aurora in her chariot pulled by winged horses. Under this plaque “The New Bride” from an ancient marble popular in 18th century Rome. All the five doors have the same over-door: Silenus, the tutor of Bacchus. On the ceiling, Eros is depicted gazing at Psyche as she sleeps. Next is an Apollo head with winged lions and lastly, Cupid with a flower.
“The door immediately to the right of the stairs leads to the Apollo Room, named after the featured frieze of Apollo the music-maker holding court with attendent putti playing a variety of instruments. The adjoining Diana Room depicts Diana, patron of the chase, in a chariot drawn by stags. The design is taken directly from Pergolesi, however, Stapleton added the outer circle of flowers.
“Finally the Venus Room’s flanking panels have lunettes representing astronomy, architecture and sculpture. Notice the beautiful over-doors in all three rooms, each with the head of the principle subject.”
Venus was taken down by the Jesuits as she was nude, and it is supposedly in the National Gallery.
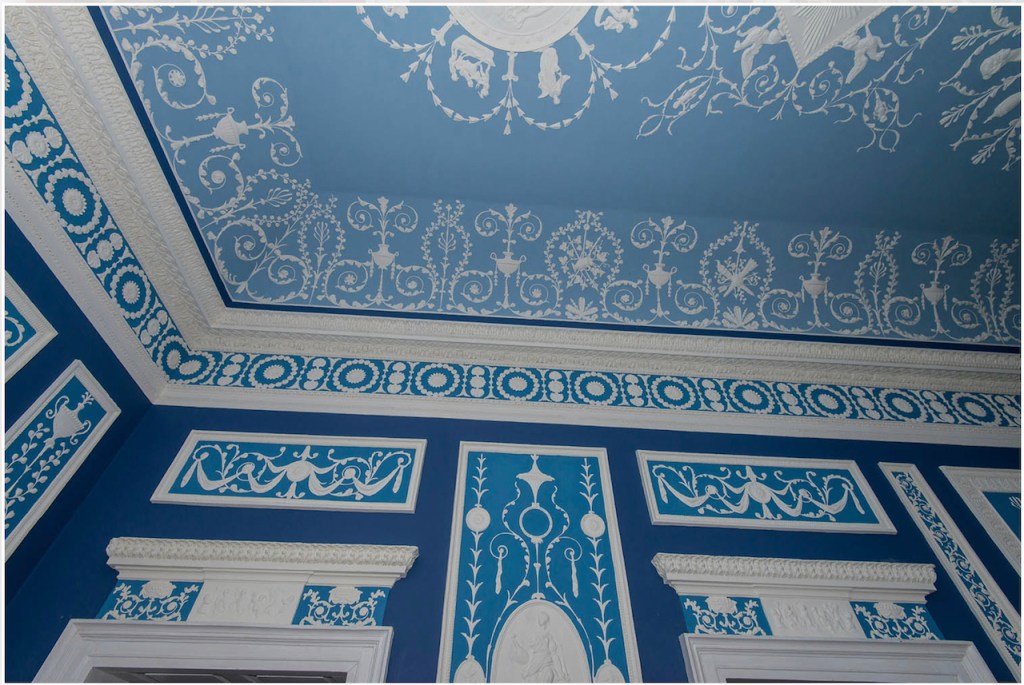





[2] https://www.dib.ie/biography/loftus-adam-a4867
[3] Loftus Hall: Formerly named Redmond Hall, it is a three-storey mansion built in 1871, incorporating parts of a previous house here, which was late 17th century or early C18.





[4] https://www.archiseek.com/1583-rathfarnham-castle-co-dublin/
[5] “Rathfarnham Castle” by C. Scantlebury, Dublin Historical Record, Vol. 12, No. 1 (Feb., 1951), pp. 20-30. https://www.jstor.org/stable/30080721