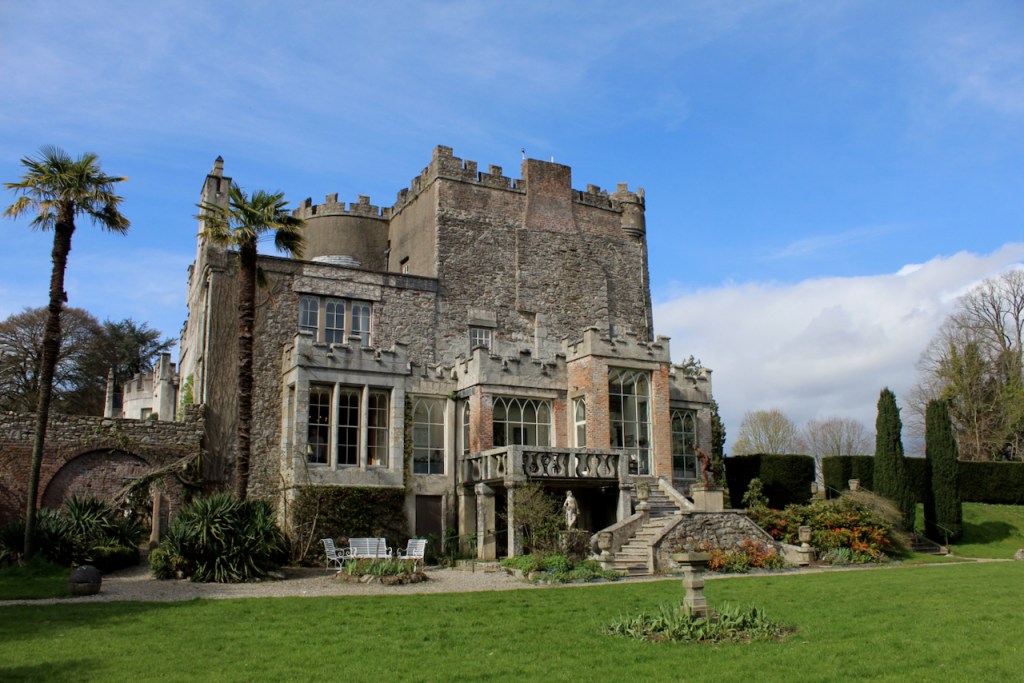
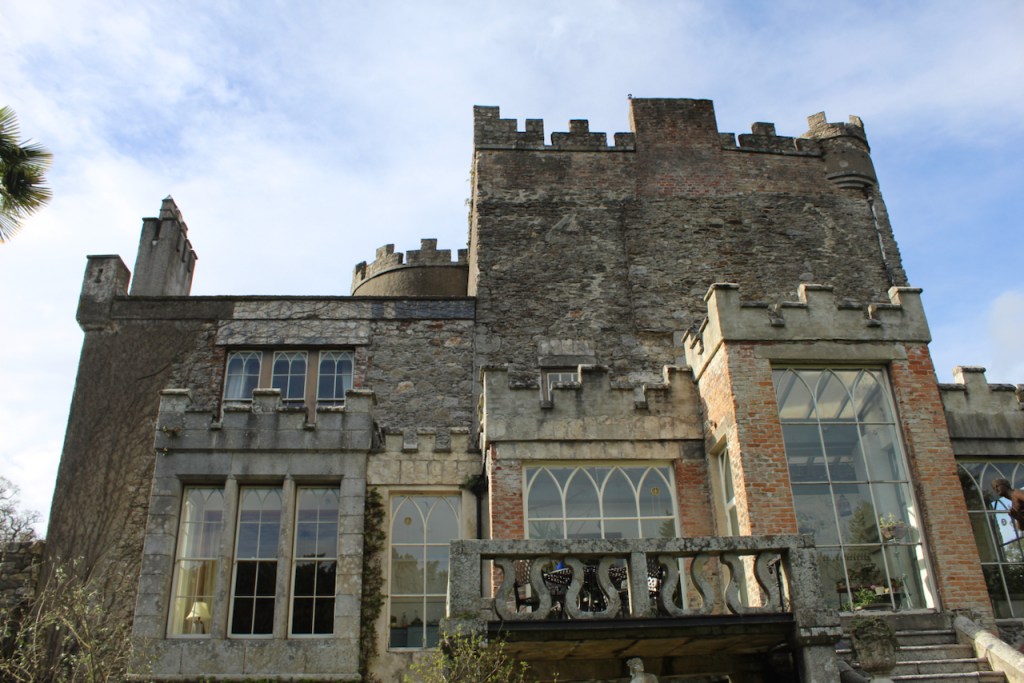
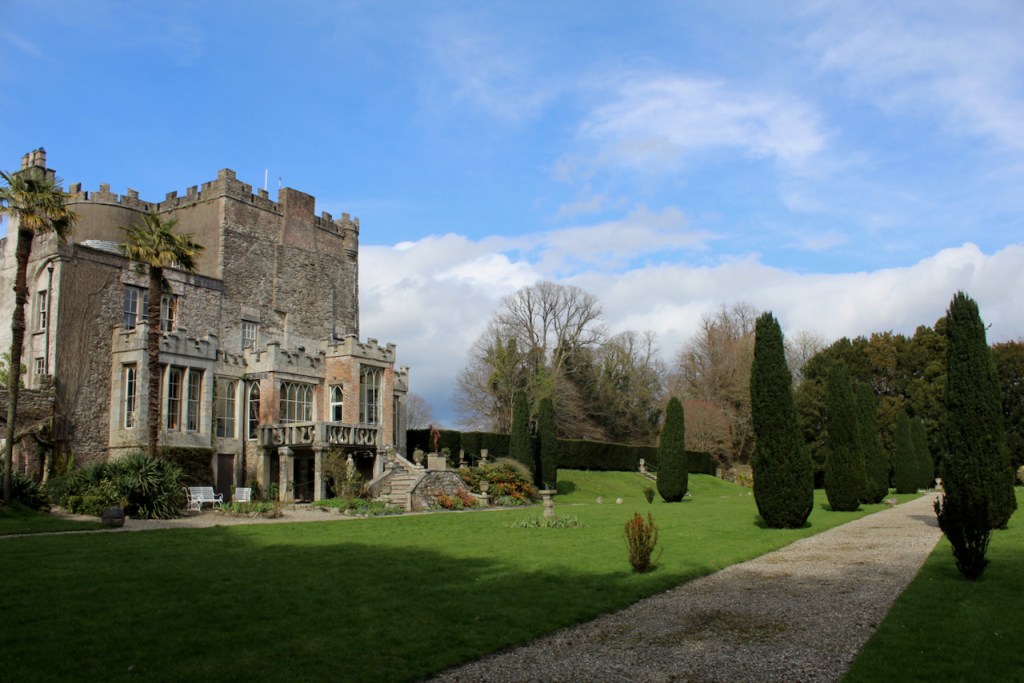
On the map above:
blue: places to visit that are not section 482
purple: section 482 properties
red: accommodation
yellow: less expensive accommodation for two
orange: “whole house rental” i.e. those properties that are only for large group accommodations or weddings, e.g. 10 or more people.
green: gardens to visit
grey: ruins

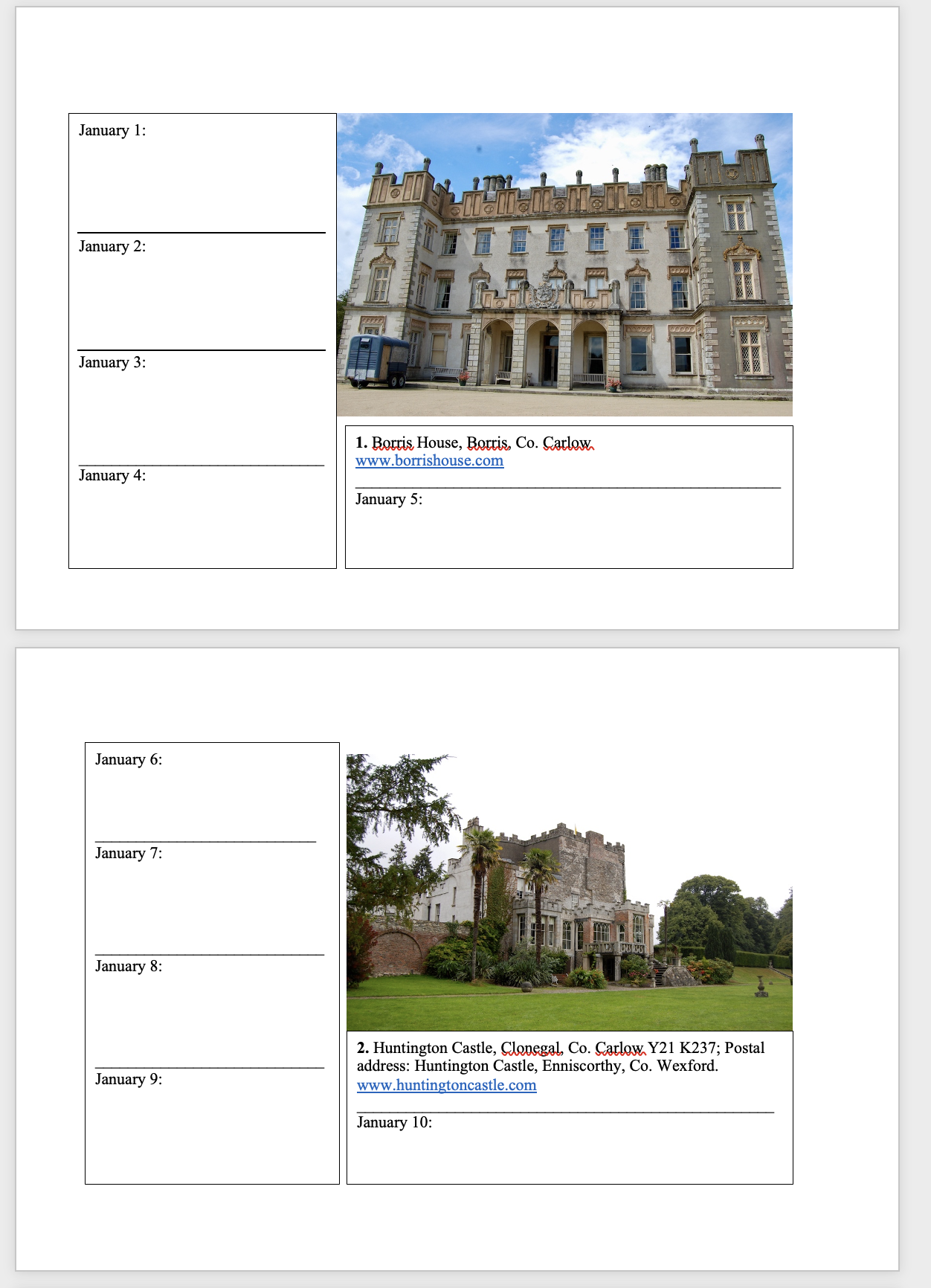
2026 Diary of Irish Historic Houses (section 482 properties)
To purchase an A5 size 2026 Diary of Historic Houses (opening times and days are not listed so the calendar is for use for recording appointments and not as a reference for opening times) send your postal address to jennifer.baggot@gmail.com along with €20 via this payment button. The calendar of 84 pages includes space for writing your appointments as well as photographs of the historic houses. The price includes postage within Ireland. Postage to U.S. is a further €10 for the A5 size calendar, so I would appreciate a donation toward the postage – you can click on the donation link.
€20.00

donation
Help me to pay the entrance fee to one of the houses on this website. This site is created purely out of love for the subject and I receive no payment so any donation is appreciated!
€15.00
Wexford:
1. Ballyhack Castle, Co. Wexford – open to public OPW
2. Ballymore, Camolin, Co Wexford – museum
3. Berkeley Forest House, County Wexford
4. Clougheast Cottage, Carne, Co. Wexford – section 482
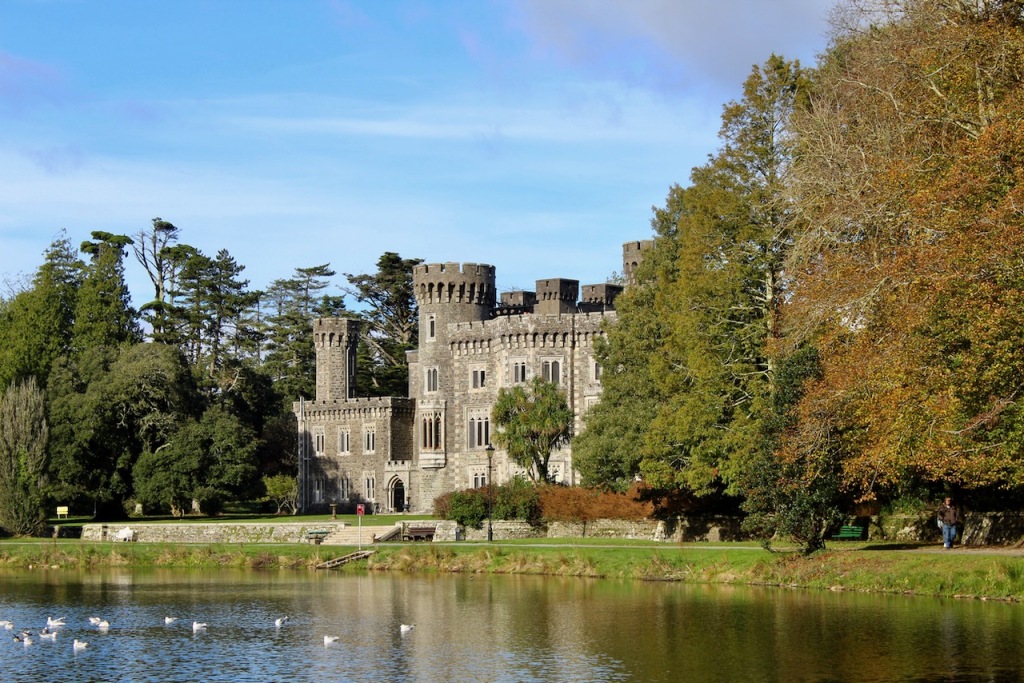
5. Enniscorthy Castle, County Wexford
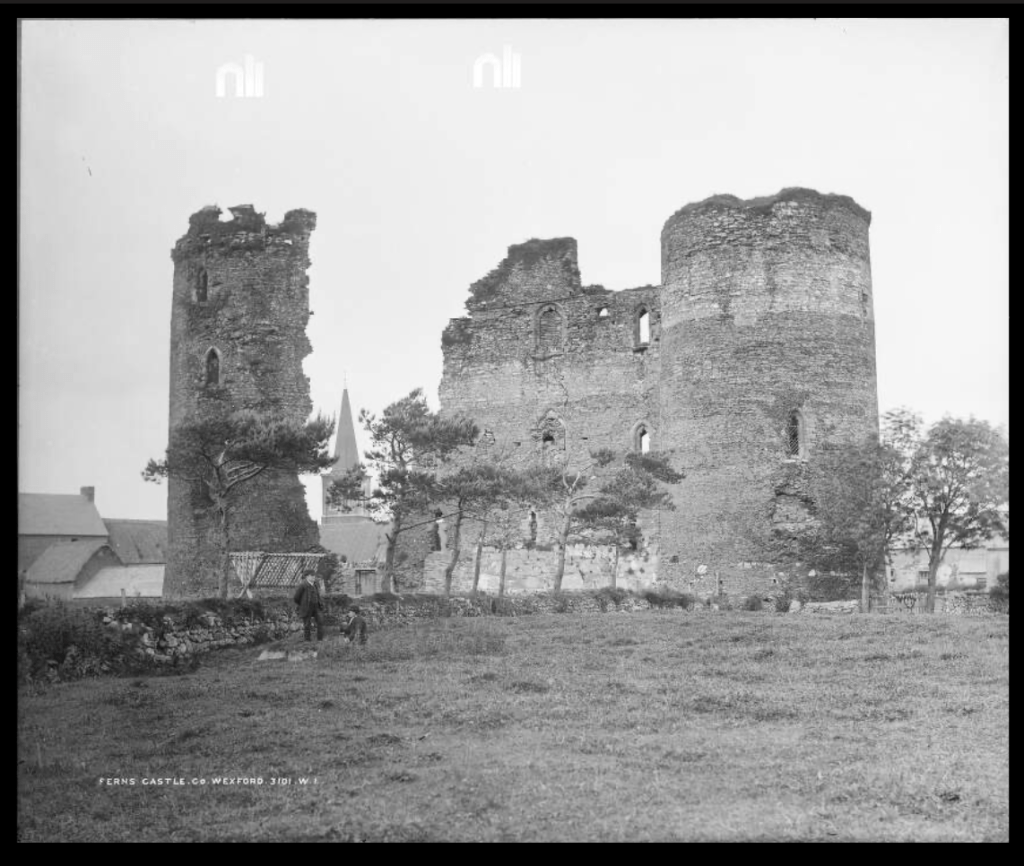
6. Ferns Castle, Wexford – open to public, OPW
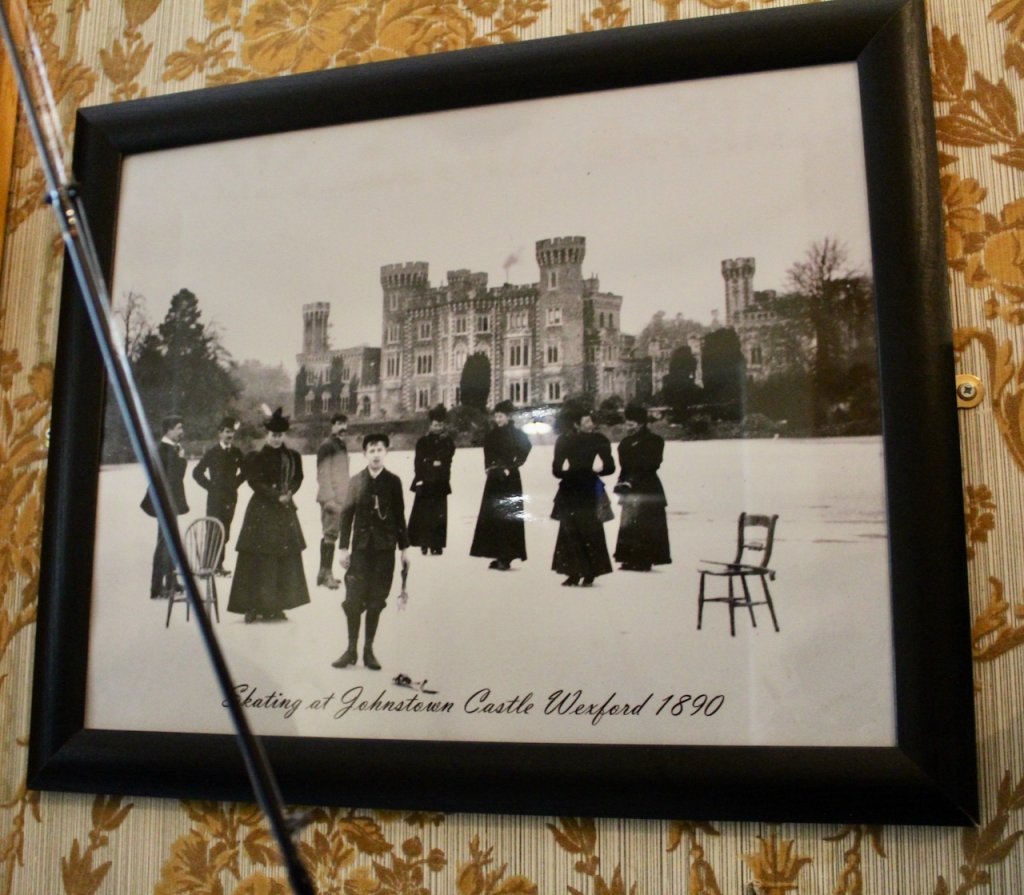
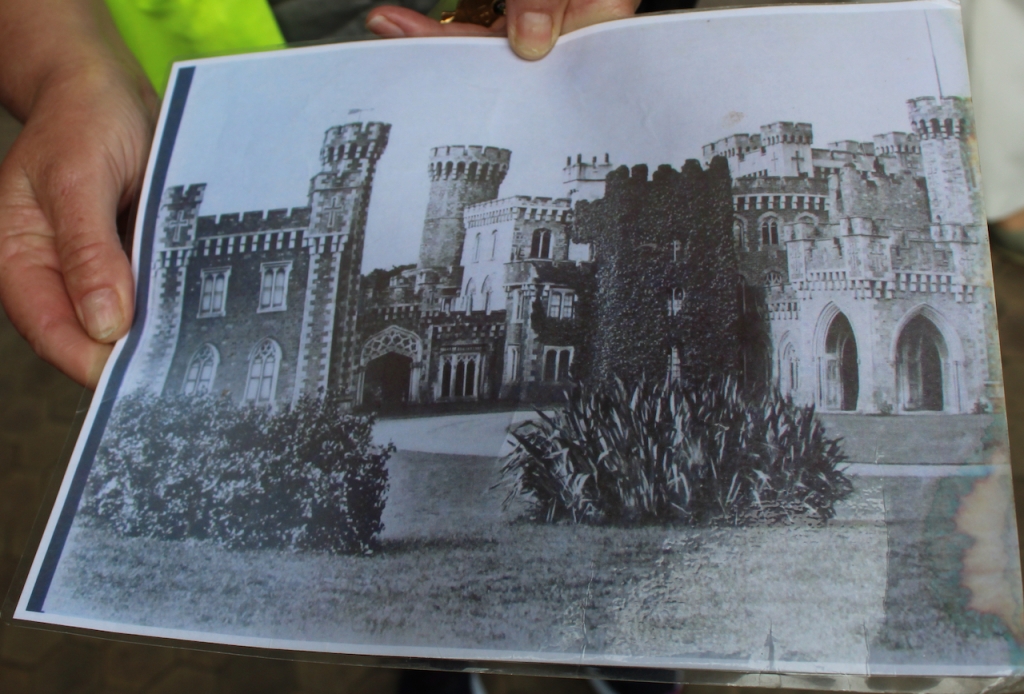
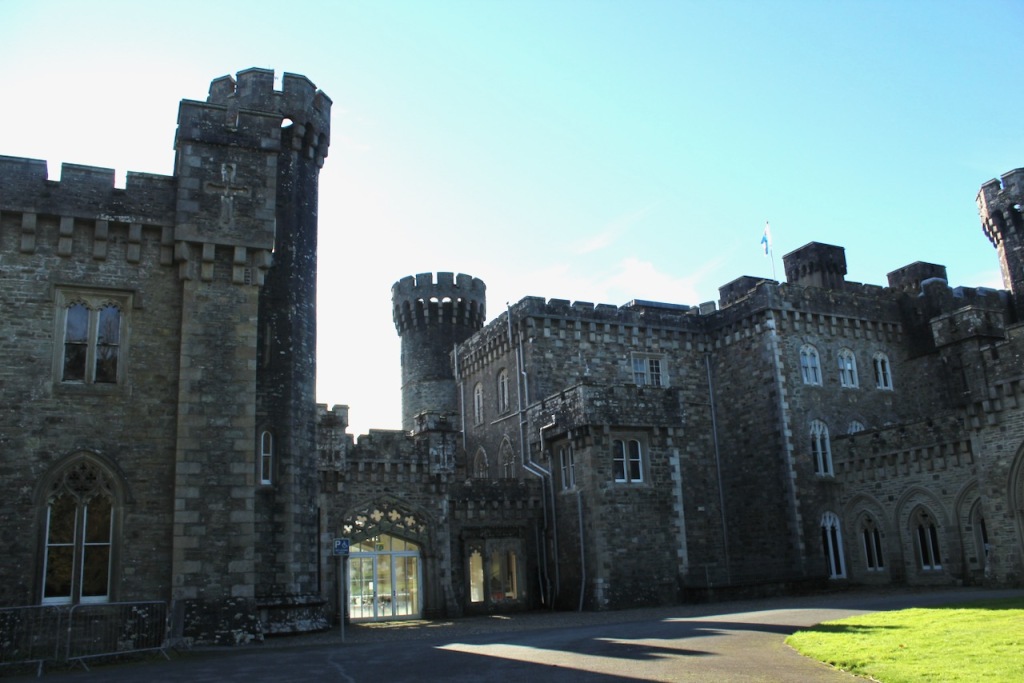
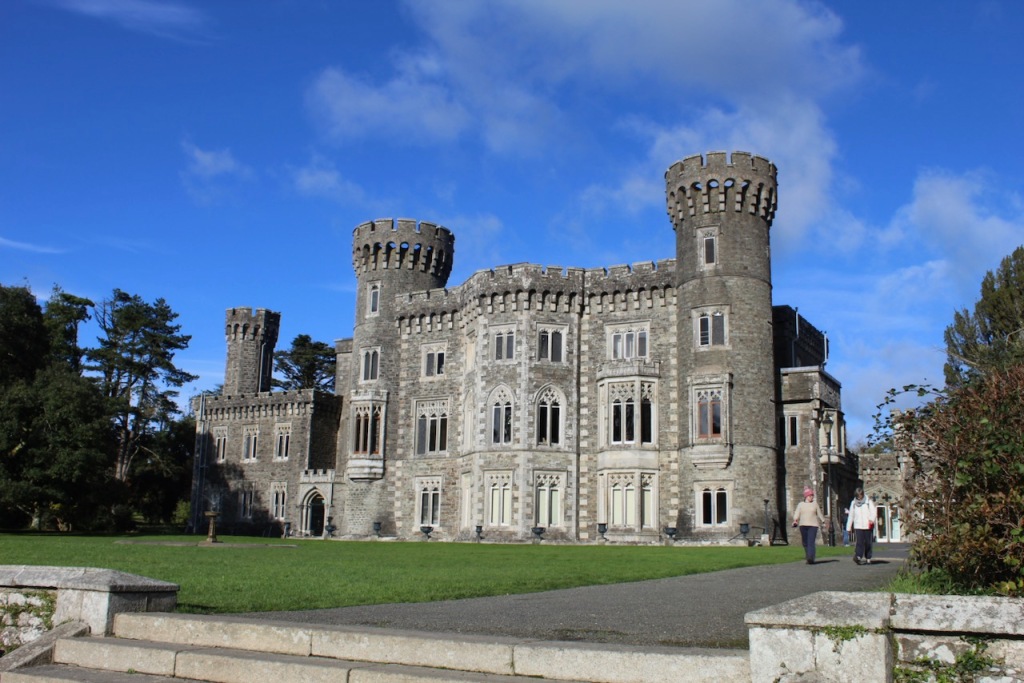
7. Johnstown Castle, County Wexford maintained by the Irish Heritage Trust
8. Kilcarbry Mill Engine House, Sweetfarm, Enniscorthy, Co Wexford – section 482
9. Kilmokea Country Manor & Gardens, Great Island, Campile, New Ross, Co. Wexford – section 482, gardens open
10. Newtownbarry House, Wexford
11. Sigginstown Castle, Sigginstown, Tacumshane, Co. Wexford – section 482
12. Tintern Abbey, Ballycullane, County Wexford – concessionary entrance to IGS members, OPW
13. Wells House, County Wexford
Places to Stay, County Wexford
1. Artramon House, Castlebridge, Co Wexford – B&B
2. Ballytrent House, Broadway, Co Wexford – B&B
3. Bellfry at Old Boley, County Wexford – self catering
4. Butlerstown Castle, Tomhaggard, Co Wexford – A ruin, coach house accommodation
5. Clonganny House, Wexford – accommodation
6. Dunbrody Park, Arthurstown, County Wexford – accommodation
7. Fruit Hill Cottages, Fruit Hill House, Campile, New Ross, County Wexford
8. Glendine House hotel, New Ross, County Wexford
9. Killiane Castle, County Wexford – B&B and self-catering
10. Kilmokea Country Manor & Gardens, Kilmokea, Great Island, Campile, New Ross, Co. Wexford – accommodation
11. Marlfield, Gorey, Co Wexford – accommodation
12. Monart, Enniscorthy, Co Wexford – 5* hotel
13. The Gate Lodge, Mount Congreve – self catering accommodation
14. Rathaspeck Manor “doll’s house” gate lodge, County Wexford and the Manor B&B
15. Riverbank House Hotel, The Bridge, Wexford, Ireland Y35 AH33
16. Rosegarland House, Wellingtonbridge, County Wexford – courtyard accommodation
17. Wells House, County Wexford – self catering cottages
18. Wilton castle, Enniscorthy, Co Wexford – B&B
19. Woodbrook, Killane, Co Wexford – B&B
20. Woodlands Country House, Killinierin, County Wexford – B&B
Whole House rental County Wexford:
1. Ballinkeele, County Wexford – whole house rental (sleeps up to 19 people)
2. Horetown House, County Wexford – whole house rental (wedding venue, up to 24 people in house, plus shepherd’s huts)
3. Newbay House, County Wexford – wedding venue
Places to visit in County Wexford:
1. Ballyhack Castle, Co. Wexford – open to public OPW
see my OPW write-up https://irishhistorichouses.com/2022/02/07/office-of-public-works-properties-leinster-laois-longford-louth-meath-offaly-westmeath-wexford-wicklow/
2. Ballymore, Camolin, Co Wexford – museum
http://www.ballymorehistoricfeatures.com
The website tells us:
“Ballymore is an old family property located away from main routes in a particularly scenic part of North Wexford. It retains many features which have survived from past periods of occupation in an attractive setting of mature trees, ordered landscape and views of the surrounding countryside.“
It is a country house erected by Richard Donovan (1697-1763). The National Inventory tells us it is:
“an estate having long-standing connections with the Donovan family including Richard Donovan (1752-1816); Richard Donovan (1781-1849) ‘of Ballymore’ (cf. 15612001); Richard Donovan (1819-84) ‘late of Ballymore Camolin County Wexford’ (Calendars of Wills and Administrations 1885, 217); Richard Donovan JP DL (1858-1916), ‘Gentleman late of Ballymore County Wexford’ (Calendars of Wills and Administrations 1916, 172); Richard Charlie Donovan (1898-1952); and Richard Alexander Donovan (1927-2005).“

“A large scale map indicates the route visitors are requested to follow. This route allows a leisurely ramble around several interesting features including the tea room, the museum, art gallery and display of old farming equipment in part of the farmyard. The residence itself is private and not open to the public.
“In the surrounding grounds you will find the church and ancient graveyard, holy well, former site of a 1798 rebel camp and the 14th century Norman castle ruins, which now is a simple labyrinth.
“The present church was built in 1869 on the site of a medieval building, of which nothing now survives except a carved wooden door lintel which can be seen at the museum.
“The holy well is covered completely by a large boulder. This was done some centuries ago to discourage its continued use for prayer and devotion.“

“The castle mound is all that remains of the 14th century motte built by Norman settlers. The ruins of the stone-built tower were pulled down in the 19th century.
“The large reconstructed greenhouse is the setting for the tea room. Its design copies the original greenhouse built around 1820, along with the walled garden behind it.
“The museum and display area open out from the small courtyard. The museum itself is in a large converted hayloft in a period farmyard building. The contents of the museum are from the family home and farmyard. They illustrate many different aspects of earlier occupation and activity. Another feature is the old water wheel now on display in the same farm building.
“The old dairy room will take you back in time. It adjoins the 1798 Room, containing a display of items from this period and from the house and family records. The further display area includes pieces of older farm equipment and hand tools used when the horse was the only source of motive power.“

“The art gallery is located below the museum in what was the farm stables. It displays a selection of paintings and drawings of local scenes and activities by the much admired artist Phoebe Donovan.
“Take one of our exclusive tours, which encompasses many features including the museum of local and family history spanning over 300 years, dairy and farming display, 1798 memorabilia room and the Phoebe Donovan art gallery.
“Venture out into the surrounding grounds and you will find the ruins of a Norman castle dating back to the 14th century, Ballymore Church and graveyard (1869), and a former 1798 rebel camp site. You may even spot a buzzard or some of the other varied wildlife in the area.
“Finally, relax and enjoy a beverage in our greenhouse tea room. Ballymore Historic Features is also part of the Wexford Heritage Trail.”
3. Berkeley Forest House, County Wexford
http://berkeleyforesthouse.com

This website tells us:
“Berkeley Forest is unusual as a period house as it has a bright and uncluttered look with a strong Scandinavian flavour -painted floors, hand stencilled wallpaper and bedcoverings designed by artist Ann Griffin-Bernstorff who lives and works here during part of the year.
“The house offers a beguiling experience. With a beautiful faded brick walled garden with a terrace, summer house and an outdoor fireplace, it is a delight throughout the day.
“In easy reach of the Wexford beaches to the South and East and the picturesque villages of Inistioge, Thomastown and Graiguenamanagh, the cities of Kilkenny (Medieval) and Waterford (Viking) are also nearby. Just off the N30, less than 2 hours from Dublin Airport, 45 mins from Kilkenny, 20 mins from Wexford or Waterford, the house is perfectly situated to visit a host of interesting historical, cultural or sporting amenities, or to hide away in complete peace and quiet.
“The house was once the home of the family of 18th century philosopher George Berkeley.
It also houses a 19th Costume museum which was created by Ann Griffin-Bernstorff and is available to costume and fashion students on request (her original 18th century Costume Collection is now to be seen at Rathfarnham Castle in Dublin) She is also the designer of the internationally acclaimed Ros Tapestry.“


“The property consists of the main house, lawns and gardens; beyond that are pasture and woodland, some mature, some more recently planted; as well as original farm buildings. All of which ideal for exploring and wandering. There is a beautifully proportioned upper drawing room (28ftx18ft) which is suitable for music rehearsal, fine dining and specialist conferences.”
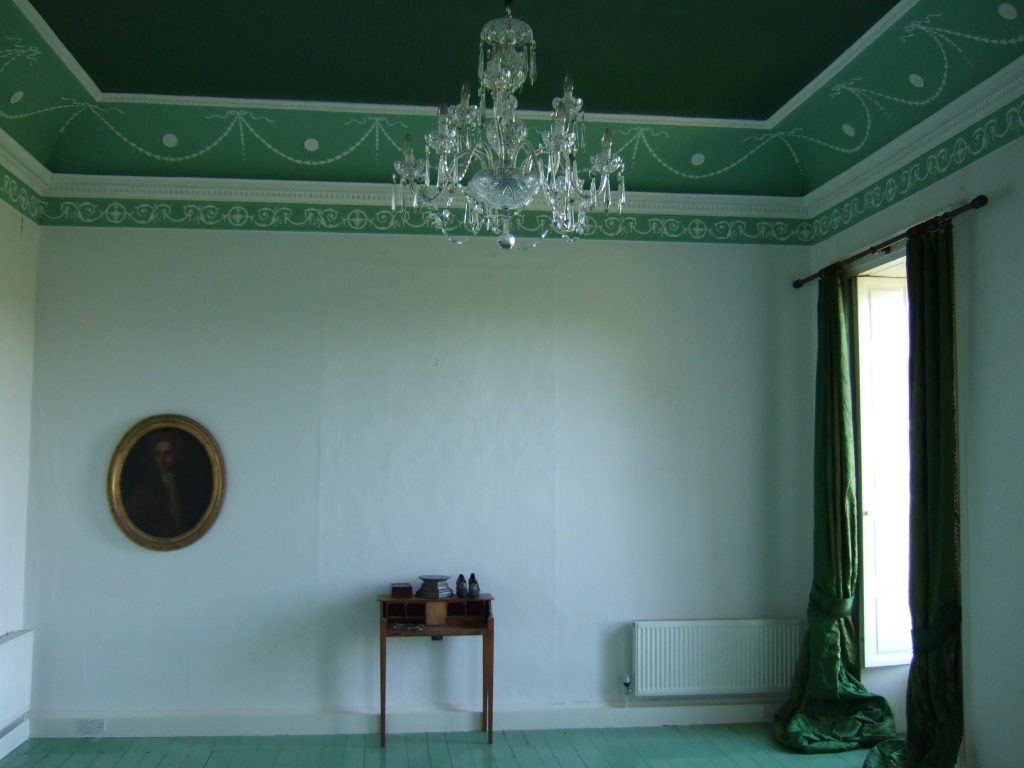


4. Clougheast Cottage, Carne, Co. Wexford – section 482
Open dates in 2026: Jan 11-31, May 1-31, August 15-23, 9am-1pm
Fee: €5
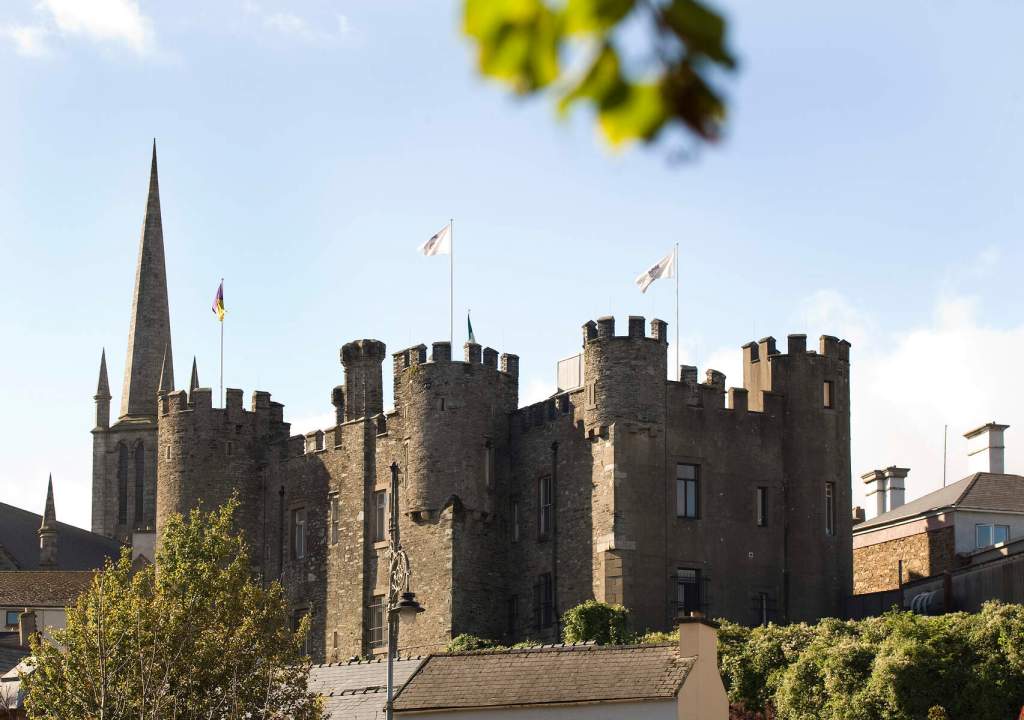
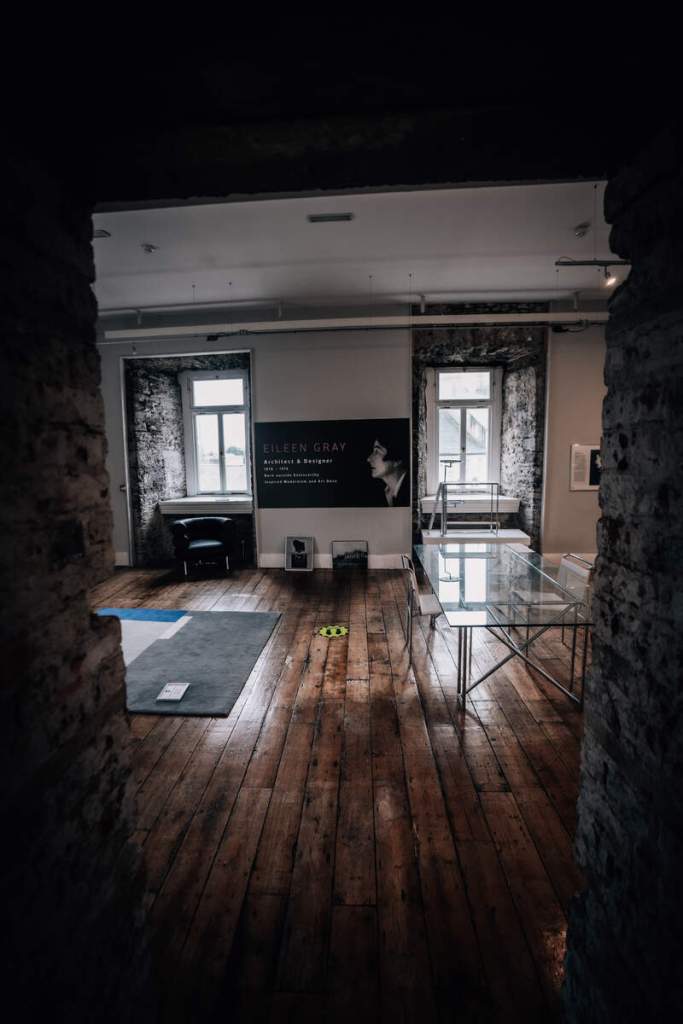
5. Enniscorthy Castle, County Wexford
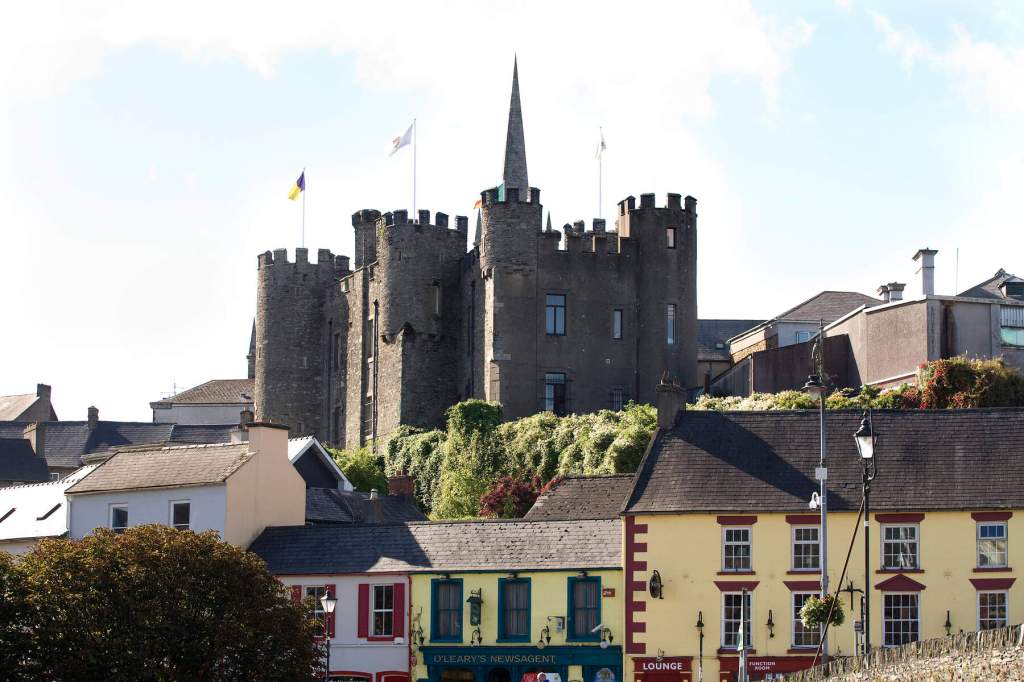

The website tells us:
“Enniscorthy Castle, in the heart of Enniscorthy town, was originally built in the 13th century, and has been ‘home’ to Norman knights, English armies, Irish rebels and prisoners, and local merchant families. Why not visit our dungeon to see the rare medieval wall art –The Swordsman, or our battlements at the top of the castle to marvel at the amazing views of Vinegar Hill Battlefield, Enniscorthy town, and the sights, flora and fauna of the surrounding countryside. Enniscorthy Castle explores the development of the Castle and town from its earliest Anglo-Norman origins, with a special focus on the Castle as a family home. Visitors can also view the ‘Enniscorthy Industries ‘exhibition on the ground floor from the early 1600’s onwards when Enniscorthy began to grow and prosper as a market town. Visitors can explore the work of the renowned Irish furniture designer and architect Eileen Gray (born in 1878 just outside the town). The roof of the castle is also accessible, with spectacular views of the surrounding buildings, Vinegar Hill, and countryside. Note that access to the roof is only possible when accompanied by a staff member. Tours of the Castle are self guided. Last admission is 30 minutes before closing. Our facilities include: craft and gift shop, toilets and baby changing area, wheelchair access to all floors (including roof) , and visitor information point (tourist office for town). We look forward to welcoming you to our town’s most public ‘home’.“

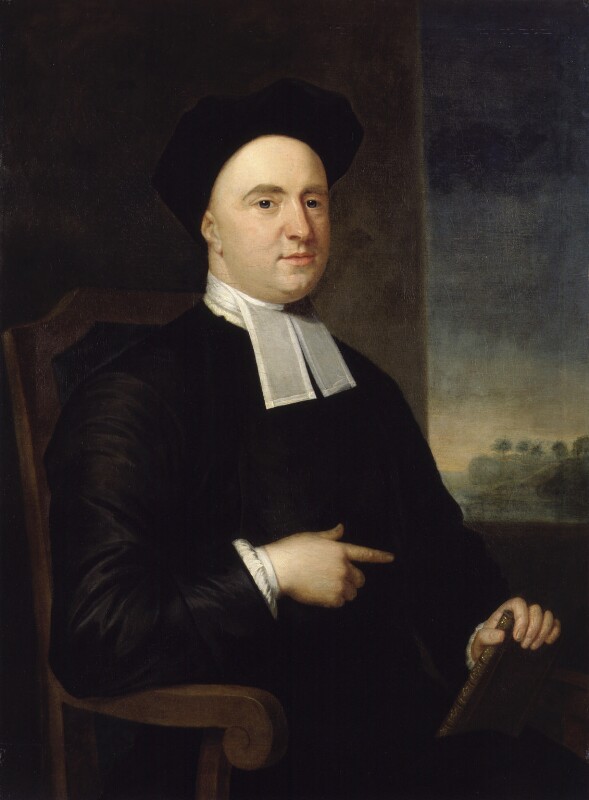
Mark Bence-Jones writes in his A Guide to Irish Country Houses (1988):
p. 121. “(Wallop, Portsmouth, E/IFR) A C13 four-towered keep, like the ruined castles at Carlow and Ferns, restored at various dates and rising above the surrounding rooftops of the town of Enniscorthy like a French chateau-fort, with its near row of tourelles. Once the home of Edmund Spenser, the poet. Now a museum.” [2]
The National Inventory of Architectural Heritage tells us that it is a two-bay three-stage over basement castle, built 1588, on a rectangular plan with single-bay full-height engaged drum towers to corners on circular plans. [3]


The website tells us more about the history of the castle:
“Maud de Quency (granddaughter of the famous Strongbow) marries Philip de Prendergast (son of Anglo-Norman Knight Maurice de Prendergast) and they reside at Enniscorthy Castle from 1190 to his death in 1229. From then until the 1370’s, their descendants, and other Anglo-Norman families rule the Duffry and reside in Enniscorthy Castle.
“In 1375: The fief (a defined area of land or territory) of the Duffry and Enniscorthy Castle are forcefully retaken by Art MacMurrough Kavanagh who regains his ancestral lands. This marks a time of Gaelic Irish revival. The MacMurrough Kavanagh dynasty rule until they eventually surrender the Castle and lands to Lord Leonard Grey in 1536. At this time Enniscorthy Castle is reported be in a ruined condition.

“In 1569, The Butlers of Kilkenny and the Earl of Kildare lead a raid on Enniscorthy town on a fair day, killing numerous civilians and burning the castle. In 1581, The poet Edmund Spenser leases the Castle but never lives in it. Historians speculate that this was because Spenser feared the MacMurrough Kavanaghs.
“In 1585, Henry Wallop receives ownership of the Duffry by Royal Appointment. He exploits the dense forests (the Duffry, An Dubh Tír in Irish, meaning “The Black Country”) surrounding Enniscorthy which brings considerable wealth to the town, and funds the rebuilding of Enniscorthy Castle which we see standing today. Enniscorthy begins to rapidly develop as a plantation town.
“1649: Oliver Cromwell arrives in Co. Wexford. Enniscorthy Castle is beseiged by his forces; its defenders surrender, leaving it intact. In December of the same year the Castle once again fell to the Irish (under Captain Daniel Farrell), but two months later Colonel Cooke, the Governor of Wexford, reoccupied the castle.
“1898: The Castle is leased by Patrick J. Roche from the Earl of Portsmouth. P.J. Roche restores and extends the Castle making it into a residence for his son Henry J. Roche.
“1951: Roche family leaves.
“1962: Castle opens as Wexford County Museum.“

6. Ferns Castle, Wexford – open to public, OPW
see my OPW entry: https://irishhistorichouses.com/2022/02/07/office-of-public-works-properties-leinster-laois-longford-louth-meath-offaly-westmeath-wexford-wicklow/

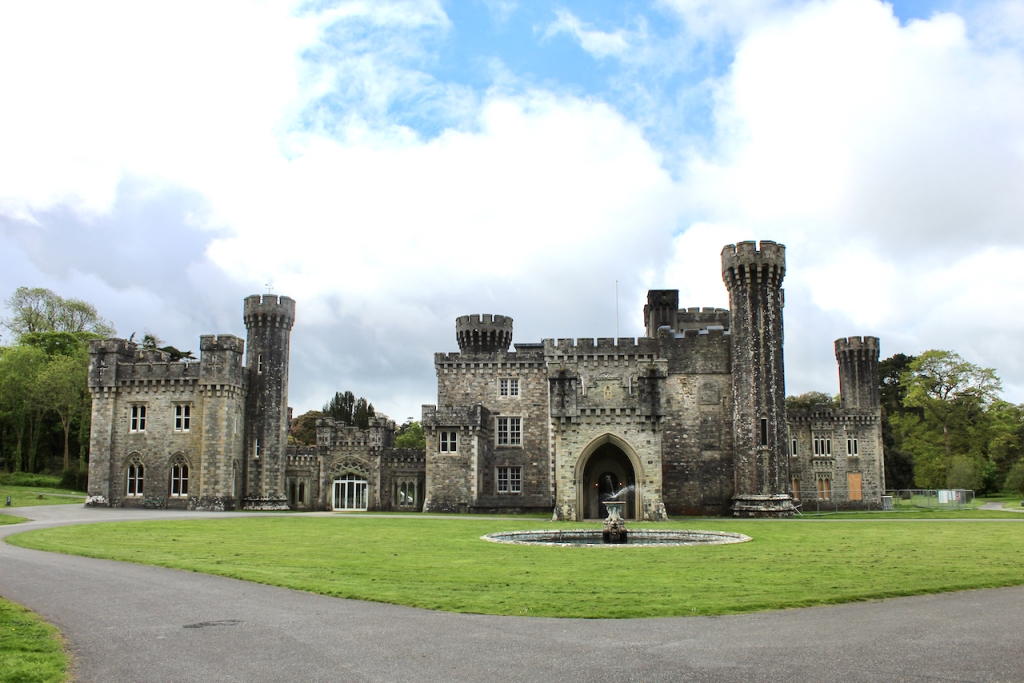
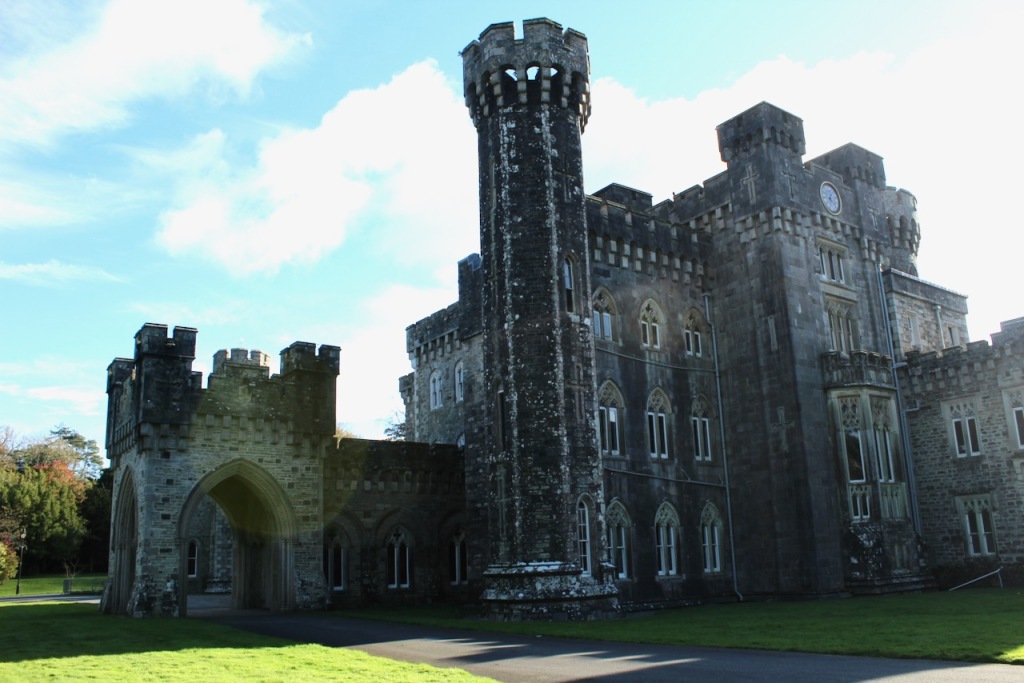
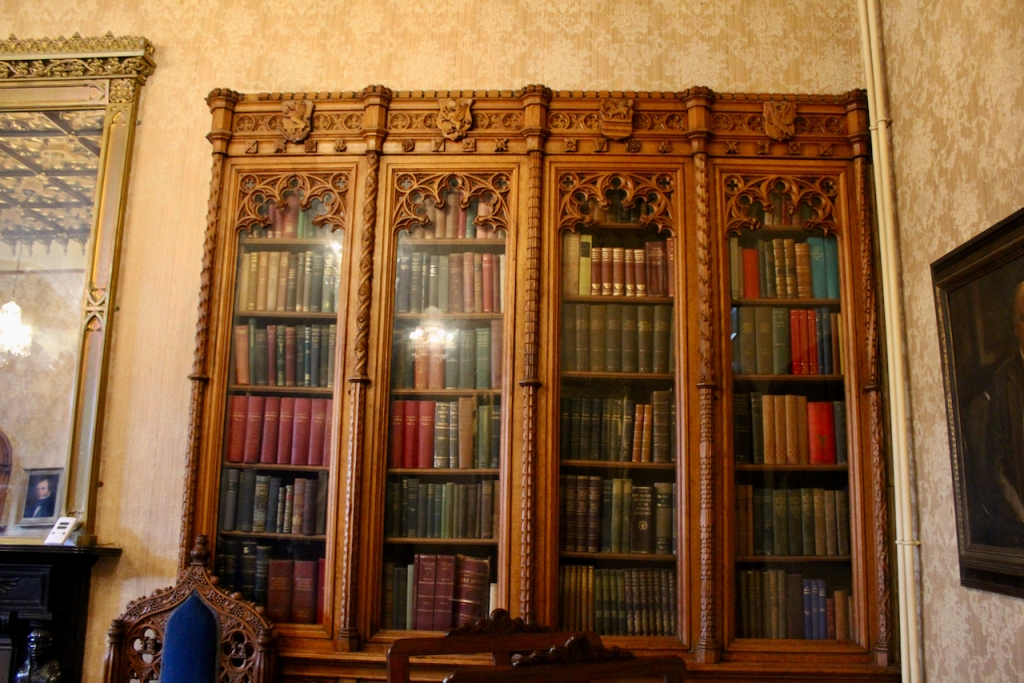
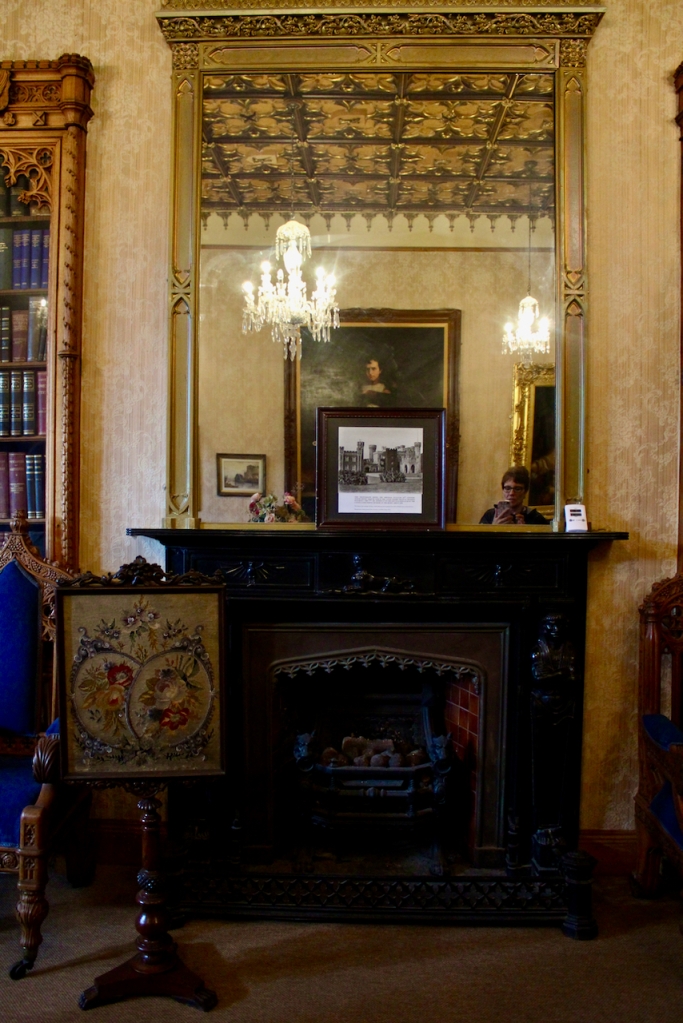
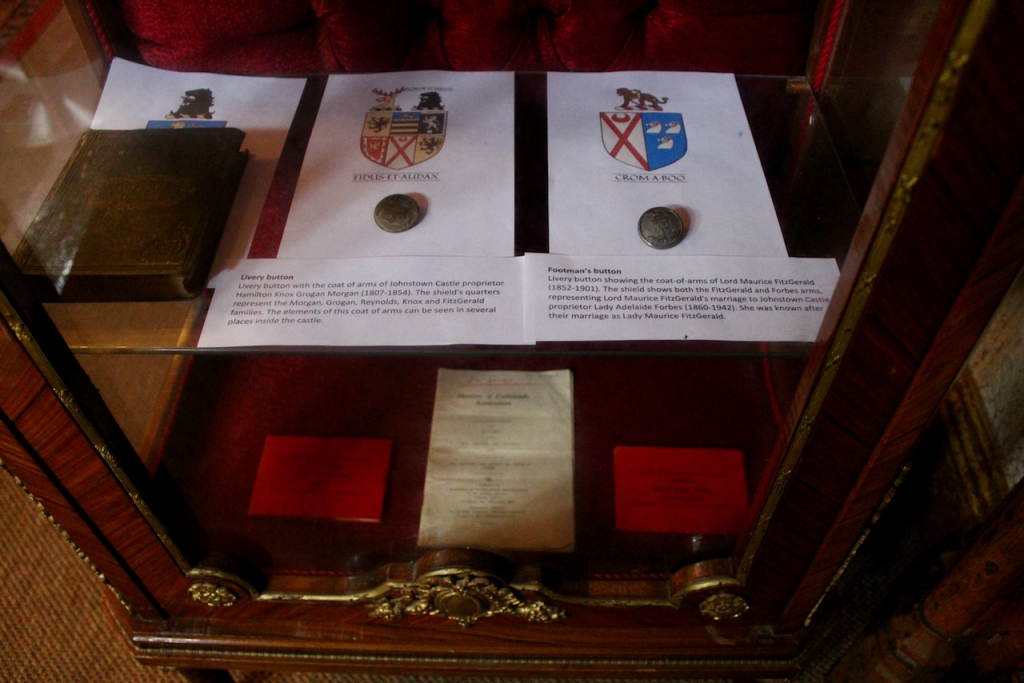
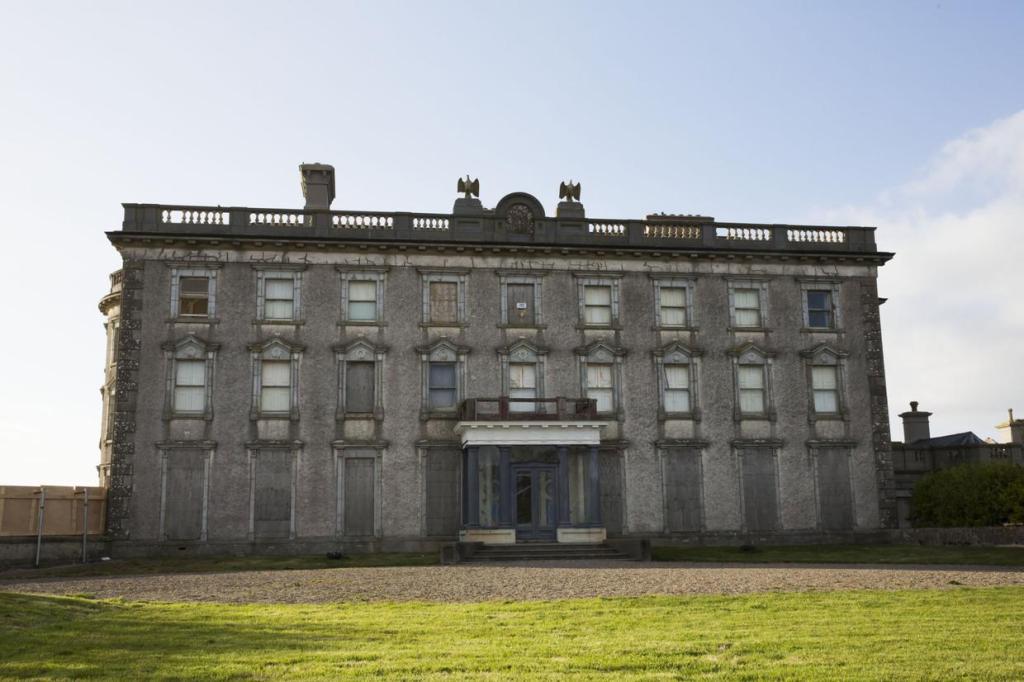
7. Johnstown Castle, County Wexford maintained by the Irish Heritage Trust
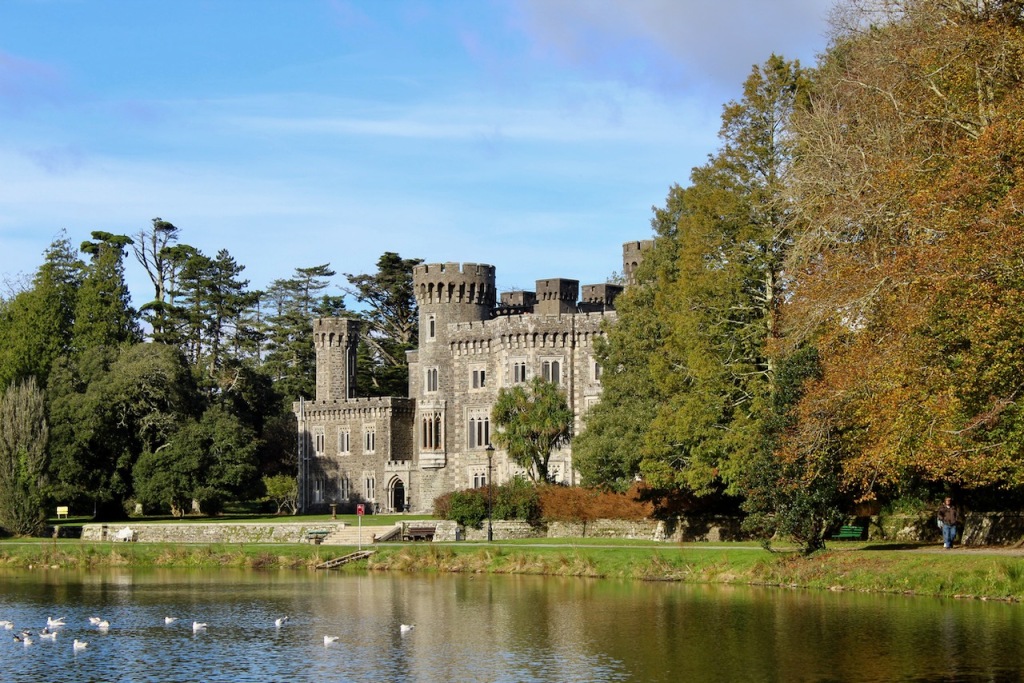

See my entry https://irishhistorichouses.com/2023/09/30/a-heritage-trust-property-johnstown-castle-county-wexford/
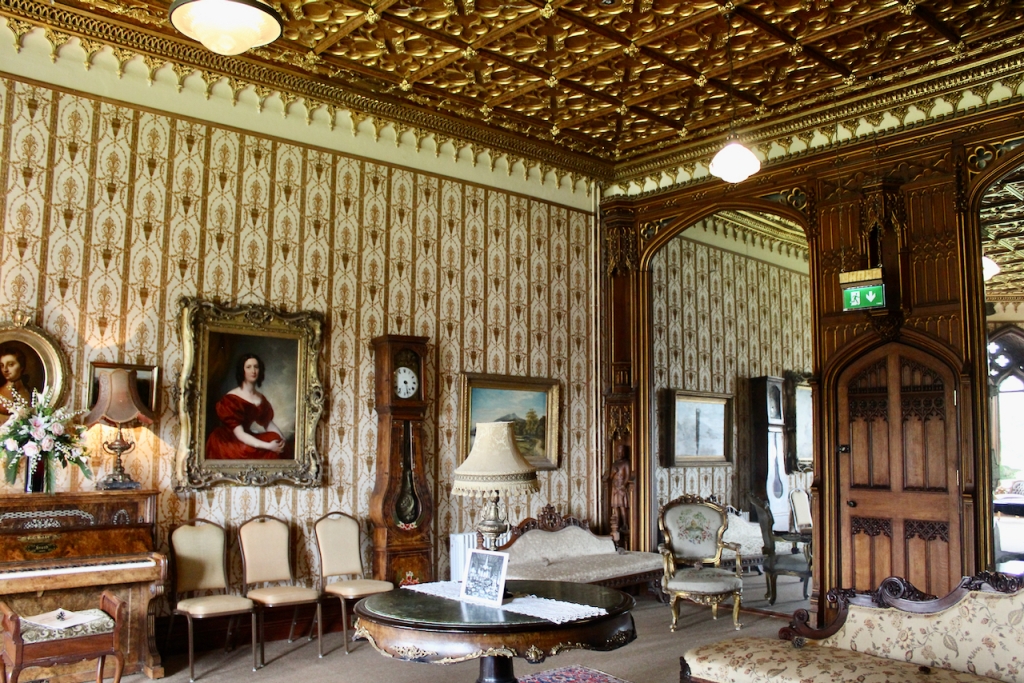
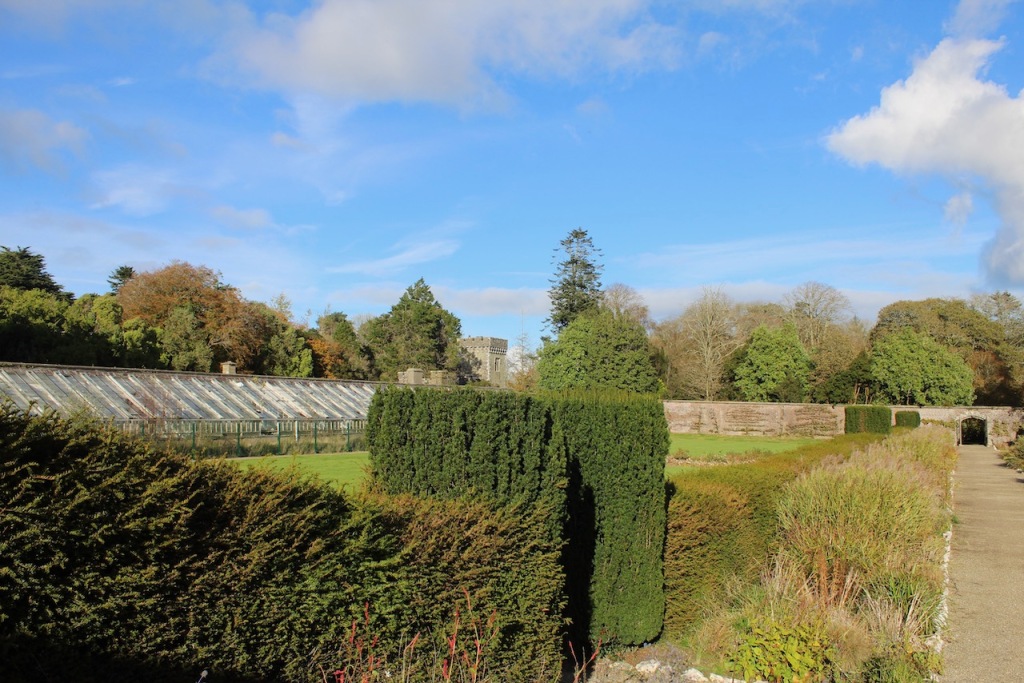
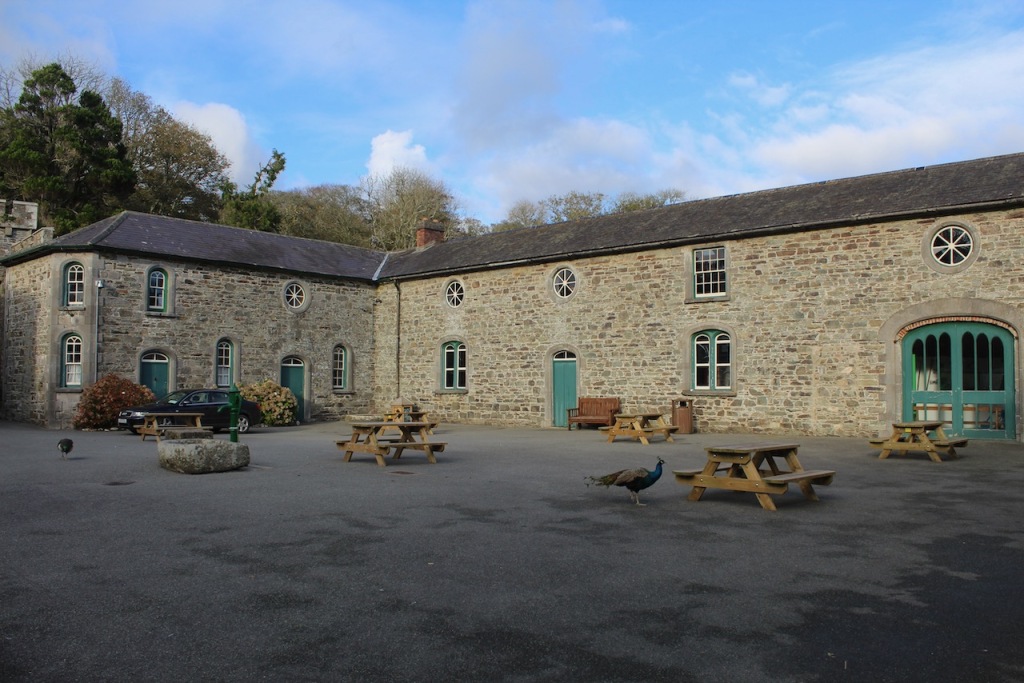



8. Kilcarbry Mill Engine House, Sweetfarm, Enniscorthy, Co Wexford – section 482
Open dates in 2026: Feb 4-5, 8-11, Mar 11-12, 16-19, May 10-11, 22-31, July 4-5, 13-14, Aug 3-30, Dec 19-22 12 noon-4pm
Fee: adult €10, student/OAP €5, child free
9. Kilmokea Country Manor & Gardens, Great Island, Campile, New Ross, Co. Wexford Y34 TH58 – section 482, gardens open to public
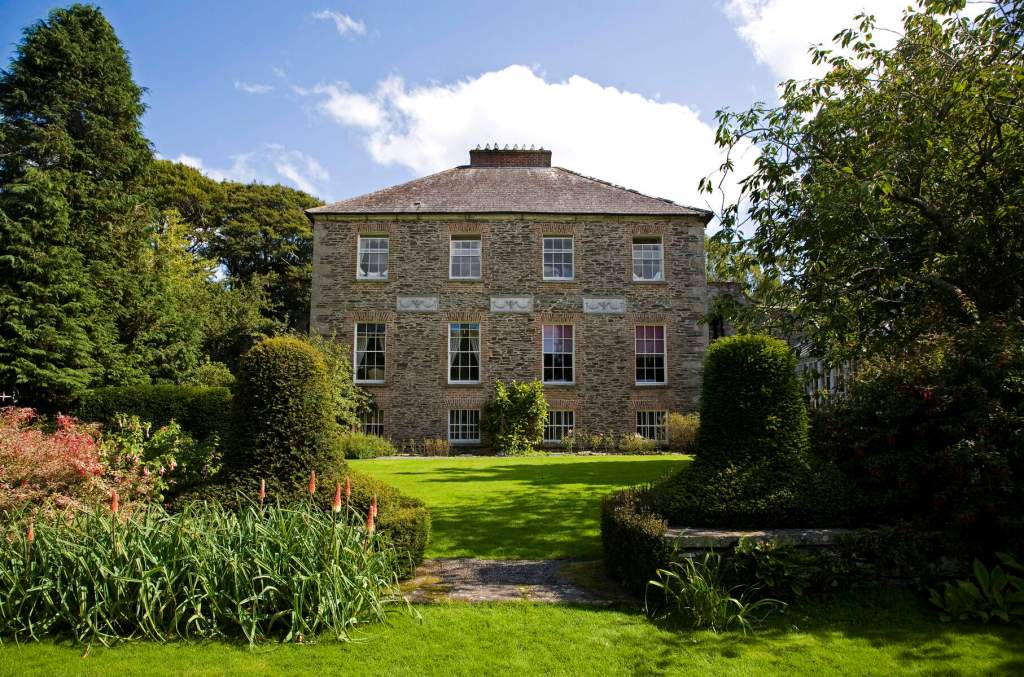

www.kilmokea.com
Tourist Accommodation Facility
Gardens Open in 2026: April 3 -Sept 27, 11am-5pm
Fee: adult €9, OAP €7, student €6, child €5, family €25
We visited in 2023 – see my entry https://irishhistorichouses.com/2023/10/12/kilmokea-country-manor-gardens-kilmokea-great-island-campile-new-ross-co-wexford-y34-th58/
10. Newtownbarry House, Wexford – gardens open to the public
https://www.gardensofireland.org/directory/52/


Contact: Clody and Alice Norton
Tel: +353 (0) 53 937 6383
Email: clodynorton@gmail.com
Mark Bence-Jones writes (1988): p. 225. “(Barry/IFR; Maxwell, Farnham, B/PB; Hall-Dare;IFR) The estate of Newtownbarry originally belonged to a branch of the Barrys; passed to the Farnhams with the marriage of Judith Barry to John Maxwell, afterwards 1st Lord Farnham, 1719. Subsequently acquired by the Hall-Dare family, who built the present house 1860s, to the design of Sir Charles Lanyon. It is in a rather restrained Classical style, of rough ashlar; the windows have surrounds of smooth ashlar, with blocking. Two storey; asymmetrical entrance front, with two bays projecting at one end; against this projection is set a balustraded open porch. Lower two storey service wing. Eaved roof on plain cornice. Impressive staircase.”

The National Inventory tells us that it is a five-bay (five-bay deep) two-storey country house, built 1863-9, on an L-shaped plan off-centred on single-bay single-storey flat-roofed projecting porch to ground floor abutting two-bay two-storey projecting end bay; eight-bay two-storey rear (south) elevation. It continues:


“A country house erected for Robert Westley Hall-Dare JP DL (1840-76) to a design by Lanyon, Lynn and Lanyon (formed 1860) of Belfast and Dublin (Dublin Builder 1864, 66) representing an important component of the mid nineteenth-century domestic built heritage of County Wexford with the architectural value of the composition, one succeeding the eighteenth-century ‘Woodfield…[a] mansion of long standing and of cottage-like character in the Grecian style of architecture’ (Lacy 1863, 485), confirmed by such attributes as the deliberate alignment maximising on panoramic vistas overlooking the meandering River Slaney with its mountainous backdrop in the near distance; the asymmetrical footprint off-centred on an Italianate porch; the construction in a rough cut granite offset by silver-grey dressings not only demonstrating good quality workmanship, but also providing an interplay of light and shade in an otherwise monochrome palette; and the slight diminishing in scale of the openings on each floor producing a feint graduated visual impression. Having been well maintained, the elementary form and massing survive intact together with substantial quantities of the original fabric, both to the exterior and to the interior arranged around a top-lit staircase hall recalling the Lanyon, Lynn and Lanyon-designed Stradbally Hall (1866-7), County Laois, where contemporary joinery; Classical-style chimneypieces; and plasterwork enrichments, all highlight the considerable artistic potential of the composition. Furthermore, adjacent outbuildings; walled gardens; all continue to contribute positively to the group and setting values of an estate having historic connections with the Hall-Dare family including Captain Robert Westley Hall-Dare JP DL (1866-1939), one-time High Sheriff of County Wexford (fl. 1891); and Robert Westley Hall-Dare (1899-1972).”
11. Sigginstown Castle, Sigginstown, Tacumshane, Co. Wexford, Y35 XK7D – section 482
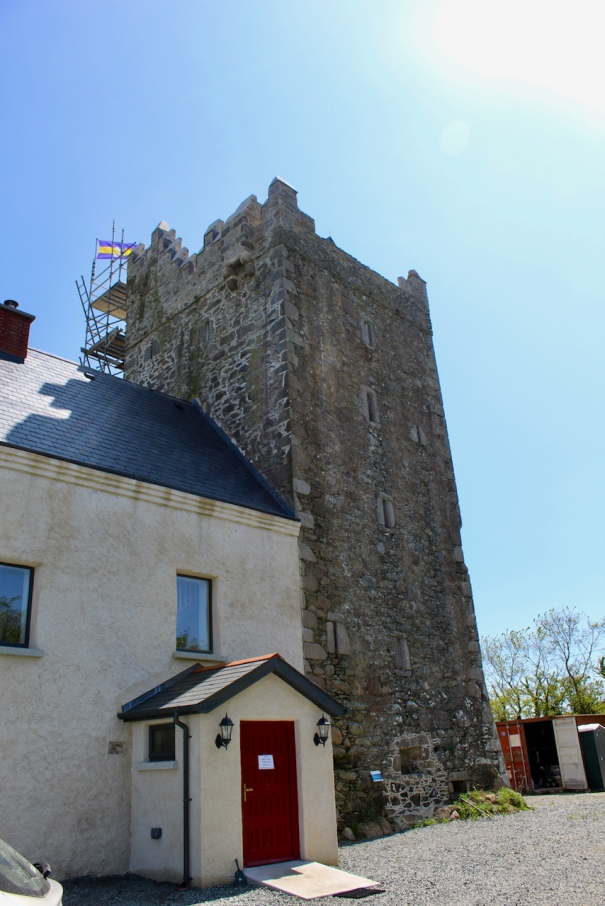

Open dates in 2026: Mar 13-15, 20-22, 27-29, April 3-6, 10-12, 24-26, May 1-4, 8-10, 15-17, 22-24, June 4-7, 11-14, 25-28, July 2-5, 9-12, 16-19, 23-28, Aug 1-3, 6-9, 13-23, 27-30, Sept 4-6, 11-13, 18-20, 25-27, 12noon-5pm
Fee: adult €12, child/OAP/student €10, groups of 6 or more €10 per person
We visited in 2023 – see my entry https://irishhistorichouses.com/2023/11/16/sigginstown-castle-tacumshane-co-wexford-y35-xk7d/
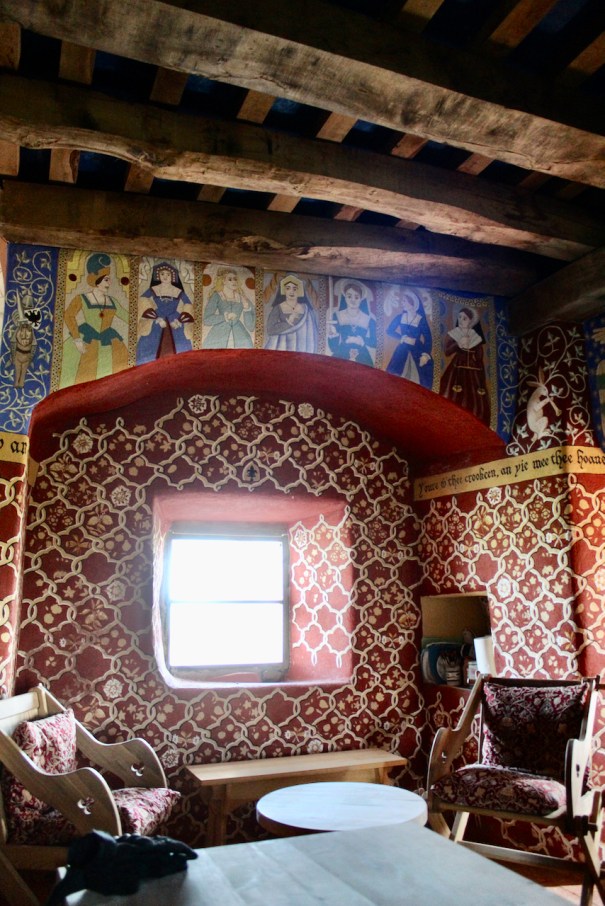

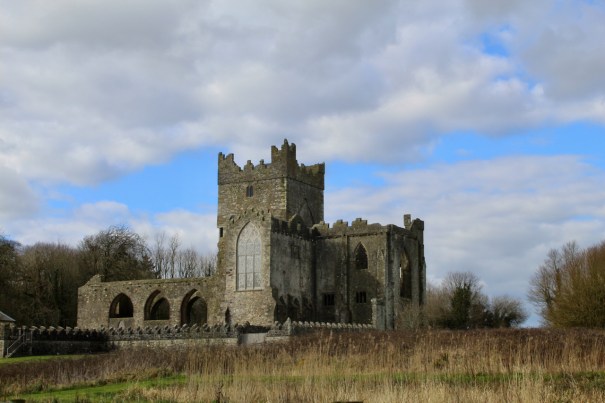
12. Tintern Abbey, Ballycullane, County Wexford – concessionary entrance to IGS members, OPW
see my entry https://irishhistorichouses.com/2025/04/07/tintern-abbey-county-wexford-an-opw-property/

13. Wells House, County Wexford – open for tours

See my entry https://irishhistorichouses.com/2025/05/29/wells-house-and-gardens-county-wexford-open-for-tours/
Web: www.wellshouse.ie
“Wells House has a stunning Victorian Terrace garden, parterre garden and arboretum designed by the renowned architect and landscape designer, Daniel Robertson.
“The terraced gardens which have been restored to their former glory sit beautifully into the large setting of his vast parkland design which spans for acres in the stunning Co. Wexford landscape.
“With two woodland walks, a craft courtyard, adventure playground, restaurant and a busy calendar of events this is a perfect day out for all the family. “
and “Discover the 400-year-old history of Wells House & Gardens by taking a guided exploration of the house. Our living house tour and expert guide in Victorian dress will bring you back to a time. To a time when the magnificent ground floor and bedrooms witnessed the stories of Cromwell, Rebellions and the Famine. Uncover the everyday lives of the wealthy, powerful families who lived in the estate and their famed architect Daniel Robertson. All giving you a unique insight into the life of previous generations all the way up until the current owners of Wells House.“
Places to Stay, County Wexford
1. Artramon House, Castlebridge, Co Wexford – B&B


https://www.artramon-farm.com/english/welcome
Mark Bence-Jones writes: p. 12. “(Le Hunte/LGI 1912; Neave, Bt/Pb) A late C18 house, remodelled after being burnt 1923. 2 storey; entrance front with pediment of which the peak is level with the coping of the parapet, and the base is well below the level of the main cornice. In the breakfront central feature below the pediment are two windows and a tripartite Venetian doorway; two bays on either side of the central feature.”
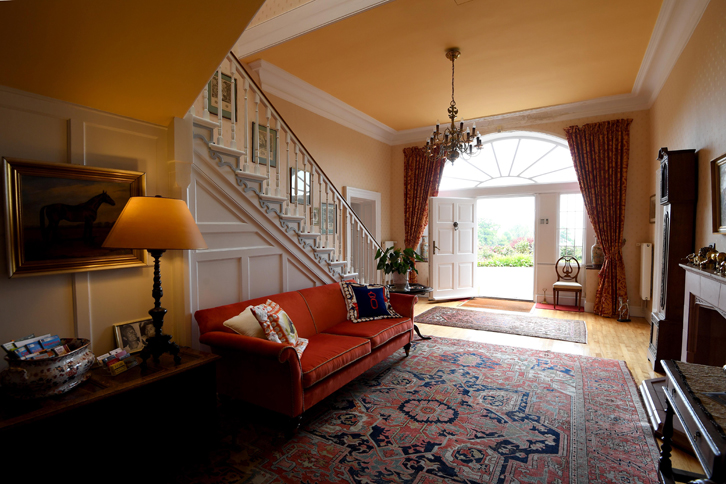

The National Inventory tells us it is a five-bay two-storey country house, rebuilt 1928-32, on an L-shaped plan centred on single-bay two-storey pedimented breakfront; seven-bay two-storey side (west) elevation… “A country house erected for Richard “Dick” Richards (Wexford County Council 17th June 1927) to a design by Patrick Joseph Brady (d. 1936) of Ballyhaise, County Cavan (Irish Builder 1928, 602), representing an important component of the domestic built heritage of County Wexford with the architectural value of the composition, one retaining at least the footings of an eighteenth-century house destroyed (1923) during “The Troubles” (1919-23), confirmed by such attributes as the deliberate alignment maximising on scenic vistas overlooking gently rolling grounds with ‘fine views of the estuary, harbour and town of Wexford’ as a backdrop (Fraser 1844, 118); the symmetrical frontage centred on a curiously compressed breakfront; the diminishing in scale of the openings on each floor producing a graduated visual impression; and the monolithic parapeted roofline. Having been well maintained, the elementary form and massing survive intact together with substantial quantities of the original fabric, both to the exterior and to the interior where contemporary joinery; reclaimed Classical-style chimneypieces; and sleek plasterwork refinements, all highlight the artistic potential of the composition. Furthermore, adjacent outbuildings (extant 1840); and a substantial walled garden (extant 1840), all continue to contribute positively to the group and setting values of an estate having historic connections with the Le Hunte family including Captain George Le Hunte (d. 1799); William Augustus Le Hunte (1774-1820), one-time High Sheriff of County Wexford (fl. 1817); George Le Hunte (1814-91), ‘late of Artramont [sic] County Waterford [sic]’ (Calendars of Wills and Administrations (1892, 481); and the largely absentee Sir George Ruthven Le Hunte KCMG (1852-1925), one-time Governor and Commander-in-Chief of Trinidad and Tobago (fl. 1908-15); and Major Sir Arundell Thomas Clifton Neave (1916-92), sixth Baronet.“
2. Ballytrent House, Broadway, Co Wexford – one wing rental.

Mark Bence-Jones writes of Ballytrent (1988):
p. 28. “Redmond/Hughes. A two storey Georgian house, 5 bays, projecting ends, each with a Wyatt window in both storeys. Adamesque plasterwork. Home of John Redmond MP, leader of Irish Parliamentary Party.”
The website tells us:
“Welcome to the Ballytrent website. Visitors to Wexford seeking a quiet, secluded location,could not choose a better location than Ballytrent. Ballytrent is a magnificent 18th century heritage house set in extensive grounds overlooking the sea towards Tuskar Rock Lighthouse.
“In the grounds of the house is located a Ráth or earthen mound dating back to prechristian times and, measuring 650 yards in circumference, is reputed to be the largest in Europe. The grounds also contain a large flag pole that was once the tallest mast in the British Isles. The Rath garden is a haven for songbirds & a visit, either early morning or late evening, is pure magic!
“Ballytrent is tranquil and secluded. The garden & lawns cover three acres and include some rare plants. Our farm is a mix of cattle, cereals and root crops. We extend a warm welcome to those interested in visiting the farm. We are fortunate in having the best weather in Ireland – the annual rainfall is approximately 35 inches and each year the Weather Station at Rosslare records the highest mean sunshine hours. We are indeed the Sunny South East!
Ballytrent House,
Ballytrent,
Rosslare Harbour,
Co. Wexford,
Ireland.
Telephone/Fax: 053 91 31147
Email: jepryan@eircom.net
“Situated in St Helen’s E.D., Ballytrent, with its double ringed ráth, is an 18th century home set in extensive ground. The history of Ballytrent is a collection of works and illustrations put together after several years of research by Mary Stratton Ryan, wife of the present owner, James Power Ryan.
“A brief look at this work could keep the most avid historian content for quite a while. It is from this book that the following list of names and facts are taken, all having connections to Ballytrent.
- Aymer De Valance; Earl of Pembroke, buried in Westminster Abbey, London.
- Robert Fitzstephens; Ballytrent bestowed on him by Strongbow.
- John le Boteller (Butler); Constable of the Kings Castle at Ballytrent.
- John Sinnot; Listed as a Juror of the Inquisition at Wexford (c1420).
- Patrick Synnot; In a 1656 Curl Survey of Ireland shown as owner of 96 acres 24 perches at Ballytrent.
- Abraham Deane; Given Ballytrent by Cromwell.
- Sarah Hughes; Daughter of Abraham Deane.
- Walter Redmond; Purchased Ballytrent from Henry Hughes.
- William Archer Redmond MP; Father of John and William – both also MP’s.
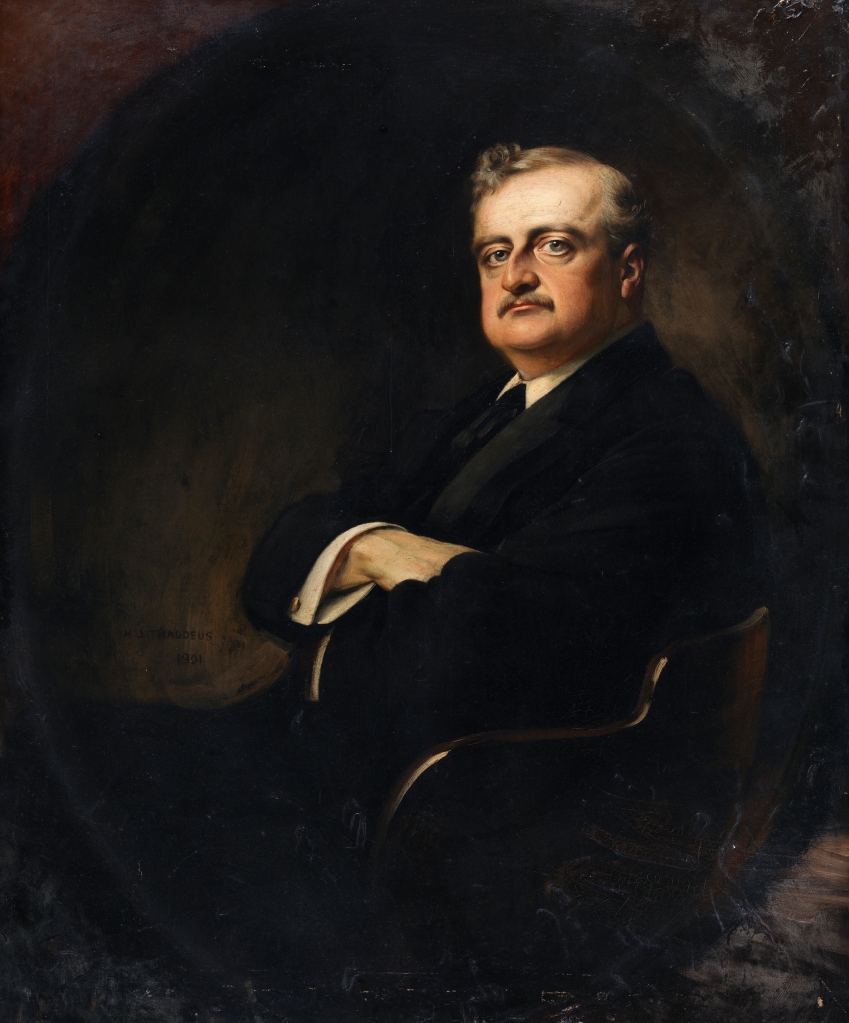

- John Edward Redmond MP; Represented North Wexford, succeeded Parnell as leader of the Nationalist Party.
- William Hoey Kearney Redmond MP; MP for Wexford and Fermanagh.
- John H. Talbot (the younger); Inherited Ballytrent from his sister Matilda Seagrave.
- William Ryan; Grandson of Sir James Power. Purchased Ballytrent from Emily Talbot (nee Considine).
- James Edward Power Ryan; Present owner and grandson of William Ryan.
“This clearly illustrates the influence and power that is part of the documented history of Ballytrent, without even considering the possibilities of the time when the ráth was in its prime.”
3. Bellfry at Old Boley, County Wexford – self catering
4. Butlerstown Castle, Tomhaggard, Co Wexford – A ruin, coach house accommodation
http://www.butlerstowncastle.com/
5. Clonganny House, Wexford – accommodation
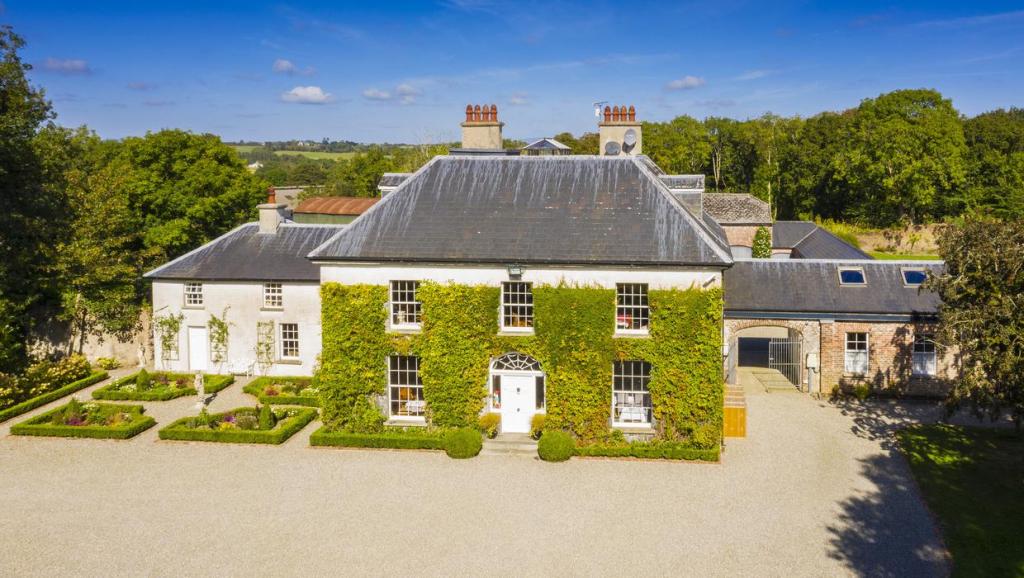

The website tells us: “Clonganny House is a fine country Georgian residence originally erected for Hawtry White (1758-1837) and sympathetically restored in the late twentieth century. Retaining many original features, Clonganny is a fine example of late Georgian architecture. Set in eight acres embracing gently rolling lawns, serene woodland, and a stunning walled garden, Clonganny House is only a short drive to a beautiful, award winning coastline and miles of golden sandy beaches.“
6. Dunbrody Park, Arthurstown, County Wexford – accommodation
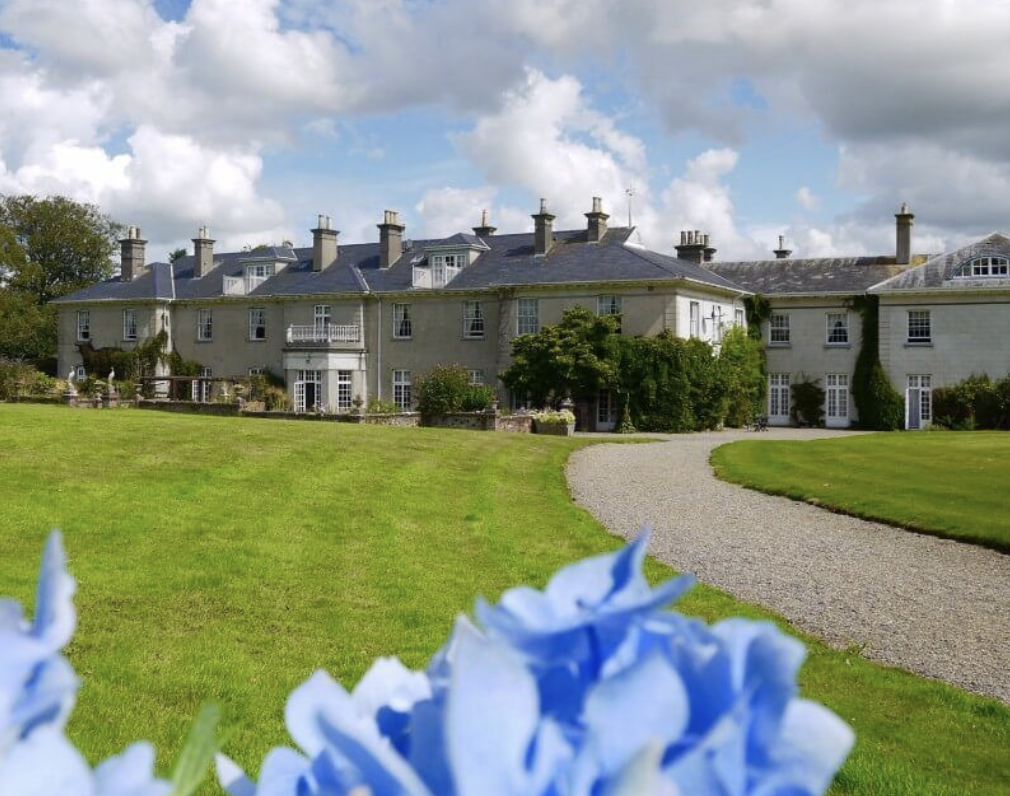

Mark Bence-Jones writes (1988): p. 114. “(Chichester, Templemore, B/PB; and Donegall, M/PB) A pleasant, comfortable unassuming house of ca 1860 which from its appearance might be a C20 house of vaguely Queen Anne flavour. Two storey, five bay centre, with middle bay breaking forward and three-sided single-storey central bow; two bay projecting ends. Moderately high roof on bracket cornice; windows with cambered heads and astragals. Wyatt windows in side elevation.”
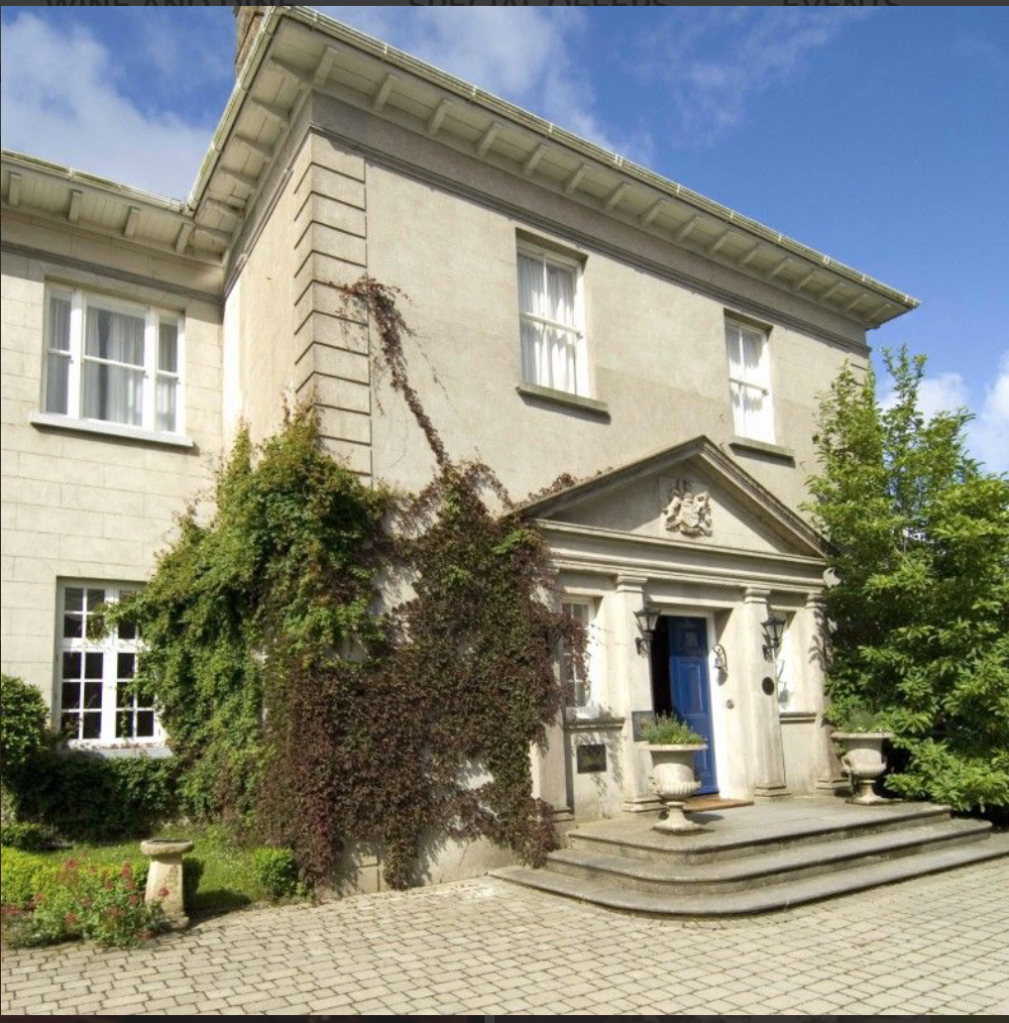


The National Inventory tells us:
“nine-bay two-storey country house with dormer attic, extant 1819, on an E-shaped plan with two-bay two-storey advanced end bays centred on single-bay two-storey breakfront originally single-bay three-storey on a rectangular plan. “Improved”, 1909-10, producing present composition…A country house erected by Lord Spencer Stanley Chichester (1775-1819) representing an integral component of the domestic built heritage of south County Wexford with the architectural value of the composition, one sometimes known as “Dunbrody Park” (Lacy 1863, 516) or “Harriet’s Lodge” after Lady Anne Harriet Chichester (née Stewart) (c.1770-1850), suggested by such attributes as the deliberate alignment maximising on scenic vistas overlooking gently rolling grounds with Waterford Harbour as a backdrop; the near-symmetrical frontage centred on a truncated breakfront; the diminishing in scale of the openings on each floor producing a graduated visual impression; and the decorative timber work embellishing the roofline: meanwhile, a photograph (30th August 1910) by A.H. Poole of Waterford captures recent “improvements” to the country house with those works ‘[presenting the] appearance [of] a twentieth-century house of vaguely “Queen Anne” flavour’ (Bence-Jones 1978, 114). Having been well maintained, the elementary form and massing survive intact together with substantial quantities of the original or sympathetically replicated fabric, both to the exterior and to the interior where contemporary joinery; Classical-style chimneypieces; and sleek plasterwork refinements, all highlight the artistic potential of the composition. Furthermore, adjacent outbuildings (extant 1840); a private burial ground; and distant gate lodges, all continue to contribute positively to the group and setting values of an estate having historic connections with the Barons Templemore including Henry “Harry” Spencer Chichester (1821-1906), second Baron Templemore ‘late of Great Cumberland-place Middlesex’ (Calendars of Wills and Administrations 1907, 508); Arthur Henry Chichester (1854-1924), third Baron Templemore; Arthur Claud Spencer Chichester (1880-1953), fourth Baron Templemore; and Dermot Richard Claud Chichester (1916-2007), fifth Baron Templemore.“
7. Fruit Hill Cottages, Fruit Hill House, Campile, New Ross, County Wexford
https://www.fruithillcottages.com/
“Set in the landscaped grounds of 18th Century Fruit Hill House, these traditional self-catering farm cottages make an ideal base for touring South-East Ireland.“
8. Glendine House hotel, New Ross, County Wexford
https://glendinehouse.com/about-us
“The Crosbies take special care of people and justifiably garnered much praise in various publications and tour guides for the splendour and comfort of its rooms, and the hospitality of its proprietors, Tom and Ann. Glendine House was presented with Georgina Campbell’s Irish Farmhouse/Guesthouse of The Year award for 2006. This much-coveted accolade confirms Glendine’s status as the establishment par excellence. Glendine Country House has also been featured in the Irish Times, Sunday Independent, Food and Wine Magazine and several other publications.
Glendine Country House is a family run period house set on its own grounds and overlooking the Barrow Estuary on the Hook Peninsula. The 18th Century former Dower House of the Marquis of Donegal was built in 1830. It was first occupied by the Chichester family and later by land agents. Home to the Crosbie family for over 70 years, Glendine retains many of its original 1830 features and is full of old world charm. The House is set high up over the village of Arthurstown and all of the rooms are stylishly beautiful and have magnificent sea views.“
9. Killiane Castle, County Wexford – B&B and self-catering

The website tells us: “The castle history is a remarkable tale of survival. Killiane Castle, a landmark in this cornerstone of Ireland’s Ancient East, has been in the Mernagh family for over one hundred years. However, its origins date back to medieval times to the Norman conquests and possibly even further to the early Irish settlers 500 years ago.
“The name ‘Killiane’ derives from ‘Cill Liadhaine’ in Gaelic, meaning the church of St Leonard which lies within the grounds of the Castle. “
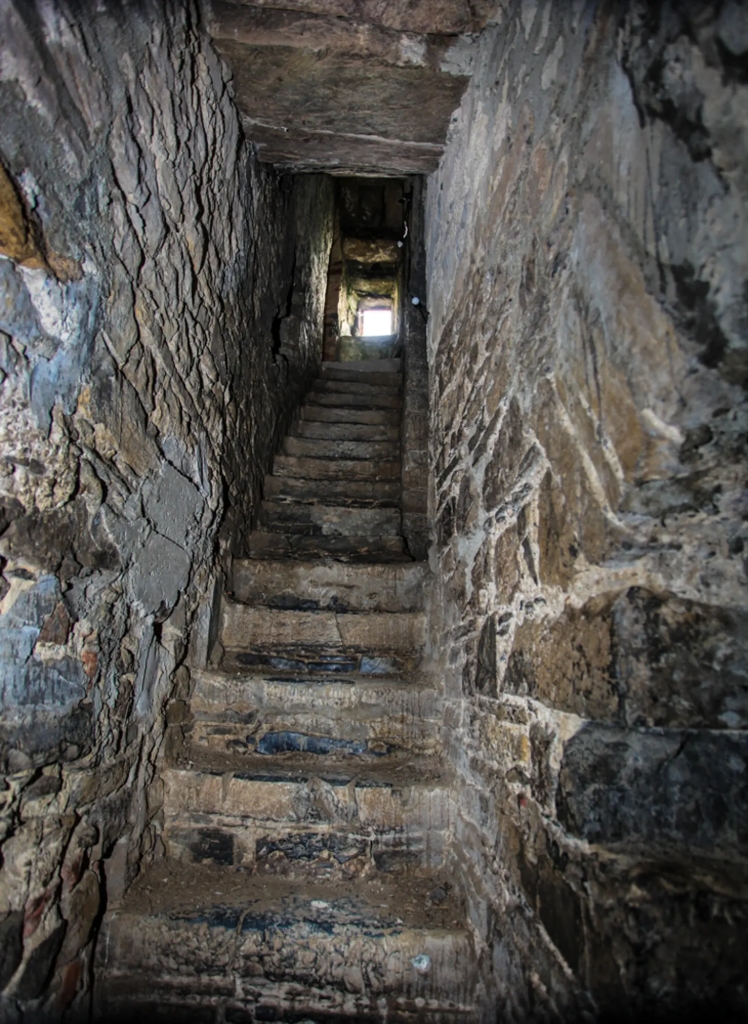

Medieval Times
“Pre-dating the castle history, it is likely that there was some form of native Irish settlement here before the Normans. However, the first recorded owner of the lands was Richard de Hay in the 13th century. Richard de Hay came over with Fitzstephen in the first Norman invasion.
“The Norman tower house is approximately 50ft high and measures 39ft x 27ft externally. The walls are between 4ft and 9ft in thick. The Normans built the tower around 1470. It is most likely one of the “£10 castles”. King Henry VIII awarded a grant of £10 for the building of fortresses in his kingdom that became known as the “£10 castles”. In recent years, an Australian visitor brought us a photo of the original deeds for Killiane Castle signed by King Henry VIII no less!
“Thomas Hay, a descendant of Richard, probably built the tower in the late 15th century c.1470. The present castle and surrounding walls bear testimony to the building genius of the Normans, over 500 years old and quite sound! Built in a prominent position, the tower most likely overlooked a harbour. However, in the intervening years, reclaimed land replaced the harbour. The surrounding lands feature a canal, slob lands and slightly further down the coast, Rosslare strand.
Local Legend…
“Legend has it that below the ground floor underneath the stair way is a dungeon leading to a passageway to a doorway that no longer exists.
“In the early 16th century c.1520, Killiane passed to the Cheevers family by marriage. They continued to fortify the site. By 1543 one Howard Cheevers held Killiane, 2000 acres of land and the office of Mayor of Wexford. The ‘Laughing Cheevers’, as they were then known, held prominence in Wexford for another 100 years until the great rebellion. They built the house sometime in the early 17th century.
“The 17th century was a tumultuous part of the castle history. George Cheevers took part in the Irish Rebellion of 1641. He played a role in both the Siege of Duncannon, and the Confederation of Kilkenny. Following the Sacking of Wexford, Cromwell dispossessed him for his part in these rebellions. Georges son, Didicus, was a blind Franciscan monk. Infamously, several clergy were murdered in Wexford town’s Bullring at this time. Didicus was one of them. Sent to Connaught by Cromwell, the Cheevers family left Killiane. Just a few remained as tenants. The last of the them, an old man, who died in 1849.
“Nearby stands the ruins of the small medieval church of Saint Helen which was in ruins by 1835. Enclosed by a wall is the adjoining cemetery. It is reputed to be the burial place of the Cheevers family.”


Cromwell’s Rule
“In 1656 the property, along with 1500 acres, was granted to one of Cromwell’s soldiers, a Colonel Bunbury. He sold it on to his friends, the Harveys of Lyme Regis. The first of these, Francis Harvey, became MP for Clonmines and Mayor of Wexford, positions his son John also held. A famous beauty known as the Rose of Killiane, a daughter of the Harveys, married the Dean of Dublin in 1809.
Victorian Times
“As time went by, the Harveys increasingly became absentee landlords. They leased the land to their tenants. Both the condition of the castle and the size of the estate materially diminished during this dark time in the castle hsitory.
“Throughout the 19th century there are references to tenants ‘Aylward’, ‘Elard’ and ‘Ellard’, possibly all the one family. By this time, the Harveys overwintered in their townhouse in Wexford at 38 Selskar Street. The family considered Killiane Castle too damp to stay at in winter.
“In 1908 Crown Solicitor, Kennan Cooper, bought the property for £1515. Cooper, a renowned character, kept racehorses and the 1911 census shows Killiane occupied by his tenant, George Grant and family. The census records Grant’s occupation as a ‘Horse trainer/jockey’.
“In 1920 John Mernagh, father of Jack the present owner, bought Killiane with 230 acres for £2000. At that time there was no roof on the tower-house. Ivy covered it. John re-roofed it and used it to store grain and potatoes. Today the castle is home to Jack & Kathleen Mernagh who run the property along with their son Paul & his wife Patrycja and their family.
The Structure of the Building
Original Norman Features
“The castle still contains one original window that dates from the 15th century. The original window is an ogee style window featuring two lights. Over the years, incumbents replaced the other windows. The main entrance to the castle was originally on the east side. It provided an adjoining door to the house at one time. The original door is bricked-up. On the south side of the tower a new door has been opened.
Murder Holes!
“Looking at the front of the castle. There are murder holes over each of the doors on the ground floor. Perfectly located to pour hot tar over any unwelcome visitors! This practice, we assure you, is not in place today!
“The third floor contains a fine granite fireplace. Small smooth stones from the beach line the chimney rising on the outer wall. Also in evidence on this floor, is a cupboard recess.
“Corrugated iron replaced the original slate roof. The parapet consists of large sloping slabs. The battlements are of the steeply stepped type. There is a square turret on each corner. On the outside of the southern turret is a carved head.
“The large bawn has a round tower on the south east corner and a square tower on the south west corner, castle occupying the north west corner. The north east tower has been removed. In order to accommodate the facade of the house, the northern apron wall was taken down.
Original 17th Century House
“The original 17th century house consisted of two storeys with a garret on top. The incumbents raised the roof at a date unknown to us. This action incorporated the original dormer windows of the garrets,converting it into a third storey. Furthermore, they also reduced the great slant on the original 17th-century roof. The staircase of the house is of a simple very wide design, typical of the 17th century. “
9. Kilmokea Country Manor & Gardens, Kilmokea, Great Island, Campile, New Ross, Co. Wexford – accommodation

www.kilmokea.com
Tourist Accommodation Facility
Gardens Open in 2026: April 3 -Sept 27, 11am-5pm
Fee: adult €9, OAP €7, student €6, child €5, family €25
We visited in 2023 – see my entry https://irishhistorichouses.com/2023/10/12/kilmokea-country-manor-gardens-kilmokea-great-island-campile-new-ross-co-wexford-y34-th58/
10. Marlfield, Gorey, Co Wexford – accommodation
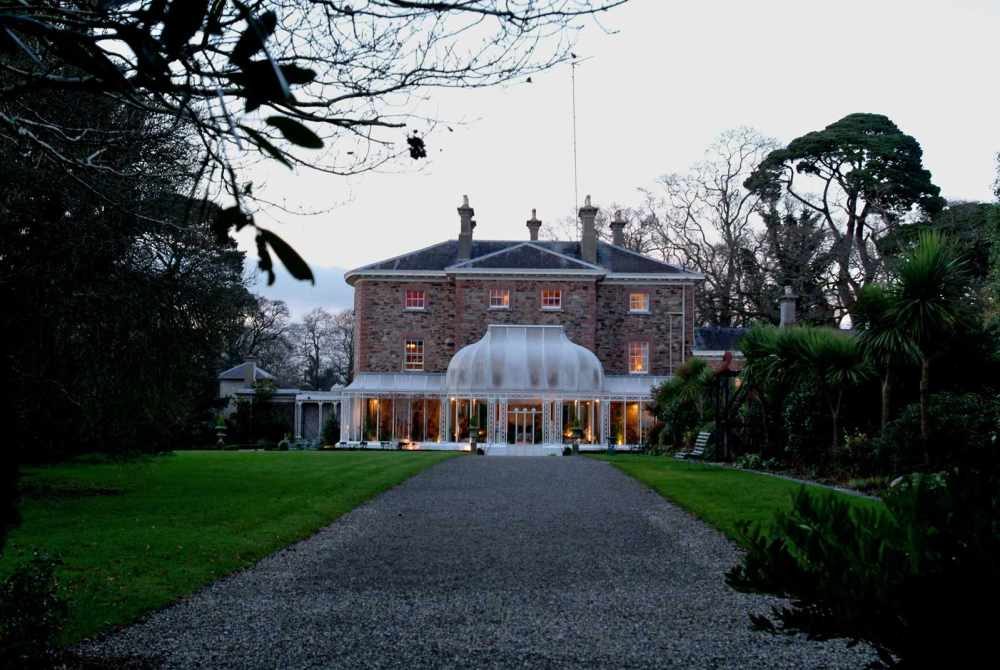

The website tells us:
“Marlfield House is renowned for its hospitality and service, welcoming guests for over 40 years, and is recognised as one of the most luxurious boutique hotels in Wexford, Ireland with the focus on environmentally sustainable practices. All rooms and suites at Marlfield House luxury hotel in County Wexford, Ireland are styled to provide you with elegant, comfortable interiors, furnished with antiques and paintings. Set in 36 acres of woodland, ornamental lake, rose, vegetable and herb gardens, it is a haven of tranquillity, with peacocks, hens, dogs and ponies waiting to greet you on your garden walk.“
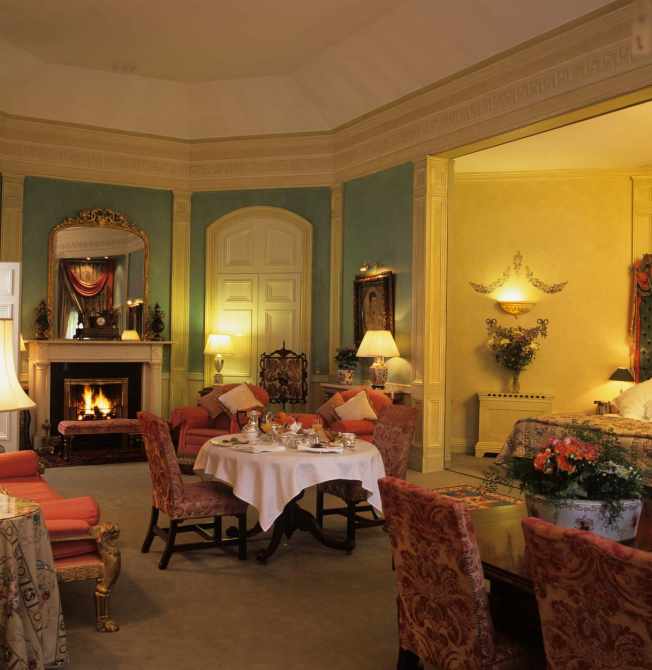



“The house is set in 40 acres of manicured gardens, encompassing a large kitchen garden, woodland walks, lake and fowl reserve, lawns and herbaceous borders. The interior bears all the signs of a much loved house filled with fresh flowers, gleaming antiques and mirrors, blazing fires and period paintings.“
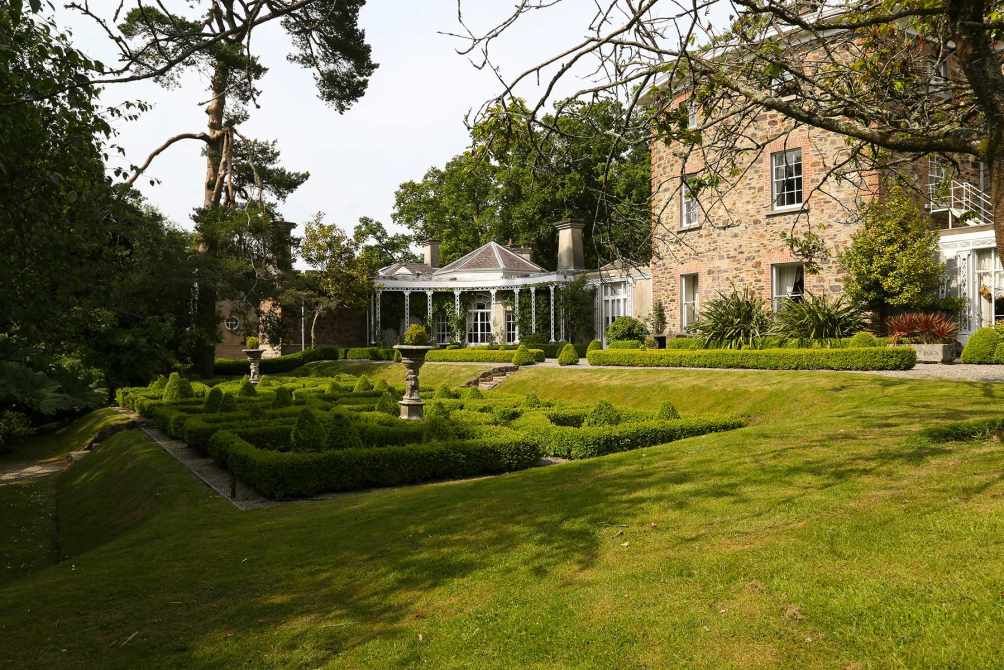

Mark Bence-Jones writes of Marlfield (1988):
Supplement
P. 299. (Stopford, Courtown, E/PB) “A three storey Regency house of random stone with brick facings; four bay front with two bay breakfront centre, eaved roof on bracket cornice, massive chimneystacks. Originally the dower house of the [Stopford] Earls of Courtown, it eventually replaced Courtown House as their Irish seat. Sold in 1979 to Mary Bowe, who has opened it as an hotel. As an extension to the dining room, a veranda and an elegant curvilinear conservatory were added to the front of the house 1983; the architects of this addition being Messrs Cochrane, Flynn-Rogers and Williams.”
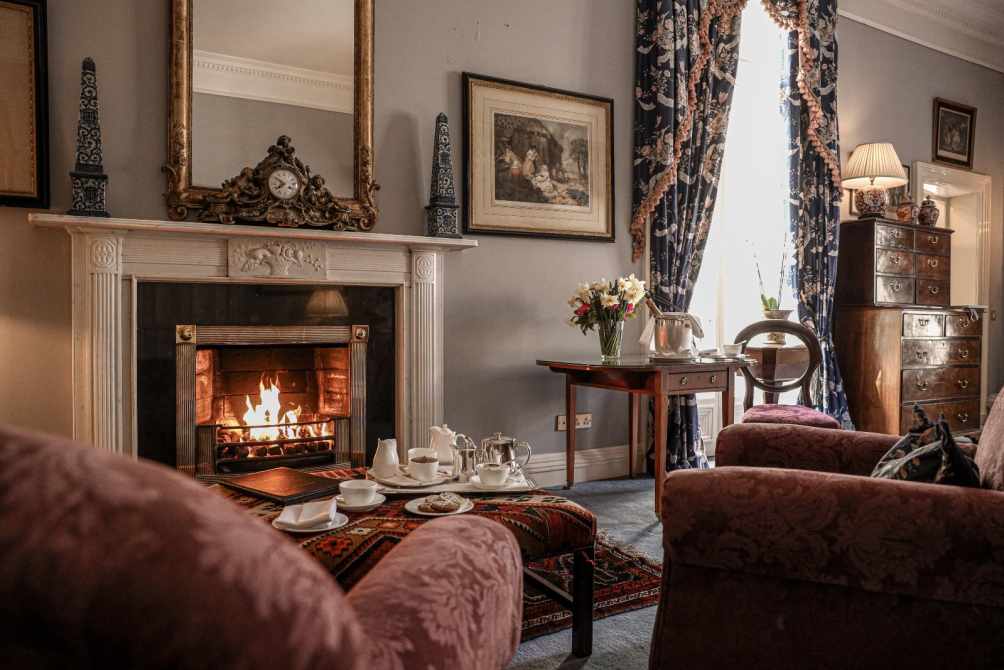
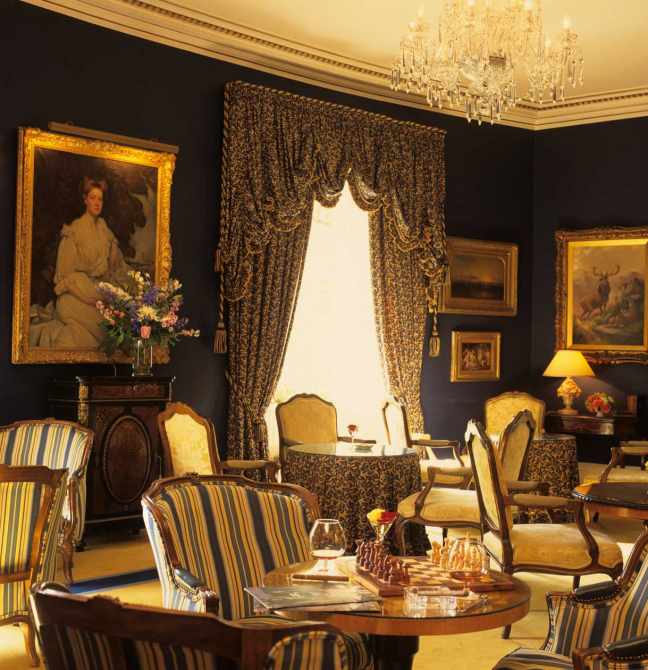


The National Inventory tells us it is a four-bay (two-bay deep) three-storey land agent’s house, built 1852, on a T-shaped plan; four-bay three-storey rear (south) elevation centred on two-bay full-height breakfront. Occupied, 1901; 1911. In occasional use, 1916-75. Vacated, 1975. Sold, 1977. Modified, 1989, producing present composition to accommodate continued alternative use… “A land agent’s house erected by James Thomas Stopford (1794-1858), fourth Earl of Courtown (Walsh 1996, 68), representing an important component of the mid nineteenth-century domestic built heritage of the outskirts of Gorey with the architectural value of the composition, one succeeding an adjacent house occupied by Reverend James Bentley Gordon (1750-1819), author of “History of the Rebellion in Ireland in the Year 1798” (1803), confirmed by such attributes as the compact plan form centred on a much-modified doorcase; the construction in an ochre-coloured fieldstone offset by vibrant red brick dressings producing a mild polychromatic palette; the diminishing in scale of the openings on each floor producing a graduated visual impression; and the monolithic timber work embellishing the roofline. Having been well maintained, the elementary form and massing survive intact together with substantial quantities of the original fabric, both to the exterior and to the interior, including some crown or cylinder glazing panels in hornless sash frames: meanwhile, contemporary joinery; Classical-style chimneypieces; and the decorative plasterwork enrichments, all highlight the artistic potential of the composition. Furthermore, adjacent outbuildings (extant 1904); a walled garden (extant 1904); and a nearby gate lodge (see 15700718), all continue to contribute positively to the group and setting values of a self-contained estate having historic connections with Colonel Robert Owen (1784-1867) and Charlotte Owen (1796-1853) ‘late of Marlfield County Wexford’ (Calendars of Wills and Administrations 1870, 447); and the Stopford family following the sale (1947) and demolition (1948-9) of Courtown House (see 15701216) including James Walter Milles Stopford (1853-1933), sixth Earl of Courtown; Major James Richard Neville Stopford DL OBE (1877-1957), seventh Earl of Courtown; and Brevet Colonel James Montagu Burgoyne Stopford OBE (1908-75), eighth Earl of Courtown.“
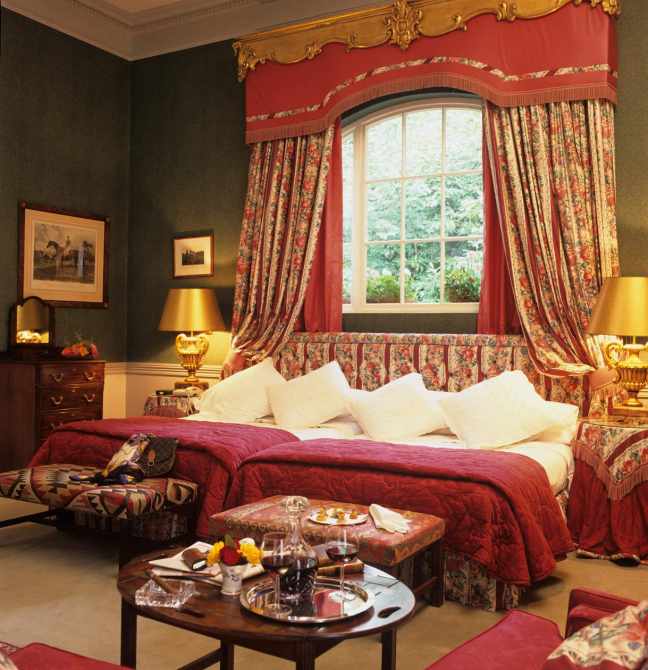
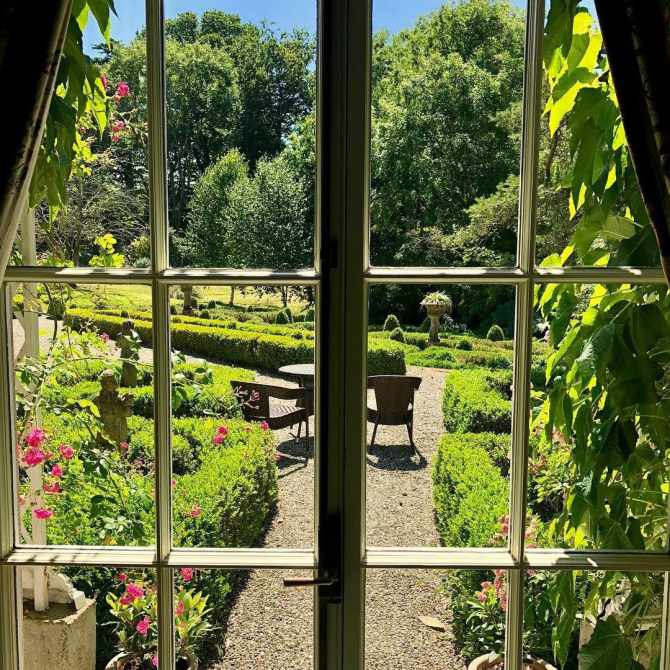
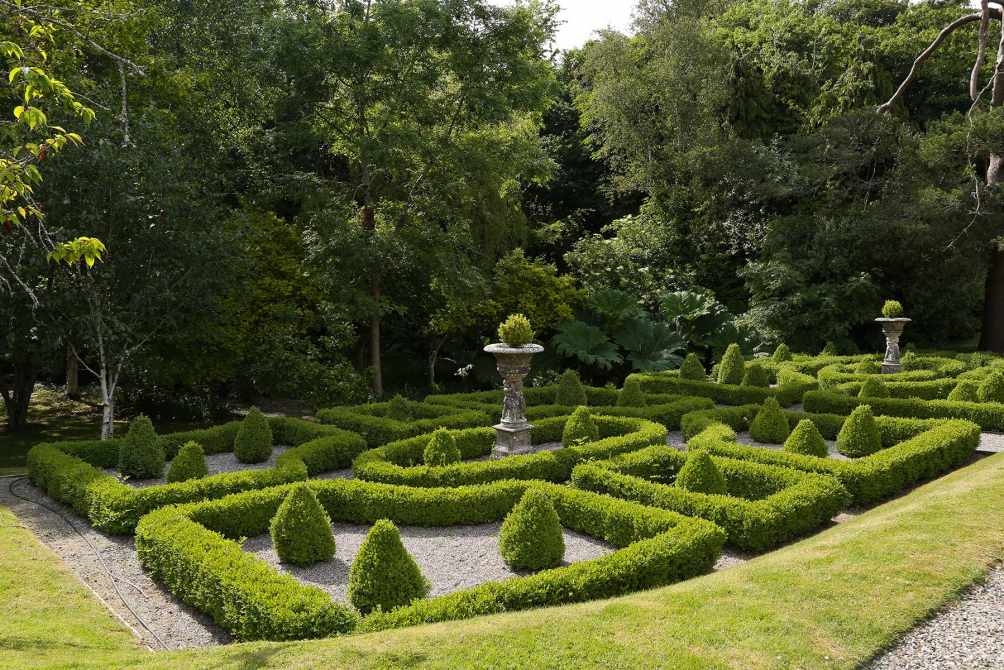
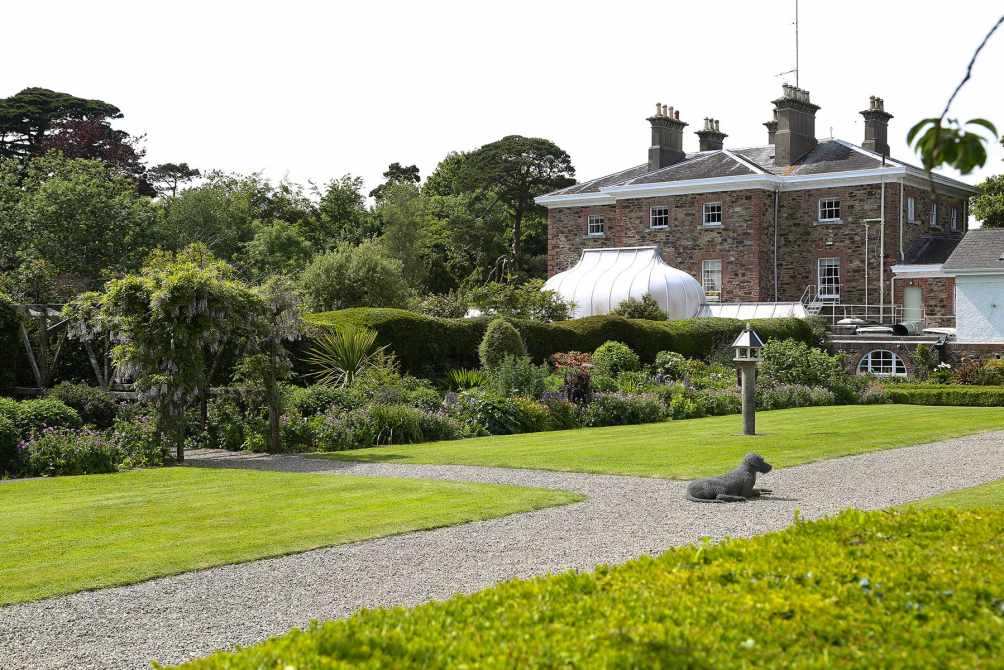





11. Monart, Enniscorthy, Co Wexford – 5* hotel

Nestled in over 100 acres of lush countryside in County Wexford, Monart offers two types of accommodation, 68 deluxe bedrooms with lake or woodland views and two luxurious suites located in the 18th century Monart House.
Mark Bence-Jones writes (1988): p. 208. “Cookman/IFR) A three storey mid-C18 house of sandstone and limestone dressings Five bay front with breakfront centre; Venetian windows in centre of middle storey, with Diocletian windows over it; modified Gibbsian doorcase. Later additions.”
The National Inventory tells us:
“A country house erected by Edward Cookman JP (d. 1774), one-time High Sheriff of County Wexford (fl. 1763), representing an important component of the eighteenth-century domestic built heritage of County Wexford with the architectural value of the composition, ‘a handsome mansion pleasantly situated on a gentle eminence above the Urrin [River] in a highly improved and richly wooded demesne’ (Lewis 1837 II, 385), confirmed by such attributes as the neo-Palladian plan form centred on a Classically-detailed breakfront; the construction in an ochre-coloured fieldstone offset by silver-grey granite dressings not only demonstrating good quality workmanship, but also producing a mild polychromatic palette; the diminishing in scale of the openings on each floor producing a graduated visual impression; and the parapeted roofline. Having been sympathetically restored following a prolonged period of unoccupancy in the later twentieth century, the elementary form and massing survive intact together with substantial quantities of the original fabric, both to the exterior and to the interior, including crown or cylinder glazing panels in hornless sash frames: meanwhile, contemporary joinery; Classical-style chimneypieces; and “bas-relief” plasterwork enrichments, all highlight the artistic potential of a country house having historic connections with the Cookman family including Nathaniel Cookman (—-); Edward Rogers Cookman JP (1788-1865) ‘late of Monart House in the County of Wexford’ (Calendars of Wills and Administrations 1865, 70); Nathaniel Narcissus Cookman JP DL (1827-1908), ‘Country Gentleman late of Monart House Enniscorthy County Wexford’ (Calendars of Wills and Administrations 1908, 96; cf. 15701922); and Captain Nathaniel Edward Rogers Cookman JP DL (1894-1983); and a succession of tenants including Lowry Cliffe Tottenham (1858-1937), ‘Gentleman [and] District Inspector of Royal Irish Constabulary’ (NA 1911).”
12. The Gate Lodge, Mount Congreve – accommodation
https://mountcongreve.com/gate-lodge/
“Located in the heart of the lush Waterford countryside, on the grounds of the historic 18th-century Mount Congreve estate, this tastefully restored gate lodge is the perfect choice if you’re looking for a luxury self-catering stay in Ireland.
“Originally built in 1775, the newly renovated Gate Lodge at Mount Congreve is home to a fully fitted galley kitchen with marble countertops, a living room with a 19th-century French walnut fold-out day bed, two mustard wingback armchairs, Smart TV, an antique bio-ethanol stove, and a bathroom complete with a walk-in shower.”Originally built in 1775, the newly renovated Gate Lodge at Mount Congreve is home to a fully fitted galley kitchen with marble countertops, a living room with a 19th-century French walnut fold-out day bed, two mustard wingback armchairs, Smart TV, an antique bio-ethanol stove, and a bathroom complete with a walk-in shower.
“With two cosy double bedrooms (sleeping up to four adults*), the Gate Lodge is the perfect choice if you’re looking for a luxury self-catering stay in Ireland.“
13. Rathaspeck Manor “doll’s house” gate lodge, County Wexford and the Manor B&B
https://www.airbnb.ie/rooms/18288598?source_impression_id=p3_1646906004_9dSSY0tDTw%2FmQ8TE

and Manor https://www.rathaspeckmanor.ie
The website tells us:
“Rathaspeck Manor Georgian House Wexford was built between 1680-1720 by the Codd Family who came to Ireland circa 1169. William Codd’s son Sir Osborne Codd settled at Rathaspeck and erected a castle there in 1351.
“A descendant Loftus Codd was succeeded by daughters, one of whom, Jane Codd, married Thomas Richards. The Richards Family came to Ireland in 1570 approx. It was this marriage which placed Rathaspeck in the Richards Family.
“Jane and Thomas had 6 sons and 2 daughters. The eldest son Thomas, born 1722 had a Family of two daughters, the oldest Martha married Count Willimsdorf from the Kingdom of Hannover in 1802. This couple had one son, Thomas William Fredrick Von Preberton Willimsdorf who died in 1834 unmarried. There were also three daughters, one of whom Elizabeth, born in 1778, died in 1863 in Holland.
“Elizabeth married Count Von Leinburg Slirrin on April 15th 1802 and they proceeded to have a Family of ten children born between 1803 and 1820 . It is believed that sometime after this the family moved to Holland. Rathaspeck was in the hands of an English Family called Moody after this until the early 1900’s. The Moody built the present gate lodge – or “Doll’s House” in 1900.
“The Meyler Family came to Rathaspeck in 1911 when it was offered for sale and it was from the Meyler Family that the Manor passed to the Cuddihy Family.
“The site of the original Castle is unknown, but it is considered that the present Rathaspeck Manor Georgian Country Home, Ireland is built on the site.
“Rath” means Fort , so the name of Rathaspeck stems from the Gaelic Ratheasbuig , meaning “Fort of the Bishop”. “
14. Riverbank House Hotel, The Bridge, Wexford, Ireland Y35 AH33
https://www.riverbankhousehotel.com
15. Rosegarland House, Wellingtonbridge, County Wexford – courtyard accommodation
“Rosegarland Estate offers visitors a unique opportunity to stay on an extremely old and unspoilt country estate. It allows you to step back in time when you walk along the avenues, woodland paths and old bridle paths which pass through the ancient woodlands and beside the River Corach.
“Relax and unwind in one of our luxury self-catering cottages in Rosegarland Estate. Our four cottages are registered with Failte Ireland (the Irish Tourist Board) and have been awarded a 4 star rating. Old world charm has been combined with modern day luxury in the cottages which are set in a picturesque courtyard. A welcome basket of home baked goodies will greet you when you arrive.
“All the cottages have complimentary WiFi and satellite television channels which can be enjoyed in front of a Waterford Stanley wood burning stove.“


Mark Bence-Jones writes (1988):
p. 245. “(Synnott/IFR; Leigh/IFR) An early C18 house of two storeys over a high basement was built by Leigh family, close to an old tower house of the Synnotts, the original owners of the estate. Later in C18, a larger two storey gable-ended range was added at right angles to the earlier building, giving the house a new seven bay front, with a very elegant columned and fanlighted doorway, in which the delicately leaded fanlight extends over the door and the sidelights. There is resemblance between this doorway and that of William Morris’s town house in Waterford (now the Chamber of Commerce) which is attributed to the Waterford architect, John Roberts; the fact is that it is also possible to see a resemblance between the gracefully curving and cantilevered top-lit staircase at Rosegarland – which is separated from the entrance hall by a doorway with an internal fanlight – and the staircase of the Morris house, would suggest that the newer range at Rosegarland and the Morris house are by the same architect. At the back of the house, the two ranges form a corner of a large and impressive office courtyard, one side of which has a pediment and a Venetian window. In another corner of the courtyard stands the old Synnott tower house, which, in C19, was decorated with little battlemented turrets and a tall and slender turret like a folly tower, with battlements and rectangular and pointed openings; this fantasy rises above the front of the house. The early C18 range contains a contemporary stair of good joinery, with panelling curved to reflect the curve of the handrail. The drawing room, in the later range, has a cornice of early C19 plasterowrk and an elaborately carved chimneypiece of white marble. The dining room, also in this range, was redecorated ca 1874, and given a timber ceiling and a carved oak chimneypiece.”

The National Inventory tells us:
“A country house erected by Robert Leigh MP (1729-1803) representing an important component of the eighteenth-century domestic built heritage of south County Wexford with the architectural value of the composition, one attributable with near certainty to John Roberts (1712-96) of Waterford, confirmed by such attributes as the deliberate alignment maximising on scenic vistas overlooking gently rolling grounds and the meandering Corock River; the symmetrical footprint centred on a Classically-detailed doorcase not only demonstrating good quality workmanship, but also showing a pretty fanlight; and the diminishing in scale of the openings on each floor producing a graduated visual impression. A prolonged period of unoccupancy notwithstanding, the elementary form and massing survive intact together with substantial quantities of the original fabric, both to the exterior and to the interior including not only crown or cylinder glazing panels in hornless sash frames, but also a partial slate hung surface finish widely regarded as an increasingly endangered hallmark of the architectural heritage of County Wexford: meanwhile, contemporary joinery; ‘elaborately carved chimneypieces of white marble’ (Bence-Jones 1978, 246); plasterwork enrichments; and a top-lit staircase recalling the Roberts-designed Morris House [Chamber of Commerce] in neighbouring Waterford (Craig and Garner 1975, 68), all highlight the considerable artistic potential of the composition. Furthermore, an adjacent stable complex (see 15704041); a walled garden (see 15704042); a nearby farmyard complex (extant 1902; coordinates 685132,615236); and a distant gate lodge (extant 1840; coordinates 685381,616928), all continue to contribute positively to the group and setting values of an estate having long-standing connections with the Leigh family including Francis Robert Leigh MP (1758-1839); Francis Augustine Leigh (1822-1900), ‘late of Rosegarland County Wexford’ (Calendars of Wills and Administrations 1900, 277); Francis Robert Leigh DL (1853-1916), ‘late of Rosegarland Wellington Bridge County Wexford’ (Calendars of Wills and Administrations 1916, 371); Francis Edward Leigh (1907-2003); and Robert Edward Francis Leigh (1937-2005).“
16. Wells House, County Wexford – self-catering cottage accommodation, see above
https://wellshouse.ie/self-catering-accommodation-wexford
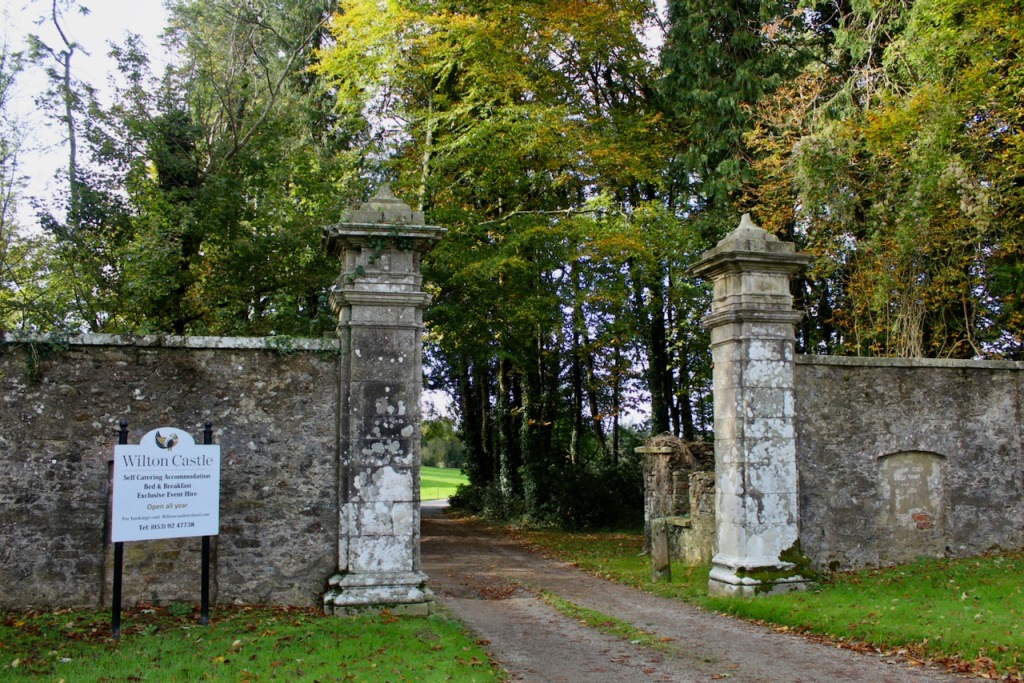
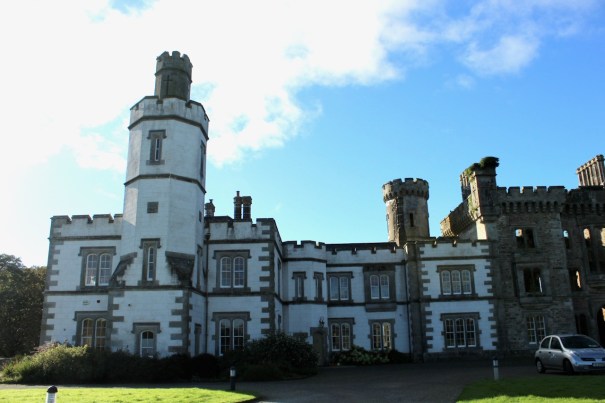
17. Wilton Castle, Bree, Enniscorthy, Co. Wexford Y21 V9P9 – section 482 accommodation
www.wiltoncastleireland.com
Open for accommodation: all year
See my write-up: www.irishhistorichouses.com/2022/02/04/wilton-castle-bree-enniscorthy-co-wexford-and-a-trip-to-johnstown-castle/

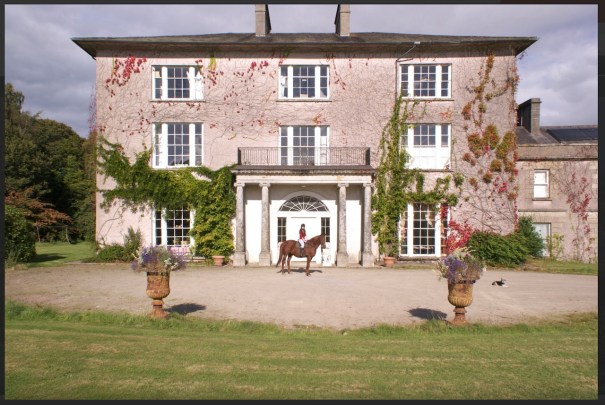
18. Woodbrook House, Killanne, Enniscorthy, Co. Wexford – B&B
See my entnry https://irishhistorichouses.com/2025/03/13/woodbrook-killanne-enniscorthy-co-wexford-y21-tp-92-section-482-accommodation/

The Historic Houses of Ireland website tells us:
“Nestling beneath the Backstairs Mountains near Enniscorthy in County Wexford, Woodbrook, which was first built in the 1770s, was occupied by a group of local rebels during the 1798 rebellion. Allegedly the leader was John Kelly, the ‘giant with the gold curling hair’ in the well known song ‘The Boy from Killanne’. It is said that Kelly made a will leaving Woodbrook to his sons but he was hanged on Wexford bridge, along with many others after the rebels defeat at Vinegar Hill. He was later given an imposing monument in nearby Killanne cemetery.
“Arthur Jacob, who originally came from Enniscorthy and became Archdeacon of Armagh, built Woodbrook for his daughter Susan, who had married Captain William Blacker, a younger son of the family at Carrigblacker near Portadown. The house was badly knocked about by the rebels and substantially rebuilt in about 1820 as a regular three storey Regency pile with overhanging eaves, a correct Ionic porch surmounted by a balcony and three bays of unusually large Wyatt windows on each floor of the facade.“
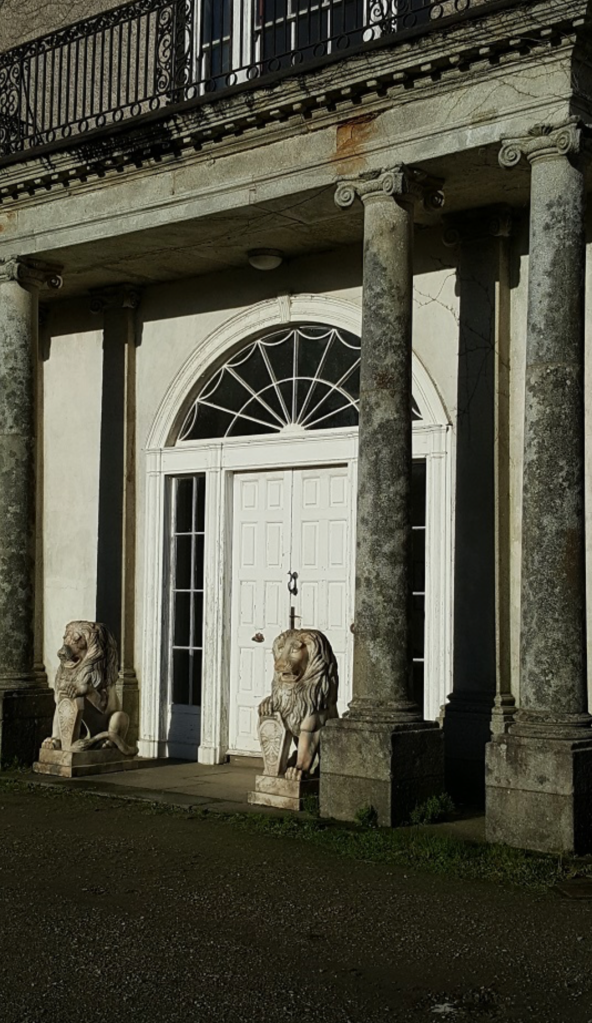


“Woodbrook lay empty for some years after E. C. Blacker’s death in 1932. The house was occupied by the Irish army during the Second World War and was then extensively modernised when his nephew Robert moved back to County Wexford with his wife and family after the sale of Carrickblacker in the 1950s. Eventually sold in the mid 1990s, Woodbrook and the remains of a once substantial estate was bought by Giles and Alexandra FitzHerbert in 1998. They continue to live in the house with their family today.” https://www.ihh.ie/index.cfm/houses/house/name/Woodbrook
19. Woodlands Country House, Killinierin, County Wexford B&B
https://www.woodlandscountryhouse.com
“Relax in comfortable old world charm in the heart of the Wexford Countryside at Woodlands Country House, a magnificently well preserved Georgian House with beautiful antiques. It is a charming and intimate place to relax, where fine food and furnishings are matched by warm and impeccable service that says you are special.
“Woodlands Country House Bed & Breakfast is ideally situated near the market town of Gorey and the picturesque seaside resort of Courtown Harbour on the Wexford/Wicklow border in South East Ireland. The Country House B&B is only 1 hour from Dublin off the M11 making it an ideal location for touring the South East of Ireland.“
Whole House rental County Wexford:
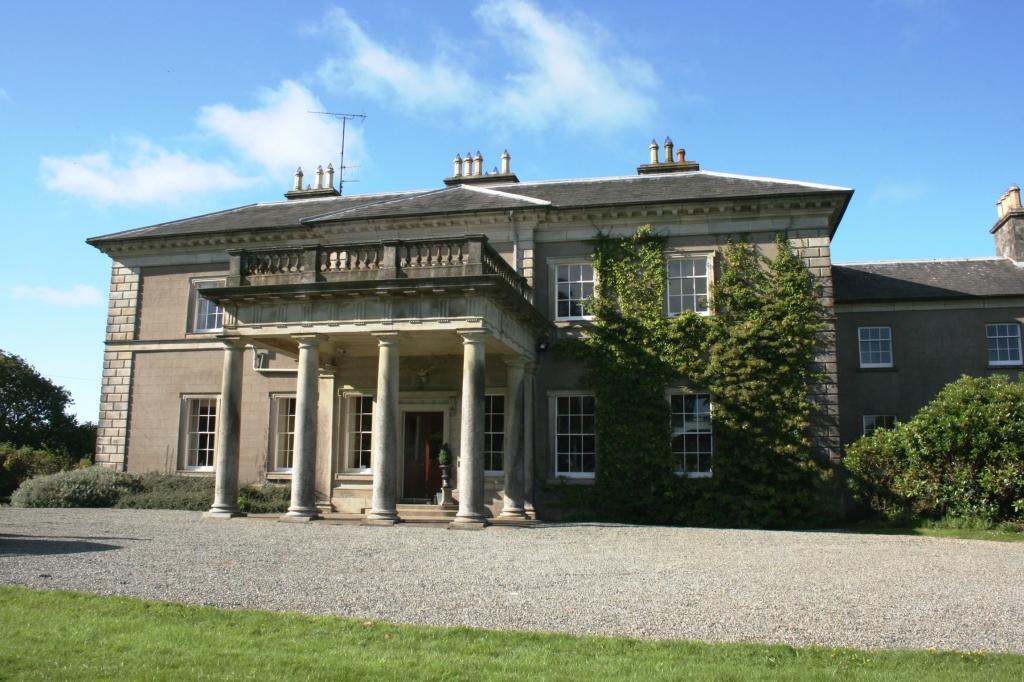
1. Ballinkeele, whole house rental (sleeps up to 19 people)


The website says:
“Make yourselves comfortable in your grand home from home. This Irish country house was built to entertain and is perfect for gathering family & friends together for a holiday, a special birthday or anniversary. With 7 bedrooms and dining table for 19 guests – there’s space for everyone. You’ll be the hero for booking Ballinkeele!
“Built in the 1840s by your host’s family, it’s a the perfect blend of modern and antique with a bespoke modern kitchen, WiFi and (Joy of Joys!) a modern heating system!”

The Historic Houses of Ireland website tells us:
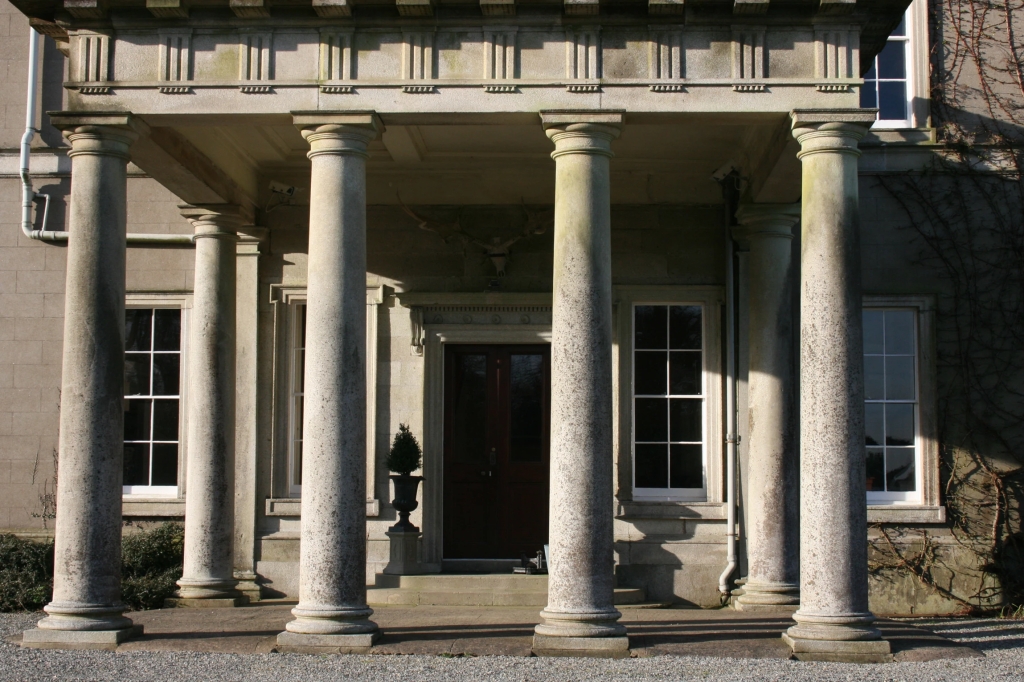
“In the first quarter of the 19th century the Maher family, who were famous for their hunting and racing exploits in County Tipperary, moved to County Wexford. They purchased Ballinkeele, near Enniscorthy, from the Hay family, one of whose members had been hanged for rebellion on Wexford bridge in 1798. John Maher, MP for County Wexford, began work on a new house in 1840 and Ballinkeele is one of Daniel Robertson’s few houses in the classical taste. The other was Lord Carew’s magnificent Castleboro, on the opposite side of the River Slaney, sadly burnt by the IRA in 1922 and now a spectacular ruin.
“The house is comprised of a ground floor and a single upper storey, with a long, slightly lower, service wing to one side in lieu of a basement. The facades are rendered with cut-granite decoration, including a grandiose central porch, supported by six Tuscan columns and surmounted by an elaborate balustrade, which projects to form a porte cochère.”

“The garden front has a central breakfront with a shallow bow, flanked by wide piers of rusticated granite. These are repeated at each corner as coigns.
“The interior is classical, with baroque overtones, and is largely unaltered with most of its original contents. The hall runs from left to right and is consequently lit from one side, with a screen of scagliola Corinthian columns at one end and an elaborate cast-iron stove at the other.
“The library and drawing room both have splendid chimneypieces of inlaid marble in the manner of Pietro Bossi, while the fine suite of interconnecting rooms on the garden front open onto a raised terrace.”
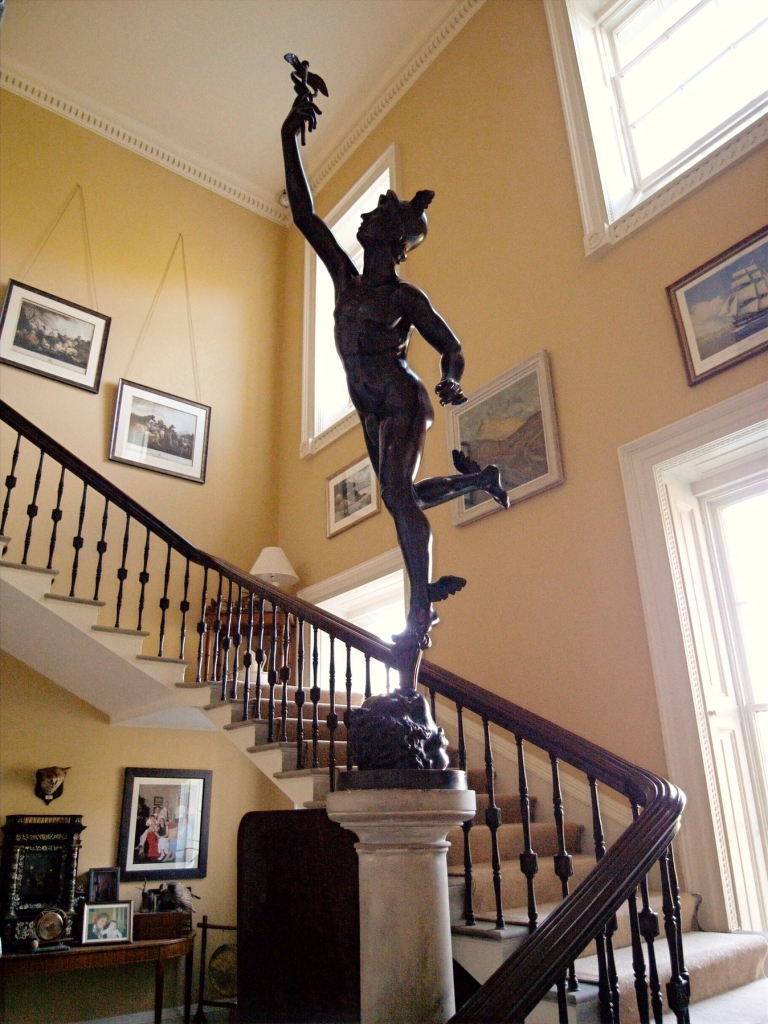
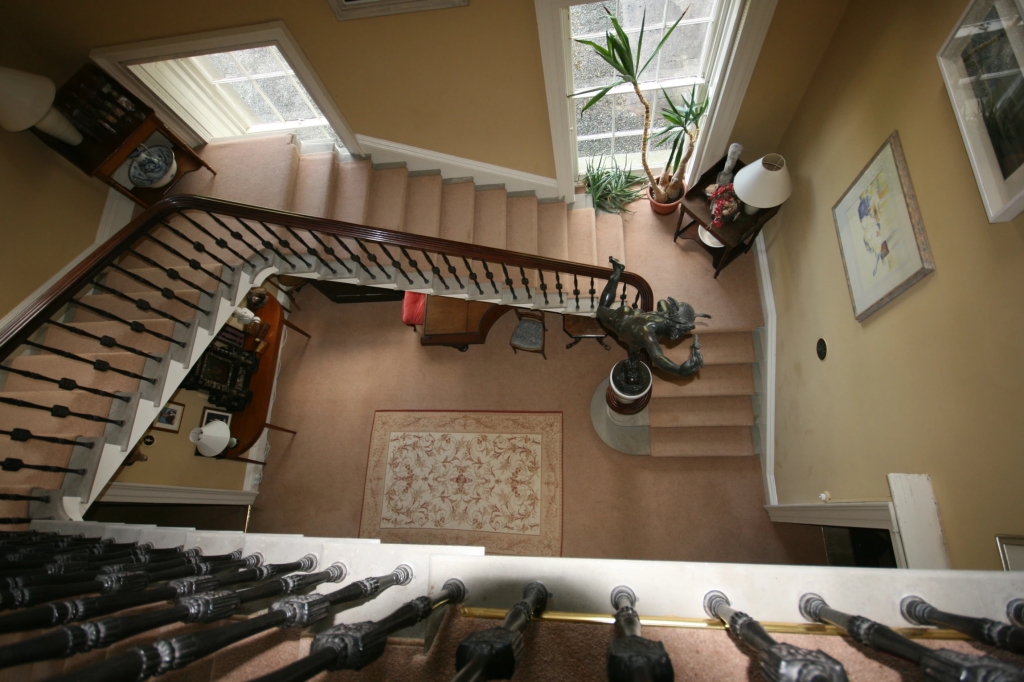


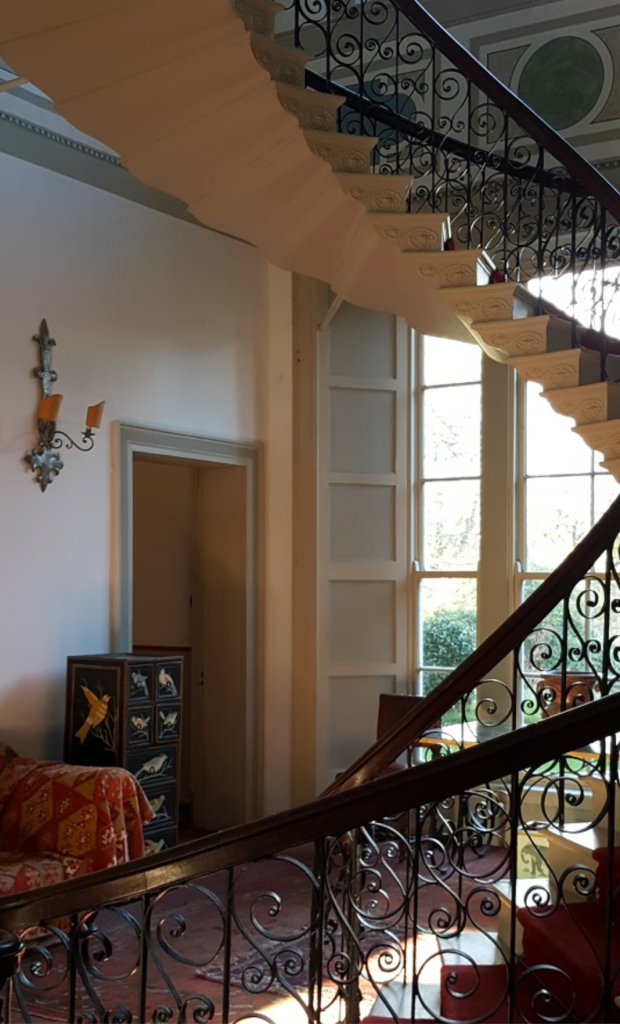
“The staircase hall has a spectacularly cantilevered stone staircase, with decorative metal balusters. As it approaches the ground floor the swooping mahogany handrail wraps itself around a Tuscan column supporting a bronze statue of Mercury, in a style that anticipates Art Nouveau by more than forty years.
“Outside, two avenues approach the house, one which provides a glimpse of a ruined keep reflected in an artificial lake, while both entrances were built to Robertson’s designs.
The present owners are Valentine and Laura Maher who live at Ballinkeele with their children.”
[ https://www.ihh.ie/index.cfm/houses/house/name/Ballinkeele ]





2. Horetown House, County Wexford (wedding venue, up to 24 people in house, plus shepherd’s huts)
The website tells us:

“Horetown House is a private country house wedding venue in County Wexford in the South-East corner of Ireland. Situated among rolling hills in the heart of rural Wexford, Horetown House is the perfect venue for a stylish, laid back wedding. Our charming country house is yours exclusively for the duration of your stay with us.
“Family owned and run, we can take care of everything from delicious food, bedrooms and Shepherds huts, to a fully licensed pub in the cellar. Horetown House is perfect for couples looking for something a little bit different, your very own country house to create your dream wedding.“
Mark Bence-Jones writes (1988): p. 155. “(Davis-Goff, Bt/PB) A three storey Georgian house. Front with two bays on either side of a recessed centre. Triple windows in centre and pillared portico joining the two projections.”
The National Inventory tells us it is:
“A country house erected to designs signed (1843) by Martin Day (d. 1861) of Gallagh (DIA; NLI) representing an important component of the mid nineteenth-century domestic built heritage of County Wexford with the architectural value of the composition, one succeeding a seventeenth-century house (1693) annotated as “Hoarstown [of] Goff Esquire” by Taylor and Skinner (1778 pl. 149), confirmed by such attributes as the deliberate alignment maximising on panoramic vistas overlooking gently rolling grounds; the symmetrical frontage centred on a pillared portico demonstrating good quality workmanship in a silver-grey granite; the diminishing in scale of the openings on each floor producing a graduated visual impression; and the parapeted roofline. Having been well maintained, the elementary form and massing survive intact together with substantial quantities of the original fabric, both to the exterior and to the interior where contemporary joinery; restrained chimneypieces; and decorative plasterwork enrichments, all highlight the artistic potential of the composition. Furthermore, a nearby quadrangle erected (1846) by ‘S.D. Goff Esq Architect [and] Johnson Builder’ continues to contribute positively to the group and setting values of an estate having historic connections with the Goff family including Strangman Davis Goff (né Davis) (1810-83) ‘late of Horetown House County Wexford’ (Calendars of Wills and Administration 1883, 318); and Sir William Goff Davis Goff (1838-1918) of Glenville, County Waterford; a succession of tenants including Joseph Russell Morris (NA 1901) and Edward Naim Townsend (NA 1911); and Major Michael Lawrence Lakin DSO (1881-1960) and Kathleen Lakin (née FitzGerald) (1892-30) of Johnstown Castle.”
3. Newbay House, County Wexford – wedding venue
“A stunning period house set on its own 16 acres of gardens and woodland on the outskirts of Wexford Town and within 2 hours from Dublin.
“Newbay House has been lovingly restored to blend its historic past with a dash of contemporary elegance. Once through the doors, it shares its elegant character and friendly hospitable atmosphere that combines informality with quality.
“In addition to boasting the most intimate of atmospheres and dedication to traditional hospitality and service, this cherished period house is sure to capture your heart.“
History:
“According to Hore’s History of Wexford there was a township called ‘Newbane’ consisting of a castle and 60 acres of land in the tenure of Patrick Roche and belonging to the Prioy of Selskar situated at what we now call Newbay. Around 1641 198 acreas of land at Newbane was owned by John Roche but ended up forfeited to Cromwell and was given to one of his officers Colonel Thomas Scott who still had possession up to 1674. In 1715 Henry Hatton, a former Mayor of Wexford, owned Newbay and it remained in the Hatton family for the next century.
“Newbay House as it is now was the product of Architect John Meason whom worked on the house for Henry Hatton between June 29th 1822 and November 13th 1824. Notable additions during this time were the present front avenue and gatelodge. However by 1853 it was now owned by the Dowager Countess of Donoghmore and consisted of 138 acres leased to four tenants with Henry Lyster residing in the big house. The Countess herself lived at Belmont.
“Thomas Jefferies of Carne House purchased the house, offices and land at Newbay on Friday 16th July 1869 when he paid £1030 for it at a public auction in the Landed Estates Court in Dublin. He officially gained ownership on November 1st 1869. Jeffries added a wing to the house circa 1886. Jefferies daughter Annie Elizabeth married George Arthur French in 1899 and it was via this matrimony that the house and lands now passed to the French family.
“Circa 1952 the porch was taken down and the door was replaced by the existing front facing window. The present porch was built from the doors and windows of the old one and the same granite steps.
“Also around this time mains electricity was brought to the house and it was in 1955 that drinking water was provided from a well dug in the garden. (Prior to this it had been brought by pony and cart to Newbay from Clonard Hill).
“In 1959 a flat was made for Mrs French who was the first member of the French family to be born in Newbay – on March 11th 1870. She died September 3rd 1963.
“Mrs French was the last surviving member of the family of seven. Mrs French was described as “one of the most beautiful women in County Wexford in the last century and she retained her lovely looks right up to the end of her long and very Christian life” in her obituary in The Free Press (September 6th 1963). Mrs French’s last surviving son, Lieutenant-Colonel George French died at Newbay in 1979. Four years later his two son’s Dominic and Arthur sold the house to Paul Drumm from Dublin. Drumm opened the house and began accommodating guests and tourists.
“In 1996 Jane Coyle purchased and refurbished Newbay House, reopening its doors as a country house hotel in 1999.“

donation
Help me to pay the entrance fee to one of the houses on this website. This site is created purely out of love for the subject and I receive no payment so any donation is appreciated!
€15.00
[1] https://www.irelandscontentpool.com/en
[2] Bence-Jones, Mark. A Guide to Irish Country Houses (originally published as Burke’s Guide to Country Houses volume 1 Ireland by Burke’s Peerage Ltd. 1978); Revised edition 1988 Constable and Company Ltd, London.
[4] https://www.archiseek.com/2014/johnstown-castle-county-wexford/
Text © Jennifer Winder-Baggot, www.irishhistorichouses.com