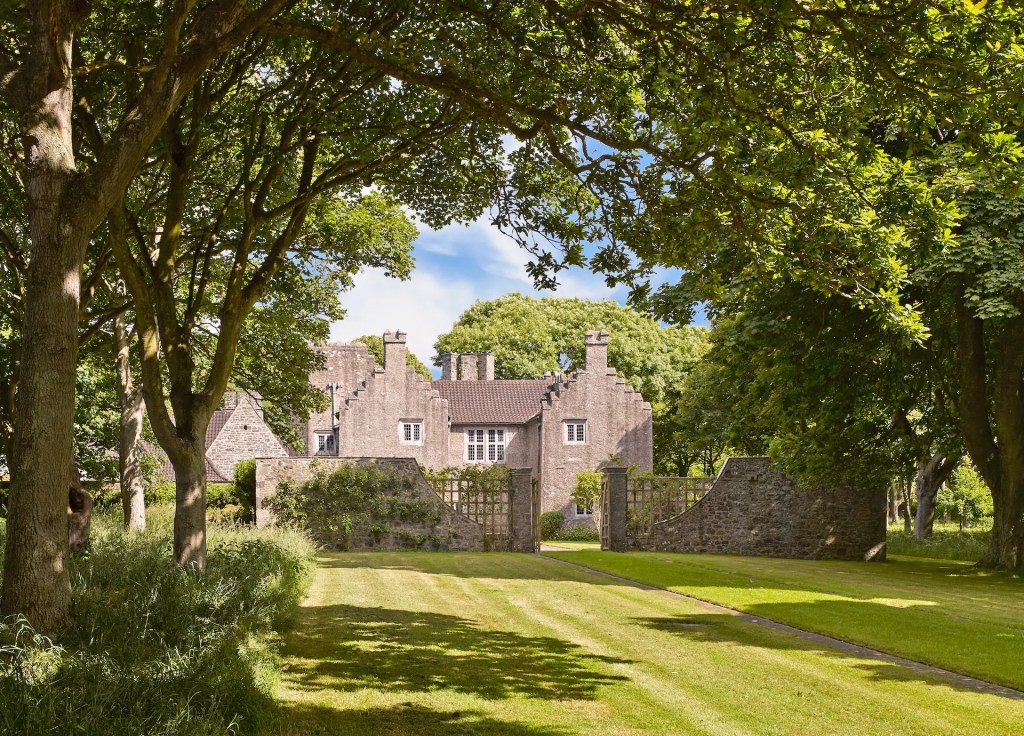
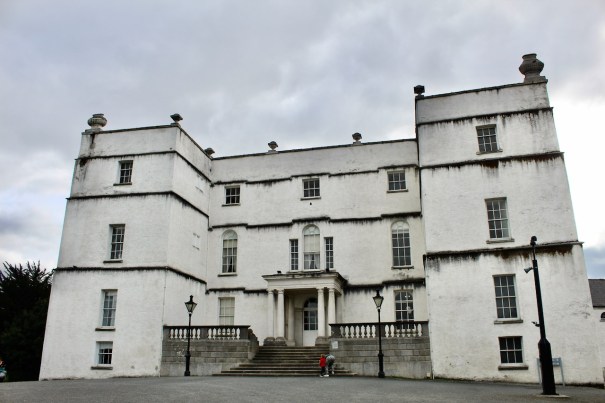
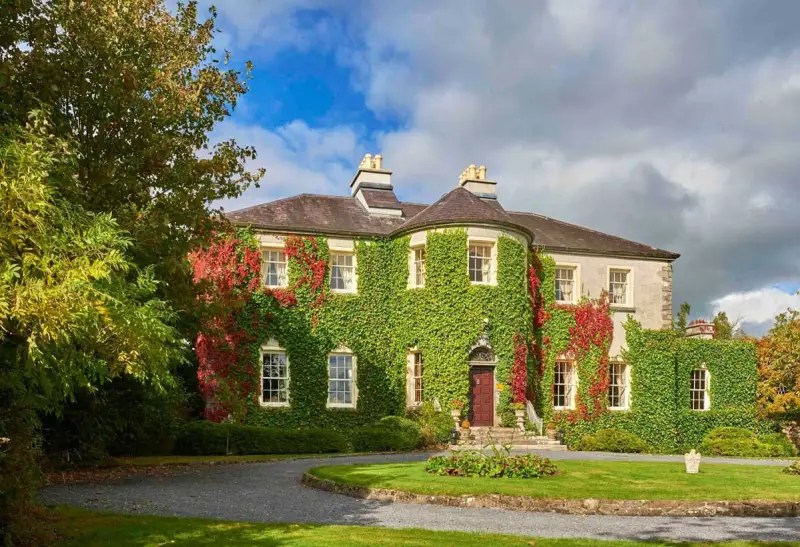
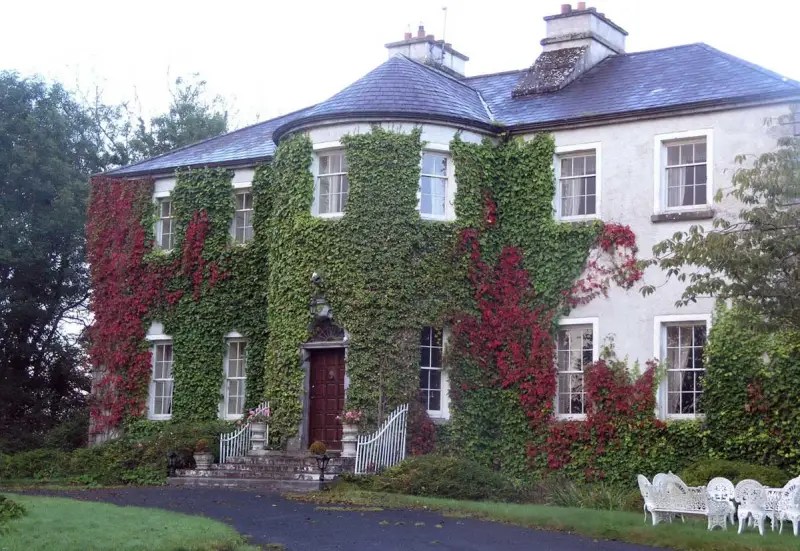
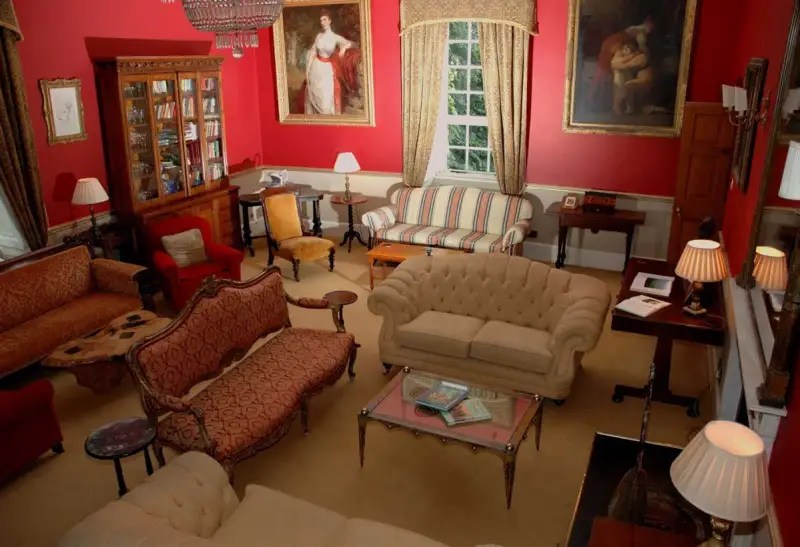
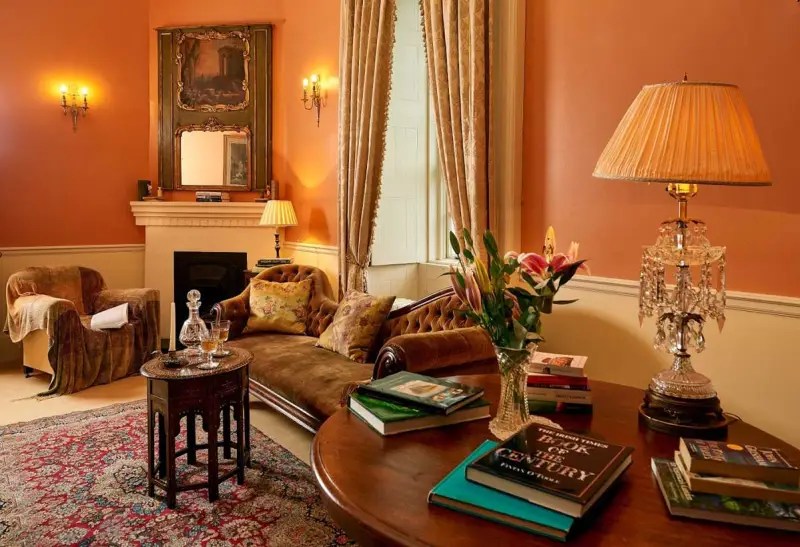
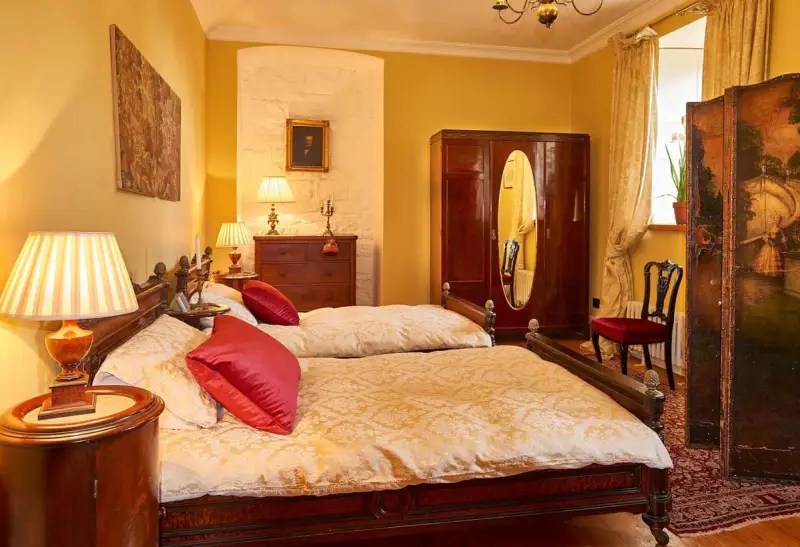
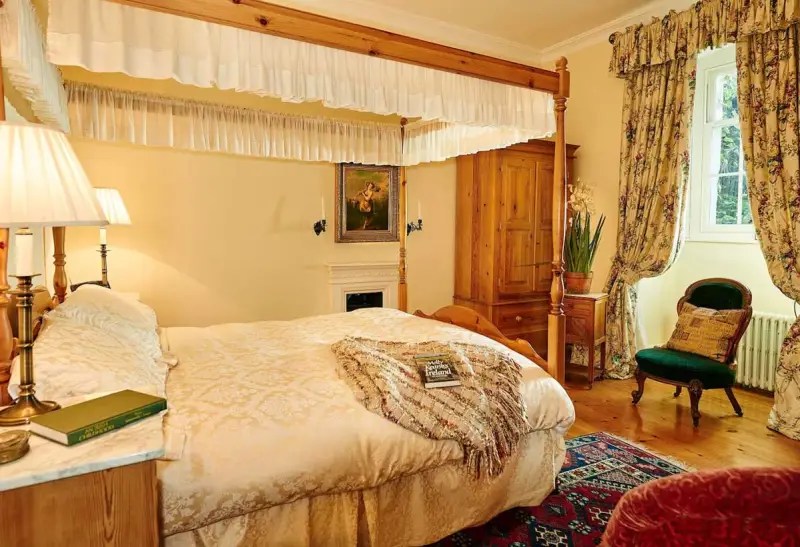
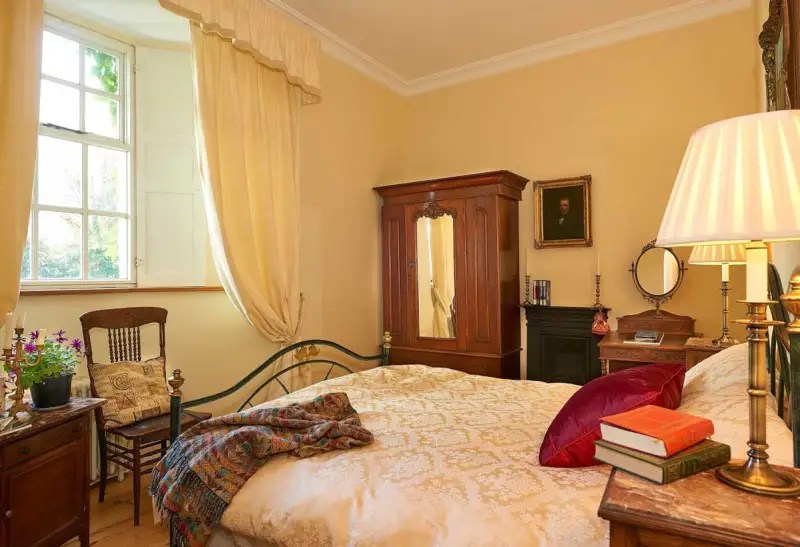
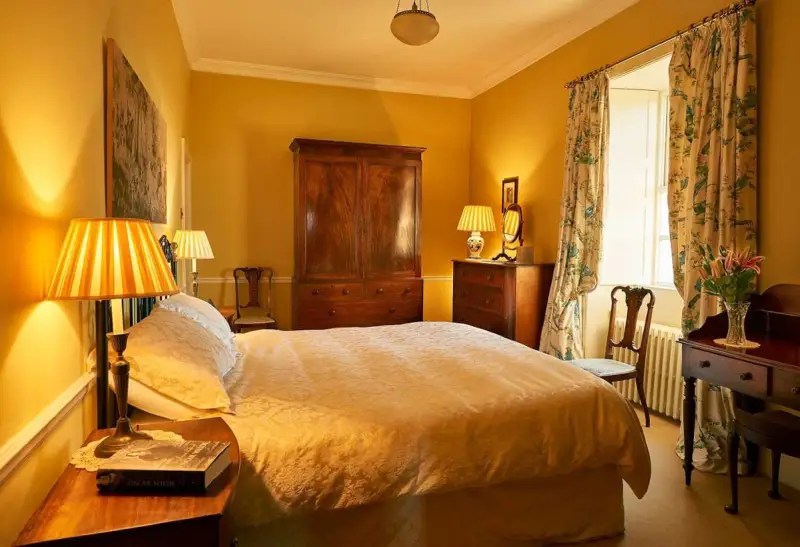
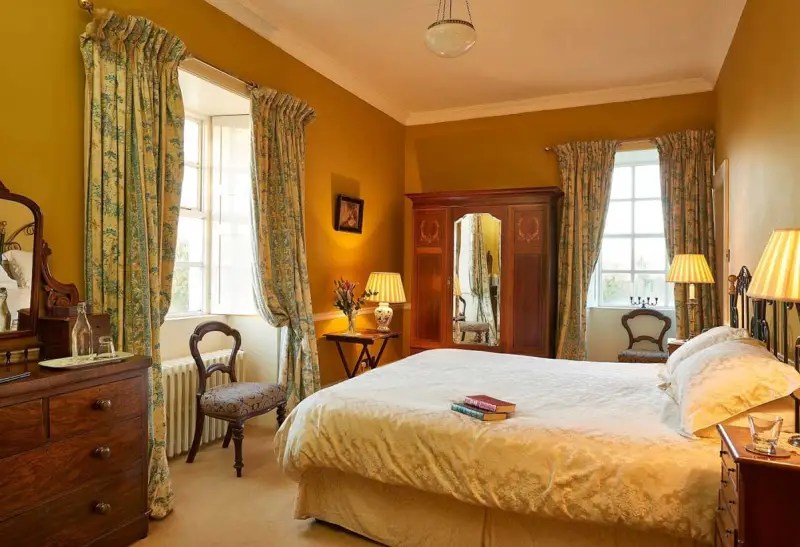
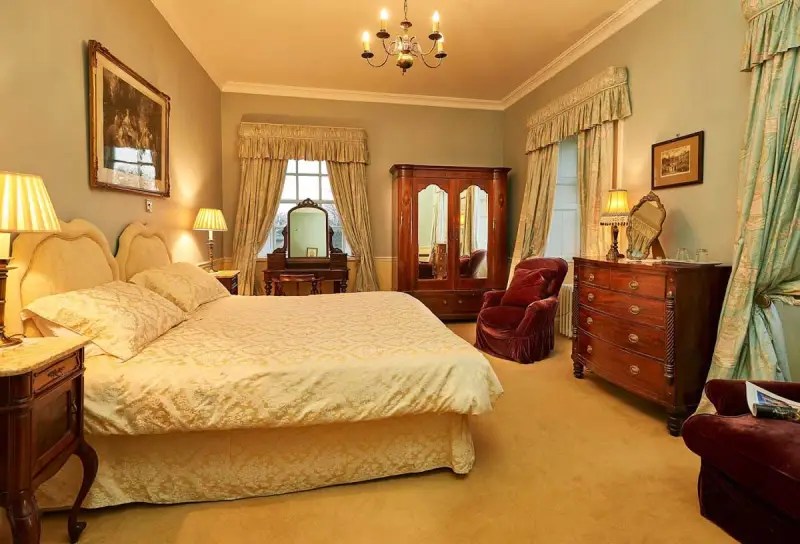
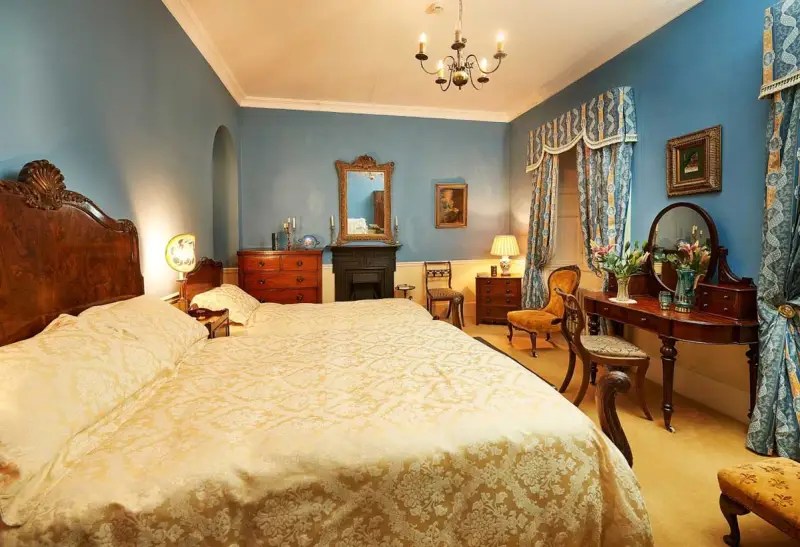
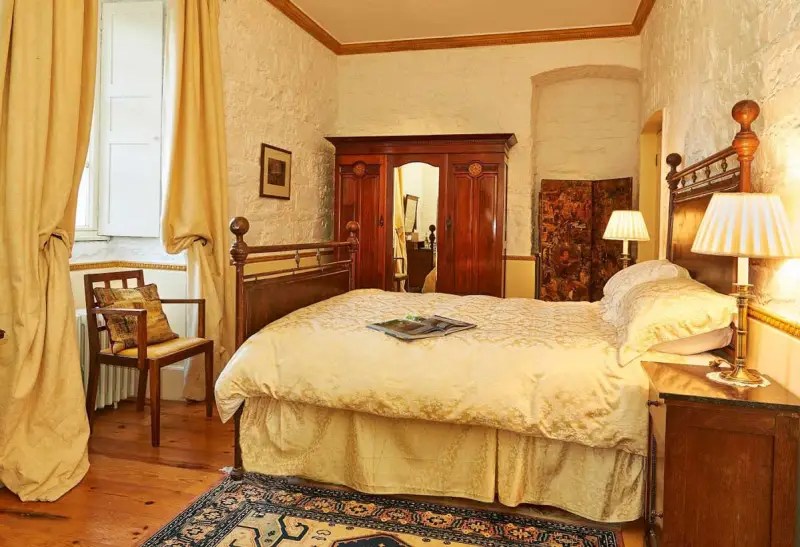
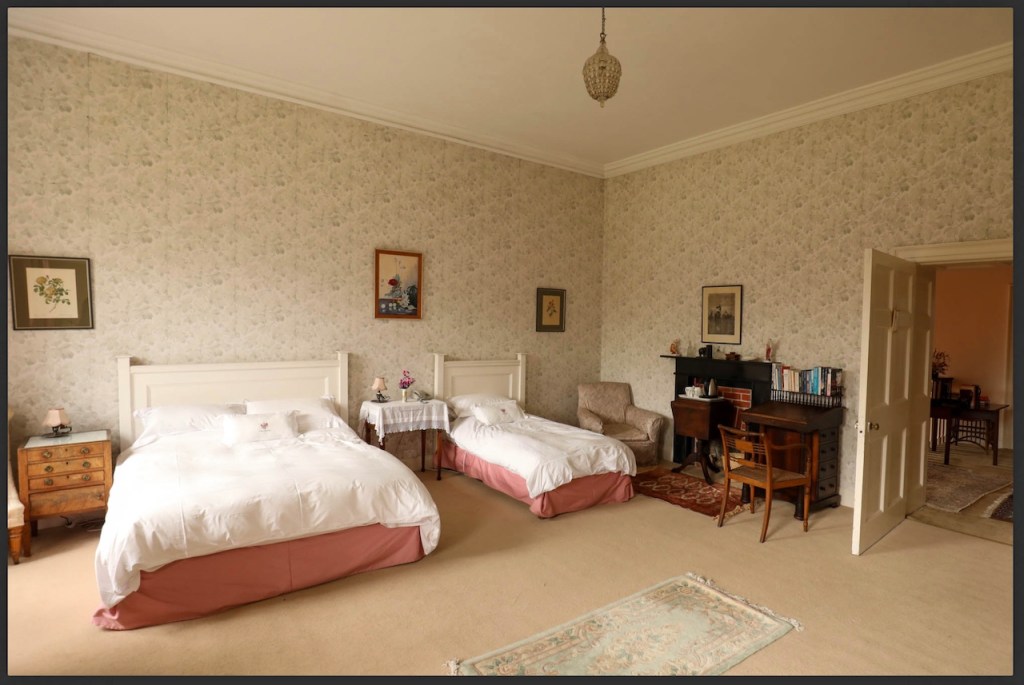
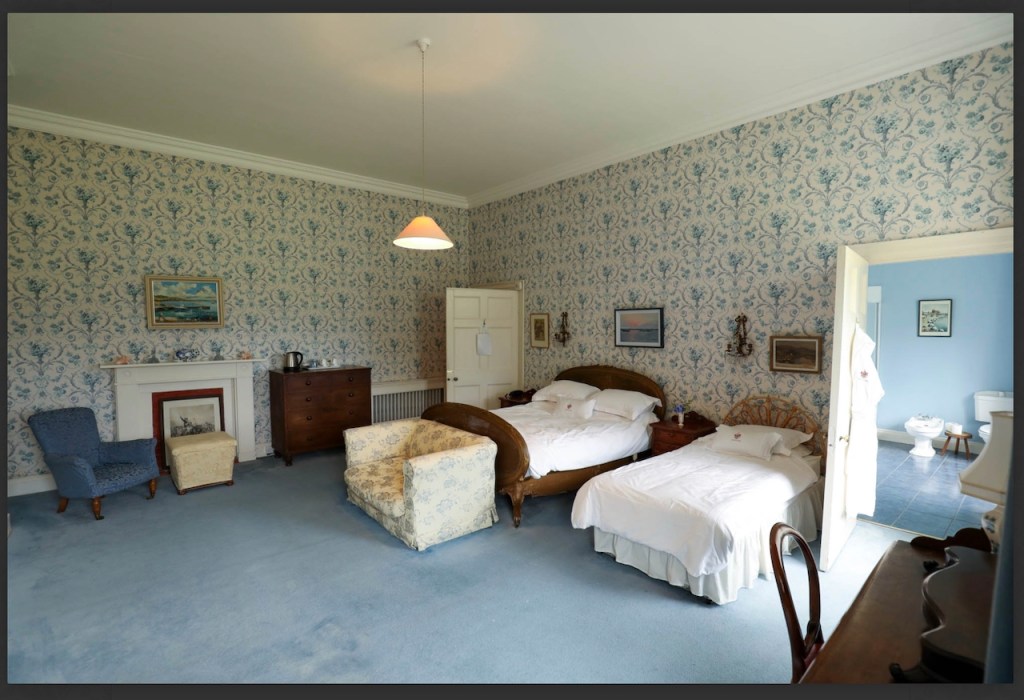
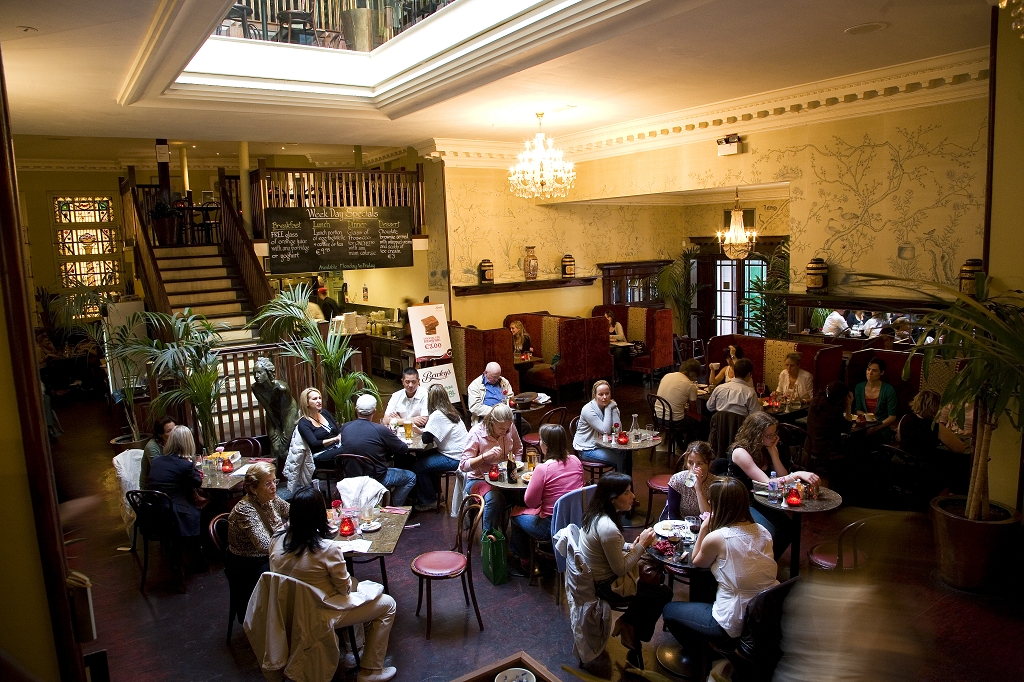
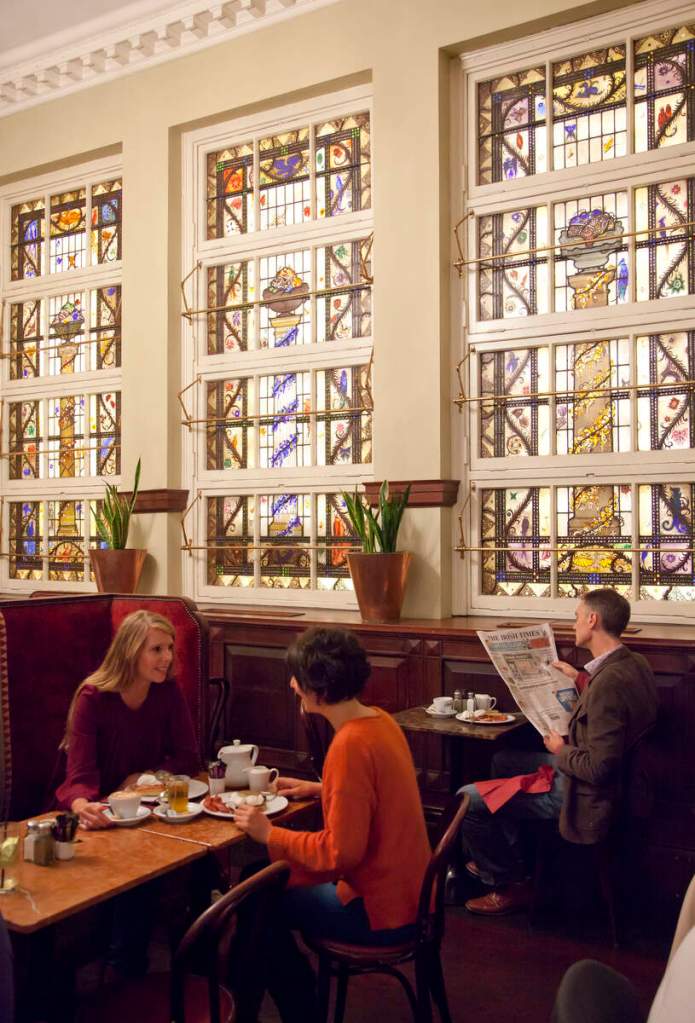
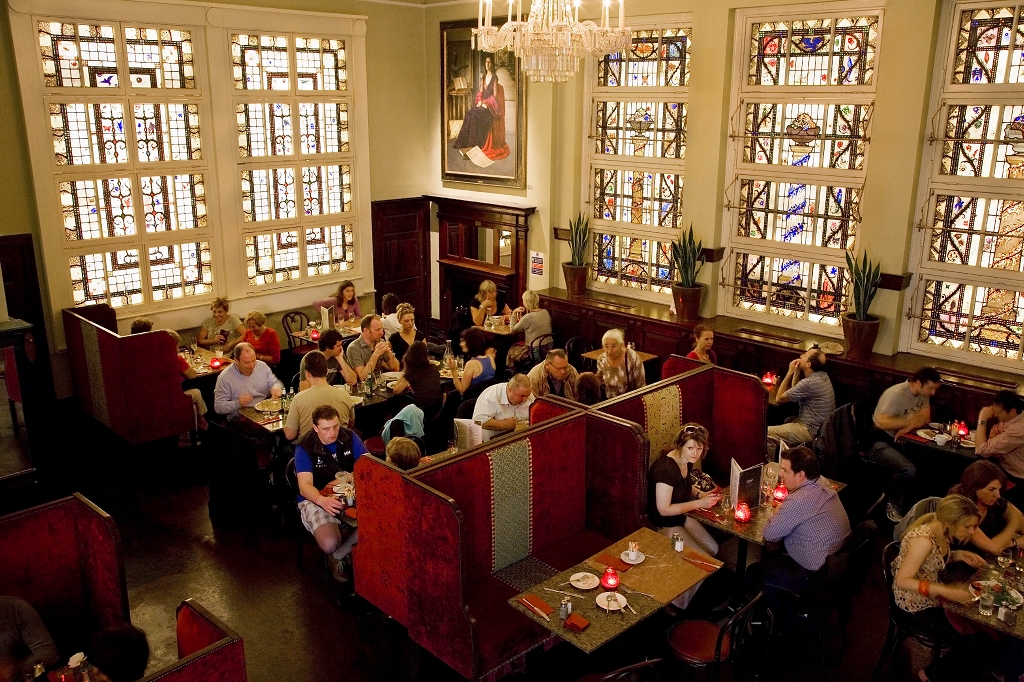
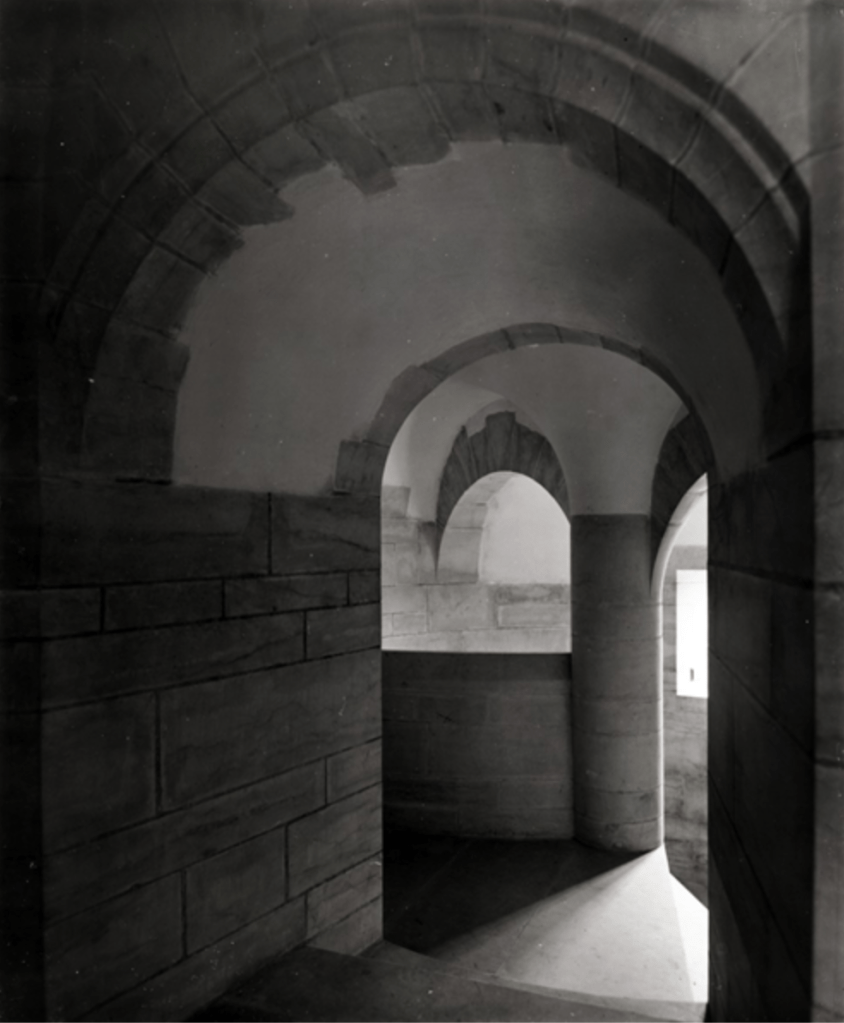
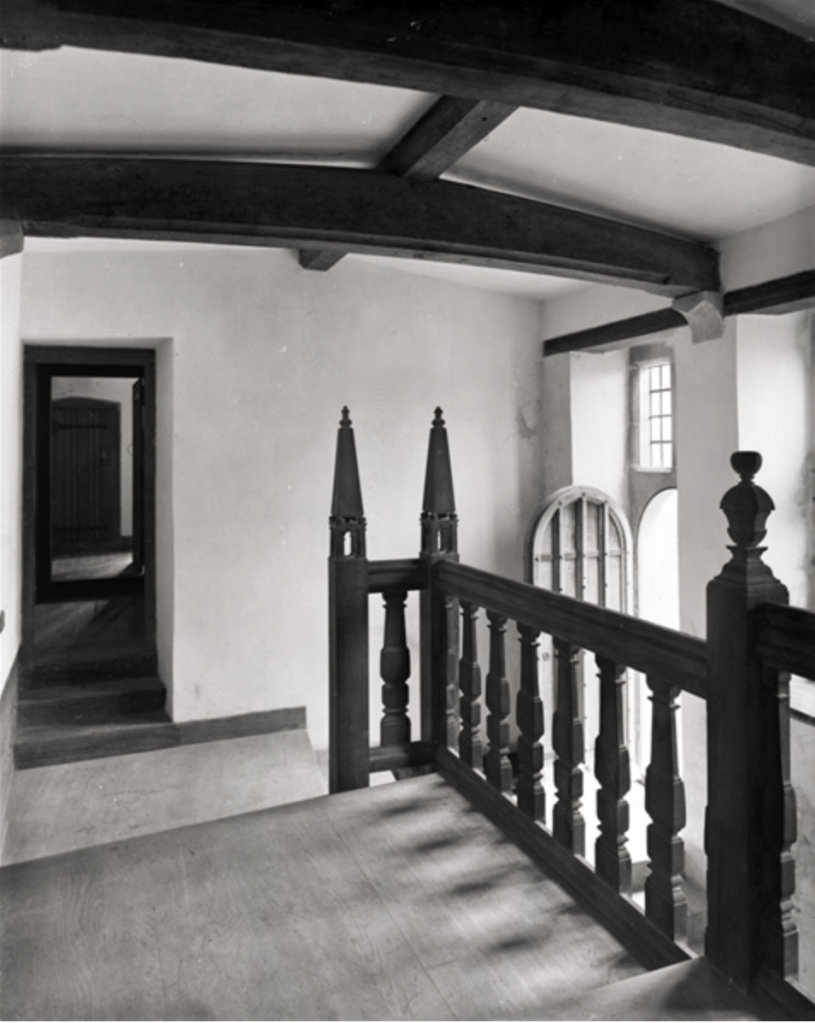
Today I am going to write about Woodbrook as it is provides holiday accommodation. In 2026, it is no longer on the Revenue Section 482 list.

donation
Help me to pay the entrance fee to one of the houses on this website. This site is created purely out of love for the subject and I receive no payment so any donation is appreciated!
€15.00
Then, below my entry, I have listed Section 482 properties that are open for a visit in March 2025!
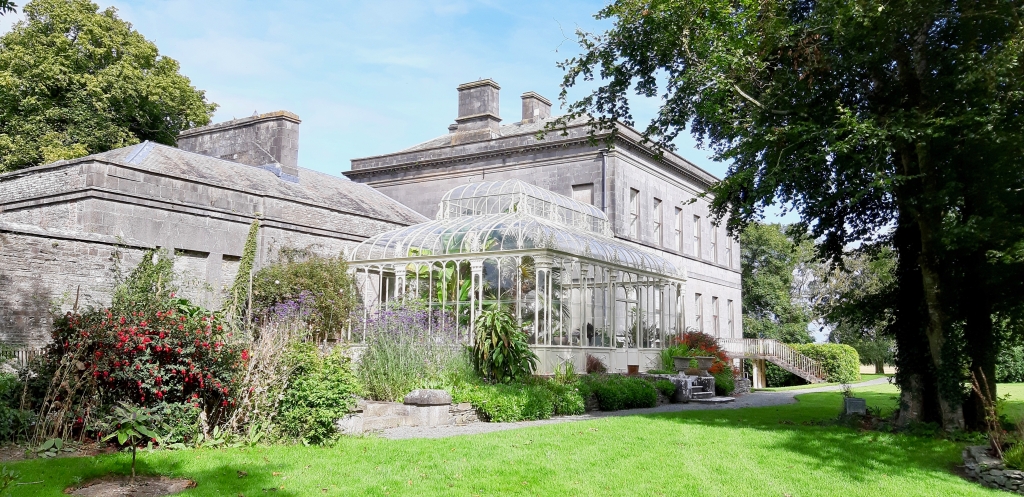
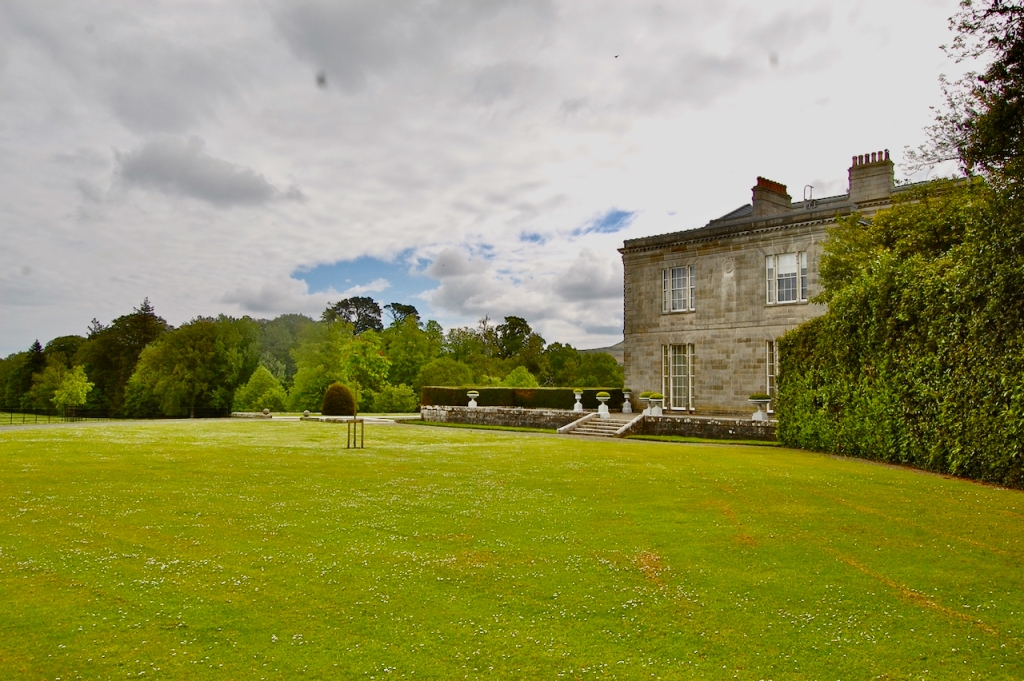
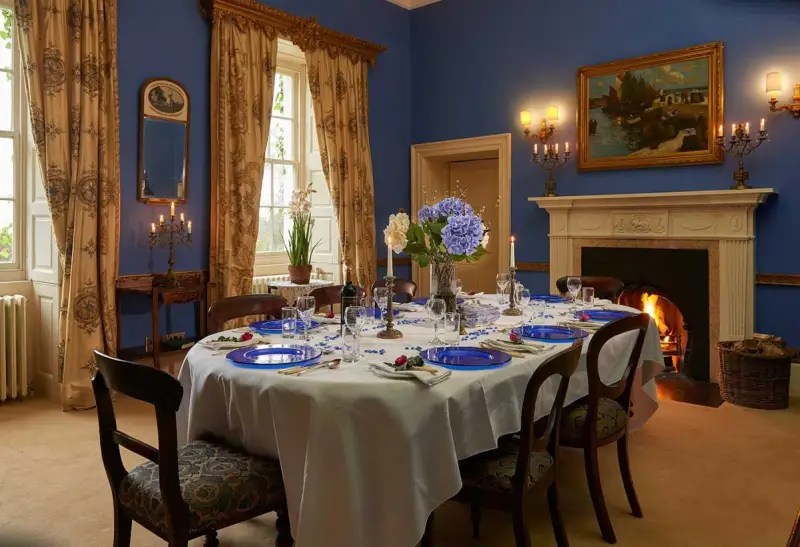
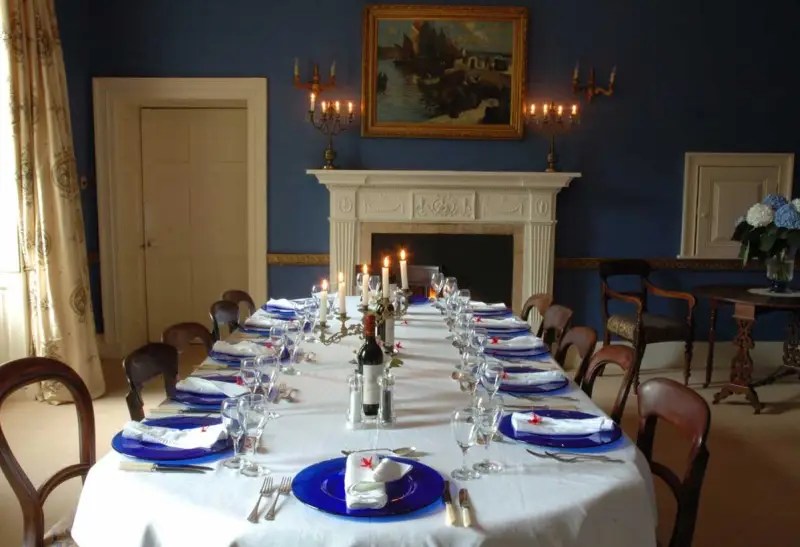
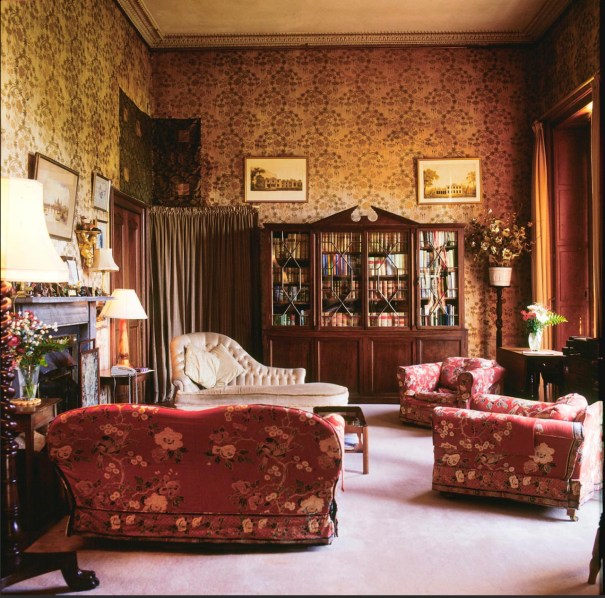
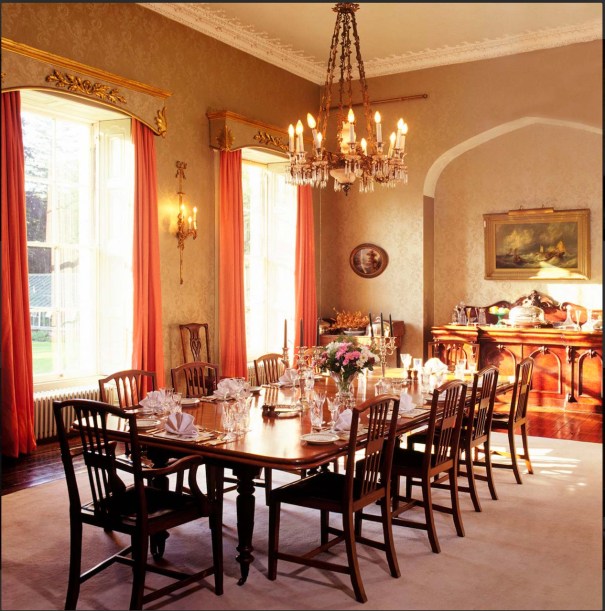
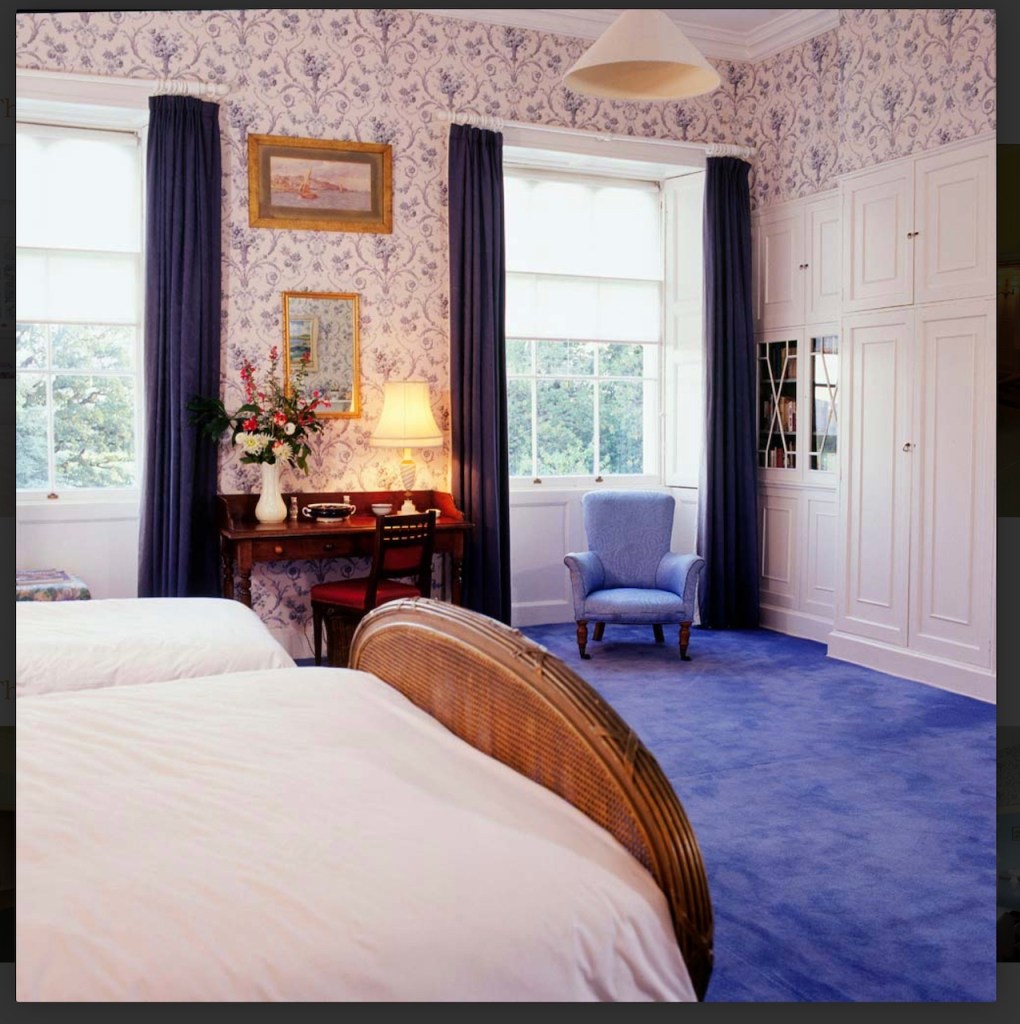
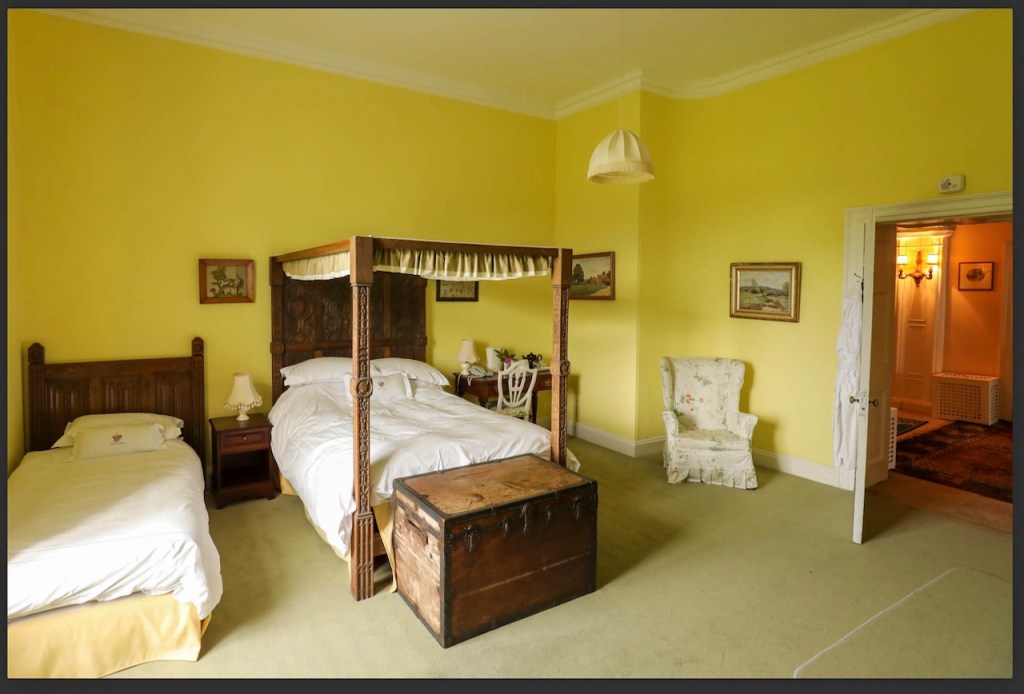
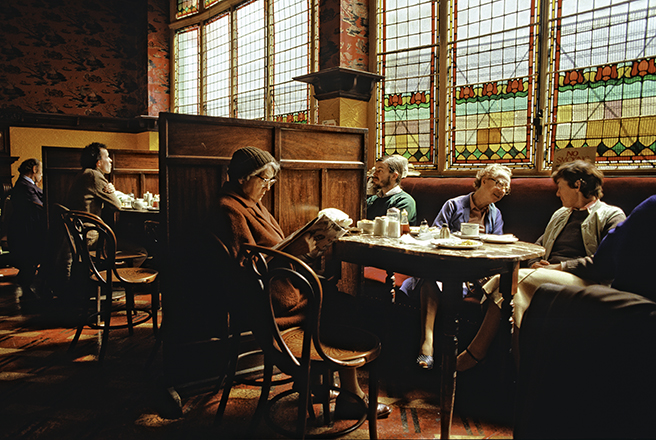
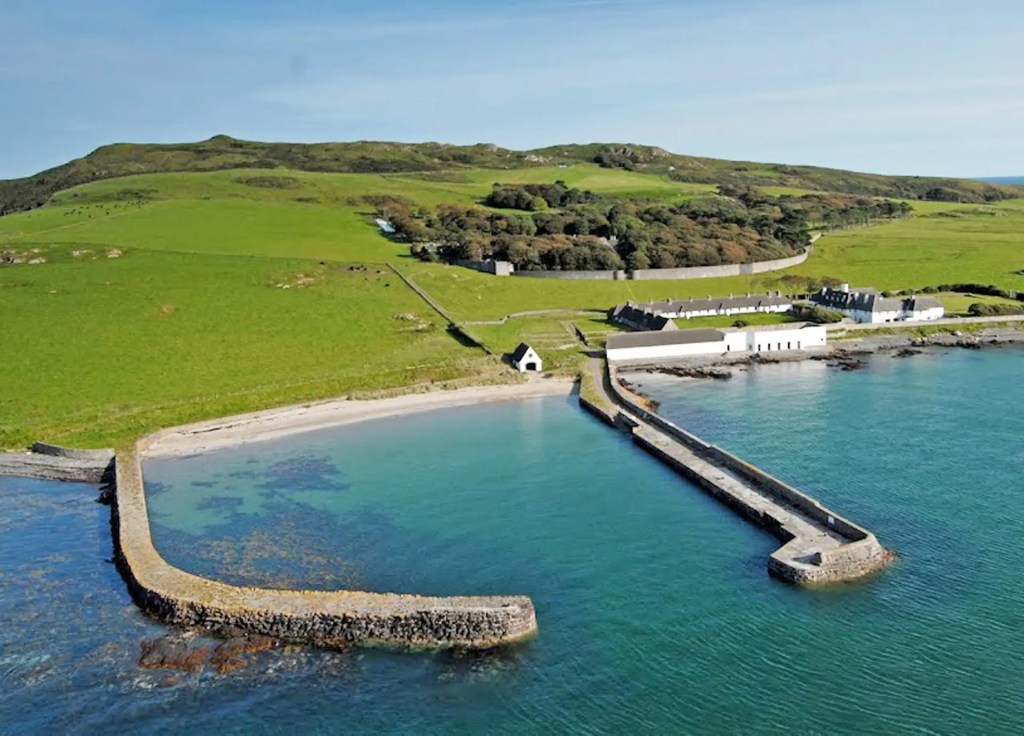
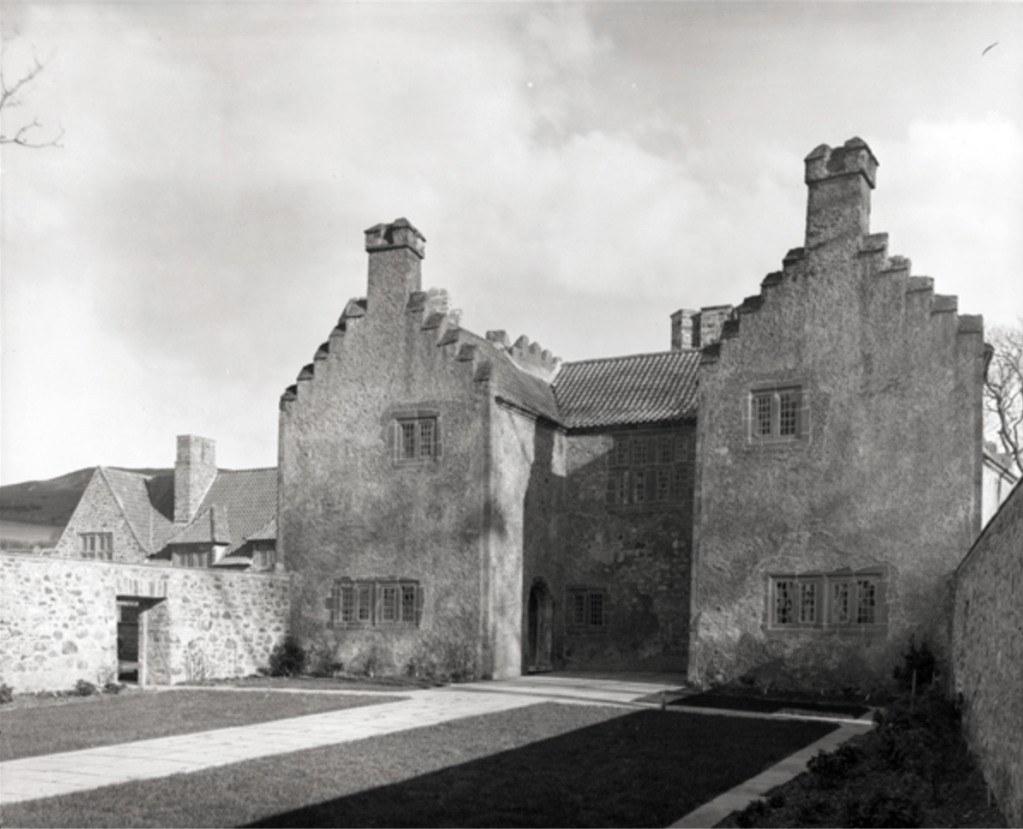
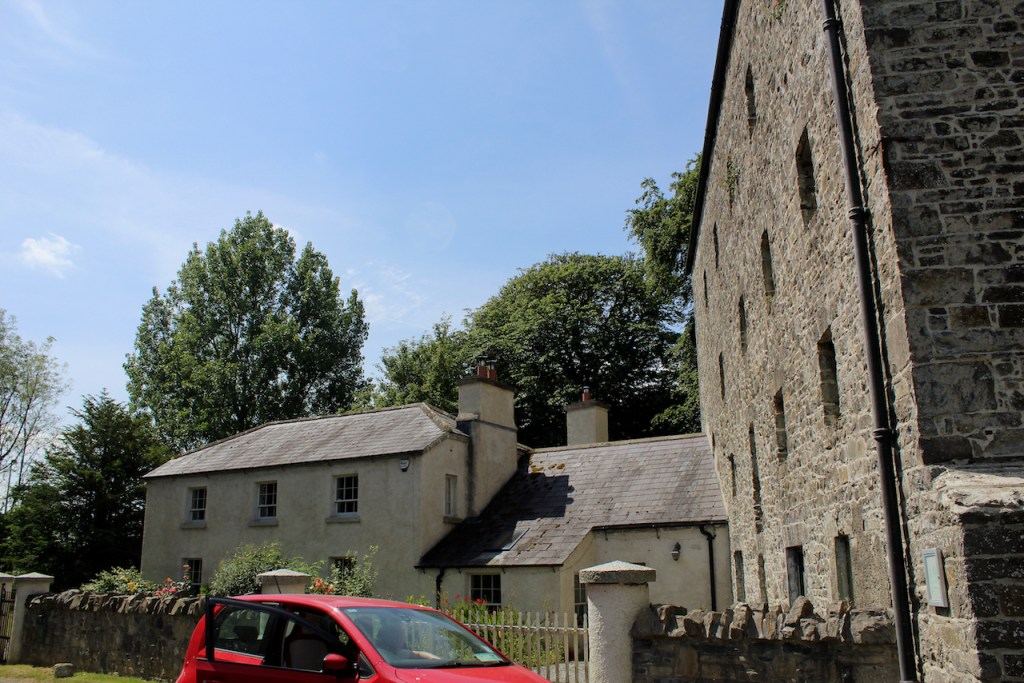
Woodbrook looks like a lovely place to stay and the hosts Giles and Alexandra Fitzherbert, who have lived there since 1998, serve dinner also if requested. Giles is a former Ambassador in South America and his wife Alexandra is of Anglo-Italian-Irish-Chilean extraction, the Hidden Ireland website tells us.
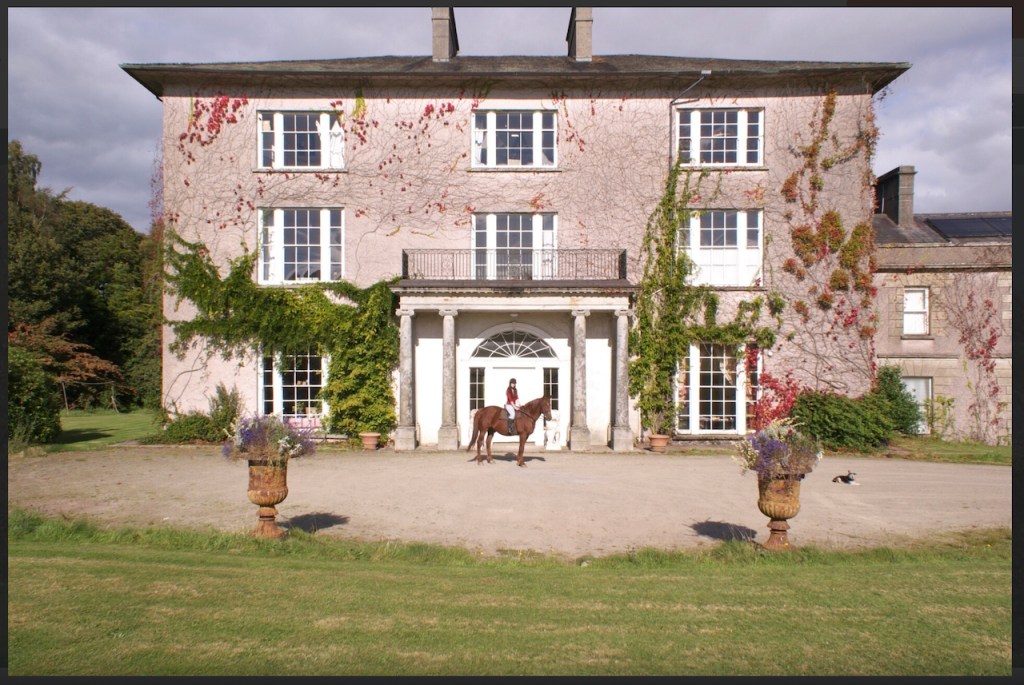

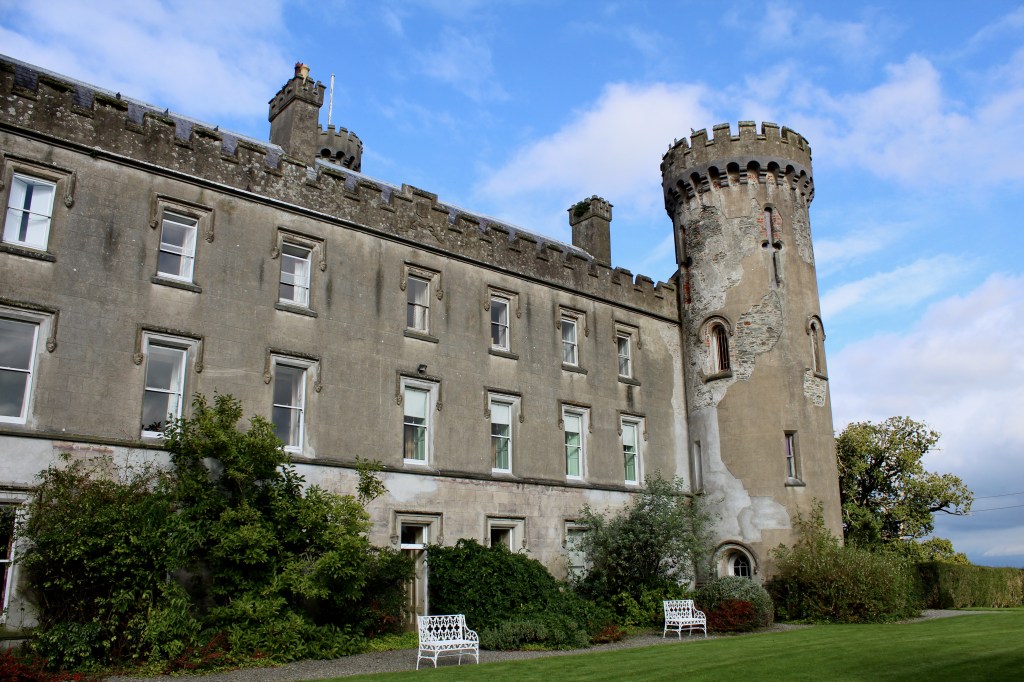
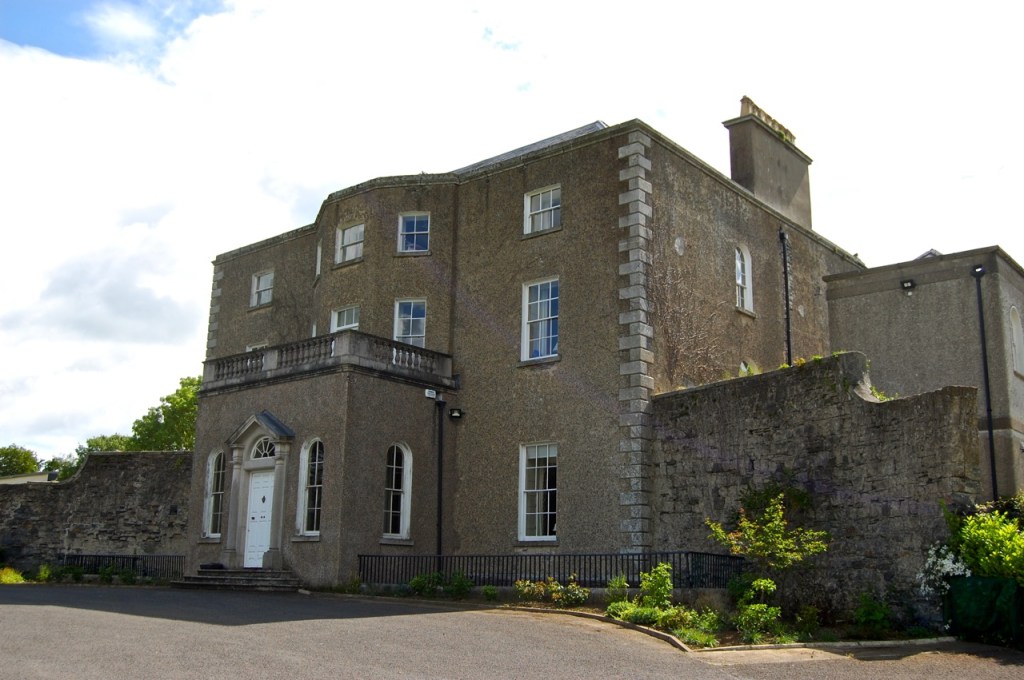
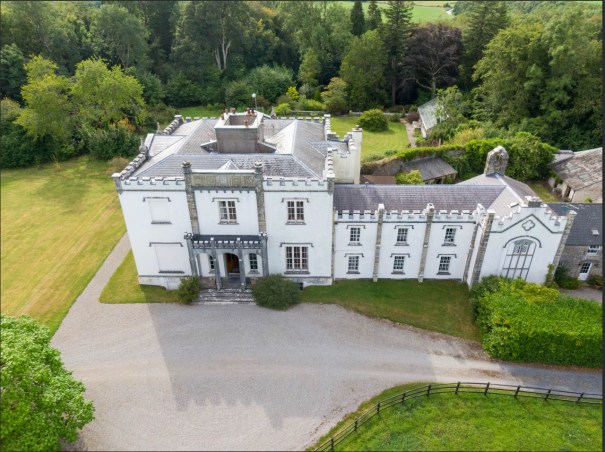
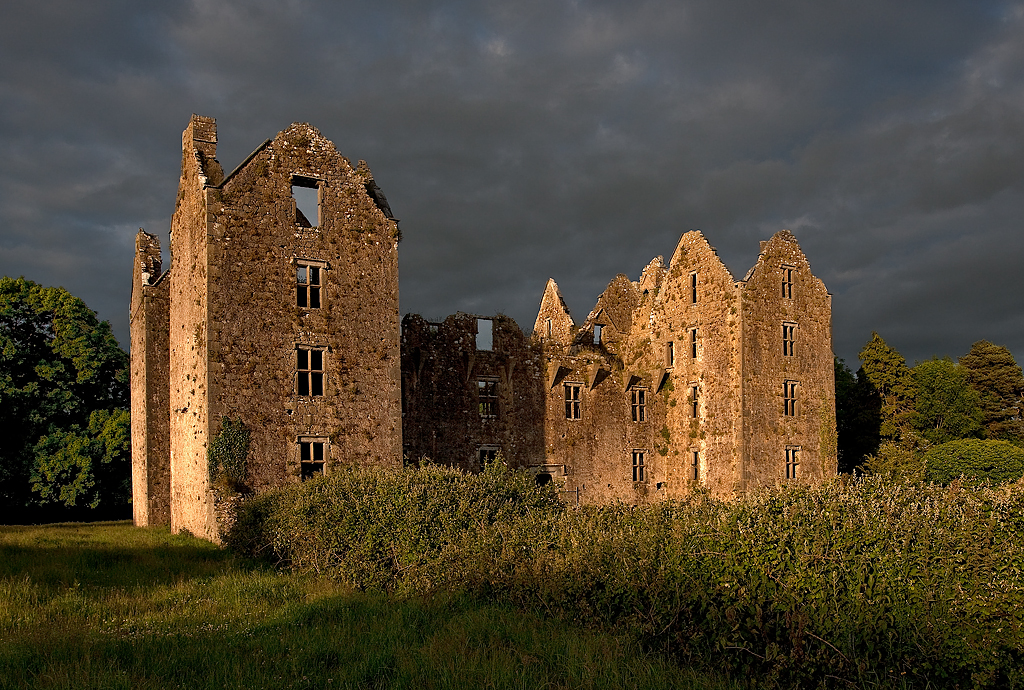
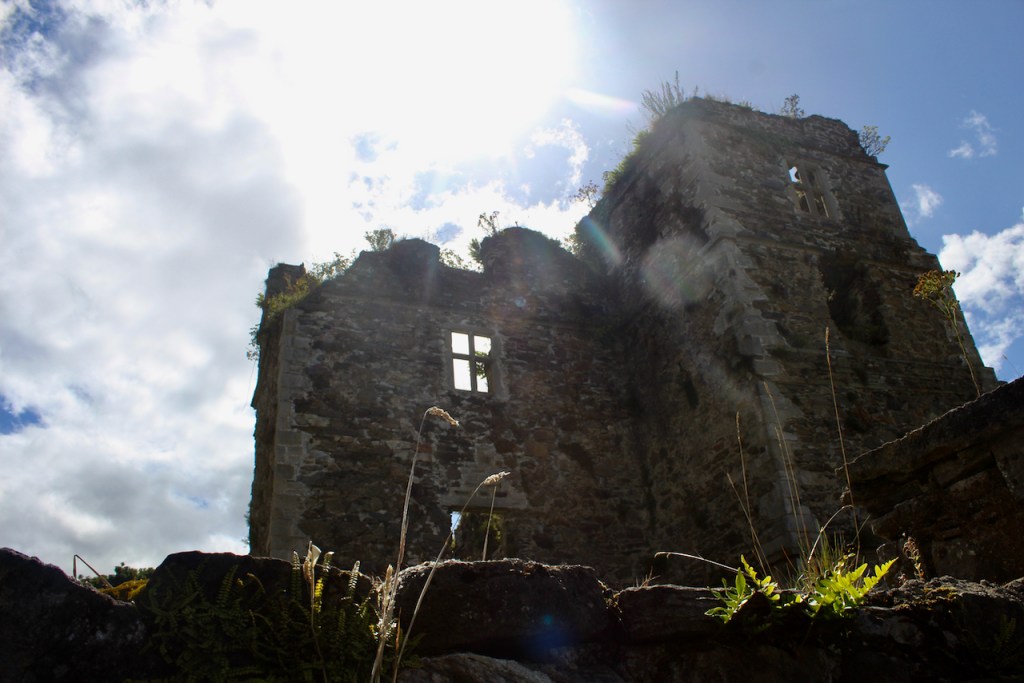
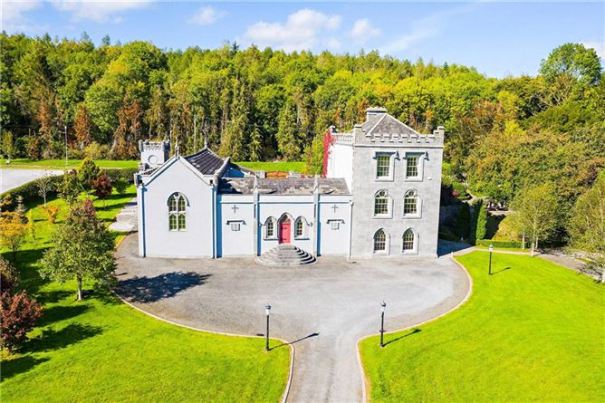
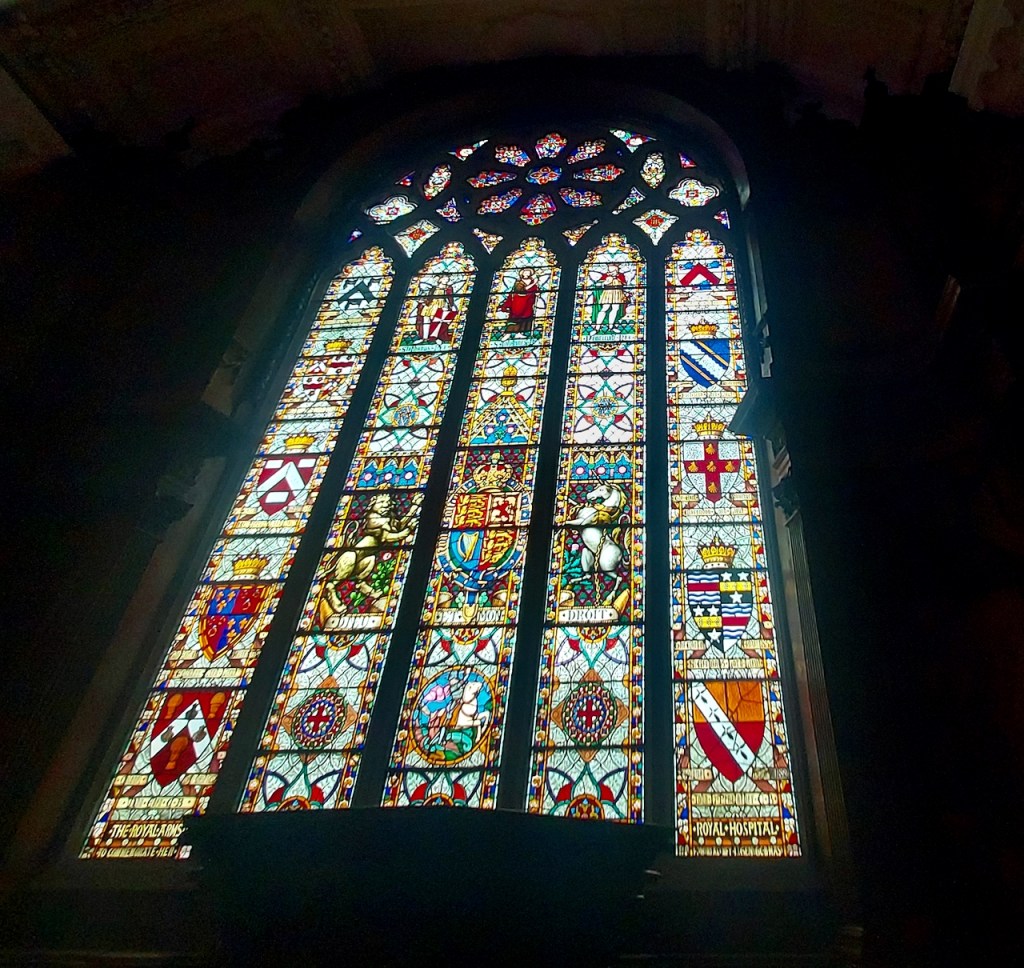
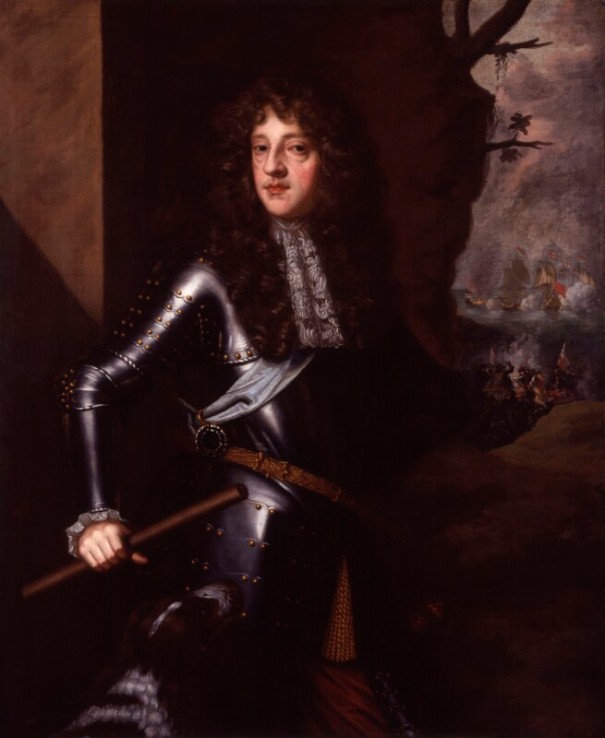
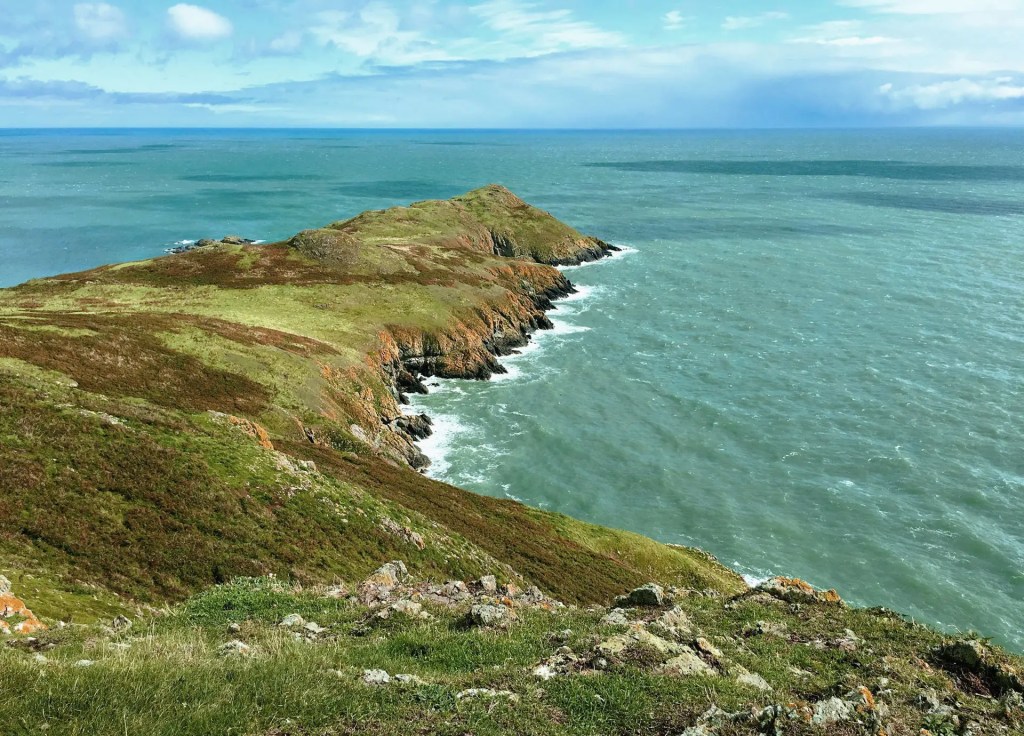
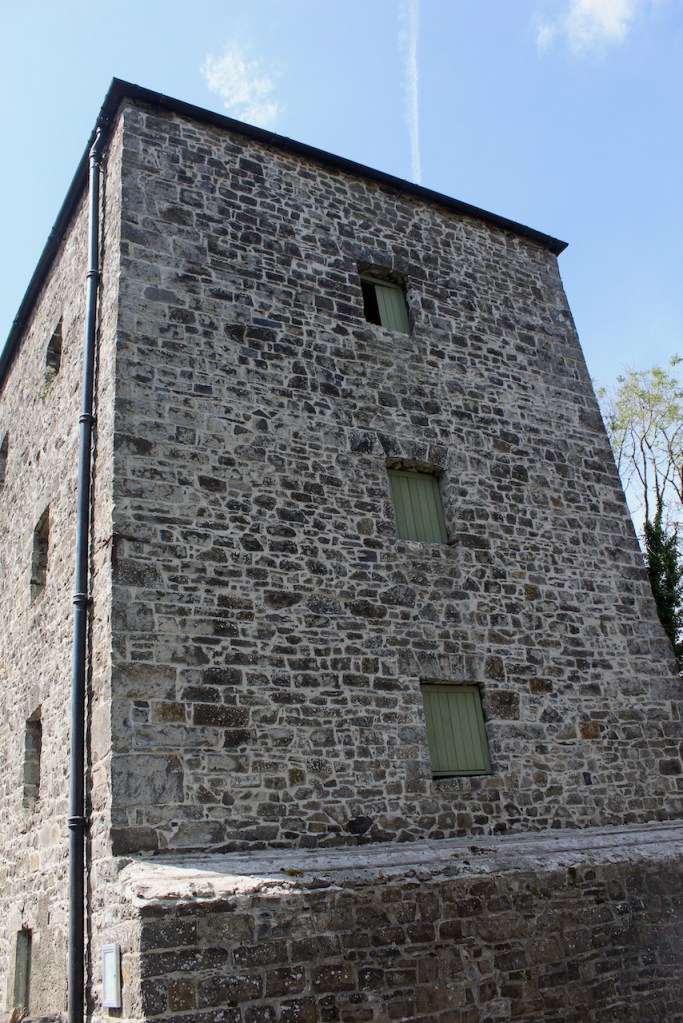
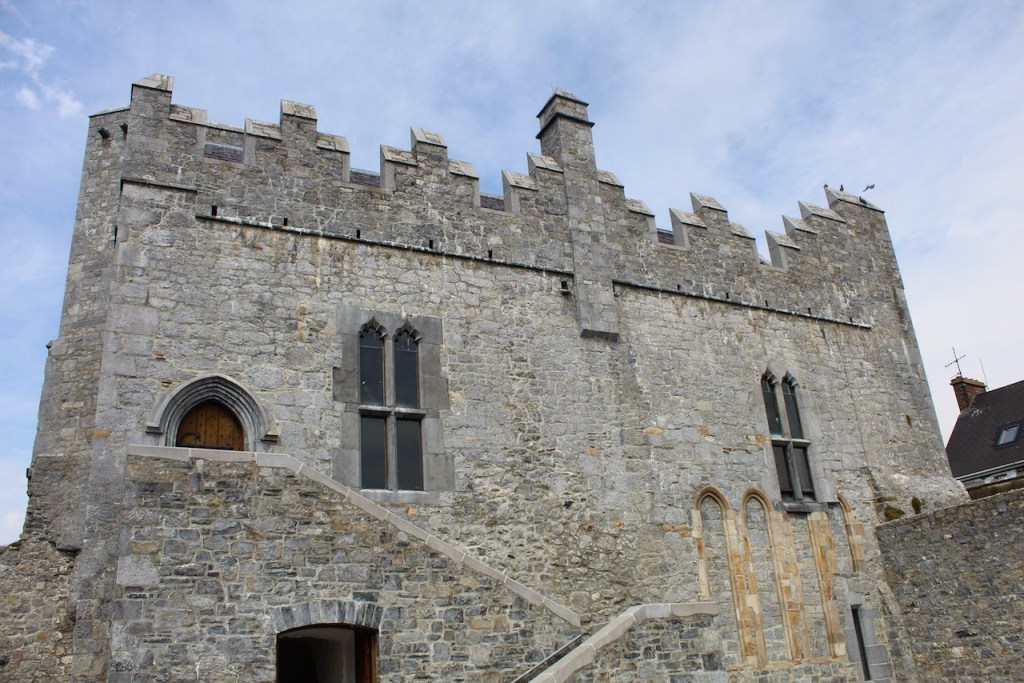
Woodbrook house was built in the 1770s. It was built by Reverend Arthur Jacob (1717-1786), Archdeacon of Armagh, for his daughter Susan and her husband Captain William Blacker, a younger son of the family at Carrigblacker near Portadown. Arthur Jacob was Rector of Killanne in County Wexford while he was also Archdeacon of Armagh. [2]
The Historic Houses of Ireland website tells us:
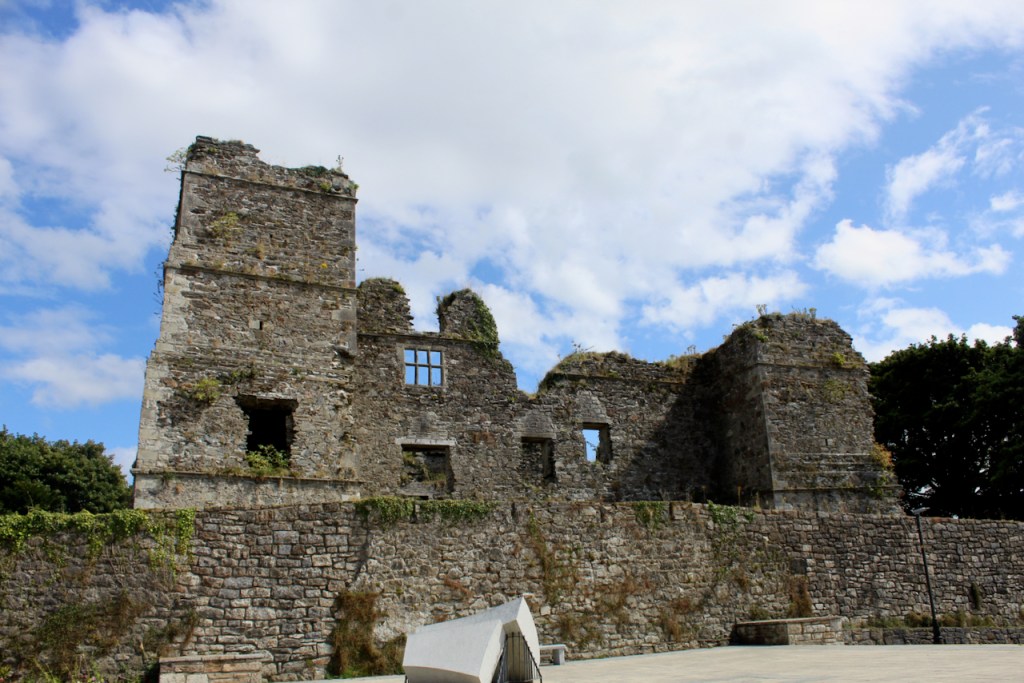
“Nestling beneath the Backstairs Mountains near Enniscorthy in County Wexford, Woodbrook, which was first built in the 1770s, was occupied by a group of local rebels during the 1798 rebellion. Allegedly the leader was John Kelly, the ‘giant with the gold curling hair’ in the well known song ‘The Boy from Killanne’. It is said that Kelly made a will leaving Woodbrook to his sons but he was hanged on Wexford bridge, along with many others after the rebels defeat at Vinegar Hill. He was later given an imposing monument in nearby Killanne cemetery.” [3]
Another rebel who occupied the house in 1798 was John Henry Colclough (c.1769-98) who was also executed for his participation in the 1798 Insurrection.
The Historic Houses of Ireland site continues:
“… The house was badly knocked about by the rebels and substantially rebuilt in about 1820 as a regular three storey Regency pile with overhanging eaves, a correct Ionic porch surmounted by a balcony and three bays of unusually large Wyatt windows on each floor of the facade.” [3]
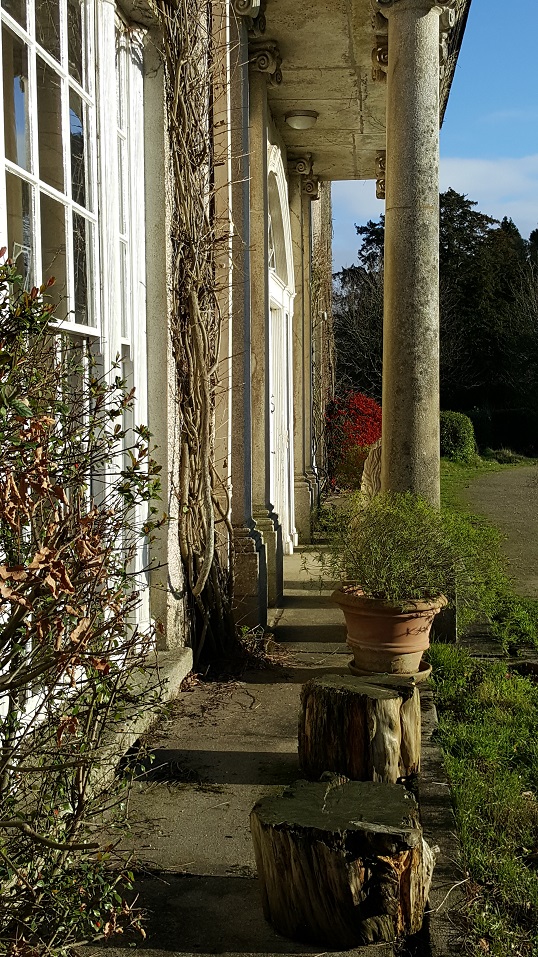


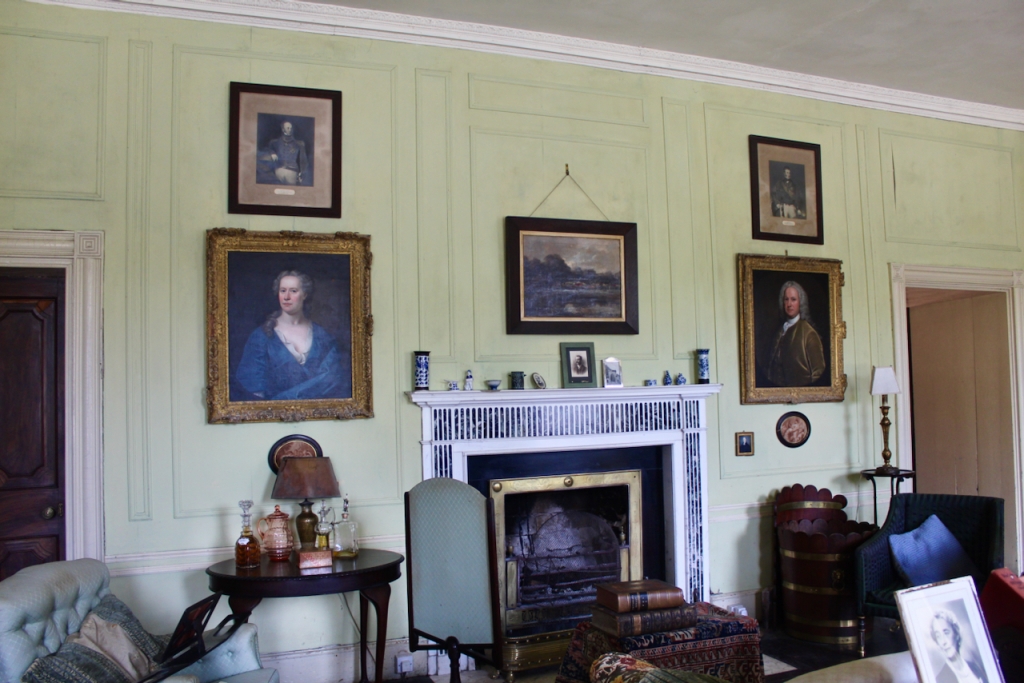
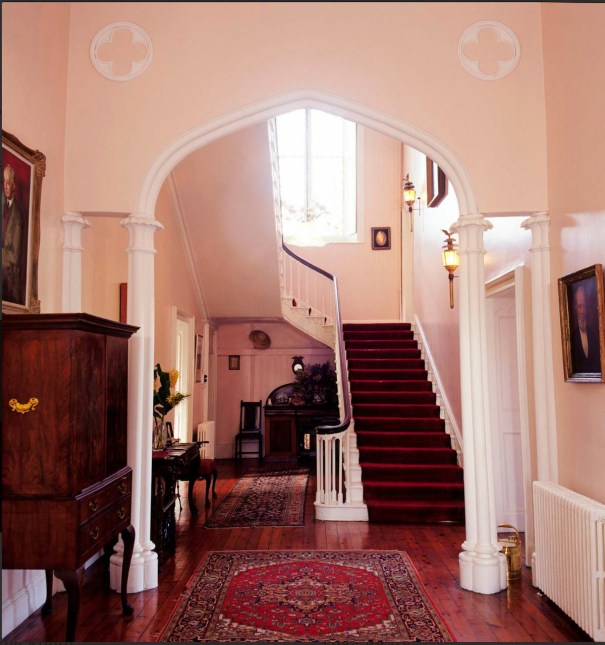
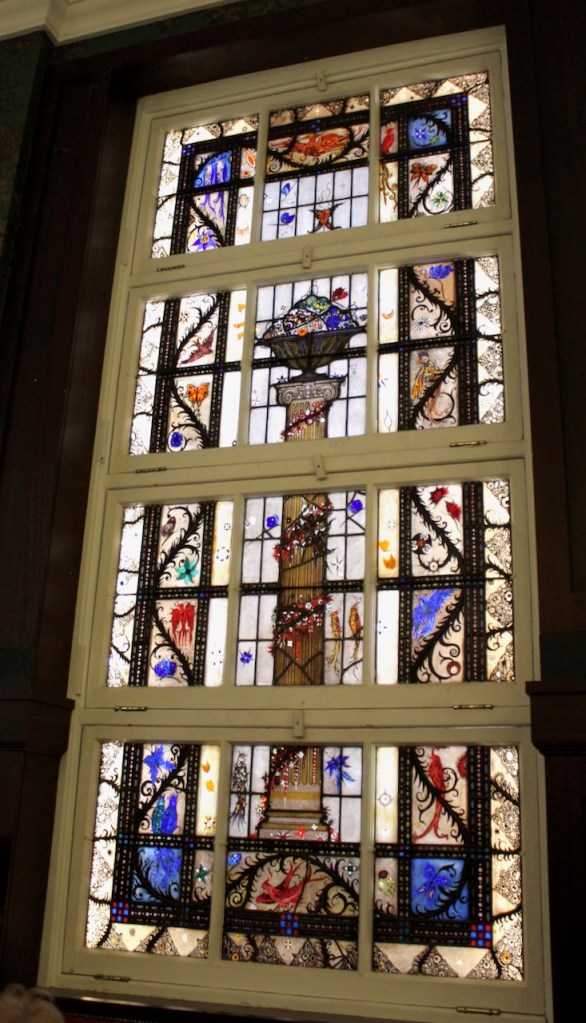
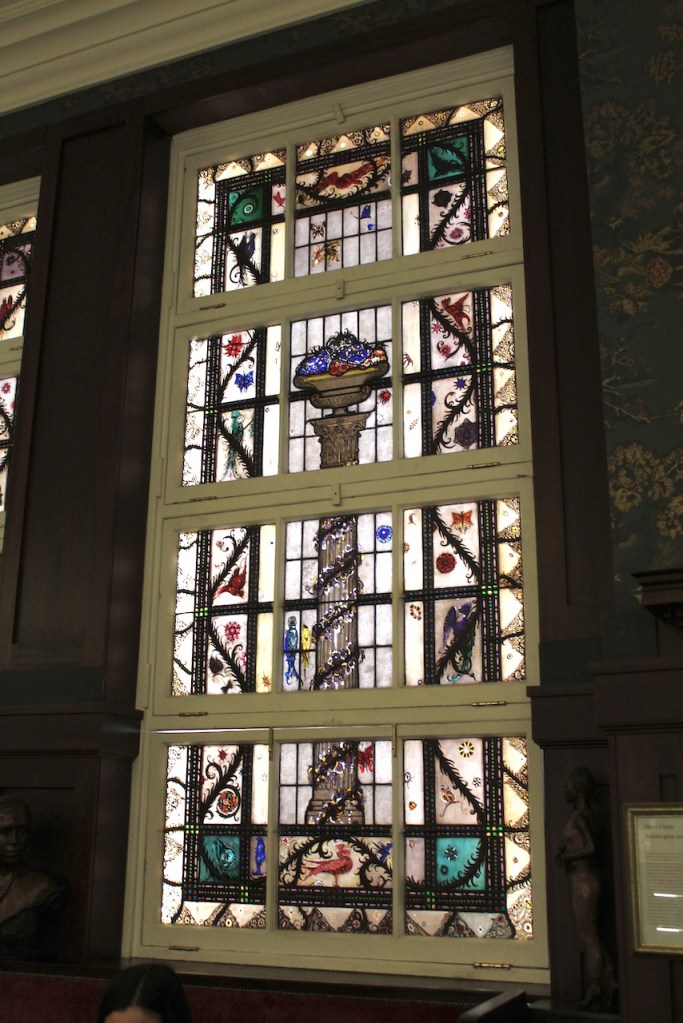
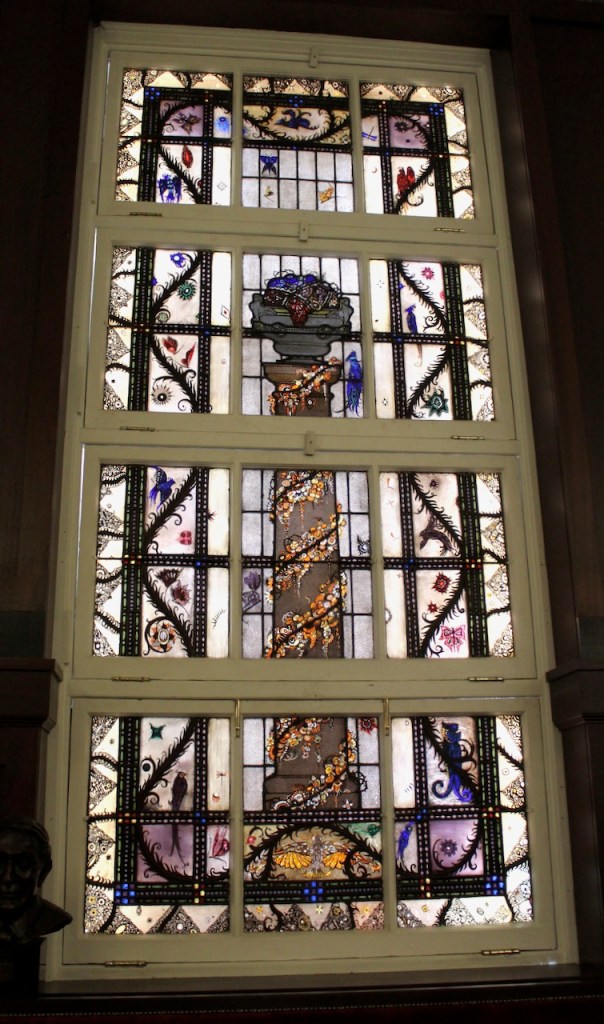
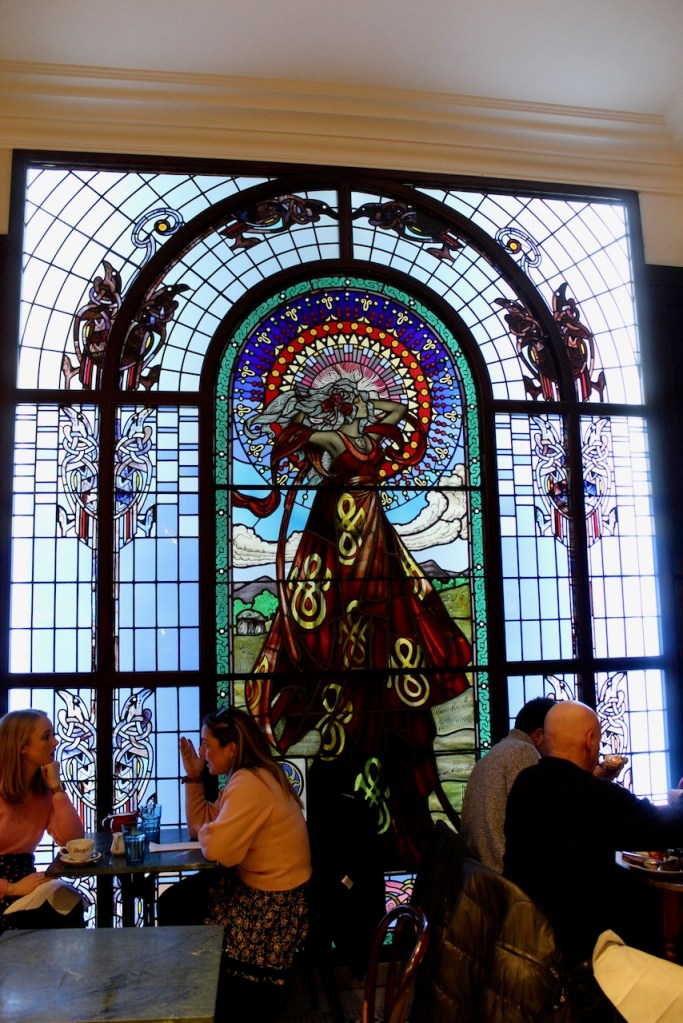
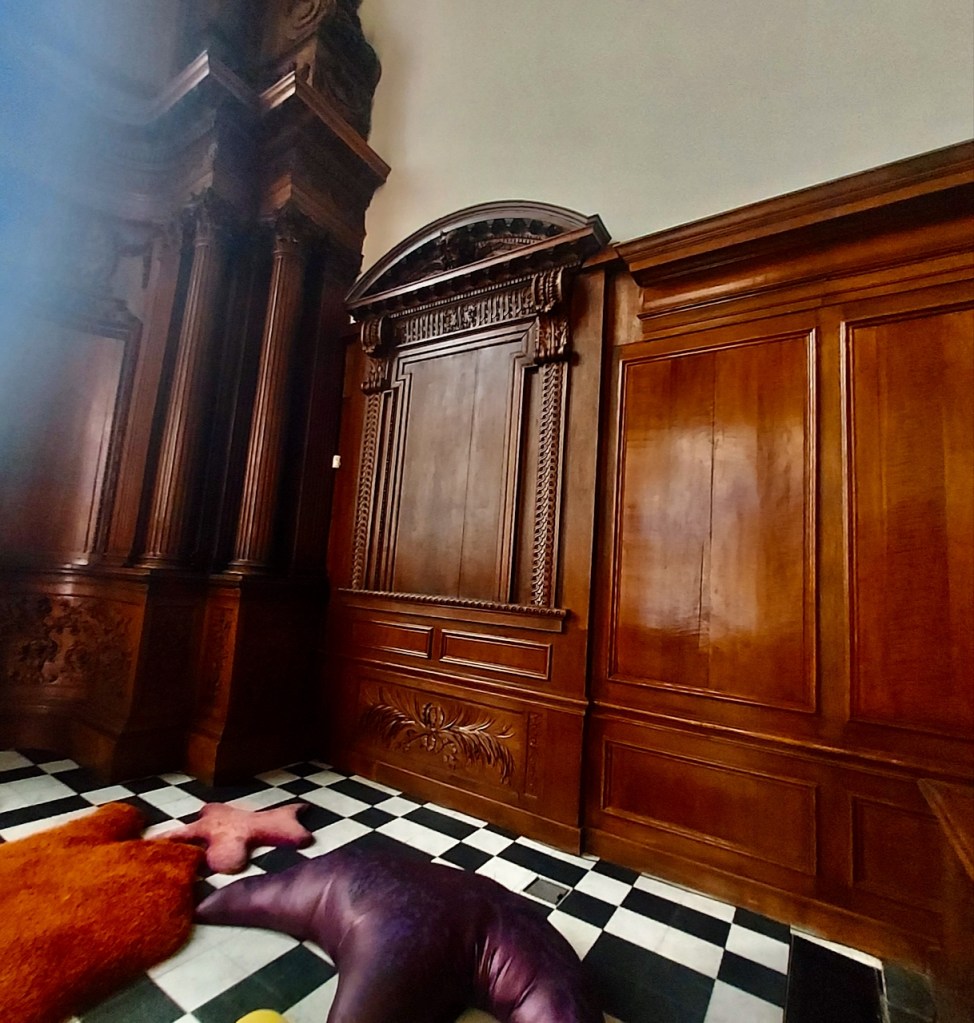
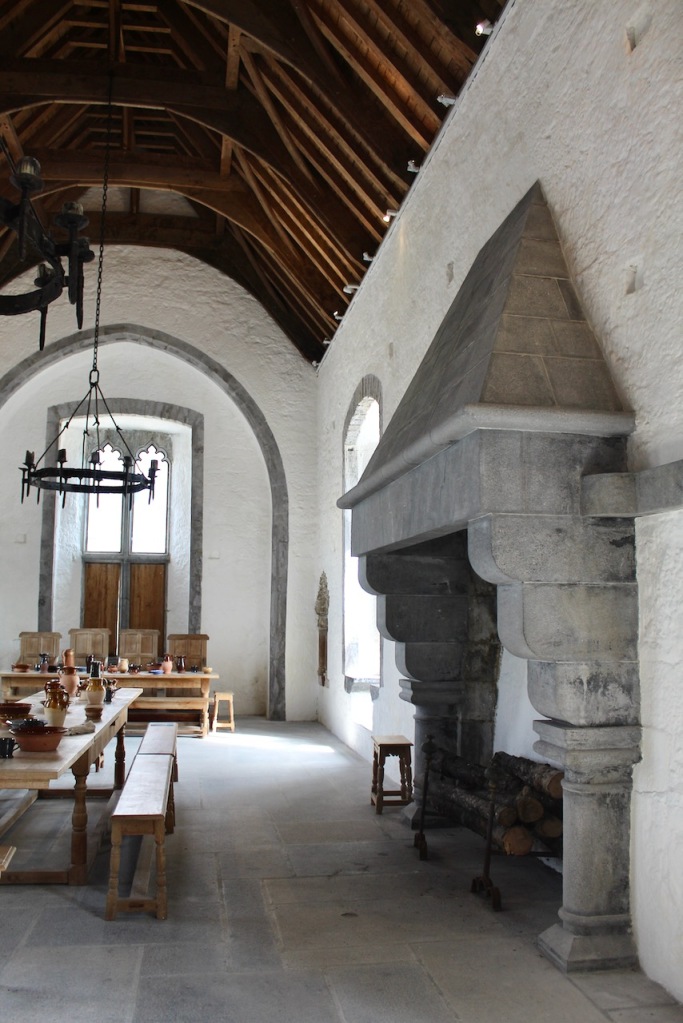
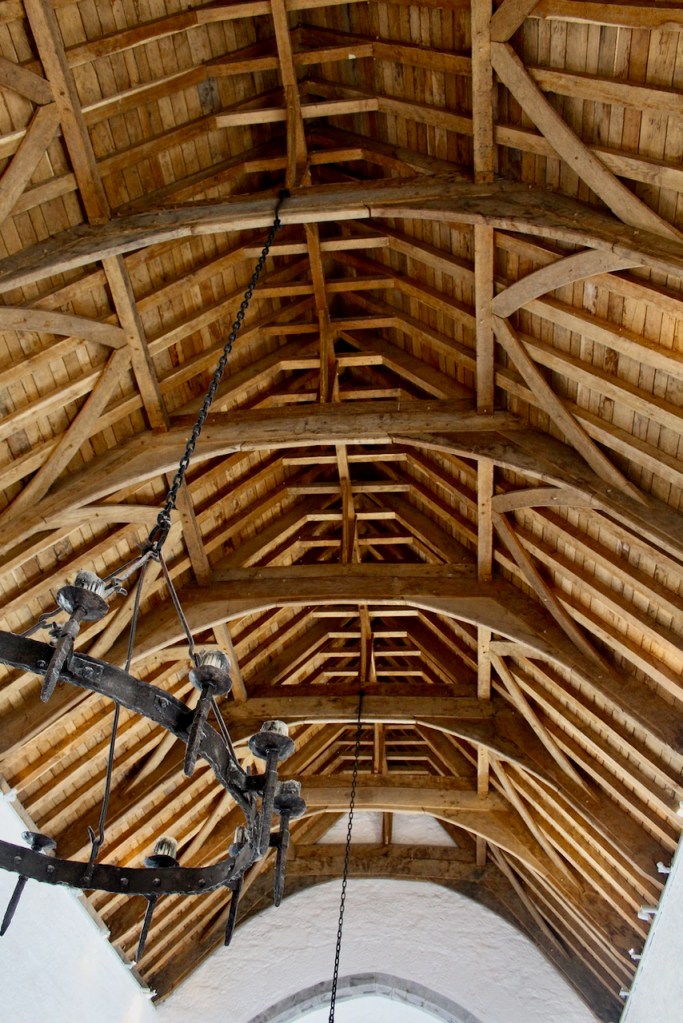
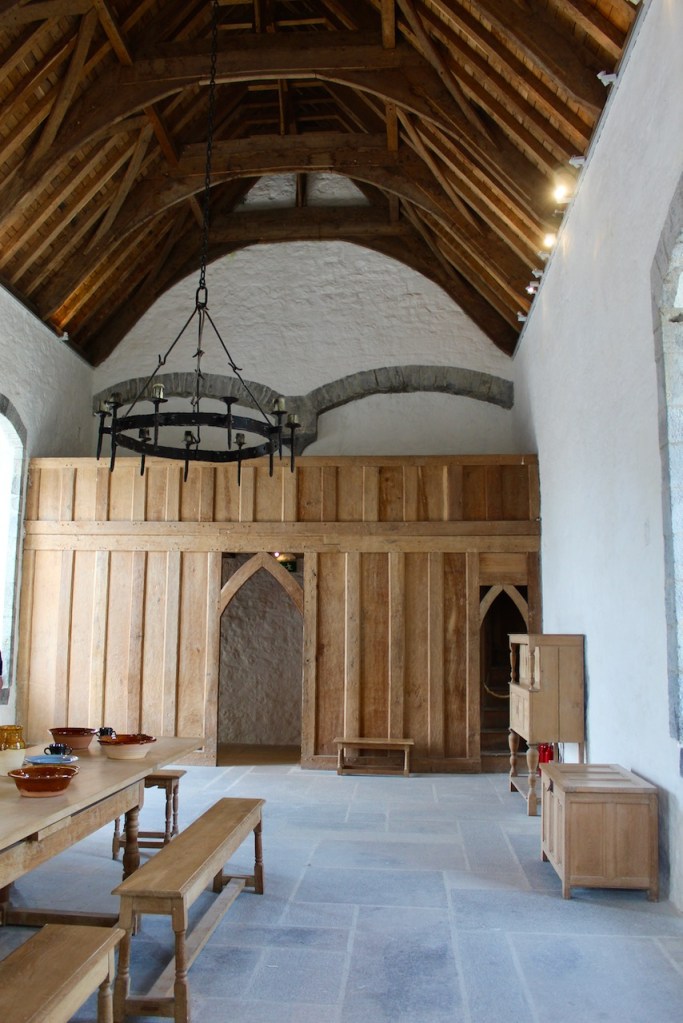
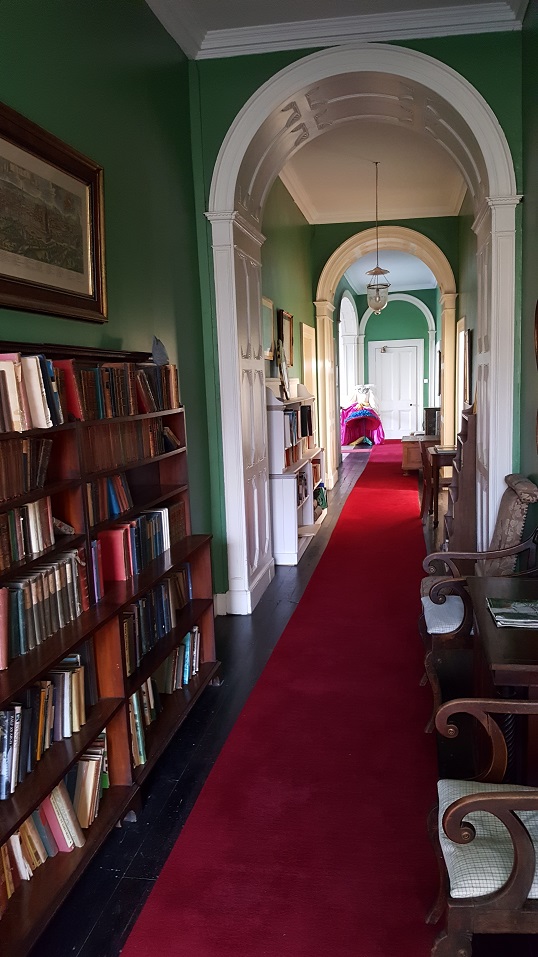
The house has tripartite entrance doorcase with large cobweb fanlight under the portico. Mark Bence-Jones writes that the hall has a “rather Soanian vaulted ceiling.” I’m not sure what he means by this – if you can enlighten me, please do let me know! He also comments on the “very spectacular spiral flying staircase of wood, with wrought iron balustrades; a remarkable and brilliant piece of design and construction.” [4] It is called “flying” because it does not touch the walls. The steps look like stone but are timber, and each was carefully made to fit perfectly together. Robert O’Byrne tells us that the stairs bounce slightly as one walks up or down, which sounds disconcerting!
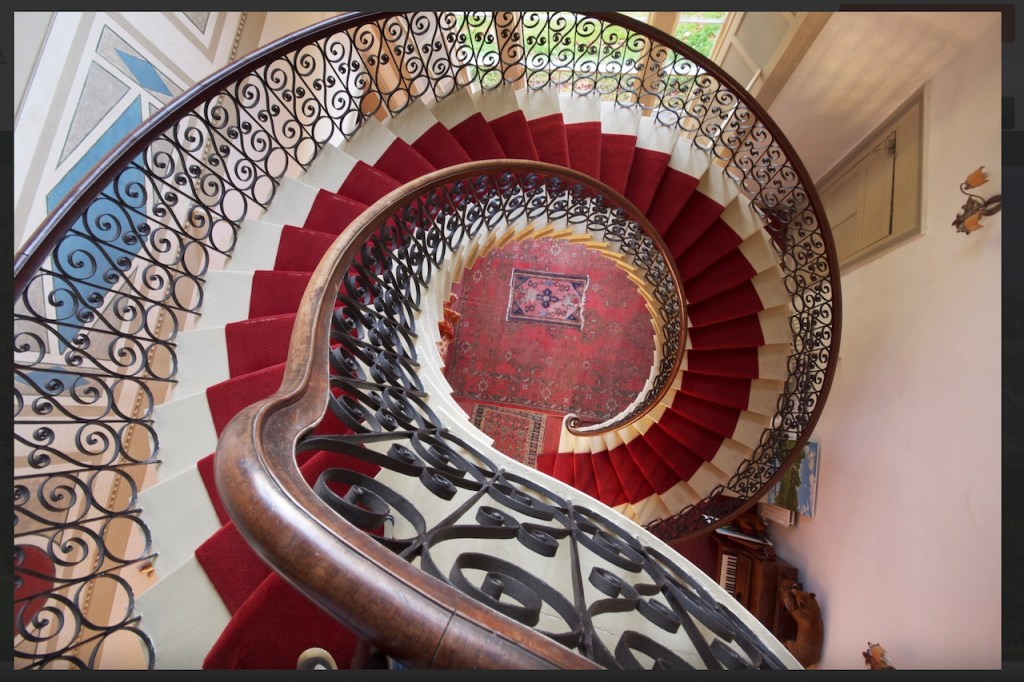


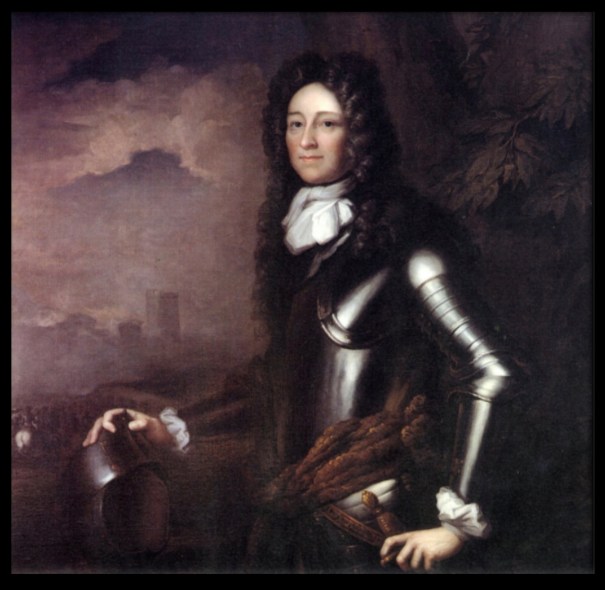
Woodbrook passed to the son, William Blacker (1790-1831). He married Elizabeth Anne Carew, from Castleboro House in County Wexford, now a splendid ruin.


William and Elizabeth Anne’s son Robert Shapland Carew Blacker (1826-1913) inherited the impressive Carrickblacker house in County Armagh from his relatives, as well as inheriting Woodbrook, from an elder brother, William Jacob, who predeceased him and had no children. William Jacob Blacker served as High Sheriff of County Wexford.
Robert Shapland married, in 1858, Theodosia Charlotte Sophia, daughter of George Meara, of May Park, County Waterford. Carrickblacker house remained in the family until the estate was purchased in 1937 by Portadown Golf Club, which demolished Carrickblacker House in 1958 to make way for a new clubhouse. [5]


The eldest son, William Robert George Blacker, died at just twenty years old. The next eldest, Edward Carew Blacker, died unmarried in 1932. He also served as High Sheriff of County Wexford. After his death, Woodbrook lay empty for some years, inherited by Edward’s brother Stewart Ward William Blacker, who also owned Carrickblacker. The Irish Historic Houses website tells us that the house was occupied by the Irish army during the Second World War.
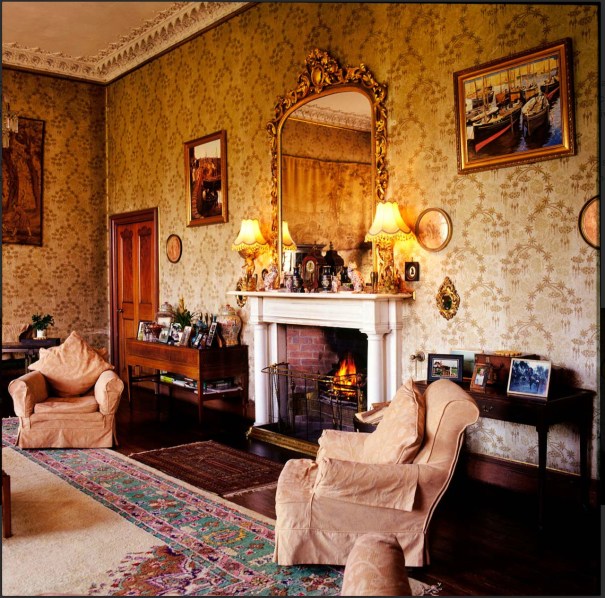
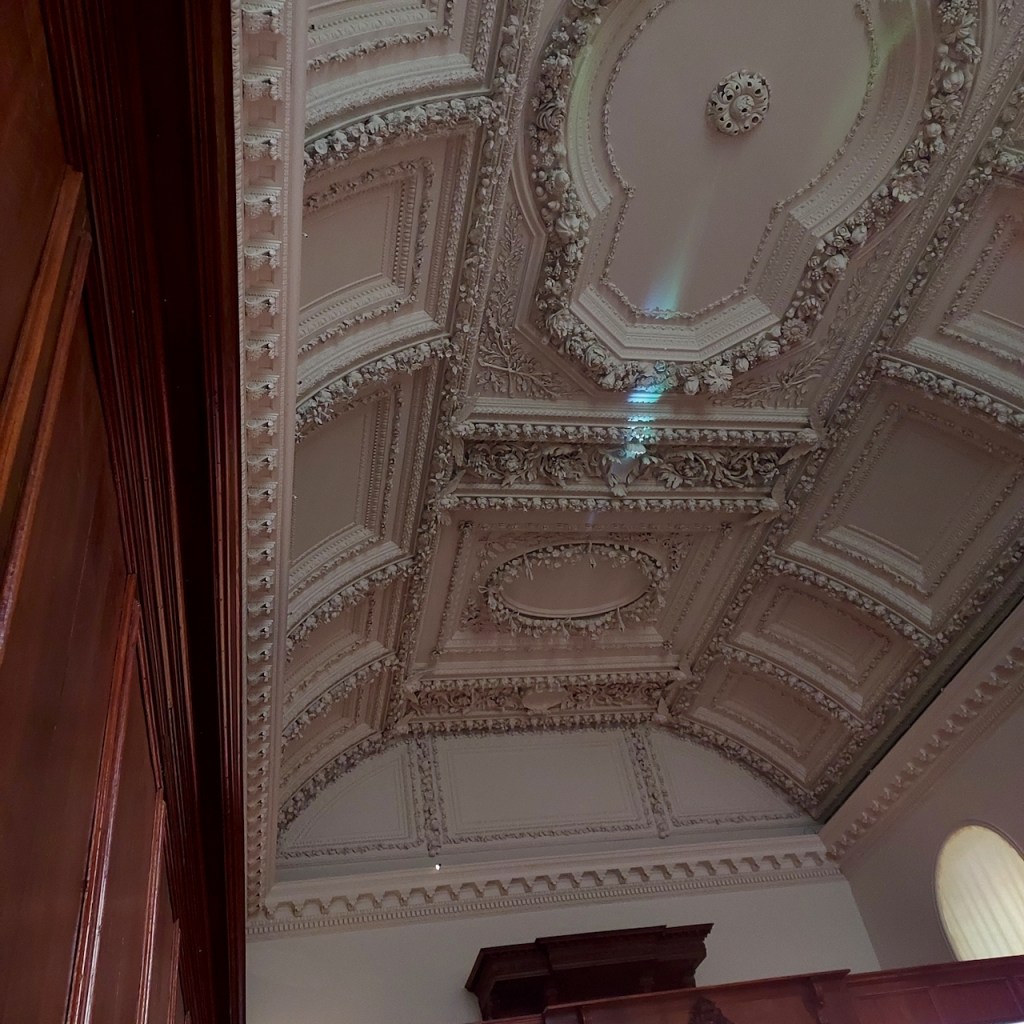
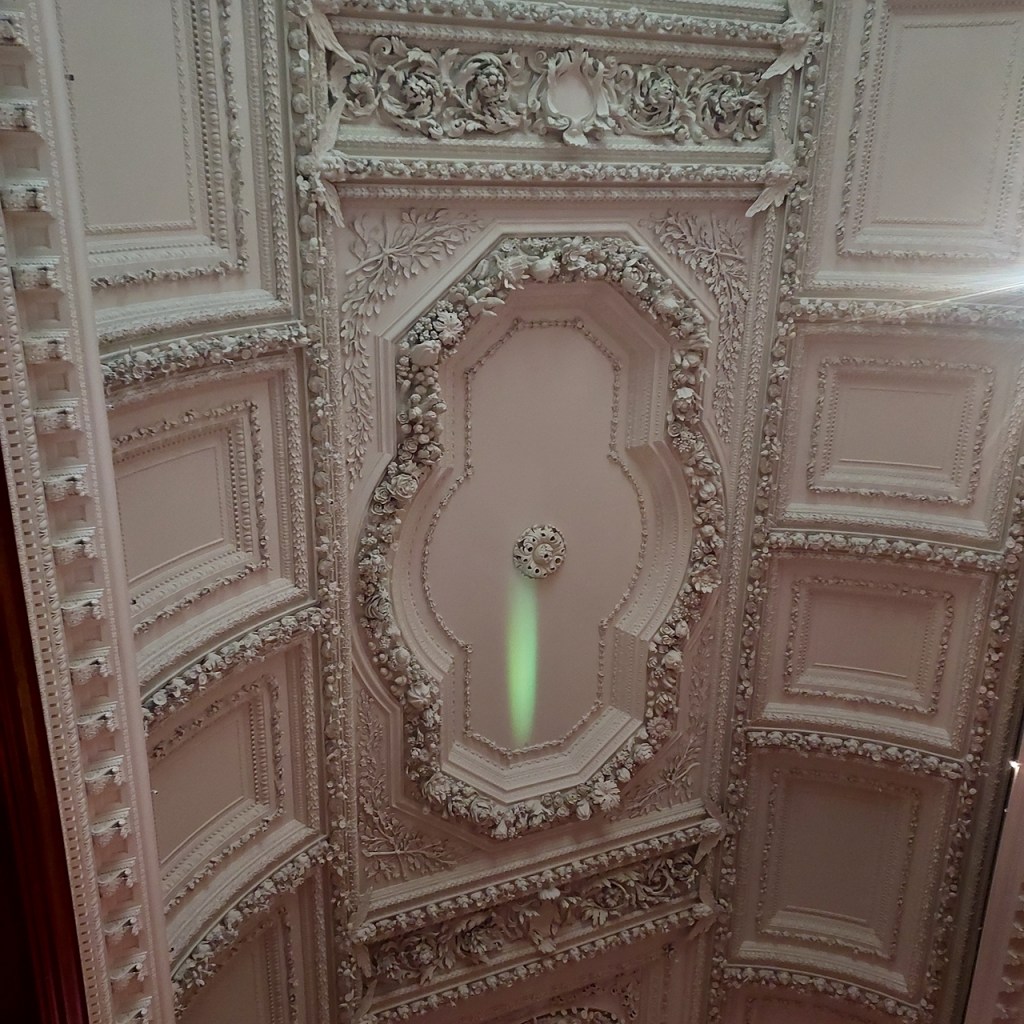
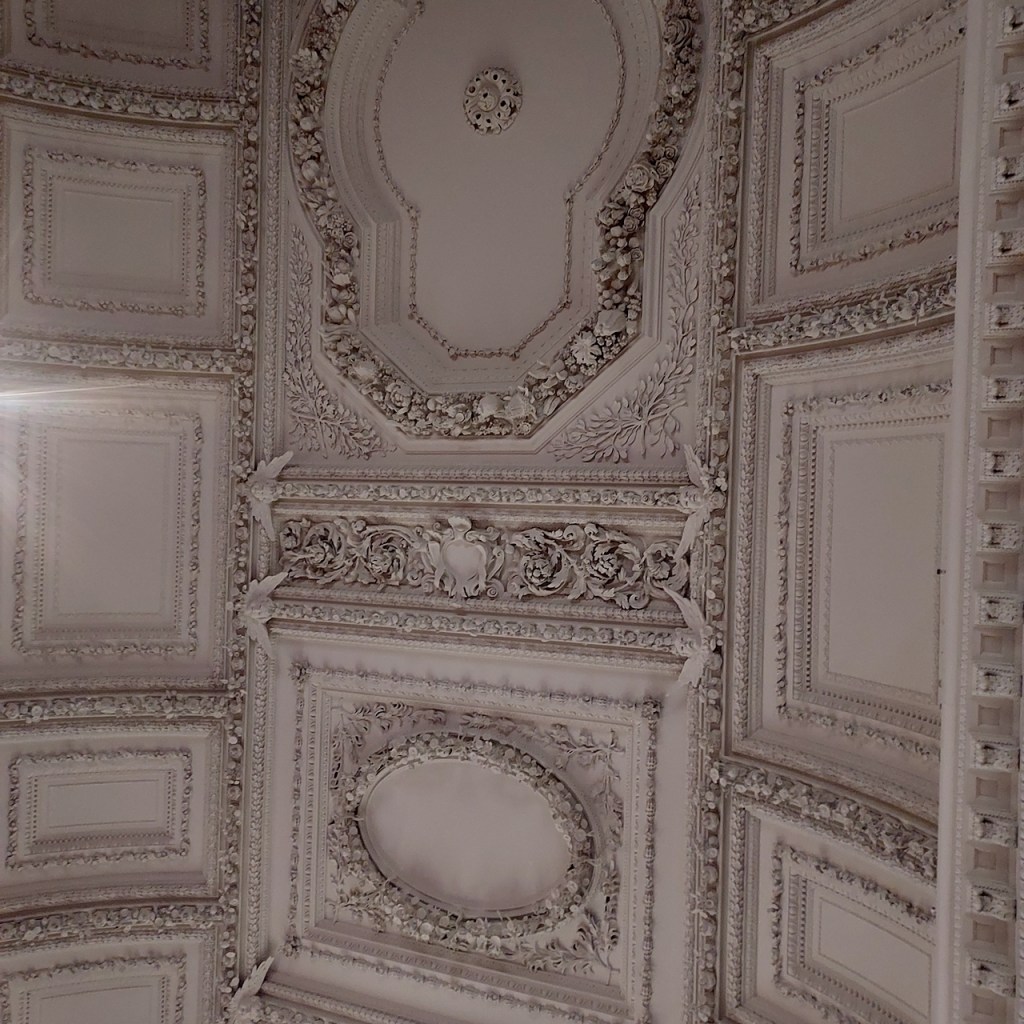
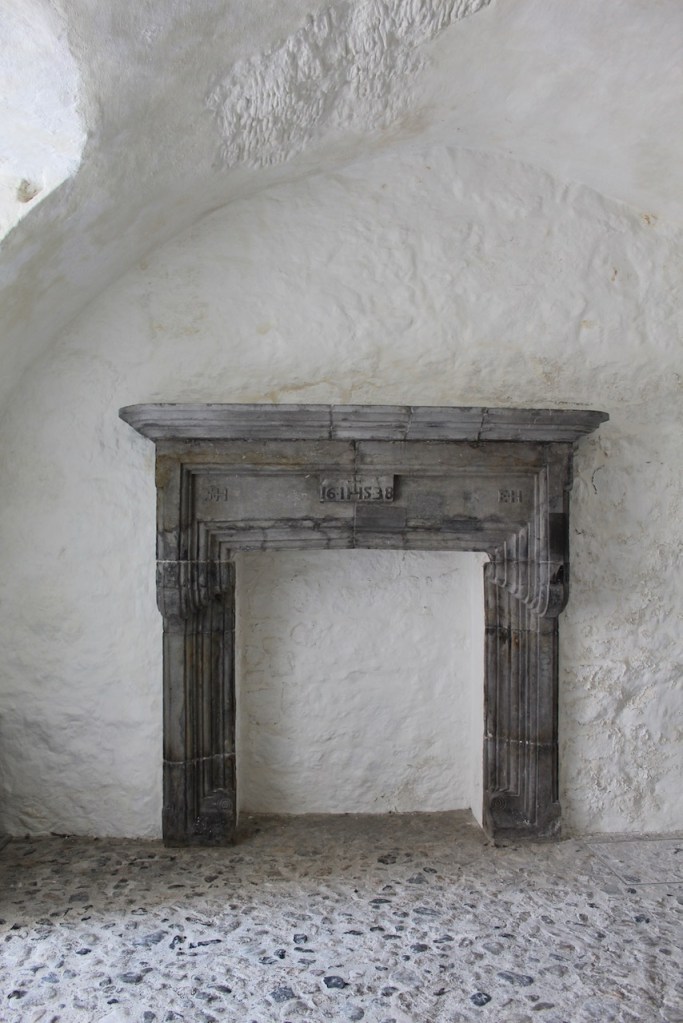
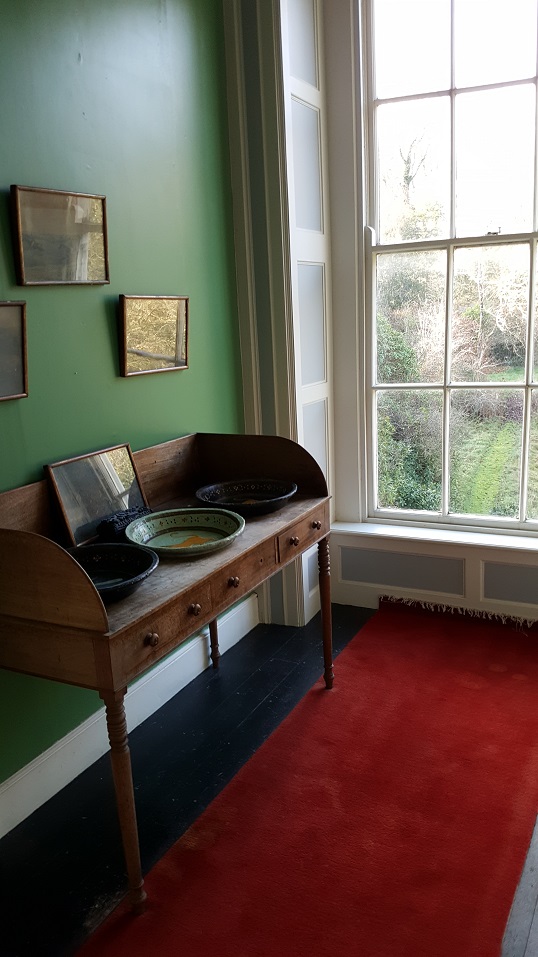
The house has a large drawing room with a chimneypiece that is from the original house.
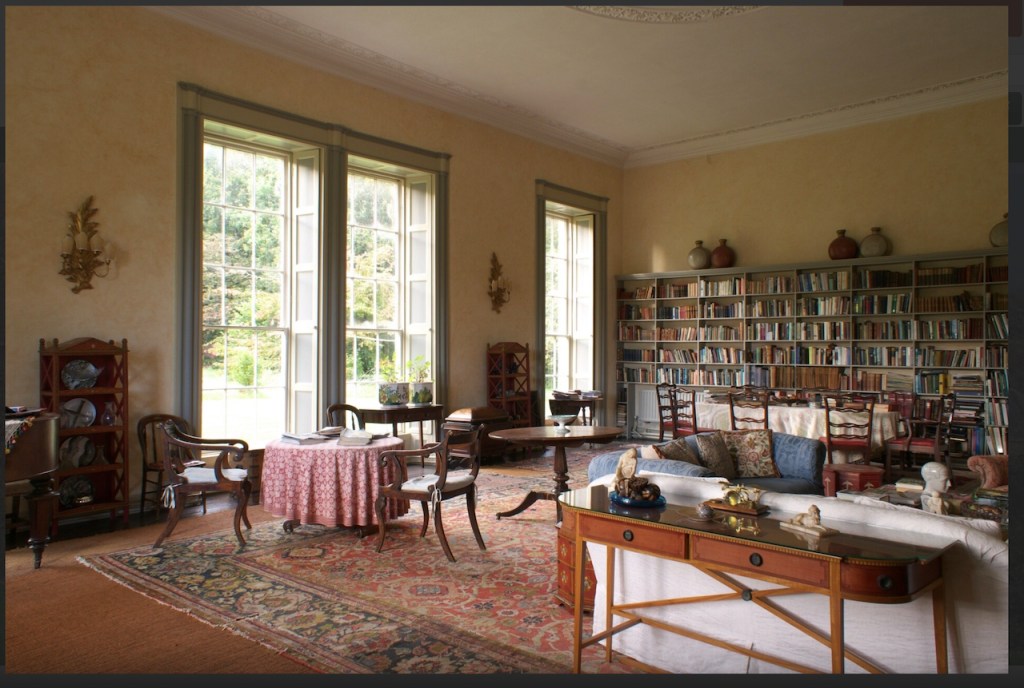
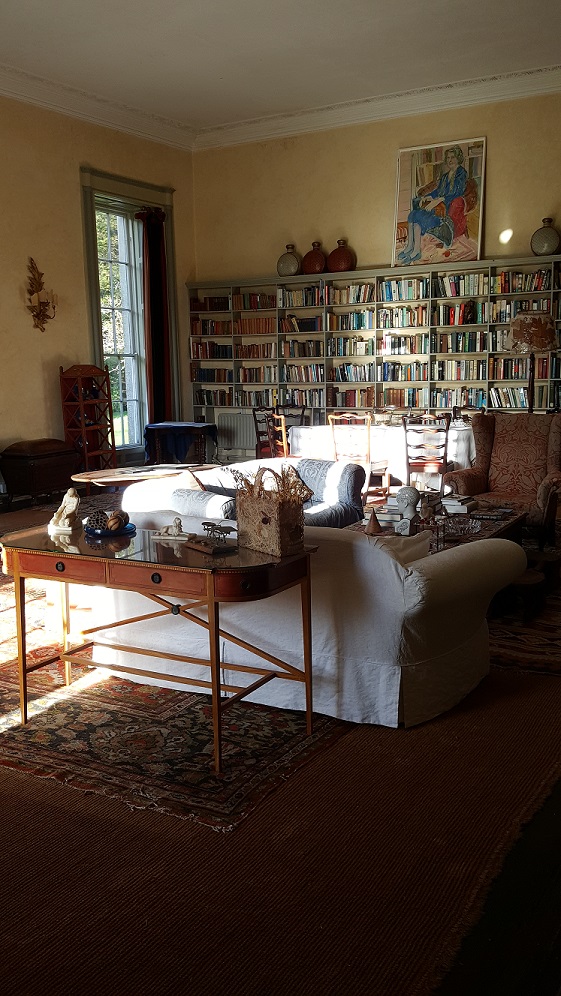


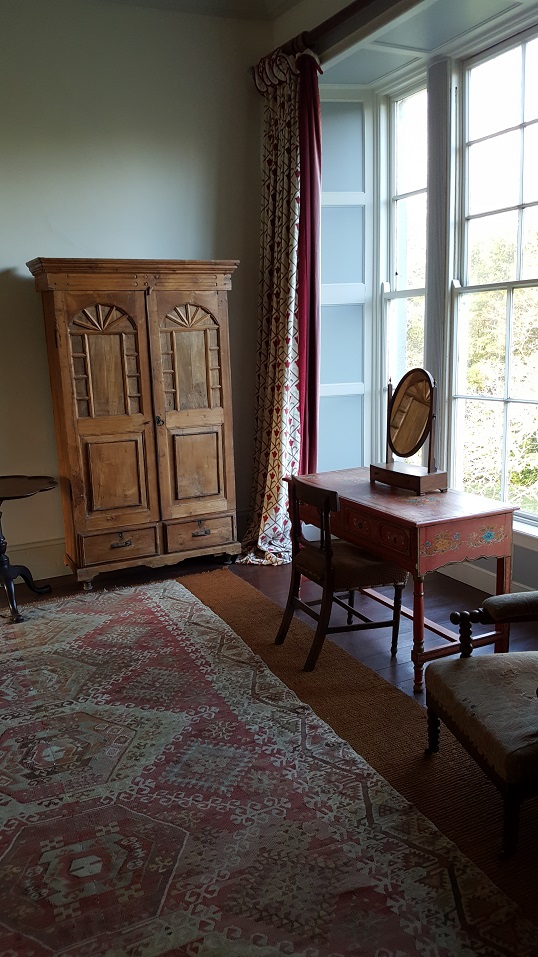
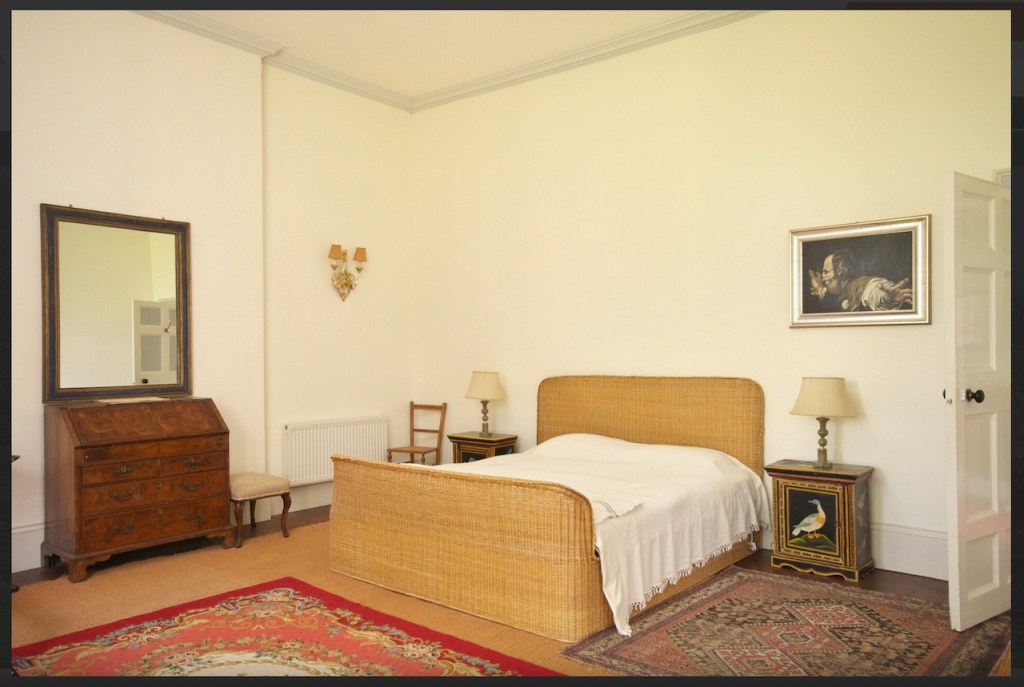
Stewart’s son Robert Stewart Blacker moved to the house in the 1950s after Carrickblacker was sold, and Woodbrook was then extensively modernised.
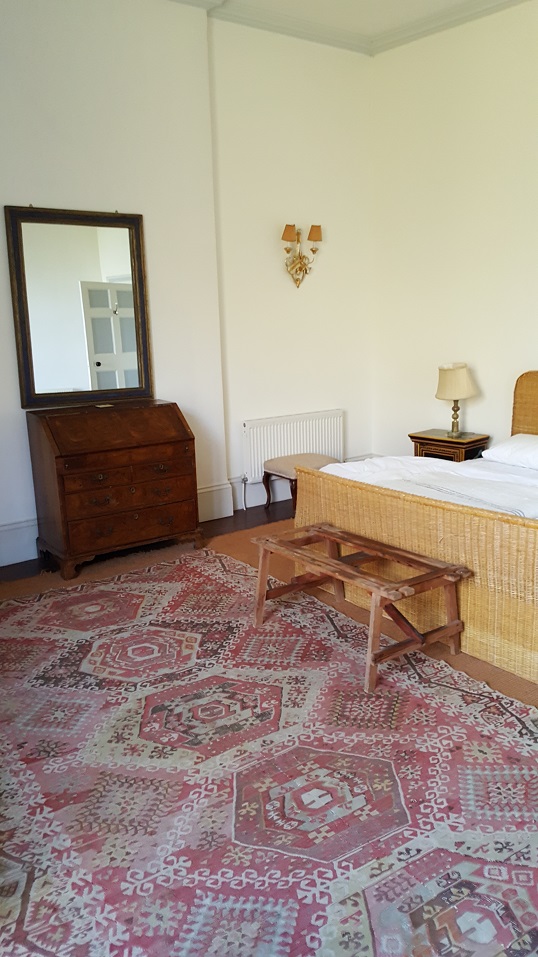
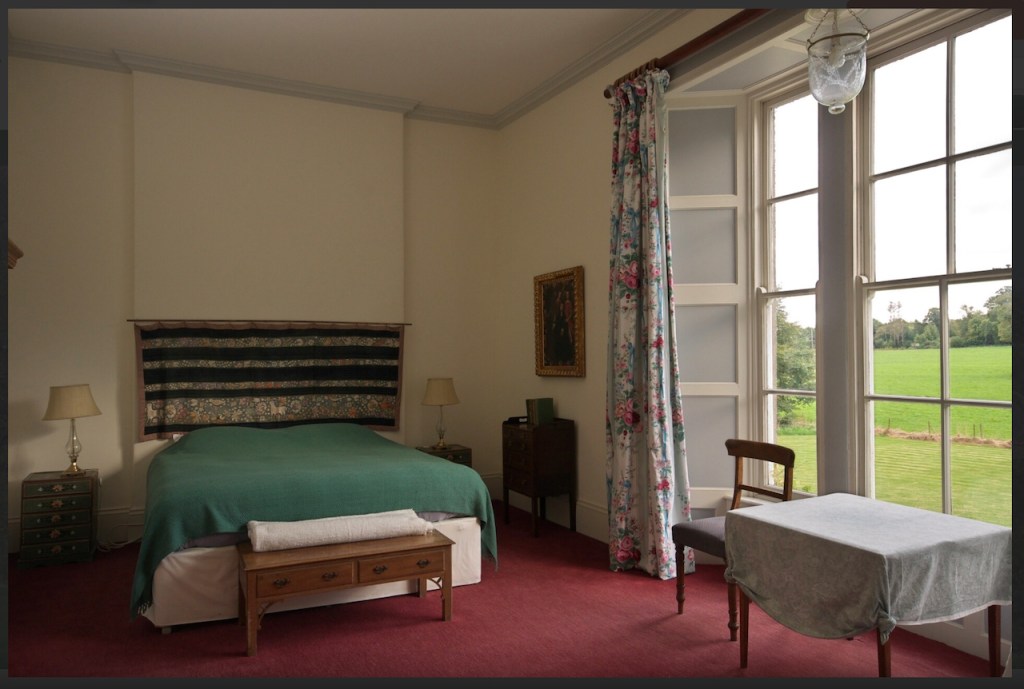
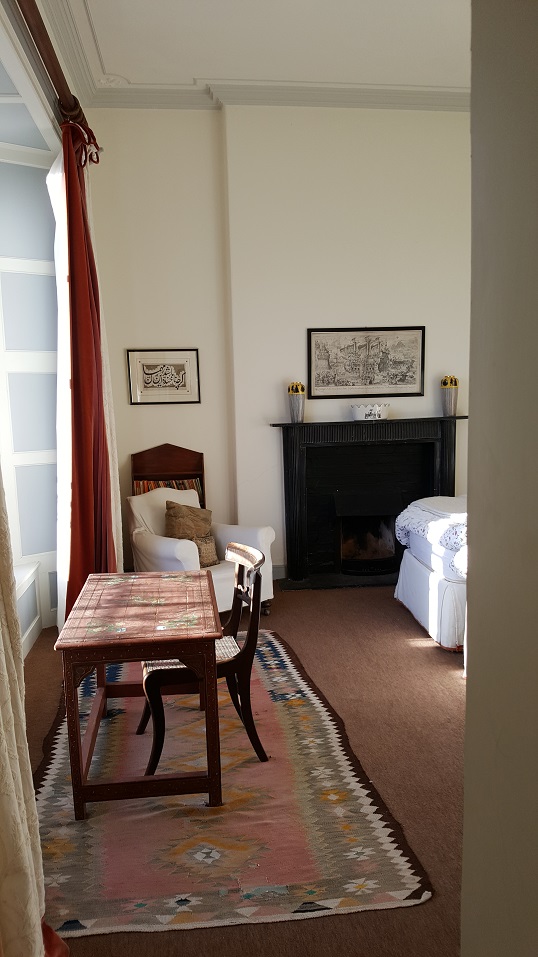







Also featured in The Wexford Gentry by Art Kavanagh and Rory Murphy. Published by Irish Family Names, Bunclody, Co Wexford, Ireland, 1994.
and The Irish Aesthete: Buildings of Ireland, Lost and Found. Robert O’Byrne. The Lilliput Press, Dublin, 2024.

Donation towards accommodation
I receive no funding nor aid to create and maintain this website, it is a labour of love. I travel all over Ireland to visit Section 482 properties and sometimes this entails an overnight stay. A donation would help to fund my accommodation.
€150.00
[1] https://hiddenireland.com/house-pages/woodbrook-house/
[2] https://theirishaesthete.com/2013/06/24/speaking-of-98/
[3] https://www.ihh.ie/index.cfm/houses/house/name/Woodbrook
[4] Mark Bence-Jones. A Guide to Irish Country Houses (originally published as Burke’s Guide to Country Houses volume 1 Ireland by Burke’s Peerage Ltd. 1978); Revised edition 1988 Constable and Company Ltd, London.
[5] http://lordbelmontinnorthernireland.blogspot.com/2013/05/house-of-blacker.html
These Section 482 listings are open on certain dates in March 2025, so you might still have time for a visit! I have separated below the places that are listed as Accommodation.
Huntington Castle, Clonegal, Co. Carlow, Y21 K237
Postal address: Huntington Castle, Enniscorthy, Co. Wexford
Open: Feb 1-2, 8-9, 15-16, 22-23, Mar 1-2, 8-9, 15-16, 22-23, 29-30, Apr 5-6, 12-30, May 1-31, June 1-30, July 1-31, Aug 1-31, Sept 1-30, Oct 4-5, 11-12, 18-19, 25-31, Nov 1-2, 8-9, 15-16, 22-23, 29-30, Dec 6-7, 13-14, 20-21, 11am-5pm
Fee: house/garden, adult €13.95, garden €6.95, OAP/student, house/garden €12.50, garden €6, child, house/garden €6.50, garden €3.50, group and family discounts available
Corravahan House & Gardens, Corravahan, Drung, Ballyhaise, Co. Cavan, H12 D860
Open: Jan 3-4, 10-11, 17-18, 24-25, 31, Feb 7-8, 14-15, 21-22, 28, Mar 1, 7-8, 14, May 8-11, 15-18, 22-25, June 12-15, 19-22, 26-29, Aug 8-10, 15-24, 29-31, 2pm-6pm
Fee: adult €10, OAP/student/child €5
Newtown Castle, Newtown, Ballyvaughan, Co. Clare
Open: Jan 6-Dec 19 Mon-Fri, National Heritage Week 16-24, 10am-5pm
Fee: Free
Ashton Grove, Ballingohig, Knockraha, Co. Cork
Open: Jan 7-10, 14-17, 21-24, Feb 10-14, 18, 25, Mar 4, May 1-5, 8-11, 13, 15-16, 20, 22-23, June 3-8, 10-15, 17-20, Aug 16-24, 8am-12 noon
Fee: adult €6, child €3, student/OAP free
Blarney Castle & Rock Close, Blarney, Co. Cork
Open: all year, Jan-Mar, Nov, Dec, 9am-5pm, Apr, Oct, 9am-5.30pm, May- Sept 9am-6pm,
Fee: adult €23, OAP/student €18, child €11
Kilshannig House, Rathcormac, Co. Cork, P61 AW77
Open: March 18-19, 21, 24, 26-27, April 2, 4-7, 9, 11-13, 21, 23, 25, May 12, 14, 16-17, 19, 21, 23-26, 28, 30, June 2, 4, 6-9, 11, 13, 16, 25, 27-29, July 2, 4-7, 14, 16, 18-20, 28, 30, Aug 1- 4, 6, 8, 11, 13, 15-25, Sept 18, 20, 22-25, 27, 29, 8.30am-3pm,
Fee: adult €14, OAP €12, student €10, child €8
Woodford Bourne Warehouse, Sheares Street, Cork
www.woodfordbournewarehouse.com
Open: all year, except Christmas Eve, Christmas Day, 12 noon-10pm
Fee: Free
Bewley’s, 78-79 Grafton Street/234 Johnson’s Court, Dublin 2
Open: all year, except Christmas Day, Jan- Nov, 8am-6.30pm, Dec 8am-8pm
Fee: Free
Doheny & Nesbitt, 4/5 Lower Baggot Street, Dublin 2
Open: all year, except Christmas Day, Mon-Wed, 9am-12 midnight, Thurs-Sat, 9am-1.30am, Sun, 9am-12 midnight
Fee: Free
Hibernian/National Irish Bank, 23-27 College Green, Dublin 2
Open: all year, except Jan1, and Dec 25, 9am-8pm
Fee: Free
The Odeon (formerly the Old Harcourt Street Railway Station), 57 Harcourt Street, Dublin 2
Open: all year Tue-Sat, National Heritage Week, Aug 16-24, 12 noon-12 midnight
Fee: Free
Powerscourt Townhouse Centre, 59 South William Street, Dublin 2
Open: all year, except New Year’s Day, Christmas Day, 10am-6pm
Fee: Free
10 South Frederick Street, Dublin 2, DO2 YT54
Open: all year, 2pm-6pm
Fee: Free
The Church, Junction of Mary’s Street/Jervis Street, Dublin 1
Open: Jan 1-Dec 23, 27-31, 11am-11pm
Fee: Free
Clonskeagh Castle, 80 Whitebeam Road, Clonskeagh, Dublin 14
Open: Jan 5-9, Feb 28, Mar 1-7, 9, May 1-10, June 1-10, July 1-10, Aug 16-25, Nov 4-6, Dec 2-4, 10am-2pm
Fee: adult €12, student/OAP/groups €8, groups over 4 people €8 each
Martello Tower, Portrane, Co. Dublin
Open: March 1- Sept 21, Sat & Sun, National Heritage Week, Aug 16-24, 9am-1pm
Fee: adult €6, student/OAP €2, child free
Tibradden House, Mutton Lane, Rathfarnham, Dublin 16, D16 XV97
Open: Jan 7-17, 24, Feb 3, 10, 17, 24, Mar 3, 10, 21, 24, Apr 4, May 2-3, 9-10, 16-17, 23, 29-30, June 13-15, 19-22, 25-28, Aug 15-24, Sept 3-6, 12-13, 19-20, 26-27, Jan-Apr, May-June, Aug, 2pm-6pm, Feb and Sept, 10am-2pm
Fee: adult €8, student/OAP/group €5
Woodville House Dovecote & Walls of Walled Garden, Craughwell, Co. Galway
Open: Feb 1-3, 7-10, 14-17, 21-24, 28, Mar 1-3, 7-10, 14-17, Apr 18-21, May 16-19, June 1-2, 6-9, 13-16, 20-23, 27-30, Aug 1-4, 8-11, 15-25, Feb-May, 12 noon-4pm, June and August, 11am-5pm, last entry 4.30pm
Fee: adult €10, OAP €9, student, €6, child €4 must be accompanied by adult, family €25 (2 adults and 2 children)
Derreen Gardens, Lauragh, Tuosist, Kenmare, Co. Kerry
Open: all year, 10am-6pm
Fee: adult/OAP/student €10, child €5, family ticket €30 (2 adults & all accompanying children under18) 20% discount for groups over 10 people
Kells Bay House & Garden, Kells, Caherciveen, Co. Kerry, V23 EP48
Open: Jan 1-4, Feb 1-Dec 21, 27-31, Jan-Apr, Oct-Dec 9am-5pm, May-Sept 9am-6pm
Fee: adult €9.50, child €7.50, family €30 (2 adults and up to 3 children 17 years or under) concessions 10% on groups up to 20 persons
Farmersvale House, Badgerhill, Kill, Co. Kildare, W91 PP99
Open: Jan 6-21, Mar 3-6, July 18-31, Aug 1-26, 9.30am-1.30pm
Fee: adult €5, student/child/OAP €3, (Irish Georgian Society members free)
Harristown House, Brannockstown, Co. Kildare, W91 E710
Open: Feb 3-7, 24-28, Mar 10-14, 17-21, May 1-14, July 23-25, 28-31, Aug 1, 5-24, 9am-1pm
Fee: adult €15, OAP/student/child €10
Leixlip Castle, Leixlip, Co. Kildare, W23 N8X6
Open: Feb 17-21, 24-28, Mar 3-7, 10-14, May 12-23, June 9-20, Aug 16-24, Sept 1-7, 9am-1pm
Fee: adult €8, OAP/student/child €4, no charge for local school visits/tours
Kilkenny Design Centre, Castle Yard, Kilkenny
Open: Jan 1 new year’s day 12 noon-5.30pm, Jan 2-Dec 23, 27-31, Jan, Feb, Mar, Apr, Oct, Nov, Dec, Sun, 11am-6pm, Mon-Sat, 10am-6pm, May, 10am-6pm, June, July, Aug, Sept, Sun, 10am-6pm, Mon- Sat, 9am-6pm,
Fee: Free
Ballaghmore Castle, Borris in Ossory, Co. Laois
Open: all year, except Christmas Day, 11am-5pm
Fee: adult €15 with Guide, child over 7 years /OAP/student €8, family of 4 €30
Manorhamilton Castle (Ruin), Castle St, Manorhamilton, Co. Leitrim
Open: Jan 3, 6, 10, 13, 17, 20, 24, 27, 31, Feb 3, 7, 10, 14, 17, 21, 24, 28, Mar 3, 7, 10, 14, 17, 21, 24, 28, 31, Apr 4, 7, 11, 14, 18, 21, 25, 28, May 2-5, 9-12, 16-19, 23, 26, 30, June 2, 6, 9, 13, 16, 20, 23, 27, July 4, 7, 11, 14, 18, 21, 25, Aug 1, 4, 8, 15-25, 29, Sept 1, 5, 8, 12, 15, 19, 22, 26, 29, 10am-4pm
Fee: adult €5, child/OAP/student free
Brookhill House, Brookhill, Claremorris, Co. Mayo
Open: Mar 13-26, Apr 17-25, June 12-26, July 8-24, Aug 15-26, 2pm-6pm
Fee: adult €8, OAP/student €4, National Heritage Week free
Beau Parc House, Beau Parc, Navan, Co. Meath, C15 D2K6
Open: Mar 1-20, May 1-31, Aug 16-24, 10am-2 pm
Fee: adult €10, OAP/student/child €8
St. Mary’s Abbey, High Street, Trim, Co. Meath
Open: Feb 8-14, 24-28, Mar 3-7, 26-28, May 10-18, June 23-30, July 21-27, Aug 16-24, Sept 14-20, 2pm-6pm
Fee: adult €5, OAP/student/child €2
Swainstown House, Kilmessan, Co. Meath, C15 Y60F
Open: Mar 4-5, 7-8, April 7-8, 10-11, May 5-11, June 2-8, July 7-13, Aug 16-24, Sept 8-12, 15-19, Oct 6-7, 9-10, Nov 3-4, 6-7, Dec 1-2, 4-5, 11am-3pm
Fee: adult €8, OAP/student/child €5, National Heritage Week free
Crotty Church, Castle Street, Birr, Co. Offaly
Open: Jan 1- Dec 31, Mon-Fri, excluding Bank Holidays, National Heritage Week Aug 16-24, 12 noon-5pm
Fee: Free
Springfield House, Mount Lucas, Daingean, Tullamore, Co. Offaly, R35 NF89
Open: Feb 1-3, 22-23, Mar 8-9, 15-17, Apr 5-6, May 3-5,10-11, 17-18, July 5-6, 26-30, Aug 1-24, Sept 29-30, Oct 1-5, 25-27, 2pm-6pm
Fee: Free
Strokestown Park House, Strokestown, Co. Roscommon
www.strokestownpark.ie www.irishheritagetrust.ie
Open: Jan 10-Dec 24, Jan-Feb, Nov-Dec 10.30am-4pm, Mar-May, Sept-Oct, 10am-5pm, June-Aug, 10am-6pm
Fee: adult house €14.50, tour of house €18.50, child €7, tour of house €10, OAP/student €12, tour of house €14.50, family €31, tour of house €39
Beechwood House, Ballbrunoge, Cullen, Co. Tipperary, E34 HK00
Open: Feb 25-27, Mar 4-6, 11-13, April 1-11, May 8-11, 15-18, 22-25, June 7-8, 14-15, Aug 16-24, Sept 2-4, 9-11, 16-18, 23-28, 9.15am-1.15pm
Fee: adult €5, OAP/student €2, child free, fees donated to charity
Clashleigh House, Clogheen, Co. Tipperary
Open: Mar 4, 6, 11, 13, 18, 20, 25, 27, Apr 1, 3, 8, 10, 15, 17, 22, 24, 30, May 6, 8, 10-11, 13, 15, 17-18, 20, 22, 24-25, 27, 29, June 3, 5, 10, 12, 17, 19, 24, 26, Aug 16-24, Sept 2, 4, 9, 11, 16, 18, 23, 25, 30, Oct 2, 7, 9, 9am-1pm
Fee: adult €8, OAP/student/child €4
Fancroft Mill , Fancroft, Roscrea, Co. Tipperary
Open: Feb 3-15, Mar 24-30, May 13-28, June 10-20, Aug 15-27, 10am-2pm
Fee: adult €8, OAP/student €6, child free under 5 years, one to one adult supervision essential, group rates available
Cappoquin House & Gardens, Cappoquin, Co. Waterford, P51 D324
www.cappoquinhouseandgardens.com
Open: Apr 7-12, 15-19, 22-26, 28-30, May 1-3, 5-10, 2-17, 19-24, 26-31, June 2-7, Aug 16-24, 9am-1pm
Gardens open all year
Fee: adult house €10, house and garden €15, garden only €6, child free
The Presentation Convent, Waterford Healthpark, Slievekeel Road, Waterford City
Open: Jan 2- Dec 23, 29-30, Mon-Fri, National Heritage Week Aug 16-24, closed Bank Holidays, 8.30am-5.30pm
Fee: Free
Lough Park House, Castlepollard, Co. Westmeath
Open: Mar 15-21, 28-31, Apr 18-21, May 1-7, June 1-9, July 12-25, Aug 1-7, 16-24, 2pm-6pm
Fee: adult €6
Tullynally Castle & Gardens, Castlepollard, Co. Westmeath, N91 HV58
Open: Castle, May 1-3, 8-10, 15-17, 22-24, 29-31, June 5-7, 12-14, 19-21, 26-28, July 3-5, 10-12, 17-19, Aug 1-2, 7-9, 14-24, 28-30, Sept 4-6, 11-13, 18-20, 11am-3pm
Garden, Mar 27-Sept 28, Thurs-Sundays, and Bank Holidays, National Heritage Week, Aug 16-24,11am-5pm
Fee: castle adult €16.50, child entry allowed for over 8 years €8.50, garden, adult €8.50, child €4, family ticket (2 adults + 2 children) €23, adult season ticket €56, family season ticket €70, special needs visitor with support carer €4, child 5 years or under is free
Kilcarbry Mill Engine House, Sweetfarm, Enniscorthy, Co Wexford
Open: Jan 1-4, 29-31, Feb 3-5, Mar 5-7, 10-11, Apr 3-4, 11-13, May 10-12, 19-23, July 5-7, Aug 2-31, Dec 19-23, 27-30, 12 noon-4pm
Fee: adult €10, student/OAP €5, child free
Sigginstown Castle, Sigginstown, Tacumshane, Co. Wexford, Y35 XK7D
Open: Mar 14-17, 21-23, April 4-6, 11-13, 18-21, May 2-5, 9-11, 16-18, 23-25, June 6-8, 13-15, 20-22, 27-29, July 4-6, 11-13, 18-20, 25-27, Aug 1-4, 8-10, 15-24, Sept 6-7, 13-14, 20-21, 27-28, 1pm-5pm
Fee: adult €10, child/OAP/student €8, groups of 6 or more €8 per person
Altidore Castle, Kilpeddar, Greystones, Co. Wicklow, A63 X227
Open: Mar 10-30, May 1-31, June 1-5, 1pm-5pm, Aug 16-24, 2pm-6pm
Fee: adult €10, OAP/child/student €8
Castle Howard, Avoca, Co. Wicklow
Open: Jan 6-8, Feb 10-14, Mar 3-5, 18-20, June 4-7, 9-11, 23-28, July 7-12, 21-24, Aug 16-24, Sept 1-6, 13, 20, 28-30, Oct 1, 6-8, 9am-1pm
Fee: adult €8.50, OAP/student €6.50, child €5
Mount Usher Gardens, Ashford, Co. Wicklow, A67 VW22
Open: all year, except Christmas Day and St. Stephen’s Day, Jan-Mar, Nov-Dec, 10am-5pm, Apr-Oct, 10am-5.30pm
Fee: adult €10, student/OAP €8, child over 4 years €5, under 4 years free, group rate (10 or more people) €8 per person
Powerscourt House & Gardens, Powerscourt Estate, Enniskerry, Co. Wicklow, A98 W0D0
Open: Jan 1-Dec 24, 27-31, house and garden, 9.30am-5.30pm, ballroom and garden rooms, 9.30am-1.30pm
Fee: Jan-Oct, adult €14, OAP, €12, student €10.50, child €5.50, family €20, Nov- Dec, adult €10.50, OAP €9.50, student €9, child €5.50, Jan- Oct, concessions-family ticket 2 adults and 3 children under 18 years €33, concession-Nov-Dec family 2 adults and 3 children under 18 €25
Russborough, The Albert Beit Foundation, Blessington, Co. Wicklow, W91 W284
Open: Feb 1-Dec 23, 27-31, Feb, Nov, Dec 9am-5.30pm, Mar-Oct 9am-6pm Fee: adult €14.
Accommodation:
Cabra Castle (Hotel), Kingscourt, Co. Cavan, A82 EC64
Open: all year, except Dec 24, 25, 26, 11am-4pm
Fee: Free
Claregalway Castle, Claregalway, Co. Galway, H91 E9T3
Tourist Accommodation Facility
Open: January 2- December 24
Ballyseede Castle, Ballyseede, Tralee, Co. Kerry
Open: Mar 14-Dec 31, 8am-12 midnight
Fee: Free
Owenmore, Garranard, Ballina, Co. Mayo
(Tourist Accommodation Facility)
Open: all year except Jan, Feb, June 15- July 10, Dec
Cillghrian Glebe now known as Boyne House Slane, Chapel Street, Slane, Co. Meath, C15 P657
(Tourists Accommodation Facility)
Open: all year, National Heritage Week, Aug 16-24, 9am-1pm
Fee: Free
Loughcrew House, Loughcrew, Old Castle, Co. Meath
(Tourist Accommodation Facility)
Open: all year
Fee: adult €8, OAP/student €6, child €4, carers free
Slane Castle, Slane, Co. Meath, C15 XP83
(Tourist Accommodation Facility)
Open: January, February, May, June, July, August, (Mar-Apr, Sept-Dec, Mon-Thurs)
Fee: adult €14, OAP/student €12.50, child €8.40 under 5 years free
Tankardstown House, Rathkenny, Slane, Co. Meath, C15 D535
Open: all year, National Heritage Week, Aug 16-24, 9am-1pm
Fee: Free
Castle Leslie, Glaslough, Co. Monaghan
(Tourist Accommodation Facility)
Open: all year, National Heritage Week events August 16-24
Fee: Free
The Maltings, Castle Street, Birr, Co. Offaly
(Tourist Accommodation Facility)
Open: all year
Lismacue House, Bansha, Co. Tipperary
(Tourist Accommodation Facility)
Open: Mar 1-Oct 31
Wilton Castle, Bree, Enniscorthy, Co. Wexford, Y21 V9P9
(Tourist Accommodation Facility)
Open: all year
Woodbrook House, Killanne, Enniscorthy, Co. Wexford, Y21 TP 92
(Tourist Accommodation Facility)
Open: all year