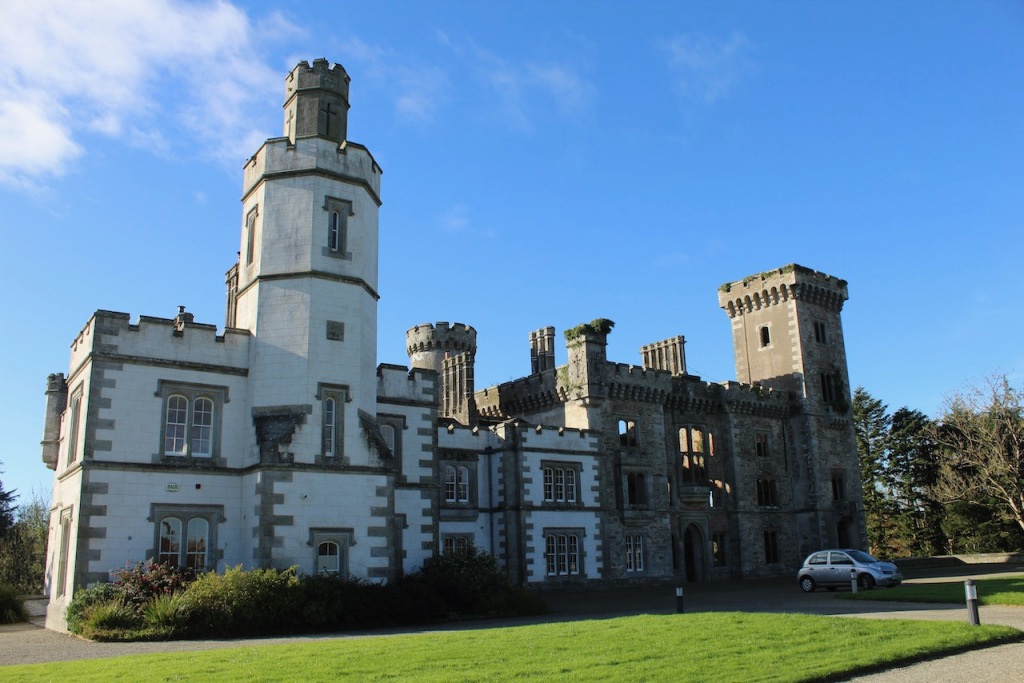
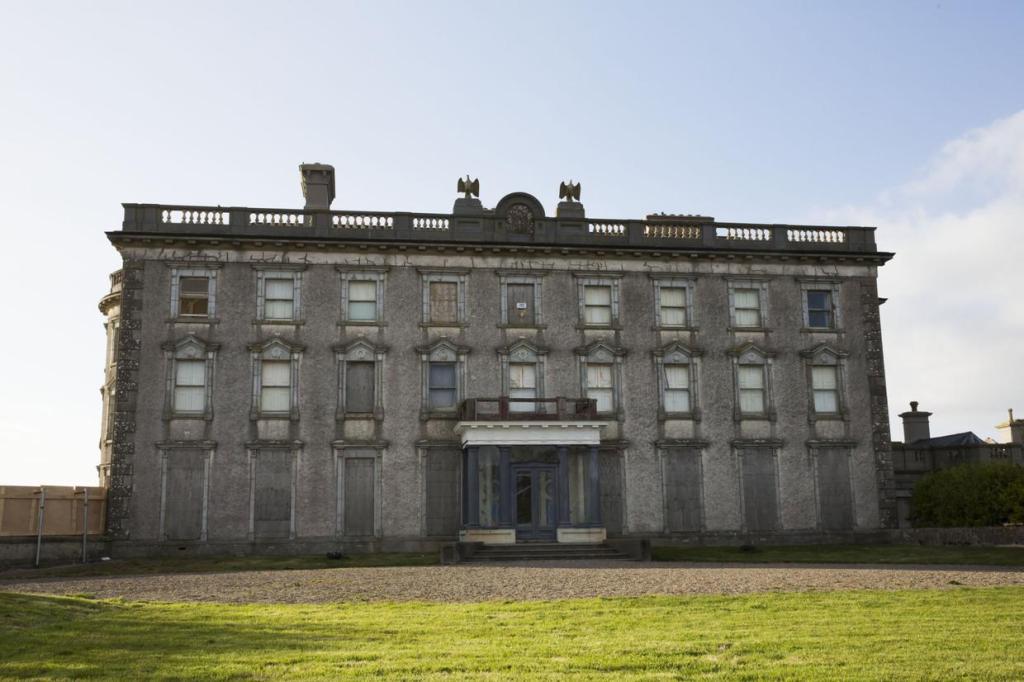
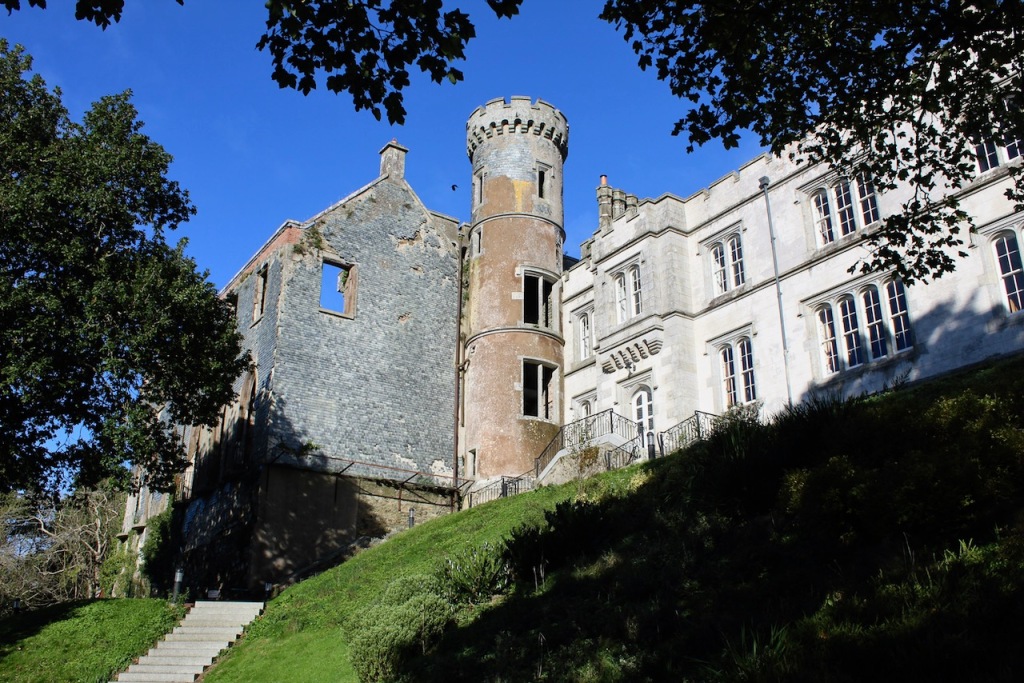
The website tells us:
OPENING TIMES: Check website for booking details of annual events programme. Group booking available at other times of the year.
Open dates in 2025: Feb 1-2, 8-9, 15-16, 22-23, Apr 5-6, 12-13, 19-20, 26-27, May 3-4, 10-11,17-18, 24-25, 31, June 1, 5-8, 12-15, 19-22, 26-29, July 3-6, 10-13, 17-20, 24-27, 31, Aug 1-3, 7-10, 14-24, 28-31, Sept 6-7, 13-14, 20-21, 27-28, Oct 4-5, 11-12, 18-19, 25-26, 11am-5pm
Fee: house & garden, adult €12 garden €6, OAP/student €10, garden €5, child €6, garden €3

2025 Diary of Irish Historic Houses (section 482 properties)
To purchase an A5 size 2025 Diary of Historic Houses (opening times and days are not listed so the calendar is for use for recording appointments and not as a reference for opening times) send your postal address to jennifer.baggot@gmail.com along with €20 via this payment button. The calendar of 84 pages includes space for writing your appointments as well as photographs of the historic houses. The price includes postage within Ireland. Postage to U.S. is a further €10 for the A5 size calendar, so I would appreciate a donation toward the postage – you can click on the donation link.
€20.00

donation
Help me to pay the entrance fee to one of the houses on this website. This site is created purely out of love for the subject and I receive no payment so any donation is appreciated!
€15.00
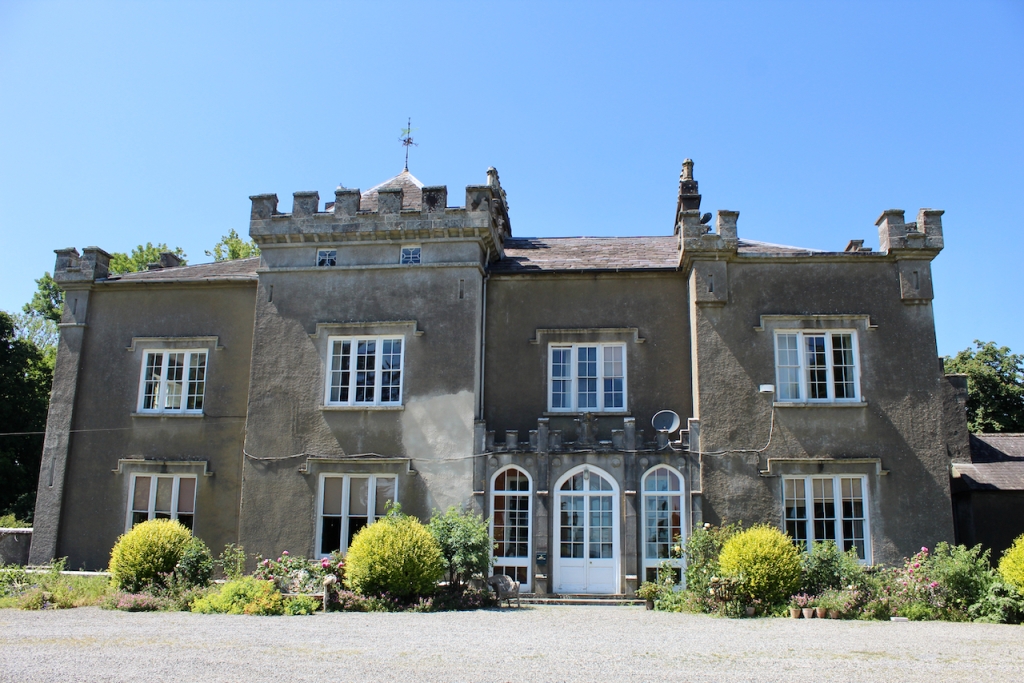

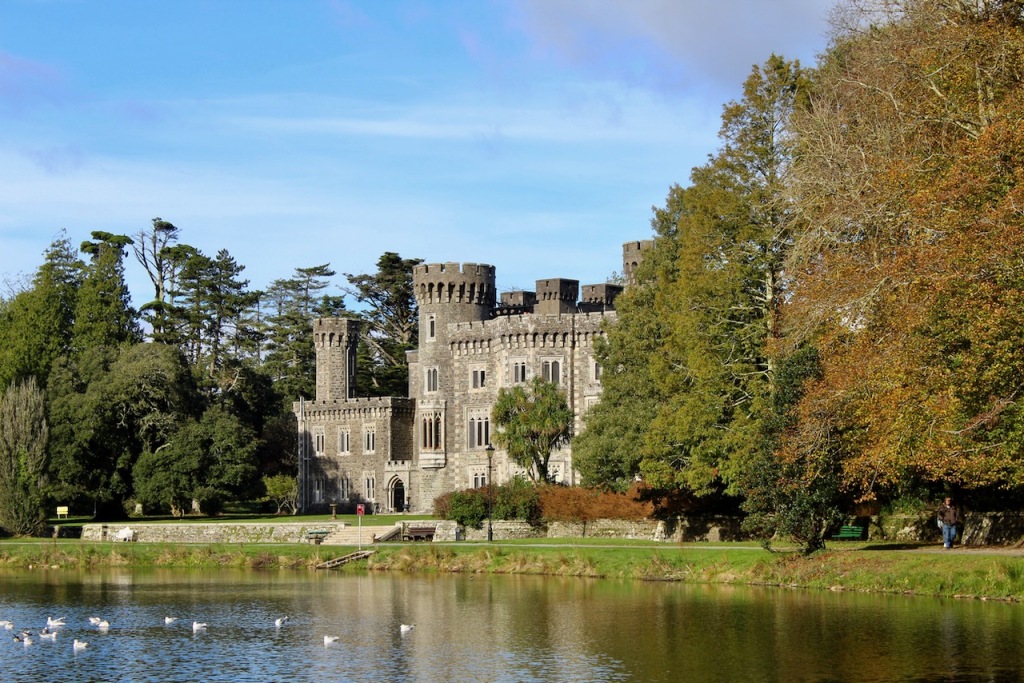
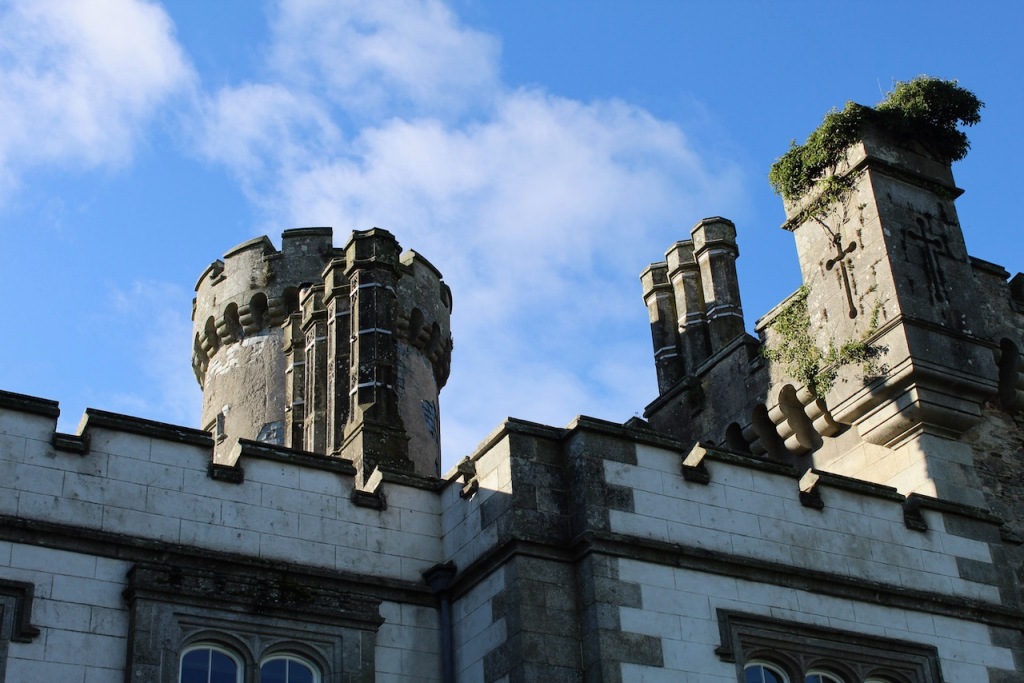
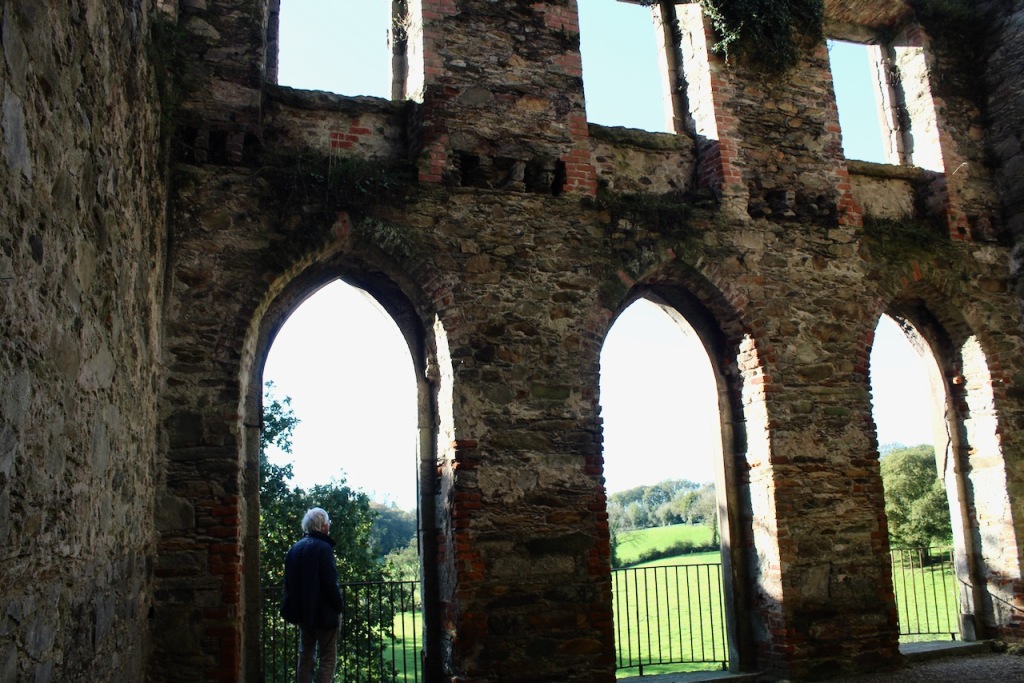
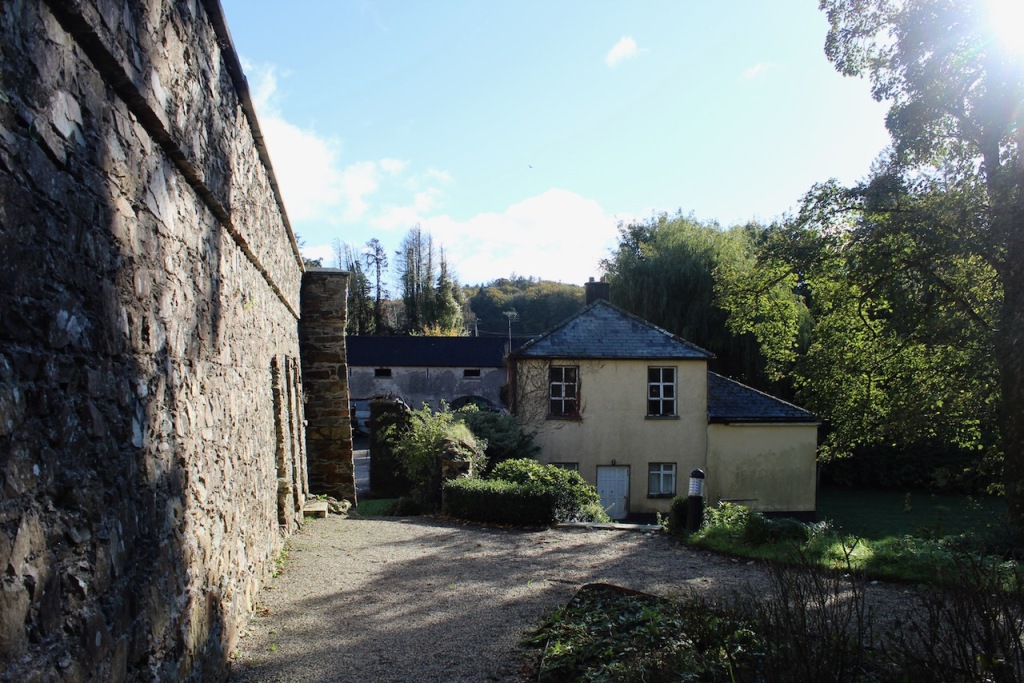
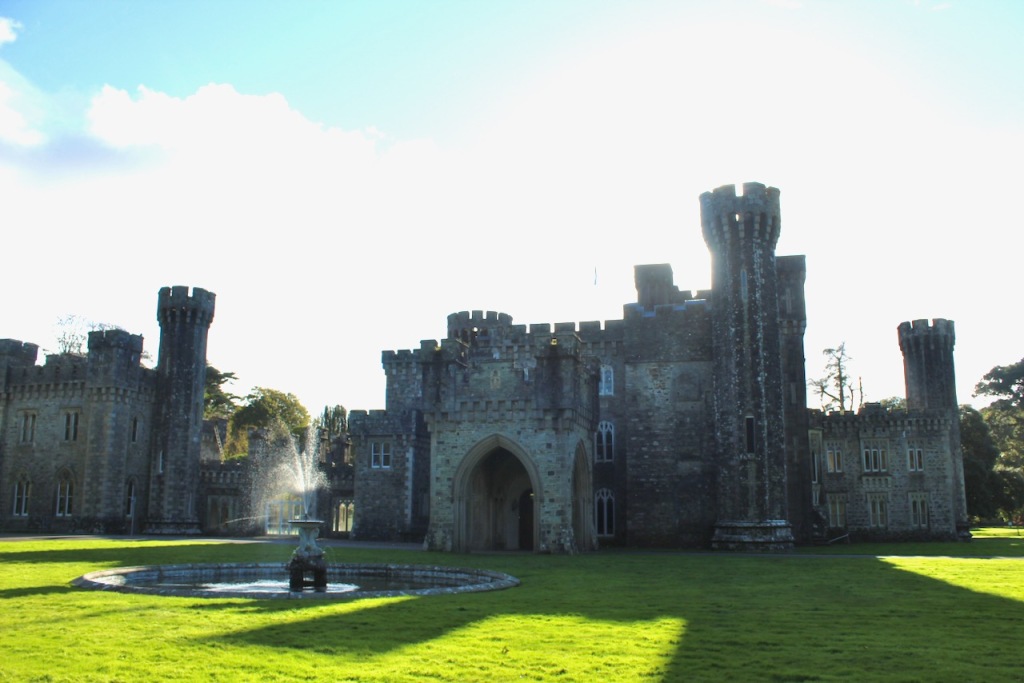
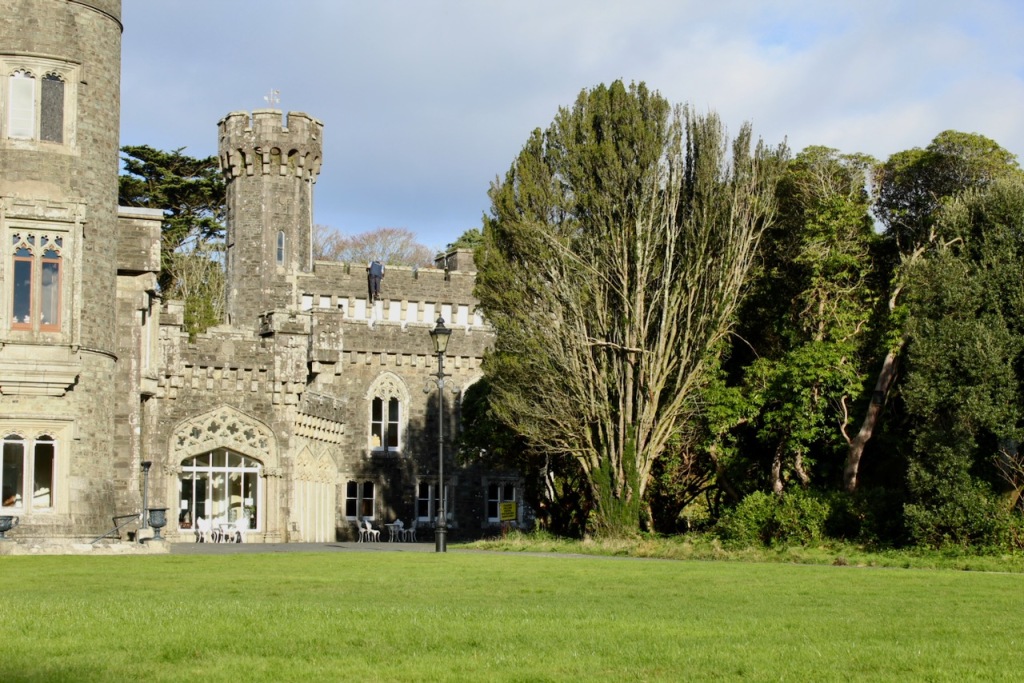
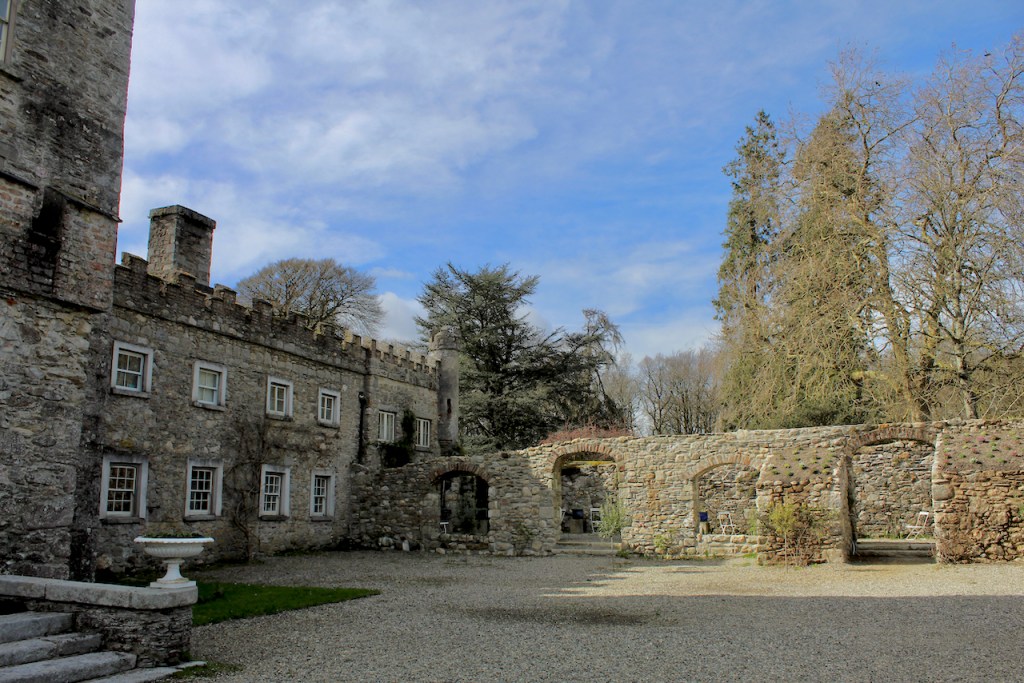
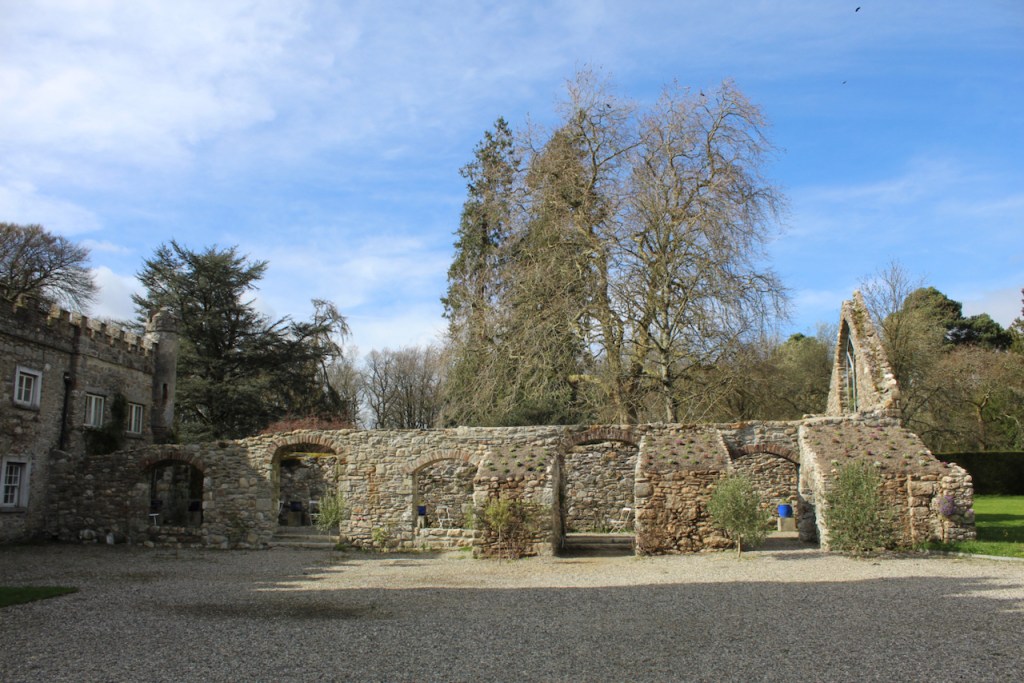
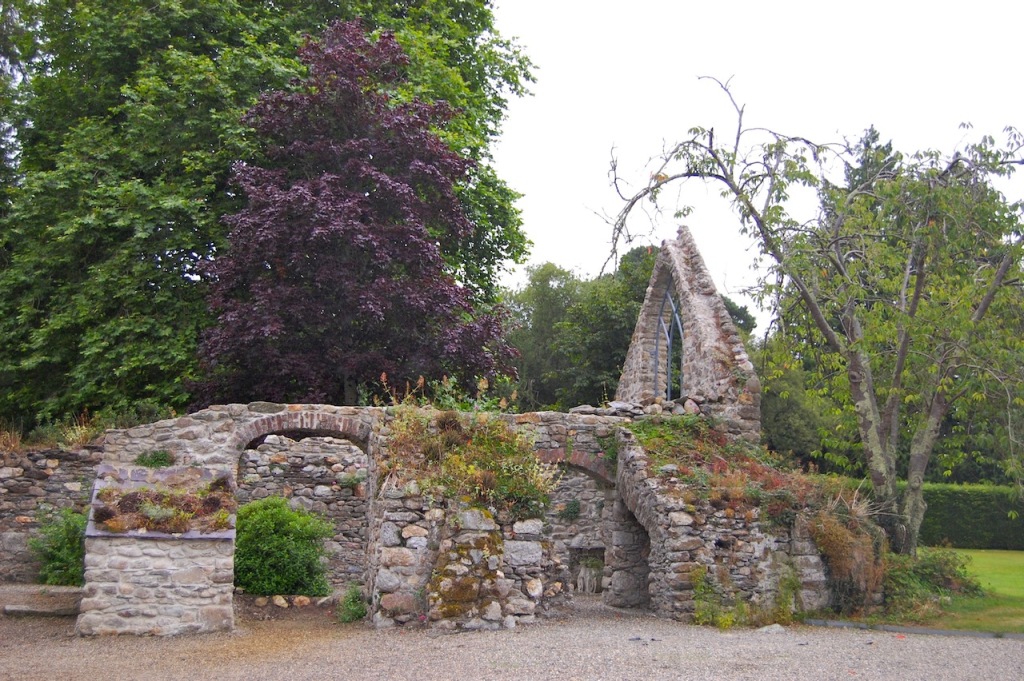
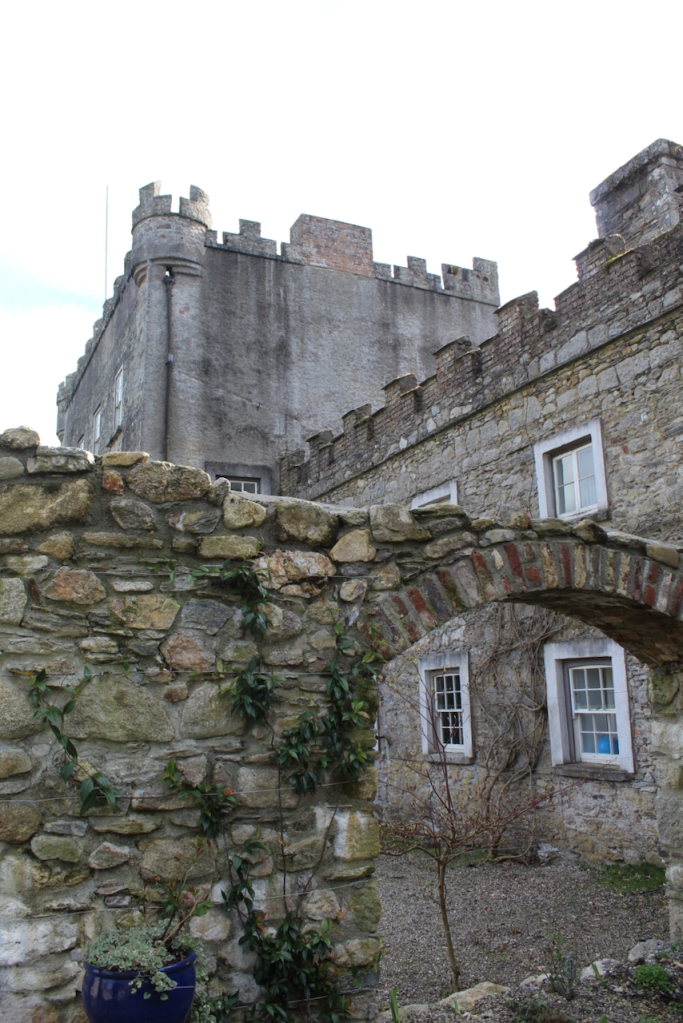
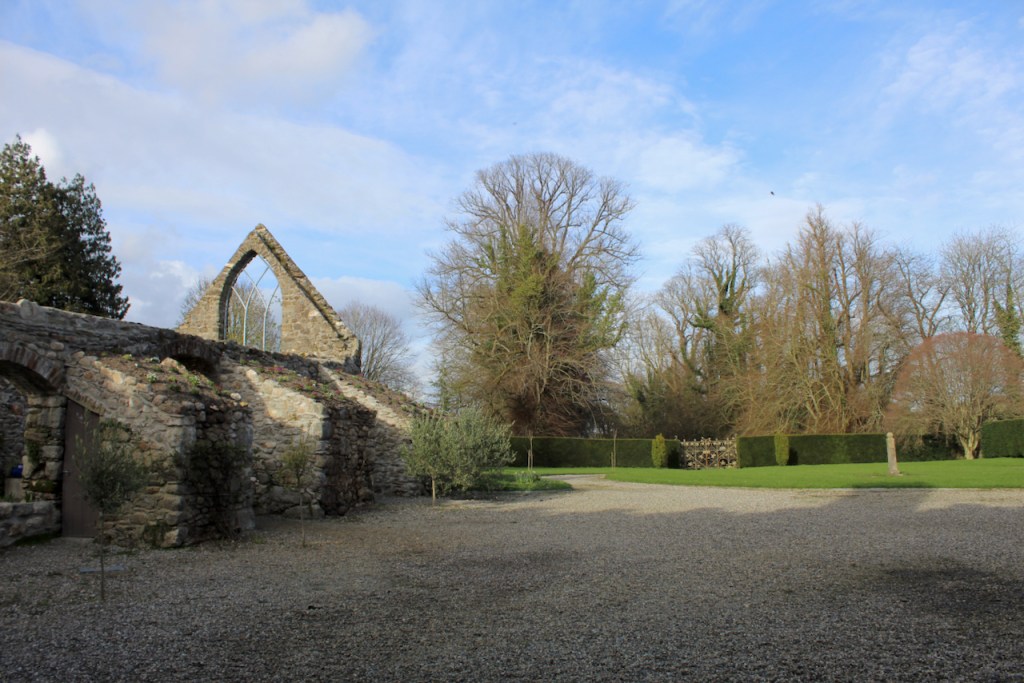
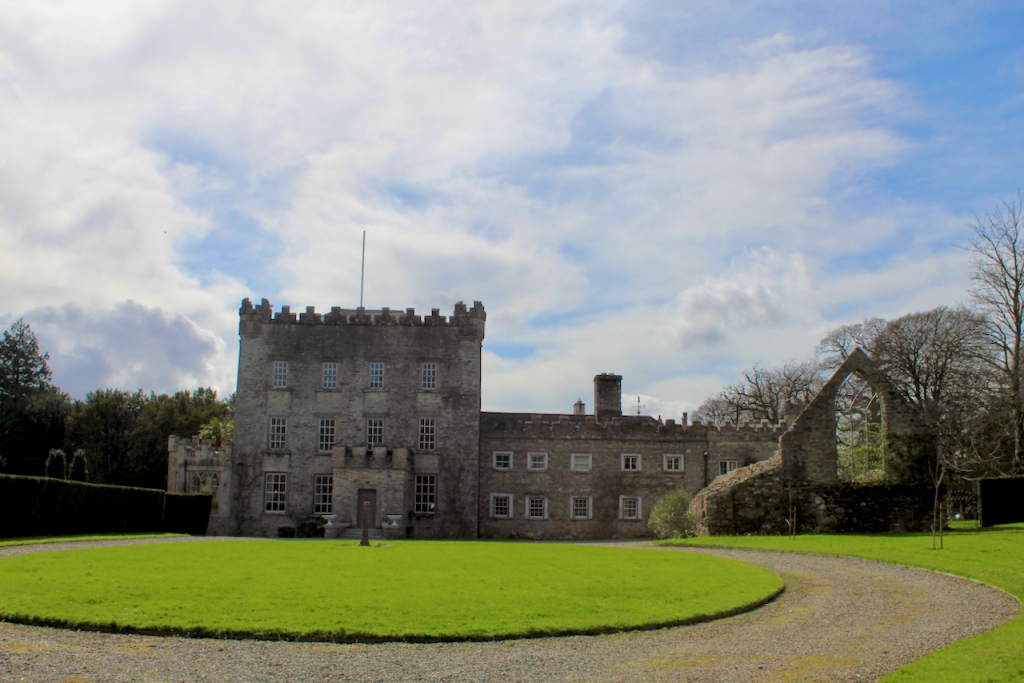
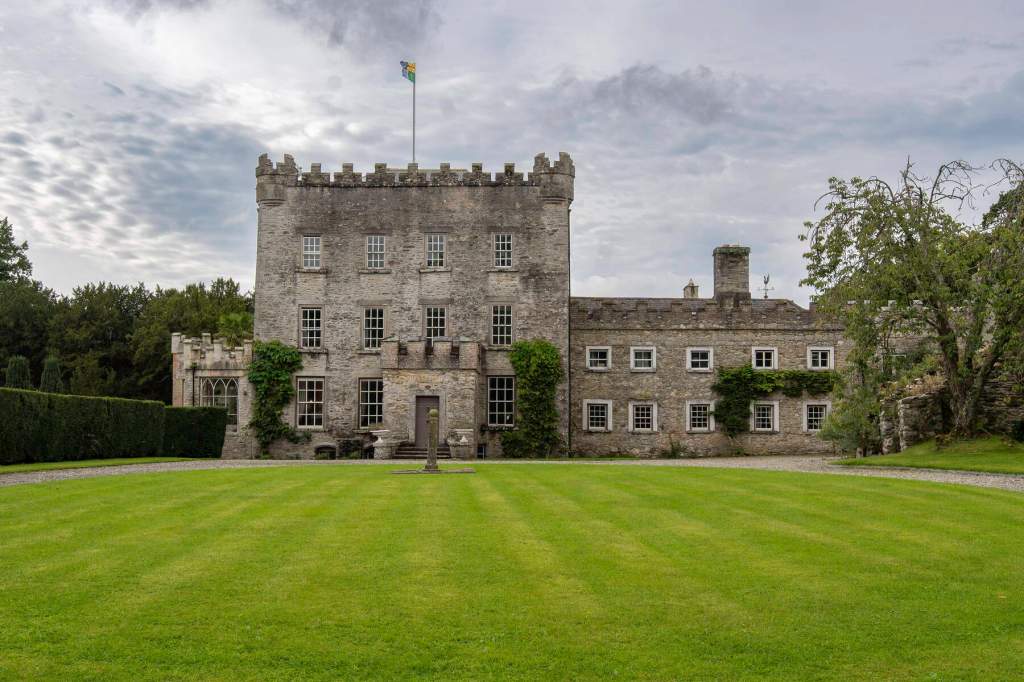
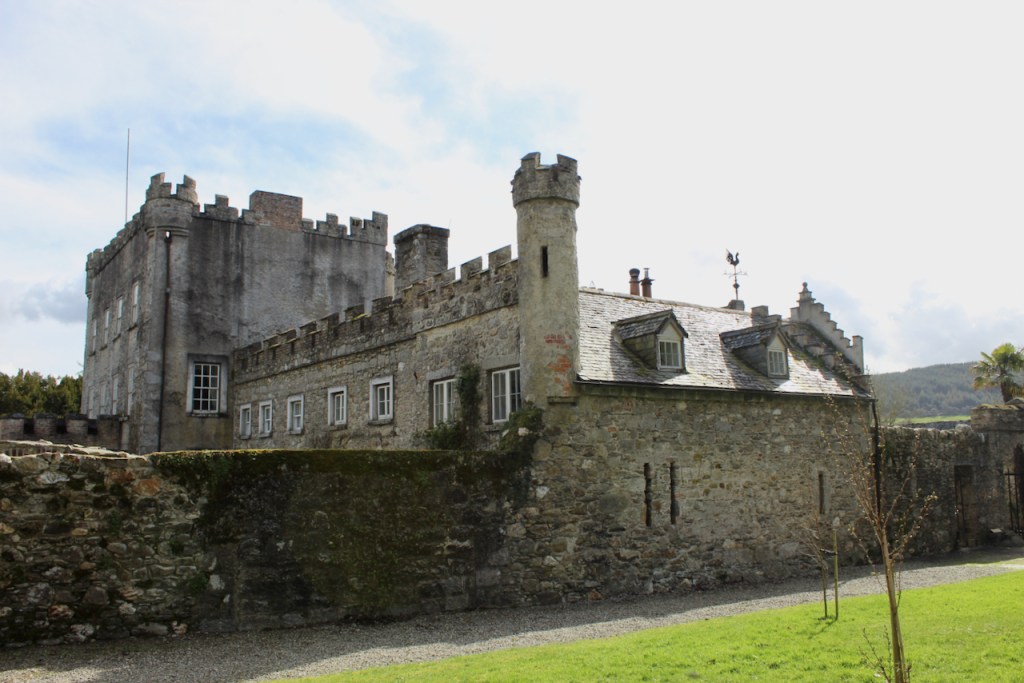
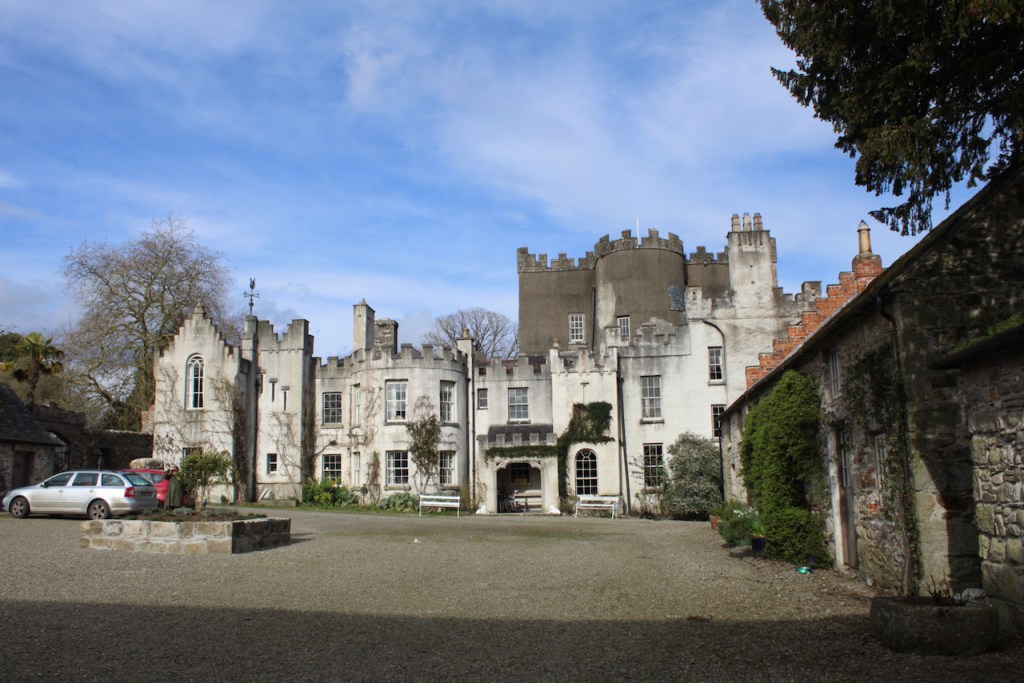
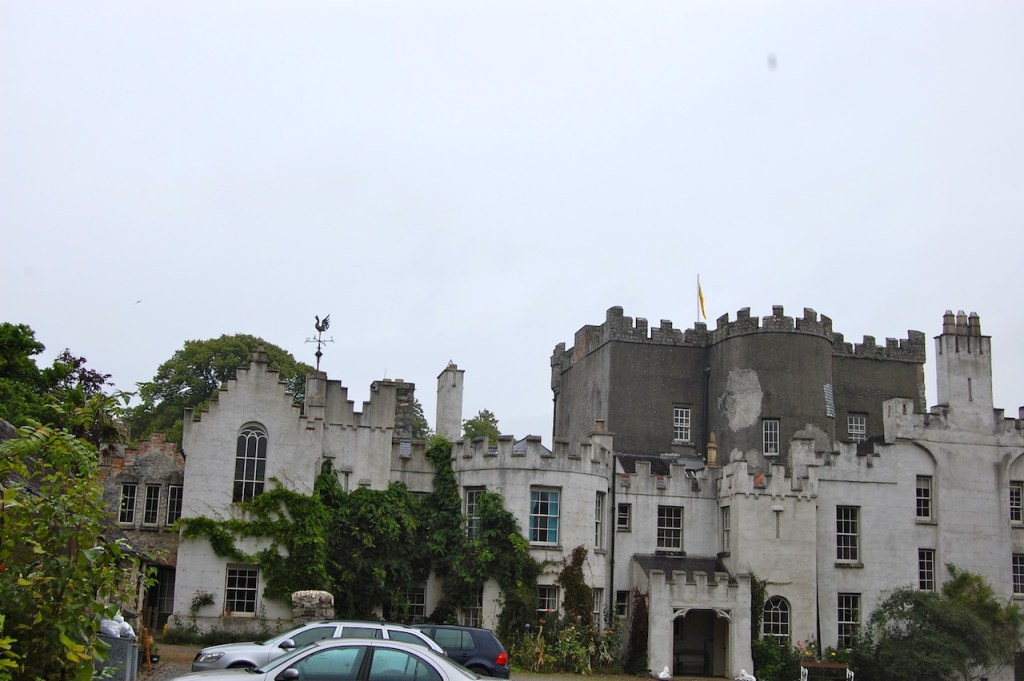
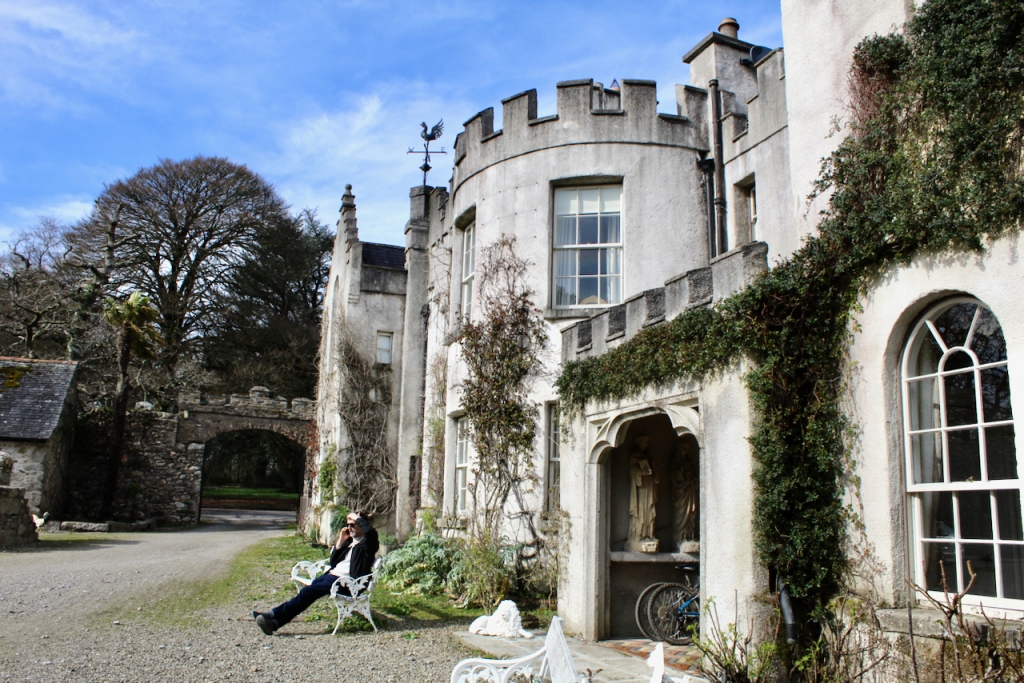
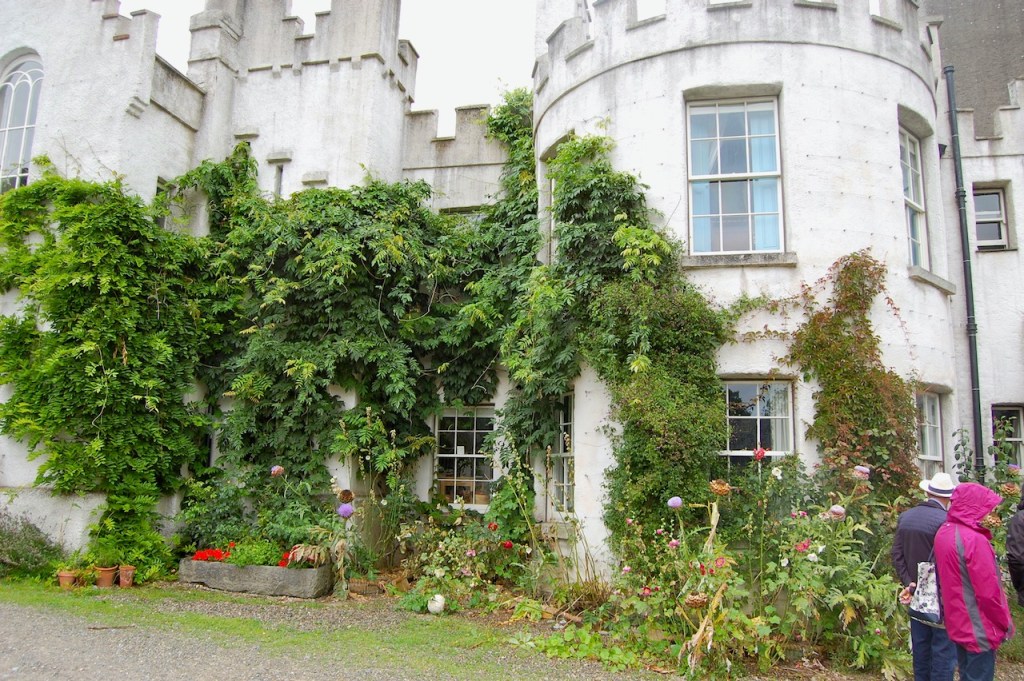
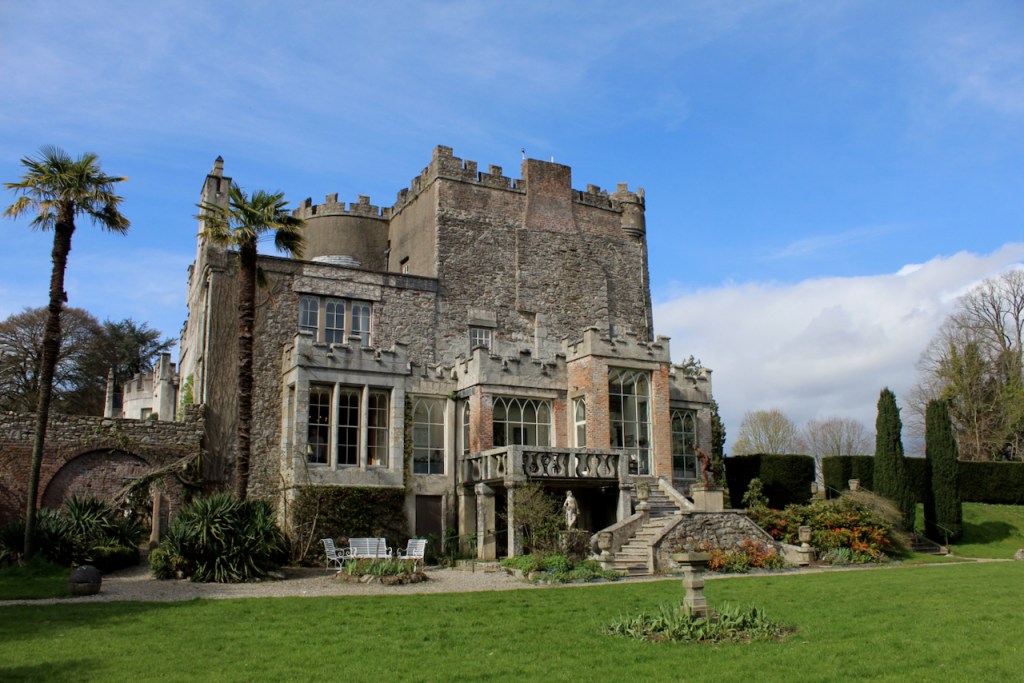
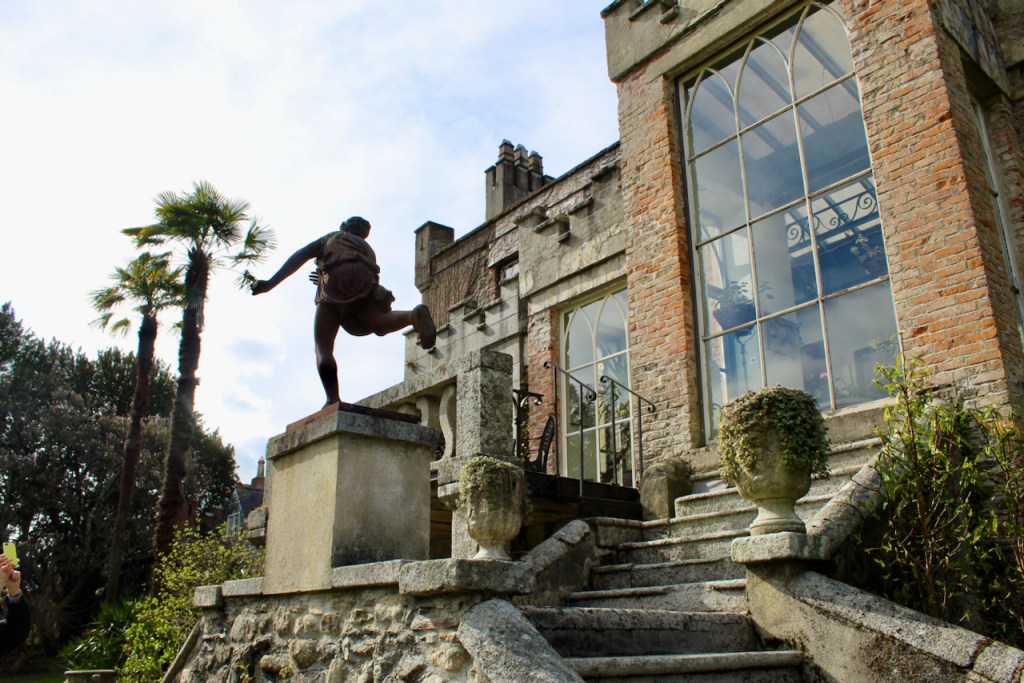
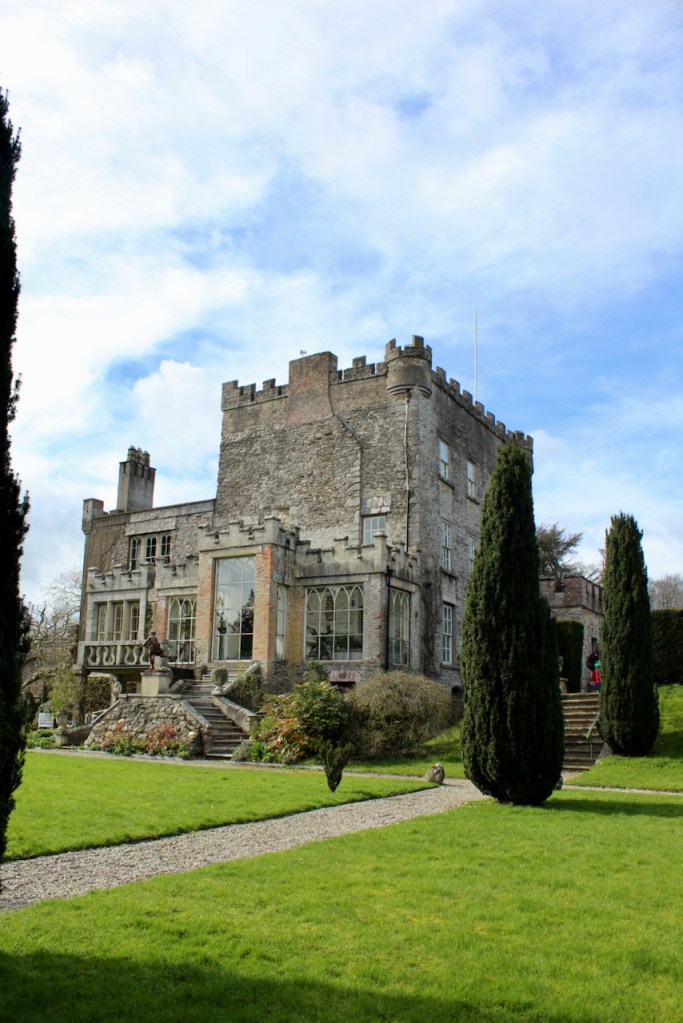
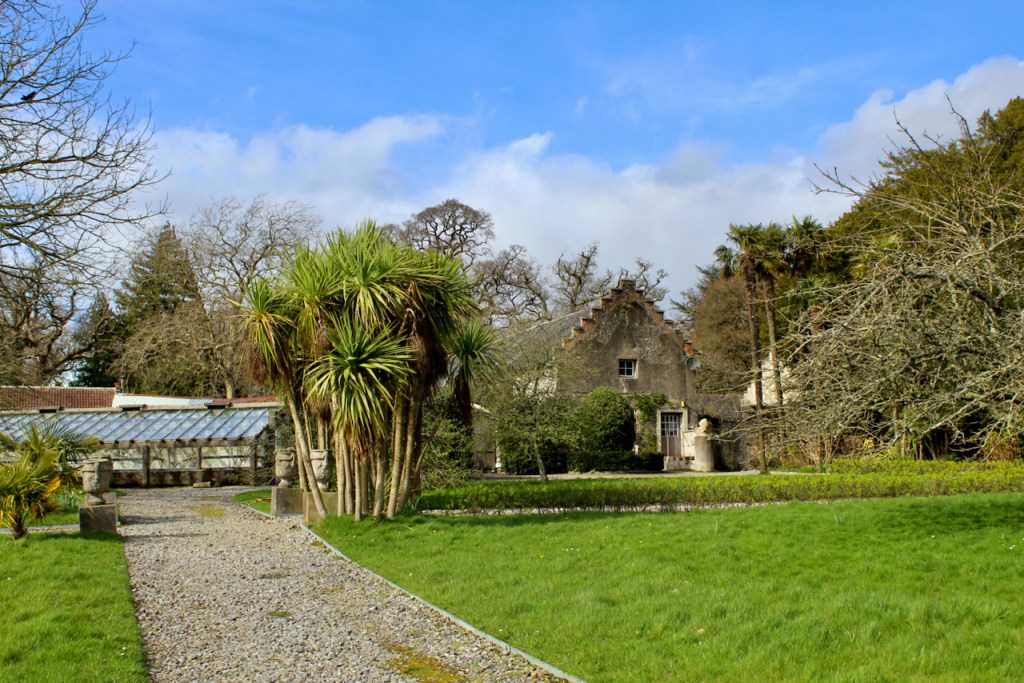
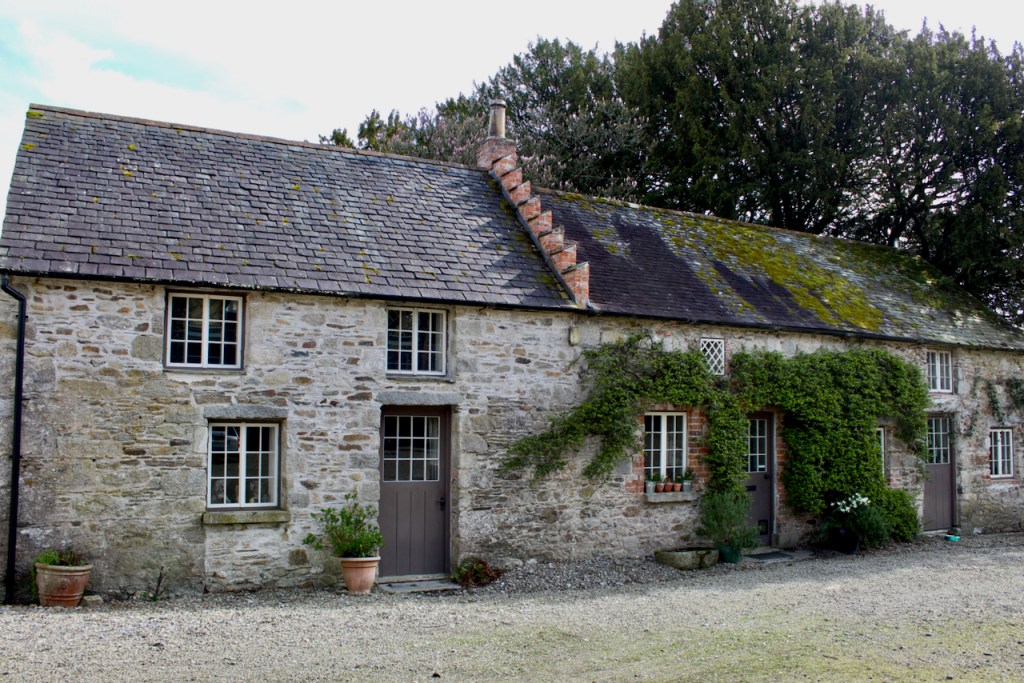
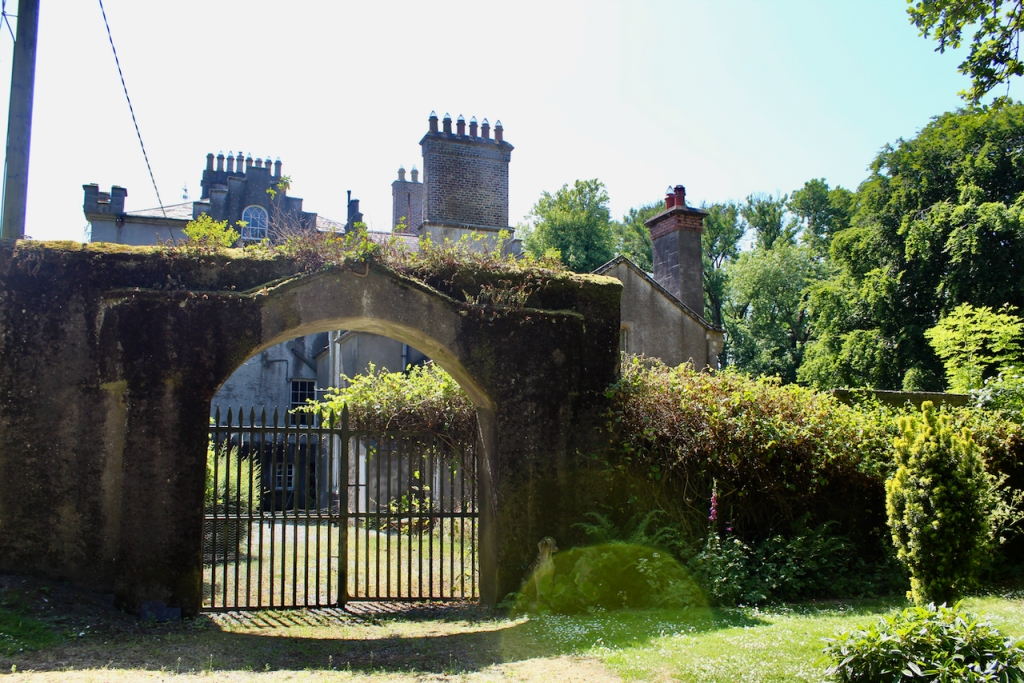
Shankill Castle is now a family home for the Cope family, since 1991. It was first built as a Butler tower house beside the ruins of a pre-reformation church – you can still see the ruins of the church in the grounds. The Copes give tours of their home and there are lovely gardens to wander and a café


The website tells us that “Elizabeth, a painter, and Geoffrey, a historian, have hosted many creative people in their home over the last twenty-five years. They have shared with them their unique and beautiful setting in Ireland’s Ancient East and have dedicated Shankill Castle to the arts and culture.“
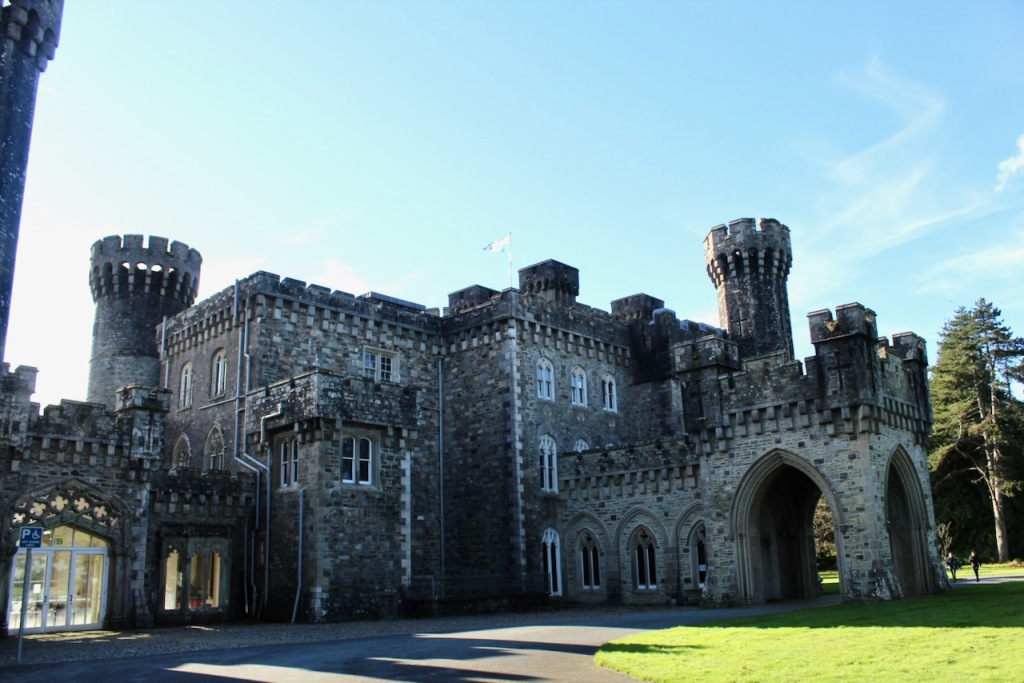
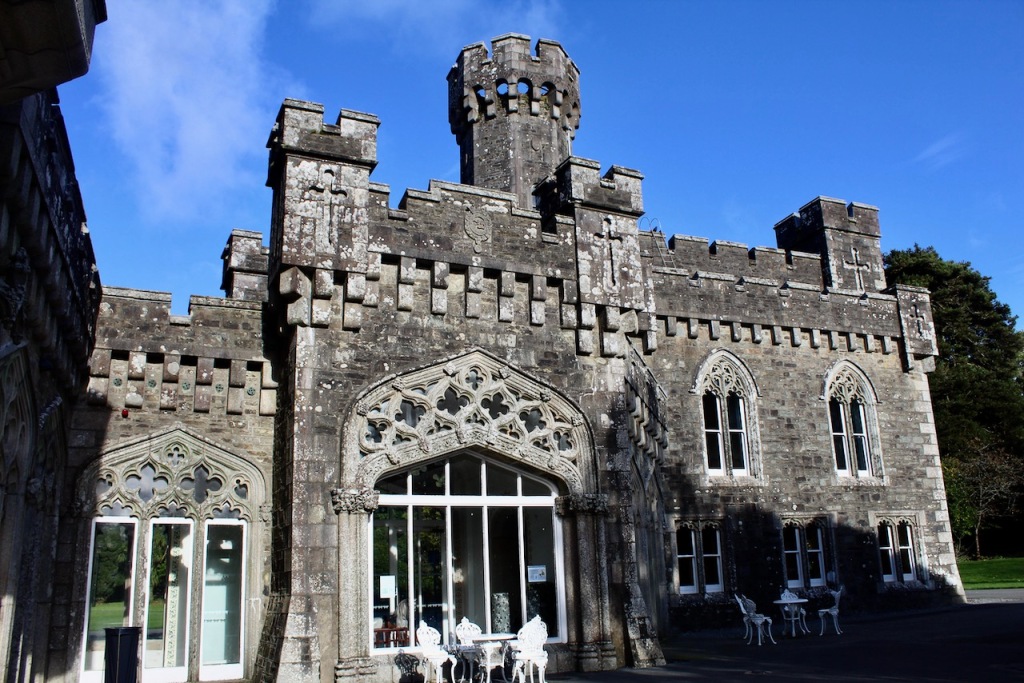
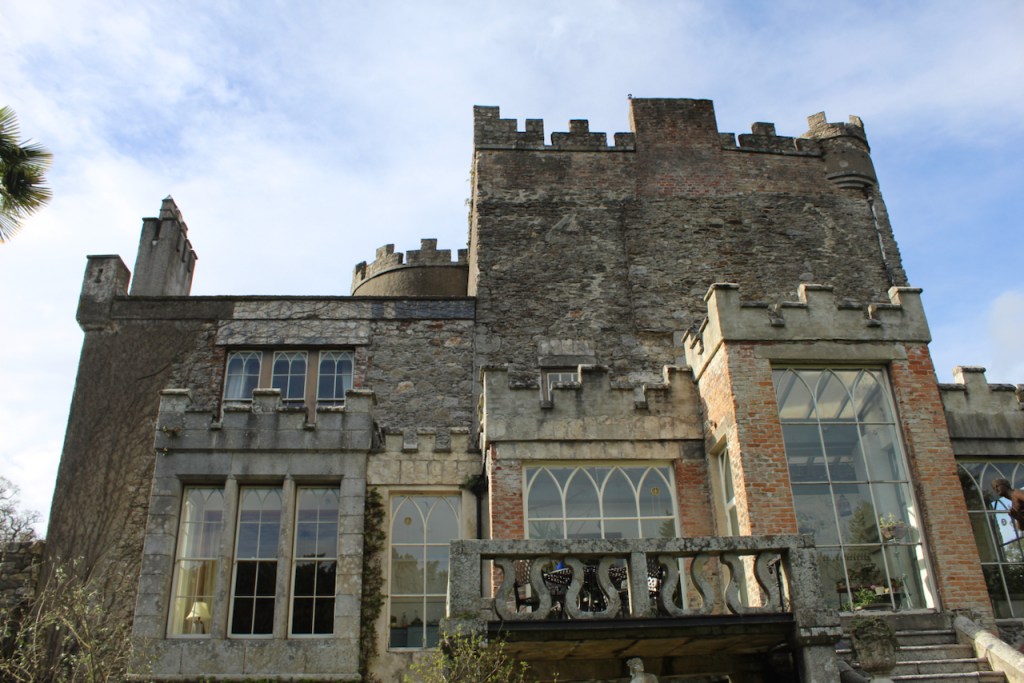
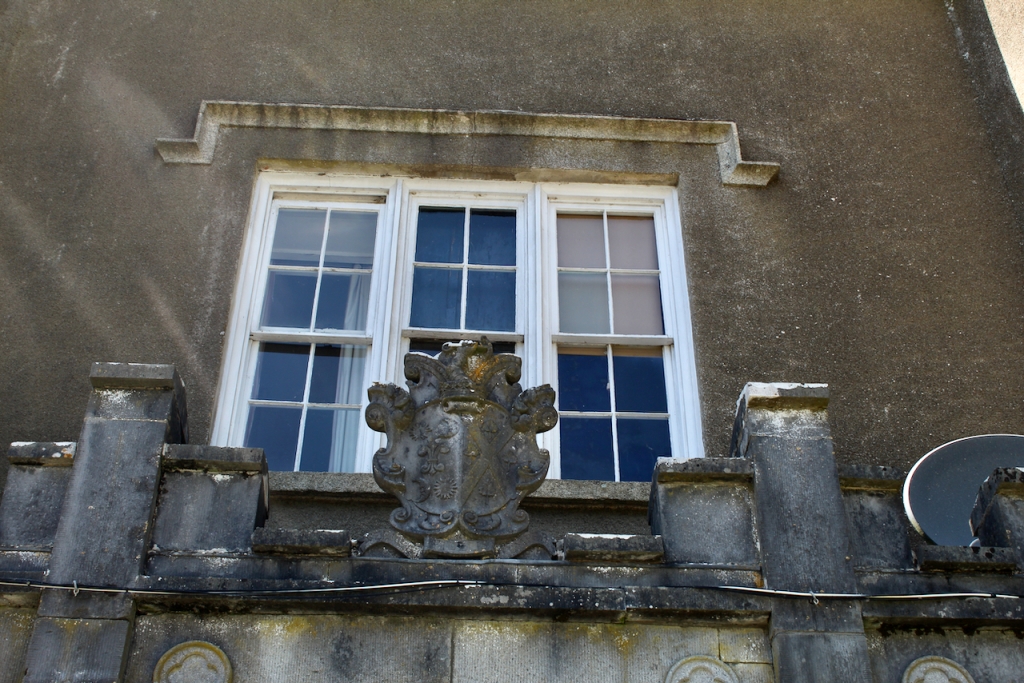
In 1708 the Castle was rebuilt and in the nineteenth century it was enlarged and castellated, adding a stable yard and the castellated entrance to the demesne. The stableyard and the castellated entrance to the demesne are attributed to Daniel Robertson. Other additions to the house include a Gothic porch bearing the Aylward crest and a conservatory.
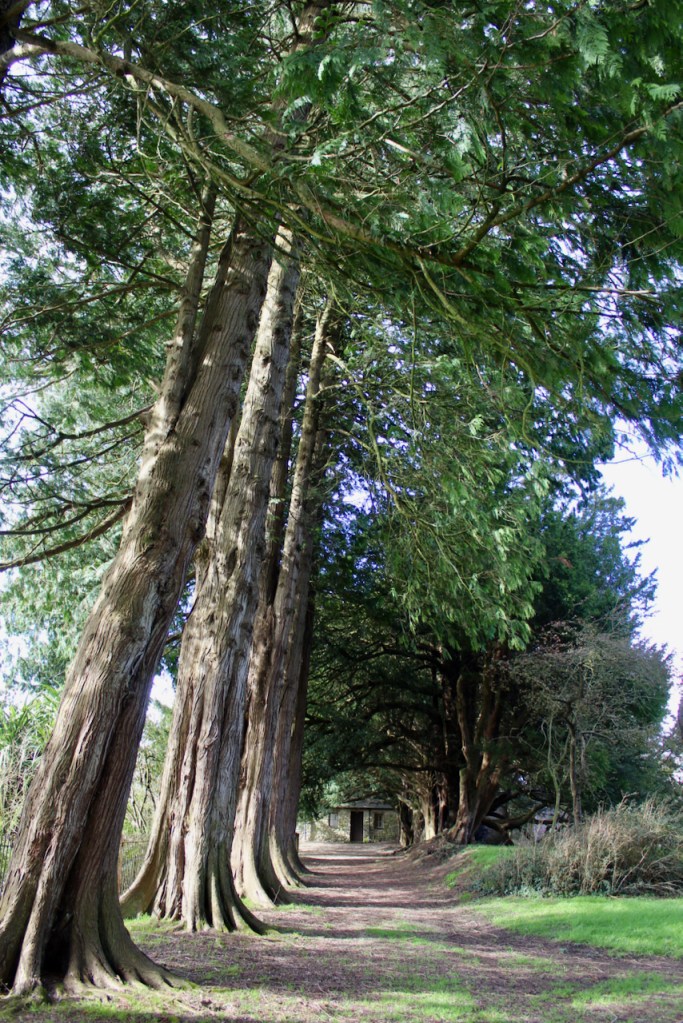
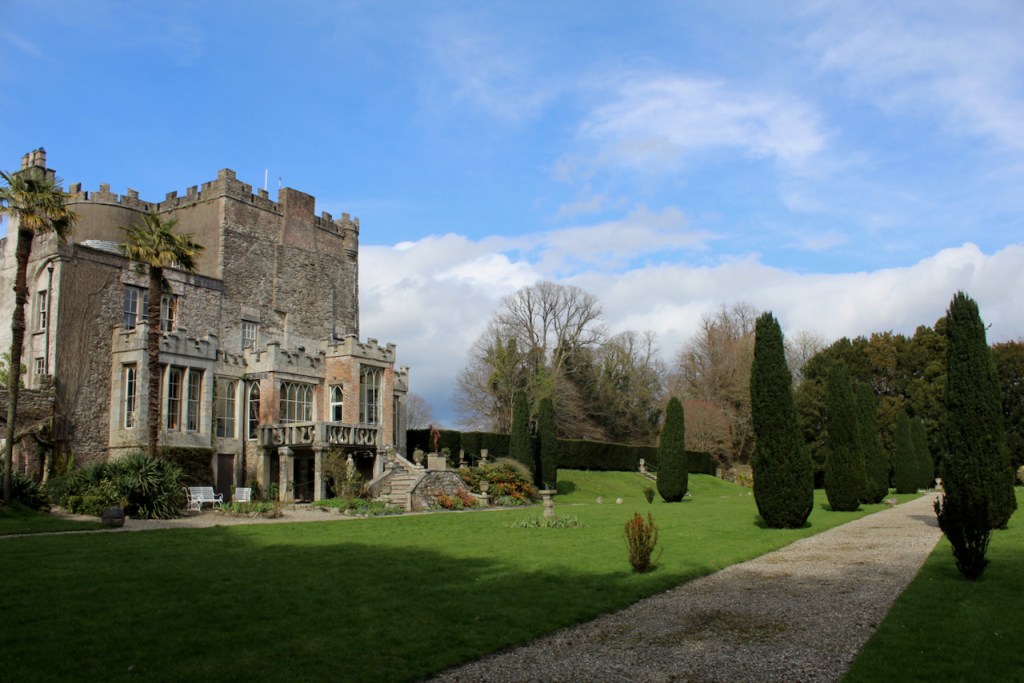
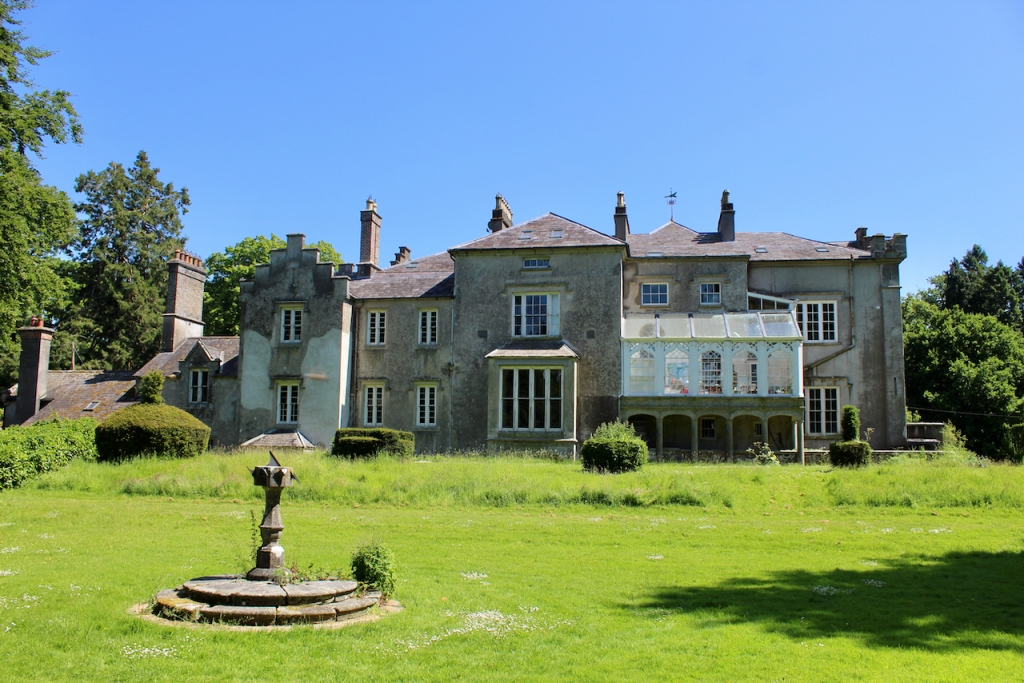
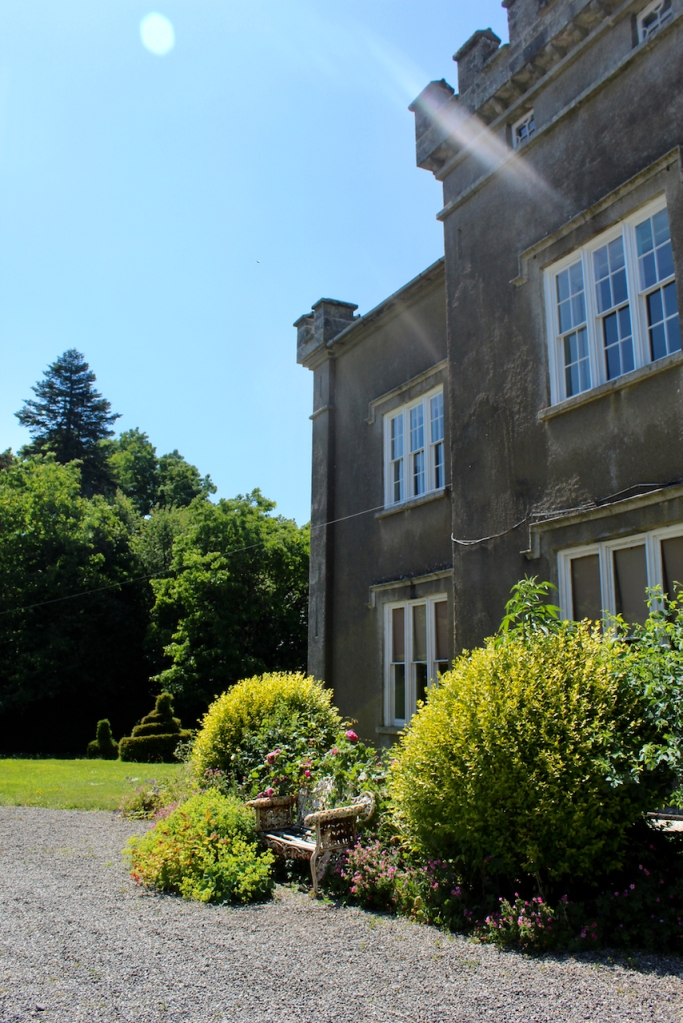
In the garden there are remnants of an eighteenth century lime walk, nineteenth century laurel lawns and some trees that were favourites in the Victorian age such as giant Sequoias.

The website tells us that “In 1708, it was rebuilt by Peter Aylward who bought the land from his wife’s family. The new Shankill Castle was constructed as a Queen Anne house, set in a formal landscape, vista to the front and canal to the rear.“
Peter Aylward was a Roman Catholic who fought in the Jacobite army in 1688-90. For this he was was outlawed, but he later conformed to the established Protestant church. [1]
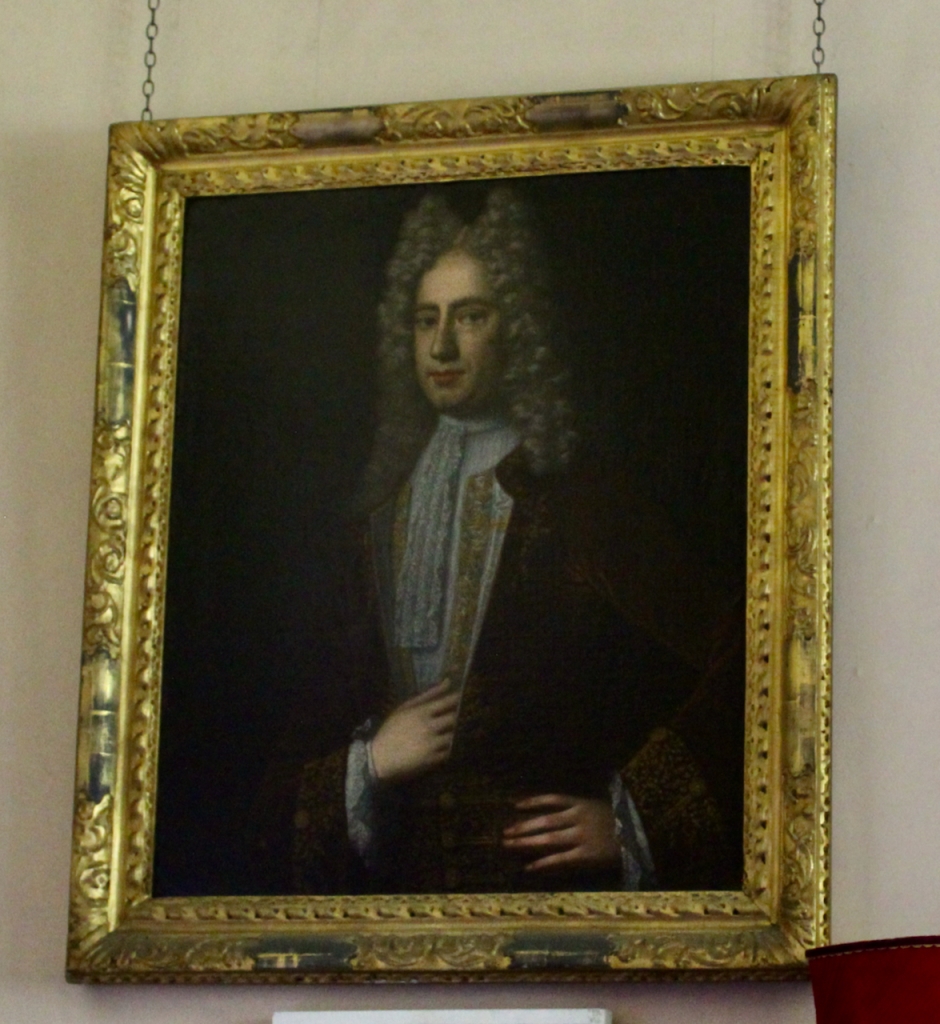
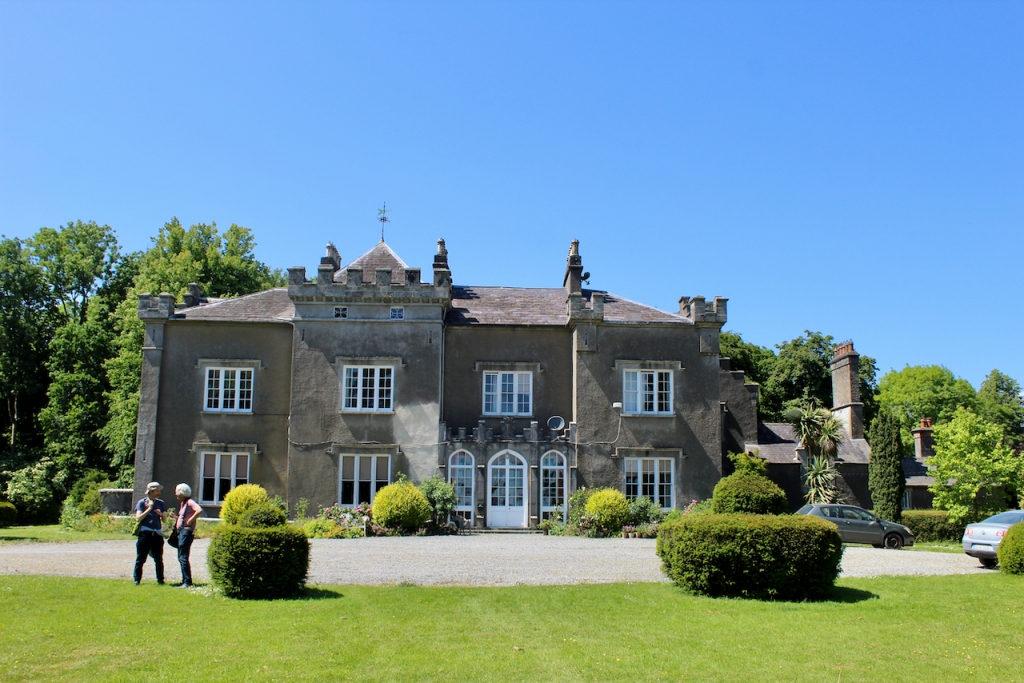




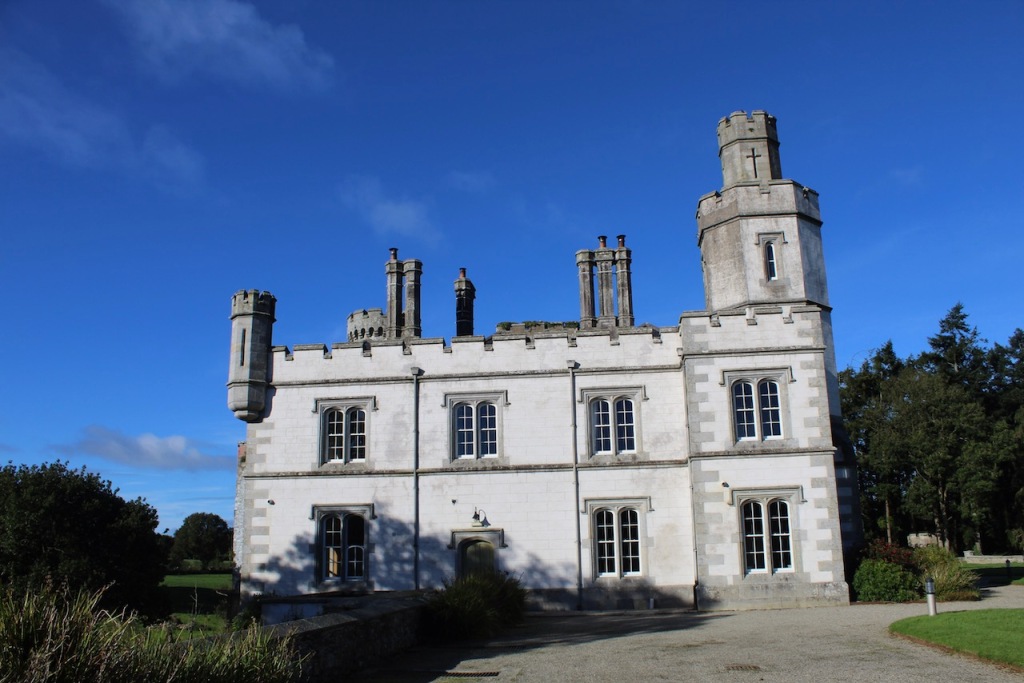
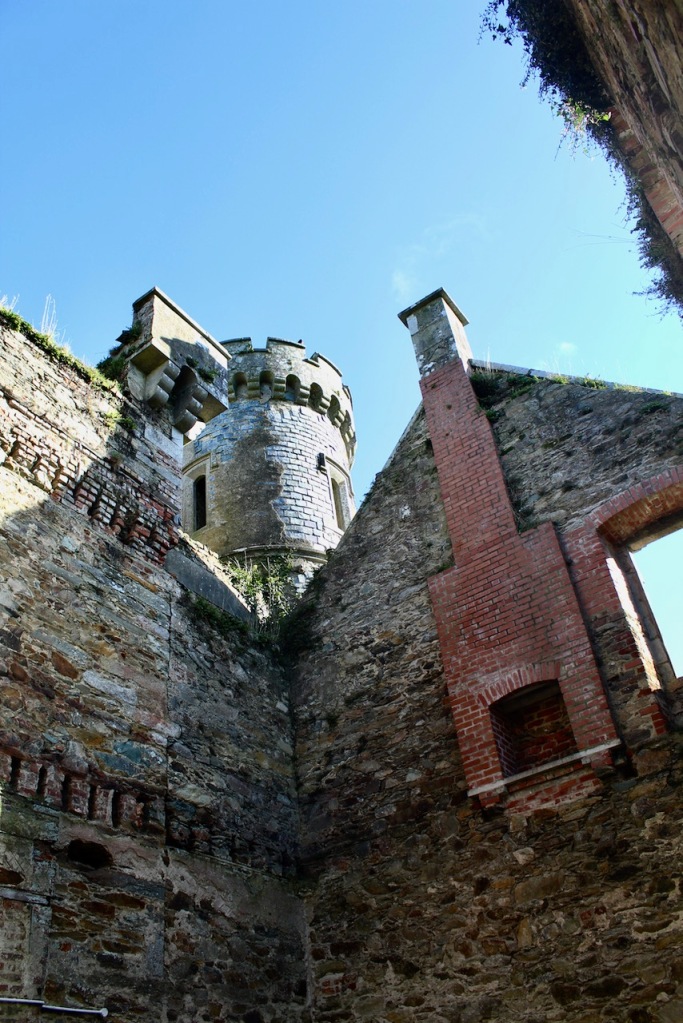
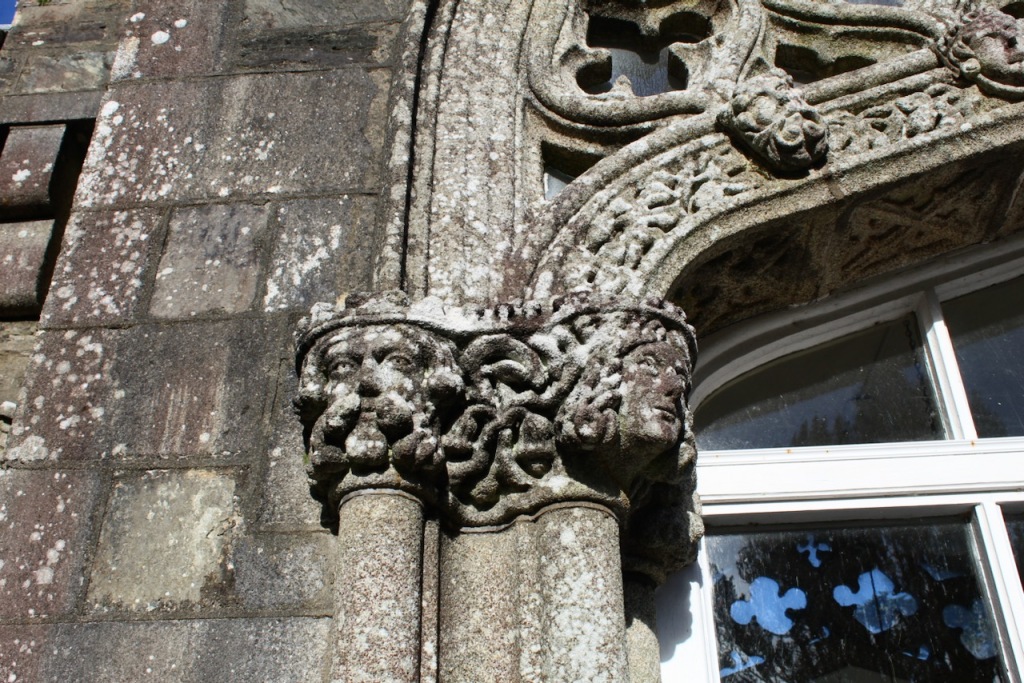
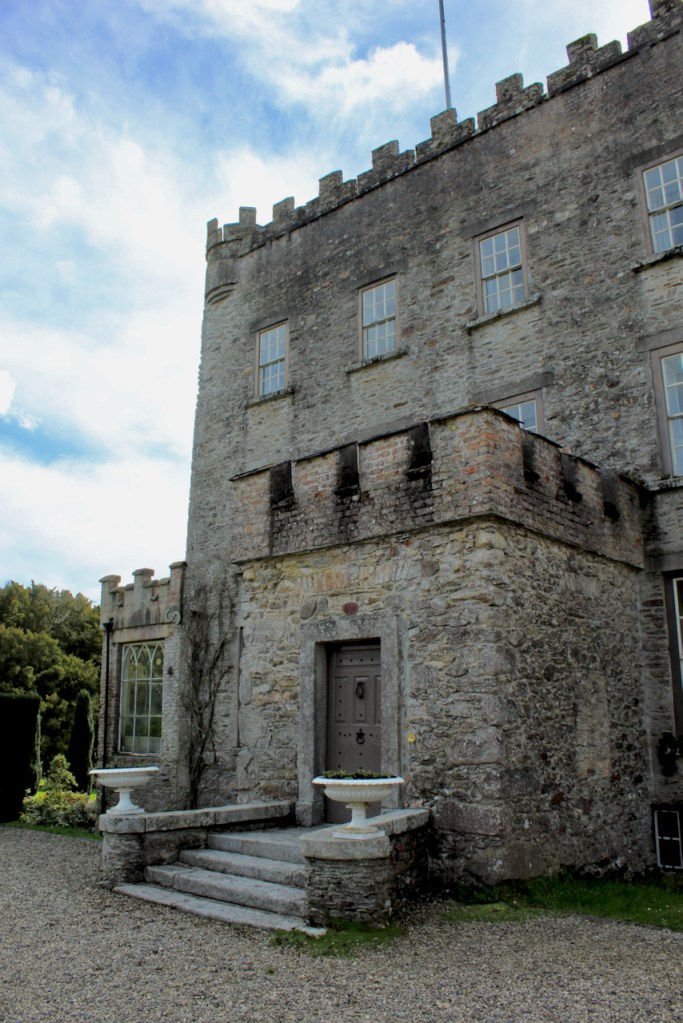
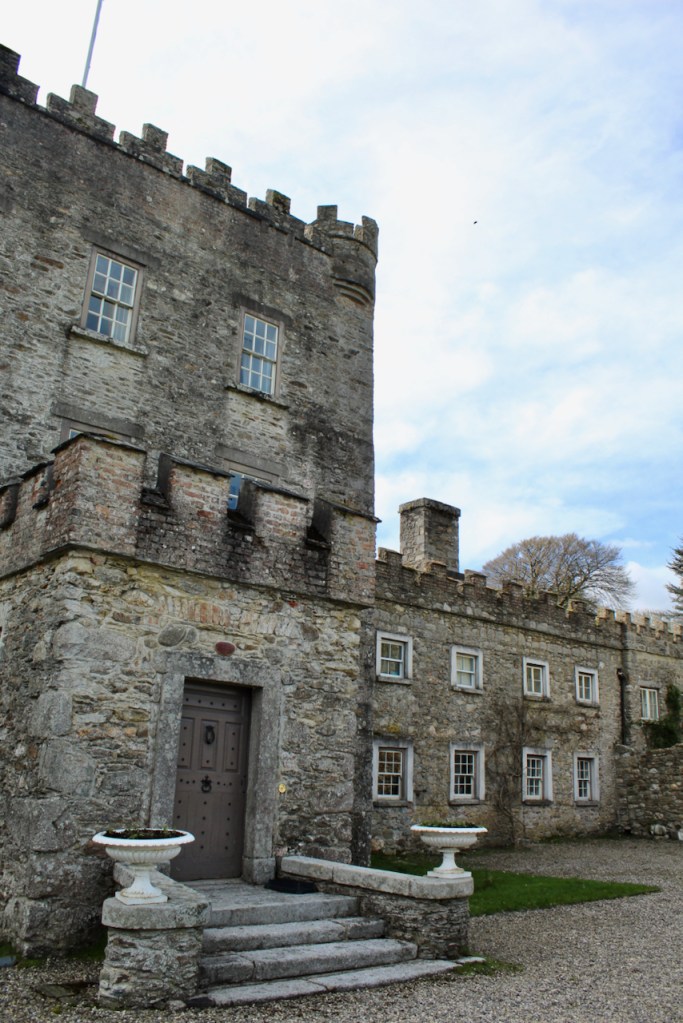
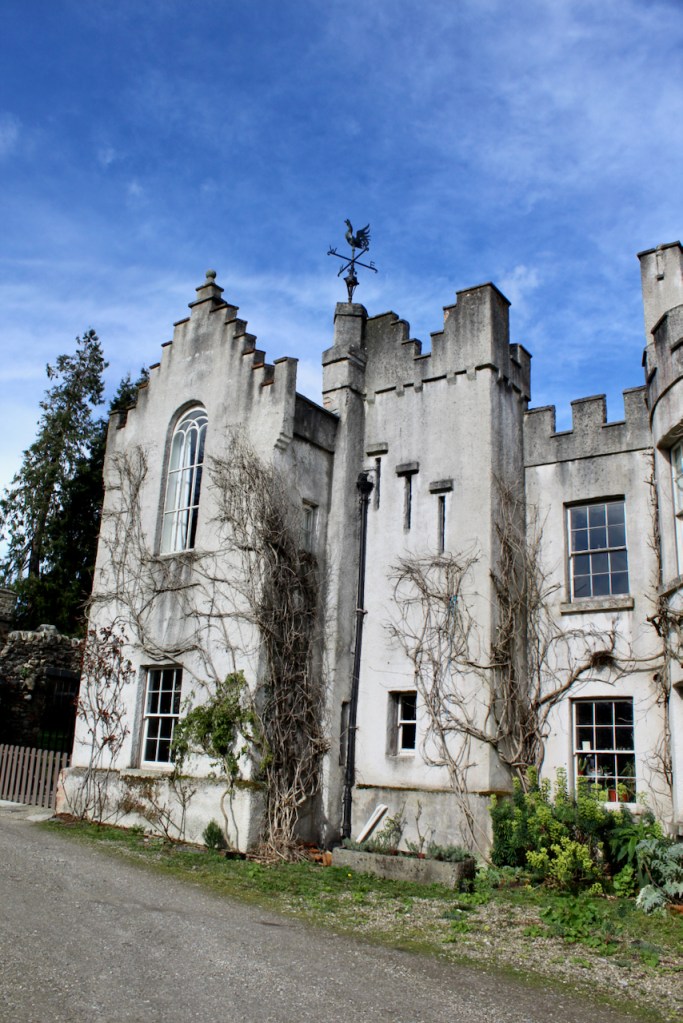
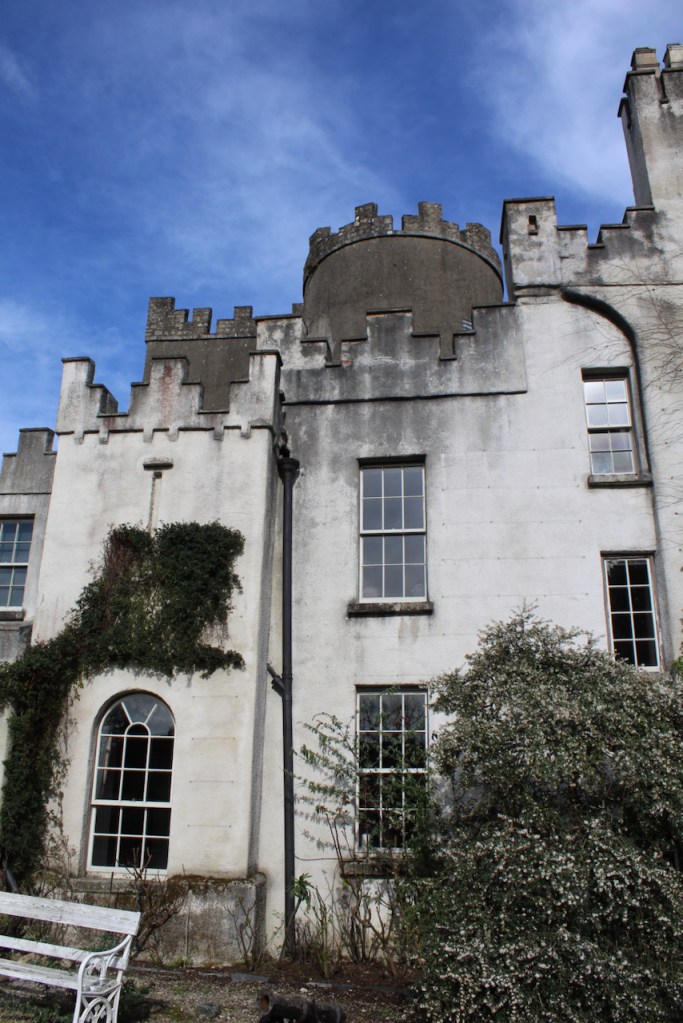
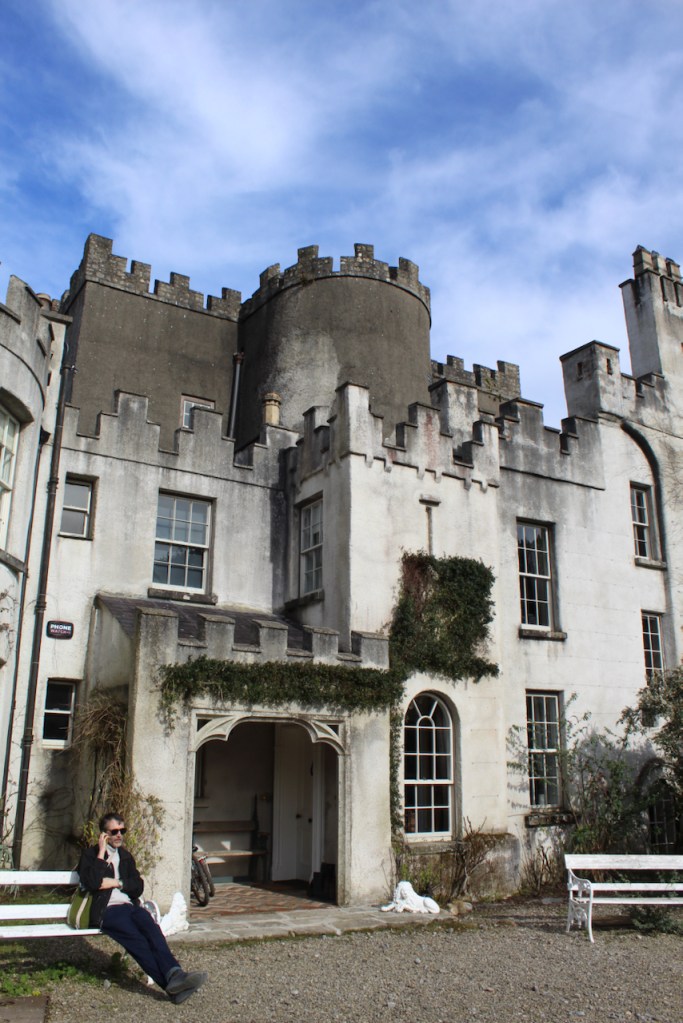
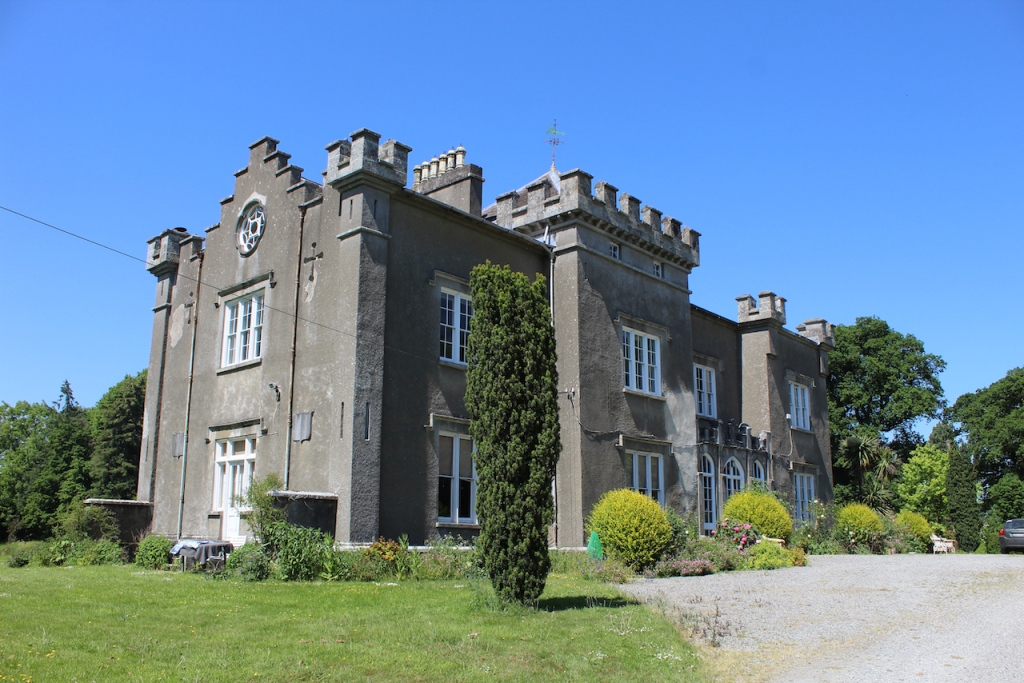
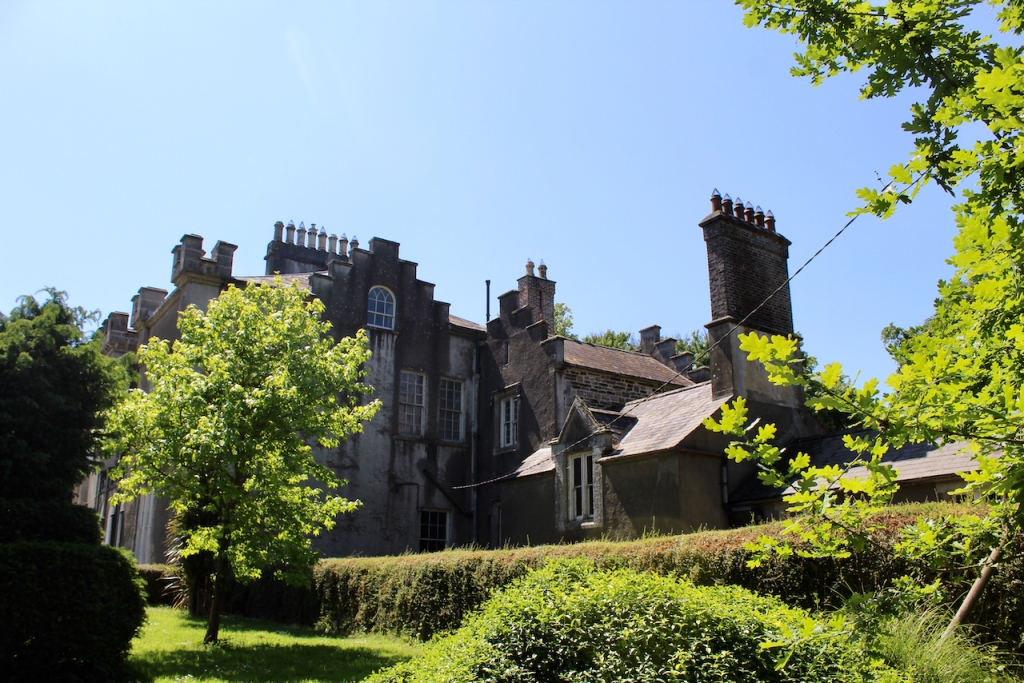
The house has battlemented full-height corner piers having slit-style blind apertures. The windows have hood mouldings. The house is delightfully higgeldy piggeldy with its enlargements and additions.

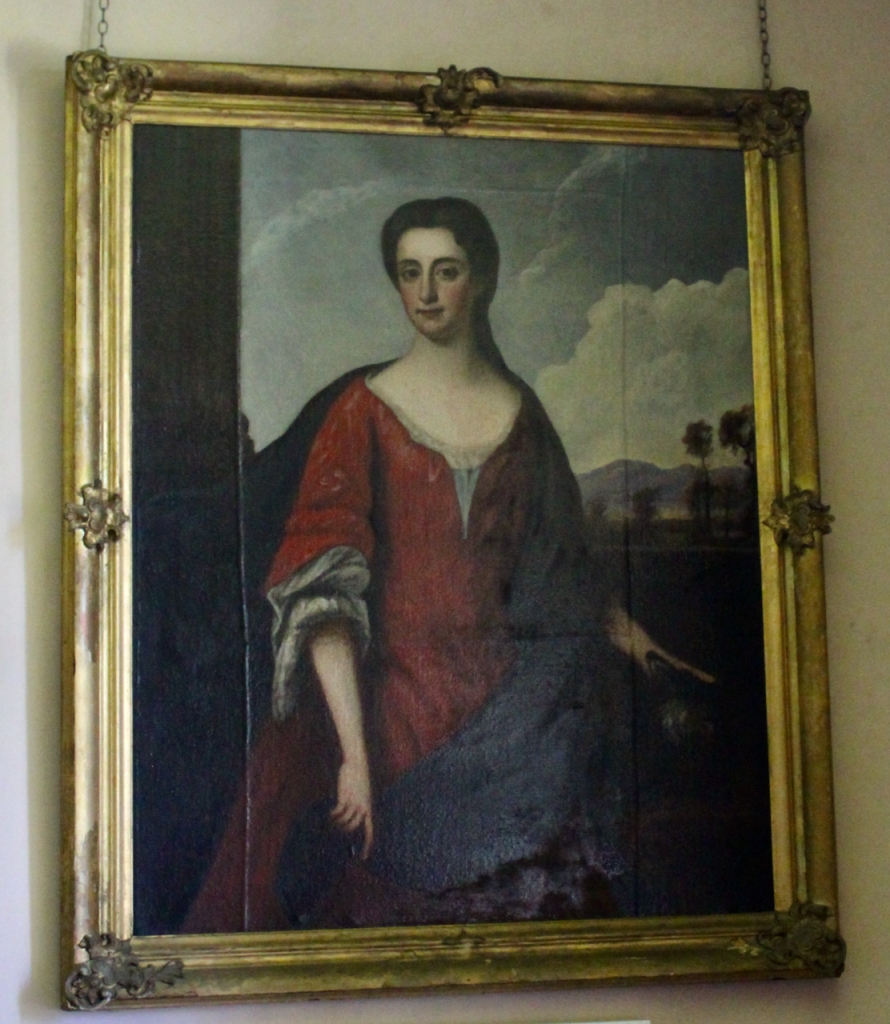
Elizabeth Butler’s family owned Paulstown Castle, which was rebuilt in 1828 but is now a ruin.

Peter Aylward and Elizabeth Butler had a son, Nicholas (d. 1756). He held the office of Member of Parliament (M.P.) for Thomastown and Sheriff of County Kilkenny in 1742. A website about landed families tells us that he was brought up Catholic but conformed to the established church in 1711. [see 1]. In August 1719 he married Catherine, second daughter of Maurice Keating of Narraghmore, Co. Kildare.
Their son, also named Nicholas (d. 1772), inherited Shankill Castle in 1756. That year, he married Mary Kearney, daughter of Benjamin Kearney of Blanchville (Co. Kilkenny). He held the office of High Sheriff in 1757. He died while his children were still young, and their mother had died in 1767, so the children were made wards of the Irish Court of Chancery, which in 1772 appointed their grandfather, Benjamin Kearney (d. 1784), as their guardian.

After Mary née Kearney died, Nicholas married Susanna (d. 1775), widow of Edmund Waring. Susanna married a third time after Nicholas’s death, in October 1772, Rev. Henry Candler, and she died 4 August 1775.

Nicholas and Mary née Kearney’s eldest son, Peter (1758-92), came of age in 1779. It is said that he was “of weak mind” and that his Guardian exercised a large influence over him. In 1780 he married Anne Kearney of New Ross (Co. Waterford). They had a son, Nicholas John Patrick Aylward (1787-1832).
This son was only five years old when his father died and he inherited Shankill Castle. He was educated at Kilkenny and Trinity College, Dublin (admitted 1804). [see 1] In 1805 at the age of just 18 he married Elizabeth (d. 1851), eldest daughter of James Kearney of Blanchville (Co. Kilkenny). This James was son of Benjamin Kearney (d. 1784), the guardian of Nicholas John Patrick’s father, so this was probably an influencing factor. He came of age three years later in 1808. He was High Sheriff of Co. Kilkenny, 1816-17. In the 1820s, he remodelled Shankill Castle, hiring William Robertson.
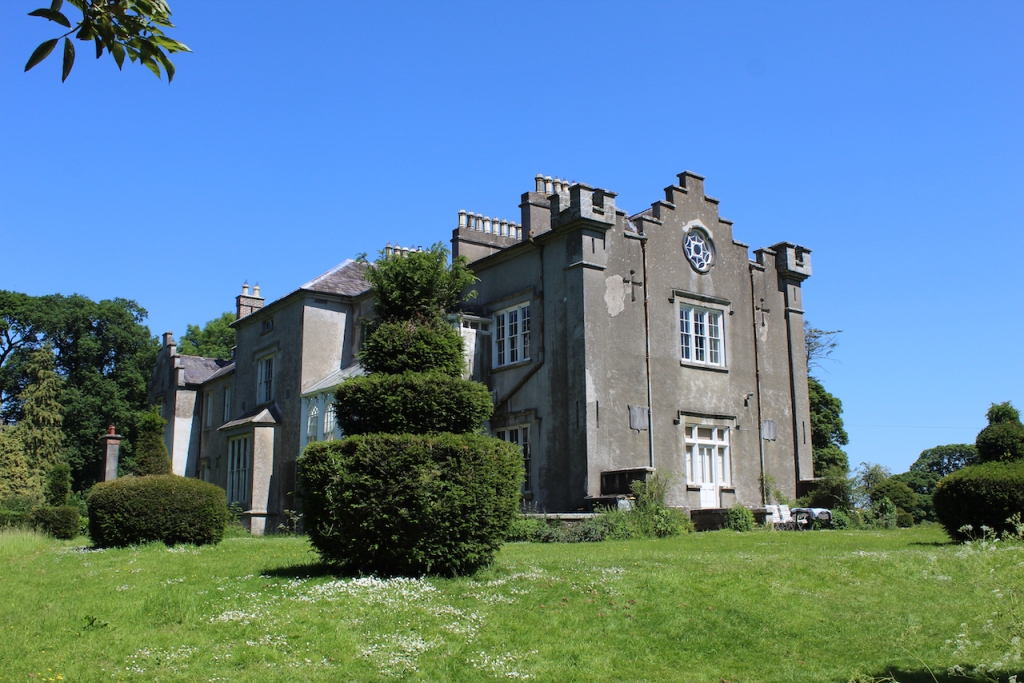

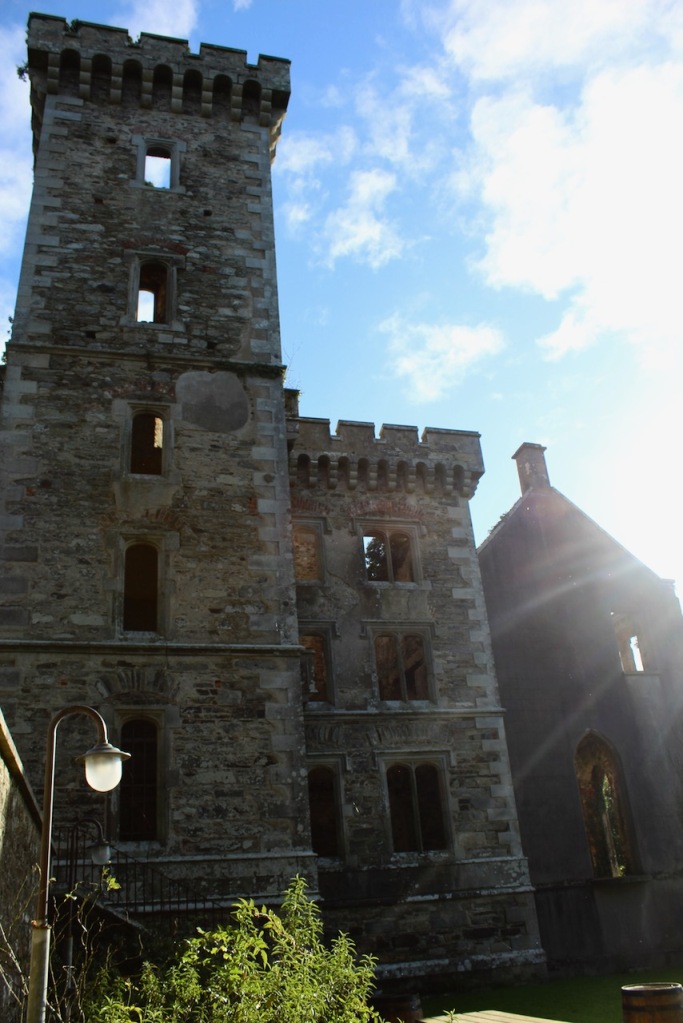
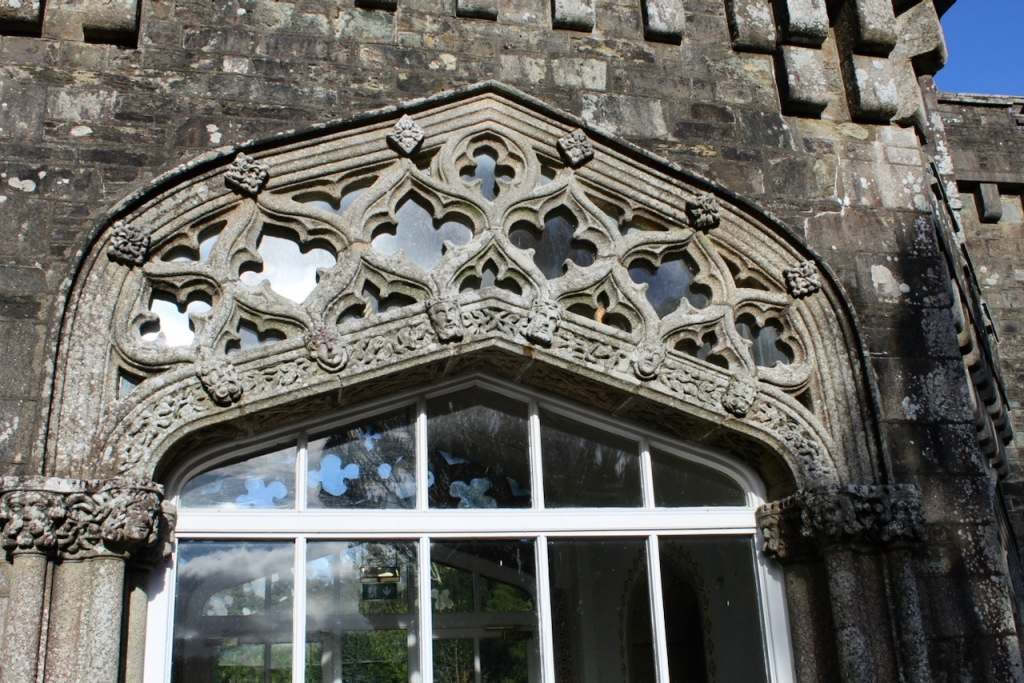
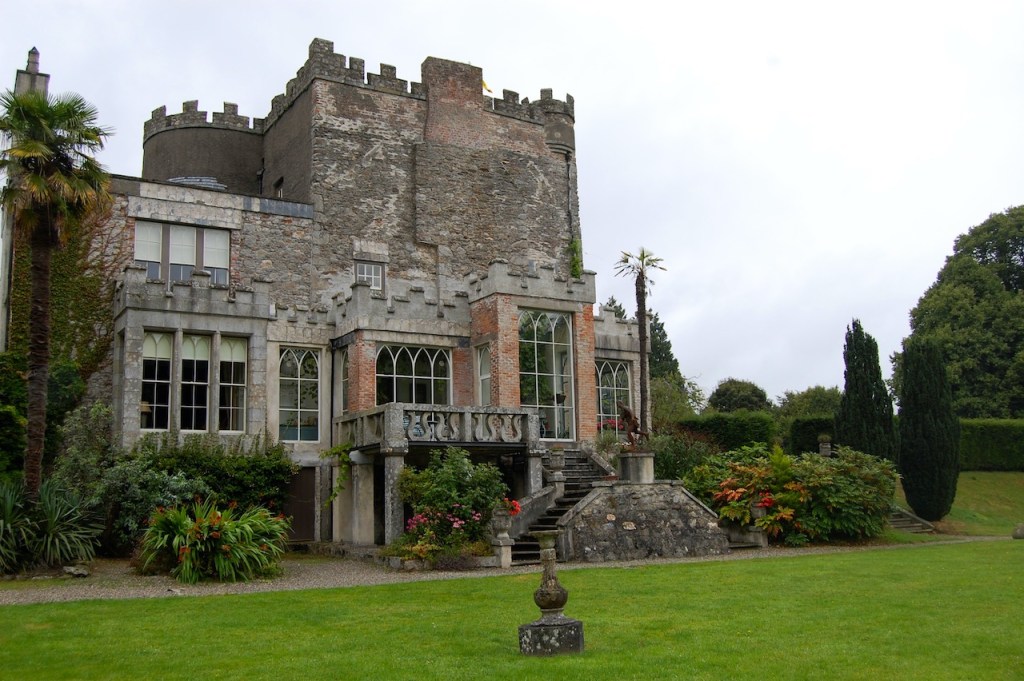
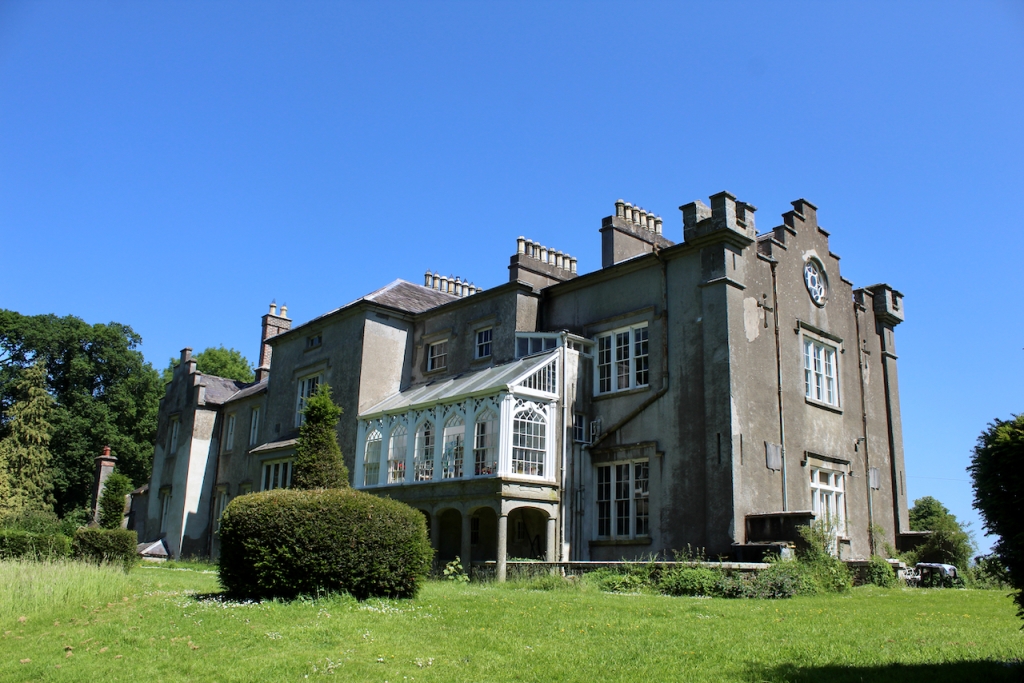
A watercolour probably dating from the 1820s attributed to William Robertson shows a design proposal for alterations. For this reason, the changes to the house which were made for Nicholas Aylward (d. 1832) in the 1820s are attributed to William Robertson, although the proposal in the watercolour were not executed exactly as pictured. The end bays were crenellated and linked by a Gothic porch, and one was raised to look like a tower. A new dining room running from the front of the house to the back was added on the left, and a castellated office wing on the right, effectively breaking up the symmetry of the original design. The back of the house, which is more irregular, is treated in much the same way, and adorned with a Gothic conservatory on the level of the half-landing of the stairs, carried on a stone arcade. [1]
The National Inventory describes it:
“An impressive large-scale house built c. 1825 to designs prepared by William Robertson (1770-1850) for the Aylward family forming a picturesque landmark of Romantic quality in the landscape. The complex form and massing of the composition attests to the evolution of the site over a number of centuries with the present house incorporating the fabric of an early eighteenth-century range together with a medieval tower house, thereby representing the continuation of a long-standing presence on site.” [2]
The architect William Robertson was born in Kilkenny in 1770. The Dictionary of Irish Architects tells us he was probably a son or close connection of the nurseryman, William Robertson, who traded as ‘William Robertson and Son’ in Kilkenny. [3] The Dictionary adds that identifying his works is complicated by the fact that the names ‘Robertson’ and ‘Robinson’ are often confused, but it is possible that he may already have received at least one architectural commission as early as 1794, for stables at Woodstock, Co. Kilkenny. He seems to have worked in London for a time then moved back to Kilkenny.
The Dictionary of Irish Architects tells us of William Robertson:
“Robertson was back in Kilkenny by 1801, when he was entrusted with the design of the new county gaol. In Kilkenny he developed a busy architectural practice. It appears that he may have had the Earl of Ormonde as a client as early as 1802 and that he was working with a partner named Wylie for a time circa 1804. Joseph Bourke, Dean of Ossory, suggesting to William Gregory in 1813 that Robertson might be employed to enlarge the barracks at Kilkenny, describes him, perhaps with some exaggeration, as ‘a very eminent architect in this part of the world, who has had the building of most of the public Edifices in the South, &c.’. In the same year Robertson reported to the Dean and Chapter of St Canice’s Cathedral on the fabric of the cathedral.
William Robertson died at Rosehill, the house which he had built for himself on the Callan road, in May 1850.” [4]

The history of Shankill Castle and Blanchville were further linked in the next generation. Nicholas John Patrick Aylward and Elizabeth née Kearney had a son, James Kearney Aylward (later Kearney-Aylward) (1811-84). He assumed the additional name of Kearney in 1876, on succeeding to a part of the estates of his cousin James Charles Kearney of Blanchville.

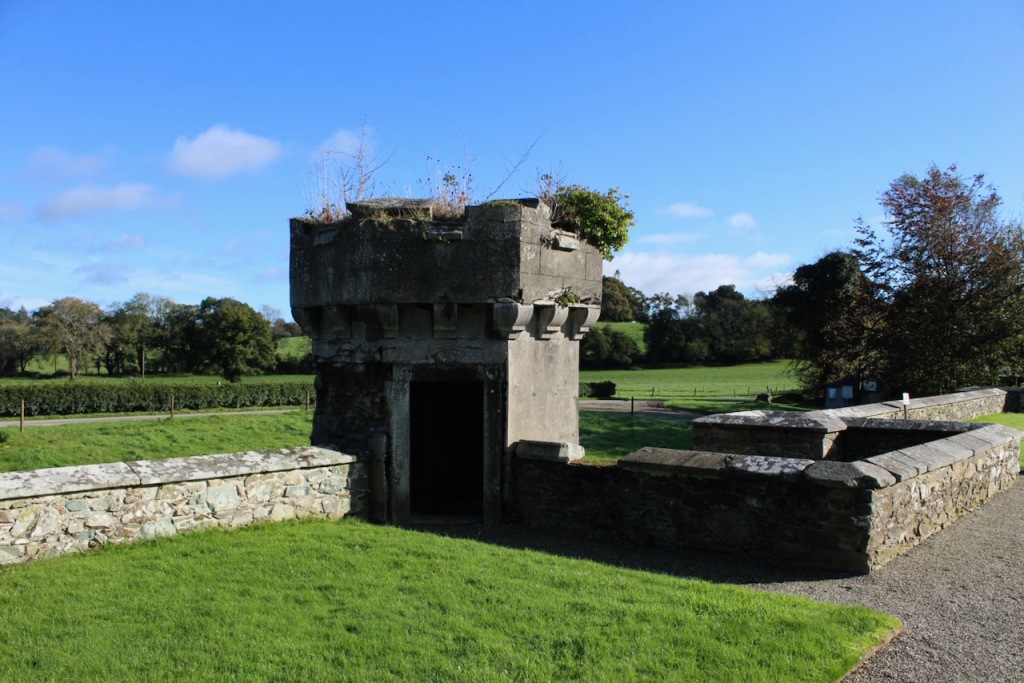
Blanchville still stands and it has notable Tudor Revival stable building, built 1834, in the style of Daniel Robertson, which are now available for accommodation (see https://blanchville.ie/ ). Daniel Robertson built a memorial for Captain James Kearney, sometime between 1834-47, according to the National Inventory.

The Heritage Council provided a grant to restore the tower in 2004.




James Kearney Aylward held roles as Sheriff, Deputy Lieutenant and Justice of the Peace. In 1853 he married Isabella Forbes. She was the widow of Beauchamp Bartholomew Newton (1798-1850) of Rathwade, County Carlow (a house attributed to Daniel Robertson). However, she did not have children by either of her marriages.
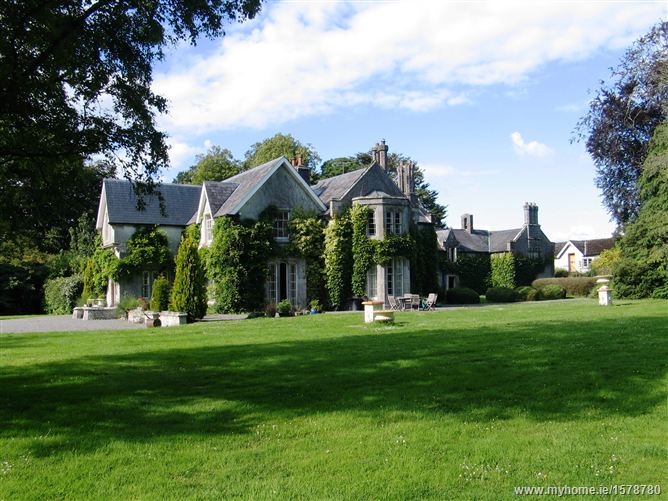

Therefore when James Kearney-Aylward died in 1884, Shankill Castle passed to his nephew, Hector James Charles Toler (1839-1918, later Toler-Aylward). [see 1] Hector was the son of James Kearney-Aylward’s sister Mary (d. 1880) who had married Reverend Peter Toler (d. 1883) of Bloomfield, County Roscommon.
Before James Kearney-Aylward died, he undertook further renovations of Shankill Castle, under the direction of William Deane Butler. The Archiseek website tells us that William Deane Butler (1793-1857) studied at the Dublin Society Schools and was a founding member of the Royal Institute of Architects in Ireland as well as the Society of Irish Artists, and he was also an engineer. Among his most important works are Amiens Street Station (now called Conolly Station) in Dublin, Kilkenny’s Catholic Cathedral, and Sligo Asylum. [5]
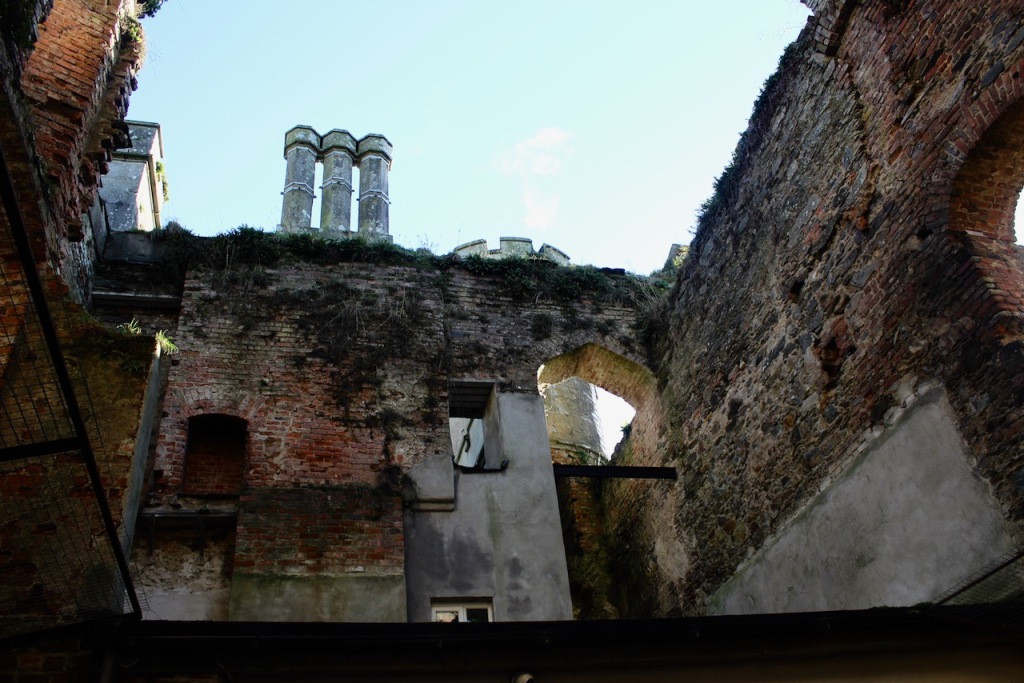
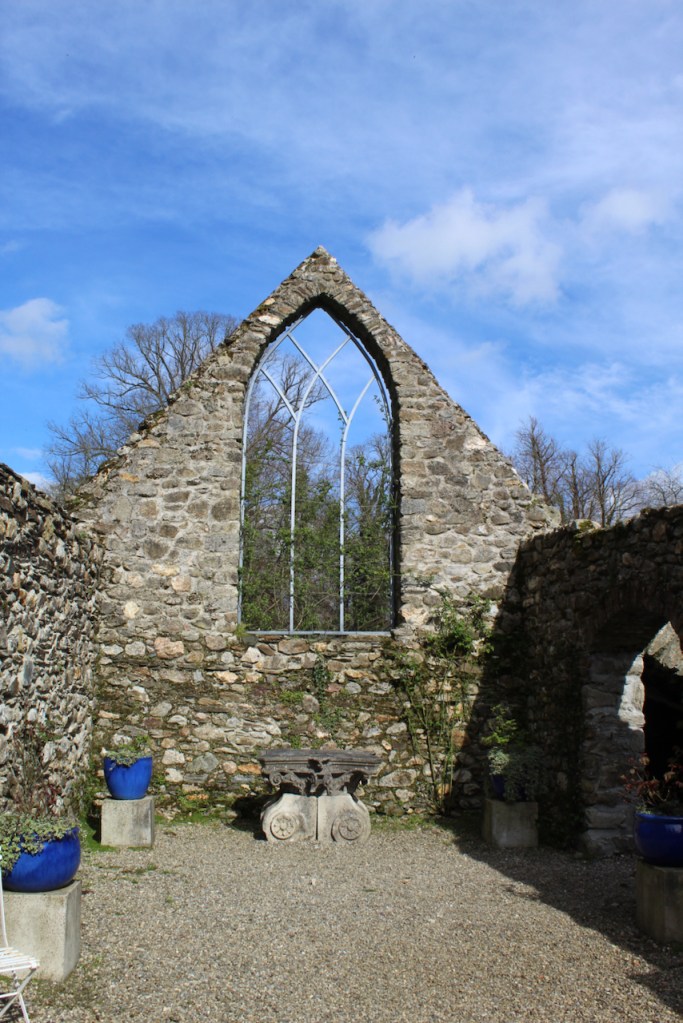
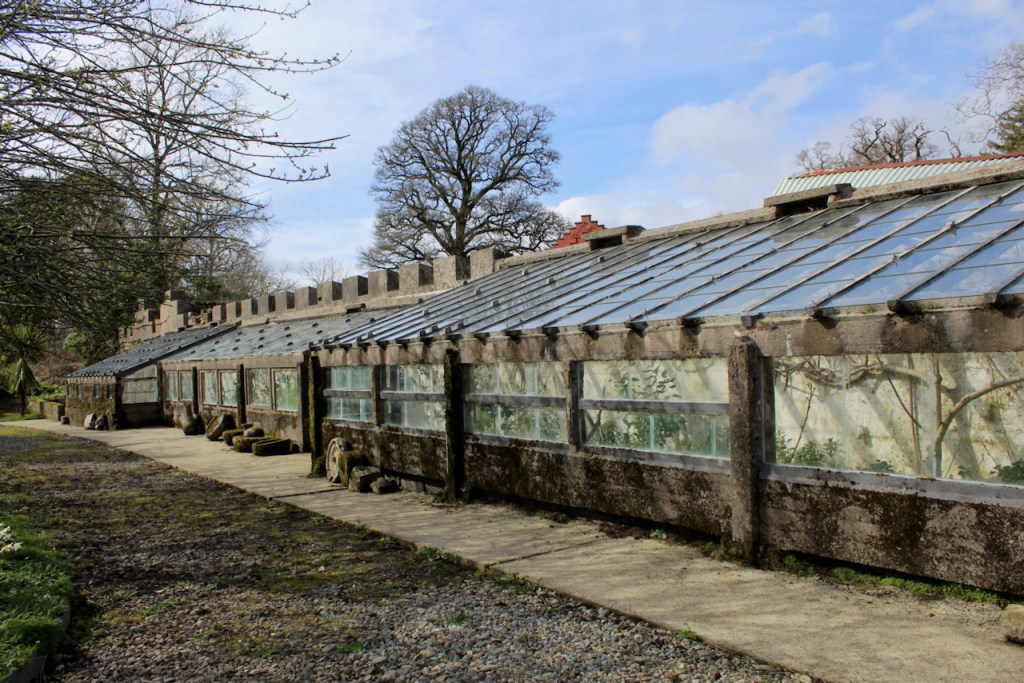
A conservatory attributed to Richard Turner or Joseph Paxton was added, but this has been removed.
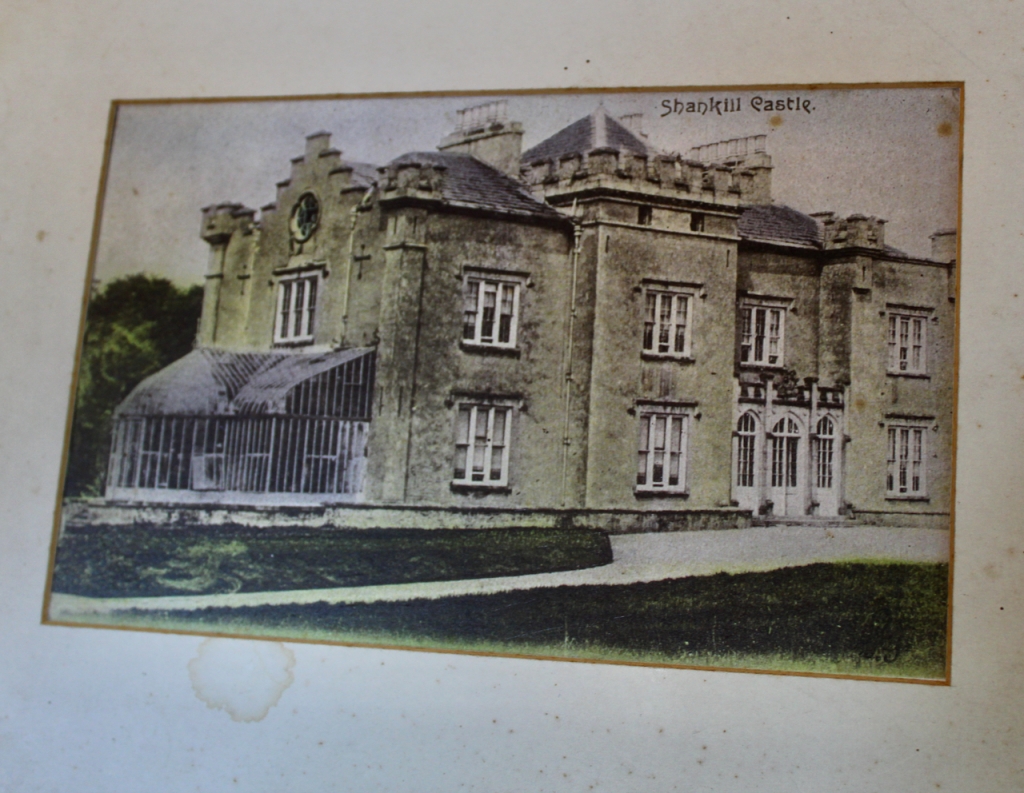

The National Inventory continues: “Meanwhile the traces of renovation works carried out under the direction of William Deane Butler (c.1794-1857) together with accounts of a conservatory (post-1859; dismantled, post-1902) attributable to Richard Turner (1798-1881) indicate the continued development of the house well into the latter half of the nineteenth century. A riot of advanced and recessed bays, battlements, crow-stepped gables, and so on are carefully orchestrated to disguise the earlier disparate ranges in a cohesive architectural skin while supplementary fine details further embellish the architectural design value of the composition. Having been well maintained the house presents an early aspect with most of the historic fabric surviving in place both to the exterior and to the interior where it is believed that an original decorative scheme of artistic significance survives largely intact.” [2]
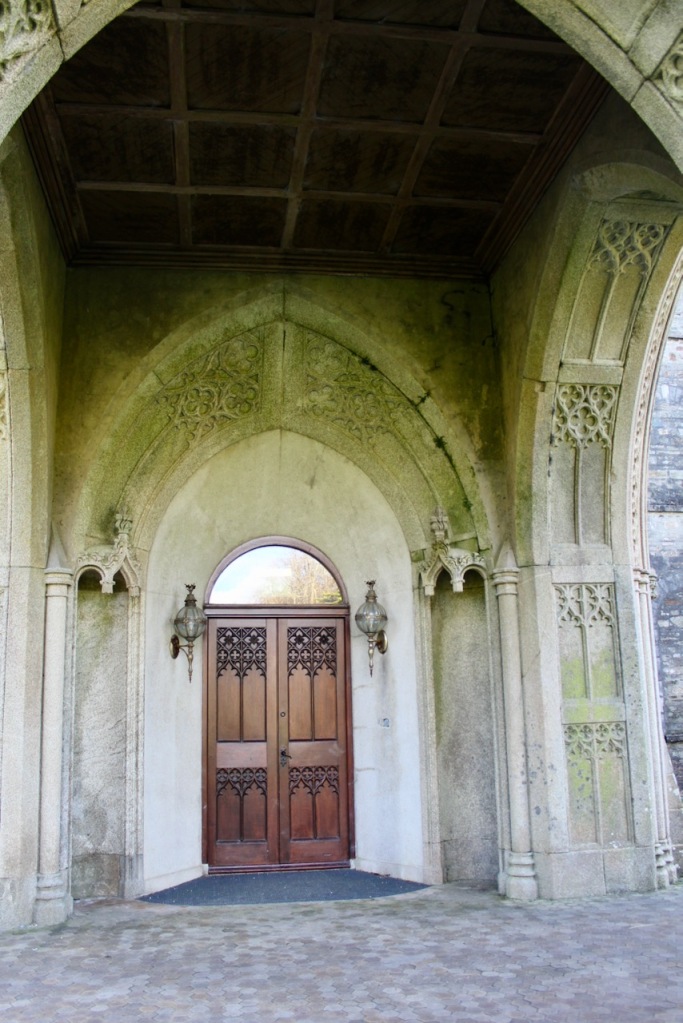
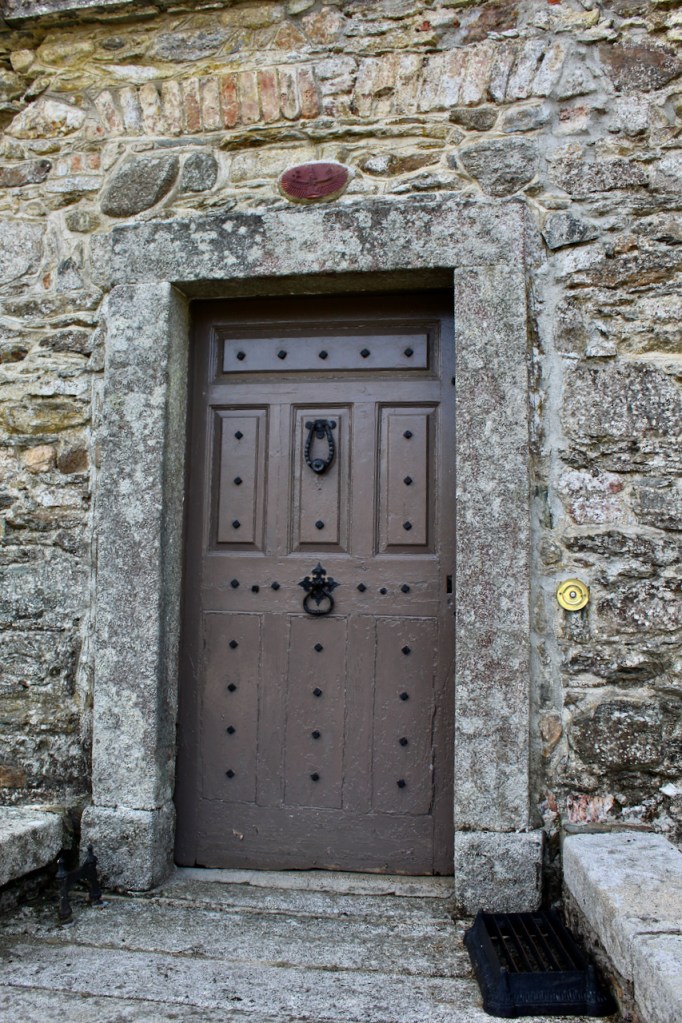
The front porch was in place when the original conservatory was still at the side of the house, as in the old postcard.
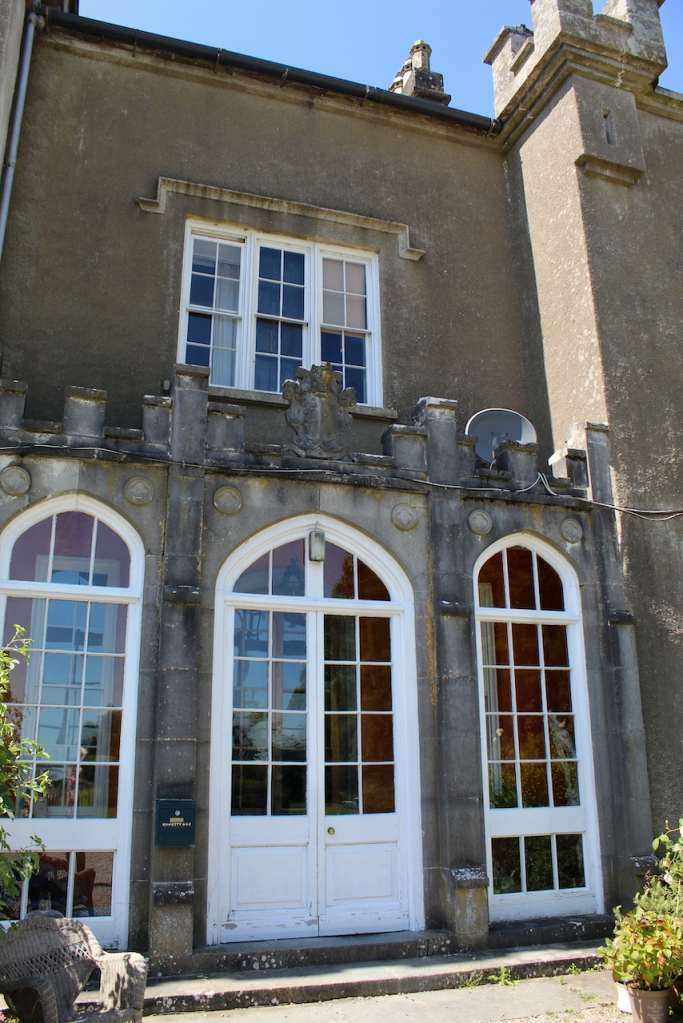


Mark Bence-Jones writes in his A Guide to Irish Country Houses (1988):
“(Toler-Aylward/IFR) ….This early C18 house appears to have had a recessed centre and projecting end bays. Some time ante 1828, the end bays were crenelated, one of them being raised to look like a tower; and they were joined by a Gothic porch. The front was extended by one bay to the left, so as to provide a new drawing room running from the front of the house to the back; and by a castellated office wing to the right. The back of the house, which is more irregular, is treated in much the same way, and adorned with a delightful Gothic conservatory on the level of the half-landing of the stairs, carried on a stone arcade.” [6]
The early conservatory was removed but one was later added to the back of the house.




Hector James Charles Toler (1839-1918) who inherited Shankill Castle in 1884 from his uncle, then assumed the additional surname of Aylward to become Toler-Aylward. He served as High Sheriff, Deputy Lieutenant and Justice of the Peace of County Kilkenny. He married Emily Mary Eliza Butler (1853-1934), daughter of James Butler of Verona, Monkstown, County Dublin. Hector undertook further redecoration at Shankill in 1894.
They had a son, Hector James Toler-Aylward (1895-1974). He inherited the Shankill Castle estate from his father in 1918. He married Zinna Ethel Knox from Greenwood Park, Crossmolina, County Mayo (now a ruin). They had three daughters. At his death Shankill Castle passed to his widow, and on her death in 1980 to his elder daughter, who sold it in 1991.



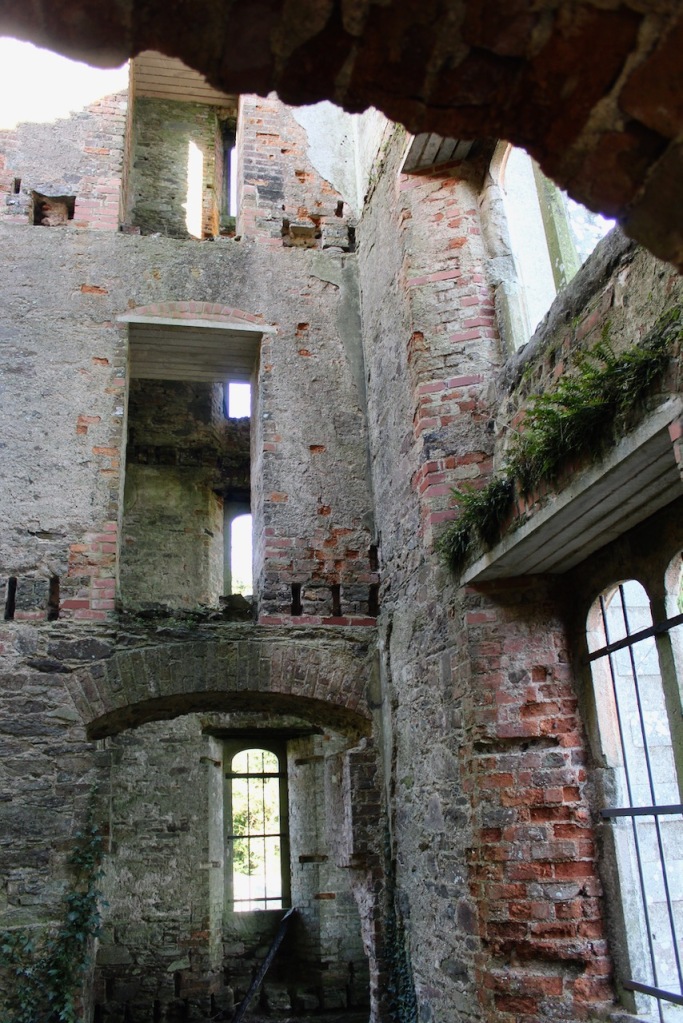
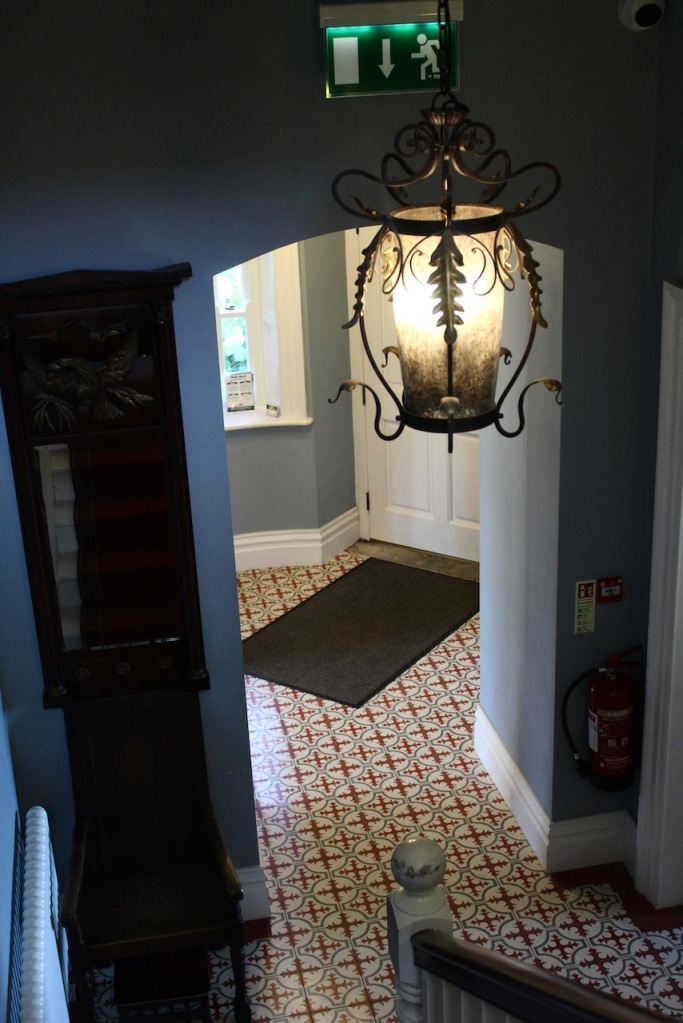
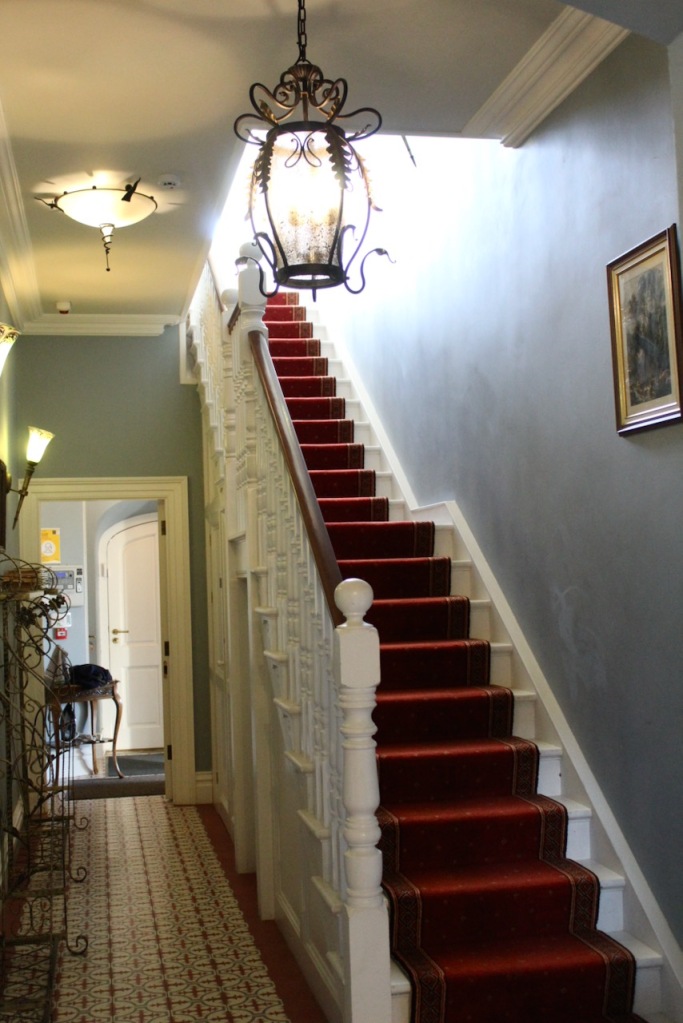
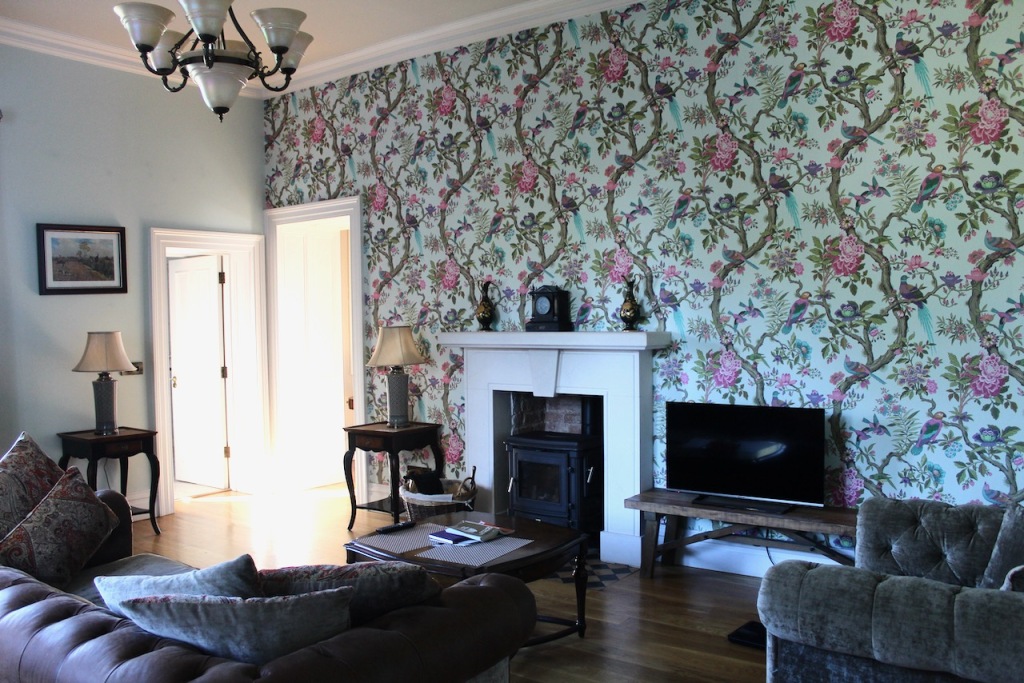
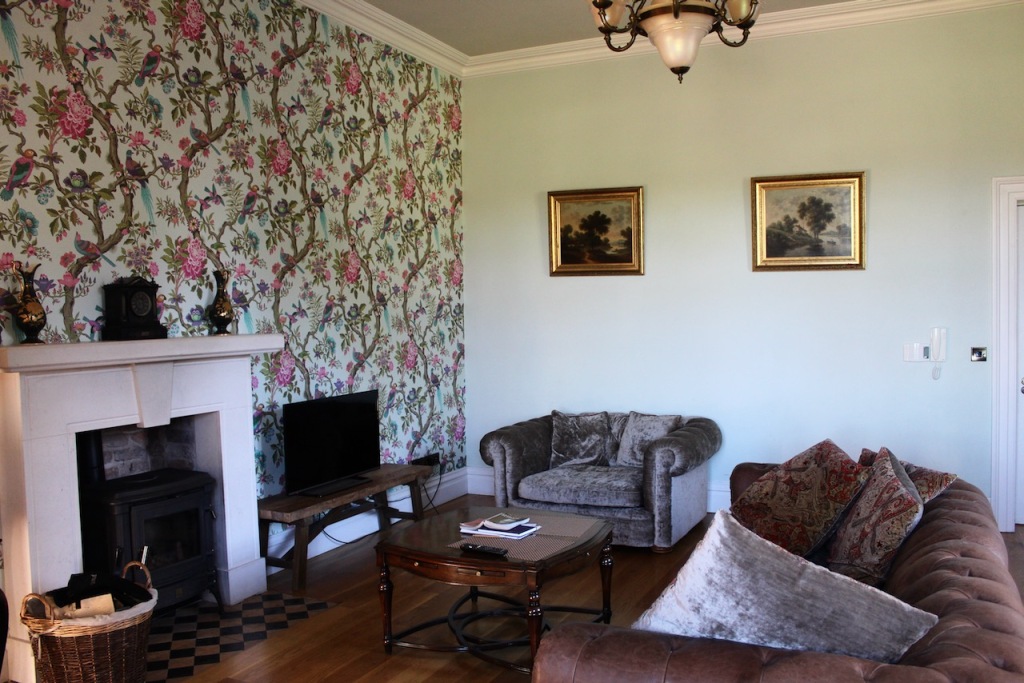
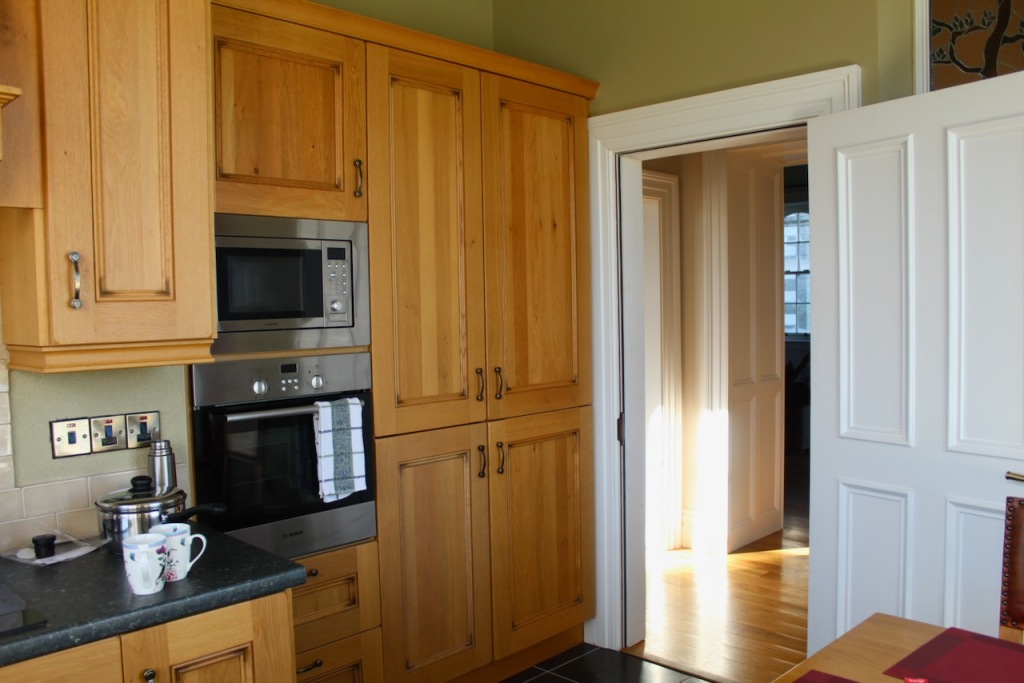
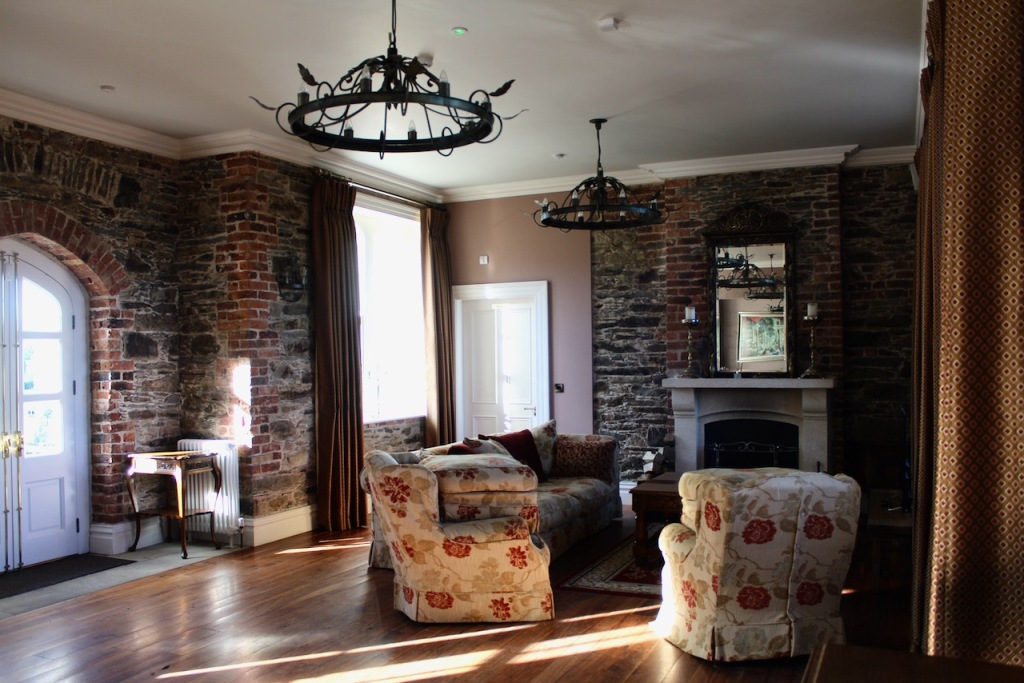
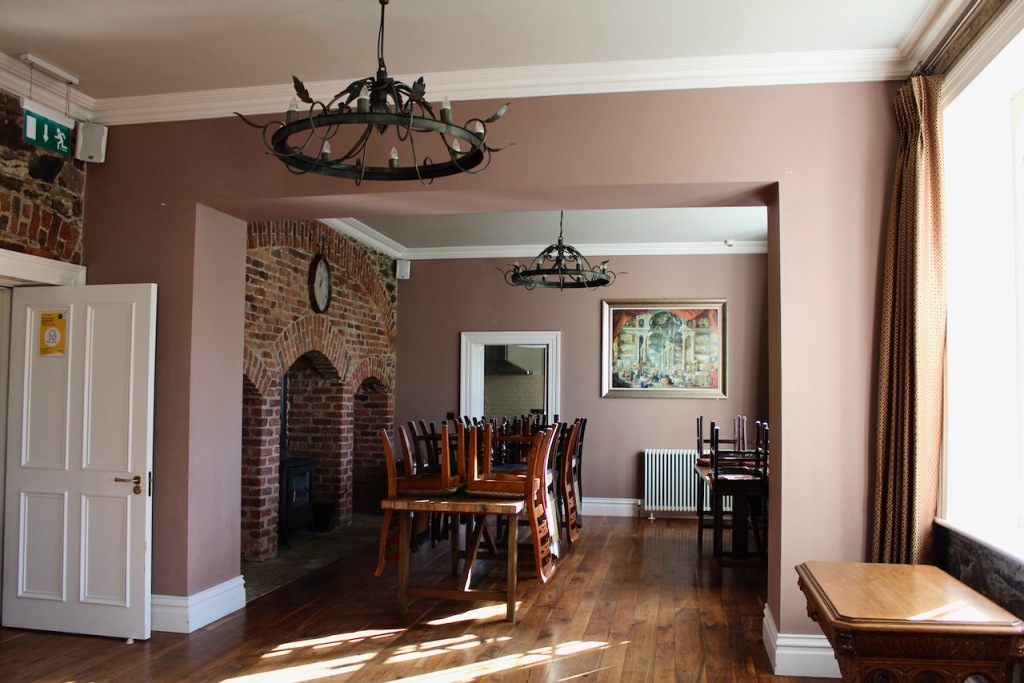
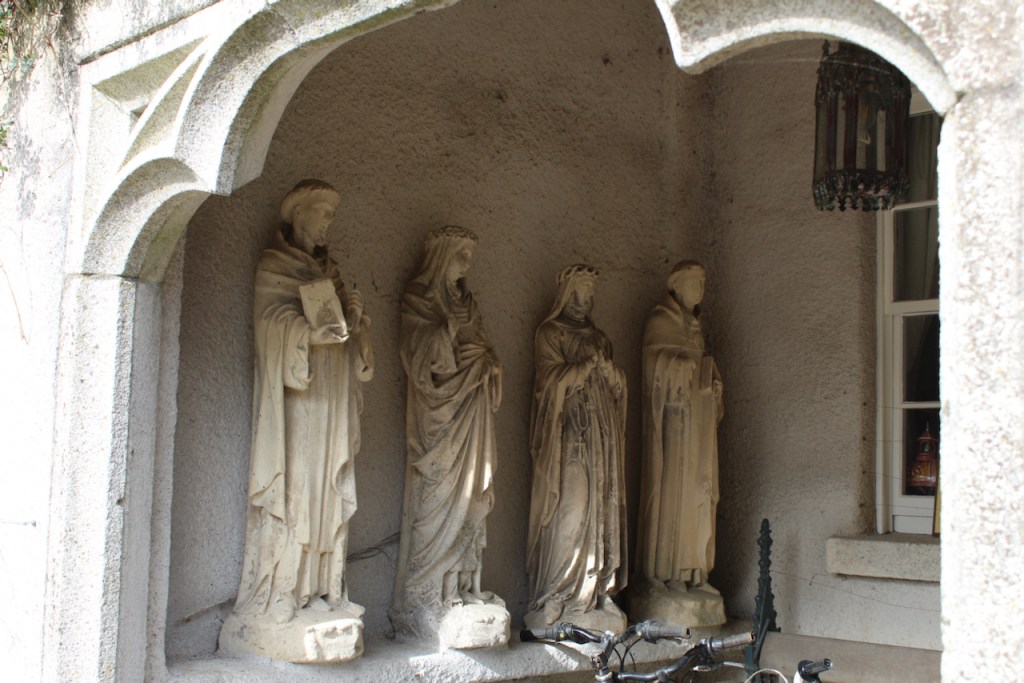
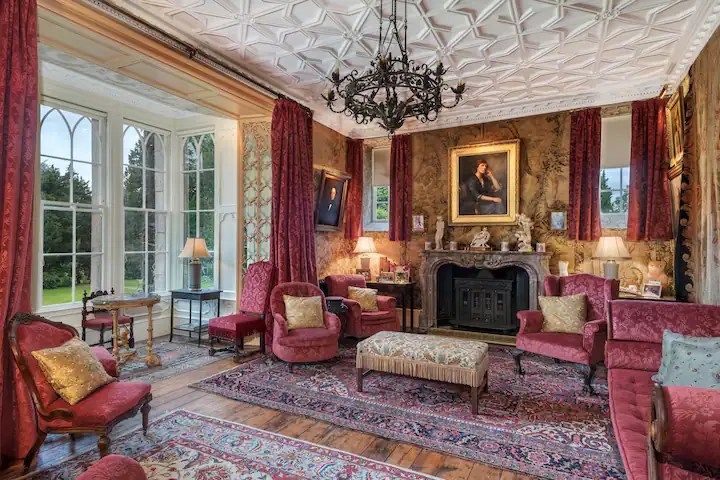
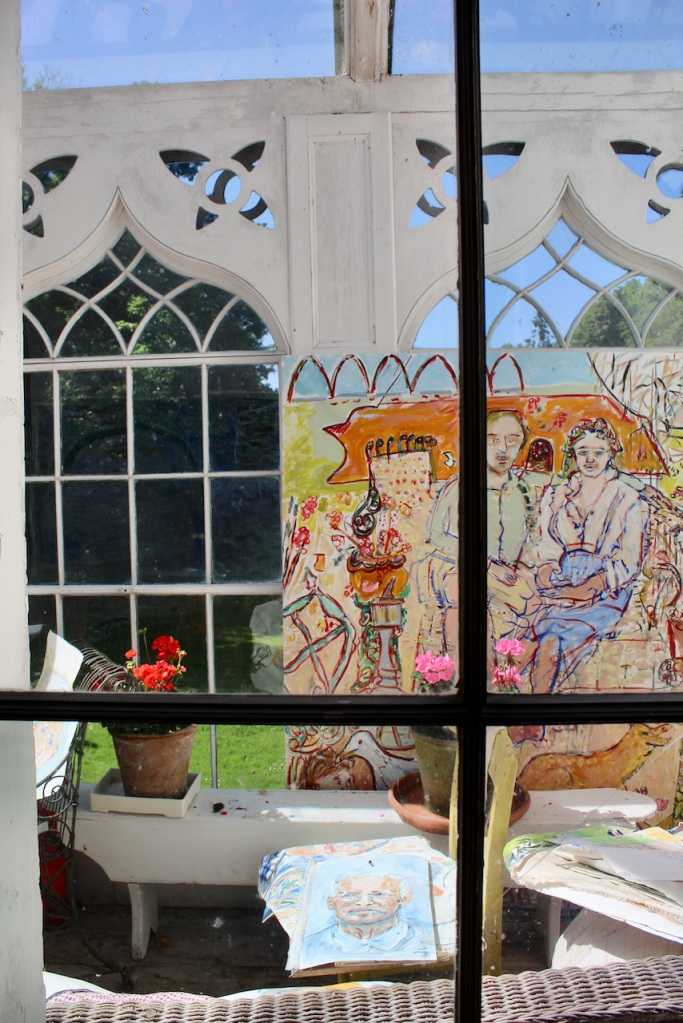
The interior of the house retains much of its early 18th century character. The central hall on the entrance front has wood panelling and a handsome black Kilkenny marble chimneypiece. The house is full of the art work of Elizabeth Cope.
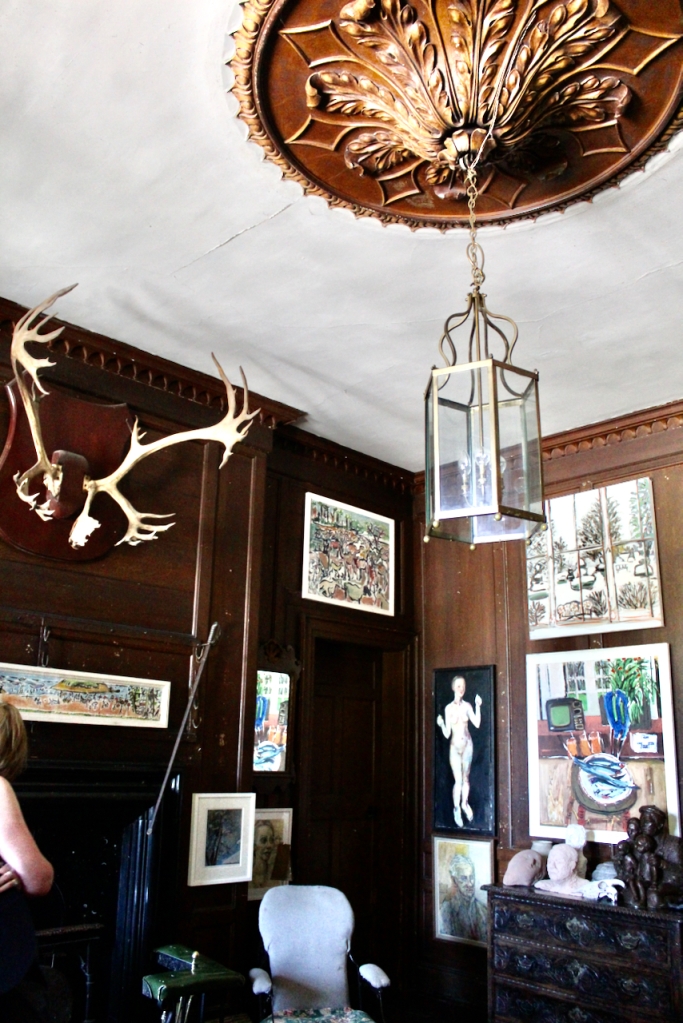

The hall is flanked by smaller rooms with corner fireplaces, which were the original dining and drawing rooms and are part of the old towerhouse.
William Deane Butler refitted the hall with floor-to-ceiling timber panelling while the room beyond, previously a saloon, became the new dining room and was given a large Tudor-headed buffet niche and a new Gothic bay window. Surviving plans show that the room to the north of the hall was intended as a billiard room while a study was provided in the new wing. [see 1]
Mark Bence-Jones describes the interior in his Guide to Irish County Houses (1988): “Late-Georgian staircase hall with graceful wooden stairs and walls marbled Siena 1894. Dining room with Gothic plasterwork in ceiling and Gothic pelmet. The drawing room is charmingly Victorian, with flowered paper and curtains of faded gold dating from 1894 and an Italian white marble chimneypiece brought back from Milan ca. 1860 by James Aylward. It formerly opened into a conservatory built 1861 to the design of Sir Joseph Paxton, but this was removed 1961. The entrance front faces along an avenue of trees to a Claire-voie [“clear view”] with rusticated stone piers which was part of C18 layout.”
William Deane Butler transformed the dining room into a Victorian drawing room featuring an impressively-carved white marble chimneypiece which James Kearney-Aylward purchased in Milan in 1860.
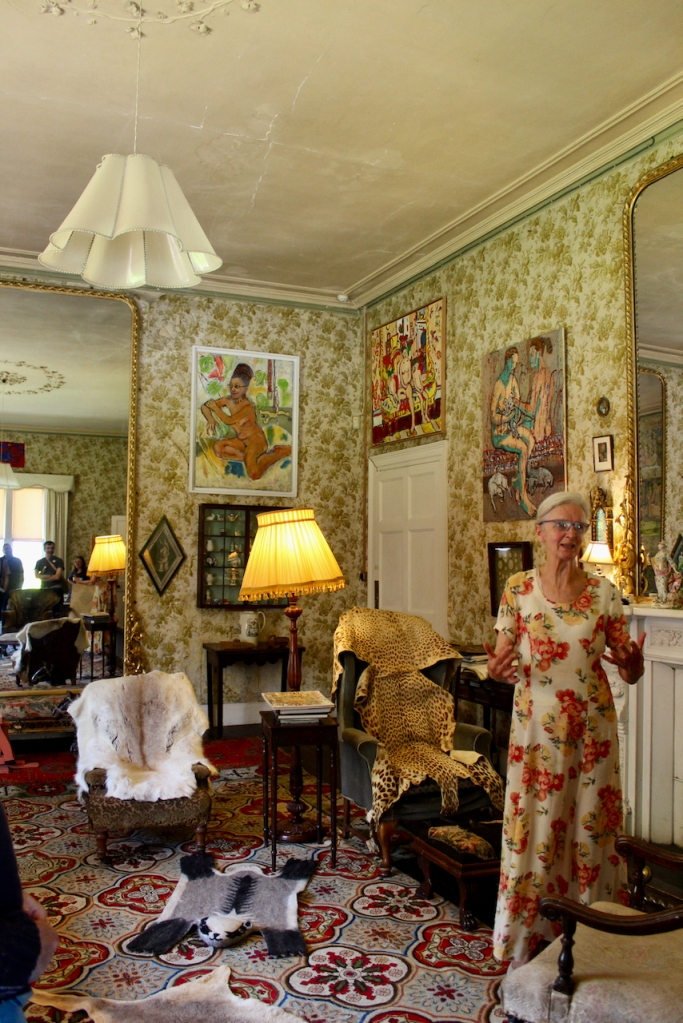
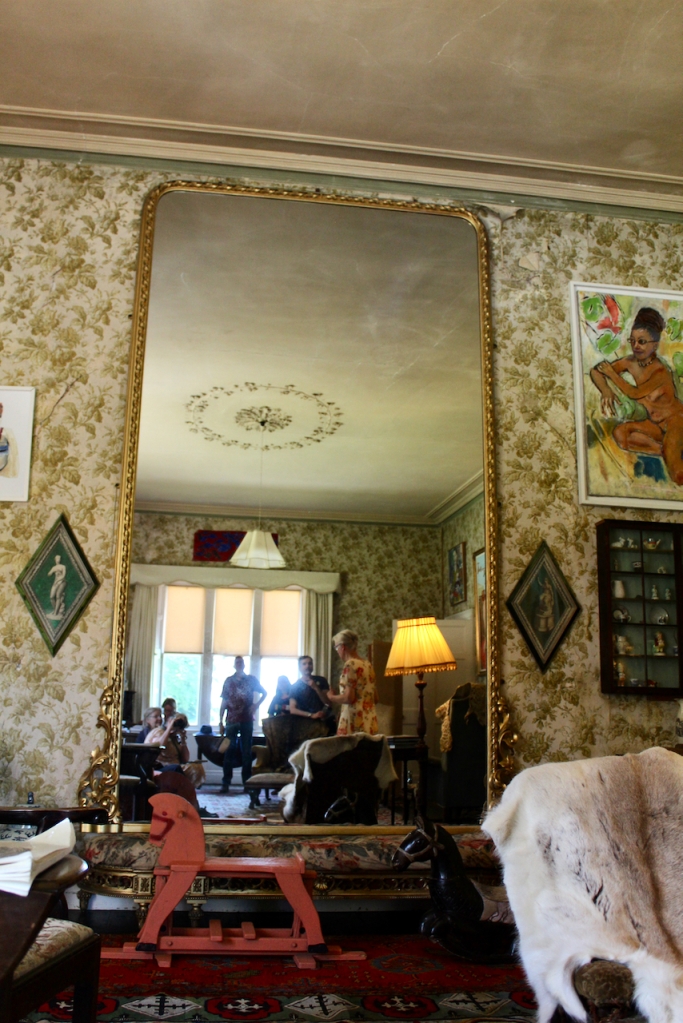




The Landed family website further describes the interior:
“The principal and secondary staircases occupy the space behind the original tower, and while the main staircase was renewed in the late 18th century, the secondary stair remains largely in its original form. Beyond the hall a saloon overlooked the grounds to the rear of the house. On the first floor, a transverse corridor down the middle of the house gives access to the principal bedrooms.” [see 1]



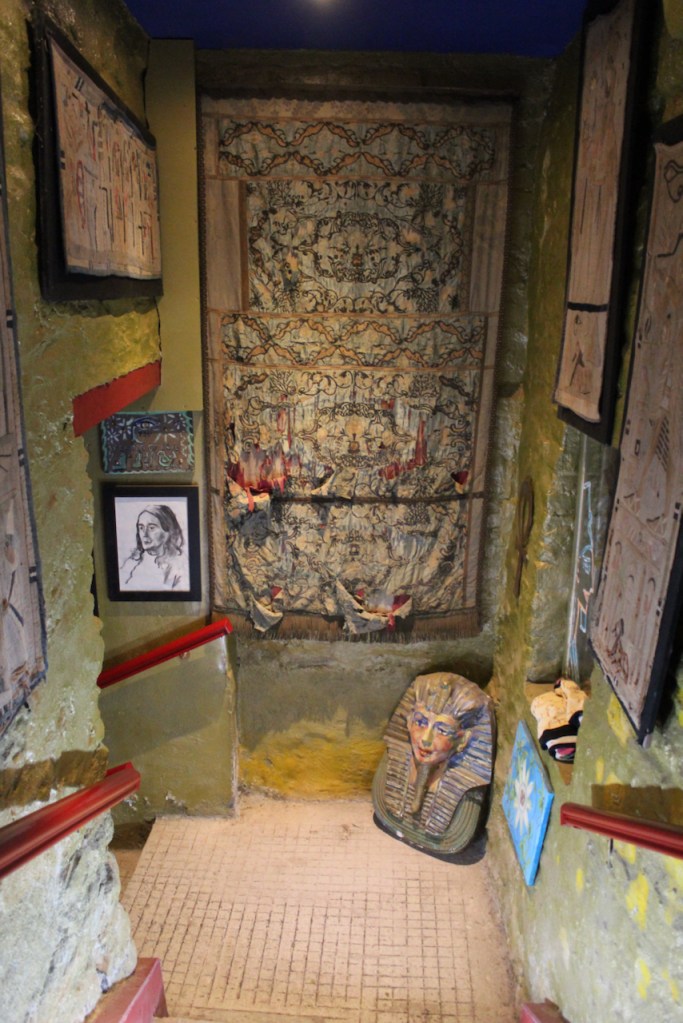
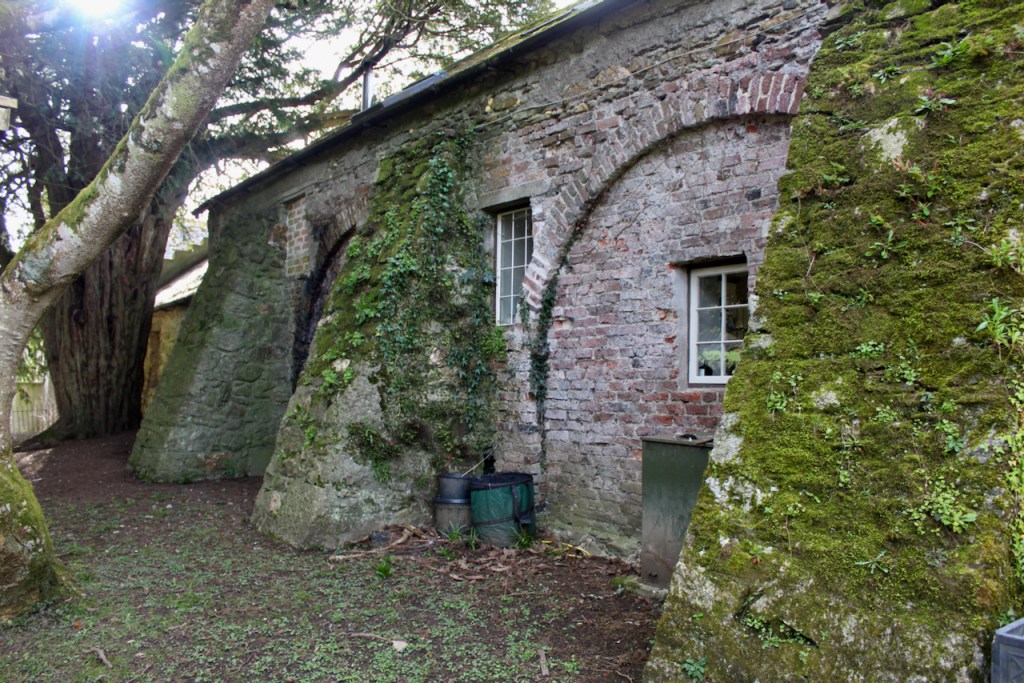
Elizabeth then took us down to the basement.



The website adds: “Steeped in such culture and heritage, Shankill Castle and Gardens has been a place of inspiration for artists for the past twenty-five years. The Cope family have dedicated themselves to the preservation and restoration of this historic house while celebrating the unique and eclectic character of the building. Consisting of three artists, one historian, and one archaeologist, the combined talents and passions of the Cope family are reflected in the inventive and lively activities offered at the castle. Exhibitions are frequently hosted in the castle and farmyard, which are also used as artists’ studios, attracting visitors not just locally, but from the whole of Ireland and internationally.“


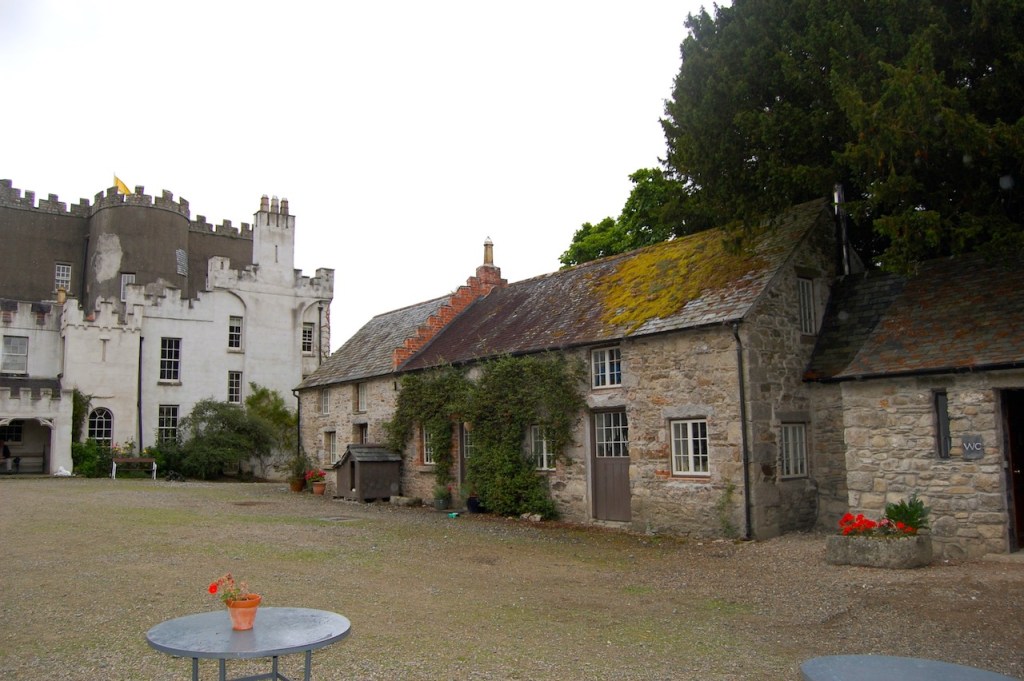
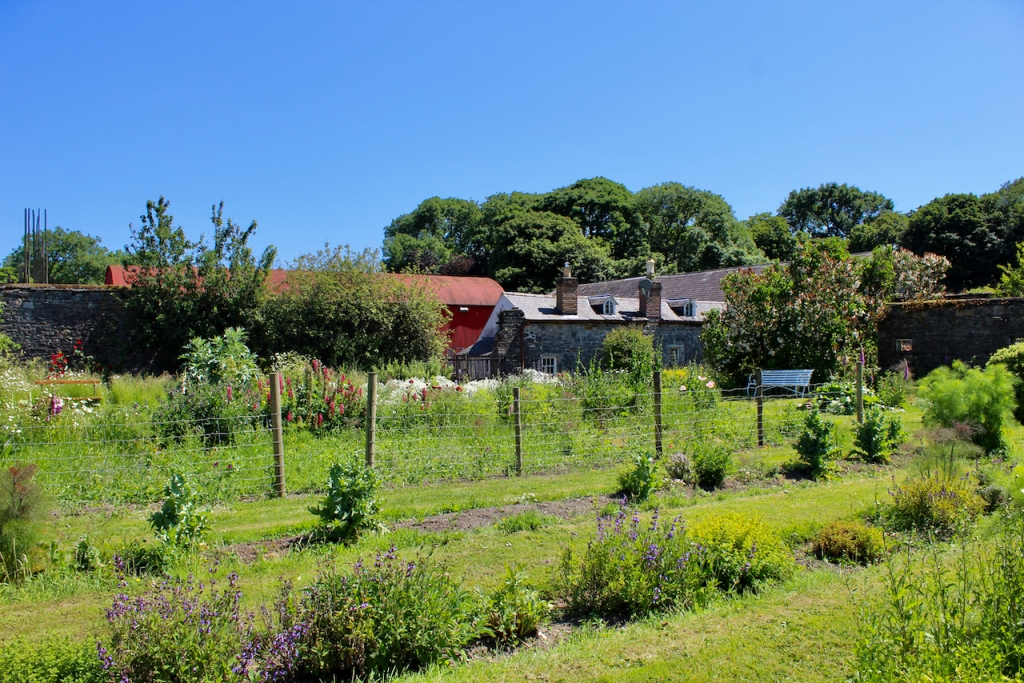
After our tour of the house we wandered back to the Café and the beautiful stableyard attributed to Daniel Robertson.
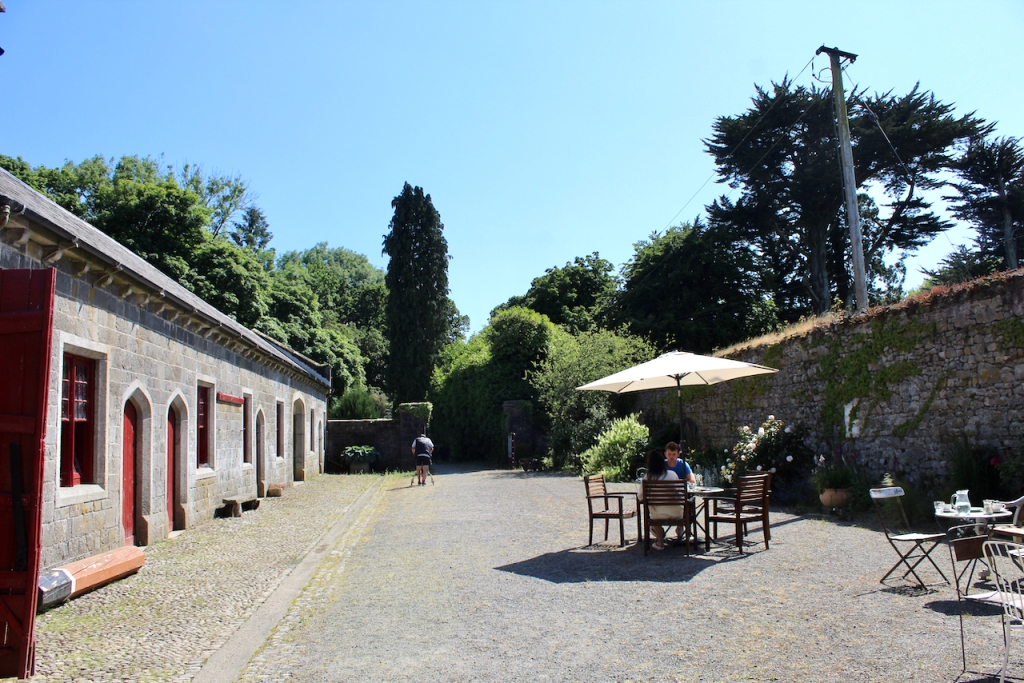
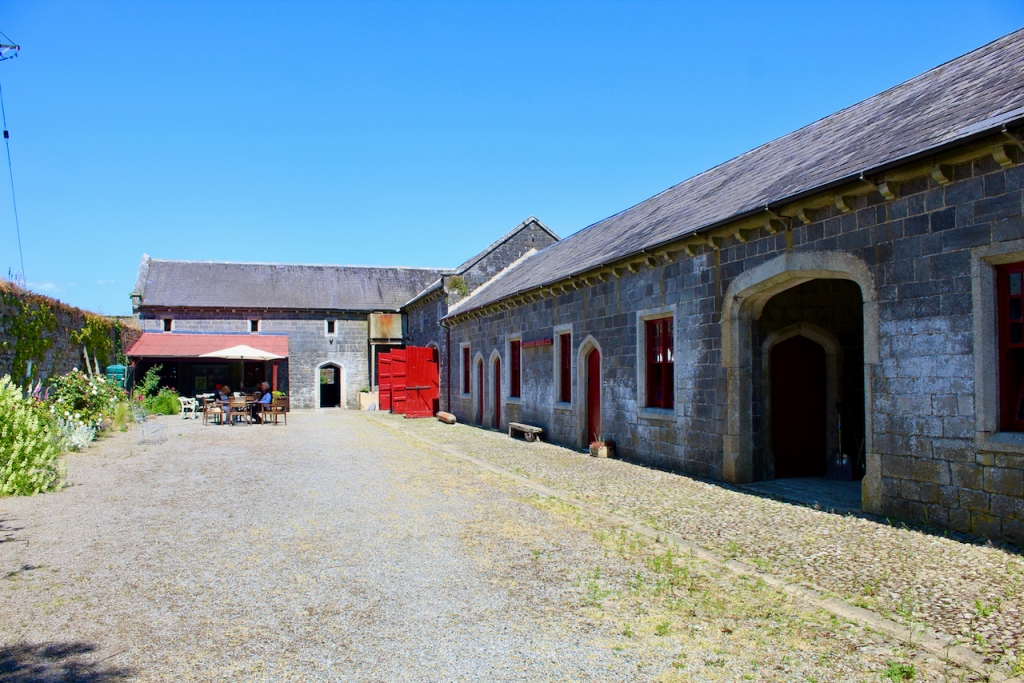



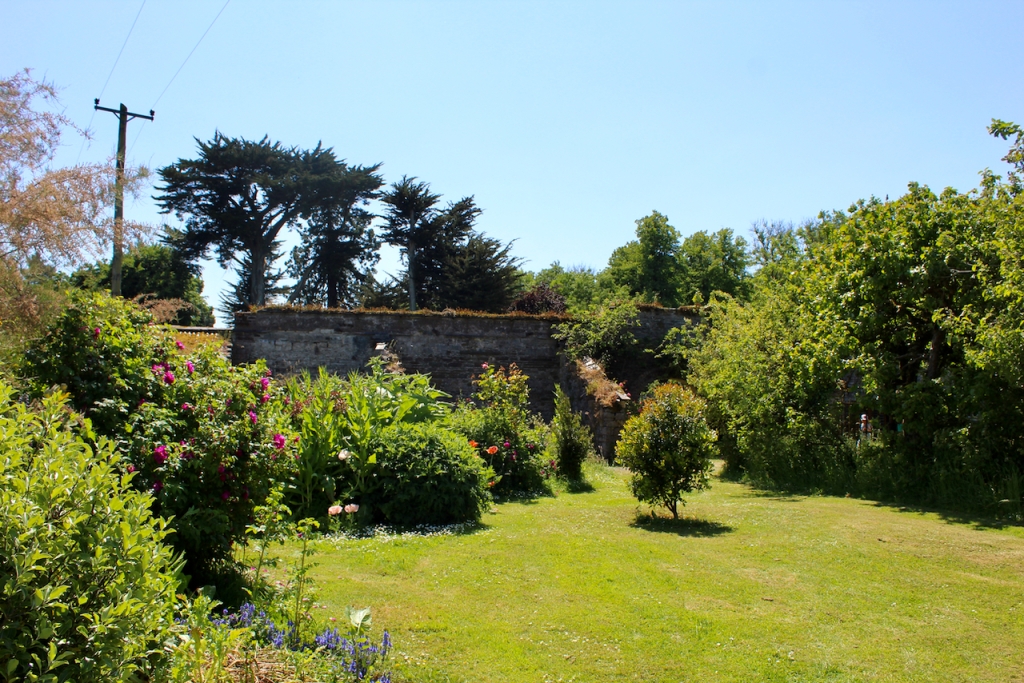
The gardens are beautiful and the Copes are so generous to share them with visitors. They run an organic farm. Our visit from Dublin was a lovely day outing.












[1] https://landedfamilies.blogspot.com/2017/05/262-aylward-of-ballynagar-and-shankill.html
[3] https://www.dia.ie/architects/view/4567/ROBERTSON,+WILLIAM#tab_biography
[4] William Robertson https://www.dia.ie/architects/view/4567/ROBERTSON,+WILLIAM#tab_biography
“In 1796, 1797 and 1798 he was in England, possibly working in the office of a London architect. His diary-cum-notebook in the National Library of Ireland records excursions from London in August 1796 and April and September 1797. Places which he visited included Painshill, Woburn Park (Surrey), Oatlands, Wanstead, Wotton House, Blenheim and Tintern. The notebook shows clearly that his main interests were architecture and gardening. He had a London address when he exhibited two views of Kilkenny and a design for the garden front of a villa at the Royal Academy in 1797 and 1798 respectively. He is almost certainly the ‘W. Robertson’ who was the author of two works published by Ackermann in London at about this time: A Collection of Various Forms of Stoves, Used for forcing Pine Plants, Fruit Trees, And Preserving Tender Exotics (1798)and Designs in Architecture, For Garden Chairs, Small Gates for Villas, Park Entrances, Aviarys, Temples, Boat Houses, Mausoleums, and Bridges (1800).
“…His large library – ‘the result of Fifty Years’ collecting’ – was sold at auction in Dublin over a number of days the following April. For many years he had been keenly interested in local history and topography. In about 1808 he had ‘employed two talented Artists to make drawings of every object remarkable for its antiquity or picturesque beauty, then to be found in the County of Kilkenny, with the intention of publishing a Topographical Work‘. Some of these he had had engraved. After building up a large collection of material, he had never found time to produce the proposed book. This task fell to James George Robertson, a Scottish-born relative, who, in about 1828, when he was a boy of about twelve, had joined William Robertson and had presumably become his pupil and assistant. James George Robertson published a selection of the material with some additional notes of his own in a rather haphazard series of parts from 1851-53 under the title The Antiquities and Scenery of the County of Kilkenny. In 1853 James George Robertson presented the Kilkenny Archaeological Society with the manuscript report on the fabric of St Canice’s Cathedral, Kilkenny, which William Robertson had prepared in 1813.
“…The Irish Architectural Archive holds presentation elevations by Robertson for the enlargement and Gothicization of Kilkenny Castle, 1826 (Acc. 80/35) and sketch designs for Powerstown glebe house, Co. Kilkenny, with a related letter from Robertson to the Rev. Thomas Mercer Vigors, dated William Street, 5 April 1818 (Acc.78/36.B4,4a). It also holds a letter from Robertson, written from Kilkenny on 7 November 1813 to the London bookseller Joseph Taylor (Acc. 2006/112) in which he discusses Sir James Hall’s Essay on the Origin, History and Principles of Gothic Architecture (1813).“
[5] https://www.archiseek.com/tag/william-deane-butler/
[6] Mark Bence-Jones A Guide to Irish Country Houses (originally published as Burke’s Guide to Country Houses volume 1 Ireland by Burke’s Peerage Ltd. 1978); Revised edition 1988, Constable and Company Ltd, London.
Text © Jennifer Winder-Baggot, www.irishhistorichouses.com